Assessment of Genetic Stability on In Vitro Propagation of Ardisia crenata var. bicolor Using ISSR Markers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Establishment of Culture Conditions
2.2. PGR Treatments for Shoot Establishment and Proliferation and Root Induction
2.3. Plantlet Acclimatization
2.4. DNA Extraction and Genetic Homogeneity Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
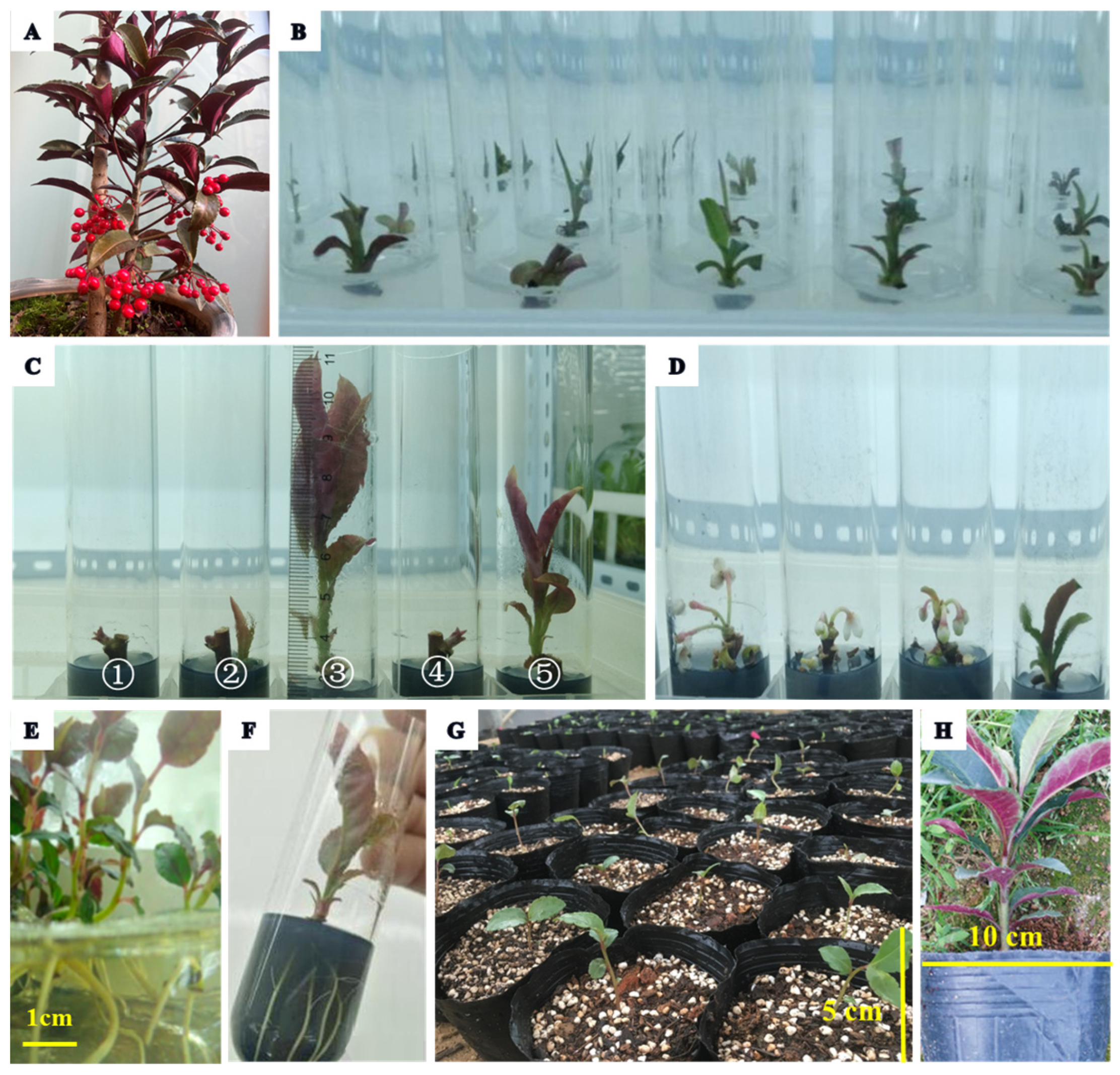
3.1. Shoot Establishment and Proliferation
3.2. Root Induction
3.3. Acclimatization
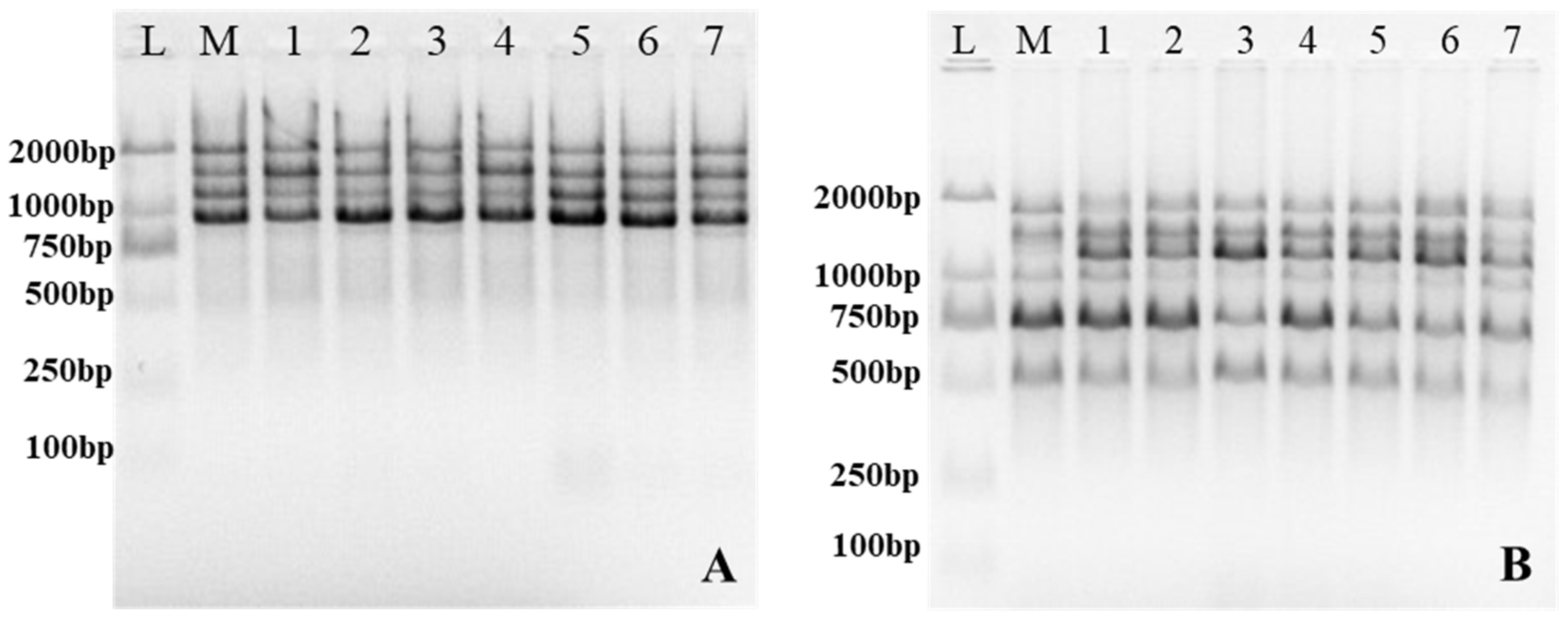
3.4. Assessment of Genetic Stability by ISSR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Pipoly, J. Flora of China (Myrsinaceae through Loganiaceae); Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1996; Volume 15, pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Podolak, I.; Mynarski, A.; Wróbel, D.; Grabowska, K.; Galanty, A. Bioactive benzoquinones content variability in red-berry and white-berry varieties of Ardisia crenata Sims. and assessment of cytotoxic activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 35, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hideka, K.; Elvira, D.M. The genus Ardisia: A novel source of health-promoting compounds and phytopharmaceuticals. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Kuang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P.; Koike, K. A simple and rapid method to identify and quantitatively analyze triterpenoid saponins in Ardisia crenata using ultrafast liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2015, 102, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, N.; Yao, X. Three new triterpenoid saponins from the roots of Ardisia crenata and their cytotoxic activities. Nat. Pro. Res. 2016, 30, 2694–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, H.; Soni, G.; Jauhari, N.; Sharma, N.; Bharadvaja, N. Phytochemical importance of medicinal plants as potential sources of anticancer agents. Turk. J. Bot. 2014, 38, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, M.S.; Lee, A.K.; Suh, J.K. Production of high quality Ardisia plants by stem tip cuttings. Sci. Hortic. 2005, 104, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.H.; Ye, W.H.; Wang, Z.M.; Yin, X.J. Seed germination physiology of Ardisia crenata var. bicolor. Seed Sci. Technol. 2009, 37, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.K.; Slovin, J.P.; Suh, J.K. Dehydration intolerant seeds of Ardisia species accumulate storage and stress proteins during development. Hortic. Environ. Biote. 2012, 53, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, T.; Yokoyama, H.; Tanaka, H.; Shiozaki, S.; Oda, M. Seed and Embryo Germination in Ardisia crenata. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 679765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohela, G.K.; Jogam, P.; Shabnam, A.A.; Shukla, P.; Abbagani, S.; Ghosh, M.K. In Vitro regeneration and assessment of genetic fidelity of acclimated plantlets by using ISSR markers in PPR-1 (Morus sp.): An economically important plant. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 241, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zou, J.; Zhang, B.; Que, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. An efficient in vitro propagation protocol for direct or ganogenesis from root explants of a multi-purpose plant, Broussonetia papyrifera (L.) L’Hér. ex Vent. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 170, 113686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, K.; Hu, X.; Zhu, M.; Deng, X.; Xi, R. An efficient micropropagation protocol for an endangered ornamental tree species (Magnolia sirindhorniae Noot. & Chalermglin) and assessment of genetic uniformity through DNA markers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demétrio, C.A.; Jacob, J.F.d.O.; Ambrosano, G.B.; Oliveira, Ê.T.D.; Rodrigues, P.H.V. In Vitro propagation of Cambuci (Campomanesia phaea): An endangered exotic fruit and ornamental plant from Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 2021, 145, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Sharma, V.; Luharch, R. Propagation of plum (Prunus salicina L.) cultivar Frontier in vitro through control of shoot tip necrosis (STN) and validation of genetic integrity using ISSR markers. Plant Physiol. Rep. 2021, 26, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathish, D.; Vasudevan, V.; Theboral, J.; Elayaraja, D.; Appunu, C.; Siva, R.; Manickavasagam, M. Efficient direct plant regeneration from immature leaf roll explants of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) using polyamines and assessment of genetic fidelity by SCoT markers. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol.-Plant 2018, 54, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, P.T.; Orłowska, R. Plant tissue culture environment as a switch-key of (epi) genetic changes. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 2020, 140, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, D.; Rai, M.K.; Shekhawat, N.S.; Kataria, V. In vitro propagation of Farsetia macrantha Blatt. & Hallb.: An endemic and threatened plant of Indian Thar Desert. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 2020, 142, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, R.; Singh, K.P.; Sharma, T.R.; Jhang, T. Evaluation of the genetic fidelity of in vitro-propagated gerbera (Gerbera jamesonii Bolus) using DNA-based markers. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 2011, 104, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Reza, M. Establishment of an efficient in vitro propagation protocol for Sumac (Rhus coriaria L.) and confirmation of the genetic homogeneity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, M.; Alatar, A.A.