Complications Associated with Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
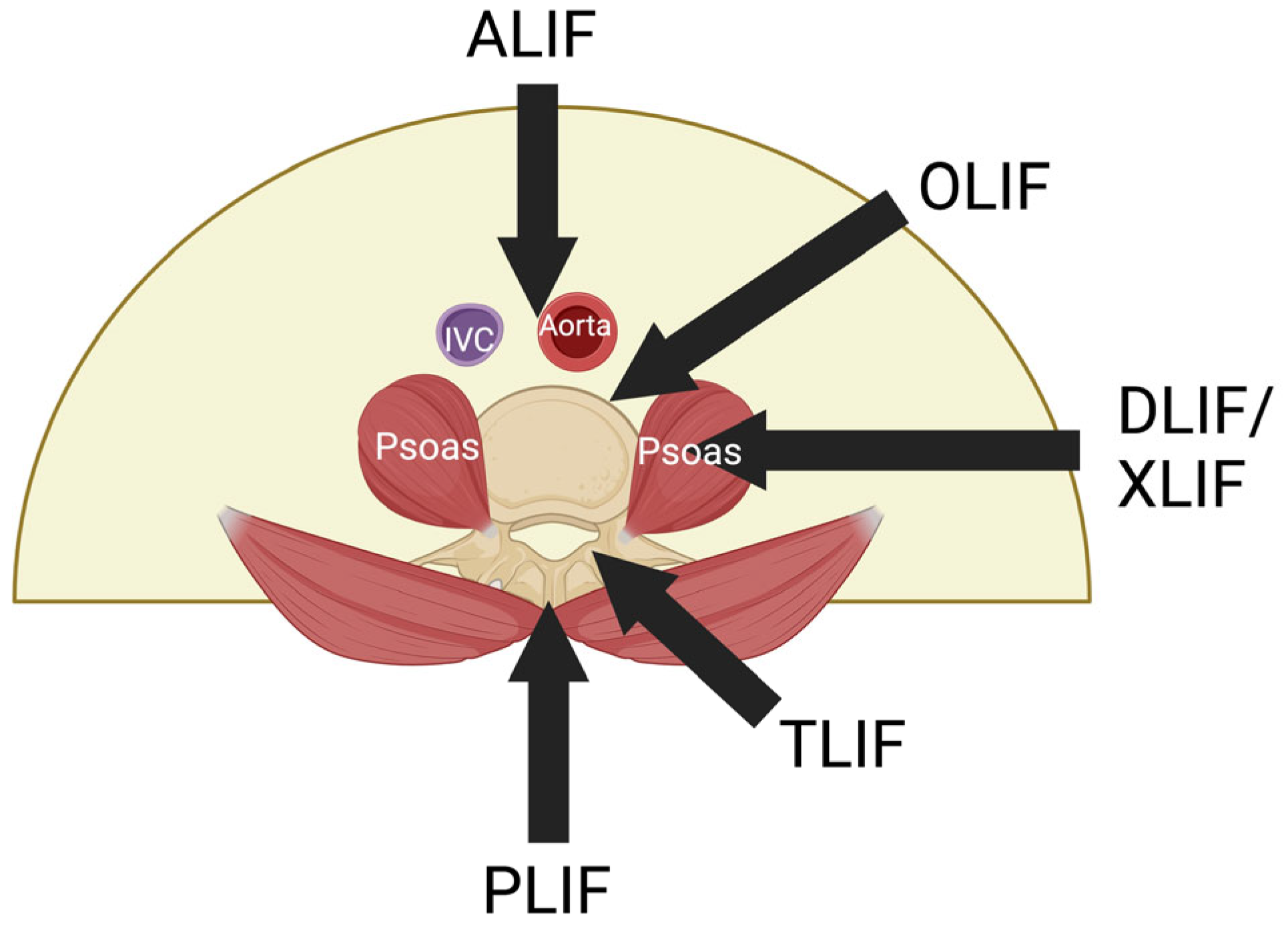
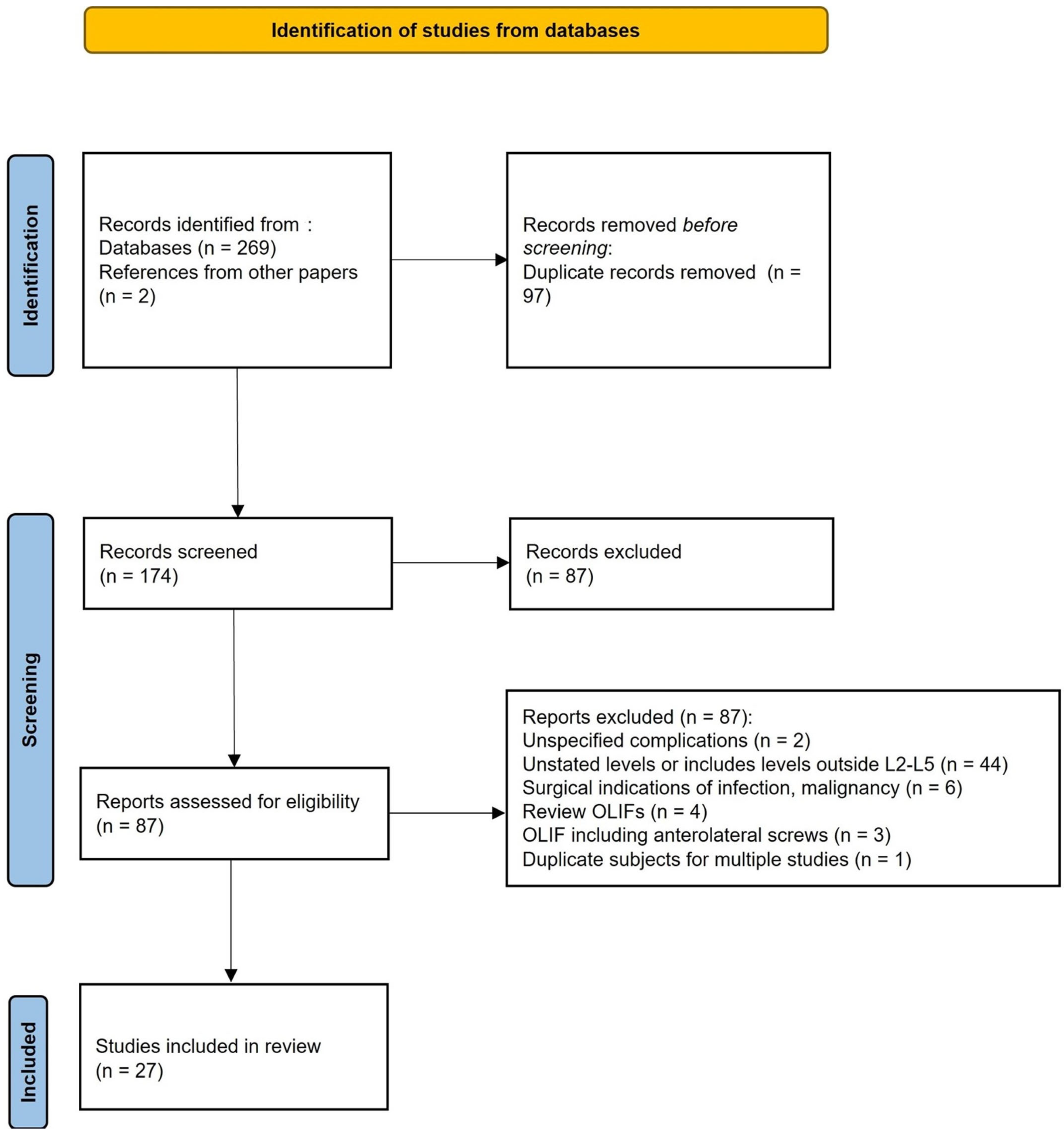
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
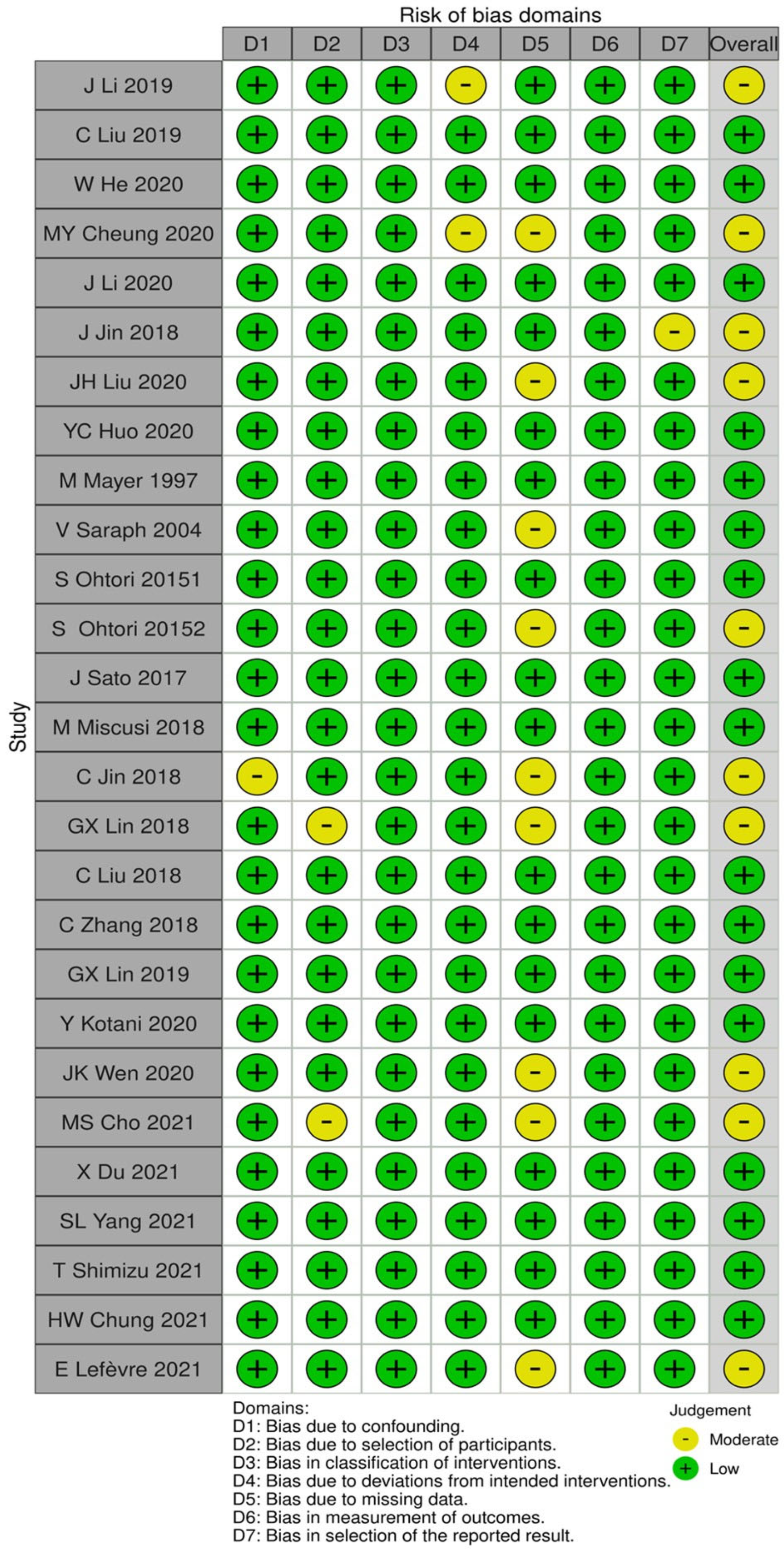
2.2. Data Extraction and Potential Biases
2.3. Statistical Analysis
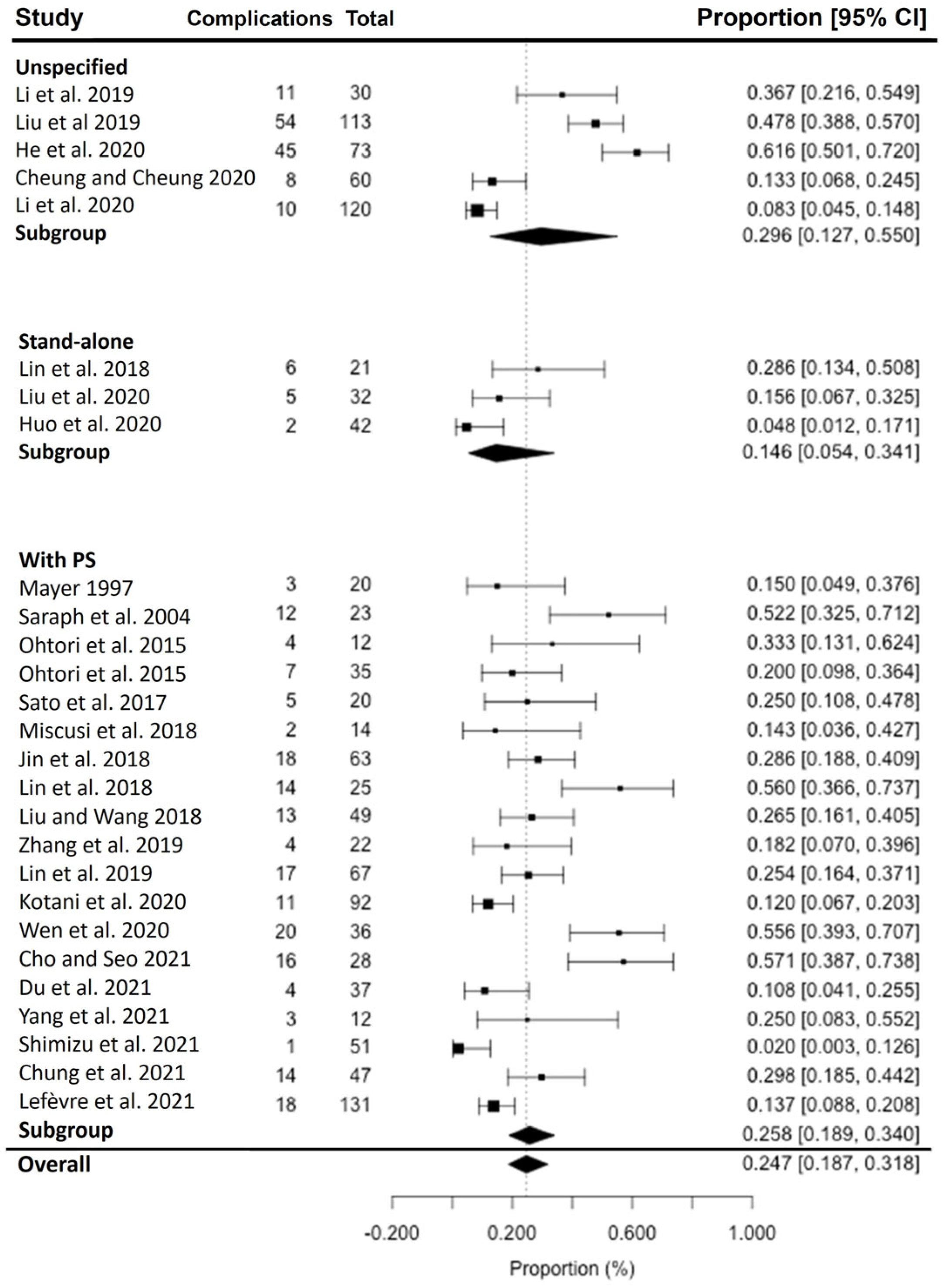
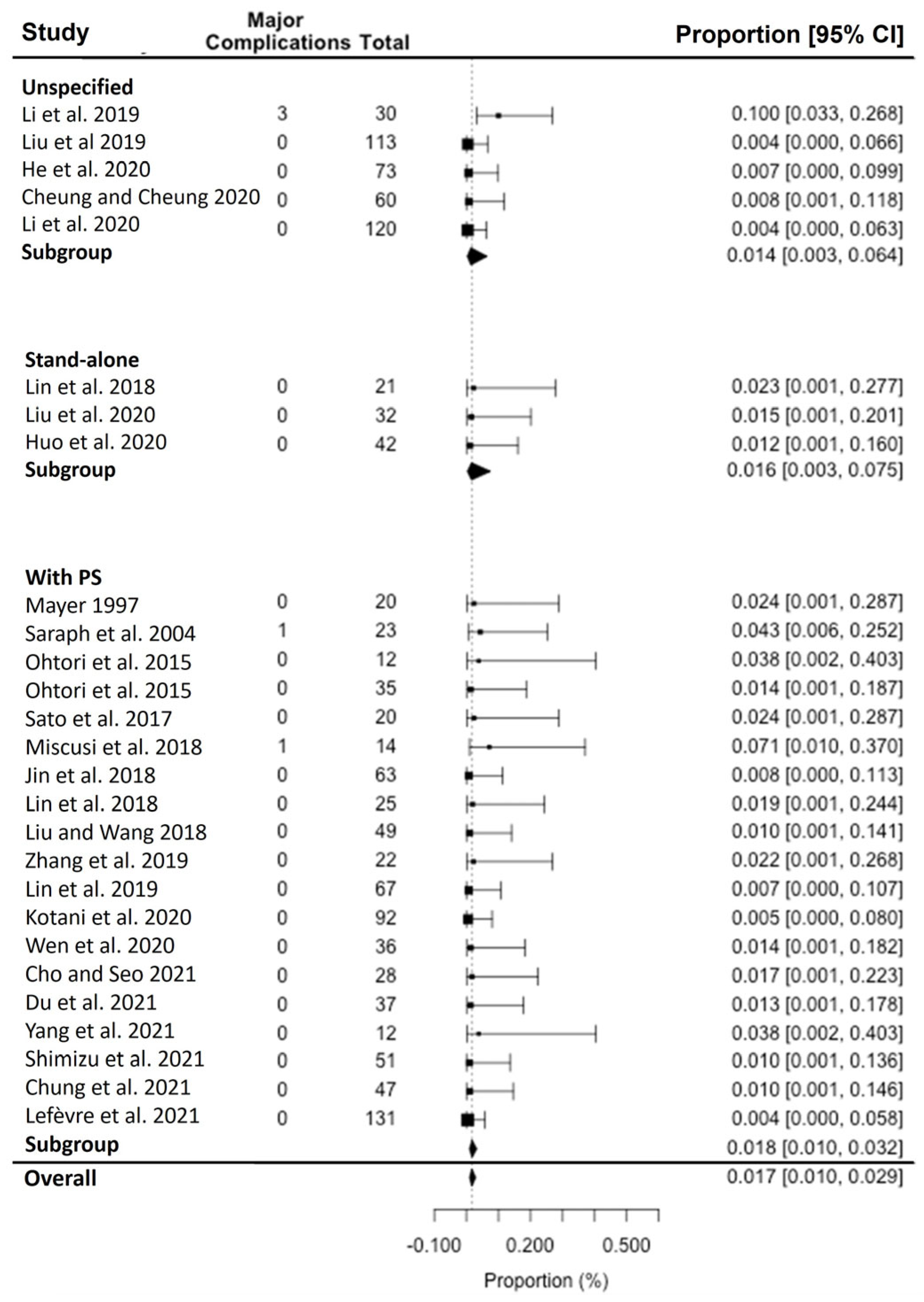
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayer, H.M. A New Microsurgical Technique for Minimally Invasive Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Spine 1997, 22, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allain, J.; Dufour, T. Anterior lumbar fusion techniques: ALIF, OLIF, DLIF, LLIF, IXLIF. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2020, 106, S149–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orita, S.; Shiga, Y.; Inage, K.; Eguchi, Y.; Maki, S.; Furuya, T.; Aoki, Y.; Inoue, M.; Hynes, R.A.; Koda, M.; et al. Technical and Conceptual Review on the L5-S1 Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion Surgery (OLIF51). Spine Surg. Relat. Res. 2021, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzmann, S.N.; Shue, J.; Hughes, A.P. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion-Outcomes and Complications. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2017, 10, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Kaliya-Perumal, A.K.; Chou, S.M.; Oh, J.Y. Does Lumbar Interbody Cage Size Influence Subsidence? A Biomechanical Study. Spine 2020, 45, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.S.; Suh, S.W.; Kang, S.H.; Nam, K.Y.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Chang, D.G.; Yang, J.H. The Radiologic and Clinical Outcomes of Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion for Correction of Adult Degenerative Lumbar Deformity. Indian J. Orthop. 2019, 53, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T.; Fujibayashi, S.; Otsuki, B.; Murata, K.; Matsuda, S. Indirect decompression via oblique lateral interbody fusion for severe degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: A comparative study with direct decompression transforaminal/posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 2021, 21, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohmeh, A.G.; Rodgers, W.B.; Peterson, M.D. Dynamically evoked, discrete-threshold electromyography in the extreme lateral interbody fusion approach. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2011, 14, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijji, F.Y.; Narain, A.S.; Bohl, D.D.; Ahn, J.; Long, W.W.; DiBattista, J.V.; Kudaravalli, K.T.; Singh, K. Lateral lumbar interbody fusion: A systematic review of complication rates. Spine J. 2017, 17, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.P.; Kaliya-Perumal, A.K.; Tandon, A.A.; Oh, J.Y. The Oblique Corridor at L4-L5: A Radiographic-Anatomical Study into the Feasibility for Lateral Interbody Fusion. Spine 2020, 45, E552–E559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, W. Development and Application of Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 12, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; He, D.; Sun, Y.; Xing, Y.; Wen, J.; Wang, W.; Xi, Y.; Liu, M.; Tian, W.; Ye, X. Standalone oblique lateral interbody fusion vs. combined with percutaneous pedicle screw in spondylolisthesis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Min, S.; Wang, S.; Jin, A. Biomechanical effects of an oblique lumbar interbody fusion combined with posterior augmentation: A finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereczki, F.; Turbucz, M.; Kiss, R.; Eltes, P.E.; Lazary, A. Stability Evaluation of Different Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion Constructs in Normal and Osteoporotic Condition—A Finite Element Based Study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 749914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, K.; Luo, K.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, K.; Yu, S.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, G. Effect of pedicle-screw rod fixation on oblique lumbar interbody fusion in patients with osteoporosis: A retrospective cohort study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraph, V.; Lerch, C.; Walochnik, N.; Bach, C.M.; Krismer, M.; Wimmer, C. Comparison of conventional versus minimally invasive extraperitoneal approach for anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Eur. Spine J. 2004, 13, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtori, S.; Mannoji, C.; Orita, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Eguchi, Y.; Ochiai, N.; Kishida, S.