Enhancing Stress Resilience in a Drought-Tolerant Zea mays Cultivar by Integrating Morpho-Physiological and Proteomic Characterization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material, Sterilization, Growth, and Treatment Conditions
2.2. Morphological Measurements
Growth Functional Traits
2.3. Physiological Measurements
2.3.1. Gas Exchange Parameters
2.3.2. Leaf Stomatal Density
2.3.3. Protein Extraction and Quantification
2.4. SDS-PAGE-Based Protein Profiling and Mass Spectrometric Identification (LC-MS/MS)
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis for Functional Annotation, Gene Mapping, and Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Construction
2.6. Statistical Analysis and Data Integration
3. Results
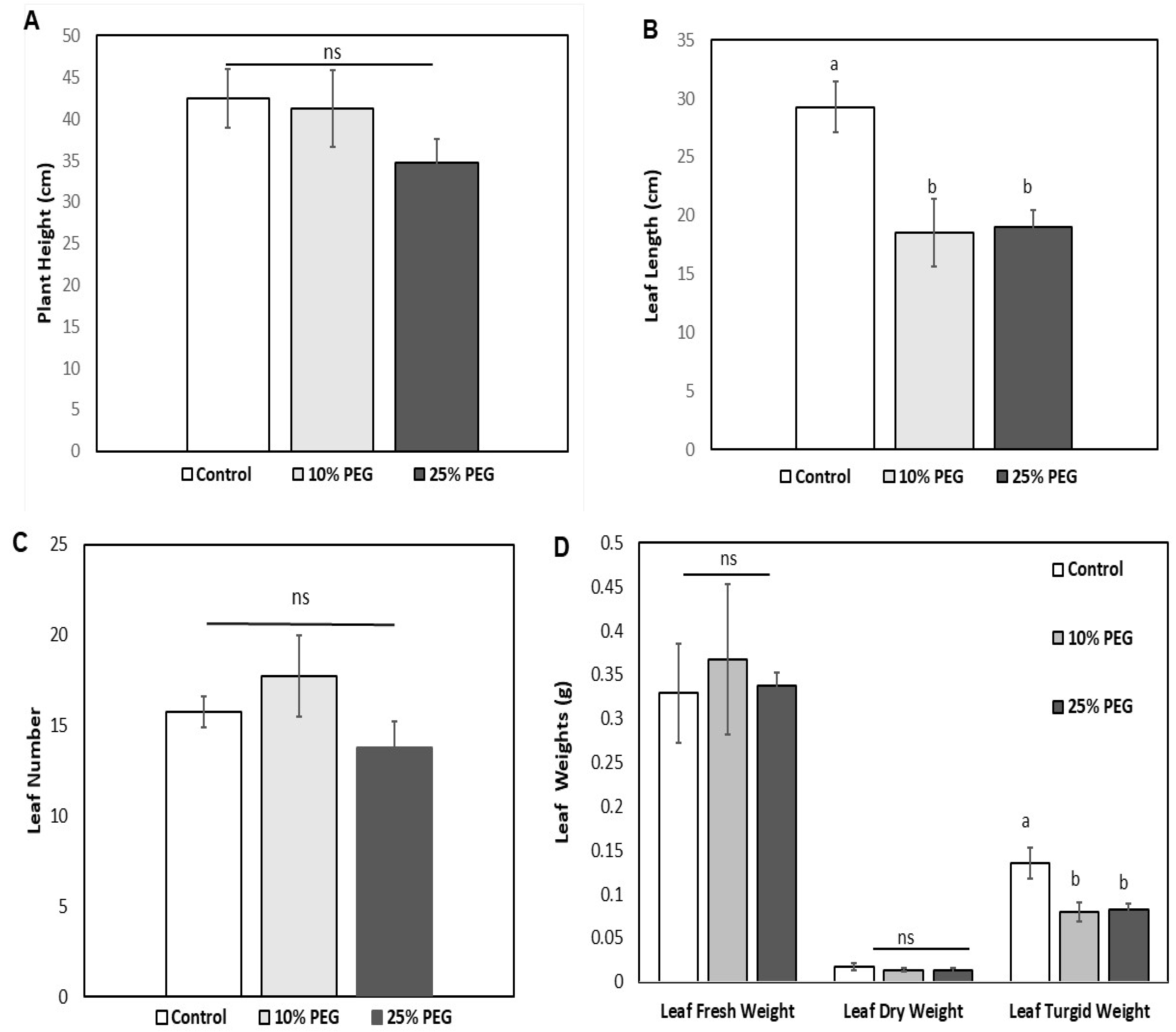
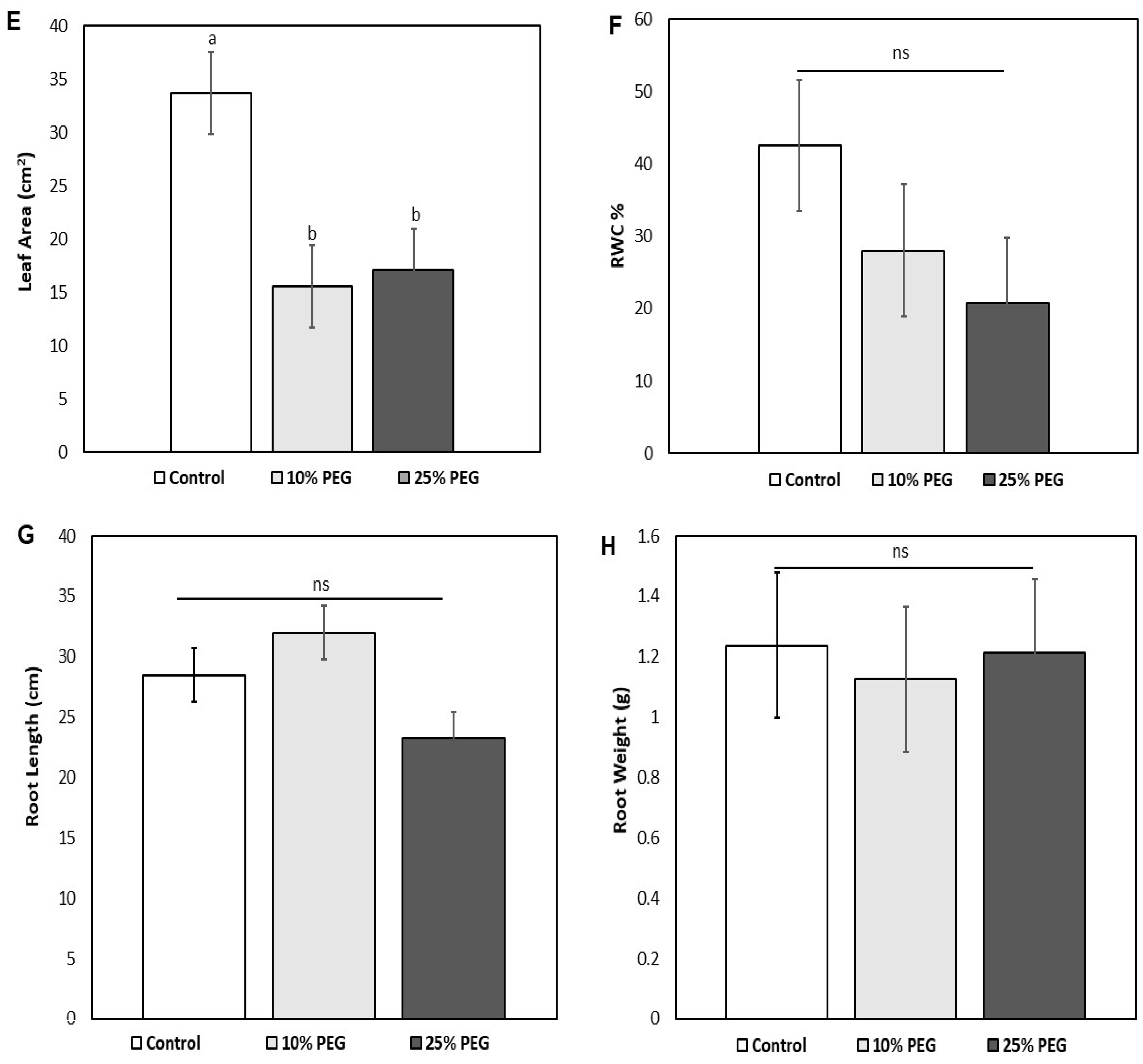
3.1. Morphological and Growth Responses of Zea mays
3.2. Effects of Osmotic Stress on the Physiological Traits of Z. mays
3.2.1. Evaluation of Osmotic Stress on the Stomatal Morphology, Number, and Density
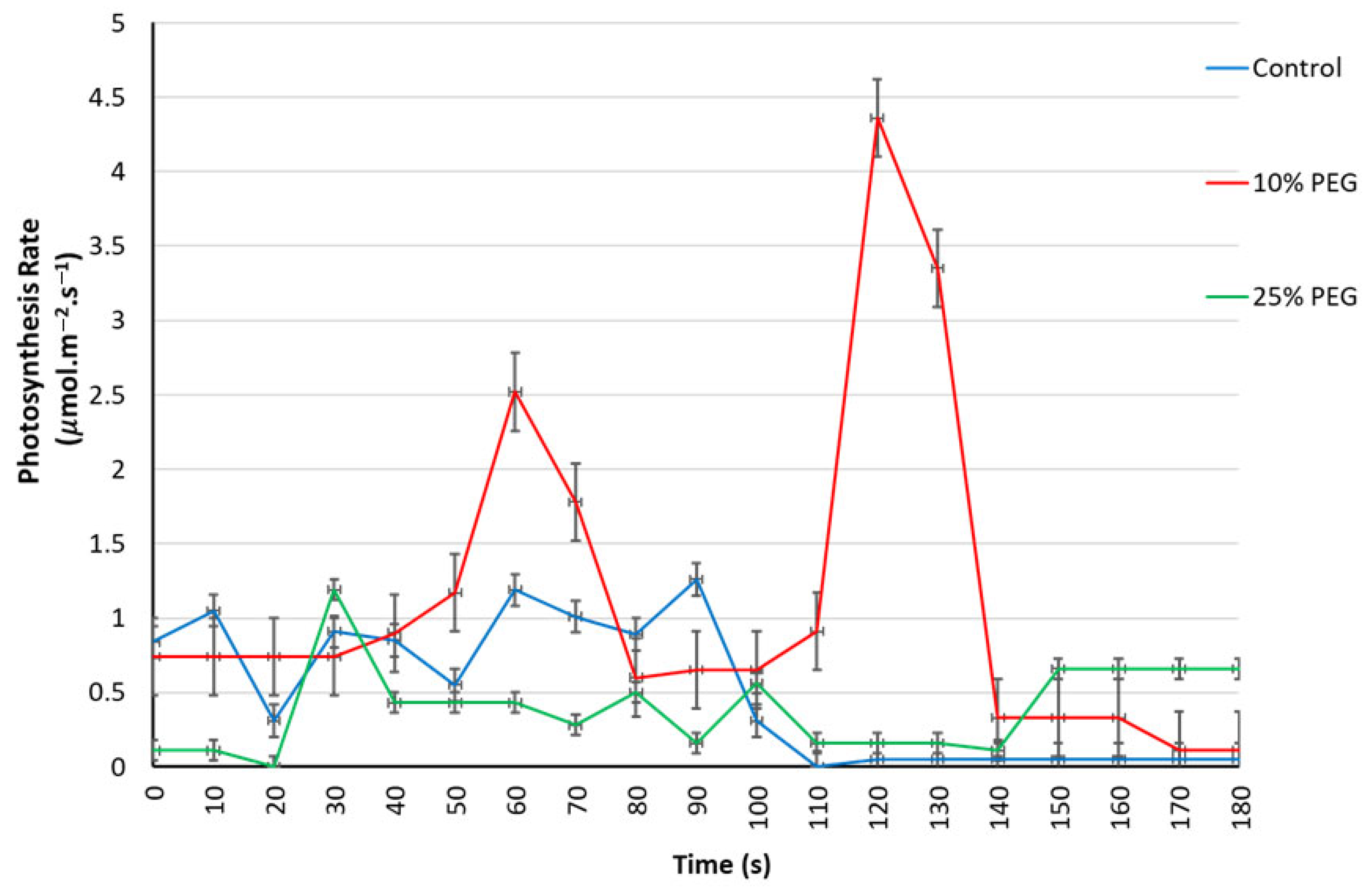
3.2.2. Effects of Osmotic Stress on the Leaf Gaseous Exchange Parameters
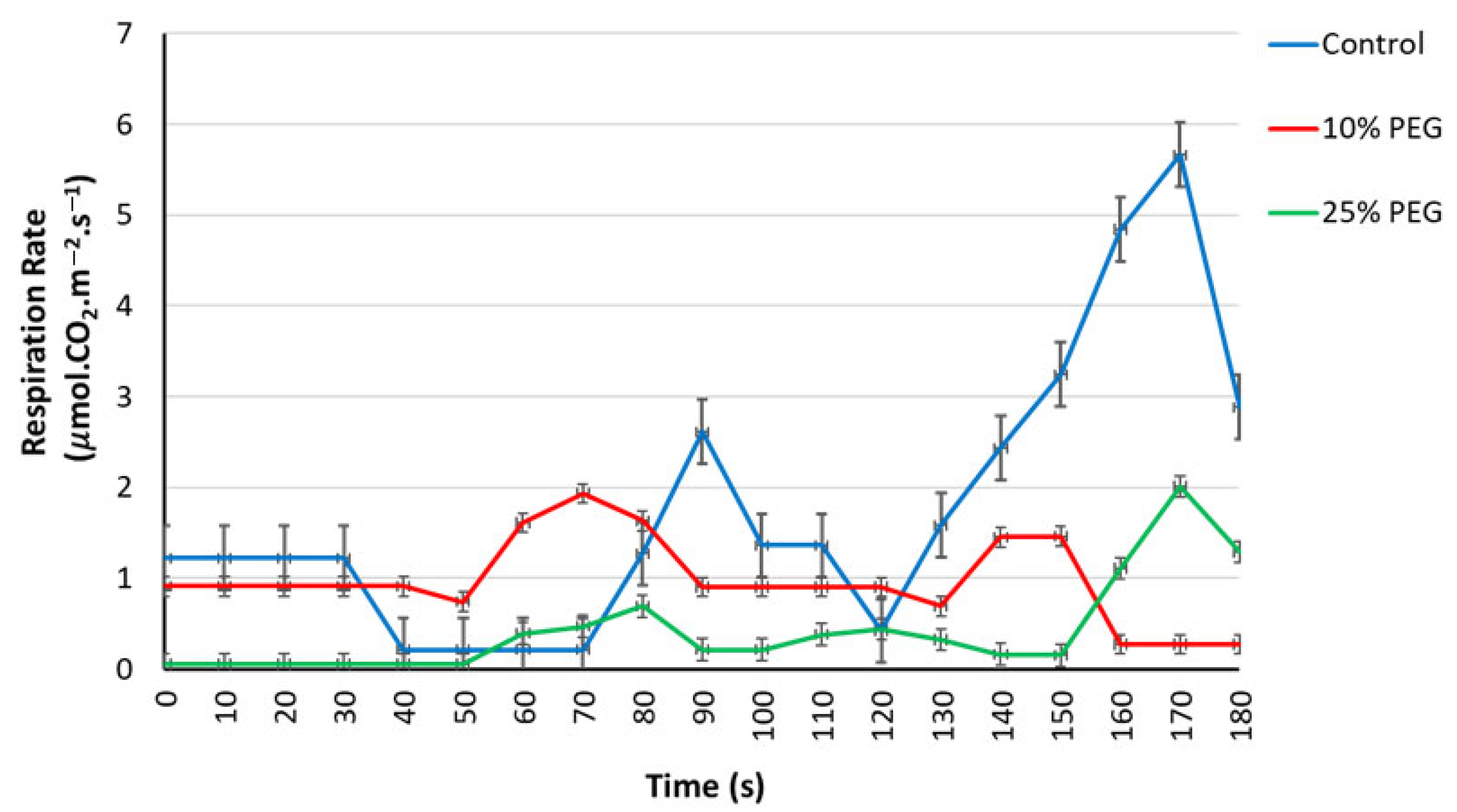
3.2.3. Respiration and Transpiration Rates Under Osmotic Stress
3.3. Assessment of Maize Protein Expressional Profiles in Response to PEG-Induced Osmotic Stress via One-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis (1DE)
3.4. Bioinformatic Analysis and Functional Annotation of Osmotic Stress Responsive Proteins in Maize Leaves
3.5. Functional Classification and Expression Pattern Analysis of the Osmotic Stress Responsive Proteins
3.6. Protein–Protein Interaction Network of Osmotic Stress-Responsive Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baptista, D.M.S.; Farid, M.M.; Fayad, D.; Kemoe, L.; Lanci, L.S.; Mitra, M.P.; Muehlschlegel, T.S.; Okou, C.; Spray, J.A.; Tuitoek, K.; et al. Climate Change and Chronic Food Insecurity in Sub-Saharan Africa; International Monetary Fund: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cammarano, D.; Valdivia, R.O.; Beletse, Y.G.; Durand, W.; Crespo, O.; Tesfuhuney, W.A.; Jones, M.R.; Walker, S.; Mpuisang, T.N.; Nhemachena, C.; et al. Integrated assessment of climate change impacts on crop productivity and income of commercial maize farms in northeast South Africa. Food Secur. 2020, 12, 659–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Wang, X.; Saleem, M.H.; Khan, M.H.U.; Afzal, J.; Fiaz, S.; Ali, S.; Ishaq, H.; Khan, A.H.; Rehman, N.; et al. Deciphering Plantago ovata forsk leaf extract mediated distinct germination, growth and physio-biochemical improvements under water stress in maize (Zea mays L.) at early growth stage. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Population Reference Bureau. World Population Data Sheet; Population Reference Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.prb.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/letter-booklet-2020-world-population.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Farooq, M.; Wahid, A.; Lee, D.J.; Ito, O.; Siddique, K.H. Advances in drought resistance of rice. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2009, 28, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavatte, P.C.; Martins, S.C.; Morais, L.E.; Silva, P.E.; DaMatta, F.M. The Physiology of Abiotic Stresses. In Plant Breeding for Abiotic Stress Tolerance; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 21–51. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi-Lisar, S.Y.; Bakhshayeshan-Agdam, H. Drought Stress in Plants: Causes, Consequences, and Tolerance. In Drought Stress Tolerance in Plants Vol 1: Physiology and Biochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yasmeen, A. Exploring the Potential of Moringa (Moringa oleifera) Leaf Extract as a Natural Plant Growth Enhancer. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Agronomy, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente, O.; Al Hassan, M.; Boscaiu, M. Contribution of Osmolyte Accumulation to Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Wild Plants Adapted to Different Stressful Environments. In Osmolytes and Plants’ Acclimation to Changing Environment: Emerging Omics Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lippmann, R.; Babben, S.; Menger, A.; Delker, C.; Quint, M. Development of wild and cultivated plants under global warming conditions. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R1326–R1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatak, A.; Chaturvedi, P.; Weckwerth, W. Cereal crop proteomics: Systemic analysis of crop drought stress responses towards marker-assisted selection breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, G.; Komatsu, S. Plant proteomic research for improvement of food crops under stresses: A review. Mol. Omics 2021, 17, 860–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.K.; Sarkar, A.; Righetti, P.G.; Pedreschi, R.; Carpentier, S.; Wang, T.; Barkla, B.J.; Kohli, A.; Ndimba, B.K.; Bykova, N.V.; et al. A decade of plant proteomics and mass spectrometry: Translation of technical advancements to food security and safety issues. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2013, 32, 335–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoli, E.; Nworji, M.; Okoronkwo, C. Potentials of proteomics in plant improvement. Int. J. Sci. Adv. 2021, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Arellano, M.; Reiser, D.; Paraforos, D.S.; Garrido-Izard, M.; Griepentrog, H.W. Leaf area estimation of reconstructed maize plants using a time-of-flight camera based on different scan directions. Robotics 2018, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, L.; González-Vilar, M. Determination of relative water content. In Handbook of Plant Ecophysiology Techniques; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhao, B. Using Clear Nail Polish to Make Arabidopsis Epidermal Impressions for Measuring the Change of Stomatal Aperture Size in Immune Response. In Plant Pattern Recognition Receptors: Methods and Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Volenikova, M.; Ticha, I. Insertion profiles in stomatal density and sizes in Nicotiana tabacum L. plantlets. Biol. Plant. 2001, 44, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, P.; Hansen, J.B.; Allen, M. Microvolume protein concentration determination using the NanoDrop 2000c spectrophotometer. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 33, e1610. [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domon, B.; Aebersold, R. Options and considerations when selecting a quantitative proteomics strategy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žydelis, R.; Weihermüller, L.; Herbst, M.; Klosterhalfen, A.; Lazauskas, S. A model study on the effect of water and cold stress on maize development under nemoral climate. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 263, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Juste, J.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Rodriguez, P.L. Plant osmotic stress signaling: MAPKKKs meet SnRK2s. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Latif Khan, A.; Shahzad, R.; Aaqil Khan, M.; Bilal, S.; Khan, A.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, I.J. Exogenous melatonin induces drought stress tolerance by promoting plant growth and the antioxidant defence system of soybean plants. AoB Plants 2021, 13, plab026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentovic, P.; Luxova, M.; Kolarovic, L.; Gasparikova, O. Effect of osmotic stress on compatible solutes content, membrane stability and water relations in two maize cultivars. Plant Soil Environ. 