The Utility of Pharmacogenetic-Guided Psychotropic Medication Selection for Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Study Population
2.2. Pharmacogenetic Testing
2.3. Prescription Trends Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Medical Profile of the Study Cohort
3.2. Prescription Trends of Psychotropic Medications
3.3. Predictors of Severe Gene-Drug Interactions
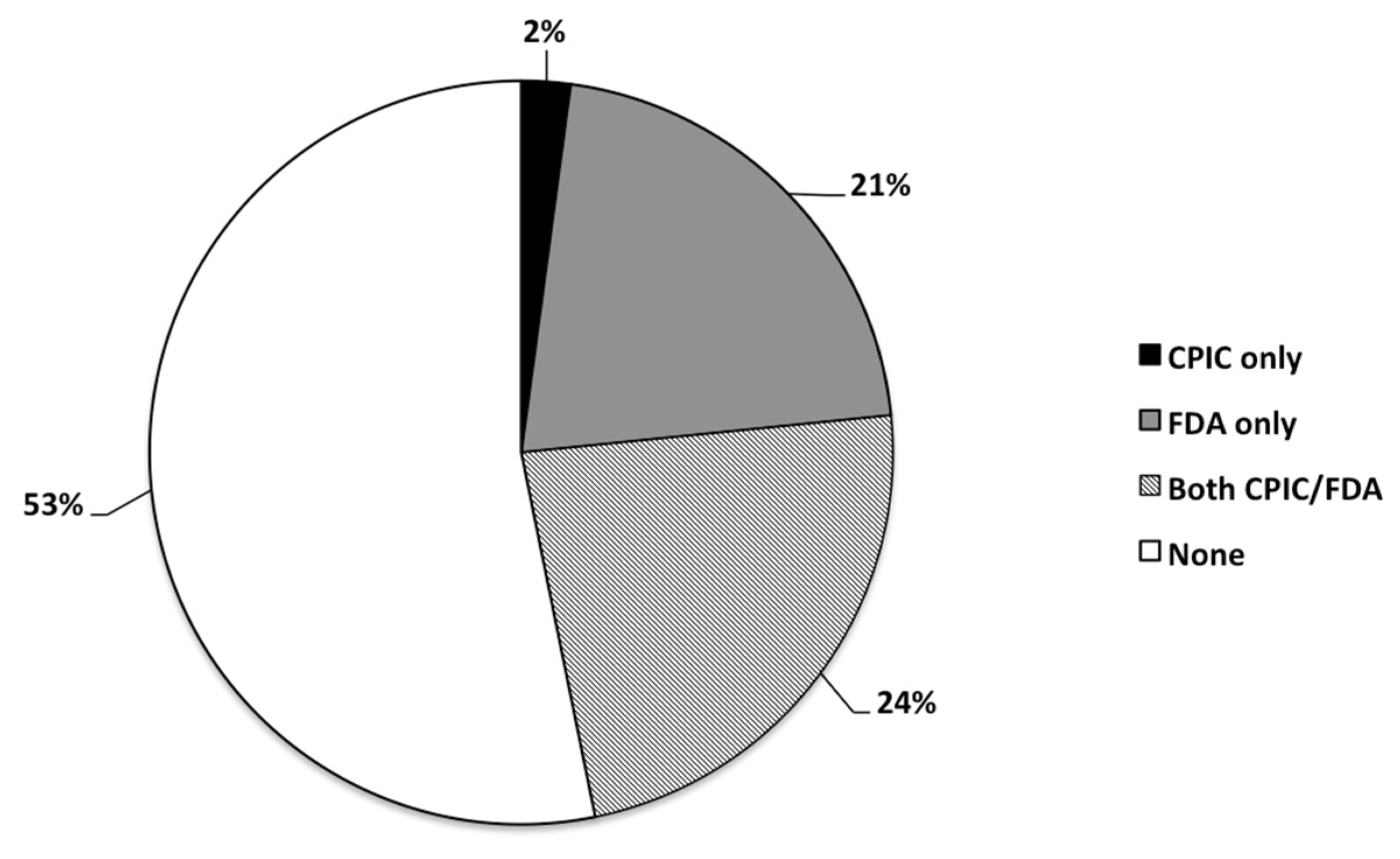
3.4. Psychotropic Medications with Pharmacogenetic Annotation
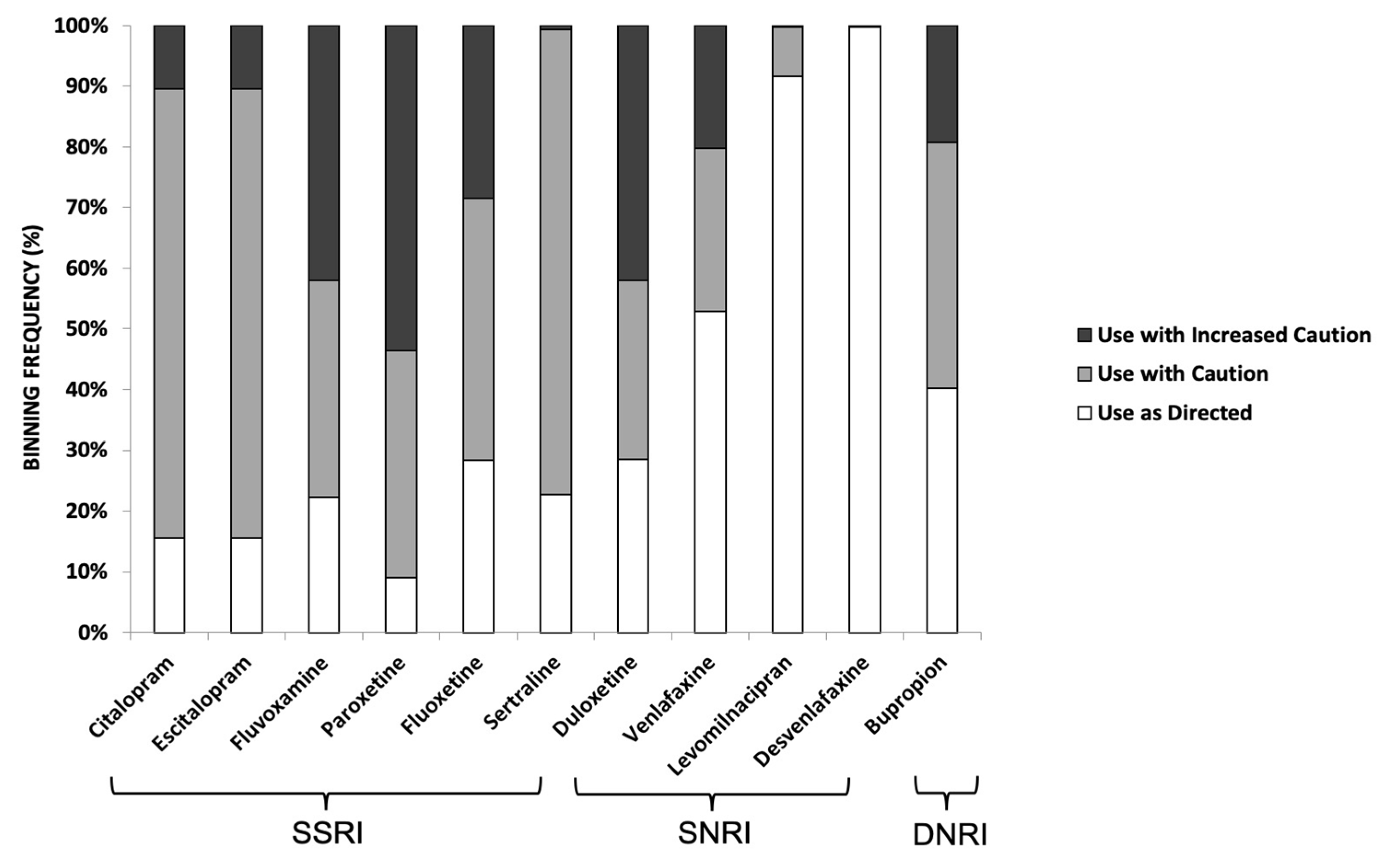
3.5. Pharmacogenetic Results for Antidepressants (SSRIs, SNRIs, DNRIs)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whitney, D.G.; Peterson, M.D. US National and State-Level Prevalence of Mental Health Disorders and Disparities of Mental Health Care Use in Children. JAMA Pediatrics 2019, 173, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielson, M.L.; Bitsko, R.H.; Ghandour, R.M.; Holbrook, J.R.; Kogan, M.D.; Blumberg, S.J. Prevalence of Parent-Reported ADHD Diagnosis and Associated Treatment Among U.S. Children and Adolescents, 2016. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2018, 47, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghandour, R.M.; Sherman, L.J.; Vladutiu, C.J.; Ali, M.M.; Lynch, S.E.; Bitsko, R.H.; Blumberg, S.J. Prevalence and Treatment of Depression, Anxiety, and Conduct Problems in US Children. J. Pediatr. 2019, 206, 256–267.e253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- CDC. Children’s Mental Health. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/childrensmentalhealth/data.html (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Tansey, K.E.; Guipponi, M.; Hu, X.; Domenici, E.; Lewis, G.; Malafosse, A.; Wendland, J.R.; Lewis, C.M.; McGuffin, P.; Uher, R. Contribution of common genetic variants to antidepressant response. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 73, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.; Shiekh, M.; Mehra, V.; Vrbicky, K.; Layle, S.; Olson, M.C.; Maciel, A.; Cullors, A.; Garces, J.A.; Lukowiak, A.A. Improved efficacy with targeted pharmacogenetic-guided treatment of patients with depression and anxiety: A randomized clinical trial demonstrating clinical utility. