Abstract
Introduction: Hemivertebrae are a common defect of vertebral formation, potentially resulting in debilitating congenital scoliosis and necessitating highly traumatic surgery. Virtual surgical planning (VSP) and 3D-printed patient-specific implants (PSIs) have increasingly been applied to complex spinal surgery, and offer a range of potential benefits. Research Question: We report the use of 3D-printed PSIs and VSP as part of a two-level anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) for the management of lateral hemivertebra and congenital scoliosis. Material and Methods: A 53-year-old male with chronic low-back pain, due to L4 hemivertebra and mild congenital scoliosis, presented with new-onset leg pain. CT revealed L4/5 and L5/S1 degeneration and foraminal stenosis. Given the complex anatomy and extensive multi-level osteophytosis, 3D-printed PSIs were designed, manufactured, and implanted as part of a two-level ALIF. Results: Excellent implant fit was achieved intraoperatively, confirmed via postoperative imaging. VSP assisted with navigating challenging bony and vascular anatomy. Three-month postoperative imaging demonstrated construct stability, early signs of bony fusion, with implant placement, spinal curvature, and disc height corrections closely matching the VSP. Clinically, the patient’s pain and functional impairment had effectively resolved by nine-month follow up, as demonstrated through subjective and objective measures. Discussion and Conclusions: Virtual surgical planning and 3D-printed PSIs can be useful surgical aids in the management of the often-complex cases involving hemivertebrae and congenital scoliosis. This case of congenital pathology adds to the growing reports of PSI application to a variety of complex spinal pathologies, with analyses showing a close match of the postoperative construct to the preoperative VSP.
1. Introduction
A hemivertebra refers to a defect of embryological vertebral formation characterised by a pathological wedge-shaped vertebral body with a single hemi-lamina and pedicle [1]. With an estimated incidence of 1–10 per 10,000 live births, they are a common cause of congenital scoliosis, which develops as a result of the normal adolescent growth spurt, driving wedge growth and the subsequent disruption of normal spinal curvature [2]. A hemivertebra may be detected through prenatal ultrasound or, if scoliosis becomes clinically apparent in early life, radiographic investigation. Asymptomatic abnormalities are likely to remain undetected. Hemivertebrae are commonly associated with a range of other vertebral and congenital abnormalities, which may also serve as the impetus for investigation. Hemivertebrae are commonly associated with a range of other vertebral and congenital abnormalities, which may also serve as the impetus for investigations [2,3,4]. There is no consensus on or widely accepted guidelines for the management of hemivertebrae, which is generally undertaken in the paediatric and adolescent years. Goals of hemivertebra and associated congenital scoliosis management include the prevention of progression to significant deformity, as well as the restoration of physiologic spinal profiles in the coronal and sagittal planes, while minimising the number of fused levels [3,5]. Broadly, management can be conservative, including monitoring and bracing, or surgical. The main surgical procedures include hemivertebrae resection through either an anteroposterior- or posterior-alone approach, in situ arthrodesis, or convex-side growth arrest (epiphysiodesis) [2,5], as well as instrumented fusion for adult scoliosis [6].
