Effect of the Duration of Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest on the Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Children Undergoing Cardiac Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Neurodevelopmental Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.4.1. Data Presentation and Group Comparison
2.4.2. Linear Regression Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preoperative Data
3.2. Operative and Postoperative Data
3.3. Neurodevelopmental Assessment
3.4. Factors Affecting Neurodevelopment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaynor, J.W.; Stopp, C.; Wypij, D.; Andropoulos, D.B.; Atallah, J.; Atz, A.M.; Beca, J.; Donofrio, M.T.; Duncan, K.; Ghanayem, N.S.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes after cardiac surgery in infancy. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellinger, D.C.; Wypij, D.; Kuban, K.C.; Rappaport, L.A.; Hickey, P.R.; Wernovsky, G.; Jonas, R.A.; Newburger, J.W. Developmental and neurological status of children at 4 years of age after heart surgery with hypothermic circulatory arrest or low-flow cardiopulmonary bypass. Circulation 1999, 100, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbess, J.M.; Visconti, K.J.; Hancock-Friesen, C.; Howe, R.C.; Bellinger, D.C.; Jonas, R.A. Neurodevelopmental outcome after congenital heart surgery: Results from an institutional registry. Circulation 2002, 106 (Suppl. S1), I95–I102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Plessis, A.J. Neurologic complications of cardiac disease in the newborn. Clin. Perinatol. 1997, 24, 807–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alenezi, A.M.; Albawardi, N.M.; Ali, A.; Househ, M.S.; Elmetwally, A. The epidemiology of congenital heart diseases in Saudi Arabia: A systematic review. J. Public Health Epidemiol. 2015, 7, 232–240. [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger, D.C.; Jonas, R.A.; Rappaport, L.A.; Wypij, D.; Wernovsky, G.; Kuban, K.C.; Barnes, P.D.; Holmes, G.L.; Hickey, P.R.; Strand, R.D.; et al. Developmental and neurologic status of children after heart surgery with hypothermic circulatory arrest or low-flow cardiopulmonary bypass. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Cardiac Collaborative on Neurodevelopment (ICCON) Investigators. Impact of operative and postoperative factors on neurodevelopmental outcomes after cardiac operations. