Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Sesame Seedlings with Gibberellin-Producing Rhodobacter sphaeroides SIR03 and Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Isolation of Photosynthetic Bacteria from Soil
2.2. Screening Bioassay for Growth Promotion in Sesame Seeds
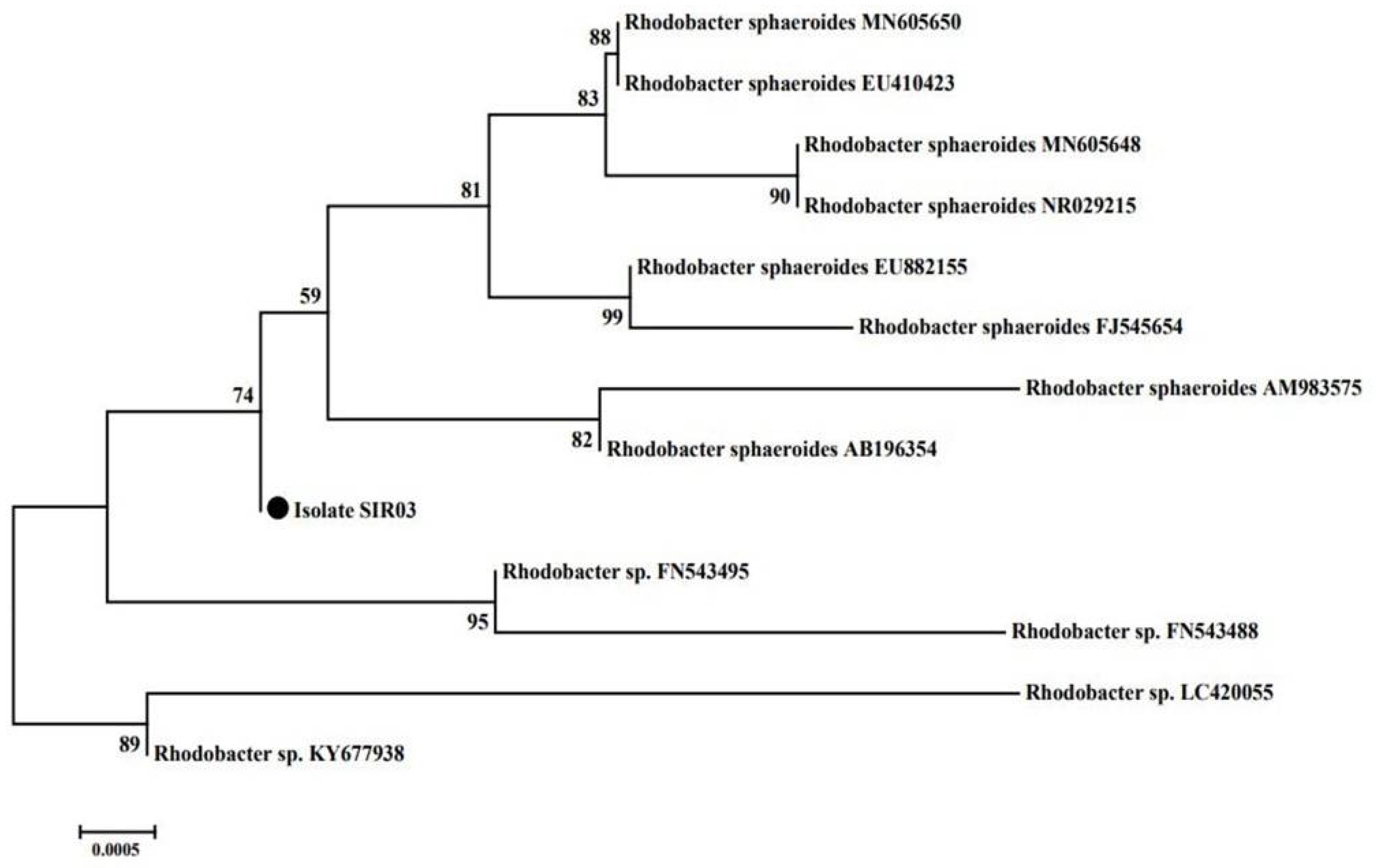
2.3. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Isolated Endophytic Bacteria
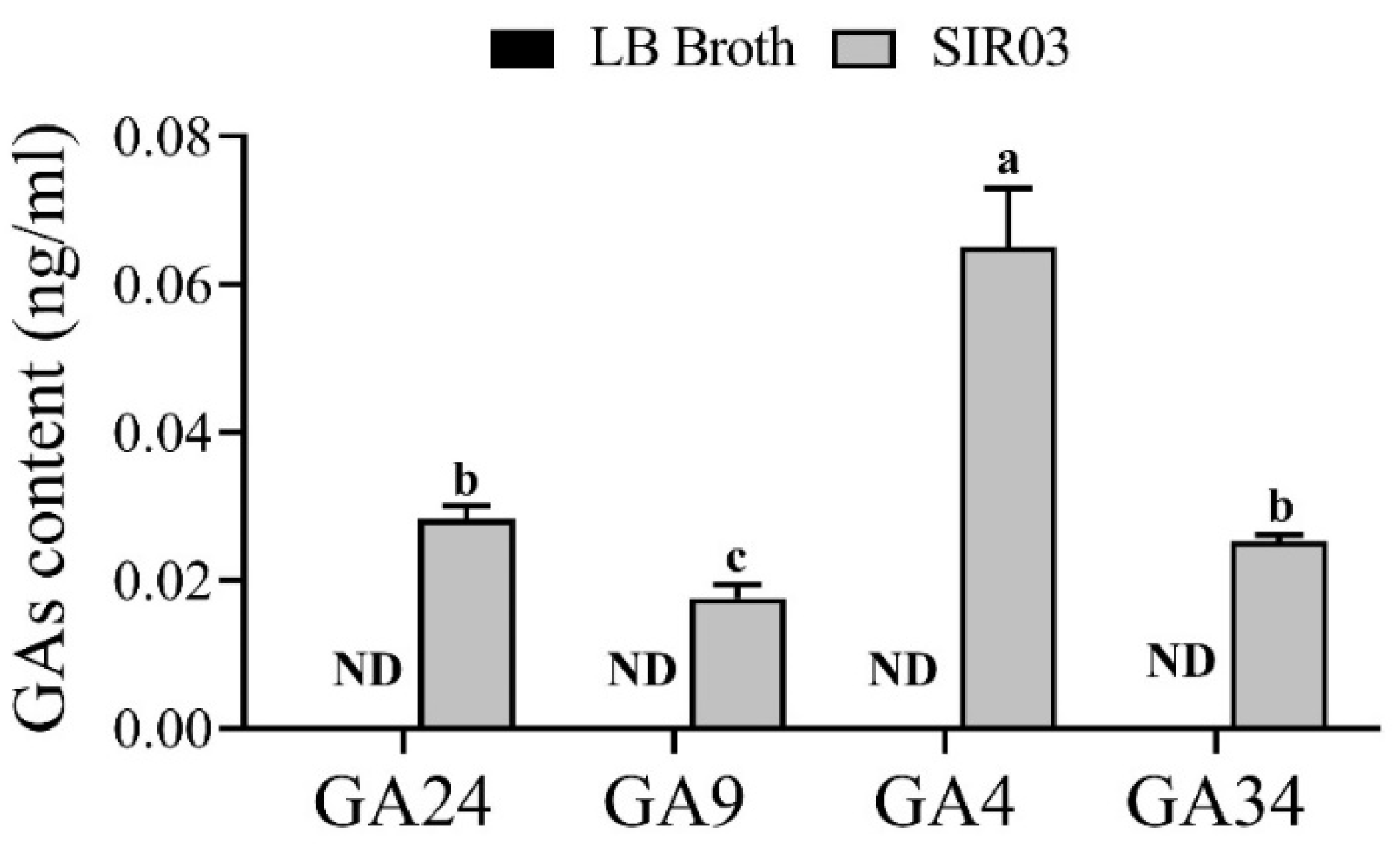
2.4. Quantification of Gibberellins in the Culture Broth
2.5. Screening Bioassay for Plant Growth Promotion in Waito-C Rice
2.6. Experiment Location, Method, and Design
2.7. Measurement of Photosynthetic Attributes
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria
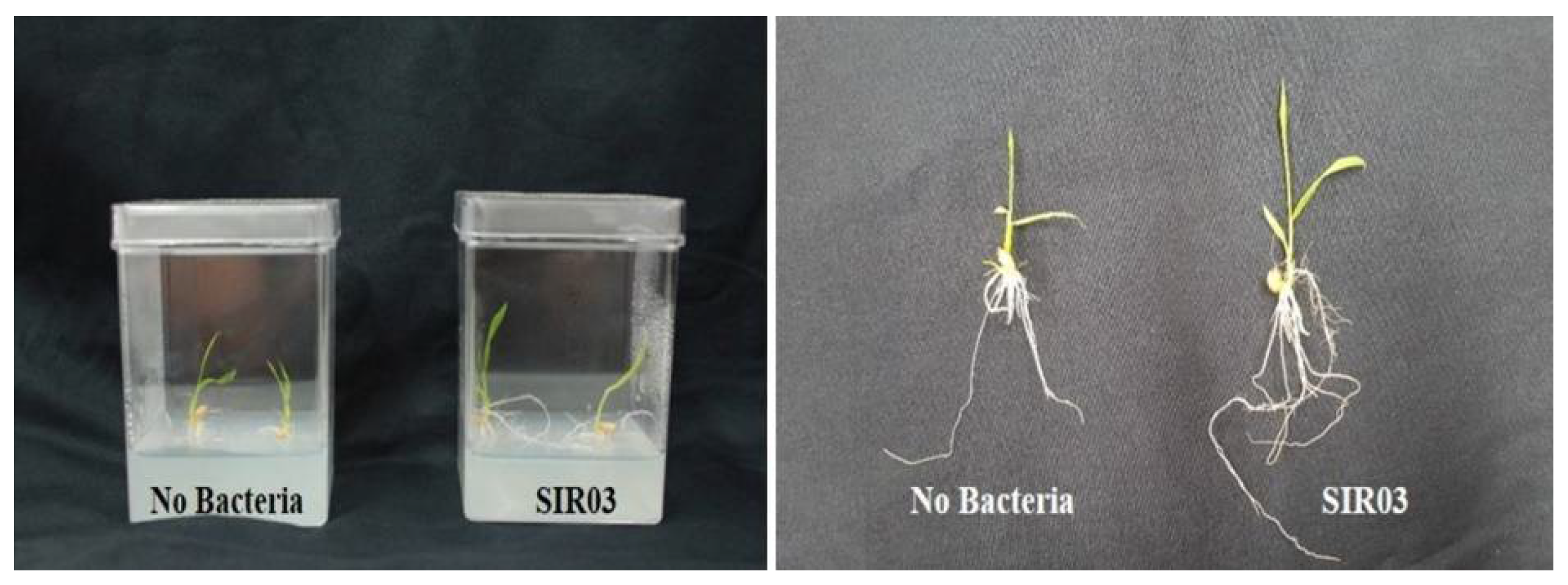
3.2. Bacterial Isolation and Initial Screening for Waito-C Rice
3.3. Identification of SIR03 Strain
3.4. Isolate SIR03 and Biochar Promote Sesame Growth
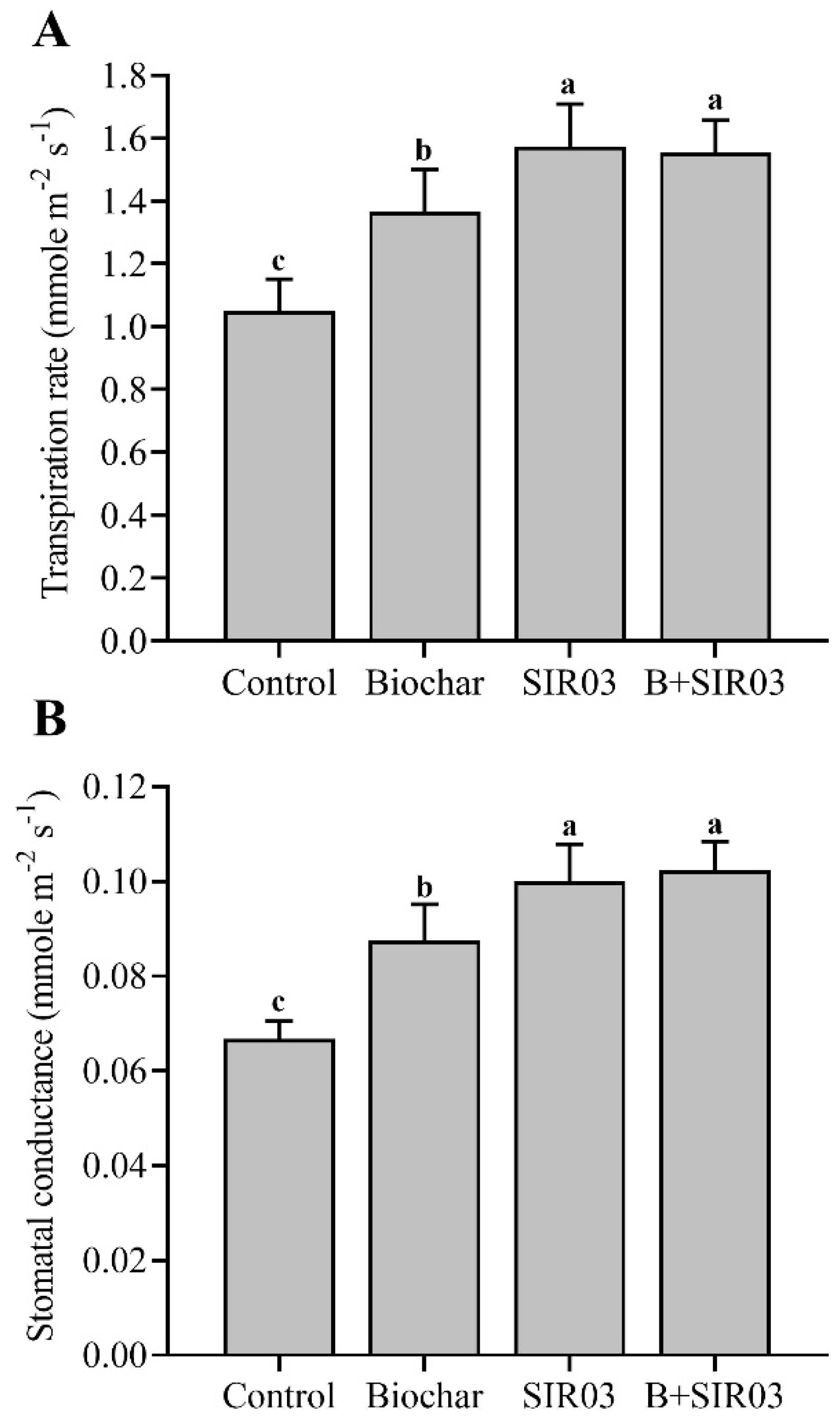
3.5. Isolate SIR03 and Biochar Improved Transpiration Rate and Stomatal Conductance of Sesame Seedlings
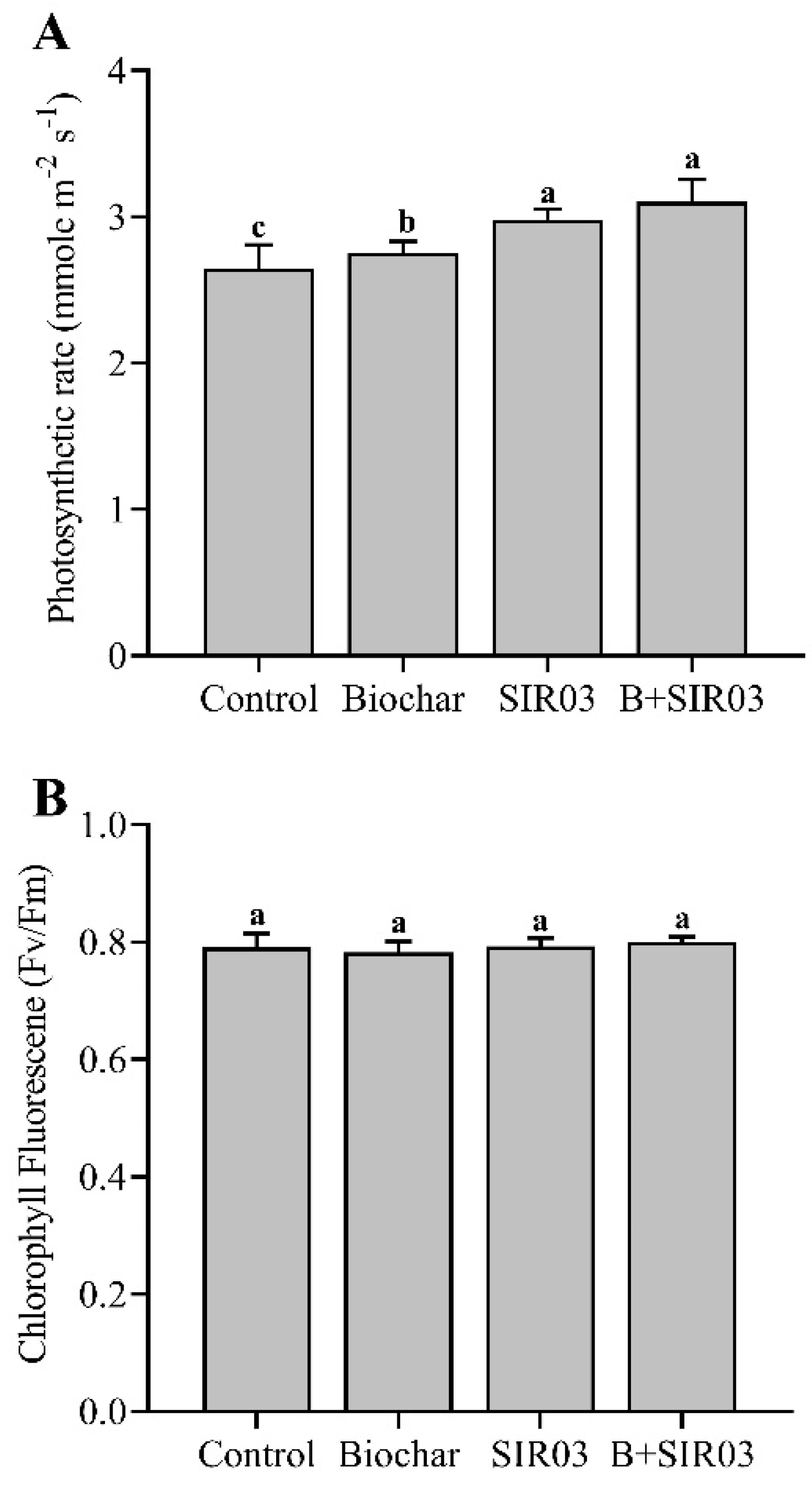
3.6. Isolate SIR03 and Biochar Improved Photosynthetic Rate and Chlorophyll Fluorescence of Sesame Seedlings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meena, K.K.; Sorty, A.M.; Bitla, U.M.; Choudhary, K.; Gupta, P.; Pareek, A.; Singh, D.P.; Prabha, R.; Sahu, P.K.; Gupta, V.K. Abiotic stress responses and microbe-mediated mitigation in plants: The omics strategies. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Aaqil Khan, M.; Shahzad, R.; Bilal, S.; Khan, M.; Yun, B.-W.; Khan, A.L.; Lee, I.-J. Melatonin Ameliorates Thermotolerance in Soybean Seedling through Balancing Redox Homeostasis and Modulating Antioxidant Defense, Phytohormones and Polyamines Biosynthesis. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummukainen, M. Changes in climate and weather extremes in the 21st century. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2012, 3, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.A.; Porter, P. Ecology in sustainable agriculture practices and systems. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark Ibekwe, A.; Ors, S.; Ferreira, J.F.S.; Liu, X.; Suarez, D.L. Seasonal induced changes in spinach rhizosphere microbial community structure with varying salinity and drought. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Cui, L.; Lin, Q.; Li, G.; Zhao, X. Efficiency of sewage sludge biochar in improving urban soil properties and promoting grass growth. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, N.R.; Schmidt, H.P.; Mulder, J.; Hale, S.E.; Husson, O.; Cornelissen, G. Nutrient effect of various composting methods with and without biochar on soil fertility and maize growth. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 66, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H. Enhanced nitrogen removal of low C/N domestic wastewater using a biochar-amended aerated vertical flow constructed wetland. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintala, R.; Mollinedo, J.; Schumacher, T.E.; Malo, D.D.; Julson, J.L. Effect of biochar on chemical properties of acidic soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2014, 60, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolton, M.; Meller Harel, Y.; Pasternak, Z.; Graber, E.R.; Elad, Y.; Cytryn, E. Impact of biochar application to soil on the root-associated bacterial community structure of fully developed greenhouse pepper plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 4924–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Z.G.; Wang, X.K.; Miao, H. Effects of forest plantations on rainfall redistribution and erosion in the red soil region of southern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, N.J. Animal communication: When i’m calling you, will you answer too? Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R713–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, J.T.; Aanderud, Z.T.; Lehmkuhl, B.K.; Schoolmaster, D.R., Jr. Mapping the niche space of soil microorganisms using taxonomy and traits. Ecology 2012, 93, 1867–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, A.; Gomez, A.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Gasco, G. Effects of sewage sludge biochar on plant metal availability after application to a Mediterranean soil. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.D.; Xue, X.Y.; Chen, D.Z.; He, P.J.; Dai, X.H. Application of biochar from sewage sludge to plant cultivation: Influence of pyrolysis temperature and biochar-to-soil ratio on yield and heavy metal accumulation. Chemosphere 2014, 109, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Chao, C.; Waqas, M.; Arp, H.P.H.; Zhu, Y.