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Aoki, Y.; Nakamura, J.; et al. Mini-Open Anterior Retroperitoneal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion for Degenerated Lumbar Spinal Kyphoscoliosis. Asian Spine J. 2015, 9, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtori, S.; Orita, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Eguchi, Y.; Ochiai, N.; Kishida, S.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Aoki, Y.; Nakamura, J.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Mini-Open Anterior Retroperitoneal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Spinal Degeneration Disease. Yonsei Med. J. 2015, 56, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, J.; Ohtori, S.; Orita, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Eguchi, Y.; Ochiai, N.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Aoki, Y.; Nakamura, J.; Miyagi, M.; et al. Radiographic evaluation of indirect decompression of mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion: Oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerated lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Jaiswal, M.S.; Jeun, S.S.; Ryu, K.S.; Hur, J.W.; Kim, J.S. Outcomes of oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease in patients under or over 65 years of age. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2018, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Ryu, K.S.; Hur, J.W.; Seong, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, H.J. Comparative Study of the Difference of Perioperative Complication and Radiologic Results: MIS-DLIF (Minimally Invasive Direct Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion) Versus MIS-OLIF (Minimally Invasive Oblique Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion). Clin. Spine Surg. 2018, 31, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.X.; Akbary, K.; Kotheeranurak, V.; Quillo-Olvera, J.; Jo, H.J.; Yang, X.W.; Mahatthanatrakul, A.; Kim, J.S. Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes of Direct Versus Indirect Decompression with Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Matched-Pair Comparison Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018, 119, e898–e909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, J. Learning Curve of Minimally Invasive Surgery Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Diseases. World Neurosurg. 