Virtual surgery planning (VSP) and 3D printing (3DP) are associated computer-based technologies, which have increasingly been applied to spinal surgery through the development of computer-aided preoperative surgical planning and 3D-printed patient-specific guides, anatomical (bio)models, and implants [7,8]. Increasing reports on spinal patient-specific implant (PSI) use have emerged over the last 10 years [7], particularly for complex cases of malignancy and degeneration [9,10,11]. This interest is driven by the range of potential benefits of PSIs, which include improved implant fit with the anatomy, resulting in an improved stability, stress distributions, and osseointegration, as well as reduced operative times and blood loss as a result of removing the need to excessively alter the anatomy by cutting away additional tissue, such as endplate bone, to accommodate the implant [7,12]. However, disadvantages also exist with increased pre-operative planning time (despite intraoperative time savings) and reduced intraoperative flexibility. Financial costs may mount with design and manufacturing challenges and the need for specialised skills and equipment [7,13]. A lack of quality data may also pose a challenging regulatory environment [14].
VSP, whilst commonly an integral part of PSI development, is itself a uniquely useful surgical aid aimed at enhancing preoperative planning by improving anatomic visualisation and simulating surgical steps, ultimately aiming to reduce surgical risk and improve outcomes for patients [8,12]. While conventional surgical management options for hemivertebra and congenital scoliosis often include ‘subtractive’ methods, including hemivertebra resection, decortication as part of in situ fusion, and osteotomies [5,15,16,17], PSIs allow for a largely ‘additive’ approach, which likely considerably minimises intraoperative trauma and secondarily may improve postoperative recovery and outcomes [18,19,20]. We describe the use of VSP and 3D-printed PSIs, as part of a two-level anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF), to manage symptomatic degeneration and congenital scoliosis associated with an L4 lateral hemivertebra in an adult male patient.
2. Technical Note
2.1. Case Presentation
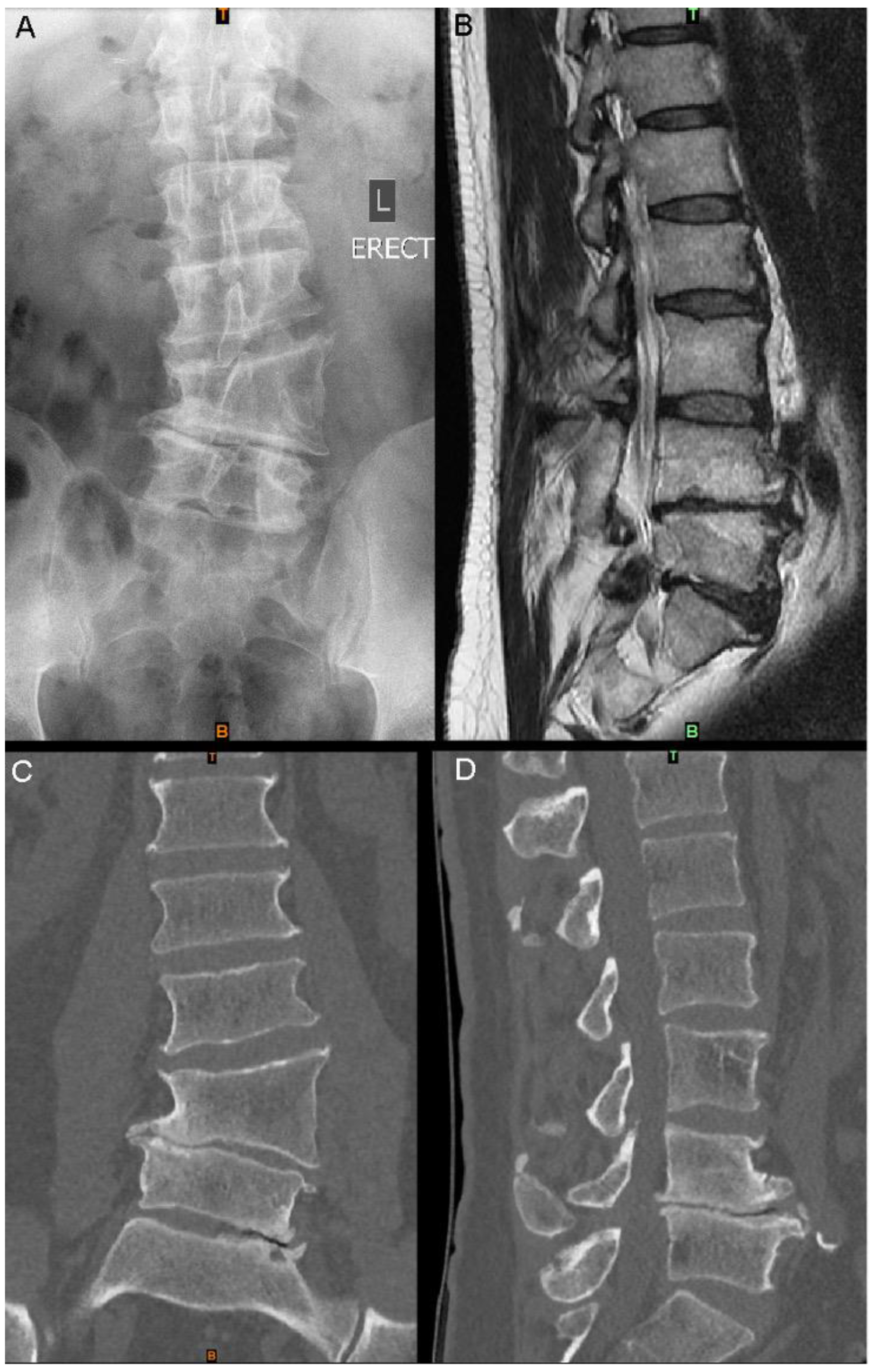
A 53-year-old man presented with a 12-month history of severe, progressive back and bilateral leg pain (visual analogue scale (VAS) pain score of 8/10). No deficits in sensory or motor deficits were present on examination; however, the patient reported difficulty in performing occupational tasks. The patient reported a background of chronic lower-back pain since childhood, secondary to an L4 lateral hemivertebra diagnosed in adolescence. Conservative management had successfully provided symptomatic relief until the recent onset of leg pain. CT imaging demonstrated the long-standing L4 hemivertebra and mild congenital scoliosis, as well as associated degenerative changes at the L4/5 and L5/S1 levels, including a loss of disc and neuroforaminal heights, and extensive osteophytosis (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
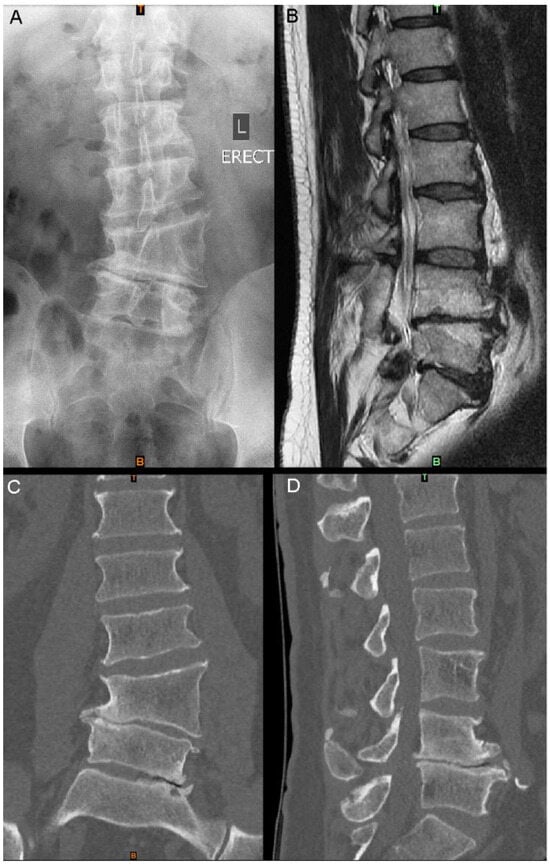
Figure 1.
Imaging at presentation: (A) standing AP X-ray; (B) sagittal slice of T2 MRI of the lumbar spine; (C) lumbar spine CT coronal slice; (D) lumbar spine CT sagittal slice at a similar position to (B).
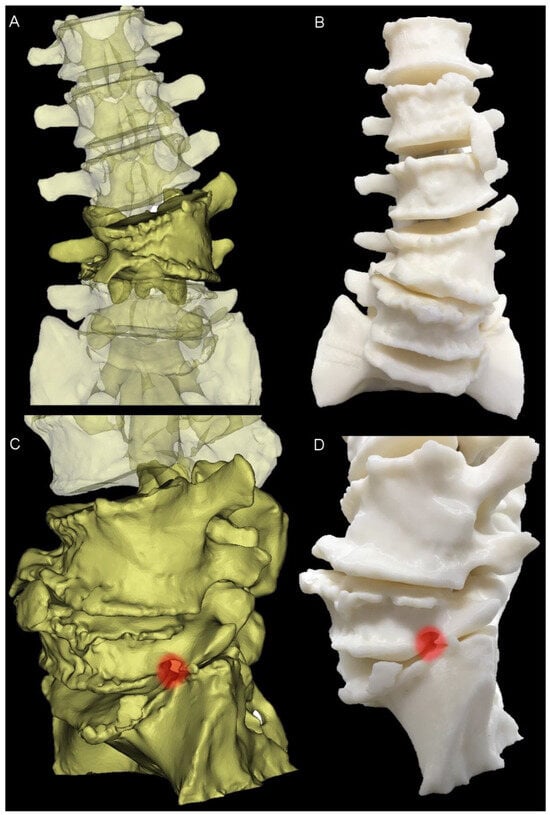
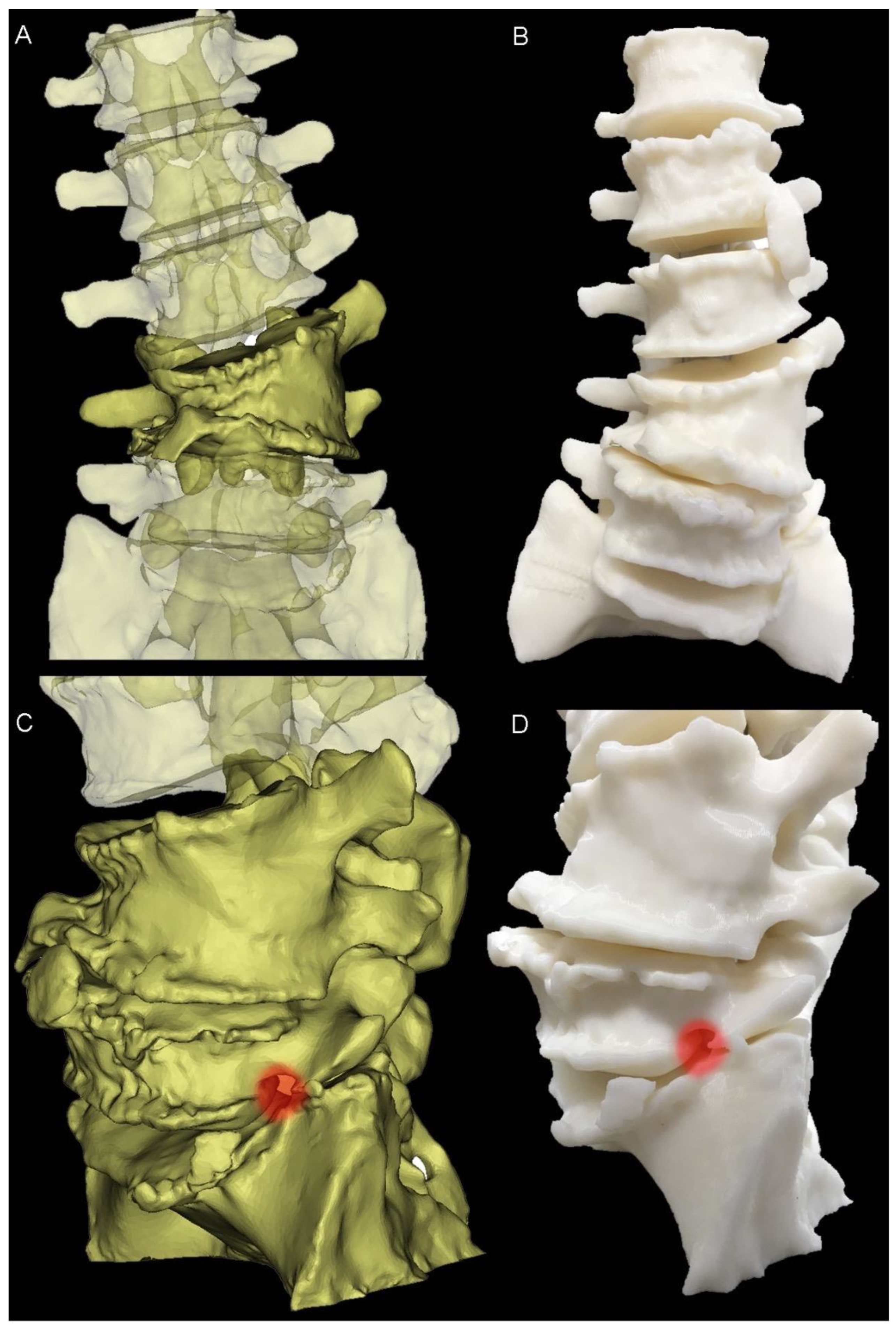
Figure 2.