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 102, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasundaram, P.; Avulakunta, I.D. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pizarro, C.; Sood, E.D.; Kerins, P.; Duncan, D.; Davies, R.R.; Woodford, E. Neurodevelopmental outcomes after infant cardiac surgery with circulatory arrest and intermittent perfusion. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 98, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, B.S.; Lipkin, P.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Peacock, G.; Gerdes, M.; Gaynor, J.W.; Wernovsky, G.; Gauthier, T.; Bellinger, D.C.; Mahle, W.T.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes in children with congenital heart disease: Evaluation and management: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2012, 126, 1143–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabbutt, S.; Nord, A.S.; Jarvik, G.P.; Bernbaum, J.; Wernovsky, G.; Gerdes, M.; Zackai, E.; Clancy, R.R.; Nicolson, S.C.; Spray, T.L.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes after staged palliation for hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Pediatrics 2008, 121, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Bove, E.L.; Devaney, E.J.; Mollen, E.; Schwartz, E.; Tindall, S.; Nowak, C.; Charpie, J.; Brown, M.B.; Kulik, T.J.; et al. A randomized clinical trial of regional cerebral perfusion versus deep hypothermic circulatory arrest: Outcomes for infants with functional single ventricle. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2007, 133, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiorek, A.; Donofrio, M.T.; Zurakowski, D.; Reitz, J.G.; Tague, L.; Murnick, J.; Axt-Fliedner, R.; Limperopoulos, C.; Yerebakan, C.; Carpenter, J.L. Predictors of neurological outcome following infant cardiac surgery without deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2022, 43, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visconti, K.J.; Rimmer, D.; Gauvreau, K.; del Nido, P.; Mayer, J.E., Jr.; Hagino, I.; Pigula, F.A. Regional low-flow perfusion versus circulatory arrest in neonates: One-year neurodevelopmental outcome. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 82, 2207–2211; discussion 2211–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, S.; Nord, A.S.; Gerdes, M.; Wernovsky, G.; Jarvik, G.P.; Bernbaum, J.; Zackai, E.; Gaynor, J.W. Predictors of impaired neurodevelopmental outcomes at one year of age after infant cardiac surgery. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2009, 36, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wypij, D.; Newburger, J.W.; Rappaport, L.A.; duPlessis, A.J.; Jonas, R.A.; Wernovsky, G.; Lin, M.; Bellinger, D.C. The effect of duration of deep hypothermic circulatory arrest in infant heart surgery on late neurodevelopment: The Boston Circulatory Arrest Trial. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2003, 126, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, P.R. Neurologic sequelae associated with deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1998, 65, S65–S69; discussion S69–S70, S74–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newburger, J.W.; Sleeper, L.A.; Bellinger, D.C.; Goldberg, C.S.; Tabbutt, S.; Lu, M.; Mussatto, K.A.; Williams, I.A.; Gustafson, K.E.; Mital, S.; et al. Early developmental outcome in children with hypoplastic left heart syndrome and related anomalies: The Single Ventricle Reconstruction trial. Circulation 2012, 125, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beca, J.; Gunn, J.K.; Coleman, L.; Hope, A.; Reed, P.W.; Hunt, R.W.; Finucane, K.; Brizard, C.; Dance, B.; Shekerdemian, L.S. New white matter brain injury after infant heart surgery is associated with diagnostic group and the use of circulatory arrest. Circulation 2013, 127, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
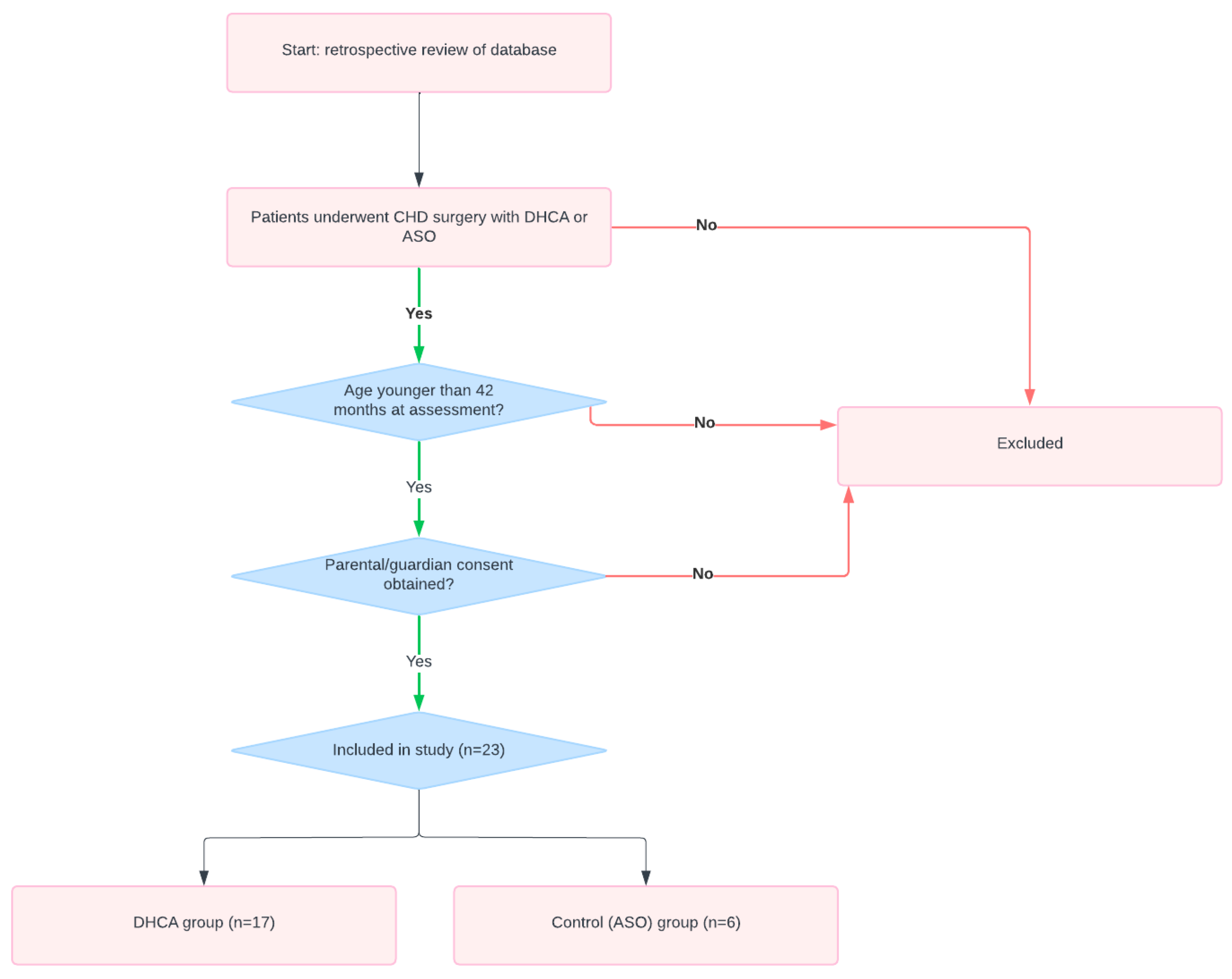
| Total Patients (n = 23) | Control (n = 6) | DHCA (n = 17) | p-Value | |
| Sex (male) | 15 (65.22) | 5 (83.33) | 10 (58.82) | 0.37 |
| Age at intervention (days) | 21 [9–82] | 6 [3–35] | 31 [14–103] | 0.05 |
| Weight at intervention (kg) | 3.2 [2.5–3.6] | 3.5 [2.9–3.7] | 2.8 [2.5–3.6] | 0.40 |
| Down syndrome | 1 (4.35) | 0 | 1 (5.88) | >0.99 |
| Prenatal diagnosis | 5 (21.74) | 3 (50) | 2 (12.5) | 0.10 |
| Preterm labor | 2 (8.7) | 0 | 2 (11.76) | >0.99 |
| Socio-economic status | 0.50 | |||
| Low | 12 (57.14) | 4 (66.67) | 8 (53.33) | |
| Middle | 7 (33.33) | 1 (16.67) | 6 (40) | |
| Upper middle | 2 (9.52) | 1 (16.67) | 1 (6.67) | |
| Father’s education | 0.13 | |||
| Primary school | 1 (4.76) | 0 | 1 (6.67) | |
| Secondary school | 10 (47.62) | 1 (16.67) | 9 (60) | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 9 (42.86) | 4 (66.67) | 5 (33.33) | |
| Master’s degree | 1 (4.76) | 1 (16.67) | 0 | |
| Mother’s education | 0.32 | |||
| Primary school | 1 (4.76) | 0 | 1 (6.667) | |