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 96, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Flavin, D.K.; Winner, J.G.; Allen, J.D.; Carhart, J.M.; Proctor, B.; Snyder, K.A.; Drews, M.S.; Eisterhold, L.L.; Geske, J.; Mrazek, D.A. Utility of integrated pharmacogenomic testing to support the treatment of major depressive disorder in a psychiatric outpatient setting. Pharm. Genom. 2013, 23, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenblat, J.D.; Lee, Y.; McIntyre, R.S. Does Pharmacogenomic Testing Improve Clinical Outcomes for Major Depressive Disorder? A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials and Cost-Effectiveness Studies. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2017, 78, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, X.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Fang, Y.; Guo, W.; Li, L. Preliminary Clinical Investigation of Combinatorial Pharmacogenomic Testing for the Optimized Treatment of Depression: A Randomized Single-Blind Study. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winner, J.G.; Carhart, J.M.; Altar, C.A.; Allen, J.D.; Dechairo, B.M. A prospective, randomized, double-blind study assessing the clinical impact of integrated pharmacogenomic testing for major depressive disorder. Discov. Med. 2013, 16, 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey, L.B.; Bishop, J.R.; Strawn, J.R. Pharmacogenetics of treating pediatric anxiety and depression. Pharmacogenomics 2019, 20, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramsey, L.B.; Prows, C.A.; Zhang, K.; Saldana, S.N.; Sorter, M.T.; Pestian, J.P.; Wenstrup, R.J.; Vinks, A.A.; Glauser, T.A. Implementation of Pharmacogenetics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center: Lessons Learned Over 14 Years of Personalizing Medicine. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2019, 105, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruf, A.A.; Greenslade, A.; Arnold, P.D.; Bousman, C. Antidepressant pharmacogenetics in children and young adults: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord 2019, 254, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CPIC. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC). Available online: https://cpicpgx.org/guidelines/ (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- Hines, R.N. Developmental expression of drug metabolizing enzymes: Impact on disposition in neonates and young children. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, S.L.; Poweleit, E.A.; Prows, C.A.; Martin, L.J.; Strawn, J.R.; Ramsey, L.B. Influence of CYP2C19 Metabolizer Status on Escitalopram/Citalopram Tolerability and Response in Youth With Anxiety and Depressive Disorders. Front. Pharm. 2019, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, J.R.; Najjar, F.; Rubin, L.H.; Guter, S.J.; Owley, T.; Mosconi, M.W.; Jacob, S.; Cook, E.H. Escitalopram pharmacogenetics: CYP2C19 relationships with dosing and clinical outcomes in autism spectrum disorder. Pharm. Genom. 2015, 25, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blasco-Fontecilla, H. Clinical utility of pharmacogenetic testing in children and adolescents with severe mental disorders. J. Neural Transm. 2019, 126, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haidar, C.E.; Relling, M.V.; Hoffman, J.M. Preemptively Precise: Returning and Updating Pharmacogenetic Test Results to Realize the Benefits of Preemptive Testing. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2019, 106, 942–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.T.; Ramsey, L.B.; Van Driest, S.L.; Aka, I.; Colace, S.I. Characterizing Pharmacogenetic Testing Among Children’s Hospitals. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudio-Campos, K.; Padrón, A.; Jerkins, G.; Nainaparampil, J.; Nelson, R.; Martin, A.; Wiisanen, K.; Smith, D.M.; Strekalova, Y.; Marsiske, M.; et al. Acceptability, Feasibility, and Utility of Integrating Pharmacogenetic Testing into a Child Psychiatry Clinic. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandritter, T.L.; Dinh, J.C.; Wagner, J.A.; Lowry, J.A. Description of an Innovative Pediatric Individualized Therapeutics Clinic: Working toward Precision Drug Therapy. Children 2019, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stutzman, D. Pharmacogenomic testing in child and adolescent psychiatry. Colo. J. Psychiatry Psychol. 