Three-Dimensional modelling. (A) Anterior view of the preoperative pathological anatomy; hemivertebra is opaque; remainder of the lumbar spine is translucent. (B) Anterior view of the 3D-printed haptic biomodel. (C) Left-hand side view of the virtual model, showing the neuroforaminal stenosis at the L5-S1 level (red highlight). (D) Similar to (C), with the red highlight showing the neuroforaminal stenosis in the 3D-printed biomodel.
Two-level (L4/5 and L5/S1) ALIF surgery was indicated, given the patient’s severe and intractable symptoms. Risks including retrograde ejaculation and infertility were discussed and patient’s sperm was cryo-banked prior to surgery. The primary operative goal was the indirect distraction of the neuroforamina, with the aim of relieving the patient’s symptoms, as well as secondarily providing lordotic and partial scoliotic correction. The surgeon deemed the use of VSP and PSIs appropriate due to the lack of suitable off-the-shelf (OTS) implants.
2.2. Surgical Planning and Implant Design
The design and manufacture process was performed using 3DMorphic Pty Ltd. (Matraville, Australia) and has been described prior [21]. In brief, this involved thresholding, segmentation, and an initial 3D reconstruction of the patient’s CT using Materialise MIMICs (version 22, Leuven, Belgium). Haptic BioModels [8] of the preoperative pathological anatomy were 3D-printed in acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (F170, Stratasys, MN, USA).
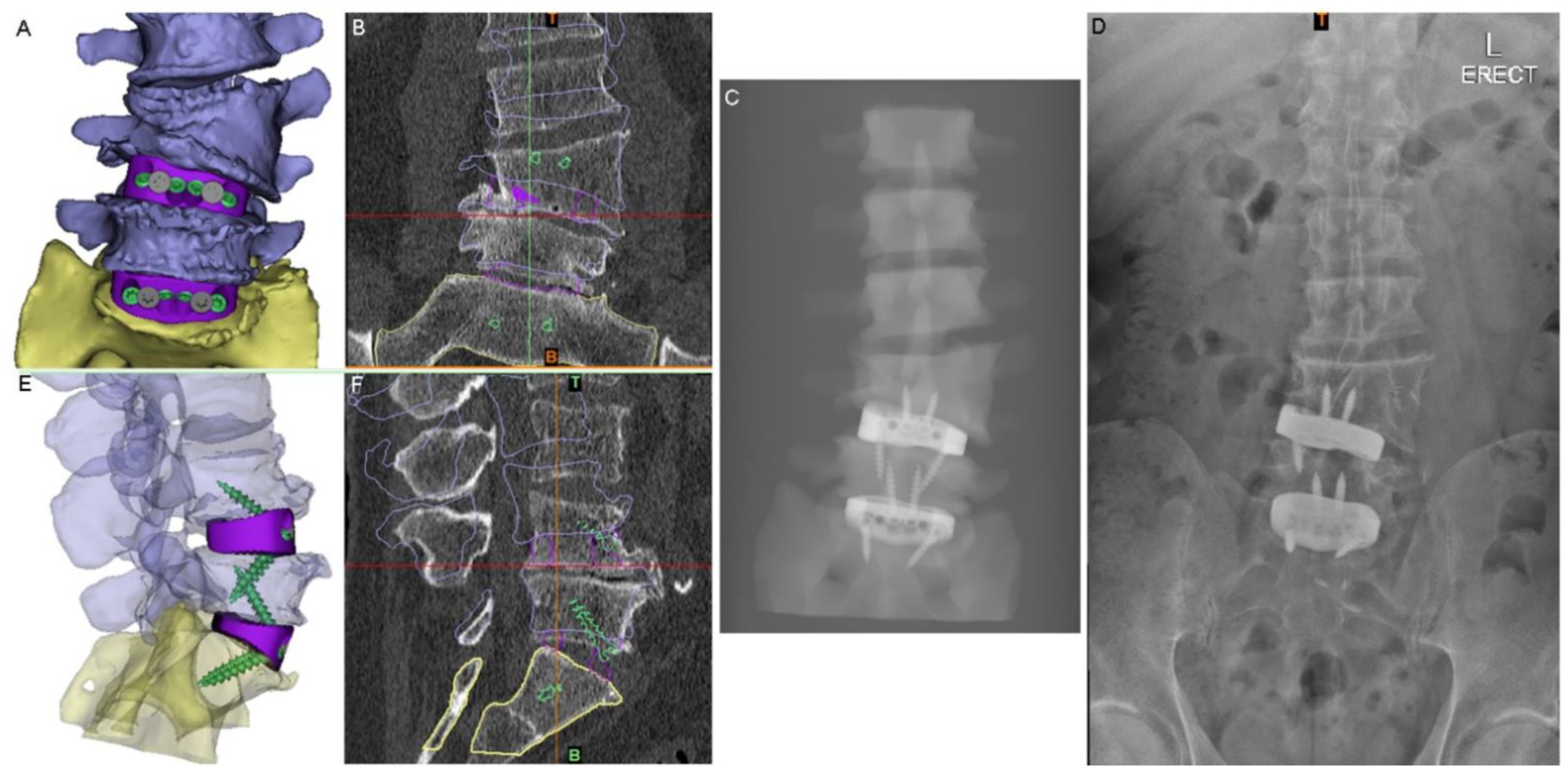
The PSIs were designed using 3DMorphicCAD (3DMorphic Pty Ltd., Sydney, Australia) and Rhinoceros (vs6, McNeel and Associates, Seattle, WA, USA) [22]. Features incorporated included: radiographic alignment assessment features, anti-expulsion teeth, integral screw fixation, variable surface topology/porosity, large central graft window for auto/allograft, pre-planned screw lengths and trajectories (Figure 3), as well as contacting surfaces designed to match the superior and inferior endplate morphologies of each (L4-5 and L5-S1) of the interbody spaces and to correct vertebral alignment in both coronal (scoliotic) and sagittal (lordotic) planes.