| Middle school | 5 (23.81) | 2 (33.33) | 3 (20) | |
| Secondary school | 6 (28.57) | 0 | 6 (40) | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 7 (33.33) | 3 (50) | 4 (26.67) | |
| Master’s degree | 2 (9.52) | 1 (16.67) | 1 (6.67) | |
| Delivery mode | 0.32 | |||
| Vaginal | 16 (69.57) | 3 (50) | 13 (76.47) | |
| Cesarean | 7 (30.43) | 3 (50) | 4 (23.53) | |
| Previous non-cardiac surgery | 1 (4.35) | 0 | 1 (5.88) | >0.99 |
| Preoperative ventilation (days) | 0 [0–3] | 0 [0–3] | 2 [0–3] | 0.56 |
| Total Patients (n = 23) | Control (n = 6) | DHCA (n = 17) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of CPB (minutes) | 68 [56–78] | 101.5 [74–123] | 61 [56–72] | 0.002 |
| Cross-clamp time (minutes) | 45.57 ± 16.52 | 61.67 ± 18.59 | 39.88 ± 11.65 | 0.003 |
| Highest creatinine (μmol/L) | 55 [46–87.8] | 54.5 [49–70] | 68 [42–91] | 0.93 |
| Highest lactate (mmol/L) | 4.67 ± 0.48 | 4.87 ± 1.14 | 4.6 ± 0.53 | 0.81 |
| Postoperative acidosis | 17 (73.91) | 3 (50) | 14 (87.5) | 0.10 |
| Postoperative hypoxia | 11 (47.83) | 4 (66.67) | 7 (41.18) | 0.37 |
| Mechanical ventilation (days) | 6 [4–8] | 5 [2–7] | 7 [4–12] | 0.29 |
| ECMO | 1 (4.35) | 0 | 1 (5.88) | >0.99 |
| Open sternum | 18 (78.36) | 4 (66.67) | 14 (82.35) | 0.58 |
| Open-chest duration (days) | 2 [1.5–3] | 3 [1.5–4] | 2 [1.5–3] | 0.53 |
| Postoperative seizures | 1 (4.35) | 1 (16.67) | 0 | 0.26 |
| Pulmonary hemorrhage | 4 (17.39) | 1 (16.67) | 3 (17.65) | >0.99 |
| Lowest Ca level (mg/dL) | 2.04 [1.88–2.14] | 1.98 [1.55–2.12] | 2.05 [1.93–2.14] | 0.34 |
| ICU stay (days) | 12 [7–18] | 9 [5–12] | 15 [7–23] | 0.13 |
| Hospital stay (days) | 16 [12–26] | 11.5 [10–14] | 19 [15–46] | >0.99 |
| Surgical re-exploration | 2 (8.7) | 0 | 2 (11.76) | >0.99 |
| Blood stream infection | 6 (26.09) | 0 | 6 (35.29) | 0.14 |
| Surgical site infection | 2 (8.7) | 2 (33.33) | 0 | 0.06 |
| Heart block | 5 (21.74) | 1 (16.67) | 4 (23.53) | >0.99 |
| Chest drain > 5 days | 2 (8.7) | 0 | 2 (11.76) | >0.99 |
| Total Patients (n = 23) | Control (n = 6) | DHCA (n = 17) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at assessment (days) | 774.78 ± 343.56 | 865 ± 184.36 | 742.94 ± 284.12 | 0.47 |
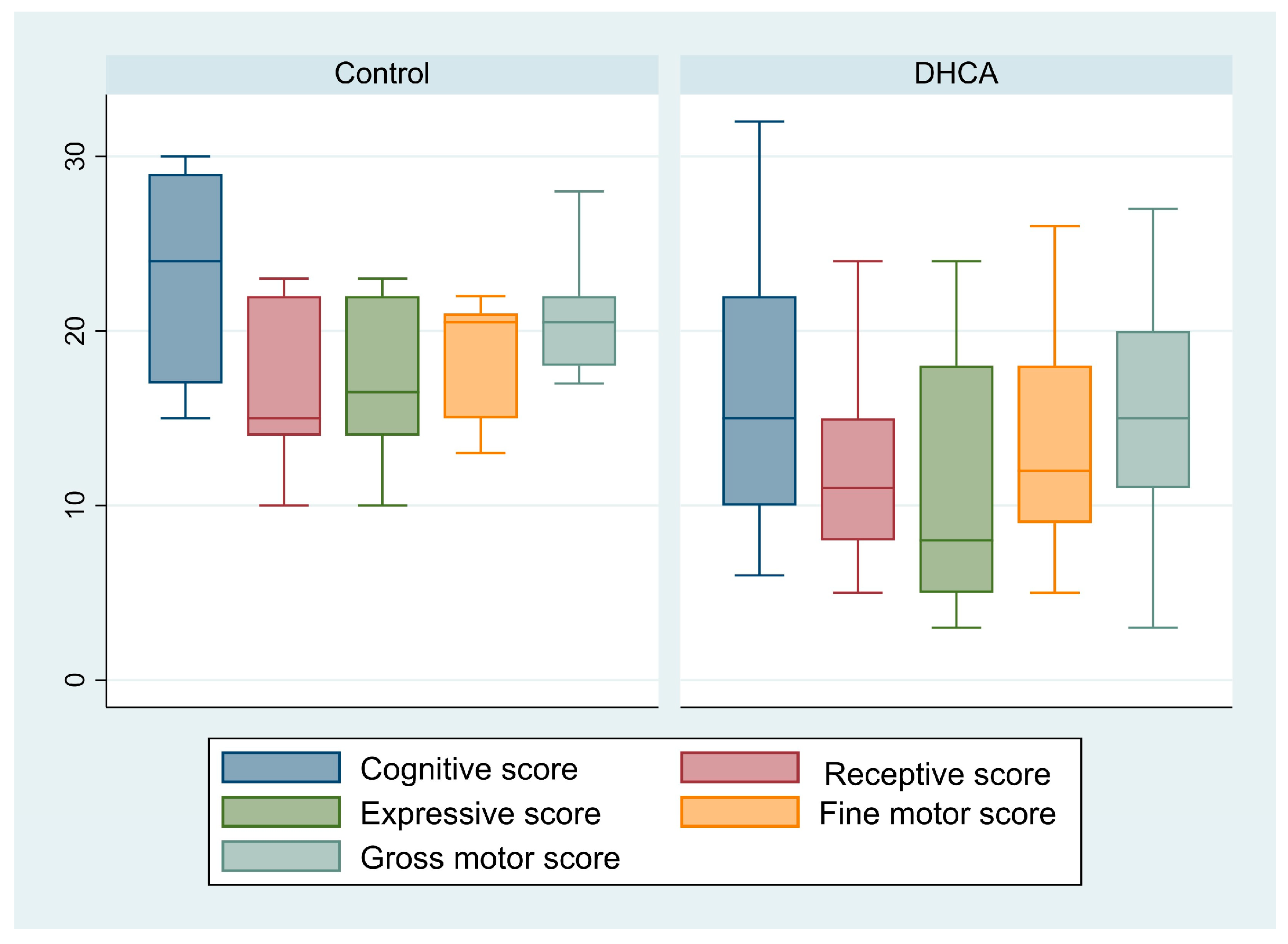
| Cognitive score | 18.26 ± 7.99 | 23.17 ± 6.62 | 16.53 ± 7.87 | 0.08 |
| Cognitive | 0.49 | |||
| At-risk | 9 (39.13) | 1 (16.67) | 8 (47.06) | |
| Emerging | 8 (34.78) | 3 (50) | 5 (29.41) | |
| Competent | 6 (26.09) | 2 (33.33) | 4 (23.53) | |