2006, 52, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavizadeh, R.; Farahzadianpoor, F.; Adabavazeh, F.; Komatsu, S. Physiological and morphological analyses of Thymus vulgaris L. in vitro cultures under polyethylene glycol (PEG)-induced osmotic stress. In Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2019, 55, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, A.H.K.; Ghosh, S.; Shahed, M.A. PEG-induced osmotic stress alters root morphology and root hair traits in wheat genotypes. Plants 2021, 10, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunami, M.; Toyofuku, K.; Kimura, N.; Ogawa, A. Osmotic stress leads to significant changes in rice root metabolic profiles between tolerant and sensitive genotypes. Plants 2020, 9, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Response mechanism of plants to drought stress. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, M.; Hussainy, S.A.; Karthik, A. Effect of moisture deficit conditions on the performance of maize (Zea mays): A review. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2020, 8, 2603–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Khalid, S.; Abdullah, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Shah, M.K.N.; Ghafoor, A.; Du, X. Insights into drought stress signaling in plants and the molecular genetic basis of cotton drought tolerance. Cells 2019, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Ratkowsky, D.A.; Hui, C.; Wang, P.; Su, J.; Shi, P. Leaf fresh weight versus dry weight: Which is better for describing the scaling relationship between leaf biomass and leaf area for broad-leaved plants? Forests 2019, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissoli, G.; Niñoles, R.; Fresquet, S.; Palombieri, S.; Bueso, E.; Rubio, L.; García-Sánchez, M.J.; Fernández, J.A.; Mulet, J.M.; Serrano, R. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase ROF2 modulates intracellular pH homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2012, 70, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.A.; Men, S.; Hussain, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ashraf, U.; Anjum, S.A.; Ali, I.; Wang, L. Maize tolerance against drought and chilling stresses varied with root morphology and the antioxidative defense system. Plants 2020, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevilly, S.; Dolz-Edo, L.; Morcillo, L.; Vilagrosa, A.; López-Nicolás, J.M.; Yenush, L.; Mulet, J.M. Identification of distinctive physiological and molecular responses to salt stress among tolerant and sensitive cultivars of broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. Italica). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Nahar, K.; Alam, M.M.; Roychowdhury, R.; Fujita, M. Physiological, biochemical and molecular mechanisms of heat stress tolerance in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9643–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibria, M.G. Physiological and biochemical responses of salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant rice genotypes to salt stress. Master’s Thesis, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Bangladesh, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.E.E. Comparative molecular, physiological and proteomic analyses of maize and sorghum subjected to water deficit stress. Master’s Thesis, University of Western Cape, Cape Town, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, S.A.; Xie, X.; Wang, L.C.; Saleem, M.F.; Man, C.; Lei, W. Morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of plants to drought stress. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 2026–2032. [Google Scholar]
- Allakhverdiev, S.I. Optimising photosynthesis for environmental fitness. Funct. Plant Biol. 2020, 47, iii–vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfqar, M.; Siddique, S.; Sehar, U.; Mustafa, H.S.B.M.; Hasan, E.; Sadaqat, H.A. Effects of climate change on field crops in the scenario of food security. Nat. Sci. J. 2016, 14, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.H.; Tao, X.P.; Hu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, W.F. Response of cotton root growth and yield to root restriction under various water and nitrogen regimes. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koevoets, I.T.; Venema, J.H.; Elzenga, J.T.M.; Testerink, C. Roots withstanding their environment: Exploiting root system architecture responses to abiotic stress to improve crop tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Pan, R.; Shen, W.; Yu, X.; Xiong, F. The relationship between characteristics of root morphology and grain filling in wheat under drought stress. Peer J. 2021, 9, 12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Langridge, P. A study of the role of root morphological traits in growth of barley in zinc-deficient soil. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2775–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhou, X.; Nie, Y.; Bai, S.H.; Zhou, L.; Shao, J.; Cheng, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, F.; Fu, Y. Drought-induced changes in root biomass largely result from altered root morphological traits: Evidence from a synthesis of global field trials. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 2589–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, N.S.; Ghasimi Hagh, Z.; Khoshghalb, H. Morphological, antioxidant enzyme activity and secondary metabolites accumulation in response to polyethylene glycol-induced osmotic stress in embryo-derived plantlets and callus cultures of Salvia leriifolia. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2020, 140, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yordanov, I.; Velikova, V.; Tsonev, T. Plant responses to drought, acclimation, and stress tolerance. Photosynthetica 2000, 38, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisele, J.F.; Fäßler, F.; Bürgel, P.F.; Chaban, C. A rapid and simple method for microscopy-based stomata analyses. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimpour, M. Effect of drought stress on RWC and chlorophyll content on wheat (Triticum durum L.) genotypes. World Essays J. 2019, 7, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Levinsh, G. Water content of plant tissues: So simple that almost forgotten? Plants 2023, 12, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapes, G.; Sala, A. Relative water content consistently predicts drought mortality risk in seedling populations with different morphology, physiology and times to death. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 3322–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeman, S.P. Physiological Measurements of Daily Daylight Fertigated Citrus Trees. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gavito, M.E.; Jakobsen, I.; Mikkelsen, T.N.; Mora, F. Direct evidence for modulation of photosynthesis by an Arbuscular mycorrhiza-induced carbon sink strength. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Hui, W.; Zhao, F.; Wang, P.; Su, C.; Gong, W. Physiology of plant responses to water stress and related genes: A review. Forests 2022, 13, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Douthe, C.; Flexas, J. Differential coordination of stomatal conductance, mesophyll conductance, and leaf hydraulic conductance in response to changing light across species. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, M.M.; Pereira, J.S.; Maroco, J. Understanding plant responses to drought from genes to the whole plant. Funct. Plant Biol. 2003, 30, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, A.; Alqudah, A.M.; Dawood, M.F.; Baenziger, P.S.; Börner, A. Drought stress tolerance in wheat and barley: Advances in physiology, breeding and genetics research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, X.G. Stomata conductance as a goalkeeper for increased photosynthetic efficiency. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2022, 70, 102310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.L.; Wang, X.F. Color change analysis and water content inversion of young sandalwood in multi-angle under water stress. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 2639–2646. [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor, D.W.; Tezara, W. Causes of decreased photosynthetic rate and metabolic capacity in water-deficient leaf cells: A critical evaluation of mechanisms and integration of processes. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas-Carbo, M.; Taylor, N.L.; Giles, L.; Busquets, S.; Finnegan, P.M.; Day, D.A.; Lambers, H.; Medrano, H.; Berry, J.A.; Flexas, J. Effects of water stress on respiration in soybean leaves. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pautov, A.; Bauer, S.; Ivanova, O.; Krylova, E.; Yakovleva, O.; Sapach, Y.; Pautova, I. Influence of stomatal rings on movements of guard cells. Trees 2019, 33, 1459–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikuku, P.A.; Netondo, G.W.; Onyango, J.C.; Musyimi, D.M. Effects of water deficit on physiology and morphology of three varieties of NERICA rainfed rice (Oryza sativa L.). ARPN J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2010, 5, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Marchin, R.M.; Backes, D.; Ossola, A.; Leishman, M.R.; Tjoelker, M.G.; Ellsworth, D.S. Extreme heat increases stomatal conductance and drought-induced mortality risk in vulnerable plant species. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Chow, W.S.; Park, Y.-I. The grand design of photosynthesis: Acclimation of the photosynthetic apparatus to environmental cues. Photosynth. Res. 2008, 98, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, M.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R. Physiological and proteomic analyses revealed the response mechanisms of two different drought-resistant maize varieties. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Hu, X. Quantitative proteomic analyses identify ABA-related proteins and signal pathways in maize leaves under drought conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenda, T.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Liu, G.; Duan, H. Comparative proteomic and physiological analyses of two divergent maize inbred lines provide more insights into drought-stress tolerance mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Eldakak, M.; Paudel, B.; Kim, D.W.; Hemmati, H.; Basu, C.; Rohila, J.S. Leaf proteome analysis reveals prospective drought and heat stress response mechanisms in soybean. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6021047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngara, R.; Ndimba, B.K. Understanding the complex nature of salinity and drought-stress response in cereals using proteomics technologies. Proteomics 2014, 14, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, A.J.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C.; Strittmatter, G.; Weber, A.P.; Taylor, S.H.; Harbinson, J.; Yin, X.; Long, S.; Paul, M.J.; Westhoff, P.; et al. Improving crop yield potential: Underlying biological processes and future prospects. Food Energy Secur. 2023, 12, e435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Li, G.; Xu, W.; Peng, X.; Han, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, T. Proteomics reveals the effects of salicylic acid on growth and tolerance to subsequent drought stress in wheat. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 6066–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthurajan, R.; Shobbar, Z.S.; Jagadish, S.V.K.; Bruskiewich, R.; Ismail, A.; Leung, H.; Bennett, J. Physiological and proteomic responses of rice peduncles to drought stress. Mol. Biotechnol. 2011, 48, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzelou, S.; Kamath, K.S.; Masoomi-Aladizgeh, F.; Johnsen, M.M.; Atwell, B.J.; Haynes, P.A. Wild and cultivated species of rice have distinctive proteomic responses to drought. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukhele, P.T.; Thamaga, L.; Ruzvidzo, O.; Dikobe, T.B. Morphological and proteomic analyses of Zea mays in response to water stress. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 19, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamaga, L.; Ruzvidzo, O.; Dikobe, T.B. Morphological and proteomic evaluation of Zea mays in response to osmotic stress. Open Biotechnol. J. 2021, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zenda, T.; Liu, S.; Liu, G.; Jin, H.; Dai, L.; Dong, A.; Yang, Y.; Duan, H. Comparative proteomics and physiological analyses reveal important maize filling-kernel drought-responsive genes and metabolic pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, C.; Zhang, D.; He, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Effects of maize organ-specific drought stress response on yields from transcriptome analysis. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Sibicky, T.; Huang, B. Protein profile analysis of salt-responsive proteins in leaves and roots in two cultivars of creeping bentgrass differing in salinity tolerance. Plant Cell Rep. 2010, 29, 595–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Xing, X.; Sun, L.; Pan, J.; Kong, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, D. ZmLEA3, a multifunctional group 3 LEA protein from maize (Zea mays L.), is involved in biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 944–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Wu, L.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, D.; Li, N.; Zhu, G.; Li, C.; Wang, W. Phosphoproteomic analysis of the response of maize leaves to drought, heat, and their combination stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Cui, J.Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, Y.Z.; Wei, L.; Yang, M.D.; Liang, F.; Ding, S.T.; Wang, T.C. Physiology and proteomics of two maize genotypes with different drought resistance. Biol. Plant. 2019, 63, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, B.; Chen, F.; Ren, B.; Zhuang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Ding, Y. Comparative proteomics analysis of the seedling root response of drought-sensitive and drought-tolerant maize varieties to drought stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, C.; Yu, C.; Dong, J.; Hu, J. Integration of multi-omics technologies for crop improvement: Status and prospects. Front. Bioinform. 2022, 2, 1027457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Würschum, T.; Liu, W. Meta-quantitative trait loci analysis and candidate gene mining for drought tolerance-associated traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Abdel Latef, A.A.; Rasool, S.; Akram, N.A.; Ashraf, M.; Gucel, S. Role of proteomics in crop stress tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, R.; Nawaz, M.S.; Siddique, M.J.; Hakim, S.; Imran, A. Plant survival under drought stress: Implications, adaptive responses, and integrated rhizosphere management strategy for stress mitigation. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 242, 126626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Bressan, R.A.; Bohnert, H.J. Molecular aspects of osmotic stress in plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1997, 16, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Tai, F.; Li, C.; Hu, X. The difference of physiological and proteomic changes in maize leaves adaptation to drought, heat, and combined both stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palotai, R.; Szalay, M.S.; Csermely, P. Chaperones as integrators of cellular networks: Changes of cellular integrity in stress and diseases. IUBMB Life 2007, 59, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

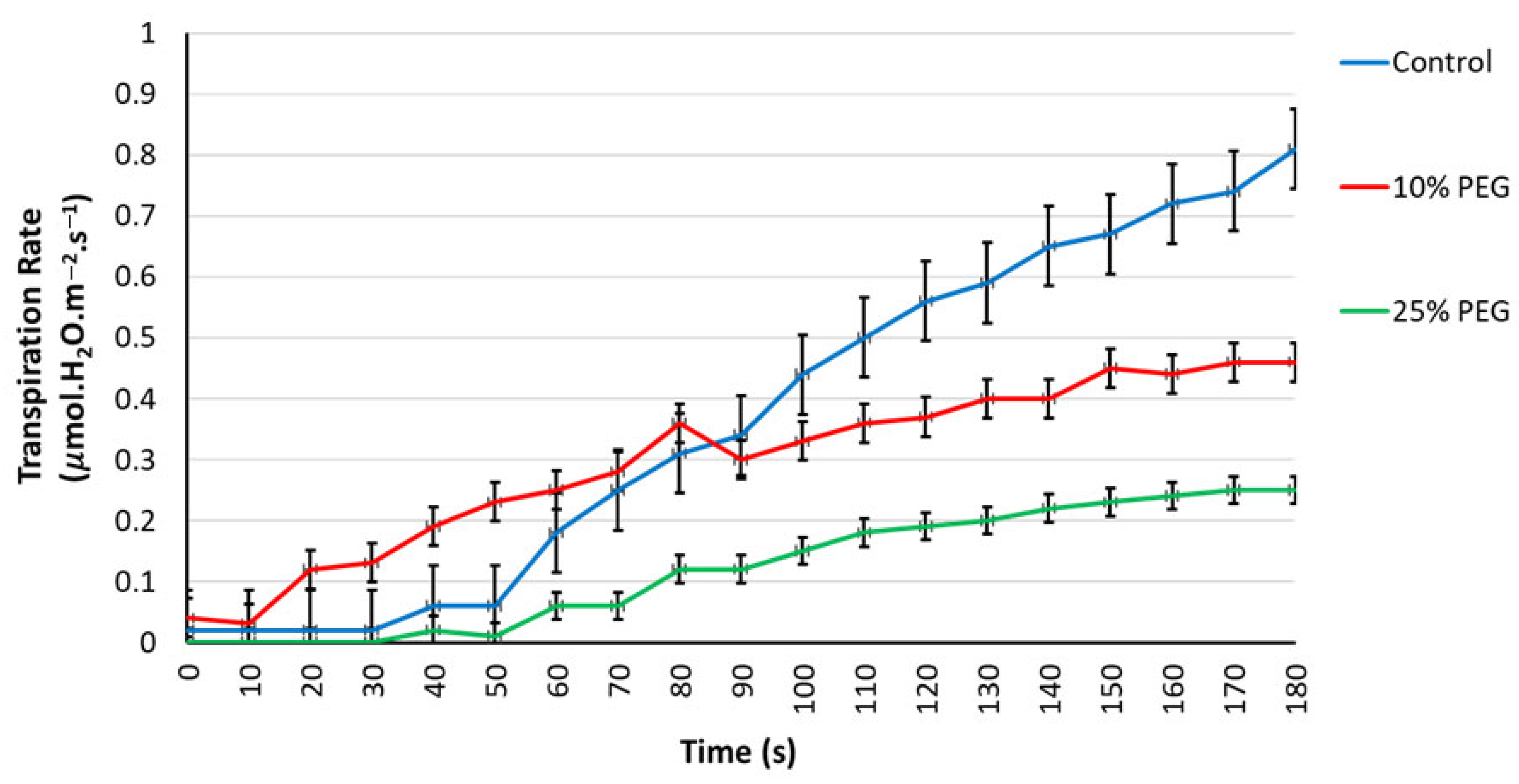
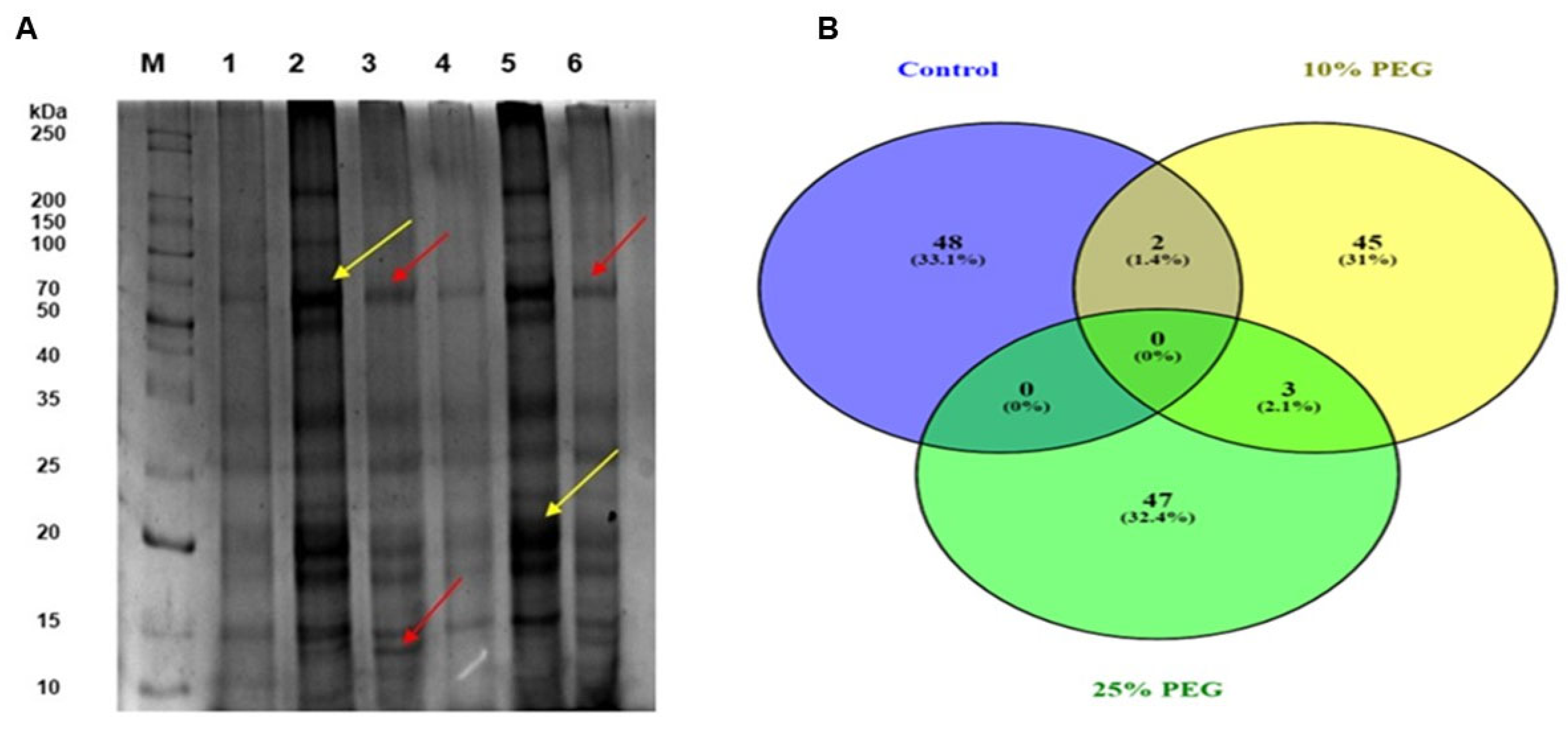
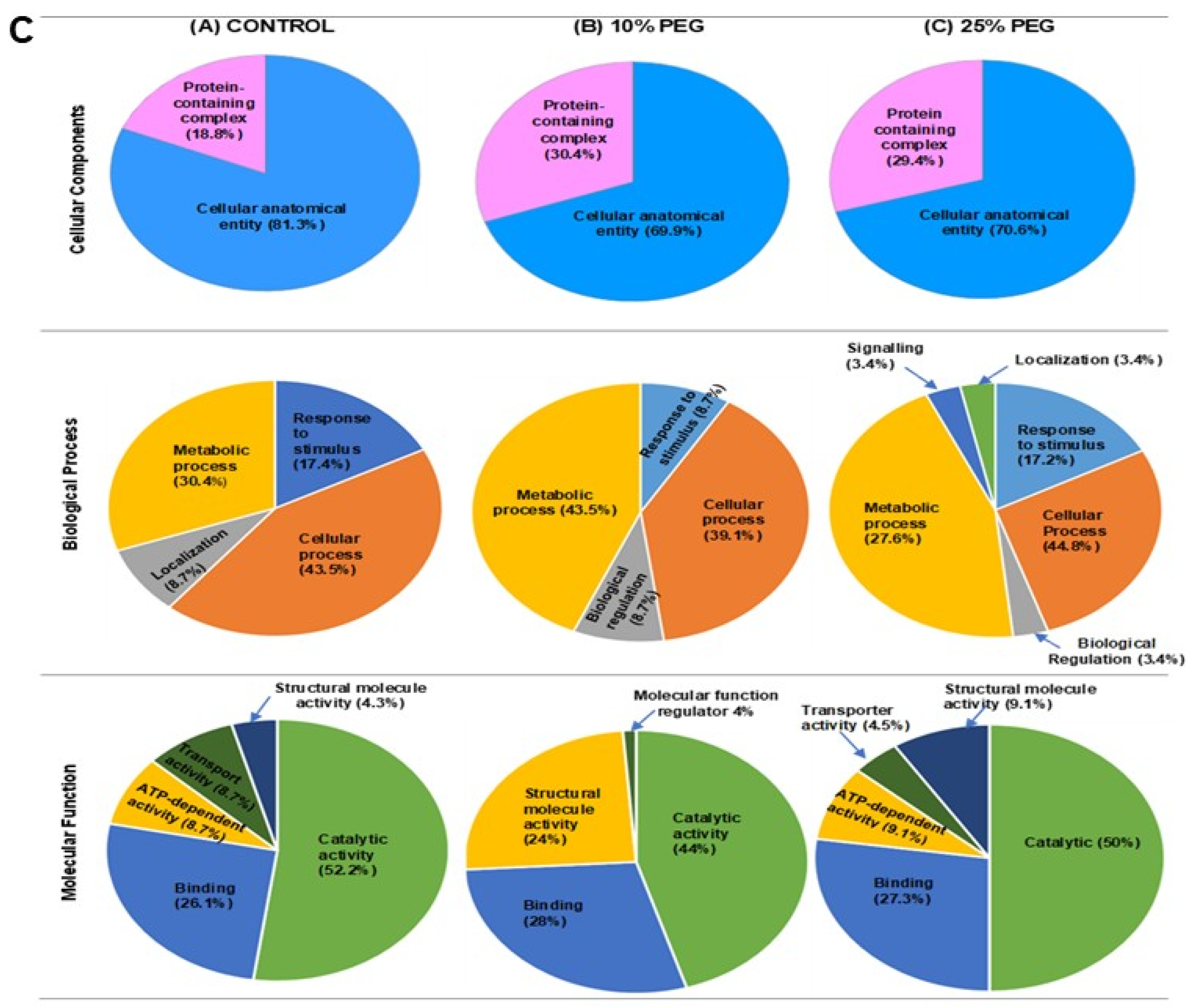
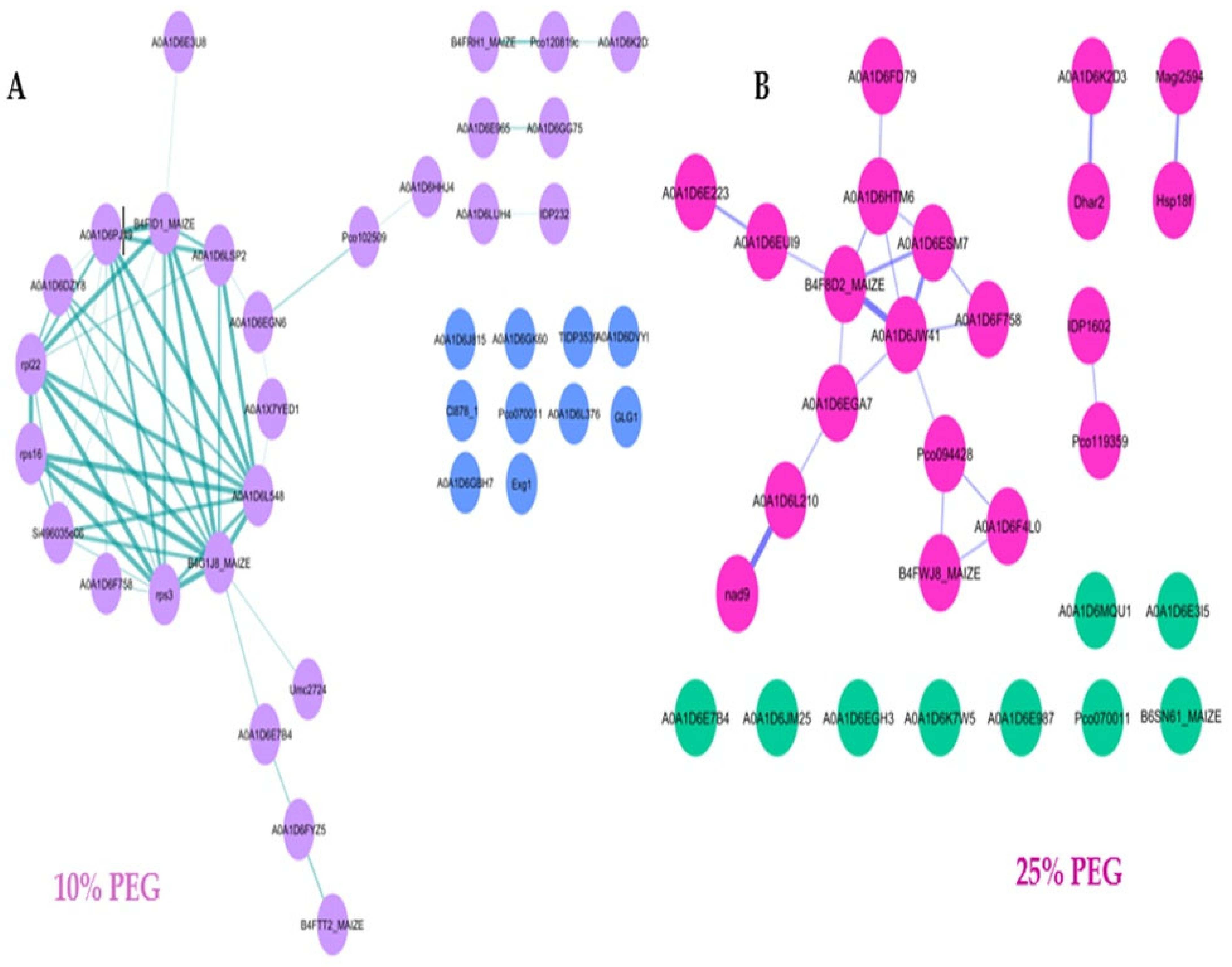
| Control | 10% PEG | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession Number | Protein Name | Gene/ Locus ID | Subcellular Location | Biological Processes | Molecular Function | PI | Mr | Accession Number | Protein Name | Gene/ Locus ID | Subcellular Location | Biological Processes | Molecular Function | PI | Mr |
| tr|B4F833 | Diaminopimelate epimerase | LOC100191234 | Cytosol | Lysine biosynthetic process via diaminopimelate | Diaminopimelate epimerase activity | 5.96 | 37,799.11 | tr|B4F833 | Diaminopimelate epimerase | LOC100191234 | Cytosol | Lysine biosynthetic process via diaminopimelate | Diaminopimelate epimerase activity | 5.96 | 37,799.11 |
