Drug-Induced Lupus Secondary to Ethosuximide in Association with Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Nephrotic Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
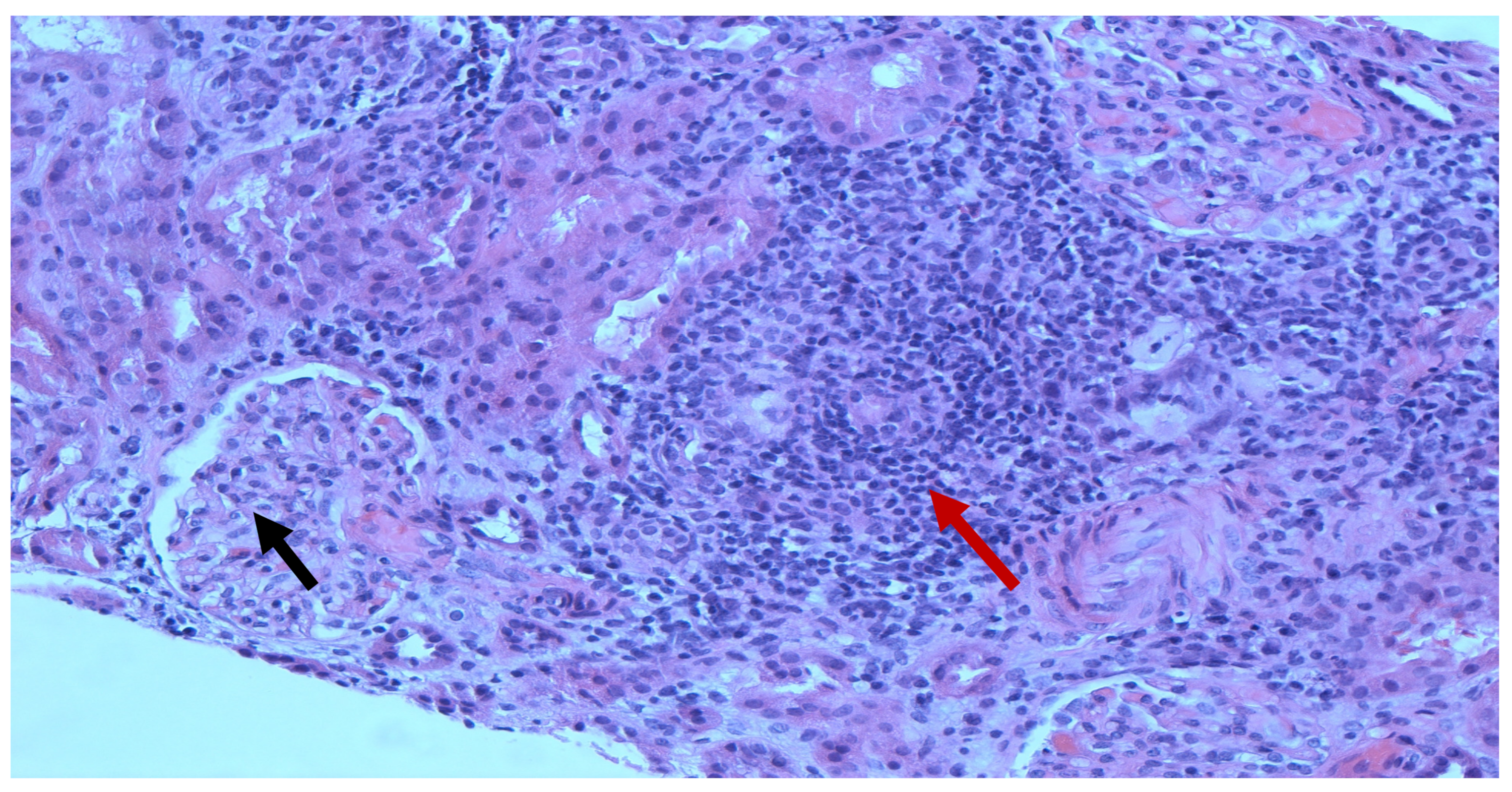
3. Case Presentation
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubin, R.L. Etiology and mechanisms of drug-induced lupus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 1999, 11, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callen, J.P. Drug-induced cutaneous lupus erythematosus, a distinct syndrome that is frequently under-recognized. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praga, M.; Sevillano, A.; Auñón, P.; González, E. Changes in the aetiology, clinical presentation and management of acute interstitial nephritis, an increasingly common cause of acute kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinhardtb, D.J.; Waldron, J.M. Lupus erythematosus-like syndrome complicating hydralazine (apresoline) therapy. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1954, 155, 1491–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchers, A.T.; Keen, C.L.; Gershwin, M.E. Drug-induced lupus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1108, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, R.L. Drug-induced lupus. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2015, 14, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, J.J.; Markowitz, G.S.; Radhakrishnan, J. Drug-induced glomerular disease: Immune-mediated injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eriksson, C.; Engstrand, S.; Sundqvist, K.G.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S. Autoantibody formation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF alpha. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aylward, P.E.; Tonkin, A.M.; Bune, A. Cardiac tamponade in hydralazine-induced systemic lupus erythematosus. Aust. N. Z. J. Med. 1982, 12, 546–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, R.L. Autoantibody specificity in drug-induced lupus and neutrophil-mediated metabolism of lupus-inducing drugs. Clin. Biochem. 1992, 25, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaglio, A.; Grayson, P.C.; Fenaroli, P.; Gianfreda, D.; Boccaletti, V.; Ghiggeri, G.M.; Moroni, G. Drug-induced lupus: Traditional and new concepts. Autoimmun Rev. 2018, 17, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bandt, M.; Sibilia, J.; Le Loët, X.; Prouzeau, S.; Fautrel, B.; Marcelli, C.; Boucquillard, E.; Siame, J.L.; Mariette, X. Club Rhumatismes et Inflammation. Systemic lupus erythematosus induced by anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy: A French national survey. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R545–R551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baum, M.; Piel, C.F.; Goodman, J.R. Antibiotic-associated interstitial nephritis and nephrotic syndrome. Am. J. Nephrol. 1986, 6, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, S.A. Drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus. Differentiating it from the real thing. Postgrad. Med. 1985, 77, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, R.L. Drug-induced lupus. Toxicology 2005, 209, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, J.R.; Welsh, K.I.; Tinoco, R.M.; Dollery, C.T.; Hughes, G.R.; Bernstein, R.; Ryan, P.; Naish, P.F.; Aber, G.M.; Bing, R.F.; et al. Hydralazine-induced systemic lupus erythematosus: Influence of HLA-DR and sex on susceptibility. Lancet 1980, 1, 1107–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, G.I.; Bing, R.F.; Jones, J.A.; Thurston, H.; Swales, J.D. Hydralazine sensitivity: Clinical features, autoantibody changes and HLA-DR phenotype. Q. J. Med. 1987, 65, 845–852. [Google Scholar]
