Potential Benefits of a Noninvasive Neuromodulation Protocol in Autism Spectrum Disorder with Multiple Comorbidities: A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
3. Methods
3.1. Psychometric Measures
3.1.1. Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist (ATEC)
3.1.2. Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS)
3.1.3. Autism Behavior Checklist (ABC)
3.2. Genetic Sequencing and Analysis
3.3. Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyor—REAC
3.4. Ethics Statement
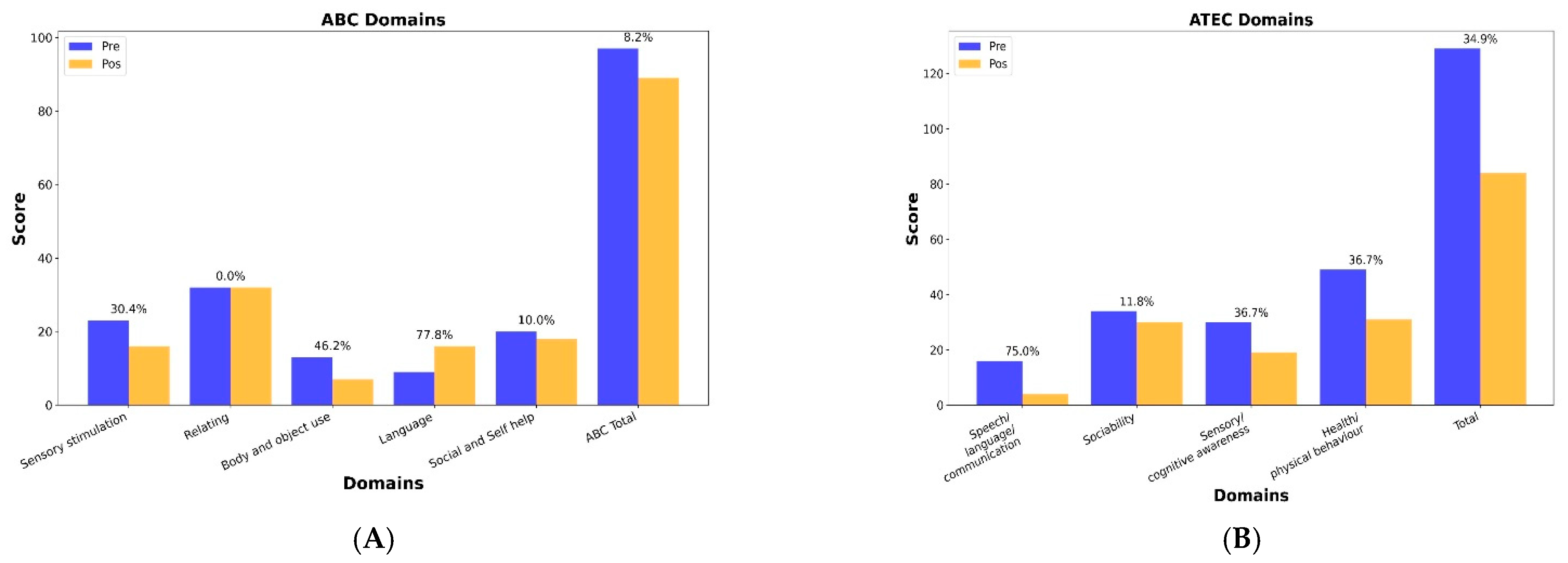
4. Results
Outcome Measures
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | Autism Behavior Checklist |
| ACP | Asymmetric conveyer probe |
| ASD | Autism Spectrum Disorder |
| ATEC | Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist |
| BOLD | Blood-oxygen-level-dependent |
| CARS | Childhood Autism Rating Scale |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| EBA | Endogenous bioelectric |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| ID | Intellectual disability |
| IED | Interictal epileptiform discharges |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| NPO | Neuro Postural Optimization |
| NPPO | Neuro Psycho Physical Optimization |
| REAC | Radioelectric asymmetric conveyer |
| VUS | Variants of uncertain significance |
| WES | Whole exome sequencing |
References
- State, M.W.; Šestan, N. Neuroscience. The Emerging Biology of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Science 2012, 337, 1301–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, D.L.; Baio, J.; Van Naarden Braun, K.; Bilder, D.; Charles, J.; Constantino, J.N.; Daniels, J.; Durkin, M.S.; Fitzgerald, R.T.; Kurzius-Spencer, M.; et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2012. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2016, 65, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Chien, Y.; Tung, Y.-H.; Ni, Y.-H.; Gau, S.S.-F. Altered Gut Microbiota Correlates with Behavioral Problems but Not Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Individuals with Autism. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 106, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symonds, J.D.; Elliott, K.S.; Shetty, J.; Armstrong, M.; Brunklaus, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Diver, L.A.; Dorris, L.; Gardiner, S.; Jollands, A.; et al. Early Childhood Epilepsies: Epidemiology, Classification, Aetiology, and Socio-Economic Determinants. Brain 2021, 144, 2879–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havdahl, K.A.; Hus Bal, V.; Huerta, M.; Pickles, A.; Øyen, A.-S.; Stoltenberg, C.; Lord, C.; Bishop, S.L. Multidimensional Influences on Autism Symptom Measures: Implications for Use in Etiological Research. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2016, 55, 1054–1063.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Torre-Ubieta, L.; Won, H.; Stein, J.L.; Geschwind, D.H. Advancing the Understanding of Autism Disease Mechanisms through Genetics. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretzsch, C.M.; Floris, D.L.; Schäfer, T.; Bletsch, A.; Gurr, C.; Lombardo, M.V.; Chatham, C.H.; Tillmann, J.; Charman, T.; Arenella, M.; et al. Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Neuroanatomical Profiles of Distinct Clinical (Adaptive) Outcomes in Autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 2158–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, B.J.; Marler, S.; Altstein, L.L.; Lee, E.B.; Akers, J.; Sohl, K.; McLaughlin, A.; Hartnett, K.; Kille, B.; Mazurek, M.; et al. Psychophysiological Associations with Gastrointestinal Symptomatology in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Autism Res. 2017, 10, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrindo, P.; Williams, K.C.; Lee, E.B.; Walker, L.S.; McGrew, S.G.; Levitt, P. Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Autism: Parental Report, Clinical Evaluation, and Associated Factors. Autism Res. 2012, 5, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulceri, F.; Morelli, M.; Santocchi, E.; Cena, H.; Del Bianco, T.; Narzisi, A.; Calderoni, S.; Muratori, F. Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Behavioral Problems in Preschoolers with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgritta, M.; Dooling, S.W.; Buffington, S.A.; Momin, E.N.; Francis, M.B.; Britton, R.A.; Costa-Mattioli, M. Mechanisms Underlying Microbial-Mediated Changes in Social Behavior in Mouse Models of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Neuron 2019, 101, 246–259.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffington, S.A.; Di Prisco, G.V.; Auchtung, T.A.; Ajami, N.J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Costa-Mattioli, M. Microbial Reconstitution Reverses Maternal Diet-Induced Social and Synaptic Deficits in Offspring. Cell 2016, 165, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoban, A.E.; Moloney, R.D.; Golubeva, A.V.; McVey Neufeld, K.A.; O’Sullivan, O.; Patterson, E.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F. Behavioural and Neurochemical Consequences of Chronic Gut Microbiota Depletion during Adulthood in the Rat. Neuroscience 2016, 339, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, J.; Marchix, J.; Aymeric, L.; Le Berre-Scoul, C.; Zoppi, J.; Bordron, P.; Burel, M.; Davidovic, L.; Richard, J.-R.; Gaman, A.; et al. Fecal Supernatant from Adult with Autism Spectrum Disorder Alters Digestive Functions, Intestinal Epithelial Barrier, and Enteric Nervous System. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet Rapidly and Reproducibly Alters the Human Gut Microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.; Blaser, M.J. The Human Microbiome: At the Interface of Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, S.J.; Richardson, G.A.; Hutcheon, J.A.; Himes, K.P.; Brooks, M.M.; Day, N.L.; Bodnar, L.M. Maternal Obesity and Excessive Gestational Weight Gain Are Associated with Components of Child Cognition. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2562–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R. Obesity, inflammation, and infection. Int. J. Infect. 2022, 6, 88–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, S.; Xu, S.; Weng, S.; Liu, Z. Maternal Body Mass Index and Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorders in Offspring: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, N.; Anixt, J.; Manning, P.; Lin, D.P.-I.; Marsolo, K.A.; Bowers, K. Maternal Metabolic Risk Factors for Autism Spectrum Disorder-An Analysis of Electronic Medical Records and Linked Birth Data. Autism Res. 2016, 9, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, G.; Cruz, N.J.; Kang, D.-W.; Gandal, M.J.; Wang, B.; Kim, Y.-M.; Zink, E.M.; Casey, C.P.; Taylor, B.C.; Lane, C.J.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota from Autism Spectrum Disorder Promote Behavioral Symptoms in Mice. Cell 2019, 177, 1600–1618.