2019, 3, 11–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wehry, A.M.; Ramsey, L.; Dulemba, S.E.; Mossman, S.A.; Strawn, J.R. Pharmacogenomic Testing in Child and Adolescent Psychiatry: An Evidence-Based Review. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2018, 48, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greden, J.F.; Parikh, S.V.; Rothschild, A.J.; Thase, M.E.; Dunlop, B.W.; DeBattista, C.; Conway, C.R.; Forester, B.P.; Mondimore, F.M.; Shelton, R.C.; et al. Impact of pharmacogenomics on clinical outcomes in major depressive disorder in the GUIDED trial: A large, patient- and rater-blinded, randomized, controlled study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 111, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblat, J.D.; Lee, Y.; McIntyre, R.S. The effect of pharmacogenomic testing on response and remission rates in the acute treatment of major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord 2018, 241, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelton, R.C.; Parikh, S.V.; Law, R.A.; Rothschild, A.J.; Thase, M.E.; Dunlop, B.W.; DeBattista, C.; Conway, C.R.; Forester, B.P.; Macaluso, M.; et al. Combinatorial Pharmacogenomic Algorithm is Predictive of Citalopram and Escitalopram Metabolism in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 290, 113017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, J.A.; Davies, P.E.; Voudouris, N.C.; Shahmirian, A.; Herbert, D.; Braganza, N.; Gugila, A.; Dechairo, B.M.; Kennedy, J.L. Combinatorial pharmacogenomics and improved patient outcomes in depression: Treatment by primary care physicians or psychiatrists. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 104, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inf. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jablonski, M.R.; King, N.; Wang, Y.; Winner, J.G.; Watterson, L.R.; Gunselman, S.; Dechairo, B.M. Analytical validation of a psychiatric pharmacogenomic test. Pers. Med. 2018, 15, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FDA. Table of Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers in Drug Labeling. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/science-and-research-drugs/table-pharmacogenomic-biomarkers-drug-labeling (accessed on 9 September 2020).