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Abdel-Salam, E.M.; Qahtan, A.A. Thidiazuron induced in vitro morphogenesis for sustainable supply of genetically true quality plantlets of Brahmi. Ind. Crop. Prod 2018, 118, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogam, P.; Sandhya, D.; Shekhawat, M.S.; Alok, A.; Abbagani, S.; Allini, V.R. Genetic stability analysis using DNA barcoding and molecular markers and foliar micro-morphological analysis of in vitro regenerated and in vivo grown plants of Artemisia vulgaris L. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 151, 112476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Sharma, V.; Chauhan, A. Genetic fidelity assessment of long term in vitro shoot cultures and regenerated plants in Japanese plum cvs Santa Rosa and Frontier through RAPD, ISSR and SCoT markers. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 140, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendra, P.A.; Bee, L.C.; Sreeramanan, S. Assessment of genetic stability on in vitro and ex vitro plants of Ficus carica var. black jack using ISSR and DAMD markers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 7223–7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostas, S.; Hatzilazarou, S.; Pipinis, E.; Vasileiadis, A.; Magklaras, P.; Smyrnioudis, I.; Vasilakis, T.; Chazakis, M.; Anastasiadi, V.; Ziogou, F.; et al. Propagation of Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia genotypes and determination of their ornamental traits combined with a genetic analysis using ISSR Markers. Agronomy 2021, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A Revised Medium for Rapid Growth and Bio Assays with Tobacco Tissue Cultures. Physiol. Plantarum 1962, 15, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Aremu, A.O.; Bairu, M.W.; Dolezal, K.; Finnie, J.F.; Staden, J.V. Topolins: A panacea to plant tissue culture challenges? Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 2012, 108, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, T.J.; Esmeralda, R.; GómezAldapa, C.A.; VillagómezIbarra, J.R.; FalfánCortes, R.N.; AcevedoSandoval, O.A.; CastroRosas, J. Isolation and molecular identification of Serratia strains producing Chitinases, Glucanases, Cellulases, and Prodigiosin and determination of their antifungal effect against Colletotrichum Siamense and Alternaria Alternata in vitro and on Mango fruit. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2022, 13, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakriti, B.; Harminder, S.; Amber, S.; Puneet, K. In vitro propagation and cytological analysis of Sophora mollis Royle: An endangered medicinal shrub. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechn. 2021, 19, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, T.; Gupta, A.K.; Patel, A.K.; Shekhawat, N.S. Micropropagation and validation of genetic homogeneity of Alhagi maurorum using SCoT, ISSR and RAPD markers. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 2015, 120, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesca, G.; Loreto, B.; Ricardo, C.; Mónica, C. Micropropagation of Citronella mucronata D. Don, a Vulnerable Chilean Endemic Tree Species. Plants 2022, 11, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, I.; Qadri, Z.A.; Rather, Z.A.; Nazki, I.T.; Banday, N.; Rafiq, S.; Masoodi, K.Z.; Noureldeen, A.; Mansoor, S. Optimization of an improved, efficient and rapid in vitro micropropagation protocol for Petunia hybrida Vilm. Cv. “Bravo”. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3701–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, F.; Hoque, M.E.; Huq, H.; Adil, M.; Ashraf-Uz-Zaman, K.; Rabin, M.H. Effect of BAP and IBA on in vitro regeneration of local banana Variety of Sabri. Biotechnol. J. Inter. 2017, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, A.M.; Yordanova, P.Z.; Kapchina-Toteva, M.V. Influence of 6-benzylaminopurine and indole-3-butyric acid on in vitro propagation and secondary metabolites accumulation in Lamium album from lozen mountain. Acta Hortic. 2012, 955, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajuria, A.K.; Bisht, N.; Bhagat, N. In vitro organogenesis and plant regeneration of Thymus serpyllum L.: An important aromatic medicinal plant. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. -Plant 2020, 56, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chao, L.; Su, X.; Wang, C.; Dong, C.; Chen, S. High-frequency in vitro plantlet regeneration in Lilium davidii var. unicolour Salisb, an important edible and medicinal plant, and confirmation of genetic fidelity of regeneration plantlets using ISSR markers. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 15, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongdam, P.; Tikendra, L. Establishment of an efficient in vitro regeneration protocol for rapid and mass propagation of Dendrobium chrysotoxum lindl. Using seed culture. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 740150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.; IllMin, C.; SeungHyun, K.; HeeYeon, C.; Yeon, Y.C.; Kumar, G.B. Direct Shoot Organogenesis from Lycium chinense Miller Leaf Explants and Assessment of Genetic Stability Using ISSR Markers. Agronomy 2021, 11, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, S.; Robinson, J.; KarthickBalan, S.; Anandhaprabhakaran, M.; Balakrishnan, V. In vitro regeneration and induction of multiple shooting in Cicer arietinum L. using cotyledonary nodal explants. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbah, E.I.; Wakil, S.M. Elimination of bacteria from in vitro yam tissue cultures using antibiotics. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 94, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Hatzilazarou, S.; Kostas, S.; Joachim, M.; Economou, A. Regeneration of Viburnum dentatum L. from alginate-encapsulated shoot explants after short-term cold storage and assessment of genetic stability using ISSR analysis. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarina, L.; Gvasaliya, M.; Koninskaya, N.; Rakhmangulov, R.; Efremov, A.; Kiselyova, N.; Ryndin, A.; Hanke, M.-V. A comparison of genetic stability in tea [Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze] plantlets derived from callus with plantlets from long-term in vitro propagation. Plant Cell. Tiss. Org. 2019, 138, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, D.M.M.; Sattler, M.C.; Ferreira, M.F.D.S.; Praça-Fontes, M.M. Assessment of genetic stability in three generations of in vitro propagated Jatropha Curcas, L. plantlets using ISSR markers. Trop. Plant Biol. 2016, 9, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, A.; Soundararajan, P.; Park, Y.G.; Wei, H.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, B.R. Blue and red light-emitting diodes improve the growth and physiology of in vitro-grown carnations ‘Green Beauty’ and ‘Purple Beauty’. Hortic. Environ. Biote. 2017, 58, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, G.J.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, M.M. Growth and acclimation of in vitro-propagated ‘M9’ apple rootstock plantlets according to light intensity. Hortic. Environ. Biote. 2020, 61, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NO. | Primer Code | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Total Bands | Polymorphic Bands | Percentage of Polymorphic Bands (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ISSR-1 | (AG)8T | 50 | 4 | 0 | 00.00 |
| 2 | ISSR-2 | (AG)8C | 51 | 7 | 0 | 00.00 |
| 3 | ISSR-3 | (GA)8C | 52 | 8 | 1 | 12.50 |
| 4 | ISSR-4 | (GA)8A | 49.5 | 8 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 5 | ISSR-5 | (CA)8G | 49 | 7 | 1 | 14.28 |
| 6 | ISSR-6 | (AC)8G | 51.5 | 9 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 7 | ISSR-7 | (TG)8C | 49.5 | 7 | 2 | 28.57 |
| 8 | ISSR-8 | (AG)8YT | 50 | 12 | 2 | 16.67 |
| 9 | ISSR-9 | (GA)8YC | 52 | 7 | 0 | 0.00 |
| 10 | ISSR-10 | (AC)8YG | 50 | 7 | 1 | 14.28 |
| 11 | ISSR-11 | BDB(CA)7 | 53 | 7 | 1 | 14.28 |
| PGRs (mg·L−1) | Nodal Segment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAP | IBA | Establishment Rates (%) Mean ± SE | No. of Shoots/Explant Mean ± SE | Shoot Length (cm) Mean ± SE |
| 0.0 | 0.00 | 11.67 ± 0.01 d | 1.0 ± 0.58 e | 1.4 ± 0.10 h |
| 0.25 | 13.33 ± 0.03 d | 1.1 ± 0.00 e | 2.0 ± 0.13 g | |
| 0.50 | 13.33 ± 0.05 d | 1.3 ± 1.53 e | 2.1 ± 0.13 g | |
| 1.00 | 15.00 ± 0.08 d | 1.4 ± 1.53 e | 2.2 ± 0.25 g | |
| 0.5 | 0.00 | 18.33 ± 0.08 d | 1.5 ± 2.08 e | 2.3 ± 0.09 g |
| 0.25 | 30.00 ± 0.06 cd | 1.6 ± 2.08 e | 2.5 ± 0.05 g | |
| 0.50 | 41.67 ± 0.08 bc | 2.2 ± 6.11 d | 3.0 ± 0.23 f | |
| 1.00 | 48.33 ± 0.06 b | 2.7 ± 1.53 bc | 3.4 ± 0.21 ef | |
| 1.0 | 0.00 | 26.67 ± 0.03 cd | 1.6 ± 2.52 e | 2.1 ± 0.16 g |