| Receptive communication score | 14 [8–15] | 15 [14–22] | 11 [8–15] | 0.17 |
| Receptive communication | >0.99 | |||
| At-risk | 6 (26.09) | 1 (16.67) | 5 (29.41) | |
| Emerging | 10 (43.48) | 3 (50) | 7 (41.18) | |
| Competent | 7 (30.43) | 2 (33.33) | 5 (29.41) | |
| Expressive communication score | 12.43 ± 6.91 | 17 ± 4.90 | 10.82 ± 6.89 | 0.06 |
| Expressive communication | 0.49 | |||
| At-risk | 9 (39.13) | 1 (16.67) | 8 (47.06) | |
| Emerging | 8 (34.78) | 3 (50) | 5 (29.41) | |
| Competent | 6 (26.09) | 2 (33.33) | 4 (23.53) | |
| Fine motor score | 14.91 ± 6.03 | 18.67 ± 3.72 | 13.59 ± 6.21 | 0.08 |
| Fine motor | 0.46 | |||
| At-risk | 5 (29.41) | 0 | 5 (29.41) | |
| Emerging | 12 (52.17) | 4 (66.67) | 8 (47.06) | |
| Competent | 6 (26.09) | 2 (33.33) | 4 (23.53) | |
| Gross motor score | 16.26 ± 7.21 | 21 ± 3.90 | 14.59 ± 7.43 | 0.06 |
| Gross motor | 0.05 | |||
| At-risk | 9 (39.13) | 0 | 9 (52.94) | |
| Emerging | 7 (30.43) | 3 (50) | 4 (23.53) | |
| Competent | 7 (30.43) | 3 (50) | 4 (23.53) |
| Univariable | Multivariable | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient (95% CI) | p-Value | Coefficient (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Cognitive score * | ||||
| Age at assessment (months) | 0.53 (0.32 to 0.74) | <0.001 | 0.59 (0.45 to 0.74) | <0.001 |
| Preterm | −9.05 (−20.94 to 2.85) | 0.13 | −13.38 (−19.22 to −7.53) | <0.001 |
| CPB duration | 0.11 (−0.02 to 0.24) | 0.09 | − | |
| DHCA | −6.64 (−14.13 to 0.86) | 0.08 | − | |
| Receptive communication score ** | ||||
| Age at assessment (months) | 0.33 (0.16 to 0.50) | 0.001 | 0.38 (0.25 to 0.50) | <0.001 |
| Preterm | −8.24 (−16.45 to 0.03) | 0.049 | −11 (−15.95 to −6.06) | <0.001 |
| CPB | 0.07 (−0.02 to 0.17) | 0.12 | − | |
| DHCA | −4.03 (−9.52 to 1.46) | 0.14 | − | |
| Expressive communication score *** | ||||
| Age at assessment (months) | 0.39 (0.17 to 0.6) | 0.001 | 0.44 (0.26 to 0.61) | <0.001 |
| Preterm | −8.14 (−18.38 to 2.09) | 0.11 | −11.35 (−18.3 to −4.4) | <0.001 |
| Down syndrome | −9.84 (−24.21 to 4.49) | 0.17 | − | |
| CPB time | 0.10 (−0.01 to 0.21) | 0.09 | − | |
| DHCA | −6.18 (−12.57 to 0.22) | 0.06 | − | |
| Fine motor score **** | ||||
| Age at assessment (months) | 0.39 (0.22 to 0.55) | <0.001 | 0.42 (0.32 to 0.53) | <0.001 |
| Male | −3.78 (−9.13 to 1.58) | 0.16 | − | |
| Preterm | −8.12 (−16.87 to 0.63) | 0.07 | −10.62 (−14.68 to −6.55) | <0.001 |
| Down syndrome | −8.27 (−20.85 to 4.30) | 0.19 | − | |