| tr|C4IZ94 | Ornithine carbamoyltransferase | LOC100284885 | Intracellular membrane | Arginine biosynthetic process via ornithine | Amino acid binding | 6.76 | 40,286.51 | tr|C4IZ94 | Ornithine carbamoyltransferase | LOC100284885 | Intracellular membrane | Arginine biosynthetic process via ornithine | Amino acid binding | 6.76 | 40,286.51 |
| tr|A0A1D6HM49 | Subtilisin-like protease SBT1.4 | LOC100279566 | None predicted | Proteolysis | Serine-type endopeptidase activity | 5.35 | 78,345.99 | sp|P21569 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase | CYP | Cytoplasm | Protein folding; protein peptidyl-prolyl isomerization | Cyclosporin A binding | 8.91 | 18,348.99 |
| tr| B4F8V5 | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron–sulfur protein 1 mitochondrial | LOC100191453 | Membrane | ATP synthesis coupled electron transport | 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding | 6.10 | 80,679.62 | tr|C0P3R8 | Glutathione peroxidase | LOC100272844 | None predicted | Response to oxidative stress | Glutathione peroxide activity | 9.55 | 24,993.61 |
| tr|B4FYD3 | TOM1-like protein 2 | LOC100282255 | Membrane | Protein transport | Phosphatidylinositol binding; ubiquitin binding | 4.58 | 43,475.92 | tr|A0A804PHY0 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase | LOC103627222 | None predicted | Protein folding | Peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase activity | 9.03 | 16,744.15 |
| tr| K7WFV1 | ATP synthase subunit gamma | ZEAMMB73_ Zm00001d048091 | Mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic sector F1F0 | Proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis | Proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism | 9.12 | 35,714.94 | tr| B6TQ06 | Aminomethyltransferase | LOC100279332 | Mitochondrion | Methylation | Aminomethyltransferase activity | 8.36 | 44,034.54 |
| tr| B5AMJ8 | Alpha-1,4 glucan phosphorylase | LOC100285259 | None predicted | Carbohydrate metabolic process | Glycogen phosphorylase activity | 6.86 | 94,452.82 | tr|A0A804NZC5 | Glutamyl-tRNA(Gln) amidotransferase subunit B, chloroplastic/mitochondrial | GATB | Chloroplast | Protein biosynthesis; mitochondrial translation | ATP binding | 6.17 | 59,841.51 |
| tr|B4FBF6 | Mitochondrial dicarboxylate/tricarboxylate transporter DTC | LOC100274318 | Membrane | Transport | Transmembrane transporter activity | 9.72 | 33,147.50 | tr|B7ZXQ3 | Cysteine proteinases superfamily protein | LOC100283689 | Lysosome | Proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process | Cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | ||
| tr|C4J410 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein | LOC100501536 | Cytoplasm | Stress response | ATP binding; ATP hydrolysis activity; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone; heat shock protein binding; misfolded protein binding; protein folding chaperone; unfolded protein binding | 5.07 | 70,882.41 | tr|A0A804NLS4 | Adenosylhomocysteinase | LOC100282150 | None predicted | One-carbon metabolism | Hydrolase activity | 5.63 | 48,377.59 |
| tr| C4JA45 | 60S ribosomal protein L5-1 homolog b | ZEAMMB73_ Zm00001d012161 | Cytosolic large ribosomal subunit; nucleus | Translation; ribosomal large subunit assembly | 5S rRNA binding; structural constituent of ribosome | 9.34 | 34,3377.83 | tr|C0P5A9 | Optic atrophy 3 protein (OPA3) | LOC100276616 | Mitochondrion | Regulation of lipid metabolic process | 10.04 | 19,103.23 | |
| tr| K7VA99 | 60S ribosomal protein L5-1 homolog b | ZEAMMB73_ Zm00001d012161 | Cytoplasm; nucleus | Translation | Structural constituent of ribosome | 5.86 | 66,539.76 | tr|B4F8L7 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | LOC542290 | Stromule | Response to sucrose; response to light stimulus; response to cold | mRNA, NAD and NADP binding | 5.95 | 47,179.90 |
| sp|P93805 | Phosphoglucomutase, cytoplasmic 2 (PGM 2) (Glucose phosphomutase 2) | None retrieved | Cytoplasm | Carbohydrate metabolism; Glucose metabolism | Magnesium ion binding; phosphoglucomutase activity | 5.47 | 63,041.31 | tr|A0A1D6LSP5 | Elongation factor gamma1 | ZEAMMB73_ Zm00001d036959 | None predicted | Protein biosynthesis | Elongation factor | 5.91 | 43,457.95 |
| tr|A0A804UKU7 | CN hydrolase domain-containing protein | LOC100279870 | None predicted | Hydrolase activity | Hydrolase activity, acting on carbon–nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds, in linear amides | 8.62 | 40,920.58 | tr|K7V2Z8 | Carbamoyl-phosphate synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) | LOC103636016 | Cytoplasm | Pyrimidine biosynthesis | ATP binding; metal ion binding | 5.49 | 12,7286.83 |
| tr|A0A1D6KEP0 | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase | ZEAMMB73_ Zm00001d030859 | None predicted | One-carbon metabolism | Glycine hydroxymethyltransferase activity; methyltransferase activity; pyridoxal phosphate binding | 7.62 | 58,546.94 | tr|A0A804PU27 | Ribosomal_S4e domain-containing protein | None retrieved | Ribosome | Translation | rRNA binding; ribosomal protein | 5.79 | 28,447.42 |
| tr|A0A804U9Z6 | Glutamate--cysteine ligase | LOC542026 | Plastid, chloroplast | Glutathione biosynthesis | ATP binding; glutamate-cysteine ligase activity | 6.46 | 56,928.23 | tr|A0A804NG48 | GTP-binding nuclear protein | LOC100282843 | Nucleus | Protein transport; Nucleocytoplasmic transport | GTP binding | 9.34 | 19,867.92 |
| tr|A0A804QKD5 | Glutathione hydrolase | LOC103634830 | Membrane | Glutathione catabolic process | Acyltransferase activity; glutathione hydrolase activity | 5.95 | 66,539.76 | sp|P09315 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase A, chloroplastic | GAPA | Chloroplast | Glucose metabolic process; reductive pentose-phosphate cycle; response to light stimulus | NAD and NADP binding | 6.25 | 36,096.26 |
| tr|K7VN08 | ATP synthase B chain | LOC100282566 | Membrane | Hydrogen ion transport | Proton transmembrane transporter activity | 5.48 | 22,715.27 | tr|A0A804MAM1 | Methionine aminopeptidase | LOC100192977 | None predicted | Protein initiator methionine removal; proteolysis | Metal ion binding; metalloaminopeptidase activity | 6.86 | 37,094.53 |
| tr|B4FBC9 | Patellin-1 | LOC100192106 | Cytoplasm | Cell cycle; cell division | Lipid binding | 4.58 | 68,035.27 | tr|B4FRH1 | Thioredoxin M1 chloroplastic | LOC100272895 | Cytoplasm | None predicted | Oxidoreductase activity; protein-disulfide reductase activity | 8.63 | 19,560.59 |
| tr|C0PAU7 | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase | LOC100382805 | Cytosol | Glycolysis | Carbohydrate derivative binding; glucose-6-phosphate isomerase activity; monosaccharide binding | 5.56 | 67,431.16 | tr|B4FTT2 | Regulator of chromosome condensation2 | LOC100273233 | Chromatin; cytosol; nucleus | Response to UV-B; entrainment of circadian clock | Chromatin binding; photoreceptor activity; protein homodimerization activity | 5.38 | 47,158.43 |
| tr|B6UBZ9 | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 7 | LOC100383274 | Mitochondrion inner membrane | Electron transport; respiratory chain | 9.64 | 14,801.20 | tr|B4FU53 | 50S ribosomal protein L9, chloroplastic (CL9) | LOC100285012 | Ribosome | Translation | Structural constituent of ribosome | 9.81 | 21,660.30 | |
| tr|Q2MJJ9 | Putative RH2 protein | RH2 | None predicted | None predicted | ATP binding; hydrolase activity; RNA binding; RNA helicase activity | 5.98 | 45,945.84 | sp|P06586 | 30S ribosomal protein S3, chloroplastic | rps3 | Chloroplast | Translation | rRNA binding | 9.76 | 25,916.37 |
| tr|B4FPJ2 | U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm3 | LOC100194361 | Nucleus | mRNA processing; mRNA splicing | RNA binding | 4.78 | 11,235.91 | tr|B4F8M8 | Exoglucanase1 | LOC100191390 | Extracellular region | Carbohydrate metabolic process | Hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds | 6.54 | 64,583.72 |
