Abstract
Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) is highly infective in poultry, causing significant economic losses to the poultry industry. As an extraintestinal pathogenic strain, adherence is a critical step in the infection. The functions of several adhesins, including type I, P, and Curli fimbriae, have been extensively studied. However, the roles of other adhesins, like Sfm, remain largely unexplored. Sfm is widely present in E. coli. Although the Sfm cluster is an ortholog of the fim gene cluster of Salmonella type I fimbriae, the biological function of Sfm in APEC has not yet been elucidated. To investigate whether Sfm in APEC CE129 plays a role in virulence, in this study, we constructed recombinant strains by expressing Sfm in the fimbriae-deficient strain SE5000. Additionally, a CE129 sfmA mutant strain was constructed. The resulting changes in adherence, biofilm formation, resistance to macrophage phagocytosis, and resistance to serum bactericidal ability were observed. The adherence ability of CE129ΔsfmA was reduced by 41%. HD-11 cells demonstrated a 30% increase in the phagocytosis of CE129ΔsfmA, and a 50% reduction in SE5000 (pBR322-sfm). The sfm deletion mutant showed a 23.9% reduction in the resistance to serum bactericidal ability, while SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) displayed a 32% increase. SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) exhibited a 34% increase in biofilm formation, and CE129ΔsfmA demonstrated a 21% decrease. Real-time PCR was employed to examine the impact of Sfm deletion on the transcription level of key virulence factors (fimA, fliC, papC, tsh, ompA, and iss). The results indicated that Sfm in CE129 is closely associated with bacterial adherence and survivability, contributing to biofilm formation and influencing the expression of key virulence factors. This study yields initial insight into the functional roles of Sfm in APEC and provides a foundation for the effective control of E. coli in the poultry industry.
1. Introduction
Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) causes various diseases in poultry, including pericarditis, perihepatitis, peritonitis, airsacculitis, and septicemia, leading to severe economic losses in the poultry industry. As an extraintestinal pathogenic strain, APEC effectively utilizes adhesins to adhere and to invade host cells, as the primary step in infection. Adhesins are bacterial structural proteins with adhesive functions, including fimbriae and non-fimbrial adhesins such as outer membrane proteins (OMPs) [1,2]. Fimbriae are short, straight, filamentous structures densely distributed on the surface of certain bacteria that promote the invasion and enhance biofilms. Common fimbrial adhesins in APEC include type I, P, and Curli fimbriae. A study demonstrated that type I fimbriae were essential for APEC colonization of avian respiratory epithelial cells [3], while further pathogenic actions depended on P fimbriae [4]. E. coli flagella and other adhesins not only aid in adherence but also interfere with host immune signaling pathways, thereby enhancing bacterial survival [5,6].
Researchers have recently discovered a type of fimbriae in E. coli known as Sfm that is homologous with Salmonella type I fimbriae, sharing highly similar gene clusters [7,8]. The sfm operon encodes the proteins responsible for the synthesis and assembly of Sfm [9]. Compared to type I fimbriae, Sfm in E. coli exhibits greater sequence homology with Salmonella type I fimbriae, but their functions remain unclear [10]. Korea et al. introduced a lac Z reporter gene at the Sfm locus of E. coli K-12ΔlacIZ and constructed a deletion mutant to explore the expression and virulence [11]. The results indicated that even under optimized culture conditions, the expression of Sfm remained extremely low. Due to its sparse expression in vitro, current studies have not comprehensively explored the biological characteristics of Sfm. Whether it plays a role in APEC pathogenesis requires further investigation. Understanding the functions of Sfm in APEC will provide a basis for characterizing virulence factors in extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli and their pathogenic mechanisms, thereby contributing to research aimed at controlling E. coli infections.
APEC CE129 possesses a variety of significant biological characteristics, including the ability to form biofilms and adhere to chicken embryo fibroblasts [11]. In this study, CE129 was chosen as the reference strain. The complete Sfm structural gene operon (excluding sfmZ) of CE129 was cloned and inserted into the engineered fimbriae-deficient E. coli SE5000 [12], enabling the soluble, non-inducible expression of Sfm. The sfmA gene encoding the subunit of Sfm in CE129 was then knocked out by λ-Red recombination technology. Using these two groups of recombinant strains, this study explored the differences in adherence, resistance to phagocytosis, to serum bactericidal capacity, and biofilm formation, investigating the functions and pathogenic roles of Sfm. Data from this research will deepen our understanding of APEC pathogenic mechanisms and support the development of effective control strategies for APEC in poultry farms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Cell Lines
The strains and plasmids are listed in Table 1. LB broth or LB agar plates were used for bacterial growth. APEC CE129 [12], SE5000 [13], plasmids pKD46, pKD3, and pCP20 [14], the chicken embryo fibroblast cell line DF-1 [15], the avian macrophage-like cell line HD-11 [15], and the SfmH polyclonal antibody were all preserved in our laboratory. Cell lines were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Penicillin (Amp+, 100 μg/mL) or chloramphenicol (Cm+, 34 μg/mL) (Yuanye Bio-Technology, Shanghai, China) was added as required.