| CPB | 0.07 (−0.28 to 0.17) | 0.15 | − | |
| DHCA | −5.08 (−10.72 to 0.56) | 0.08 | −2.1 (−4.70 to −0.49) | 0.10 |
| Gross motor score ***** | ||||
| Age at assessment (months) | 0.48 (0.30 to 0.67) | <0.001 | 0.51 (0.39 to 0.64) | <0.001 |
| Male | −4.78 (−11.13 to 1.58) | 0.13 | −10.85 (−15.82 to −5.87) | <0.001 |
| Preterm | −7.95 (−18.71 to 2.81) | 0.14 | − | |
| Down syndrome | −10.73 (−25.63 to 4.18) | 0.15 | − | |
| CPB | 0.10 (−0.01 to 0.22) | 0.08 | − | |
| DHCA | −6.41 (−13.09 to 0.27) | 0.06 | −3.04 (−6.22 to −0.14) | 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghunaim, A.H.; Aljabri, B.; Dohain, A.; Althinayyan, G.S.; Aleissa, A.I.; Alshebly, A.T.; Alyafi, R.A.; Alhablany, T.M.; Nashar, A.M.; Al-Radi, O.O. Effect of the Duration of Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest on the Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Children Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16, 753-762. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16030063
Ghunaim AH, Aljabri B, Dohain A, Althinayyan GS, Aleissa AI, Alshebly AT, Alyafi RA, Alhablany TM, Nashar AM, Al-Radi OO. Effect of the Duration of Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest on the Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Children Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. Pediatric Reports. 2024; 16(3):753-762. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16030063
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhunaim, Abdullah H., Basma Aljabri, Ahmed Dohain, Ghassan S. Althinayyan, Abdulaziz I. Aleissa, Ahmad T. Alshebly, Rayan A. Alyafi, Tareg M. Alhablany, Ahmed M. Nashar, and Osman O. Al-Radi. 2024. "Effect of the Duration of Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest on the Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Children Undergoing Cardiac Surgery" Pediatric Reports 16, no. 3: 753-762. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16030063
APA StyleGhunaim, A. H., Aljabri, B., Dohain, A., Althinayyan, G. S., Aleissa, A. I., Alshebly, A. T., Alyafi, R. A., Alhablany, T. M., Nashar, A. M., & Al-Radi, O. O. (2024). Effect of the Duration of Deep Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest on the Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Children Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. Pediatric Reports, 16(3), 753-762. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16030063