| tr|C0P7G8 | Photosystem II repair protein PSB27-H1 chloroplastic | LOC100282043 | Chloroplast thylakoid lumen | Photosystem II assembly and repair | None predicted | 9.86 | 17,757.36 | tr|K7VDJ2 | 40S ribosomal protein S17-4 | LOC100282953 | Ribonucleoprotein complex; ribosome | Translation | Structural constituent of ribosome | 10.14 | 16,443.05 |
| tr|Q9M640 | Coatomer subunit delta | LOC541810 | Cytoplasm; Golgi membrane | ER–Golgi transport; protein transport | Retrograde Golgi-to-ER transport of dilysine-tagged proteins | 5.54 | 57,498.47 | tr| B8A2X5 | Pectinesterase | LOC100280285 | None predicted | Cell wall modification; pectin catabolic process | Aspartyl esterase activity; pectinesterase activity | 8.76 | 31,742.89 |
| tr|K7TXI5 | Chlorophyll a-b binding protein, chloroplastic | LOC542321 | Plastid, chloroplast thylakoid membrane | Photosynthesis | Chlorophyll binding | 7.90 | 26,586.76 | tr|A0A1D6HT50 | Polyribonucleotide nucleotidyltransferase | LOC103631988 | None predicted | mRNA catabolic process; RNA processing | Polyribonucleotide nucleotidyltransferase activity | 5.69 | 95,115.02 |
| tr|B6TCK3 | NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase | LOC103649684 | None predicted | None predicted | Cytochrome-b5 reductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H | 9.03 | 33,845.03 | tr|B4FRD6 | Peroxidase | LOC100281280 | Plant-type cell wall; extracellular region | Hydrogen peroxide | Heme binding; peroxidase activity | 7.12 | 33,116.72 |
| tr|B4FT19 | Oxygen evolving enhancer protein 3 containing protein | LOC100273120 | thylakoid | Photosynthesis | Calcium ion binding | 7.65 | 25,342.86 | tr|B4FW06 | 40S ribosomal protein S10-1 | LOC100273505 | Cytosolic small ribosomal subunit | None predicted | RNA binding; structural constituent of ribosome | 9.78 | 19,938.47 |
| tr|A0A1D6MUE8 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 6 chloroplastic | LOC103650436 | Chloroplast | Stress response | ATP binding; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone; unfolded protein binding | 5.08 | 74,493.16 | tr| Q947B9 | Glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase | GLG1 | Chloroplast | Starch biosynthesis | ATP binding; glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase activity | 6.48 | 56,482.41 |
| sp|P69388 | Cytochrome b559 subunit alpha (PSII reaction center subunit V) | psbE | Plastid, chloroplast thylakoid membrane | Photosynthetic electron transport chain | Electron transfer activity; heme binding; iron ion binding | 4.64 | 9444.60 | sp|P06589 | 50S ribosomal protein L22, chloroplastic | rpl22 | Chloroplast | Translation; ribosome assembly | rRNA binding; structural constituent of ribosome | 10.82 | 17,655.21 |
| tr|C0P3S5 | Fumarylacetoacetate (FAA) hydrolase family | ZEAMMB73_ Zm00001d034739 | Mitochondrion | None predicted | Acetylpyruvate hydrolase activity | 5.41 | 24,731.55 | tr|B6TGG7 | 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase | LOC100279917 | None predicted | Fatty acid biosynthetic process | 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase activity | 7.57 | 48,864.83 |
| tr|A0A1D6H5M2 | Chalcone-flavonone isomerase family protein | LOC100285485 | None predicted | None predicted | Intramolecular lyase activity | 7.72 | 29,540.85 | tr|B4FCX3 | Proteasome subunit beta | LOC100192865 | Cytoplasm; nucleus | Proteasomal protein catabolic process | Threonine-type endopeptidase activity | 7.77 | 28,912.76 |
| tr|A0A804R1C2 | Starch synthase, chloroplastic/ amyloplastic | None retrieved | Plastid, chloroplast | Starch biosynthesis | Glycogen (starch) synthase activity | 5.61 | 68,900.48 | tr|B6TNT5 | Peptide-methionine (S)-S-oxide reductase | LOC100283982 | Cytoplasm | Cellular response to oxidative stress | L-methionine-(S)-S-oxide reductase activity; peptide-methionine (S)-S-oxide reductase activity | 5.85 | 20,504.80 |
| tr|B4FQ59 | Phosphoribulokinase | LOC100282845 | Cytoplasm | Phosphorylation | ATP binding; phosphoribulokinase activity | 5.84 | 44,749.89 | tr| P55240 | Glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase small subunit | GLG1 | Chloroplast; amyloplast | Starch biosynthesis | ATP binding | N/A | N/A |
| tr|A0A804NUX2 | Phosphoribulokinase | None retrieved | None predicted | Reductive pentose-phosphate cycle | ATP binding; phosphoribulokinase activity | 9.51 | 27,481.52 | tr|A0A804P7H7 | Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase | None retrieved | None predicted | Pentose-phosphate shunt, non-oxidative branch | Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase activity | 5.44 | 31,500.71 |
| sp|P33488 | Auxin-binding protein 4 (ABP) | ABP4 | Endoplasmic reticulum lumen | Auxin signaling pathway | Receptor | 6.14 | 18,583.08 | tr|B4FRC4 | Serine-tRNA ligase | LOC541989 | Cytosol | Seryl-tRNA aminoacylation | Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase | 6.27 | 51,663.79 |
| tr|A0A1D6LE55 | Peroxidase | LOC103628960 | Extracellular region | Hydrogen peroxide catabolic process | Lactoperoxidase activity; heme binding | 5.25 | 34,847.89 | tr|A0A804MJA1 | Fn3_like domain-containing protein | None retrieved | Extracellular region | Xylan catabolic process | Xylan 1,4-beta-xylosidase activity | 8.52 | 82,057.02 |
| tr|A0A1X7YHG9 | ATP synthase subunit alpha, chloroplastic | LOC118474820 | Plastid, chloroplast thylakoid membrane | ATP synthesis; Hydrogen ion transport | ATP binding; proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism; proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism | 5.87 | 55,690.85 | tr|A0A1D6L554 | 60S ribosomal protein L13a-1 | LOC100191912 | Large ribosomal subunit | Translation | Structural constituent of ribosome | 10.35 | 21,187.48 |
| tr|A0A804LI62 | PsbP domain-containing protein | LOC103634474 | Extrinsic component of membrane | Photosynthesis | Calcium ion binding | 7.59 | 26,587.16 | tr| B4FAM6 | 60S ribosomal protein L13a-1 | LOC100191912 | Large ribosomal subunit | Translation | Lyase activity; magnesium ion binding; thiamine pyrophosphate binding | 10.20 | 23,600.17 |
| sp|P48186 | ATP synthase subunit b, chloroplastic (ATP synthase F(0) sector subunit b) (ATP se subunit I) | atpF | Plastid, chloroplast thylakoid membrane | ATP synthesis | ATP binding; proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism | 9.27 | 20,981.12 | tr|K7UMB3 | Signal recognition particle 54 kDa protein chloroplastic | LOC103654352 | Signal recognition particle, endoplasmic reticulum targeting | SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane | 7S RNA binding; GTP binding; GTPase activity | 9.56 | 59,737.25 |
| tr|A0A804NI62 | Legumain | LOC542609 | Cellular anatomical entity | Proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process | Cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | 5.07 | 44,767.98 | tr| B4FYT5 | Protein Kinase C630.09c | LOC100274052 | None predicted | Phosphorylation | ATP binding; kinase activity | 5.62 | 47,498.13 |
| tr|A0A1D6E958 | Protease Do-like 8 chloroplastic | LOC100272554 | Chloroplast thylakoid lumen | Proteolysis; photosystem II repair | Serine-type endopeptidase activity | 9.07 | 51,190.49 | sp|P27723 | 30S ribosomal protein S16, chloroplastic | rps16 | Chloroplast | Translation | Structural constituent of ribosome | 10.33 | 10,089.90 |
| tr|A0A3L6EGC3 | Germin-like protein | Os08g0459700_1 | Secreted, extracellular space, apoplast | None predicted | Manganese ion binding | 5.89 | 20,101.08 | tr|A0A804UA42 | PRK domain-containing protein | LOC100274052 | Integral component of membrane | ATP binding; kinase activity | DNA binding | 6.61 | 58,115.71 |
| tr|A0A096S078 | 4-coumarate--CoA ligase-like 7 | LOC100191850 | Membrane | Phenylpropanoid metabolic process | 4-coumarate-CoA ligase activity | 7.00 | 53,052.88 | tr|B8A1H0 | Glucose-6-phosphate 1-epimerase | LOC100273735 | Cytoplasm | Carbohydrate metabolic process | Carbohydrate binding | 5.68 | 34,240.88 |
| tr|A0A804N9X8 | Pectinesterase | None retrieved | None predicted | Cell wall modification; Pectin catabolic process | Aspartyl esterase activity; pectinesterase activity | 6.19 | 54,997.66 | tr|B4G1J8 | 50S ribosomal protein L3-1 chloroplastic | LOC100193892 | Ribonucleoprotein complex; ribosome | Translation | mRNA binding | 10.59 | 27,867.52 |