-G. Sewage sludge biochar influence upon rice (Oryza sativa L) yield, metal bioaccumulation and greenhouse gas emissions from acidic paddy soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8624–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Lal, R.; Zimmerman, A.R. Effects of biochar and other amendments on the physical properties and greenhouse gas emissions of an artificially degraded soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Liang, G.; Song, D.; Zhang, X. Characteristics of maize biochar with different pyrolysis temperatures and its effects on organic carbon, nitrogen and enzymatic activities after addition to fluvo-aquic soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, J.E.; Rillig, M.C.; Graber, E.R. Biochar effects on the abundance, activity and diversity of the soil biota. Biochar Environ. Manag. Sci. Technol. Implement. 2015, 2, 327–389. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, C.; Das, K.C.; Melear, N.; Lakly, D. Reducing nitrogen loss during poultry litter composting using biochar. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Lan, Y.; Xu, E.G.; Meng, J.; Chen, W. Biochar as a novel niche for culturing microbial communities in composting. Waste Manag. 2016, 54, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.T.; Asghar, H.N.; Saleem, M.; Khan, M.Y.; Zahir, Z.A. Synergistic effect of rhizobia and biochar on growth and physiology of maize. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.S.; Andersen, M.N.; Liu, F. Biochar mitigates salinity stress in potato. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2015, 201, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idi, A.; Md Nor, M.H.; Abdul Wahab, M.F.; Ibrahim, Z. Photosynthetic bacteria: An eco-friendly and cheap tool for bioremediation. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2015, 14, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechter, K.B.; Gallagher, L.; Pyles, H.; Manoil, C.S.; Harwood, C.S. Essential genome of the metabolically versatile alphaproteobacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, M.; Falkow, S.; Rosenberg, E.; Schleifer, K.-H.; Stackebrandt, E. The Prokaryotes: Volume 5: Proteobacteria: Alpha and Beta Subclasses; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Crovadore, J.; Xu, S.; Chablais, R.; Cochard, B.; Lukito, D.; Calmin, G.; Lefort, F. Metagenome-assembled genome sequence of Rhodopseudomonas palustris strain eli 1980, commercialized as a biostimulant. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00221-00217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, Y.; Wanders, W.; Huisman, L.A.; Meijer, W.G.; Gottschal, J.C.; Forney, L.J. Genotypic and phenotypic diversity within species of purple nonsulfur bacteria isolated from aquatic sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3467–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baig, K.S.; Arshad, M.; Khalid, A.; Hussain, S.; Abbas, M.N.; Imran, M. Improving growth and yield of maize through bioinoculants carrying auxin production and phosphate solubilizing activity. Soil Environ. 2014, 33, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Fazal, A.; Bano, A. Role of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), biochar, and chemical fertilizer under salinity stress. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 1985–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubi, H.A.A.; Khan, M.A.; Adhikari, A.; Imran, M.; Kang, S.-M.; Hamayun, M.; Lee, I.-J. Silicon and plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria Pseudomonas psychrotolerans CS51 mitigates salt stress in Zea mays L. Agriculture 2021, 11, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazerooni, E.A.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Adhikari, A.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Kang, S.-M.; Kim, L.-R.; Lee, I.-J. Rhizospheric Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Protects Capsicum annuum cv. Geumsugangsan From Multiple Abiotic Stresses via Multifarious Plant Growth-Promoting Attributes. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 669693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danish, S.; Zafar-ul-Hye, M. Co-application of ACC-deaminase producing PGPR and timber-waste biochar improves pigments formation, growth and yield of wheat under drought stress. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abideen, Z.; Koyro, H.W.; Huchzermeyer, B.; Ansari, R.; Zulfiqar, F.; Gul, B. Ameliorating effects of biochar on photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant defence of Phragmites karka under drought stress. Plant Biol. 2020, 22, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammann, C.I.; Linsel, S.; Gößling, J.W.; Koyro, H.-W. Influence of biochar on drought tolerance of Chenopodium quinoa Willd and on soil–plant relations. Plant Soil 2011, 345, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabborova, D.; Wirth, S.; Kannepalli, A.; Narimanov, A.; Desouky, S.; Davranov, K.; Sayyed, R.Z.; El Enshasy, H.; Malek, R.A.; Syed, A. Co-inoculation of rhizobacteria and biochar application improves growth and