Table 1.
Strains and plasmids used in this study.
2.2. Construction of Recombinant Strains
The complete sfm operon (excluding the regulatory gene sfmZ) was amplified from APEC CE129 genomic DNA using primers sfm-Operon-F and sfm-Operon-R (Table 2). The PCR product was ligated into the pBR322 vector at the NheI and SalI restriction sites. The recombinant plasmid pBR322-sfm was transformed into the fimbriae-deficient E. coli SE5000 strain via electroporation. Transformants were selected on LB agar containing ampicillin (Amp+, 100 μg/mL). Positive clones were confirmed by PCR amplification and sequencing of the sfm operon. The recombinant SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) was constructed. The empty plasmid pBR322 was transformed into SE5000 to construct the negative control strain SE5000 (pBR322). All primers were synthesized by Tsingke Biotechnology (Beijing, China).

Table 2.
Primers used in this study.
An additional set of recombinant strains was constructed. The sfmA gene was inactivated using λ-Red recombination technology [14]. A chloramphenicol resistance cassette (cat) was amplified from plasmid pKD3 using primers ΔsfmA-1 and ΔsfmA-2, which contained 50 bp homology arms flanking the sfmA gene. The PCR product was electroporated into CE129 harboring the helper plasmid pKD46. Recombinants were selected on LB agar containing chloramphenicol (Cm+, 34 μg/mL). The cat cassette was subsequently excised by transforming the mutant with plasmid pCP20 (encoding Flp recombinase), resulting in the markerless deletion mutant CE129ΔsfmA. The mutant was verified by PCR (using primers sfmA-1/sfmA-2) and DNA sequencing. The open reading frame (ORF) of sfmA was amplified with the sfmA-1/sfmA-2 primers (Table 2), and subsequently ligated onto the pBR322 plasmid to construct the plasmid pBR-sfmA. This plasmid was transformed into the CE129ΔsfmA mutant, successfully creating the complemented strain CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA.
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Observation
The following experiment was performed as described previously [16]. Bacterial cultures were grown statically in LB broth at 37 °C for 24 h. Cells were washed twice with PBS buffer. A small aliquot of bacterial suspension was applied to copper grids and allowed to adhere for 10 min. Excess liquid was gently removed with filter paper. Samples were negatively stained with 1% phosphotungstic acid (pH 7.4) for 5 min, then immediately blotted dry with filter paper. Finally, grids were dried under a lamp at 65 °C prior to observation using an FEI Tecnai T12 TEM (FEI, Hillsboro, OR, USA). CE129 was used as the positive control, and SE5000 (pBR322) was used as the negative control.
2.4. Sfm Fimbrial Extraction and Validation
The following experiment was performed as described previously [17]. The fimbrial proteins were extracted using a heat-shock extraction method. Extracted proteins were determined by SDS-PAGE and a Western blot analysis in SE5000 (pBR322-sfm).
2.5. Growth Curve Assays
SE5000, SE5000 (pBR322-sfm), SE5000 (pBR322), CE129, CE129ΔsfmA, and CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA were inoculated into LB and cultured at 37 °C. Aliquots were taken at various time points, and the absorbance at OD600 was measured using an Epoch spectrophotometer (BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA) [18].
2.6. Serum Bactericidal Assays
Serum bactericidal assays were performed as previously described [15]. A 50 μL aliquot of bacterial suspension was added to 450 μL of fresh SPF chicken serum (Huaen, Nanjing, China), mixed thoroughly, and incubated undisturbed at 37 °C for four hours. The bacterial suspensions were serially diluted and plated for colony counting.
2.7. Bacterial Adherence Assays
The following experiment was performed as described previously [16,19]. Overnight cultures of bacteria were diluted 1:100 in fresh LB broth and grown to mid-log phase (OD600 ≈ 0.6). Cells were harvested by centrifugation (4000× g, 10 min), washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4), and resuspended in PBS. Monolayers of DF-1 chicken embryo fibroblast cells (≈105 cells/well in 96-well plates) were washed with PBS. A 100 μL aliquot of bacterial suspension (107 CFU) was added to each well and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. Non-adherent bacteria were removed by washing three times with PBS. Cells were lysed with 0.5% (v/v) Triton X-100 (Huaen, Nanjing, China) in PBS for 30 min. Serial dilutions of the lysate were plated on LB agar for CFU enumeration.
2.8. Chicken Macrophage Engulfment and Survival Assays
Bacteria were prepared as described in Section 2.7 HD-11 avian macrophage-like cells (≈105 cells/well) were infected with bacteria at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 100:1 [15,20,21]. After 1.5 h of co-incubation at 37 °C in 5% CO2, extracellular bacteria were removed by washing three times with PBS. Cells were treated with gentamicin (Yuanye Bio-Technology, Shanghai, China) (100 μg/mL in DMEM) for 1 h to kill residual extracellular bacteria. After gentamicin treatment, cells were washed with PBS and lysed with 0.5% Triton X-100. Serial dilutions of the lysate were plated to quantify viable intracellular bacteria (CFU).
