Litter Deposition and Nutrient Cycling of Invaded Environments by Cryptostegia madagascariensis at Tropical Cambisols from Northeastern Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Studied Plant Species
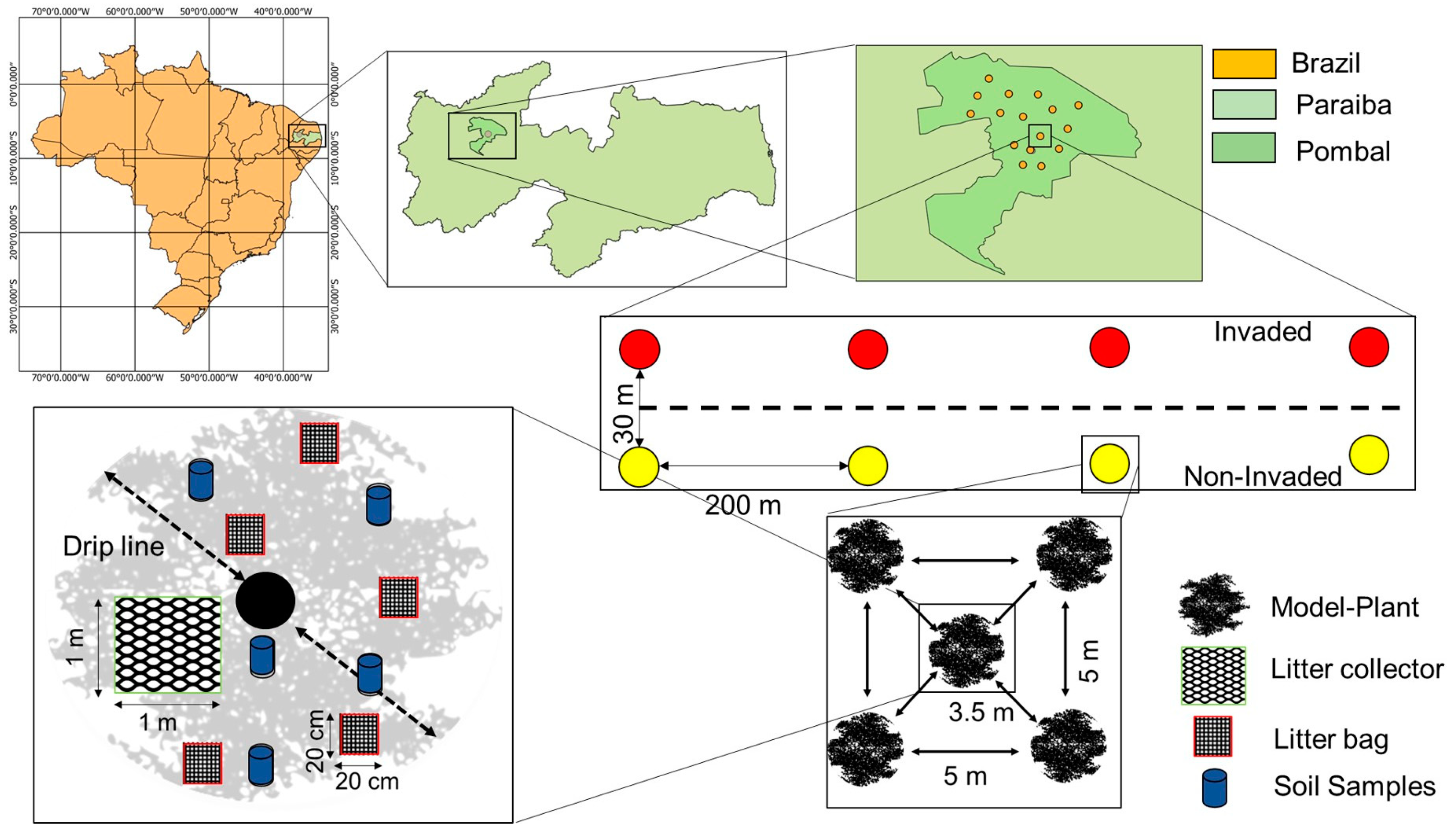
2.2. Study Sites and Experimental Design
2.3. Litter Deposition
2.4. Litter Quality and Soil Properties
2.5. Litter Preparation
2.6. Litter Decomposition (Litter Decay Rate)
2.7. Data Analysis
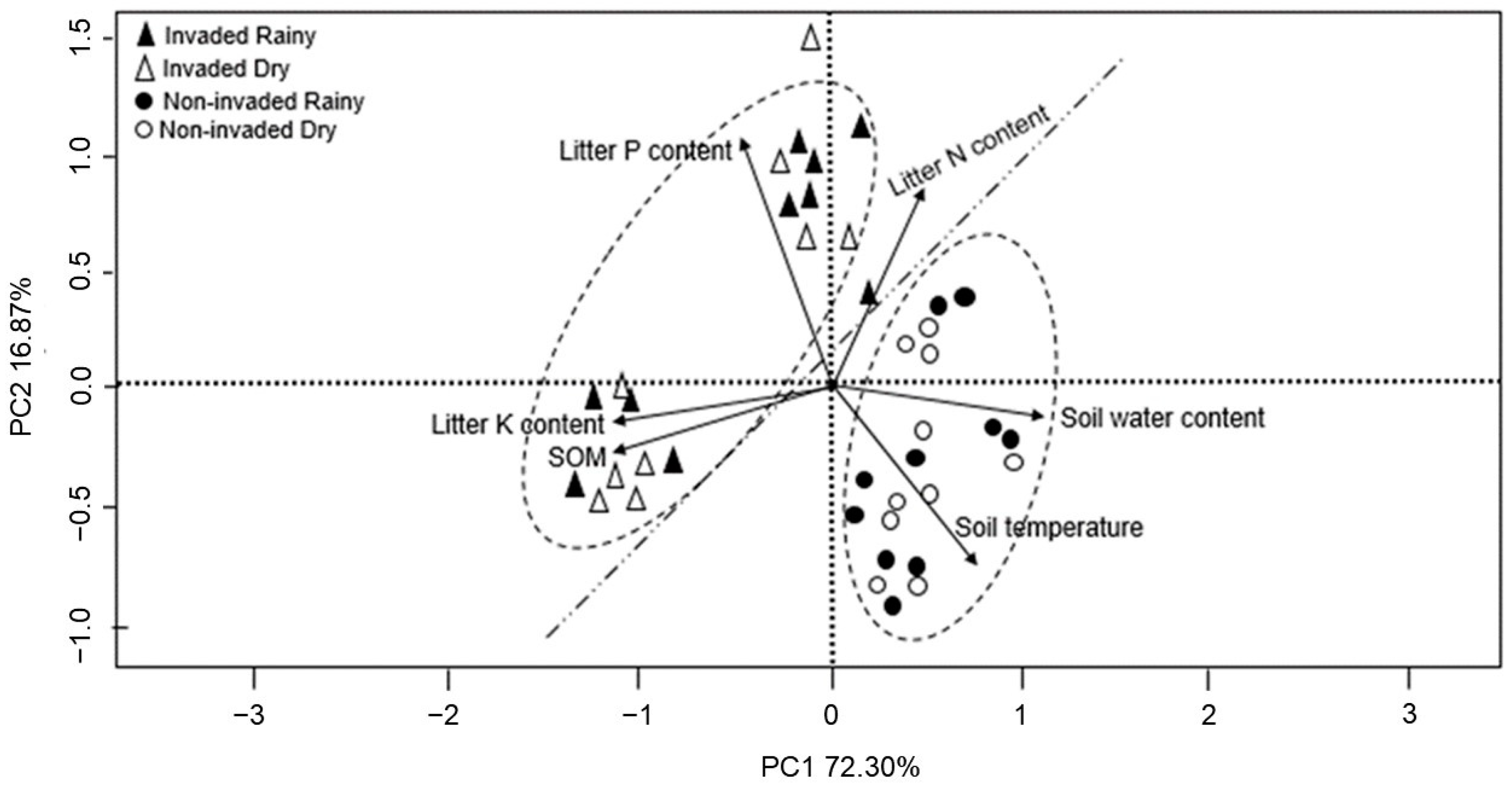
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gentili, R.; Ferrè, C.; Cardarelli, E.; Montagnani, C.; Bogliani, G.; Citterio, S.; Comolli, R. Comparing negative impacts of Prunus serotina, Quercus rubra, and Robinia pseudoacacia on native forest ecosystems. Forests 2019, 10, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, F.Q.; Andrade, L.A.; Xavier, K.R.F. Cryptostegia madagascariensis Bojer ex Decne.: Impactos sobre a regeneração natural em fragmentos de caatinga. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Agrárias 2016, 11, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.A.F.; Rodriguez-Echeverría, S.; Andrade, L.A.; Freitas, H. Could biological invasion by Cryptostegia madagascariensis alter the composition of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community in semi-arid Brazil? Acta Bot. Bras. 2016, 30, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, E.O.; Souza, T.A.F.; Araújo, J.S.; Andrade, L.A.; Santos, D.; Podestá, G.S. Occurrence and distribution of Gigaspora under Cryptostegia madagascariensis Bojer Ex Decne in Brazilian tropical seasonal dry forest. Rev. Agropec. Tec. 2018, 39, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, E.O.; Souza, T.A.F.; da Silva, S.I.A.; Kormann, S.; da Silva, L.J.R.; Laurindo, L.K.; Forstall-Sosa, K.S.; de Andrade, L.A. Soil biota community composition as affected by Cryptostegia madagascariensis invasion in a tropical Cambisol from North-eastern Brazil. Trop. Ecol. 2021, 62, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.A.F.; de Andrade, L.A.; Freitas, H.; Sandim, A.S. Biological Invasion Influences the Outcome of Plant-Soil Feedback in the Invasive Plant Species from the Brazilian Semi-arid. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.G.; Silva, T.G.F.; Zolneira, S.; Souza, C.A.A.; Souza, L.S.B.; Steidle Neto, A.J.; Araújo, G.G.L.; Ferreira, W.P.M. Seasonal patterns of deposition litterfall in a seasonal dry tropical forest. Agric. For. Meteor. 2019, 279, e107712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, J.; Nóbrega, R.L.B.; Rufinod, I.; Erasmie, S.; Galvão, C.; Valentef, F. Surface albedo as a proxy for land-cover clearing in seasonally dry forests: Evidence from the Brazilian Caatinga. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, e111250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, D.C.; Souza, T.A.F.; Pech, T.M.; Bartz, M.L.C.; Baretta, D.; Siminski, A.; Niemeyer, J.C. Soil ecosystem changes by vegetation on old-field sites over five decades in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. J. For. Res. 2021, 33, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Sardans, J.; Ouyang, L.; Tong, C.; Asensio, D.; Gargallo-Garriga, A.; Wiesmeier, M.; Peñuelas, J. Higher fluxes of C, N and P in plant/soil cycles associated with plant invasion in a subtropical estuarine wetland in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, e139124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Sardans, J.; Tong, C.; Ouyang, L.; Asensio, D.; Gargallo-Garriga, A.; Peñuelas, J. Storage and release of nutrients during litter decomposition for native and invasive species under different flooding intensities in a Chinese wetland. Aquat. Bot. 2018, 49, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keet, J.H.; Ellis, A.G.; Hui, C.; Novoa, A.; Roux, J.J.L. Impacts of Invasive Australian Acacias on Soil Bacterial Community Composition, Microbial Enzymatic Activities, and Nutrient Availability in Fynbos Soils. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 82, 704–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurindo, L.K.; Souza, T.A.F.; Silva, L.J.R.; Casal, T.B.; Pires, K.J.C.; Kormann, S.; Scmitt, D.E.; Siminski, A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community assembly in agroforestry systems from the Southern Brazil. Biologia 2021, 76, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Whalen, J.K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W.; Chang, S.X. Functional diversity of decomposers modulates litter decomposition affected by plant invasion along a climate gradient. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, F.Y.; Song, X.; Wang, X.; Suri, G.; Baoyin, T. Changes in litter decomposition rate of dominant plants in a semi-arid steppe across different land-use types: Soil moisture, not home-field advantage, plays a dominant role. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 303, e107119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.C.M.; Mesléard, F.; Buisson, E. Priority effects: Emerging principles for invasive plant species management. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, J.; Yongpeng, M.; Tian, X. Dispersal and germination of winged seeds of Brandisia hancei, a shrub in karst regions of China. Plant Divers. 2021, 43, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, G.S.; Souza, T.A.F.; Silva, L.J.R.; Santos, D. Soil physico-chemical properties, biomass production, and root density in a green manure farming system from tropical ecosystem, North-eastern Brazil. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, W.A.C.; Almeida, R.V.; Xavier, R.O.; Bianchini, I.; Moya, H.; Matos, D.M.S. Litter accumulation and biomass dynamics in riparian zones in tropical South America of the Asian invasive plant Hedychium coronarium J. König (Zingiberaceae). Plant Ecol. Divers. 2019, 13, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, I.; Fridley, J.D.; Frank, D.A. Rapid leaf litter decomposition of deciduous understory shrubs and lianas mediated by mesofauna. Plant Ecol. 2020, 221, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.S.A.; Santos, G.C.; Albuquerque, U.P. Mimosa tenuiflora (Willd.) Poir. In Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of South America. Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of the World; Albuquerque, U., Patil, U., Máthé, Á., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netharlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS WORKING GROUP WRB. World Reference Base for Soil. World Soil Resources Reports. n. 103; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.J.; Asakawa, N.M. Decomposition of leaf litter from tropical forage grasses and legumes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1993, 25, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döbert, T.F.; Webber, B.L.; Sugau, J.B.; Dickinson, J.M.; Didham, R.K. Logging, exotic plant invasions, and native plant reassembly in a lowland tropical rain forest. Biotropica 2018, 50, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, P.C.; Donagemma, G.K.; Fontana, A.; Teixeira, W.G. Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solo; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Black, C.A. Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. In Agronomy Monograph No. 9; Black, C.A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 771–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.; Yin, R.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; et al. Temperature and Moisture Modulate the Contribution of Soil Fauna to Litter Decomposition via Different Pathways. Ecosystems 2021, 24, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Anning, A.K.; Gyamfi, B.; Effah, A.T. Broussonetia papyrifera controls nutrient return to soil to facilitate its invasion in a tropical forest of Ghana. J. Plant Ecol. 2018, 11, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhaure, S.E.; McCarthy, H.C.; O’del, J.N.; Giguere, H.; Symonds, C.J.; Lee, T.D. Effects of turf, leaf litter, and soil compaction on emergence and establishment of invasive glossy buckthorn (Frangula alnus). For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 484, e118933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyawasam, C.S.; Kumar, L.; Ratnayake, S.S. Potential risks of invasive alien plant species on agriculture under climate change scenarios in Sri Lanka. Curr. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 3, e100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Khuroo, A.A.; Hamid, M.; Rashid, I.; Rather, Z.A. Disentangling the determinants of litter decomposition among invaded and uninvaded habitats: A field experiment from the Kashmir Himalaya. Acta Oecol. 2021, 110, e103708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.S.; Monteiro, F.K.S.; Ramos, M.B.; Araújo, R.C.C.; Lopes, S.F. Invasive plants in the Brazilian Caatinga: A scientometric analysis with prospects for conservation. Neotrop. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 15, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Colff, D.; Dreyer, L.L.; Valentine, A.; Roets, F. Comparison of nutrient cycling abilities between the invasive Acacia mearnsii and the native Virgilia divaricata trees growing sympatrically in forest margins in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 11, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Railoun, M.Z.; Simaika, J.P.; Jacobs, S.M. Leaf litter production and litter nutrient dynamics of invasive Acacia mearnsii and native tree species in riparian forests of the Fynbos biome, South Africa. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 498, 119515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E.A.; Galvão, F.C.A.; Barros, A.L. Influence of water limitation on the competitive interaction between two Cerrado species and the invasive grass Brachiaria brizantha cv. Piatã. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiferaw, W.; Demissew, S.; Bekele, T.; Aynekulu, E.; Pitroff, W. Invasion of Prosopis juliflora and its effects on soil physico-chemical properties in Afar region, Northeast Ethiopia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weand, M.P. Chinese privet (Ligustrum sinense Lour.) alters the timing of litterfall and nutrient quality of leaf litter inputs in invaded riparian forests. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 3561–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallerman, J.; Itria, R.; Alarcón-Gutiérrez, E.; Hernández, C.; Levin, L.; Saparrat, M. Exotic litter of the invasive plant Ligustrum lucidum alters enzymatic production and lignin degradation by selected saprotrophic fungi. Can. J. For. Res. 2018, 48, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa, A.; Foxcroft, L.C.; Keet, J.H.; Pyšek, P.; Le Roux, J.J. The invasive cactus Opuntia stricta creates fertility islands in African savannas and benefits from those created by native trees. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, e20748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, T.A.F.; Santos, D.; Andrade, L.A.; Freitas, H. Plant-soil feedback of two legume species in semi-arid Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2019, 50, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, M.L.; Bullington, L.; Cleveland, C.C.; Rousk, J.; Lekberg, Y. Invasive plant-derived dissolved organic matter alters microbial communities and carbon cycling in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, e108191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, H.M.; Jenerette, G.D. Exotic grass litter modulates seasonal pulse dynamics of CO2 and N2O, but not NO, in Medi-terranean-type coastal sage scrub at the wildland-urban interface. Plant Soil 2020, 456, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Tsang, Y.F.; Qian, L.; Fu, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, P. Conversion of organic carbon from decayed native and invasive plant litter in Jiuduansha wetland and its implications for SOC formation and sequestration. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qu, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, D.; Morrissey, E.; Miao, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Fang, Y.; Bai, E. Large-scale importance of microbial carbon use efficiency and necromass to soil organic carbon. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Suseela, V. Nitrogen availability modulates the impacts of plant invasion on the chemical composition of soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, e108195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Cheema, N.K.; Kaur, R.; Bhatti, R.; Singh, N.A. Comparative litter decomposability traits of selected native and exotic woody species from an urban environment of north-western Siwalik region, India. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, e7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanek, M.; Piechnik, L.; Stefanowicz, A.M. Invasive red oak (Quercus rubra L.) modifies soil physicochemical properties and forest understory vegetation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 472, e118253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Rai, A.; Banyal, R.; Chauhan, P.S.; Singh, N. Plant community regulates soil multifunctionality in a tropical dry forest. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupers, S.J.; Wirth, C.; Engelberecht, B.M.J.; Hernández, A.; Condit, R.; Wright, S.J.; Rüger, N. Performance of tropical forest seedlings under shade and drought: An interspecific trade-off in demographic responses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, e18784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Nunes, A.; Rodrigues, R.G.; Branquinho, C. The response of plant functional traits to aridity in a tropical dry forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, e141177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeraragavan, S.; Duraisamy, R.; Mani, S. Seasonal variation of soil enzyme activities in relation to nutrient and carbon cycling in Senna alata (L.) Roxb invaded sites of Puducherry region, India. Geol. Ecol. Lands 2018, 2, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Jian, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, D. Litter decomposition and the degradation of recalcitrant components in Pinus massoniana plantations with various canopy densities. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 139–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.A.F.; Freitas, H. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community assembly in the Brazilian tropical seasonal dry forest. Ecol. Proc. 2017, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jina, Y.; Xua, J.; He, H.; Tao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Bai, Y. Effects of exogenous N and endogenous nutrients on alpine tundra litter decomposition in an area of high nitrogen deposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, e150388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Gao, P.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; Niu, X. Decomposition dynamics and ecological stoichiometry of Quercus acutissima and Pinus densiflora litter in the Grain to Green Program Area of northern China. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Ferreira, V. Invasion of Native Riparian Forests by Acacia Species Affects In-Stream Litter Decomposition and Associated Microbial Decomposers. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 81, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Costa, W.A.J.M.; Atapattu, A.M.L.K. Decomposition and nutrient loss from prunings of different contour hedgerow species in tea plantations in the sloping highlands of Sri Lanka. Agrofor. Syst. 2001, 51, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer, D.A.; Kurokawa, H.; Wardle, D.A. Soil fertility and disturbance interact to drive contrasting responses of co-occurring native and non-native species. Ecology 2016, 97, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardans, J.; Bartrons, M.; Margalef, O.; Gargallo-Garriga, A.; Janssens, I.A.; Ciais, P.; Obersteiner, M.; Sigurdsson, B.D.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Peñuelas, J. Plant invasion is associated with higher plant-soil nutrient concentrations in nutrient-poor environments. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 23, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanowicz, A.M.; Stanek, M.; Majewska, M.L.; Nobis, M.; Zubek, S. Invasive plant species identity affects soil microbial communities in a mesocosm experiment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 136, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, A.; Tennakoon, K.U.; Jaafar, S.M.; Zaman, N.A.N.P.; Sukri, R.S. Effects of Acacia invasion on leaf litter nutrient and soil properties of coastal Kerangas forests in Brunei Darussalam. Sci. Bruneiana 2019, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.L.; Barreto, R.W.; Pereira, O.L. Pseudocercospora cryptostegiae-madagascariensis sp. nov. on Cryptostegia madagascariensis, an exotic vine involved in major biological invasions in Northeast Brazil. Mycopathologia 2008, 166, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elgawad, M.; El-Mougy, N.S.; El-Gamal, N.G.; Abdel-Kader, M.M.; Mohamed, M. Protective treatments against soilborne pathogens in citrus orchards. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2010, 50, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montasser, S.A.; Abd El-Wahab, A.E.; Abd-Elgawad, M.M.M.; Abd-El-Khair, H.; Koura Faika, F.H.; Hammam, M.M.A. Effects of some fungi and bacteria as bio-control agents against citrus nematode Tylenchulus semipenetrans Cobb. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 8, 5436–5444. [Google Scholar]