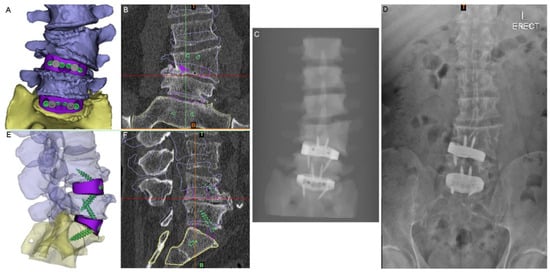
Figure 3.
Virtual surgery planning (VSP). (A) Anterior view of the 3D model of the planned anatomical reconstruction and cage positions for medium-sized cages (NB: a small cage was actually used at the L4-5 level). (B) The 3D model shown in (A) superimposed on S1 in the preoperative CT (coronal slice shown). (C) Simulated X-ray of the 3D model in (A). (D) Postoperative standing X-ray. (E) Lateral view of the planned reconstruction with translucent vertebrae to show the screws and devices. (F) Sagittal-plane CT slice with the 3D reconstruction shown in (E) superimposed on S1 to show the planned postoperative state compared to the pathological state.
The PSIs were 3D-printed using biomedical grade 5 titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V) (3Dmorphic Pty Ltd., Matraville, NSW, Australia) on an EOSM100 (EOS GmbH, Krailling/Munich, Germany) using parameters described by Amin et al. [21]. Mechanical post-processing was performed to remove support material and powder residue, refine the surface topology and chemistry, and improve crack resistance and fatigue lifespan. The surface roughness of the bone-contacting areas of the device had an Ra of 1.5–4 µm and the devices were coated with hydroxyapatite to encourage early osseointegration [23]. Three device heights were provided to provide intraoperative options as the degree of mobilisation; and therefore, the degree of interbody height and angle restoration achievable is dependent on the extent of the intraoperative discectomy.
2.3. Surgery
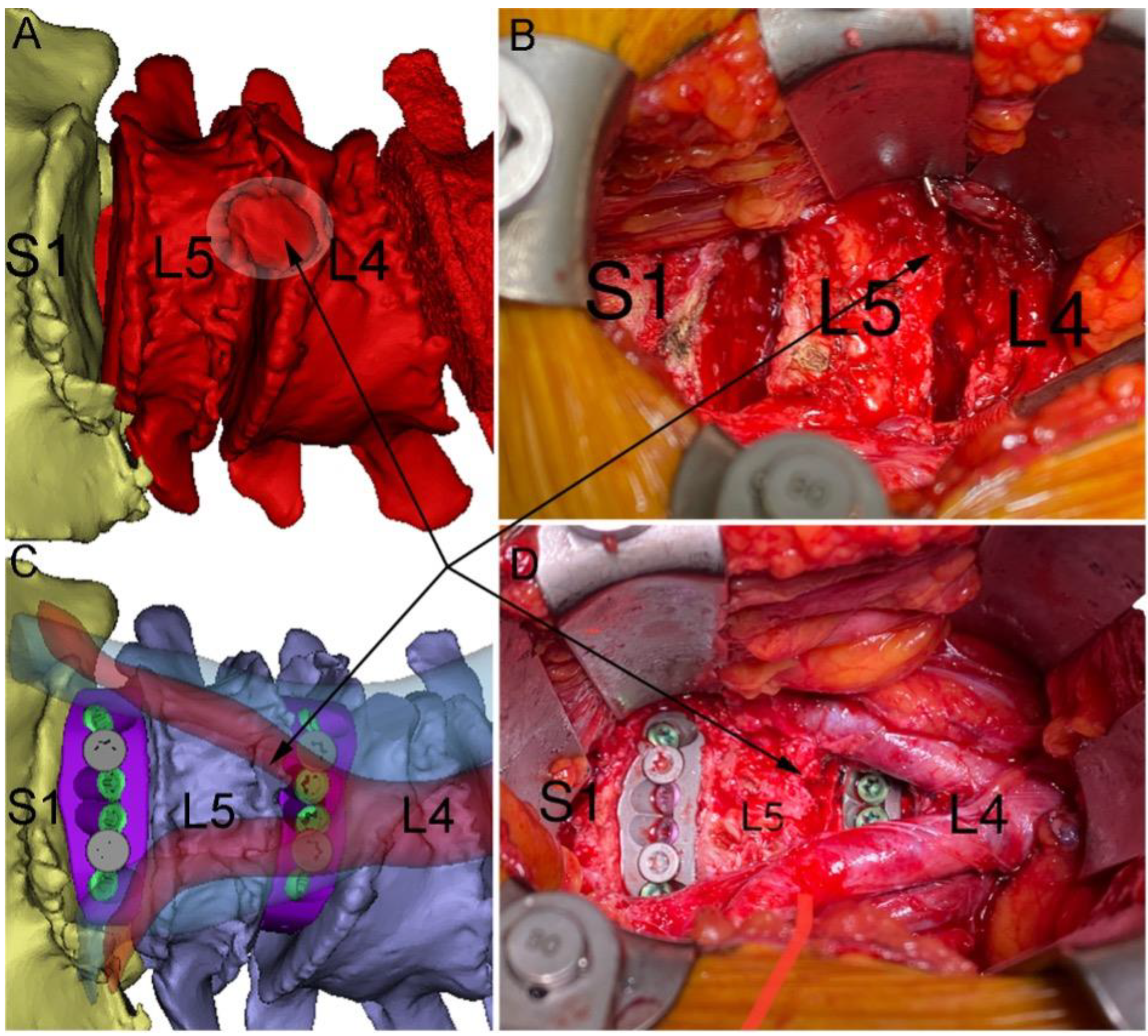
The patient was positioned supine. Using image-intensified fluoroscopy, the level of the first ALIF (L5/S1) was confirmed prior to incision. A linear mini-Pfannenstiel incision was made, with a circular retractor system, used for retroperitoneal exposure. Anterior vessels required mobilization to allow for exposure of the anterior vertebral body at the L5 level. Exposure was performed by a vascular surgeon. Image intensification was again used to confirm the level of pathology. Discectomy of both disc spaces was performed, with careful endplate preparation via curetting to avoid damaging the endplates (Figure 4). Single-shot exposure fluoroscopy was used to check the alignment and depth of the implants, with the surgeon selecting the best fitting (L4/5: small; L5/S1: medium) for final implantation. The cages were packed with allograft cancellous bone block (Australian Biotechnologies, Sydney, Australia) and i-factor Putty (Cerapedics, Broomfield, CO, USA). Single-shot exposure fluoroscopy was used to confirm their final placement. A small tear occurred at the aortic bifurcation during this trialling process, likely due to significant vascular adhesions. This was successfully managed using suture repair. Copious antibiotic irrigation was used. Further bone graft was packed around the cages. Fascial and skin layers were closed. Skin-to-skin operative time was 3 h 20 min and estimated blood loss was 140 cc. Throughout the procedure, the 3D-printed biomodels of the patient’s spine and the custom cages, as well as the VSP, were referred to as needed to confirm bony anatomy, vessel position, and implant placement.