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.B.; Valakh, V. Excitatory/Inhibitory Balance and Circuit Homeostasis in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Neuron 2015, 87, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, V.S.; Rubenstein, J.L.R. Excitation-Inhibition Balance as a Framework for Investigating Mechanisms in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, S.; Fontani, V. Radioelectric Asymmetric Conveyer for Therapeutic Use. U.S. Patent EP1301241 B1, 29 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, C.; Elsabbagh, M.; Baird, G.; Veenstra-Vanderweele, J. Autism Spectrum Disorder. Lancet 2018, 392, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B.A.; Wink, L.K.; Early, M.; Shaffer, R.; Minshawi, N.; McDougle, C.J.; Erickson, C.A. Drug-Refractory Aggression, Self-Injurious Behavior, and Severe Tantrums in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Chart Review Study. Autism 2015, 19, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.Y.; Chan, M.M.Y.; Shea, C.K.S.; Lai, O.L.-H.; Krishnamurthy, K.; Cheung, M.-C.; Chan, A.S. Neurophysiological and Behavioral Effects of Multisession Prefrontal TDCS and Concurrent Cognitive Remediation Training in Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled FNIRS Study. Brain Stimul. 2022, 15, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.; Rinaldi, C.; Coelho Pereira, J.A.; Lotti Margotti, M.; Bittencourt, M.N.; Barcessat, A.R.P.; Fontani, V.; Rinaldi, S. Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyer Neuromodulation in Depression, Anxiety, and Stress. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontani, V.; Rinaldi, A.; Rinaldi, C.; Araldi, L.; Azzarà, A.; Carta, A.M.; Casale, N.; Castagna, A.; Del Medico, M.; Di Stasio, M.; et al. Long-Lasting Efficacy of Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyer Neuromodulation Treatment on Functional Dysmetria, an Adaptive Motor Behavior. Cureus 2022, 14, e25768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.d.J.M.; Pereira, J.A.C.; Fontani, V.; Rinaldi, S. REAC Reparative Treatment: A Promising Therapeutic Option for Alcoholic Cirrhosis of the Liver. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, S.; Fontani, V.; Castagna, A. Brain Activity Modification Produced by a Single Radioelectric Asymmetric Brain Stimulation Pulse: A New Tool for Neuropsychiatric Treatments. Preliminary FMRI Study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2011, 7, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rinaldi, A.; Marins Martins, M.C.; De Almeida Martins Oliveira, A.C.; Rinaldi, S.; Fontani, V. Improving Functional Abilities in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Non-Invasive REAC Neuro Psycho Physical Optimization Treatments: A PEDI-CAT Study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, M.; Egberts, K.J.; Samtani, A.; Scholten, R.J.; Hooft, L.; Livingstone, N.; Sterling-Levis, K.; Woolfenden, S.; Williams, K. Diagnostic Tests for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in Preschool Children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 7, CD009044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurek, L.; Baltazar, M.; Gulati, S.; Novakovic, N.; Núñez, M.; Oakley, J.; O’Hagan, A. Response (Minimum Clinically Relevant Change) in ASD Symptoms after an Intervention According to CARS-2: Consensus from an Expert Elicitation Procedure. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rellini, E.; Tortolani, D.; Trillo, S.; Carbone, S.; Montecchi, F. Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS) and Autism Behavior Checklist (ABC) Correspondence and Conflicts with DSM-IV Criteria in Diagnosis of Autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2004, 34, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaldiz, B.; Kucuk, E.; Hampstead, J.; Hofste, T.; Pfundt, R.; Corominas Galbany, J.; Rinne, T.; Yntema, H.G.; Hoischen, A.; Nelen, M.; et al. Twist Exome Capture Allows for Lower Average Sequence Coverage in Clinical Exome Sequencing. Hum. Genom. 