2.9. Biofilm Formation Assays
Six strains were seeded on biofilm-inducing media in 96-well plates as previously described [16]. The OD600 values of each well were recorded (Epoch, BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA) to measure the amount of biofilm production using a crystal violet staining method.
2.10. mRNA Level of Important Virulence Factors
A Tiangen RNA Extraction Kit (DP419) was used to prepare RNA samples. The primers for virulence-related genes (fimA, fliC, papC, tsh, ompA, iss, ish) are listed in Table 2. The gapA was used as a housekeeping gene. SYBR® Premix Ex Taq II (Takara, Shiga, Japan) and ABI 7500 Real-Time System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) were used for subsequent experiments. Data were analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCT method [22,23].
2.11. Statistical Analyses
All experiments were performed in triplicate with three technical replicates per condition. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). For comparisons between two groups, Student’s t-test was used. For comparisons involving three or more groups, a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied followed by Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05. Analyses were performed using the SPSS software package version 25.0.
3. Results
3.1. Construction of Recombinant Strains
The amplified 5.6 kb sfm operon was ligated into the pBR322 plasmid and transformed into SE5000, resulting in the successful construction of SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) (Figure S1). The construction was confirmed through PCR amplification and the sequencing of the sfm operon (Tsingke Biotechnology). TEM was used to observe the presence of fimbriae on the surface of SE5000 (pBR322-sfm). Dense fimbrial structures were observed on the surface of CE129, whereas no significant fimbriae were detected on the surface of SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) (Figure 1). After fimbriae extraction and enrichment using the heat-shock method, SDS-PAGE revealed protein bands at 20 kDa and 35 kDa, corresponding to the main structural subunit SfmA and the fimbrial tip SfmH, respectively. A Western blot analysis further confirmed that the 35 kDa band was recognized by the SfmH polyclonal antibody (Figure S2). The results verified the expression of Sfm in SE5000 (pBR322-sfm).
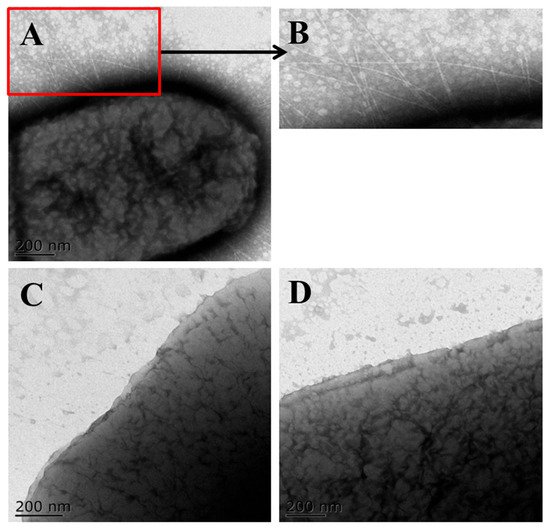
Figure 1.
TEM observation of fimbriae expression. (A) TEM images of CE129; (B) enlarged image of CE129 fimbriae; (C) TEM images of SE5000 (pBR322-sfm); (D) TEM images of SE5000 (pBR322).
The deletion mutant CE129ΔsfmA and complemented strain CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA were constructed and confirmed by sequencing (Figure S1).
The growth curves showed no significant differences in the growth characteristics of SE5000, SE5000 (pBR322-sfm), SE5000 (pBR322), CE129, CE129ΔsfmA, or CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA during the growth phases (Figure S3).
3.2. Bacterial Adhesion Assays
For SE5000, SE5000 (pBR322-sfm), and SE5000 (pBR322), there was no significant difference in adherence ability toward DF-1 cells (p > 0.05) (Figure 2A).
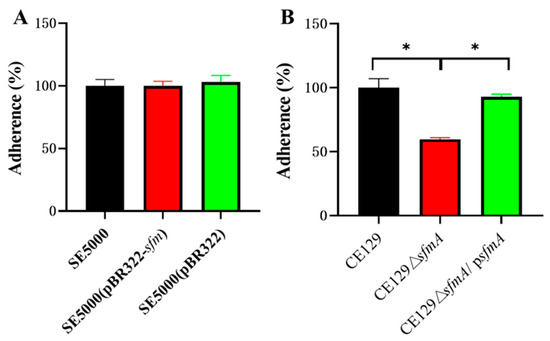
Figure 2.
Adherence assay. (A) Adherence of SE5000, SE5000 (pBR322), and SE5000 (pBR322-sfm). Y-axes indicate the ratio of average adhered CFU compared with CFU in SE5000. (B) Adherence of CE129, CE129ΔsfmA, and CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA. Y-axes indicate the ratio of average adhered CFU compared with CE129. * indicates significantly different values (p < 0.05).