- Speirs, C.; Fielder, A.H.; Chapel, H.; Davey, N.J.; Batchelor, J.R. Complement system protein C4 and susceptibility to hydralazine-induced systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 1989, 1, 922–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, E.; Dodds, A.W.; Goldin, A. Inhibition of the covalent binding reaction of complement component C4 by penicillamine, an antirheumatic agent. Biochem. J. 1989, 259, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sim, E.; Gill, E.W.; Sim, R.B. Drugs that induce systemic lupus erythematosus inhibit complement component C4. Lancet 1984, 2, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, R.L.; Curnutte, J.T. Metabolism of procainamide to the cytotoxic hydroxylamine by neutrophils activated in vitro. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 83, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasoo, S. Drug-induced lupus: An update. Lupus 2006, 15, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, C.; Bates, W.D.; Moosa, M.R. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis related to antituberculous drug therapy. Clin. Nephrol. 2010, 73, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, J.S. Allergic interstitial nephritis: Clinical features and pathogenesis. Q. J. Med. 1998, 66, 97–115. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, D.M.; Kelly, C.J. Acute interstitial nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1998, 9, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, E. Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Ren. Fail. 1998, 20, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Gershwin, M.E. Drugs and autoimmunity: A contemporary review and mechanistic approach. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, J266–J275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Chang, C. Diagnosis, and classification of drug-induced autoimmunity (DIA). J. Autoimmun. 2014, 48–49, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazella, M.A. Diagnosing drug-induced AIN in the hospitalized patient: A challenge for the clinician. Clin. Nephrol. 2014, 81, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Appel, G.B.; Garvey, G.; Silva, F.; Francke, E.; Neu, H.C.; Weissman, J. Acute interstitial nephritis due to amoxicillin therapy. Nephron 1981, 27, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, P.; D’Aleo, C.M.; Rigante, D.; Paolini Paoletti, F.; Zannoni, G.; Venuti, L.; Fundarò, C.; Rendeli, C.; Salvaggio, E. Amoxicillin-induced nephritis and tubulitis in a child. Urol. Int. 2003, 71, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praga, M.; González, E. Acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korinthenberg, R.; Wehrle, L.; Zimmerhackl, L.B. Renal tubular dysfunction following treatment with anti-epileptic drugs. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1994, 153, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, H.; Watanabe, T.; Abe, T. Tubulo-interstitial nephritis caused by sodium valproate. Brain Dev. 2002, 24, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijgenraam, J.W.; Buurke, E.J.; van der Laan, J.S. Carbamazepine-associated acute tubulointerstitial nephritis. Neth. J. Med. 1997, 50, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, A.; Assalie, N.A.; Gupta, R.K.; Del Pilar Morales, M.; Conti, R. A rare case of lamotrigine-induced acute interstitial nephritis. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2016, 6, 32976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bansal, A.D.; Hill, C.E.; Berns, J.S. Use of antiepileptic drugs in patients with chronic kidney disease and end stage renal disease. Semin. Dial. 2015, 28, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghane Shahrbaf, F.; Assadi, F. Drug-induced renal disorders. J. Renal. Inj. Prev. 2015, 4, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz, G.S.; Bomback, A.S.; Perazella, M.A. Drug-induced glomerular disease: Direct cellular injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mérida, E.; Praga, M. NSAIDs and Nephrotic Syndrome. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaughan, W.J.; Sheth, V.R.; Francos, G.C.; Michael, H.J.; Burke, J.F. Ranitidine-induced acute interstitial nephritis with epithelial cell foot process fusion. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1993, 22, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clive, D.M.; Stoff, J.S. Renal syndromes associated with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neugarten, J.; Gallo, G.R.; Baldwin, D.S. Rifampin-induced nephrotic syndrome and acute interstitial nephritis. Am. J. Nephrol. 1983, 3, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perazella, M.A.; Markowitz, G.S. Bisphosphonate nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Initial Labs | |
|---|---|
| Sodium | 134 mmol/L |
| Potassium | 4.1 mmol/L |
| Chloride | 102 mmol/L |
| Bicarbonate | 24 mmol/L |
| BUN | 41 mg/dL |
| Creatinine | 1.5 mg/dL (schwartz eGFR 40 mL/min/1.73 m2) |
| Albumin | 1.7 g/dL |
| White blood cell count | 7.6 × 109/L |
| Hemoglobin | 11.7 gm/dL |
| Platelet count | 443 × 109/L |
| ANCA | Negative |
| ASO | Negative |
| C-reactive protein | Normal |
| Uric acid | 3.7 mg/dL |
| Initial Labs | 2 Months Follow-Up | |
|---|---|---|
| ANA pattern | Homogeneous | Homogeneous |
| ANA Titer | 1:1280 | 1:160 |
| DNA Ab (dS) Crithidia, IFA | 1:2560 | 1:80 |
| ds DNA Ab, IgG ELISA, IU | 287 | 10 |
| Histone Ab, U | 8.5 | 1 |
| Myeloperoxidase Ab, AU/mL | 7 | |
| Proteinase 3 Ab, AU/mL | 7 | |
| Ribonucleic Protein Ab, ENA IgG | 6 | |
| Scleroderma (SCL-70) Ab, AU/mL | 10 | |
| SSA (Ro) IgG Ab, AU/mL | 5 | |
| SSB (La) (ENA) Ab IgG, AU/mL | 3 | |
| Smith Ab, IgG, AU/mL | 5 | |
| 25 hydroxy vitamin D, ng/mL | <7.0 | 9.39 |
| Albumin, gm/dL | 2.2 | 3.4 |
| C3 Complement, mg/dL | 94 | 104 |
| C4 Complement, mg/dL | 13 | 15 |
| IgG, KU/L | 1227 | |
| IgM, KU/L | 139 | |
| IgA, KU/L | 49 | |
| IgE, KU/L | 5811 | 3451 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aly, R.; Zeng, X.; Upadhyay, K. Drug-Induced Lupus Secondary to Ethosuximide in Association with Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Nephrotic Syndrome. Pediatr. Rep. 2022, 14, 190-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric14020026
Aly R, Zeng X, Upadhyay K. Drug-Induced Lupus Secondary to Ethosuximide in Association with Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Nephrotic Syndrome. Pediatric Reports. 2022; 14(2):190-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric14020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleAly, Rasha, Xu Zeng, and Kiran Upadhyay. 2022. "Drug-Induced Lupus Secondary to Ethosuximide in Association with Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Nephrotic Syndrome" Pediatric Reports 14, no. 2: 190-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric14020026
APA StyleAly, R., Zeng, X., & Upadhyay, K. (2022). Drug-Induced Lupus Secondary to Ethosuximide in Association with Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Nephrotic Syndrome. Pediatric Reports, 14(2), 190-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric14020026