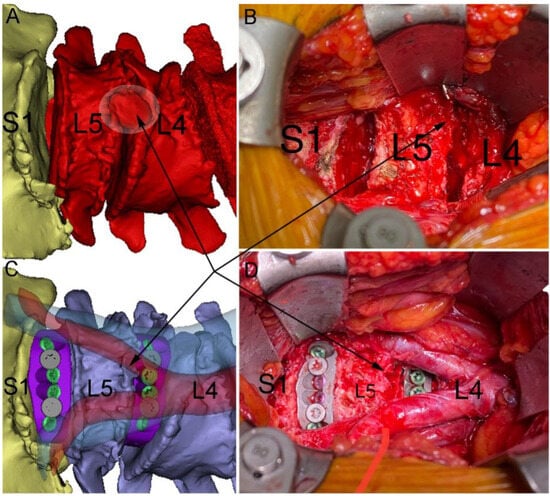
Figure 4.
Virtual surgery planning (VSP) of anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) as compared to intraoperative view. (A) Preoperative pathology, showing a large L4-L5 osteophyte (black arrows and halo in (A)). This osteophyte was used during surgery as a landmark to aid with anatomical navigation and subsequently resected (B) after access was complete. (B) shows L4-L5 and L5-S1 discectomies. (C) VSP of major vessels and the ALIF devices in position with the aorta (translucent red) bifurcation occurring just above the L4-L5 disc space (vena cava shown in translucent blue). (D) Surgical view after ALIF devices implanted with the aorta and common iliac arteries showing (vascular retraction eased). Note the similarities between the VSP vessel and device positions and those observed in surgery.
2.4. Clinical Follow-Up
The patient was followed up clinically, using subjective and objective measures, and radiographically. The patient’s back and leg pain improved postoperatively with an overall return to pre-morbid function; a preoperative VAS pain score of 8/10 and an Oswestry Disability Index of 42 improved to 1/10 and 3, respectively, at 9-month follow-up.
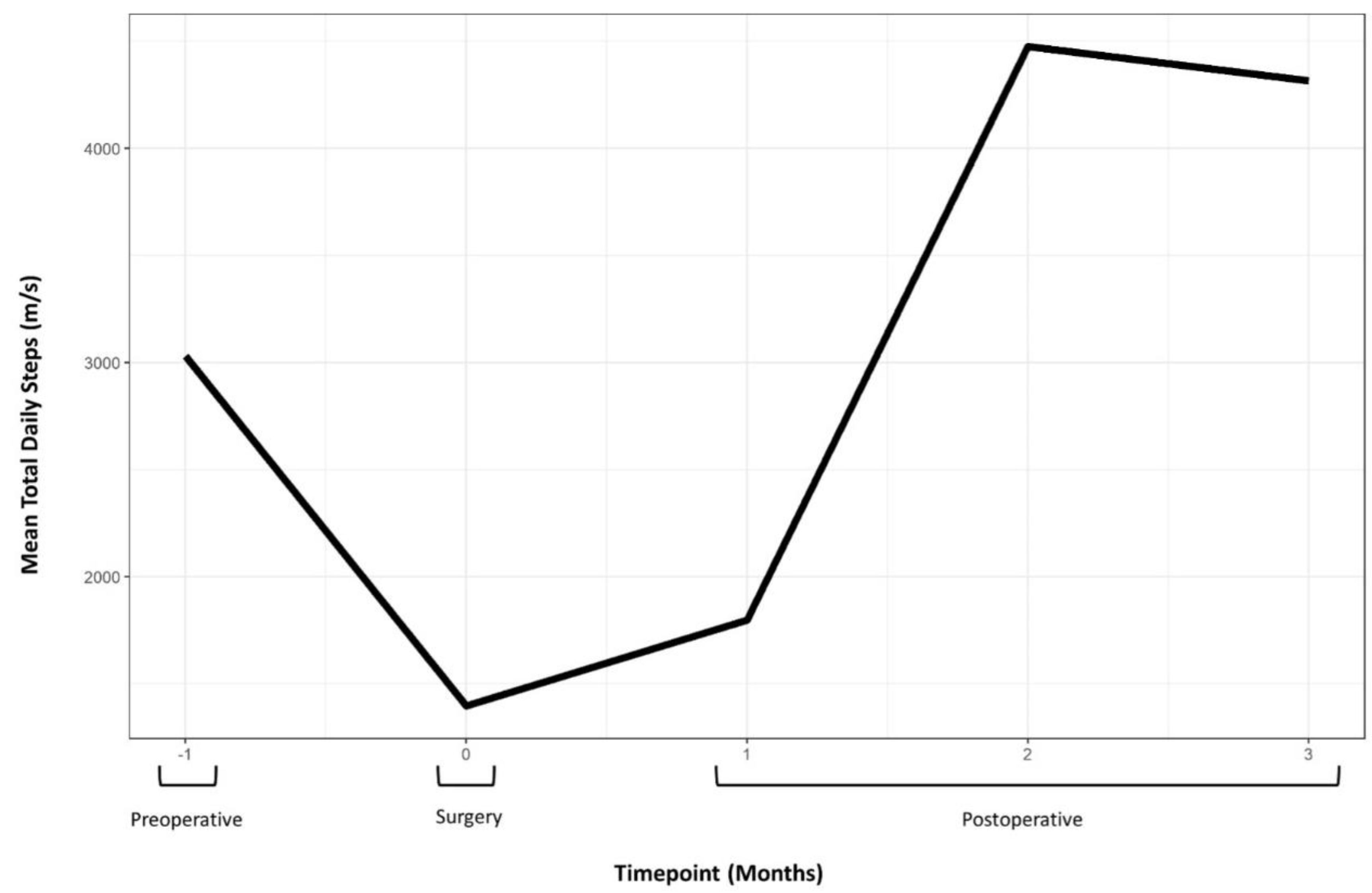
Objective monitoring was undertaken using smartphone-based wearable accelerometry (Apple Health application on the iPhone smartphone; Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA, USA). Gait parameters recovered progressively over the first three postoperative months (Table 1; Figure 5). The mean total daily step-count improved from 3030 steps preoperatively to over 12,000 by 9-month follow-up.

Table 1.
Perioperative objective functional data. Note: Data were collected via smartphone-based wearable accelerometry (Apple Health application on the iPhone smartphone; Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA, USA).