The adherence ability of CE129ΔsfmA was reduced by 41% compared to CE129 (p < 0.01) (Figure 2B). Adherence ability was partially restored in CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA.
3.3. Bacterial Survival-Related Assays
This study explored the possible influence of Sfm on bacterial survival using macrophage engulfment and survival assays, serum bactericidal assays, and biofilm formation assays.
For SE5000, SE5000 (pBR322-sfm), and SE5000 (pBR322), HD-11 cells exhibited a 50% reduction in their phagocytosis of the recombinant strain SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) compared to the phagocytosis of SE5000 and SE5000 (pBR322) (p < 0.01) (Figure 3A).
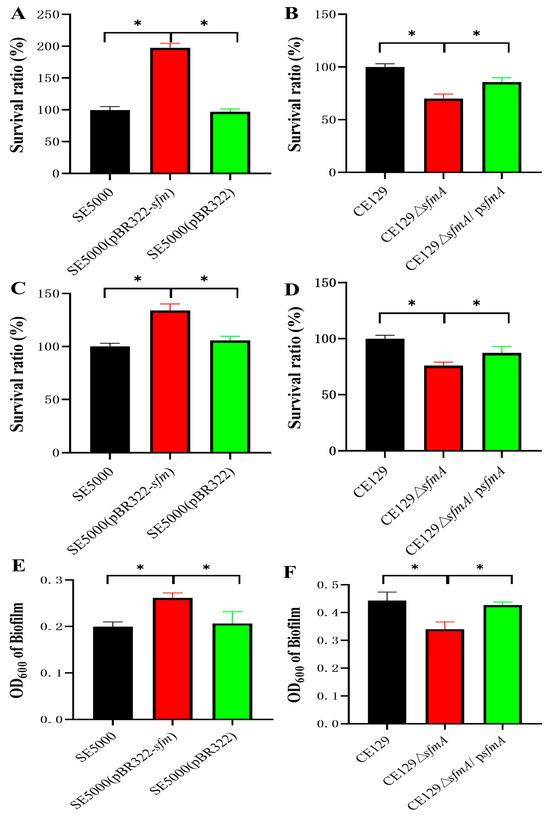
Figure 3.
Effect of Sfm on survival ability. (A) Survival ratio of SE5000, SE5000 (pBR322), and SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) in HD11 engulfment experiments. Y-axes indicate the ratio of average survival CFU compared with SE5000. (B) Survival ratio of CE129, CE129ΔsfmA, and CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA in HD11 engulfment experiments. Y-axes indicate the ratio of average survival CFU compared with CE129. (C) Survival ratio of SE5000, SE5000 (pBR322), and SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) in SPF chicken serum sterilization experiments. Y-axes indicate the ratio of average survival CFU compared with SE5000. (D) Survival ratio of CE129, CE129ΔsfmA, and CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA in SPF chicken serum sterilization experiments. Y-axes indicate the ratio of average survival CFU compared with CE129. (E,F) Qualitative analyses of biofilm formation. Results of the crystal violet method were observed at OD600. * indicates significantly different values (p < 0.05).
For CE129, CE129ΔsfmA, and CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA, HD-11 cells demonstrated a 30% increase in their phagocytosis of CE129ΔsfmA compared to the phagocytosis of CE129 (p < 0.01). The survival of bacteria within macrophages was partially restored in CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA (Figure 3B).
In the serum bactericidal assay, the survival rates of SE5000, SE5000 (pBR322-sfm), and SE5000 (pBR322) were 100%, 132%, and 105%, respectively (Figure 3C).
The survival rates of CE129, CE129ΔsfmA, and CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA were 100%, 76.1%, and 87%, respectively, with the deletion mutant showing a 23.9% reduction in the resistance to serum bactericidal ability (p < 0.05) (Figure 3D).
3.4. Relative mRNA Expression Levels
The changes in the transcription levels of key virulence genes (fimA, fliC, papC, tsh, ompA, and iss) in CE129 under the influence of Sfm were analyzed using fluorescence RT-qPCR. The deletion of Sfm led to transcription reductions of 40% (fimA), 23% (fliC), 43% (papC), 21% (ompA), and 18% (iss), while the transcription level of tsh was unaffected (p > 0.05). The transcription levels of these genes were partially or fully restored in CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA (Figure 4).
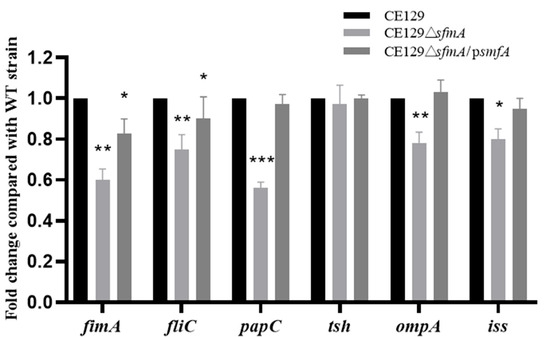
Figure 4.