| tr|Q94F78 | Nucleosome/chromatin assembly factor A | nfa104 | Cytoplasm; chromatin; nucleus | Nucleus assembly; double-stand break repair | Chromatin binding; histone binding | 4.08 | 29,331.84 | tr|B4FGN4 | 50S ribosomal protein L3-1 chloroplastic | LOC100193892 | Ribosome | Translation | Structural constituent of ribosome | 7.63 | 24,415.30 |
| tr|A0A1D6L6U6 | Glutathione transferase | LOC542734 | cytoplasm | Glutathione metabolic process | Glutathione transferase activity | 6.20 | 25,258.20 | tr|C0HFM4 | 60S ribosomal protein L13a-1 | LOC100283655 | Cytosolic large ribosomal subunit; ribosome | Negative regulation of translation; translation | mRNA binding; structural constituent of ribosome | 10.22 | 23,629.10 |
| tr|A0A1D6N672 | Photosystem II subunit PsbS1 | LOC542126 | Membrane; plastid | Nonphotochemical quenching; response to high light intensity | None predicted | 9.07 | 28,452.15 | tr|B4F9N8 | RNA-binding (RRM/RBD/RNP motifs) family protein | LOC100191663 | Ribonucleoprotein complex | None predicted | RNA binding | 4.99 | 51,279.59 |
| tr|A0A804LJD2 | Guanylate kinase | LOC100283207 | None predicted | Phosphorylation | ATP binding; guanylate kinase activity | 9.18 | 32,388.47 | tr|A0A804RFJ4 | Gp_dh_N domain-containing protein | None retrieved | None predicted | None predicted | NAD binding | 6.51 | 28,369.38 |
| tr|Q6R9G1 | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase subunit H | nad7 | Mitochondrion; thylakoid | Mitochondrial electron transport | NAD binding; NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity; quinone binding | 6.74 | 44,280.13 | tr|A0A804PBS5 | Inorganic diphosphatase | LOC103626225 | Cytoplasm | Phosphate-containing compound metabolic process | Inorganic diphosphate phosphatase activity; magnesium ion binding | 5.99 | 20,994.02 |
| tr|A0A804UKI0 | CN hydrolase domain-containing protein | LOC100279870 | None predicted | Hydrolase activity | Hydrolase activity, acting on carbon–nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds, in linear amides | 8.89 | 29,227.53 | tr|A0A804NZ53 | SRP54 domain-containing protein | LOC103654352 | Cytoplasm | SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane | RNA-binding; GTPase activity | 9.36 | 56,091.99 |
| Control | 25% PEG | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession Number | Protein Name | Gene/ Locus ID | Subcellular Location | Biological Processes | Molecular Function | PI | Mr | Accession Number | Protein Name | Gene/ Locus ID | Subcellular Location | Biological Processes | Molecular Function | PI | Mr |
| TR|B4F833 | Diaminopimelate epimerase | LOC100191234 | Cytosol | Lysine biosynthetic process via diaminopimelate | Diaminopimelate epimerase activity | 5.96 | 37,799.11 | sp|P21569 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase | CYP | Cytoplasm | Protein folding; protein peptidyl-prolyl isomerization | Cyclosporin A binding | 8.91 | 18,348.99 |
| TR|C4IZ94 | Ornithine carbamoyltransferase | LOC100284885 | Intracellular membrane | Arginine biosynthetic process via ornithine | Amino acid binding | 6.76 | 40,286.51 | tr|C0P3R8 | Glutathione peroxidase | LOC100272844 | None predicted | Response to oxidative stress | Glutathione peroxide activity | 9.55 | 24,993.61 |
| TR|A0A1D6HM49 | Subtilisin-like protease SBT1.4 | LOC100279566 | None predicted | Proteolysis | Serine-type endopeptidase activity | 5.35 | 78,345.99 | tr|A0A804PHY0 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase | LOC103627222 | None predicted | Protein folding | Peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase activity | 9.03 | 16,744.15 |
| TR| B4F8V5 | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron–sulfur protein 1 mitochondrial | LOC100191453 | Membrane | ATP synthesis coupled electron transport | 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding | 6.10 | 80,679.62 | tr|C0P4P5 | Non-reducing end alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase | LOC100193890 | None predicted | Cellular carbohydrate catabolic process; L-arabinose metabolic process | Alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase activity | 5.05 | 69,535.87 |
| TR|B4FYD3 | TOM1-like protein 2 | LOC100282255 | Membrane | Protein transport | Phosphatidylinositol binding; ubiquitin binding | 4.58 | 43,475.92 | tr|K7VNQ7 | Mitochondrial import receptor subunit TOM40-1 | LOC110120361 | Integral component of membrane | Protein import into mitochondrial matrix | Protein transmembrane transporter activity | 6.01 | 37,345.36 |
| TR| K7WFV1 | ATP synthase subunit gamma | LOC100274172 | Mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, catalytic sector F1F0 | Proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis | Proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism | 9.12 | 35,714.94 | tr|B4FMF7 | Aldose 1-epimerase | LOC100217298 | None predicted | Hexose metabolic process | Aldose 1-epimerase activity | 8.89 | 36,388.96 |
| TR| B5AMJ8 | Alpha-1,4 glucan phosphorylase | LOC100285259 | None predicted | Carbohydrate metabolic process | Glycogen phosphorylase activity | 6.86 | 94,452.82 | tr|C0P5Y3 | 5-methyltetrahydropteroyltriglutamate--homocysteine S-methyltransferase | LOC541942 | None predicted | Methionine biosynthetic process; methylation | 5-methyltetrahydropteroyltriglutamate-homocysteine S-methyltransferase activity; zinc ion binding | 5.54 | 84,492.46 |
| TR|B4FBF6 | Mitochondrial dicarboxylate/tricarboxylate transporter DTC | LOC100274318 | Membrane | Transport | Transmembrane transporter activity | 9.72 | 33,147.50 | tr|Q6RW09 | Allene-oxide cyclase | aoc | Chloroplast | Jasmonic acid biosynthetic process | Allene-oxide cyclase activity | 9.05 | 25,777.29 |
| TR|C4J410 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein | LOC100501536 | Cytoplasm | Stress response | ATP binding; ATP hydrolysis activity; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone; heat shock protein binding; misfolded protein binding; protein folding chaperone; unfolded protein binding | 5.07 | 70,882.41 | tr|A0A804MQI0 | Valine-tRNA ligase | LOC100383209 | None predicted | Post-embryonic development]; reproductive structure development; valyl-tRNA aminoacylation | Aminoacyl-tRNA editing activity; ATP binding; valine-tRNA ligase activity | 6.60 | 11,6740.55 |
| TR| C4JA45 | 60S ribosomal protein L5-1 homolog b | LOC10028491 | Cytosolic large ribosomal subunit; nucleus | Translation; ribosomal large subunit assembly | 5S rRNA binding; structural constituent of ribosome | 9.34 | 34,3377.83 | tr|B4FYH2 | Pyruvate kinase | LOC100273990 | Chloroplast stroma; cytoplasm | Glycolytic process; photosynthesis | ATP binding; kinase activity; magnesium ion binding; potassium ion binding; pyruvate kinase activity | 6.26 | 61,479.03 |
| TR| K7VA99 | 60S ribosomal protein L5-1 homolog b | LOC100284917 | Cytoplasm; nucleus | Translation | Structural constituent of ribosome | 5.86 | 66,539.76 | tr|B4FEA2 | Mitochondrial carnitine/acylcarnitine carrier-like protein | LOC118476033 | Membrane | Nitrogen compound transport; organic anion transport; organophosphate ester transport; transmembrane transport | None predicted | 9.54 | 30,155.95 |
| SP|P93805 | Phosphoglucomutase, cytoplasmic 2 (PGM 2) (Glucose phosphomutase 2) | LOC542358 | Cytoplasm | Carbohydrate metabolism; Glucose metabolism | Magnesium ion binding; phosphoglucomutase activity | 5.47 | 63,041.31 | tr|A0A804R5D8 | Ribosomal_S4e domain-containing protein | None retrieved | Ribosome | Translation | Structural constituent of ribosome | 6.88 | 45,232.88 |
| TR|A0A804UKU7 | CN hydrolase domain-containing protein | LOC100279870 | None predicted | Hydrolase activity | Hydrolase activity, acting on carbon–nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds, in linear amides | 8.62 | 40,920.58 | tr|O22453 | 40S ribosomal protein S4 | rps4 | Ribosome | Translation | RNA binding | 10.20 | 30,171.37 |