- APA. American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; APA: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Del Tredici, A.L.; Malhotra, A.; Dedek, M.; Espin, F.; Roach, D.; Zhu, G.D.; Voland, J.; Moreno, T.A. Frequency of CYP2D6 Alleles Including Structural Variants in the United States. Front. Pharm. 2018, 9, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strom, C.M.; Goos, D.; Crossley, B.; Zhang, K.; Buller-Burkle, A.; Jarvis, M.; Quan, F.; Peng, M.; Sun, W. Testing for variants in CYP2C19: Population frequencies and testing experience in a clinical laboratory. Genet. Med. 2012, 14, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, L.; Eum, S.; Haga, S.B.; Strawn, J.R.; Zierhut, H. Clinical Utilization of Pharmacogenetics in Psychiatry—Perspectives of Pharmacists, Genetic Counselors, Implementation Science, Clinicians, and Industry. Pharmacopsychiatry 2020, 53, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousman, C.; Maruf, A.A.; Muller, D.J. Towards the integration of pharmacogenetics in psychiatry: A minimum, evidence-based genetic testing panel. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2019, 32, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.T.; Bishop, J.R.; Sangkuhl, K.; Nurmi, E.L.; Mueller, D.J.; Dinh, J.C.; Gaedigk, A.; Klein, T.E.; Caudle, K.E.; McCracken, J.T.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Cytochrome P450 (CYP)2D6 Genotype and Atomoxetine Therapy. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2019, 106, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hicks, J.K.; Sangkuhl, K.; Swen, J.J.; Ellingrod, V.L.; Muller, D.J.; Shimoda, K.; Bishop, J.R.; Kharasch, E.D.; Skaar, T.C.; Gaedigk, A.; et al. Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants: 2016 update. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 102, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bousman, C.A.; Hopwood, M. Commercial pharmacogenetic-based decision-support tools in psychiatry. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousman, C.A.; Dunlop, B.W. Genotype, phenotype, and medication recommendation agreement among commercial pharmacogenetic-based decision support tools. Pharm. J. 2018, 18, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Flavin, D.K.; Winner, J.G.; Allen, J.D.; Jordan, J.J.; Nesheim, R.S.; Snyder, K.A.; Drews, M.S.; Eisterhold, L.L.; Biernacka, J.M.; Mrazek, D.A. Using a pharmacogenomic algorithm to guide the treatment of depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kennard, B.D.; Emslie, G.J.; Mayes, T.L.; Nightingale-Teresi, J.; Nakonezny, P.A.; Hughes, J.L.; Jones, J.M.; Tao, R.; Stewart, S.M.; Jarrett, R.B. Cognitive-behavioral therapy to prevent relapse in pediatric responders to pharmacotherapy for major depressive disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2008, 47, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corponi, F.; Fabbri, C.; Serretti, A. Pharmacogenetics and Depression: A Critical Perspective. Psychiatry Investig. 2019, 16, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubovsky, S.L. The Limitations of Genetic Testing in Psychiatry. Psychother. Psychosom. 2016, 85, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.J.; Mummaneni, P.; Kim, I.W.; Oh, J.M.; Pacanowski, M.; Burckart, G.J. Pharmacogenomic information in FDA-approved drug labels: Application to pediatric patients. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2016, 99, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. The FDA Warns against the Use of Many Genetic Tests with Unapproved Claims to Predict Patient Response to Specific Medications: FDA Safety Communication. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/fda-warns-against-use-many-genetic-tests-unapproved-claims-predict-patient-response-specific#actions (accessed on 9 September 2020).