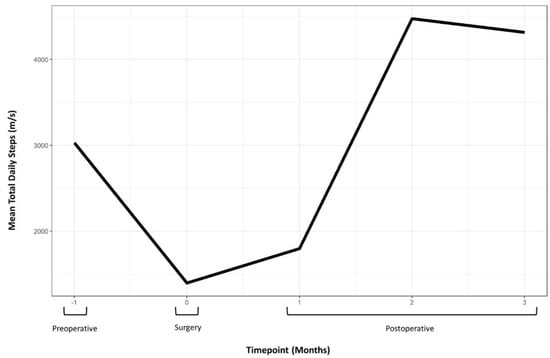
Figure 5.
Perioperative mean total daily step count data demonstrating postoperative recovery and improvement over preoperative function. Note: Data were collected via smartphone-based wearable accelerometry (Apple Health application on the iPhone smartphone; Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA, USA).
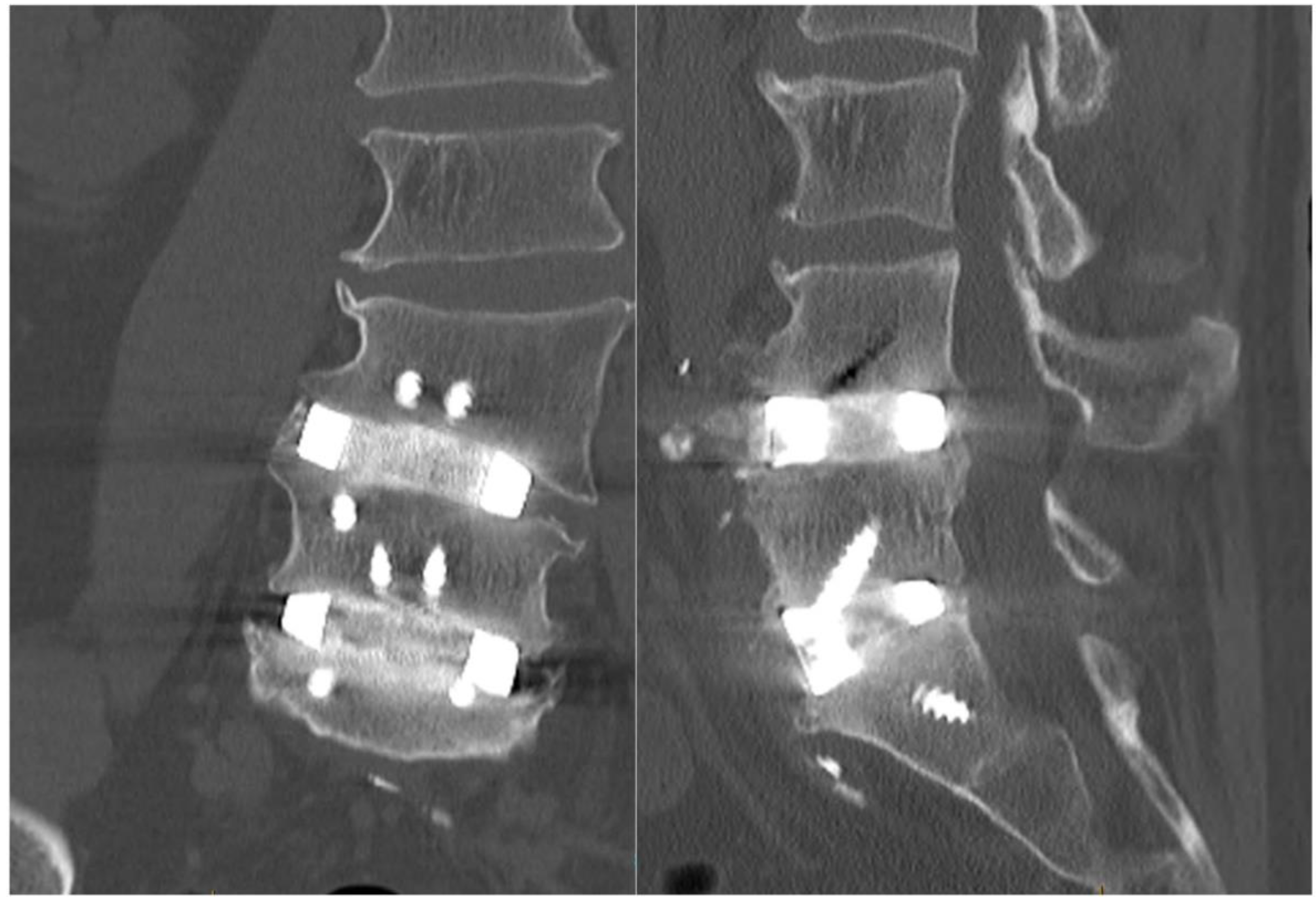
Imaging at day 1 postoperatively demonstrated excellent implant positioning (Figure 6). Disc and neuroforaminal height correction, as well as lordotic and partial scoliotic correction closely matched the planned correction in the VSP. At 9-month postoperative imaging, implant positioning and parameter corrections were stable. Early radiographic evidence of bony fusion at both operative levels and osteophyte resorption were appreciable (Figure 7).
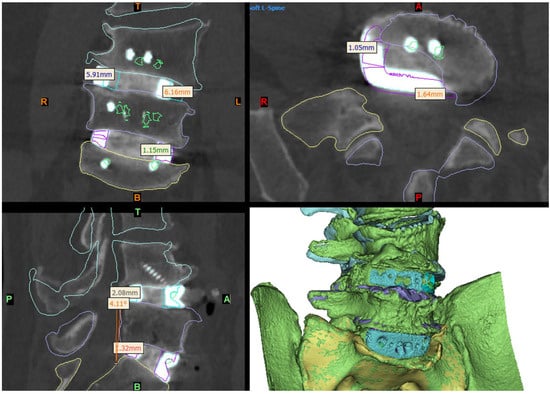
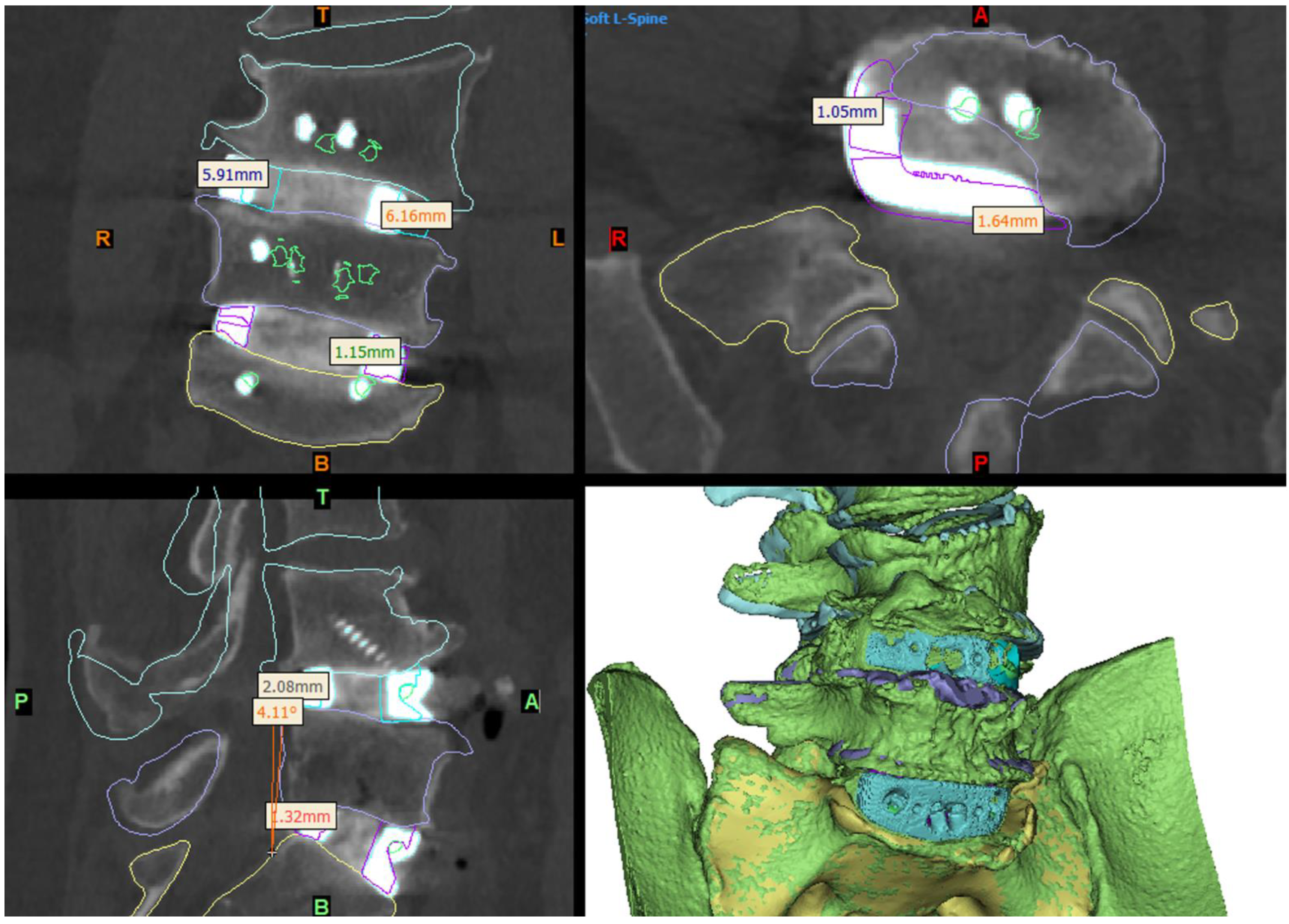
Figure 6.
Day-1 postoperative CT and 3D reconstruction of the construct (bottom right panel) compared to the virtual surgery planned (VSP) device and anatomy positioning (shown by the coloured outlines). The L5-S1 device was positioned very close to the VSP position, being ~1–1.5 mm further to the right and anterior than planned. The L4-L5 device was implanted ~6 mm to the left and ~2 mm anterior to the VSP position (see Section 3), which resulted in slightly less coronal and a sagittal-plane angle adjustment of the L4 hemivertebra being achieved than planned.
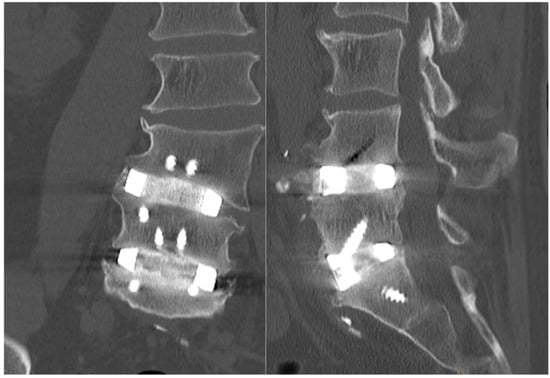
Figure 7.
Nine-month postoperative CT imaging sagittal (left) and coronal (right) slices showing adequate fusion with osteophyte demineralisation as well as osseointegration. Both CTs are shown with the same contrast settings.
3. Discussion
Hemivertebra and congenital scoliosis may produce complex anatomies and challenging operative scenarios, particularly in cases of delayed management where degenerative processes and secondary structural curves may be significantly progressed [3]. The lack of literary consensus on management and the focus on paediatric and adolescent cases further adds to management difficulty [15,24]. The characteristic customisability of PSIs, allowing for the profile of prostheses to be matched to the specific anatomy of each patient [25], as well as the growing reports of their application to complex spinal pathoanatomies [7,11,26,27,28], are suggestive of their utility in the management of hemivertebrae and congenital scoliosis.