| TR|A0A1D6KEP0 | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase | LOC100381786 | None predicted | One-carbon metabolism | Glycine hydroxymethyltransferase activity; methyltransferase activity; pyridoxal phosphate binding | 7.62 | 58,546.94 | tr|C0P455 | 60S ribosomal protein L4-1 | LOC100382075 | Cytosolic large ribosomal subunit | Translation | RNA binding | 10.65 | 44,292.54 |
| TR|A0A804U9Z6 | Glutamate--cysteine ligase | LOC542026 | Plastid, chloroplast | Glutathione biosynthesis | ATP binding; glutamate-cysteine ligase activity | 6.46 | 56,928.23 | tr|B4FWJ8 | Binding protein homolog2 | LOC732809 | Cytoplasm | Protein refolding | Heat shock protein binding | 5.10 | 70,546.74 |
| TR|A0A804QKD5 | Glutathione hydrolase | LOC103634830 | Membrane | Glutathione catabolic process | Acyltransferase activity; glutathione hydrolase activity | 5.95 | 66,539.76 | tr|A0A1D6L210 | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron–sulfur protein 1 mitochondrial | LOC100280404 | Membrane | ATP synthesis coupled electron transport | 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding; NADH dehydrogenase | 6.01 | 80,717.71 |
| TR|K7VN08 | ATP synthase B chain | LOC100282566 | Membrane | Hydrogen ion transport | Proton transmembrane transporter activity | 5.48 | 22,715.27 | tr|A0A804MU73 | T-complex protein 1 subunit zeta | LOC100193477 | Cytoplasm | ATP binding | 6.82 | 53,590.56 | |
| TR|B4FBC9 | Patellin-1 | LOC100192106 | Cytoplasm | Cell cycle; cell division | Lipid binding | 4.58 | 68,035.27 | tr|B6THZ8 | Threonine synthase | LOC100283397 | Cytoplasm | Cysteine biosynthetic process | Pyridoxal phosphate binding | 6.44 | 57,614.35 |
| TR|C0PAU7 | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase | LOC100382805 | Cytosol | Glycolysis | Carbohydrate derivative binding; glucose-6-phosphate isomerase activity; monosaccharide binding | 5.56 | 67,431.16 | tr|B4FAL9 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase | LOC542261 | Cytosol | Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate metabolic process; glycolytic process | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase activity | 7.52 | 38,590.16 |
| TR|B6UBZ9 | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 7 | LOC100383274 | Mitochondrion inner membrane | Electron transport; respiratory chain | None predicted | 9.64 | 14,801.20 | tr|K7UDG5 | Proline--tRNA ligase | LOC100272402 | Cytoplasm | Prolyl-tRNA aminoacylation | ATP binding | 6.71 | 58,133.54 |
| TR|Q2MJJ9 | Putative RH2 protein | LOC732749 | None predicted | None predicted | ATP binding; hydrolase activity; RNA binding; RNA helicase activity | 5.98 | 45,945.84 | tr|C0PFN4 | Glucose-6-phosphate 1-epimerase | LOC100282752 | None predicted | Carbohydrate metabolic process | Carbohydrate binding; glucose-6-phosphate 1-epimerase activity | 6.26 | 36,652.84 |
| TR|B4FPJ2 | U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm3 | LOC100194361 | Nucleus | mRNA processing; mRNA splicing | RNA binding | 4.78 | 11,235.91 | tr|B4F938 | Coproporphyrinogen oxidase | LOC100500945 | Cytoplasm | Protoporphyrinogen IX biosynthetic process | Coproporphyrinogen oxidase activity | 8.19 | 44,112.77 |
| TR|C0P7G8 | Photosystem II repair protein PSB27-H1 chloroplastic | LOC100282043 | Chloroplast thylakoid lumen | Photosystem II assembly and repair | None predicted | 9.86 | 17,757.36 | tr|B4F871 | Protein DJ-1 homolog D (YLS5) | LOC100280536 | None predicted | None predicted | Glyoxalase III activity | 5.37 | 41,209.28 |
| TR|Q9M640 | Coatomer subunit delta | LOC541810 | Cytoplasm; Golgi membrane | ER-Golgi transport; Protein transport | Retrograde Golgi-to-ER transport of dilysine-tagged proteins | 5.54 | 57,498.47 | tr|B4FIH9 | Xylose isomerase | LOC100194385 | None predicted | D-xylose metabolic process | Metal ion binding; xylose isomerase activity | 5.40 | 51,045.66 |
| TR|K7TXI5 | Chlorophyll a-b binding protein, chloroplastic | LOC542321 | Plastid, chloroplast thylakoid membrane | photosynthesis | Chlorophyll binding | 7.90 | 26,586.76 | tr|B4G1K3 | Calcyclin-binding protein Prolyl aminopeptidase) SGT1 | LOC100282523 | None predicted | None predicted | S100 protein binding; tubulin binding; ubiquitin protein ligase binding | 8.69 | 24,644.44 |
| TR|B6TCK3 | NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase | LOC103649684 | None predicted | None predicted | Cytochrome-b5 reductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H | 9.03 | 33,845.03 | tr|B4FR32 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate deHaseN1 (NADP-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) | LOC542583 | None predicted | None predicted | Oxidoreductase activity, acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor | 6.80 | 53,284.58 |
| TR|B4FT19 | Oxygen evolving enhancer protein 3 containing protein | LOC100273120 | Thylakoid | Photosynthesis | Calcium ion binding | 7.65 | 25,342.86 | tr|B4FFZ2 | Ketol-acid reductoisomerase (EC 1.1.1.86) (Acetohydroxy-acid reductoisomerase) (Alpha-keto-beta-hydroxylacyl reductoisomerase) | LOC100193695 | None predicted | Isoleucine biosynthetic process; valine biosynthetic process. | Isomerase activity; ketol-acid reductoisomerase activity; metal ion binding | 6.31 | 63,002.80 |
| TR|A0A1D6MUE8 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 6 chloroplastic | LOC103650436 | Chloroplast | Stress response | ATP binding; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone; unfolded protein binding | 5.08 | 74,493.16 | tr|B4FAD4 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] catalytic subunit 5 mitochondrial | LOC100191841 | Mitochondrion | Isocitrate metabolic process; tricarboxylic acid cycle | Isocitrate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity; magnesium ion binding; NAD binding. | 6.52 | 39,724.58 |
| SP|P69388 | Cytochrome b559 subunit alpha (PSII reaction center subunit V) | psbE | Plastid, chloroplast thylakoid membrane | Photosynthetic electron transport chain | Electron transfer activity; heme binding; iron ion binding | 4.64 | 9444.60 | tr|B4F9K0 | Late embryogenesis abundant protein group 2 | LOC100191638 | None predicted | Response to desiccation | None predicted | 4.92 | 35,274.07 |
| TR|C0P3S5 | Fumarylacetoacetate (FAA) hydrolase family | Mitochondrion | None predicted | Acetylpyruvate hydrolase activity | 5.41 | 24,731.55 | tr|A0A1D6JYM4 | Glutathione S-transferase L2 chloroplastic | LOC100282747 | None predicted | Response to chemical | Glutathione transferase activity | 6.15 | 33,860.53 | |
| TR|A0A1D6H5M2 | Chalcone-flavonone isomerase family protein | LOC100285485 | None predicted | None predicted | Intramolecular lyase activity | 7.72 | 29,540.85 | tr|Q6R9L0 | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 9 | nad9 | Mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I | None predicted | NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity | 8.51 | 22,594.41 |
| TR|A0A804R1C2 | Starch synthase, chloroplastic/amyloplastic | LOC100283765 | Plastid, chloroplast | Starch biosynthesis | Glycogen (starch) synthase activity | 5.61 | 68,900.48 | tr|B4FT31 | Dehydroascorbate reductase | DHAR3 | None predicted | Ascorbate glutathione cycle | Glutathione transferase activity | 5.54 | 23,355.73 |
| TR|B4FQ59 | Phosphoribulokinase | LOC100282845 | Cytoplasm | Phosphorylation | ATP binding; phosphoribulokinase activity | 5.84 | 44,749.89 | tr|B4F9K4 | 17.5 kDa class II heat shock protein | LOC542723 | None predicted | Stress response | Protein self-association | 5.95 | 17,868.64 |
| TR|A0A804NUX2 | Phosphoribulokinase | None retrieved | None predicted | Reductive pentose-phosphate cycle | ATP binding; phosphoribulokinase activity | 9.51 | 27,481.52 | tr|B4F9E8 | 17.4 kDa class III heat shock protein | LOC100191598 | None predicted | Protein complex Oligomerization; protein folding; response to heat; response to hydrogen peroxide; response to salt stress | Protein self-association; unfolded protein binding | 6.60 | 18,347.76 |