| 0.25 | 60.00 ± 0.03 a | 4.5 ± 1.53 a | 4.4 ± 0.24 cd | |
| 0.50 | 76.67 ± 0.02 a | 2.9 ± 2.52 b | 6.6 ± 0.20 a | |
| 1.00 | 53.33 ± 0.04 ab | 2.8 ± 2.00 bc | 5.8 ± 0.09 b | |
| 1.5 | 0.00 | 35.00 ± 0.05 c | 1.3 ± 0.58 e | 2.5 ± 0.13 g |
| 0.25 | 56.67 ± 0.06 ab | 2.5 ± 1.53 c | 3.7 ± 0.15 de | |
| 0.50 | 65.00 ± 0.03 a | 3.0 ± 3.51 b | 4.8 ± 0.13 c | |
| 1.00 | 53.33 ± 0.02 ab | 2.2 ± 1.53 d | 4.0 ± 0.16 d | |
| PGRs (mg·L−1) | Full-Strength MS | Half-Strength MS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBA | NAA | Percentage of Rooting (%) Mean ± SE | Root Number Mean ± SE | Percentage of Rooting (%) Mean ± SE | Root Number Mean ± SE |
| 0 | 0.00 | 8.33 ± 0.03 e | 1.0 ± 0.00 c | 11.67 ± 0.08 d | 1.3 ± 0.58 d |
| 0.25 | 18.33 ± 0.18 d | 1.3 ± 0.16 c | 30.00 ± 0.30 c | 1.4 ± 0.22 d | |
| 0.50 | 20.00 ± 0.20 d | 1.5 ± 0.41 c | 33.33 ± 0.33 c | 2.0 ± 0.42 cd | |
| 0.25 | 0.00 | 21.67 ± 0.22 d | 1.1 ± 0.27 c | 30.00 ± 0.30 c | 1.3 ± 0.39 d |
| 0.25 | 43.33 ± 0.43 b | 1.7 ± 0.44 c | 55.00 ± 0.55 c | 2.0 ± 0.05 cd | |
| 0.50 | 55.00 ± 0.55 ab | 2.2 ± 0.47 b | 65.00 ± 0.65 b | 2.0 ± 0.04 cd | |
| 0.5 | 0.00 | 26.67 ± 0.27 cd | 1.2 ± 0.05 c | 31.67 ± 0.32 c | 1.5 ± 0.42 d |
| 0.25 | 56.67 ± 0.57 ab | 3.7 ± 0.58 a | 63.33 ± 0.63 b | 4.0 ± 0.27 ab | |
| 0.50 | 63.33 ± 0.63 ab | 3.3 ± 0.43 ab | 65.00 ± 0.65 b | 3.1 ± 0.68 bc | |
| 1.0 | 0.00 | 33.33 ± 0.33 c | 1.3 ± 0.30 c | 36.67 ± 0.37 c | 1.6 ± 0.19 d |
| 0.25 | 71.67 ± 0.72 a | 4.2 ± 0.55 a | 83.33 ± 0.83 a | 4.5 ± 0.50 a | |
| 0.50 | 68.33 ± 0.68 ab | 3.4 ± 0.64 ab | 70.00 ± 0.70 b | 3.2 ± 0.88 b | |
| Treatment | Substrate Mixture Peat:Vermiculite:Perlite | Shading | Survival Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 2:1:1 | 75% | 84.4 ± 0.13 a |
| Ⅱ | 2:1:1 | 50% | 63.3 ± 0.15 b |
| Ⅲ | 2:1:1 | 0% | 20.0 ± 0.03 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ai, X.; Wen, Y.; Wang, B. Assessment of Genetic Stability on In Vitro Propagation of Ardisia crenata var. bicolor Using ISSR Markers. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2023, 14, 218-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14010018
Ai X, Wen Y, Wang B. Assessment of Genetic Stability on In Vitro Propagation of Ardisia crenata var. bicolor Using ISSR Markers. International Journal of Plant Biology. 2023; 14(1):218-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleAi, Xingmei, Yonghui Wen, and Bin Wang. 2023. "Assessment of Genetic Stability on In Vitro Propagation of Ardisia crenata var. bicolor Using ISSR Markers" International Journal of Plant Biology 14, no. 1: 218-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14010018
APA StyleAi, X., Wen, Y., & Wang, B. (2023). Assessment of Genetic Stability on In Vitro Propagation of Ardisia crenata var. bicolor Using ISSR Markers. International Journal of Plant Biology, 14(1), 218-227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb14010018