Relative transcript abundances of virulence factors genes. Relative transcript abundances of fimA, fliC, papC, tsh, ompA, and iss. *, **, and *** indicate significantly different gene levels compared with CE129 (p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
Sfm fimbriae occur in common pathogenic E. coli strains such as enterotoxigenic E. coli, APEC, and uropathogenic E. coli as well as in non-pathogenic E. coli. A previous study investigated the presence and virulence of Sfm in K-12 [11]. They observed an extremely low expression of Sfm, which was related to the expression of virulence factors such as type I fimbriae. However, no study has explored the function of Sfm in APEC, a significant pathogen in the poultry industry causing substantial economic losses. Given the prevalence of Sfm across diverse E. coli pathotypes and its potential role in adhesion, a key virulence trait, elucidating its function in APEC pathogenesis represents a critical knowledge gap. Therefore, we constructed two complementary sets of recombinant APEC strains for a targeted functional investigation of Sfm fimbriae: a gain-of-function model expressing Sfm in a fimbriae-deficient background and a loss-of-function model through specific gene deletion in the pathogenic CE129 strain.
The Sfm gene sequence is conserved and complete, with its fimbrial operon containing genes of the essential subunit proteins, chaperones, usher protein, and adhesins [24]. This operon structure suggests functional capability for fimbrial assembly and surface expression [25]. The sequence homology, particularly with the well-characterized Salmonella type I fimbriae operon, further supports the potential functional relevance of Sfm. The entire sfm operon, except for the regulatory sfmZ, was cloned, resulting in the successful construction of SE5000 (pBR322-sfm). The TEM failed to detect fimbriae on the surface of the recombinant strain, consistent with the observation of a low expression level of Sfm in K-12. This represents a technical limitation of our study, as the lack of visible surface structures conflicts with biochemical evidence of Sfm expression. This highlights a potential intrinsic limitation in expression regulation or surface assembly under standard laboratory conditions and underscores the necessity for highly sensitive detection methods. A modified heat shock method successfully extracted fimbrial proteins from the recombinant strain, which was confirmed via Western blotting, yet definitive surface localization requires advanced methods like immunogold labeling or flow cytometry with Sfm-specific antibodies in future investigations. WB validation confirmed the functional expression and assembly of Sfm components despite the lack of visible surface structures detected by TEM. Strains utilized for the Sfm investigation included the SE5000 parental strain inherently devoid of fimbriae, the Sfm-expressing SE5000 (pBR322-sfm), and SE5000 (pBR322), containing the empty plasmid as a vector control. Additionally, the wild-type APEC CE129 (possessing native Sfm among other potential adhesins), the isogenic deletion mutant CE129ΔsfmA, and the genetically complemented strain CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA were employed. Growth curve analyses confirmed that plasmid carriage or the sfmA deletion did not significantly alter the in vitro growth kinetics of any strain, indicating that the observed phenotypic differences in subsequent assays were attributable to the presence or absence of functional Sfm and not general growth defects.
Upon ingestion by poultry, pathogenic APEC must adhere to the epithelial cells lining the respiratory tract or other mucosal surfaces via specific adhesins [26]. This adherence is the critical initial step preceding the penetration of the mucosal epithelium and subsequent entry into the bloodstream to establish systemic infection [1,2,27]. While it is generally accepted that APEC primarily relies on type I and P fimbriae for adherence to host tissues [28], the contribution of other fimbrial systems like Sfm remains less defined. Previous studies demonstrated that Sfm expression could enhance the adherence of E. coli K-12 to bladder epithelial cells by approximately 10-fold [11]. However, the relevance of this finding to APEC pathogenesis in its natural avian host context was unknown. In the present study, SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) did not exhibit a statistically significant increase in adherence to chicken embryo fibroblast (DF-1) cells compared to SE5000 or SE5000 (pBR322) (Figure 2A). This lack of effect in the heterologous expression system is likely attributable to the persistently low levels of surface-localized Sfm fimbriae, as evidenced by TEM, or potential failures in the proper localization or functional display of the adhesin tip protein SfmH on the SE5000 surface. We acknowledge this discrepancy remains mechanistically unresolved in our current work. While likely attributable to low surface expression levels or improper adhesin localization in the heterologous system, definitive confirmation would require a comparative analysis of membrane fractions through surface protein extraction and Western blotting to quantify Sfm subunit localization efficiency. Crucially, however, the adherence of the pathogenic CE129ΔsfmA mutant to DF-1 cells was significantly decreased by 41% compared to the wild-type CE129 (p < 0.01), a substantial reduction highlighting the functional importance of Sfm in the context of a native APEC background. This contrast highlights the necessity of complementary methods for surface protein validation in heterologous expression systems. This adherence defect was partially rescued in the genetically complemented strain CE129ΔsfmA/psfmA, further strengthening the causal link between SfmA expression and the adhesive phenotype. Collectively, these results demonstrate that Sfm fimbriae contribute significantly to the adherence capacity of APEC CE129 to avian cells, likely acting as a functional adhesin system within the pathogen’s virulence repertoire.
