Microbiological Profile and Resistance Patterns in Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Regional Multicenter Study in Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Study Definitions
2.3. Diagnostic Methods
2.3.1. Periprosthetic Tissue
2.3.2. Sonication of Removed Implants
2.3.3. Microbiological Culture
2.3.4. Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing
2.3.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Outcomes
3.2. Microbiological Results
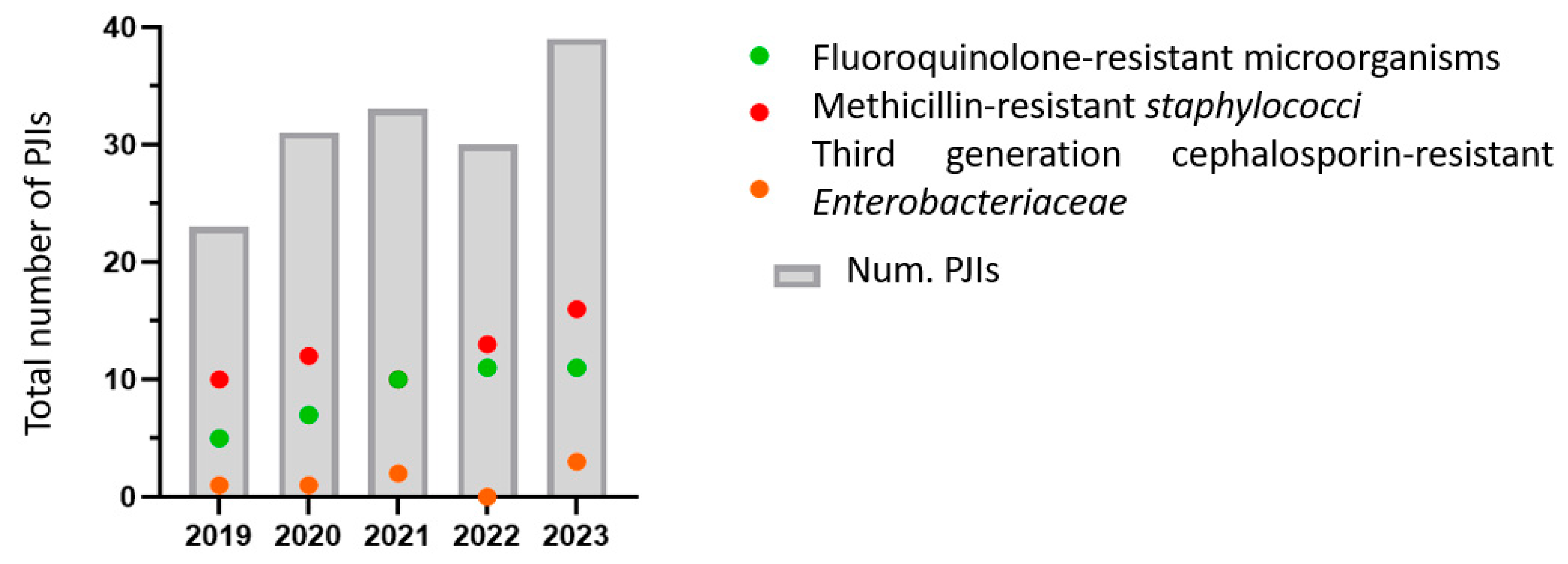
3.3. Antimicrobial Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, R. Periprosthetic Joint Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portillo, M.E.; Sancho, I. Advances in the Microbiological Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infections. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, T.N.; Sedarski, J.A.; Dylla, B.L.; Shannon, S.K.; Amirahmadi, F.; Hughes, J.G.; Cheng, A.C.; Patel, R. Laboratory Workflow Analysis of Culture of Periprosthetic Tissues in Blood Culture Bottles. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henríquez, L.; Martín, C.; Echeverz, M.; Lasa, Í.; Ezpeleta, C.; Portillo, M.E. Evaluation of the Use of Sonication Combined with Enzymatic Treatment for Biofilm Removal in the Microbiological Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0002024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivy, M.I.; Thoendel, M.J.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Hanssen, A.D.; Abdel, M.P.; Chia, N.; Yao, J.Z.; Tande, A.J.; Mandrekar, J.N.; et al. Direct Detection and Identification of Prosthetic Joint Infection Pathogens in Synovial Fluid by Metagenomic Shotgun Sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00402-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullar, R.; Chisari, E.; Snyder, J.; Cooper, C.; Parvizi, J.; Sniffen, J. Next-Generation Sequencing Supports Targeted Antibiotic Treatment for Culture Negative Orthopedic Infections. Clinical. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, J.; Gómez-Barrena, E. An Update about Molecular Biology Techniques to Detect Orthopaedic Implant-Related Infections. EFORT Open. Rev. 2021, 6, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.L.; Kheir, M.M.; Shohat, N.; Tan, D.D.; Kheir, M.; Chen, C.; Parvizi, J. Culture-Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infection: An Update on What to Expect. JB JS Open Access 2018, 3, e0060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.L.; Flurin, L.; Thoendel, M.J.; Wolf, M.J.; Abdel, M.P.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Patel, R. Targeted Versus Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing-Based Detection of Microorganisms in Sonicate Fluid for Periprosthetic Joint Infection Diagnosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, e1456–e1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe 2023–2021 Data; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control and World Health Organization: Stockholm, Sweden, 2023.