2018, 120, e88–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miscusi, M.; Ramieri, A.; Forcato, S.; Giuffre, M.; Trungu, S.; Cimatti, M.; Pesce, A.; Familiari, P.; Piazza, A.; Carnevali, C.; et al. Comparison of pure lateral and oblique lateral inter-body fusion for treatment of lumbar degenerative disk disease: A multicentric cohort study. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27 (Suppl. S2), 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, K.; Jian, F.; Wu, H. Efficacy of Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion in Treatment of Degenerative Lumbar Disease. World Neurosurg. 2019, 124, e17–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, F.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Ding, W.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W. Safety Analysis of Two Anterior Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusions at the Initial Stage of Learning Curve. World Neurosurg. 2019, 127, e901–e909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.X.; Kotheeranurak, V.; Zeng, T.H.; Mahatthanatrakul, A.; Kim, J.S. A longitudinal investigation of the endplate cystic lesion effect on oblique lumbar interbody fusion. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 184, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Perioperative complications associated with minimally invasive surgery of oblique lumbar interbody fusions for degenerative lumbar diseases in 113 patients. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 184, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, M.Y.; Cheung, P. Oblique lumbar interbody fusion in management of lumbar degenerative spinal stenosis in Chinese population. J. Orthop. Trauma Rehabil. 2020, 27, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Yang, D.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Ding, W.; Yang, S. Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Stand-Alone Cages for the Treatment of Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Retrospective Study with 1-Year Follow-Up. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 9016219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, Y.; Koike, Y.; Ikeura, A.; Tokunaga, H.; Saito, T. Clinical and radiologic comparison of anterior-posterior single-position lateral surgery versus MIS-TLIF for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. J. Orthop. Sci. 2020, 26, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Shen, Y.; Qi, X. Lumbar degenerative disease after oblique lateral interbody fusion: Sagittal spinopelvic alignment and its impact on low back pain. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; He, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhang, X.; Shan, Z.; Chen, J.; Fan, S.; Zhao, F. Reoccurring discogenic low back pain (LBP) after discoblock treated by oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF). J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Shi, C.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Xi, Y.; Ye, X. Unilateral Versus Bilateral Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation in Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion. World Neurosurg. 2020, 134, e920–e927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.S.; Seo, E.M. Efficacy and radiographic analysis of oblique lumbar interbody fusion in treating lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis with sagittal imbalance. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 2181–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.W.; Lee, H.D.; Jeon, C.H.; Chung, N.S. Comparison of surgical outcomes between oblique lateral interbody fusion (OLIF) and anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF). Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2021, 209, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; She, Y.; Ou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, W.; Jiang, D. Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion versus Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Degenerative Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Single-Center Retrospective Comparative Study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6693446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefevre, E.; d’Astorg, H.; Fiere, V.; Gauthe, R.; Vieira, T.D.; Ould Slimane, M.; Szadkowski, M. Treatment of one-level degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with severe stenosis by oblique lateral interbody fusion: Clinical and radiological results after a minimal 1-year follow-up. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2021, 26, 101321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Ma, R.; Zhang, J.Q.; Liang, S.M.; Chen, Z.; Pan, Z.; Ma, Z.J.; Ding, X.L.; Kang, Y.; et al. Treatment of Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis with Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Conjunction with Unilateral Pedicle Screw Fixation via the Wiltse Approach. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 13, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernan, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savovic, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, K.R.; Billys, J.B.; Hynes, R.A. Technical description of oblique lateral interbody fusion at L1-L5 (OLIF25) and at L5-S1 (OLIF51) and evaluation of complication and fusion rates. Spine J. 2017, 17, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.T.; Hynes, R.A.; Fung, D.A.; Spann, S.W.; MacMillan, M.; Kwon, B.; Liu, J.; Acosta, F.; Drochner, T.E. Retroperitoneal oblique corridor to the L2-S1 intervertebral discs in the lateral position: An anatomic study. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2014, 21, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.M.; Zhang, R.J.; Shen, C.L. Differences in radiographic and clinical outcomes of oblique lateral interbody fusion and lateral lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease: A meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, C.; Mac-Thiong, J.M.; Hilmi, R.; Roussouly, P. Complications and Morbidities of Mini-open Anterior Retroperitoneal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion in 179 Patients. Asian Spine J. 2012, 6, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.X.; Phan, K.; Mobbs, R. Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Technical Aspects, Operative Outcomes, and Complications. World Neurosurg. 2017, 98, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Choi, S.W. Adjacent Segment Pathology after Lumbar Spinal Fusion. Asian Spine J. 2015, 9, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnally III, C.J.; Patel, P.D.; Canseco, J.A.; Divi, S.N.; Goz, V.; Sherman, M.B.; Shenoy, K.; Markowitz, M.; Rihn, J.A.; Vaccaro, A.R. Current incidence of adjacent segment pathology following lumbar fusion versus motion-preserving procedures: A systematic review and meta-analysis of recent projections. Spine J. 2020, 20, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, M.B.; Wiegers, N.W.; Patil, S.; Nourbakhsh, A. Incidence and risk factors of reoperation in patients with adjacent segment disease: A meta-analysis. J. Craniovertebr. Junction Spine 2020, 11, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Lin, Y.; Wu, J.; Cui, W.