- FDA. FDA Issues Warning Letter to Genomics Lab for Illegally Marketing Genetic Test that Claims to Predict Patients’ Responses to Specific Medications. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-issues-warning-letter-genomics-lab-illegally-marketing-genetic-test-claims-predict-patients (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- ISPG. Genetic Testing Statement. Available online: https://ispg.net/genetic-testing-statement/ (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Liko, I.; Lee, Y.M.; Stutzman, D.L.; Blackmer, A.B.; Deininger, K.M.; Reynolds, A.M.; Aquilante, C.L. Providers’ perspectives on the clinical utility of pharmacogenomic testing in pediatric patients. Pharmacogenomics 2021, 22, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, L.; Butler, R.; Wheeler, A.; Pulford, J.; Miles, W.; Sheridan, J. Clinician experiences of employing the AmpliChip(R) CYP450 test in routine psychiatric practice. J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoop, J.G.; Lapid, M.I.; Paulson, R.M.; Roberts, L.W. Clinical and ethical considerations in pharmacogenetic testing: Views of physicians in 3 “early adopting” departments of psychiatry. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2010, 71, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishko, I.; Almeida, K.; Silvia, R.J.; Tataronis, G.R. Psychiatric pharmacists’ perception on the use of pharmacogenomic testing in the mental health population. Pharmacogenomics 2015, 16, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.; Steven, P.H.; Catriona, H. Psychiatrist attitudes towards pharmacogenetic testing, direct-to-consumer genetic testing, and integrating genetic counseling into psychiatric patient care. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 226, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.Y.; Chua, B.Y.; Subramaniam, M.; Suen, E.L.; Lee, J. Clinicians’ perceptions of pharmacogenomics use in psychiatry. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregornik, D.; Salyakina, D.; Brown, M.; Roiko, S.; Ramos, K. Pediatric pharmacogenomics: Challenges and opportunities: On behalf of the Sanford Children’s Genomic Medicine Consortium. Pharm. J. 2021, 21, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichmeyer, J.; Rogers, S.; Formea, C.M.; Giri, J.; Jones, J.S.; Schnettler, E.; Schmidlen, T.; Glogowski, E.; Kurz, R.N. Parc Report: A Perspective on the State of Clinical Pharmacogenomics Testing. Pharmacogenomics 2020, 21, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Empey, P.E.; Pratt, V.M.; Hoffman, J.M.; Caudle, K.E.; Klein, T.E. Expanding Evidence Leads to New Pharmacogenomics Payer Coverage. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 830–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Healthcare. Pharmacogenetic Testing. Available online: https://www.uhcprovider.com/content/dam/provider/docs/public/policies/medicaid-comm-plan/pharmacogenetic-testing-cs.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Tanner, J.A.; Davies, P.E.; Overall, C.C.; Grima, D.; Nam, J.; Dechairo, B.M. Cost-Effectiveness of Combinatorial Pharmacogenomic Testing for Depression from the Canadian Public Payer Perspective. Pharmacogenomics 2020, 21, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitropoulou, C.; Litinski, V.; Kabakchiev, B.; Rogers, S.; Patrinos, G. Parc Report: Health Outcomes and Value of Personalized Medicine Interventions: Impact on Patient Care. Pharmacogenomics 2020, 21, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Result |
|---|---|
| Age (in years)—mean (SD) | 12 (4.3) |
| Male—n (%) | 289 (64) |
| Race—n (%) | |
| White/Caucasian | 340 (76) |
| Other | 33 (7) |
| Multi-racial | 29 (6) |
| Unknown/Not reported | 24 (5) |
| Black/African American | 14 (3) |
| Asian | 10 (2) |
| Ethnicity—n (%) | |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 362 (81) |
| Hispanic or Latino | 54 (12) |
| Unknown/Not reported | 34 (8) |
| Mental health diagnosis—n (%) | |
| Anxiety Disorder | 199 (44) |
| ADHD a | 172 (38) |
| ASD a | 156 (35) |
| Any Mood Disorder | 144 (32) |
| Other Depressive Disorder | 114 (25) |
| MDD a | 67 (15) |
| No. of patients with concurrent psychiatric diagnoses—n (%) | |
| 1 diagnosis | 176 (39) |
| 2 diagnoses | 189 (42) |
| 3 diagnoses | 81 (18) |
| ≥4 diagnoses | 4 (0.9) |
| Generic Name | Medication Type | Prescribing Frequency (%) | Guideline | Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guanfacine | ADHD Medication | 49.9 | None | None |
