The Treatment of Three-Part Fractures of Humeral Head: A Retrospective Study to Compare Nail vs. Plate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
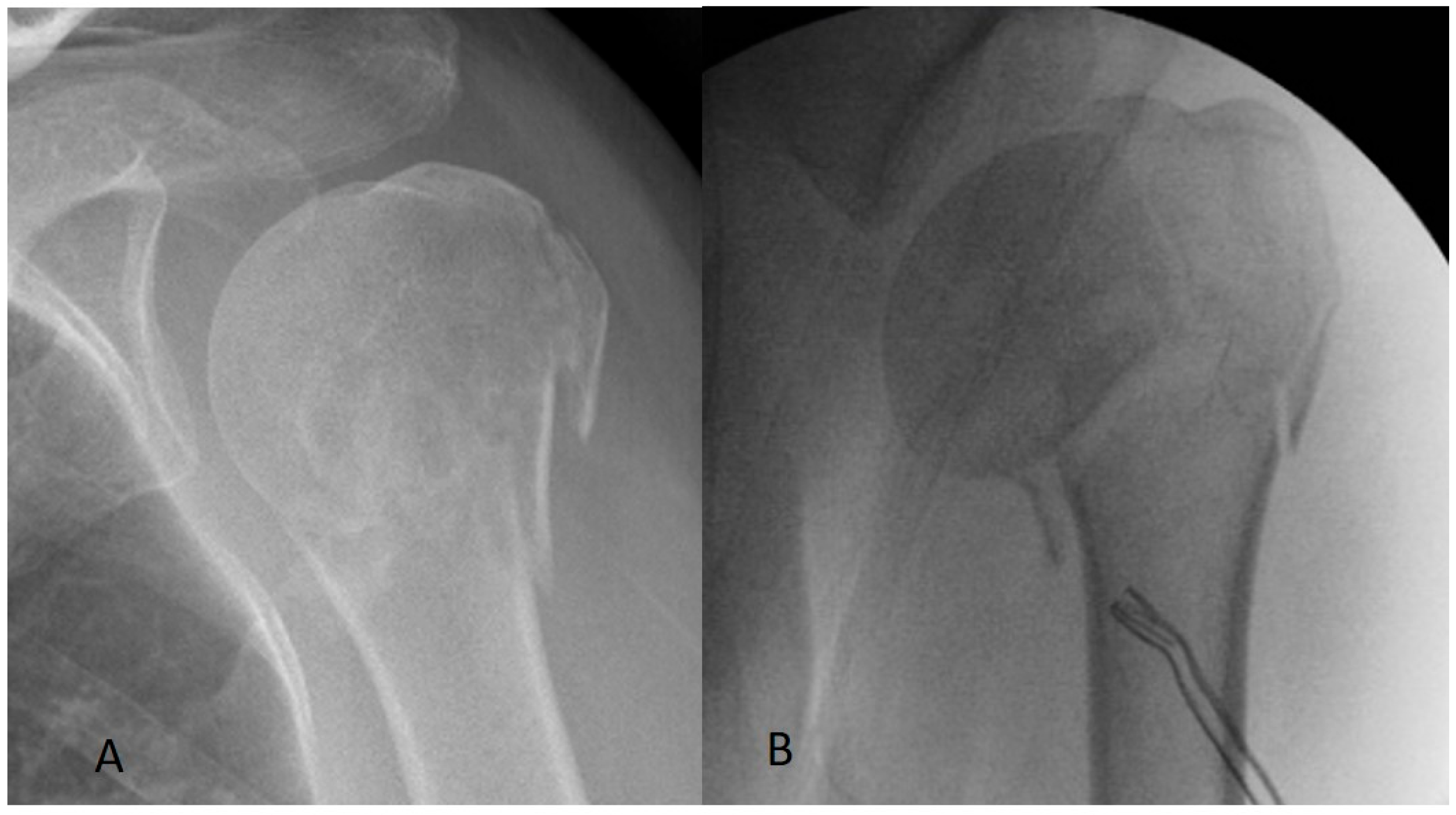
2.2. Surgical Procedure
2.3. Postoperative Treatment
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roux, A.; Decroocq, L.; El Batti, S.; Bonnevialle, N.; Moineau, G.; Trojani, C.; Boileau, P.; de Peretti, F. Epidemiology of proximal humerus fractures managed in a trauma center. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2012, 98, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, T.P.; Beeres, F.J.P.; Ferree, S.; Schipper, I.B.; Camenzind, R.S.; Hoepelman, R.J.; Link, B.C.; Rompen, I.F.; Babst, R.; van de Wall, B.J.M. Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty versus Non-Operative Treatment of Three-Part and Four-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in the Elderly Patient: A Pooled Analysis and Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzetti, R.M.; Gaj, E.; Berlinberg, E.J.; Patel, H.H.; Spoliti, M. Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Demonstrates Better Outcomes Than Angular Stable Plate in the Treatment of Three-part and Four-part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Patients Older Than 70 Years. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2023, 481, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumaier, A.; Grawe, B. Proximal Humerus Fractures: Evaluation and Management in the Elderly Patient. Geriatr. Orthop. Surg. Rehabil. 2018, 9, 2151458517750516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzari, B.J.; Yoo, C.J.; Kamson, A.O.; Muzio, A.E.; Lippe, R.W. Hawkins wiring for three-part fractures of the proximal humerus: A case series. Trauma Case Rep. 2022, 38, 100614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, J.L.; Slongo, T.F.; Agel, J.; Broderick, J.S.; Creevey, W.; DeCoster, T.A.; Prokuski, L.; Sirkin, M.S.; Ziran, B.; Henley, B.; et al. Fracture and dislocation classification compendium—2007: Orthopaedic Trauma Association classification, database and outcomes committee. J. Orthop. Trauma 2007, 21 (Suppl. S10), S1–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, A.; Rosinsky, P.J.; Gafni, N.; Kosashvili, Y.; Kaban, A. Proximal humeral nail for treatment of 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures in the elderly population: Effective and safe in experienced hands. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2021, 31, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neer, C.S. Displaced proximal humeral fractures. I. Classification and evaluation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1970, 52, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekmezci, T.; Çepni, S.K. Subgroups and differences of fixation in 3-part proximal humerus fractures. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2023, 29, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Dong, J.; He, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, F.; Dong, J. A novel surgical approach and technique and short-term clinical efficacy for the treatment of proximal humerus fractures with the combined use of medial anatomical locking plate fixation and minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, J.; Mihalj, M.; Čukelj, F.; Ivanišević, A. MIPO of proximal humerus fractures through an anterolateral acromial approach. Is the axillary nerve at risk? Injury 2017, 48 (Suppl. S5), S15–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, D. Current concepts in plate and screw fixation of osteoporotic proximal humerus fractures. Injury 2007, 38 (Suppl. S3), S59–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solberg, B.D.; Moon, C.N.; Franco, D.P.; Paiement, G.D. Surgical treatment of three and four-part proximal humeral fractures. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2009, 91, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Cai, P.; Guo, S.; Fu, B. Locking plate fixation versus intramedullary nail fixation for the treatment of multifragmentary proximal humerus fractures (OTA/AO type 11C): A preliminary comparison of clinical efficacy. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ding, C.; Zhu, Y.; Nian, S.; Tang, H. A comparative study of locking plate combined with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of Neer classification of two-part and three-part fractures of the proximal humerus. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2024, 342, 743–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Yang, L.; Cao, Z.Y.; Cheng, S.D.; Tian, S.L.; Sun, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Xu, B.P.; Hu, X.C.; Wang, Y.J.; et al. Chinese version of the Constant-Murley questionnaire for shoulder pain and disability: A reliability and validation study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2017, 15, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, B.A.; Thompson, K.J.; Raghava, P.; Eberhardt, A.W.; Tate, J.P.; Volgas, D.A.; Stannard, J.P. The role of medial comminution and calcar restoration in varus collapse of proximal humeral fractures treated with locking plates. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2013, 95, e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, R.; Hempfing, A.; Stiehler, M.; Leunig, M. Predictors of humeral head ischemia after intracapsular fracture of the proximal humerus. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2004, 3, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, H. Proximal humeral fractures: Current controversies. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011, 20, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boileau, P.; Walch, G. The three-dimensional geometry of the proximal humerus. Implications for surgical technique and prosthetic design. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1997, 79, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayvargiya, M.; Pathak, A.; Gaur, S. Outcome Analysis of Locking Plate Fixation in Proximal Humerus Fracture. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, RC01-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handoll, H.H.; Brorson, S. Interventions for treating proximal humeral fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 11, CD000434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangan, A.; Handoll, H.; Brealey, S.; Jefferson, L.; Keding, A.; Martin, B.C.; Goodchild, L.; Chuang, L.H.; Hewitt, C. Surgical vs nonsurgical treatment of adults with displaced fractures of the proximal humerus: The PROFHER randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2015, 313, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallier, H.A. Treatment of proximal humerus fractures. J. Orthop. Trauma 2007, 21, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erasmo, R.; Guerra, G.; Guerra, L. Fractures and fracture-dislocations of the proximal humerus: A retrospective analysis of 82 cases treated with the Philos® locking plate. Injury 2014, 45 (Suppl. S6), S43–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agudelo, J.; Schürmann, M.; Stahel, P.; Helwig, P.; Morgan, S.J.; Zechel, W.; Bahrs, C.; Parekh, A.; Ziran, B.; Williams, A.; et al. Analysis of efficacy and failure in proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plates. J. Orthop. Trauma 2007, 21, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterhoff, G.; Ossendorf, C.; Wanner, G.A.; Simmen, H.P.; Werner, C.M. The calcar screw in angular stable plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures: A case study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2011, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Wang, W.; Lin, G.