The abilities to match the prosthesis profile to the patient’s exact pathoanatomy and to add custom features underpin the primary benefits of using PSIs in this case, which include optimal fit and a likely minimised surgical trauma, an improved primary stabilisation, and a more precise correction to height and curvature parameters. In this case, 3D-printed PSIs allowed for ALIF surgery to be a feasible surgical option, preventing more radical surgeries, like hemivertebra resection, being needed as well as minimising the need for significant endplate preparation if OTS implants were used, which could have increased surgical time as well as cage subsidence risk through the loss of stiffer cortical bone [22,29]. These advantages are highlighted by Khan et al.’s description of a comparatively more complex and prolonged two-stage ALIF-based procedure to treat lumbar hemivertebra and congenital scoliosis in an adult [15].
The close adherence of the relative implant and anatomy positioning in postoperative imaging to the preoperative VSP demonstrates the accurate realisation of VSP correction goals and the validity of this technique (Figure 6). The ability to assess the vascular anatomy preoperatively and refer to the VSP intraoperatively allowed the surgical team to be better prepared, particularly in dealing with the extensive adhesions at the aortic bifurcation, and more rapidly successfully manage the intraoperative aortic tear [8]. The use of prominent osteophytes as patient-specific pathoanatomical landmarks also aided surgical navigation.
Additionally, while Mobbs et al. reported a similar case of an L5 hemivertebra managed with a PSI [30], the sagittal orientation of their patient’s hemivertebra wedge created a different operative challenge, given the better alignment with the essentially sagittal access tunnel, and therefore likely improved visualisation, surgical ergonomics, and ease of implantation. In contrast, the laterally oriented wedge in this case presented significant difficulty in implantation due to the wedge shape creating a lateral expulsive force. This was overcome through thorough cartilaginous endplate preparation and optimal adjacent vertebral body distraction prior to implantation.
4. Limitations
While early clinical and radiographic outcomes in this case have been encouraging, this application of VSP and PSIs required a highly experienced team. This includes both preoperatively and intraoperatively. Preoperatively, implants needed to be designed such that all nine combinations of implant sizes in this two-level operation can combine to result in an acceptable total correction. Intraoperatively, there were challenges with implantation, mobilising significantly adherent vessels and managing an aortic bifurcation tear. Other limitations include the VSP not including an additional transverse vessel on approach. Future studies may also investigate global balance in PSIs to compare pre- and postoperative spino–pelvic relationships in relation to OTS implants.