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L.; Sang, H.; Huang, W. Biomechanical Comparison of Stand-Alone and Bilateral Pedicle Screw Fixation for Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery-A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2020, 141, e204–e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotheeranurak, V.; Jitpakdee, K.; Lin, G.X.; Mahatthanatrakul, A.; Singhatanadgige, W.; Limthongkul, W.; Yingsakmongkol, W.; Kim, J.S. Subsidence of Interbody Cage Following Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion: An Analysis and Potential Risk Factors. Glob. Spine J. 2021, 13, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Number |
|---|---|
| Total no. of studies included | 27 |
| Total no. of patients | 1275 |
| Type of OLIF L2-5 | 19 (with PS); 3 (Stand-alone); 5 (Unspecified) |
| Type of Studies | 21 (Retrospective); 6 (prospective) |
| No. of studies with CT Navigation used | 1 |
| Number of complications | 327 (Total); 50 (Intra-op), 184 (Post-op), 93 (Late post-op); 3 (Re-operations) |
| Group of OLIF | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complication Category | Complication Sub-Group | Specific Complication | Stand-Alone, n (%) | With Posterior Stabilisation, n (%) | Unspecified (+/− Posterior Stabilisation), n (%) | |
| Cumulative no. of patients | 95 | 784 | 396 | 1275 | ||
| Intra-operative | Vascular injury | Major | 0 | 2 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 3 (0.2) |
| Minor | 0 | 8 (1.0) | 8 (2.0) | 16 (1.3) | ||
| Endplate damage | Endplate damage | 0 | 0 | 22 (5.6) | 22 (1.7) | |
| Vertebral body fracture | Vertebral body fracture | 0 | 3 (0.4) | 0 | 3 (0.2) | |
| Membrane Laceration | Peritoneal laceration | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.3) | 1 (0.1) | |
| Ventral dural tear | 0 | 2 (0.3) | 1 (0.3) | 3 (0.2) | ||
| Ureteral injury | 0 | 2 (0.3) | 0 | 2 (0.2) | ||
| Total | 0 | 17 (2.2) | 33 (8.3) | 50 (3.9) | ||