nutrientsin soybean and enriches soil nutrients and enzymes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.C.; Travaglia, C.N.; Bottini, R.; Piccoli, P.N. Participation of abscisic acid and gibberellins produced by endophytic Azospirillum in the alleviation of drought effects in maize. Botany 2009, 87, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-M.; Waqas, M.; Hamayun, M.; Asaf, S.; Khan, A.L.; Kim, A.-Y.; Park, Y.-G.; Lee, I.-J. Gibberellins and indole-3-acetic acid producing rhizospheric bacterium Leifsonia xyli SE134 mitigates the adverse effects of copper-mediated stress on tomato. J. Plant Interact. 2017, 12, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Khan, M.A.; Lee, K.-E.; Kang, S.-M.; Dhungana, S.K.; Bhusal, N.; Lee, I.-J. The halotolerant rhizobacterium—Pseudomonas koreensis MU2 enhances inorganic silicon and phosphorus use efficiency and augments salt stress tolerance in soybean (Glycine max L.). Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavili, E.; Moosavi, A.A.; Kamgar Haghighi, A.A. Does biochar mitigate the adverse effects of drought on the agronomic traits and yield components of soybean? Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 128, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossa, K.; Wei, X.; Li, D.; Fonceka, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Boshou, L.; Diouf, D.; Cissé, N. Insight into the AP2/ERF transcription factor superfamily in sesame and expression profiling of DREB subfamily under drought stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhaleefa, A.; Shigidi, I. Optimization of sesame oil extraction process conditions. Adv. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 5, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibullah, M.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Mofijur, M.; Mobarak, H.M.; Ashraful, A.M. Potential of biodiesel as a renewable energy source in Bangladesh. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, D.; Gilani, S.A.; Kawase, M.; Watanabe, K.N. Sustainable sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) production through improved technology: An overview of production, challenges, and opportunities in Myanmar. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faostat, F.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAOSTAT). Data of Crop Production. 2017. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Saini, I.; Aggarwal, A.; Kaushik, P. Inoculation with mycorrhizal fungi and other microbes to improve the morpho-physiological and floral traits of Gazania rigens (L.) Gaertn. Agriculture 2019, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-E.; Adhikari, A.; Kang, S.-M.; You, Y.-H.; Joo, G.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, I.-J. Isolation and Characterization of the High Silicate and Phosphate Solubilizing Novel Strain Enterobacter ludwigii GAK2 that Promotes Growth in Rice Plants. Agronomy 2019, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Khan, M.A.; Imran, M.; Lee, K.-E.; Kang, S.-M.; Shin, J.Y.; Joo, G.-J.; Khan, M.; Yun, B.-W.; Lee, I.-J. The Combined Inoculation of Curvularia lunata AR11 and Biochar Stimulates Synthetic Silicon and Potassium Phosphate Use Efficiency, and Mitigates Salt and Drought Stresses in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Kalsoom; Imran, M.; Lubna; Shaffique, S.; Kwon, E.-H.; Kang, S.-M.; Kim, S.-H.; Hamayun, M.; Lee, I.-J. Mitigation of Commercial Food Waste-Related Salinity Stress Using Halotolerant Rhizobacteria in Chinese Cabbage Plants. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorovtsov, A.V.; Minkina, T.M.; Mandzhieva, S.S.; Perelomov, L.V.; Soja, G.; Zamulina, I.V.; Rajput, V.D.; Sushkova, S.N.; Mohan, D.; Yao, J. The mechanisms of biochar interactions with microorganisms in soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 2495–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafez, E.M.; Alsohim, A.S.; Farig, M.; Omara, A.E.-D.; Rashwan, E.; Kamara, M.M. Synergistic effect of biochar and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on alleviation of water deficit in rice plants under salt-affected soil. Agronomy 2019, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Dawar, K.; Tariq, M.; Sharif, M.; Fahad, S.; Adnan, M.; Ilahi, H.; Nawaz, T.; Alam, M.; Ullah, A. Gibberellic acid and urease inhibitor optimize nitrogen uptake and yield of maize at varying nitrogen levels under changing climate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 6568–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ma, J.; Wei, J.; Gong, X.; Yu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y. Biochar increases plant growth and alters microbial communities via regulating the moisture and temperature of green roof substrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rady, M.M.; Boriek, S.H.K.