5. Conclusions
VSP and 3D-printed PSIs allowed the surgical team to provide optimally fitting implants in a less traumatic procedure, allowing for an improved stabilisation and a more precise correction in hemivertebra and congenital scoliosis management. This case of congenital pathology also adds to the growing reports of 3D-printed PSI use for complex spinal cases, supporting their important role in the surgical arsenal of spinal teams.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: T.A., W.C.H.P., P.N., A.L., L.K. and R.J.M. Methodology: T.A., W.C.H.P., P.N., A.L. and R.J.M.; software: W.C.H.P.; validation, L.K. and R.J.M.; data curation: T.A., W.C.H.P., P.N., A.L., L.K. and R.J.M.; writing—original draft preparation: T.A.; writing—review and editing: T.A., W.C.H.P., P.N., A.L., L.K. and R.J.M.; supervision: W.C.H.P., A.L. and R.J.M.; project administration: L.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three-Dimensional |
| 3DP | Three-Dimensional Printing |
| ABS | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene |
| ALIF | Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion |
| AP | Anteroposterior |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NSURG | NeuroSpine Surgery Research Group |
| NSW | New South Wales |
| OTS | Off-The-Shelf |
| ODI | Oswestry Disability Index |
| PSIs | Patient-Specific Implants |
| SORL | Surgical and Orthopaedic Research Labs |
| UNSW | University of New South Wales |
| USA | United States of America |
| VAS | Visual Analogue Scale |
| VSP | Virtual Surgery Planning |
References
- Steinmetz, M.P.; Benzel, E.C. Benzel’s Spine Surgery E-Book: Techniques, Complication Avoidance, and Management; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Johal, J.; Loukas, M.; Fisahn, C.; Chapman, J.R.; Oskouian, R.J.; Tubbs, R.S. Hemivertebrae: A comprehensive review of embryology, imaging, classification, and management. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2016, 32, 2105–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, B.; Yan, H.; Tang, J. A review of the hemivertebrae and hemivertebra resection. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 36, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMaster, M.J.; Ohtsuka, K. The natural history of congenital scoliosis. A study of two hundred and fifty-one patients. J. Bone Jt. Surg Am. 1982, 64, 1128–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollini, G.; Docquier, P.-L.; Viehweger, E.; Launay, F.; Jouve, J.-L. Lumbar Hemivertebra Resection. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2006, 88, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.E.; Lenke, L.G. Adult degenerative scoliosis: Evaluation and management. Neurosurg. Focus 2010, 28, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, B.; Mobbs, R.J.; Wu, A.-M.; Phan, K. Systematic review of 3D printing in spinal surgery: The current state of play. J. Spine Surg. 2017, 3, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, W.C.H.; Burnard, J.L.; Wilson, P.J.; Mobbs, R.J. 3D printed anatomical (bio)models in spine surgery: Clinical benefits and value to health care providers. J. Spine Surg. 2019, 5, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lim, J.-Y.; Shim, K.-W.; Han, J.W.; Yi, S.; Yoon, D.H.; Kim, K.N.; Ha, Y.; Ji, G.Y.; Shin, D.A. Sacral Reconstruction with a 3D-Printed Implant after Hemisacrectomy in a Patient with Sacral Osteosarcoma: 1-Year Follow-Up Result. Yonsei Med. J. 2017, 58, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wei, F.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Cai, H.; Li, Z.; Yu, M.; Wu, F.; Liu, Z. Reconstruction of the Upper Cervical Spine Using a Personalized 3D-Printed Vertebral Body in an Adolescent With Ewing Sarcoma. Spine 2016, 41, E50–E54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, T.L.; Rogers, J.M.; Lin, K.; Thompson, R.; Owbridge, M. Custom-Made Titanium 3-Dimensional Printed Interbody Cages for Treatment of Osteoporotic Fracture–Related Spinal Deformity. World Neurosurg. 2018, 111, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheha, E.D.; Gandhi, S.D.; Colman, M.W. 3D printing in spine surgery. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7 (Suppl. S5), S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, N.; Schaffer, N.E.; Aleem, I.S.M.; Patel, R. 3D-printed Patient-specific Spine Implantss: A systematic review. Clin. Spine Surgery A Spine Publ. 2020, 33, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, T.; Parr, W.C.; Mobbs, R.J. Opinion Piece: Patient-Specific Implants May Be the Next Big Thing in Spinal Surgery. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Barrey, C.; Massourides, H.; Perrin, G. Lumbar Hemivertebra in an Adult Treated by Transpedicular Osteotomy. World Neurosurg. 2012, 77, 592.e5–592.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruf, M.; Jensen, R.; Letko, L.; Harms, J. Hemivertebra Resection and Osteotomies in Congenital Spine Deformity. Spine 2009, 34, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedden, D. Management themes in congenital scoliosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2007, 89 (Suppl. S1), 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Desborough, J. The stress response to trauma and surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2000, 85, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, G.P. Addressing the Global Burden of Trauma in Major Surgery. Front. Surg. 2015, 2, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Turner, P.; Gagner, M. Stress response to laparoscopic liver resection. HPB 2004, 6, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Amin, T.; Lin, H.; Parr, W.C.H.; Lim, P.; Mobbs, R.J. Revision of a Failed C5-7 Corpectomy Complicated by Esophageal Fistula Using a 3-Dimensional−Printed Zero-Profile Patient-Specific Implant: A Technical Case Report. World Neurosurg. 2021, 151, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, W.C.H.; Burnard, J.L.; Singh, T.; McEvoy, A.; Walsh, W.R.; Mobbs, R.J. C3-C5 Chordoma Resection and Reconstruction with a Three-Dimensional Printed Titanium Patient-Specific Implant. World Neurosurg. 2020, 136, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, W.R.; Pelletier, M.H.; Bertollo, N.; Lovric, V.; Wang, T.; Morberg, P.; Parr, W.C.H.; Bergadano, D. Bone ongrowth and mechanical fixation of implants in cortical and cancellous bone. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polly, D.W.; Rosner, M.K.; Monacci, W.; Moquin, R.R. Thoracic hemivertebra excision in adults via a posterior-only approach. Neurosurg. Focus 2003, 14, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Kaplan, D.J.; Spivak, J.M.; Bendo, J.A. Three-dimensional printing in spine surgery: A review of current applications. Spine J. 2020, 20, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girolami, M.; Boriani, S.; Bandiera, S.; Barbanti-Bródano, G.; Ghermandi, R.; Terzi, S.; Tedesco, G.; Evangelisti, G.; Pipola, V.; Gasbarrini, A. Biomimetic 3D-printed custom-made prosthesis for anterior column reconstruction in the thoracolumbar spine: A tailored option following en bloc resection for spinal tumors: Preliminary results on a case-series of 13 patients. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 3073–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Yu, M.; Xu, N.; Wu, F.; Dang, L.; Zhou, H.; et al. Upper cervical spine reconstruction using customized 3D-printed vertebral body in 9 patients with primary tumors involving C2. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willemsen, K.; Nizak, R.; Noordmans, H.J.; Castelein, R.M.; Weinans, H.; Kruyt, M.C. Challenges in the design and regulatory approval of 3D-printed surgical implants: A two-case series. Lancet Digit. Health 2019, 1, e163–e171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobbs, R.J.; Parr, W.C.H.; Choy, W.J.; McEvoy, A.; Walsh, W.R.; Phan, K. Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using a Personalized Approach: Is Custom the Future of Implants for Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery? World Neurosurg. 2019, 124, 452–458.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobbs, R.; Coughlan, M.; Thompson, R.; Sutterlin, C.E.; Phan, K. The utility of 3D printing for surgical planning and patient-specific implant design for complex spinal pathologies: Case report. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2017, 26, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).