The ability of pathogenic bacteria to evade host innate immune defenses and persist within the host environment is paramount for establishing successful infection [29,30,31]. Certain virulence factors, such as capsules and specific fimbriae, play important roles in resisting phagocytosis by macrophages and complement-mediated killing in serum. A well-studied example is the contribution of SEF17 fimbriae of Salmonella to immune evasion [32]. This study focused on investigating whether Sfm fimbriae in APEC play a similar role in bacterial survival against key host defenses. In macrophage phagocytosis and survival assays using the avian macrophage-like HD-11 cell line, CE129ΔsfmA showed a significantly reduced ability to evade phagocytosis and survive intracellularly compared to the wild-type CE129, with HD-11 cells demonstrating a 30% increase in phagocytosis of the mutant (Figure 3B). Conversely, the recombinant strain SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) exhibited an enhanced ability to evade phagocytosis compared to the controls SE5000 and SE5000 (pBR322), showing a 50% reduction in phagocytosis (Figure 3A). This diametrically opposed phenotype in the two model systems strongly suggests a close association between Sfm expression and bacterial defense against macrophage-mediated clearance. The ability of Sfm to confer this resistance even in the non-pathogenic SE5000 background implies a direct protective function for the fimbriae. Complementing this finding, serum bactericidal assays revealed that CE129ΔsfmA exhibited significantly reduced resistance toward fresh chicken serum, showing a 23.9% reduction in survival rate compared to the wild-type CE129 (Figure 3D). Simultaneously, SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) displayed a 32% increase in serum survival compared to SE5000 (pBR322) (Figure 3C), confirming the involvement of Sfm in conferring resistance against complement-mediated serum bactericidal activity. Biofilms represent structured microbial communities encased in an extracellular matrix composed of polysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. Biofilms confer enhanced tolerance to antibiotics, environmental stresses, and crucially, host immune attacks [22,33,34]. Our biofilm formation assays demonstrated that while biofilm production in CE129ΔsfmA was significantly impaired (a 21% decrease compared to CE129, Figure 3F), its synthesis was upregulated in SE5000 (pBR322-sfm) (a 34% increase compared to SE5000 (pBR322), Figure 3E). These results highlight a robust correlation between Sfm expression and the capacity for biofilm formation, a major determinant of bacterial persistence and environmental survival. Taken together, the data from phagocytosis, serum resistance, and biofilm assays provide compelling evidence that Sfm fimbriae contribute substantially to multiple aspects of APEC survival, enabling the evasion of key innate immune defenses and enhancing environmental persistence, thereby facilitating pathogenesis.
Virulence factors in E. coli are often subject to complex synergistic and hierarchical regulation [35]. To explore potential regulatory interplay, we examined the impact of Sfm deletion on the transcription levels of key virulence genes in CE129. A real-time PCR analysis revealed that the absence of sfmA caused significant downregulation in the transcription of fimA (encoding Type 1 fimbrial subunit, 40% reduction), fliC (encoding flagellin, 23% reduction), papC (encoding P fimbriae usher protein, 43% reduction), ompA (encoding outer membrane protein A, 21% reduction), and iss (encoding increased serum survival protein, 18% reduction) (Figure 4). This broad transcriptional downregulation suggests that Sfm may function as a modulator within the APEC virulence regulatory network, potentially influencing the expression of other key colonization and survival factors. The observed reduction in fimA and papC transcription aligns well with the significant decrease in adherence measured in the CE129ΔsfmA mutant, being consistent with the established roles of Type 1 and P fimbriae as major APEC adhesins. While these correlations strongly suggest Sfm’s involvement in regulatory networks, the precise mechanistic pathways remain speculative based on current data. A key limitation is our inability to determine whether Sfm influences these genes directly through physical interactions or indirectly via global regulators (e.g., quorum-sensing systems). Korea et al. previously concluded that Sfm acts synergistically with Type I fimbriae in E. coli K-12 [11], a finding supported and extended by the transcriptional co-regulation observed here in APEC, yet comprehensive transcriptomic or proteomic profiling would be required to map the complete regulatory circuitry connecting Sfm to these virulence determinants. Furthermore, the downregulation of the flagellar gene fliC in CE129ΔsfmA provides a plausible explanation for the concurrent reductions in biofilm formation and adherence [5,19,36], as flagella contribute to both initial surface attachment and biofilm maturation. Finally, the downregulation of iss in the mutant correlates with its observed sensitivity to serum killing (Figure 3D), as Iss is a known outer membrane protein implicated in conferring resistance to complement-mediated bacteriolysis, phagocytosis, and serum killing in APEC [31]. Therefore, the phenotypic alterations observed in the CE129ΔsfmA mutant likely result from both the direct loss of Sfm function and the indirect consequence of downregulating this suite of co-regulated virulence genes. This underscores the complexity of APEC virulence regulation and positions Sfm as a potentially influential component within this network.