| Studied Environments | Species Richness (S) | Shannon’s Diversity Index | Clay Content (g kg−1) | Soil pH (1:2.5 Soil:Water, v:v) | Total Nitrogen (g kg−1) | Available P (mg kg−1) | K+ (mg kg−1) | Ca2+ (cmolc kg−1) | Mg2+ (cmolc kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invaded environment | 5 (1) | 1.17 (0.23) | 634.0 (23.0) | 5.85 (1.18) | 0.60 (0.04) | 246.16 (1.06) | 132.28 (0.75) | 7.04 (0.13) | 6.50 (0.67) |
| Non-invaded environment | 20 (3) | 2.72 (0.45) | 631.0 (36.0) | 6.00 (0.57) | 0.10 (0.05) | 200.16 (1.04) | 125.18 (3.16) | 5.85 (0.15) | 6.05 (0.29) |
| Lignin (%) | TOC (%) | N (%) | P (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 47.9 ± 0.8 | 24.7 ± 2.5 | 2.11 ± 0.11 | 63.8 ± 6.8 |
| Traits | Invaded | Non-Invaded | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainy | Dry | Rainy | Dry | |
| Litter N content (g kg−1) | 20.05 (0.47) Aa | 20.25 (0.11) Aa | 19.75 (0.63) Ab | 19.65 (0.21) Ab |
| Litter P content (g kg−1) | 3.01 (0.03) Aa | 2.9 (0.02) Aa | 2.27 (0.04) Ab | 2.30 (0.05) Ab |
| Litter K content (g kg−1) | 7.60 (0.04) Aa | 7.64 (0.14) Aa | 6.26 (0.26) Ab | 6.34 (0.10) Ab |
| Soil temperature (°C) | 26.2 (0.85) Ab | 26.5 (0.42) Ab | 31.8 (0.42) Aa | 32.7 (0.91) Aa |
| Soil water content (g g−1) | 12.44 (3.44) Ab | 5.51 (1.73) Ba | 17.66 (4.70) Aa | 5.56 (4.70) Ba |
| Soil organic matter (g kg−1) | 8.45 (1.73) Ba | 9.83 (1.74) Aa | 4.91 (1.74) Ab | 4.78 (1.41) Ab |
| Studied Environments | k (Years−1) | hd (Days) | td (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invaded environment | 1.10 (0.48) a | 0.75 (0.39) b | 3.45 (2.00) b |
| Non-invaded environment | 0.94 (0.71) b | 1.00 (0.64) a | 4.37 (2.78) a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souza, T.; Lucena, E.O.d.; de Andrade, L.A.; da Silva, L.J.R.; Nascimento, G.d.S.; Freitas, H. Litter Deposition and Nutrient Cycling of Invaded Environments by Cryptostegia madagascariensis at Tropical Cambisols from Northeastern Brazil. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2023, 14, 254-265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14010021
Souza T, Lucena EOd, de Andrade LA, da Silva LJR, Nascimento GdS, Freitas H. Litter Deposition and Nutrient Cycling of Invaded Environments by Cryptostegia madagascariensis at Tropical Cambisols from Northeastern Brazil. International Journal of Plant Biology. 2023; 14(1):254-265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouza, Tancredo, Edjane Oliveira de Lucena, Leonaldo Alves de Andrade, Lucas Jónatan Rodrigues da Silva, Gislaine dos Santos Nascimento, and Helena Freitas. 2023. "Litter Deposition and Nutrient Cycling of Invaded Environments by Cryptostegia madagascariensis at Tropical Cambisols from Northeastern Brazil" International Journal of Plant Biology 14, no. 1: 254-265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14010021
APA StyleSouza, T., Lucena, E. O. d., de Andrade, L. A., da Silva, L. J. R., Nascimento, G. d. S., & Freitas, H. (2023). Litter Deposition and Nutrient Cycling of Invaded Environments by Cryptostegia madagascariensis at Tropical Cambisols from Northeastern Brazil. International Journal of Plant Biology, 14(1), 254-265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14010021