| Immediate post-operative | Nerve deficits | Spinal nerve/Nerve root injury | 0 | 0 | 2 (0.5) | 2 (0.2) |
| Sympathetic chain | 0 | 23 (2.9) | 12 (3.0) | 35 (2.7) | ||
| Ileus | 4 (4.2) | 6 (0.8) | 2 (0.5) | 12 (0.9) | ||
| Transient Lower limb weakness | Psoas weakness | 2 (2.1) | 27 (3.4) | 17 (4.3) | 46 (3.6) | |
| Quadriceps weakness | 0 | 2 (0.3) | 0 | 2 (0.2) | ||
| Lower Limb Numbness/pain | Numbness | 2 (2.1) | 36 (4.6) | 31 (7.8) | 69 (5.4) | |
| Pain | 1 (1.1) | 10 (1.3) | 0 | 11 (0.9) | ||
| Local Infection | 1 (1.1) | 5 (0.6) | 1 (0.3) | 7 (0.5) | ||
| Total | 10 (10.5) | 109 (13.9) | 65 (16.4) | 184 (14.4) | ||
| Late post-operative | Cage shifting/malpositioning/displacement | 0 | 1 (0.1) | 1 (0.3) | 2 (0.2) | |
| Screw malposition/breakage | 0 | 2 (0.3) | 0 | 2 (0.2) | ||
| Adjacent Segment Degeneration | 0 | 18 (2.3) | 0 | 18 (1.4) | ||
| Subsidence | 3 (3.16) | 31 (4.91) | 29 (7.3) | 63 (5.6) | ||
| Pseudoarthrosis | 0 | 8 (1.02) | 0 | 8 (0.6) | ||
| Total | 3 (3.16) | 60 (7.65) | 30 (7.6) | 93 (7.3) | ||
| Total | Reoperations | 0 | 3 (0.38) | 0 | 3 (0.2) | |
| Overall total complications | 13 (13.7) | 186 (23.7) | 128 (32.3) | 327 (25.6) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Q.R.; Wong, R.A.; Kaliya-Perumal, A.-K.; Oh, J.Y.-L. Complications Associated with Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Systematic Review. Surg. Tech. Dev. 2023, 12, 211-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/std12040020
Tan QR, Wong RA, Kaliya-Perumal A-K, Oh JY-L. Complications Associated with Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Systematic Review. Surgical Techniques Development. 2023; 12(4):211-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/std12040020
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Quan Rui, Russell Andrew Wong, Arun-Kumar Kaliya-Perumal, and Jacob Yoong-Leong Oh. 2023. "Complications Associated with Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Systematic Review" Surgical Techniques Development 12, no. 4: 211-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/std12040020
APA StyleTan, Q. R., Wong, R. A., Kaliya-Perumal, A.-K., & Oh, J. Y.-L. (2023). Complications Associated with Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Systematic Review. Surgical Techniques Development, 12(4), 211-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/std12040020