Future studies should prioritize three key directions: first, applying nanoscale imaging techniques (immunogold-TEM) and quantitative flow cytometry to resolve the paradox between Sfm expression and surface display; second, conducting comparative membrane proteomics to establish whether Sfm assembly deficiencies underlie the adhesion phenotype in heterologous systems; and most critically, the RNA sequencing of wild-type versus ΔsfmA strains under infection-relevant conditions, which could reveal whether Sfm modulates virulence through master regulators (e.g., H-NS, Lrp) or quorum-sensing pathways like LuxS/AI-2, thereby explaining its broad transcriptional influence. Such mechanistic insights would substantially advance our understanding of fimbrial crosstalk in Enterobacteriaceae pathogenesis.
5. Conclusions
This study successfully constructed recombinant strains that enabled Sfm expression in fimbriae-deficient SE5000, and created a mutant CE129 lacking the sfm gene. Using these recombinant strains, the role of Sfm in the pathogenicity of APEC CE129 was examined. The study demonstrated the impact of Sfm on biofilm formation, adherence, and bacterial survival. These findings form a basis for the identification of APEC virulence factors and pathogenic mechanisms, offering novel insights for infection prevention and control.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microbiolres16070160/s1, Figure S1: Molecular validation of sfm operon cloning and mutant construction; Figure S2: Western blot analysis of SfmH adhesion protein expression; Figure S3: Growth curves.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Y. and G.Z.; methodology, Y.Y., M.C., and Z.H.; validation, J.L. and Z.W.; formal analysis, Y.Y.; investigation, Y.Y.; data curation, M.C. and J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Y. and C.Z.; writing—review and editing, G.Z.; supervision, Y.Y. and G.Z.; funding acquisition, Y.Y. and G.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded from the Chinese National Science Foundation Grant (No. 31972708, No. 32202693), the Yangzhou City Science and Technology Bureau Sponsored Program 2022- Social Development (Grant No. YZ2022092), the Open Project Program of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Zoonosis (R2302), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Song, X.; Hou, M.; Jiang, H.; Shen, X.; Xue, M.; Shao, Y.; Wang, L.; He, Q.; Zheng, L.; Tu, J.; et al. Hcp2a of type VI secretion system contributes to IL8 and IL1β expression of chicken tracheal epithelium by affecting APEC colonization. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 132, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathayat, D.; Lokesh, D.; Ranjit, S.; Rajashekara, G. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC): An Overview of Virulence and Pathogenesis Factors, Zoonotic Potential, and Control Strategies. Pathogens 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Pace, F.; Nakazato, G.; Pacheco, A.; Boldrin De Paiva, J.; Sperandio, V.; Dias Da Silveira, W. Type VI Secretion System Plays a Role in Type 1 Fimbria Expression and Pathogenesis of an Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strain. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4990–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avalos Vizcarra, I.; Hosseini, V.; Kollmannsberger, P.; Meier, S.; Weber, S.S.; Arnoldini, M.; Ackermann, M.; Vogel, V. How type 1 fimbriae help Escherichia coli to evade extracellular antibiotics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, X.; Bao, W.; Wu, S.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, G. The flagella of F18ab Escherichia coli is a virulence factor that contributes to infection in a IPEC-J2 cell model in vitro. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 160, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, E.B.; Elvidge, J.; Tahoun, A.; Gillespie, T.; Mantell, J.; McAteer, S.P.; Rossez, Y.; Paxton, E.; Lane, F.; Shaw, D.J.; et al. The interaction of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium flagella with host cell membranes and cytoskeletal components. Microbiology 2020, 166, 947–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuccio, S.P.; Baumler, A.J. Evolution of the chaperone/usher assembly pathway: Fimbrial classification goes Greek. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 551–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk-Martinez, A.; Ugorski, M. Unraveling the role of type 1 fimbriae in Salmonella pathogenesis: Insights from a comparative analysis of Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Gallinarum. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurpel, D.J.; Beatson, S.A.; Totsika, M.; Petty, N.K.; Schembri, M.A.; Wandersman, C. Chaperone-usher fimbriae of Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e52835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zav’Yalov, V.; Zavialov, A.; Zav’Yalova, G.; Korpela, T. Adhesive organelles of Gram-negative pathogens assembled with the classical chaperone/usher machinery: Structure and function from a clinical standpoint. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 317–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea, C.; Badouraly, R.; Prevost, M.; Ghigo, J.; Beloin, C. Escherichia coli K-12 possesses multiple cryptic but functional chaperone-usher fimbriae with distinct surface specificities. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1957–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Quan, G.; Zhang, D.; Ren, W.; Liao, Y.; Xia, P.; Zhu, G. The different roles of hcp1 and hcp2 of the type VI secretion system in Escherichia coli strain CE129. J. Basic Microbiol. 2018, 58, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Hou, Q.; Liu, J.; Xia, P.; Duan, Q.; Zhu, G. Sef fimbria operon construction, expression, and function for direct rapid detection of Salmonella Enteritidis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 5631–5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Q.