| Sertraline | Antidepressant | 43.0 | CPIC | CYP2C19 |
| Risperidone | Antipsychotic | 34.9 | FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Methylphenidate | ADHD Medication | 33.3 | None | None |
| Aripiprazole | Antipsychotic | 32.6 | FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Fluoxetine | Antidepressant | 29.4 | FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Mixed amphetamine salts | ADHD Medication | 25.3 | None | None |
| Lamotrigine | Mood stabilizer | 18.9 | None | None |
| Atomoxetine | ADHD Medication | 16.3 | CPIC, FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Lisdexamfetamine | ADHD Medication | 14.9 | None | None |
| Citalopram | Antidepressant | 14.7 | CPIC, FDA | CYP2C19, CYP2D6 |
| Trazodone | Antidepressant | 14.7 | None | None |
| Quetiapine | Antipsychotic | 14.5 | None | None |
| Dexmethylphenidate | ADHD Medication | 13.3 | None | None |
| Escitalopram | Antidepressant | 12.6 | CPIC, FDA | CYP2C19, CYP2D6 |
| Valproic acid | Mood stabilizer | 9.0 | FDA | POLG |
| Olanzapine | Antipsychotic | 8.3 | None | None |
| Topiramate | Mood stabilizer | 8.3 | None | None |
| Venlafaxine | Antidepressant | 8.3 | FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Bupropion | Antidepressant | 7.6 | None | None |
| Desvenlafaxine | Antidepressant | 7.4 | FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Oxcarbazepine | Mood stabilizer | 7.4 | CPIC, FDA | HLA-B*1502 |
| Gabapentin | Mood stabilizer | 6.9 | None | None |
| Clonidine | ADHD Medication | 6.5 | None | None |
| Lithium | Mood stabilizer | 6.4 | None | None |
| Amitriptyline | Antidepressant | 5.5 | CPIC, FDA | CYP2C19, CYP2D6 |
| Lurasidone | Antipsychotic | 4.1 | None | None |
| Ziprasidone | Antipsychotic | 3.7 | None | None |
| Duloxetine | Antidepressant | 2.8 | FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Fluvoxamine | Antidepressant | 2.5 | CPIC, FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Dextroamphetamine | ADHD Medication | 2.1 | None | None |
| Mirtazapine | Antidepressant | 1.8 | None | None |
| Asenapine | Antipsychotic | 1.6 | None | None |
| Carbamazepine | Mood stabilizer | 1.2 | CPIC, FDA | HLA-B*1502, HLA-A*3101 |
| Vilazodone | Antidepressant | 0.9 | None | None |
| Clomipramine | Antidepressant | 0.7 | CPIC, FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Paliperidone | Antipsychotic | 0.7 | None | None |
| Clozapine | Antipsychotic | 0.5 | FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Imipramine | Antidepressant | 0.5 | CPIC, FDA | CYP2D6, CYP2C19 |
| Doxepin | Antidepressant | 0.2 | CPIC, FDA | CYP2C19, CYP2D6 |
| Haloperidol | Antipsychotic | 0.2 | None | None |
| Iloperidone | Antipsychotic | 0.2 | FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Levomilnacipran | Antidepressant | 0.2 | None | None |
| Paroxetine | Antidepressant | 0.2 | CPIC, FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Perphenazine | Antipsychotic | 0.2 | FDA | CYP2D6 |
| Selegiline | Antidepressant | 0.2 | None | None |
| Thiothixene | Antipsychotic | 0.2 | None | None |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ariefdjohan, M.; Lee, Y.M.; Stutzman, D.L.; LeNoue, S.; Wamboldt, M.Z. The Utility of Pharmacogenetic-Guided Psychotropic Medication Selection for Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective Study. Pediatr. Rep. 2021, 13, 421-433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric13030049
Ariefdjohan M, Lee YM, Stutzman DL, LeNoue S, Wamboldt MZ. The Utility of Pharmacogenetic-Guided Psychotropic Medication Selection for Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective Study. Pediatric Reports. 2021; 13(3):421-433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric13030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleAriefdjohan, Merlin, Yee Ming Lee, Danielle L. Stutzman, Sean LeNoue, and Marianne Z. Wamboldt. 2021. "The Utility of Pharmacogenetic-Guided Psychotropic Medication Selection for Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective Study" Pediatric Reports 13, no. 3: 421-433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric13030049
APA StyleAriefdjohan, M., Lee, Y. M., Stutzman, D. L., LeNoue, S., & Wamboldt, M. Z. (2021). The Utility of Pharmacogenetic-Guided Psychotropic Medication Selection for Pediatric Patients: A Retrospective Study. Pediatric Reports, 13(3), 421-433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric13030049