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Seif El-Yazal, M.A.; Ali, E.F.; Hassan, F.A.S.; Abdelkhalik, A. Exogenous gibberellic acid or dilute bee honey boosts drought stress tolerance in Vicia faba by rebalancing osmoprotectants, antioxidants, nutrients, and phytohormones. Plants 2021, 10, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M.H.; Wang, X.; Ali, S.; Zafar, S.; Nawaz, M.; Adnan, M.; Fahad, S.; Shah, A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Hefft, D.I. Interactive effects of gibberellic acid and NPK on morpho-physio-biochemical traits and organic acid exudation pattern in coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) grown in soil artificially spiked with boron. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Hoang, S.A.; Beiyuan, J.; Gupta, S.; Hou, D.; Karakoti, A.; Joseph, S.; Jung, S.; Kim, K.-H.; Kirkham, M.B. Multifunctional applications of biochar beyond carbon storage. Int. Mater. Rev. 2022, 67, 150–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Niu, Q.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Qin, L.; Liu, X.; Li, B. New notion of biochar: A review on the mechanism of biochar applications in advannced oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 129027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, R.; Ali, S.; Amara, U.; Khalid, R.; Ahmed, I. Soil beneficial bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion: A review. Ann. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 579–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, H.; Nosheen, A.; Naz, R.; Bano, A.; Keyani, R. L-tryptophan-assisted PGPR-mediated induction of drought tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.). J. Plant Interact. 2017, 12, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddikee, M.A.; Chauhan, P.S.; Anandham, R.; Han, G.-H.; Sa, T.-M. Isolation, characterization, and use for plant growth promotion under salt stress, of ACC deaminase-producing halotolerant bacteria derived from coastal soil. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, P.; Eslamian, S. Exploitation of agro-chemicals and its effect on health of farmers and environment on south-easter n coast of Bangladesh. Front. Agric. Food Technol. 2022, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar]

| Strains | FW(g) | SL(cm) | Strains | FW(g) | SL(cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d.H2O | 11.2 ± 0.08 b | 1.5 ± 0.54 c | SIR05 | 10.2 ± 0.04 bc | 1.6 ± 0.39 b |
| SIR01 | 15.1 ± 0.02 a | 2.1 ± 0.24 b | SIR06 | 9.8 ± 0.08 c | 1.3 ± 0.14 c |