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Bao, W.; Wu, S.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, G. Flagella from F18+Escherichia coli play a role in adhesion to pig epithelial cell lines. Microb. Pathog. 2013, 55, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, M.; Duan, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, G. Quorum sensing-1 signaling of N-hexanoyl-l-homoserine lactone contributes to virulence in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 6079–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yao, F.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Bao, W.; Wu, S.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Zhu, G. F18ab Escherichia coli flagella expression is regulated by acyl-homoserine lactone and contributes to bacterial virulence. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyet, L.T.Y.; Ounjai, P.; Kaeoket, K.; Ngamwongsatit, N. Feasibility of crude F4 fimbriae extract as a vaccine candidate for preventing Escherichia coli-induced diarrhea in piglets. Vet. World 2023, 16, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Duan, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Zhu, G. Flagellin and F4 fimbriae have opposite effects on biofilm formation and quorum sensing in F4ac+ enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas Boas, D.; Castro, J.; Araujo, D.; Nobrega, F.L.; Keevil, C.W.; Azevedo, N.F.; Vieira, M.J.; Almeida, C. The Role of Flagellum and Flagellum-Based Motility on Salmonella Enteritidis and Escherichia coli Biofilm Formation. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniyandi, S.; Mitra, A.; Herren, C.D.; Zhu, X.; Mukhopadhyay, S. LuxS contributes to virulence in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O78:K80:H9. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Bai, H.; Liu, L.; Dong, H.; Liu, R.; Song, J.; Ding, C.; Qi, K.; Liu, H.; Yu, S. The luxS gene functions in the pathogenesis of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Microb. Pathog. 2013, 55, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Meng, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, C.; Ni, J.; Zhu, G. Small non-coding RNA STnc640 regulates expression of fimA fimbrial gene and virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Xia, P.; Wang, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhu, G. RyhB Paralogs Downregulate the Expressions of Multiple Survival-Associated Genes and Attenuate the Survival of Salmonella Enteritidis in the Chicken Macrophage HD11. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallas, P.; Haugen, H.J.; Gadegaard, N.; Stormonth-Darling, J.; Hulander, M.; Andersson, M.; Valen, H. Adhesion of Escherichia coli to Nanostructured Surfaces and the Role of Type 1 Fimbriae. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Caballero, A.; Schonfelder, J.; Poly, S.; Corsetti, F.; De Sancho, D.; Artacho, E.; Perez-Jimenez, R. Mechanical architecture and folding of E. coli type 1 pilus domains. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Afayibo, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, H.; Yao, L.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Peng, H.; et al. Characteristics, pathogenic mechanism, zoonotic potential, drug resistance, and prevention of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1049391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golpasand, T.; Keshvari, M.; Behzadi, P. Distribution of chaperone-usher fimbriae and curli fimbriae among uropathogenic Escherichia coli. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidro-Coxca, M.I.; Ortiz-Jimenez, S.; Puente, J.L. Type 1 fimbria and P pili: Regulatory mechanisms of the prototypical members of the chaperone-usher fimbrial family. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Raheem, M.A.; Gu, Y.; Lu, H.; Song, X.; Tu, J.; Xue, T.; Qi, K. The KdpD/KdpE two-component system contributes to the motility and virulence of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 131, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Meng, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhong, H.; Xia, P.; Cui, L.; Zhu, G.; Wang, H. Transcriptome profiling of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli and the mouse microvascular endothelial cell line bEnd.3 during interaction. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9172. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Xue, T. Oxidative stress response in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Res. Vet. Sci. 2024, 180, 105426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, G.; Xia, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, C.; Meng, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhu, G. Fimbriae and related receptors for Salmonella Enteritidis. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 126, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondakindi, V.R.; Nalam, R.S.S.; Pabbati, R.; Maddela, N.R. Quorum quenching a sustainable biofilm mitigation strategy. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 17, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, P.; Chandola, D.; Dang, S.; Gupta, S.; Gabrani, R. Escherichia coli biofilm: Development and therapeutic strategies. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakbin, B.; Brück, W.M.; Rossen, J.W.A. Virulence Factors of Enteric Pathogenic Escherichia coli: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feenstra, T.; Thogersen, M.S.; Wieser, E.; Peschel, A.; Ball, M.J.; Brandes, R.; Satchell, S.C.; Stockner, T.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Rees, A.J.; et al. Adhesion of Escherichia coli under flow conditions reveals potential novel effects of FimH mutations. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).