2023, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.; Gallagher, L.; Leader, G.; Shen, S. Coupling of Autism Genes to Tissue-Wide Expression and Dysfunction of Synapse, Calcium Signalling and Transcriptional Regulation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuchman, R.; Rapin, I. Epilepsy in Autism. Lancet Neurol. 2002, 1, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strati, F.; Cavalieri, D.; Albanese, D.; De Felice, C.; Donati, C.; Hayek, J.; Jousson, O.; Leoncini, S.; Renzi, D.; Calabrò, A.; et al. New Evidences on the Altered Gut Microbiota in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Microbiome 2017, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimbeyoglu, A.; Kim, C.K.; Inoue, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Hong, A.S.O.; Kauvar, I.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Fenno, L.E.; Davidson, T.J.; Wright, M.; et al. Modulation of Prefrontal Cortex Excitation/Inhibition Balance Rescues Social Behavior in CNTNAP2-Deficient Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaah6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.R.; Yen, E.F.; Grinspan, A.M.; Kahn, S.A.; Atreja, A.; Lewis, J.D.; Moore, T.A.; Rubin, D.T.; Kim, A.M.; Serra, S.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Is Highly Effective in Real-World Practice: Initial Results From the FMT National Registry. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 183–192.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Hou, W.; Bi, D.; Yin, F.; Gao, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yan, Y.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Improves VPA-Induced ASD Mice by Modulating the Serotonergic and Glutamatergic Synapse Signaling Pathways. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, L.M.; Smith, E.G.; Pedapati, E.V.; Horn, P.S.; Will, M.; Lamy, M.; Barber, L.; Trebley, J.; Meyer, K.; Heiman, M.; et al. Results of a Phase Ib Study of SB-121, an Investigational Probiotic Formulation, a Randomized Controlled Trial in Participants with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, K.K.; Orsso, C.E.; Richard, C.; Haqq, A.M.; Zwaigenbaum, L. Risk Factors for Unhealthy Weight Gain and Obesity among Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, P.-T.; Chen, Y.-W.; Stubbs, B.; Carvalho, A.F.; Whiteley, P.; Tang, C.-H.; Yang, W.-C.; Chen, T.-Y.; Li, D.-J.; Chu, C.-S.; et al. Maternal Breastfeeding and Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, E.W.; Must, A.; Anderson, S.E.; Curtin, C.; Scampini, R.; Maslin, M.; Bandini, L. Dietary Patterns and Body Mass Index in Children with Autism and Typically Developing Children. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2012, 6, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correll, C.U.; Manu, P.; Olshanskiy, V.; Napolitano, B.; Kane, J.M.; Malhotra, A.K. Cardiometabolic Risk of Second-Generation Antipsychotic Medications during First-Time Use in Children and Adolescents. JAMA 2009, 302, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.B.; Lin, H.-Y.; Wang, L.-J.; Hung, K.-C.; Brunoni, A.R.; Chou, P.-H.; Tseng, P.-T.; Liang, C.-S.; Tu, Y.-K.; Lin, P.-Y.; et al. A Network Meta-Analysis of Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation Interventions for Autism Spectrum Disorder: Evidence from Randomized Controlled Trials. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 164, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewdie, E.; Ciechanski, P.; Kuo, H.C.; Giuffre, A.; Kahl, C.; King, R.; Cole, L.; Godfrey, H.; Seeger, T.; Swansburg, R.; et al. Safety and Tolerability of Transcranial Magnetic and Direct Current Stimulation in Children: Prospective Single Center Evidence from 3.5 Million Stimulations. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maioli, M.; Rinaldi, S.; Migheli, R.; Pigliaru, G.; Rocchitta, G.; Santaniello, S.; Basoli, V.; Castagna, A.; Fontani, V.; Ventura, C.; et al. Neurological Morphofunctional Differentiation Induced by REAC Technology in PC12. A Neuro Protective Model for Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zippo, A.G.; Rinaldi, S.; Pellegata, G.; Caramenti, G.C.; Valente, M.; Fontani, V.; Biella, G.E.M. Electrophysiological Effects of Non-Invasive Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyor (REAC) on Thalamocortical Neural Activities and Perturbed Experimental Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Class | Medication | Form | Dose | Days | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esomeprazole | Oral | Variable | 0–end | ||
| Antiemetic | Ondansetron | Oral | Variable | 01 | |
| α2A-adrenergic receptor agonist | Clonidine | Oral | Variable | 0–12 | |
| Benzodiazepine | Clonazepam | Oral | 1–50 mg | 0–12 | |
| Antiepileptic | Valproic acid | Oral | 8.2 mL | Variable | Substitute for Lamotrigine |
| Antiepileptic | Lamotrigine | Oral | Variable | 0–5 | Limited effect |
| Antiepileptic | Topiramate | Oral | 150 mg | 0–end | Substitute for Levetiracetam |
| Antiepileptic | Levetiracetam | Oral | 750–2500 mg | 0–end | Stopped seizures |
| Hypnotic | Melatonin | Oral | 5 mg | 0–end | |
| Antipsychotic | Aripiprazole | Oral | 20 mg | 0–end | |
| Antidepressant | Sertraline | Oral | 50 mg | 0–end |
| Gene | Transcript | c.DNA | gnomAD Frequency | REVEL | CADD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRID2 | NM_001510.4 | c.1472C>T | 0.00005304 | 0.19 | 22 |
| GRID2 | NM_001510.4 | c.2444C>T | 0.0024 | 0.39 | 29 |
| REAC | ||
|---|---|---|
| CARS Domains | Pre | Post |
| Personal relationships | 3 | 3 |
| Imitative Behavior | 4 | 4 |
| Emotional Response | 4 | 4 |
| Body Use | 3 | 3 |
| Object Use | 3 | 3 |
| Adaptation to Change | 4 | 3 |
| Visual Response | 3 | 3 |
| Auditory Response | 4 | 4 |
| Taste, Smell, and Touch Response | 4 | 4 |
| Fear or Nervousness | 4 | 4 |
| Verbal Communication | 3 | 3 |
| Nonverbal Communication | 4 | 4 |
| Activity Level | 4 | 3 |
| Level and Consistency of Intellectual Response | 3 | 4 |
| General Impressions | 4 | 4 |
| CARS Total | 54 | 53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira, C.A.; Iorio, E.L.; Espíndola, F.S. Potential Benefits of a Noninvasive Neuromodulation Protocol in Autism Spectrum Disorder with Multiple Comorbidities: A Case Report. Pediatr. Rep. 2025, 17, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050092
de Oliveira CA, Iorio EL, Espíndola FS. Potential Benefits of a Noninvasive Neuromodulation Protocol in Autism Spectrum Disorder with Multiple Comorbidities: A Case Report. Pediatric Reports. 2025; 17(5):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050092
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira, Clarissa Aires, Eugenio Luigi Iorio, and Foued Salmen Espíndola. 2025. "Potential Benefits of a Noninvasive Neuromodulation Protocol in Autism Spectrum Disorder with Multiple Comorbidities: A Case Report" Pediatric Reports 17, no. 5: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050092
APA Stylede Oliveira, C. A., Iorio, E. L., & Espíndola, F. S. (2025). Potential Benefits of a Noninvasive Neuromodulation Protocol in Autism Spectrum Disorder with Multiple Comorbidities: A Case Report. Pediatric Reports, 17(5), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050092