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Edem Prince, G.A.; Yang, G. The clinical benefit of medial support screws in locking plating of proximal humerus fractures: A prospective randomized study. Int. Orthop. 2011, 35, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Fu, Z.; An, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, B. Effect of Calcar Screw Use in Surgical Neck Fractures of the Proximal Humerus with Unstable Medial Support: A Biomechanical Study. J. Orthop. Trauma 2014, 28, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepass, A.; Rolauffs, B.; Weise, K.; Bahrs, S.D.; Dietz, K.; Bahrs, C. Complication rates and outcomes stratified by treatment modalities in proximal humeral fractures: A systematic literature review from 1970–2009. Patient Saf. Surg. 2013, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, T.M.; Vandenbussche, E.; Augereau, B. Surgical treatment of three and four-part proximal humeral fractures. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2013, 99 (Suppl. S1), S197–S207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Garcia-Maya, B.; Pérez-Barragans, F.; Lainez Galvez, J.R.; Paez Gallego, J.; Vaquero-Picado, A.; Barco, R.; Antuña, S. Percutaneous plate fixation of displaced proximal humerus fractures: Do minimally invasive techniques improve outcomes and reduce complications? Injury 2023, 54 (Suppl. S7), 111042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastrow, R.K.; Patterson, D.C.; Cagle, P.J. Operative Management of Proximal Humerus Nonunions in Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 34, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sproul, R.C.; Iyengar, J.J.; Devcic, Z.; Feeley, B.T. A systematic review of locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures. Injury 2011, 42, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, G.; Evola, F.R.; Costarella, L. Osteosynthesis systems in fragility fracture. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 23 (Suppl. S2), 69–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klug, A.; Harth, J.; Hoffmann, R.; Gramlich, Y. Surgical treatment of complex proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients: A matched-pair analysis of angular-stable plating vs. reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020, 29, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernstbrunner, L.; Rahm, S.; Suter, A.; Imam, M.A.; Catanzaro, S.; Grubhofer, F.; Gerber, C. Salvage reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for failed operative treatment of proximal humeral fractures in patients younger than 60 years: Long-term results. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020, 29, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euler, S.A.; Petri, M.; Venderley, M.B.; Dornan, G.J.; Schmoelz, W.; Turnbull, T.L.; Plecko, M.; Kralinger, F.S.; Millett, P.J. Biomechanical evaluation of straight antegrade nailing in proximal humeral fractures: The rationale of the “proximal anchoring point”. Int. Orthop. 2017, 41, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørdal, J.; Fraser, A.N.; Wagle, T.M.; Kleven, L.; Lien, O.A.; Eilertsen, L.; Mader, K.; Apold, H.; Larsen, L.B.; Madsen, J.E.; et al. A cost-effectiveness analysis of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty compared with locking plates in the management of displaced proximal humerus fractures in the elderly: The DelPhi trial. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022, 31, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.; Chin, M.; Sanville, J.; Namdari, S.; Hast, M.W. Calcar screw position in proximal humerus fracture fixation: Don’t miss high! Injury 2018, 49, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Newman, J.M.; Gruson, K.I. Outcomes of intramedullary nailing for acute proximal humerus fractures: A systematic review. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2016, 17, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konrad, G.; Audigé, L.; Lambert, S.; Hertel, R.; Südkamp, N.P. Similar outcomes for nail versus plate fixation of three-part proximal humeral fractures. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadea, F.; Favard, L.; Boileau, P.; Cuny, C.; d’Ollone, T.; Saragaglia, D.; Sirveaux, F.; SOFCOT. Fixation of 4-part fractures of the proximal humerus: Can we identify radiological criteria that support locking plates or IM nailing? Comparative, retrospective study of 107 cases. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2016, 102, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capriccioso, C.E.; Zuckerman, J.D.; Egol, K.A. Initial varus displacement of proximal humerus fractures results in similar function but higher complication rates. Injury 2016, 47, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| GROUP | Locking-Plate Group (69) | Intramedullary Nail Group (77) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| AVERAGE AGE | 6.1 ± 3.2 years | 62.4 ± 2.9 years | p = 0.42 |
| SEX | 22 (M)–47 (F) | 28 (M)–49 (F) | p = 0.35 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.2 ± 3.1 | 25.4 ± 2.1 | p = 0.43 |
| PATIENTS WITH AT LEAST ONE RELEVANT COMORBIDITY | 31 | 35 | p = 0.27 |
| FRACTURE TYPE | |||
| Subgroup 1 | 49 | ||
| Subgroup 2 | 45 | ||
| Subgroup 3 | 20 | 32 |
| PARAMETER | Locking-Plate Group (69) | Intramedullary Nail Group (77) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| AVERAGE OPERATION TIME | 88.7 ± 10.5 min | 70.2 ± 8.3 min | p = 0.03 |
| HEALING TIME (MONTHS) | 8.7 ± 2.2 weeks | 7.9 ± 2.4 weeks | p = 0.11 |
| INITIAL NECK SHAFT ANGLES (°) | 134.6° ± 6.1° | 135.7° ± 5.6° | p = 0.29 |
| LAST NECK SHAFT ANGLES (°) | 132.5° ± 5.3° | 133.4° ± 6.4° | p = 0.23 |
| CONSTANT–MURLEY SCORE | 91.2 ± 6.7 | 90.5 ± 7.7 | p = 0.27 |
| COMPLICATIONS | 16 patients (23.2%) | 7 patients (9.1%) | p = 0.02 |
| PARAMETER | Locking-Plate Group (20) | Intramedullary Nail Group (32) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| AVERAGE OPERATION TIME | 89.5 ± 9.8 min | 70.9 ± 9.1 min | p = 0.03 |
| HEALING TIME (MONTHS) | 9.2 ± 2.6 weeks | 8.7± 2.2 weeks | p = 0.09 |
| INITIAL NECK SHAFT ANGLES (°) | 133.2° ± 5.6° | 134.9° ± 4.3° | p = 0.32 |
| LAST NECK SHAFT ANGLES (°) | 130.4° ± 4.6° | 132.1° ± 4.7° | p = 0.25 |
| CONSTANT–MURLEY SCORE | 89.3 ± 4.3 | 88.7 ± 5.9 | p = 0.19 |
| COMPLICATIONS | 6 patients (30%) | 3 patients (9.3%) | p = 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evola, F.R.; Vecchio, M.; Vacante, M.; Evola, G. The Treatment of Three-Part Fractures of Humeral Head: A Retrospective Study to Compare Nail vs. Plate. Surg. Tech. Dev. 2025, 14, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14030023
Evola FR, Vecchio M, Vacante M, Evola G. The Treatment of Three-Part Fractures of Humeral Head: A Retrospective Study to Compare Nail vs. Plate. Surgical Techniques Development. 2025; 14(3):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvola, Francesco Roberto, Michele Vecchio, Marco Vacante, and Giuseppe Evola. 2025. "The Treatment of Three-Part Fractures of Humeral Head: A Retrospective Study to Compare Nail vs. Plate" Surgical Techniques Development 14, no. 3: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14030023
APA StyleEvola, F. R., Vecchio, M., Vacante, M., & Evola, G. (2025). The Treatment of Three-Part Fractures of Humeral Head: A Retrospective Study to Compare Nail vs. Plate. Surgical Techniques Development, 14(3), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/std14030023