| SIR02 | 10.3 ± 0.05 c | 1.6 ± 0.30 c | SIR07 | 14.8 ± 0.05 a | 2.2 ± 0.38 a |
| SIR03 | 15.3 ± 0.05 a | 2.4 ± 0.46 a | SIR08 | 11.6 ± 0.06 b | 1.5 ± 0.10 b |
| SIR04 | 9.5 ± 0.04 cd | 1.3 ± 0.37 d | SIR09 | 10.5 ± 0.05 bc | 1.5 ± 0.32 b |
| Shoot Length | Root Length | Fresh Weight (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3.2 ± 0.25 b | 5.1 ± 0.27 b | 0.10 ± 0.012 b |
| SIR01 | 3.3 ± 0.31 b | 4.8 ± 0.96 b | 0.10 ± 0.011 b |
| SIR03 | 4.5 ± 0.31 a | 8.1 ± 0.56 a | 0.17 ± 0.012 a |
| SIR07 | 3.3 ± 0.21 b | 5.4 ± 0.34 b | 0.11 ± 0.013 b |
| Shoot Length | Root Length | Shoot F.W (g) | Root F.W (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 24.6 ± 1.25 b | 11.1 ± 0.94 c | 6.05 ± 0.654 b | 1.56 ± 0.065 c |
| Biochar | 25.5 ± 1.95 b | 13.5 ± 1.04 b | 6.55 ± 0.423 b | 1.88 ± 0.042 b |
| R. Sphaeroides SIR03 | 27.8 ± 1.03 ab | 13.4 ± 0.93 b | 7.75 ± 0.214 a | 1.87 ± 0.038 b |
| Biochar + R. Sphaeroides SIR03 | 28.5 ± 0.52 a | 14.3 ± 0.51 a | 7.91 ± 0.131 a | 1.97 ± 0.070 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.-M.; Imran, M.; Shaffique, S.; Kwon, E.-H.; Park, Y.-S.; Lee, I.-J. Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Sesame Seedlings with Gibberellin-Producing Rhodobacter sphaeroides SIR03 and Biochar. Int. J. Plant Biol. 2022, 13, 257-269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb13030022
Kang S-M, Imran M, Shaffique S, Kwon E-H, Park Y-S, Lee I-J. Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Sesame Seedlings with Gibberellin-Producing Rhodobacter sphaeroides SIR03 and Biochar. International Journal of Plant Biology. 2022; 13(3):257-269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb13030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Sang-Mo, Muhammad Imran, Shifa Shaffique, Eun-Hae Kwon, Yong-Sung Park, and In-Jung Lee. 2022. "Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Sesame Seedlings with Gibberellin-Producing Rhodobacter sphaeroides SIR03 and Biochar" International Journal of Plant Biology 13, no. 3: 257-269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb13030022
APA StyleKang, S.-M., Imran, M., Shaffique, S., Kwon, E.-H., Park, Y.-S., & Lee, I.-J. (2022). Growth and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Sesame Seedlings with Gibberellin-Producing Rhodobacter sphaeroides SIR03 and Biochar. International Journal of Plant Biology, 13(3), 257-269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijpb13030022