| SP|P33488 | Auxin-binding protein 4 (ABP) | ABP4 | Endoplasmic reticulum lumen | Auxin signaling pathway | Receptor | 6.14 | 18,583.08 | tr|B4FQC9 | Proline iminopeptidase (PIP) | LOC100272740 | Cytoplasm | Aminopeptidase activity | Proteolysis | 5.24 | 36,602.16 |
| TR|A0A1D6LE55 | Peroxidase | LOC103628960 | Extracellular region | Hydrogen peroxide catabolic process | Lactoperoxidase activity; heme binding | 5.25 | 34,847.89 | tr|A0A804NGN9 | SGT1 | LOC100282745 | Plastid; Thylakoid | None predicted | Chaperone binding | 5.02 | 40,229.33 |
| TR|A0A1X7YHG9 | ATP synthase subunit alpha, chloroplastic | LOC118474820 | Plastid, chloroplast thylakoid membrane | ATP synthesis; Hydrogen ion transport | ATP binding; proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism; proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism | 5.87 | 55,690.85 | tr|B6SN61 | Grx_C2.1-glutaredoxin subgroup I | LOC100303864 | Cytoplasm | Cellular response to oxidative stress | Glutathione disulfide oxidoreductase activity; glutathione oxidoreductase activity; protein-disulfide reductase (glutathione) activity | 7.71 | 13,932.16 |
| TR|A0A804LI62 | PsbP domain-containing protein | LOC103634474 | Extrinsic component of membrane | Photosynthesis | Calcium ion binding | 7.59 | 26,587.16 | tr|A0A1D6MNJ0 | 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase | LOC542023 | None predicted | Isopentenyl diphosphate biosynthetic process, methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway | 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase activity; isomerase activity; metal ion binding; NADPH binding | 6.44 | 51,257.01 |
| SP|P48186 | ATP synthase subunit b, chloroplastic (ATP synthase F(0) sector subunit b) (ATP se subunit I) | atpF | Plastid, chloroplast thylakoid membrane | ATP synthesis | ATP binding; proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism | 9.27 | 20,981.12 | tr|A0A804PDW7 | Luminal-binding protein 5 | LOC732808 | Endoplasmic reticulum | None predicted | ATP binding; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone | 5.05 | 69,401.51 |
| TR|A0A804NI62 | Legumain | LOC542609 | Cellular anatomical entity | proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process | Cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | 5.07 | 44,767.98 | tr|A0A804LN04 | Branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase | LOC100191754 | None predicted | Branched-chain amino acid biosynthetic process; cellular amino acid biosynthetic process | Branched-chain amino acid transaminase activity | 5.80 | 43,223.76 |
| TR|A0A1D6E958 | Protease Do-like 8 chloroplastic | LOC100272554 | Chloroplast thylakoid lumen | Proteolysis; photosystem II repair | Serine-type endopeptidase activity | 9.07 | 51,190.49 | tr|A0A804MU73 | T-complex protein 1 subunit zeta | LOC100193477 | Cytoplasm | None predicted | ATP binding; ATP hydrolysis activity; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone; unfolded protein binding | 6.82 | 53,590.56 |
| TR|A0A3L6EGC3 | Germin-like protein | LOC100191976 | Secreted, extracellular space, apoplast | None predicted | Manganese ion binding | 5.89 | 20,101.08 | tr|A0A804RJL5 | Aconitate hydratase | LOC100281040 | None predicted | 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding; hydro-lyase activity; metal ion binding | Oxoacid metabolic process | 6.01 | 966,932.89 |
| TR|A0A096S078 | 4-coumarate--CoA ligase-like 7 | LOC100191850 | Membrane | Phenylpropanoid metabolic process | 4-coumarate-CoA ligase activity | 7.00 | 53,052.88 | tr|A0A1D6JW41 | 40S ribosomal protein S20-1 | LOC103633583 | Cytosolic small ribosomal subunit; small ribosomal subunit | Translation | Structural constituent of ribosome | 9.51 | 13,824.16 |
| TR|A0A804N9X8 | Pectinesterase | LOC103650921 | None predicted | Cell wall modification; Pectin catabolic process | Aspartyl esterase activity; pectinesterase activity | 6.19 | 54,997.66 | tr|B6U237 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 14 (Heat shock 70 kDa protein 4) | LOC100285213 | None predicted | ATP binding; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone | None predicted | 5.28 | 93,569.13 |
| TR|Q94F78 | Nucleosome/chromatin assembly factor A | nfa104 | Cytoplasm; chromatin; nucleus | Nucleus assembly; double-stand break repair | Chromatin binding; histone binding | 4.08 | 29,331.84 | tr|A0A1D6JW41 | 40S ribosomal protein S20-1 | LOC103633583 | Component cytosolic small ribosomal subunit | Translation | Ribosomal protein | 9.51 | 13,824.16 |
| TR|A0A1D6L6U6 | Glutathione transferase | LOC542734 | Cytoplasm | Glutathione metabolic process | Glutathione transferase activity | 6.20 | 25,258.20 | tr|B4F9K4 | 17.5 kDa class II heat shock protein | LOC542723 | None predicted | Protein self-association; unfolded protein binding | Protein complex oligomerization; protein folding; response to heat; response to hydrogen peroxide; response to salt stress | 5.95 | 17,868.64 |
| TR|A0A1D6N672 | Photosystem II subunit PsbS1 | LOC542126 | Membrane; plastid | Nonphotochemical quenching; response to high light intensity | None predicted | 9.07 | 28,452.15 | tr|A0A804RJL5 | Aconitate hydratase | LOC100281040 | None predicted | Oxoacid metabolic process | Metal ion binding | 6.01 | 96,932.89 |
| TR|A0A804LJD2 | Guanylate kinase | LOC100283207 | None predicted | Phosphorylation | ATP binding; guanylate kinase activity | 9.18 | 32,388.47 | tr|B6T8Q5 | T-complex protein 1 subunit zeta | LOC100193477 | Cytoplasm | None predicted | ATP binding | 6.23 | 59,087.02 |
| TR|Q6R9G1 | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase subunit H | nad7 | Mitochondrion; thylakoid | Mitochondrial electron transport | NAD binding; NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity; quinone binding | 6.74 | 44,280.13 | tr|B4FT31 | Dehydroascorbate reductase | DHAR3 | None predicted | Glutathione dehydrogenase (ascorbate) activity; glutathione transferase activity | Ascorbate glutathione cycle | ||
| TR|A0A804UKI0 | CN hydrolase domain-containing protein | LOC100279870 | None predicted | Hydrolase activity | Hydrolase activity, acting on carbon–nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds, in linear amides | 8.89 | 29,227.53 | tr|K7VJF3 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 5 | LOC100272911 | Cytoplasm | ATP binding; ATP hydrolysis activity; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone; heat shock protein binding; misfolded protein binding; protein folding chaperone; unfolded protein binding | Cellular response to unfolded protein; chaperone cofactor-dependent protein refolding; protein refolding | 5.22 | 71,502.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sinthumule, R.R.; Sithole, C.; Gaorongwe, J.L.; Matebele, K.M.; Ruzvidzo, O.; Dikobe, T.B. Enhancing Stress Resilience in a Drought-Tolerant Zea mays Cultivar by Integrating Morpho-Physiological and Proteomic Characterization. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2025, 16, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16040133
Sinthumule RR, Sithole C, Gaorongwe JL, Matebele KM, Ruzvidzo O, Dikobe TB. Enhancing Stress Resilience in a Drought-Tolerant Zea mays Cultivar by Integrating Morpho-Physiological and Proteomic Characterization. International Journal of Plant Biology. 2025; 16(4):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16040133
Chicago/Turabian StyleSinthumule, Rotondwa Rabelani, Charlie Sithole, Joseph Lesibe Gaorongwe, Kegomoditswe Martha Matebele, Oziniel Ruzvidzo, and Tshegofatso Bridget Dikobe. 2025. "Enhancing Stress Resilience in a Drought-Tolerant Zea mays Cultivar by Integrating Morpho-Physiological and Proteomic Characterization" International Journal of Plant Biology 16, no. 4: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16040133
APA StyleSinthumule, R. R., Sithole, C., Gaorongwe, J. L., Matebele, K. M., Ruzvidzo, O., & Dikobe, T. B. (2025). Enhancing Stress Resilience in a Drought-Tolerant Zea mays Cultivar by Integrating Morpho-Physiological and Proteomic Characterization. International Journal of Plant Biology, 16(4), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb16040133