- da Silva, R.B.; Salles, M.J. Outcomes and Risk Factors in Prosthetic Joint Infections by Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendi, P.; Zimmerli, W. Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infections in Clinical Practice. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2012, 35, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardi, E.M.; Franceschi, F. Prosthetic joint infection. A relevant public health issue. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1888–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussa, M.; Manciulli, T.; Corbella, M.; Mariani, B.; Cambieri, P.; Gipsz, N.; Scudeller, L.; Abbott, D.M.; Brunetti, E.; Mosconi, M.; et al. Epidemiology and Microbiology of Prosthetic Joint Infections: A Nine-Year, Single-Center Experience in Pavia, Northern Italy. Musculoskelet. Surg. 2021, 105, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, S.; Sezgin, E.A.; Stučinskas, J.; Tarasevičius, Š.; Liu, Y.; Raina, D.B.; Tägil, M.; Lidgren, L.; W-Dahl, A. Different Microbial and Resistance Patterns in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty Infections—A Report on 283 Patients from Lithuania and Sweden. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbian, I.; Park, J.W.; Goswami, K.; Lee, Y.K.; Parvizi, J.; Koo, K.H. Culture-Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Prevalence, Aetiology, Evaluation, Recommendations, and Treatment. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellova, P.; Knop-Hammad, V.; Königshausen, M.; Mempel, E.; Frieler, S.; Gessmann, J.; Schildhauer, T.A.; Baecker, H. Sonication of Retrieved Implants Improves Sensitivity in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsma, D.T.; Ploegmakers, J.J.W.; Jutte, P.C.; Kampinga, G.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M. Time to Positivity of Acute and Chronic Periprosthetic Joint Infection Cultures. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 99, 115178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.; Fang, X. Alteration of M6A-Tagged RNA Profiles in Bone Originated from Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ding, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; et al. Optimization and Standardization of MNGS-Based Procedures for the Diagnosis of Mycoplasma Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Novel Diagnostic Strategy for Rare Bacterial Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1089919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Hagihara, M.; Asai, N.; Umemura, T.; Hirai, J.; Yamagishi, Y.; Iwamoto, T.; Mikamo, H. Comparison of Microbial Detection Rates in Microbial Culture Methods versus Next-Generation Sequencing in Patients with Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henríquez, L.; Uribarri, A.; Portillo, M.E. Revisiting Diagnostics: Practical Application of next-Generation Sequencing Technologies for Infectious Diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olearo, F.; El Zein, S.; Portillo, M.E.; Zapf, A.; Rohde, H.; Berbari, E.F.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M. Diagnostic Accuracy of 16S RDNA PCR, Multiplex PCR and Metagenomic next-Generation Sequencing in Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2025, 37, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casenaz, A.; Piroth, L.; Labattut, L.; Sixt, T.; Magallon, A.; Guilloteau, A.; Neuwirth, C.; Amoureux, L. Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance of Prosthetic Joint Infections According to Time of Occurrence, a 10-Year Study. J. Infect. 2022, 85, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, N.; Mur, I.; Ribera, A.; Soriano, A.; Rodríguez-Pardo, D.; Sorlí, L.; Cobo, J.; Fernández-Sampedro, M.; Del Toro, M.D.; Guío, L.; et al. The Different Microbial Etiology of Prosthetic Joint Infections According to Route of Acquisition and Time after Prosthesis Implantation, Including the Role of Multidrug-Resistant Organisms. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, D.B.G.; Patel, R.; Abdel, M.P.; Berbari, E.F.; Tande, A.J. Microbiology of Hip and Knee Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Database Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbero Allende, J.M.; Gómez-Junyent, J.; Sorlí Redó, L.; Rodríguez-Pardo, D.; Murillo Rubio, Ó.; Fernández Sampedro, M.; Escudero-Sánchez, R.; García Gutiérrez, M.; Portillo, M.E.; Sancho, I.; et al. Description of Reinfection of Joint Prosthesis after 2-Stage Replacement (Infection of the 2nd Stage Prosthesis): A Multicenter Study. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2024, 42, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, M.R.; Kildow, B.J.; Hartman, C.W.; Lyden, E.R.; Springer, B.D.; Fehring, T.K.; Garvin, K.L. Increased Incidence of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in Knee and Hip Prosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, S326–S330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izakovicova, P.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Current Concepts and Outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Ding, H.; Lyu, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Fang, X.; Zhang, W. Detection of Rare Microorganisms in Bone and Joint Infections by Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing: Discrimination, Decision-Making, and Clinical Benefits. Bone Jt. Res. 2024, 13, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisrenoult, P. Cutibacterium Acnes Prosthetic Joint Infection: Diagnosis and Treatment. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2018, 104, S19–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flurin, L.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Patel, R. Microbiology of Polymicrobial Prosthetic Joint Infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 94, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallimann, A.; Achermann, Y.; Ferris, C.; Morgenstern, M.; Clauss, M.; Stadelmann, V.; Rüdiger, H.A.; O’Mahony, L.; Moriarty, T.F. Emergence of Rifampicin-Resistant Staphylococci on the Skin and Nose of Rifampicin-Treated Patients with an Orthopaedic-Device-Related Infection. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2024, 9, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achermann, Y.; Eigenmann, K.; Ledergerber, B.; Derksen, L.; Rafeiner, P.; Clauss, M.; Nüesch, R.; Zellweger, C.; Vogt, M.; Zimmerli, W. Factors Associated with Rifampin Resistance in Staphylococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infections (PJI): A Matched Case-Control Study. Infection 2013, 41, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, S.; Khan, I.; Chowdhury, O.; Heydemann, J.; Antony, N.; Heydemann, J.; Isaac, D. Proposed Guidelines for the Management of ESBL in Prosthetic Joint Infections. Infect. Disord. Drug. Targets. 2020, 20, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triffault-Fillit, C.; Mabrut, E.; Corbin, K.; Braun, E.; Becker, A.; Goutelle, S.; Chaudier, P.; Fessy, M.H.; Dupieux, C.; Laurent, F.; et al. Tolerance and Microbiological Efficacy of Cefepime or Piperacillin/Tazobactam in Combination with Vancomycin as Empirical Antimicrobial Therapy of Prosthetic Joint Infection: A Propensity-Matched Cohort Study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeshchenko, D.; Slullitel, P.A.; Farinati, A.; Albani-Forneris, A.F.; Piuzzi, N.S.; Buttaro, M.A. Unconventional Therapies in Periprosthetic Joint Infections: Prevention and Treatment: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce Benavente, L.; Wagemans, J.; Hinkel, D.; Aguerri Lajusticia, A.; Lavigne, R.; Trampuz, A.; Gonzalez Moreno, M. Targeted Enhancement of Bacteriophage Activity against Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilms through an Evolutionary Assay. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1372325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tkhilaishvili, T.; Jiang, Z.; Pirlar, R.F.; Ning, Y.; Millán Laleona, A.; Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Wang, Q.; Trampuz, A.; et al. Phage-Liposome Nanoconjugates for Orthopedic Biofilm Eradication. J. Control. Release 2024, 376, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Wang, R.; Zhou, R.; Bai, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, F. Higher Diagnostic Value of Next-Generation Sequencing versus Culture in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2024, 32, 2277–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Early (<3 Months) (n = 59) | Delayed (3–24 Months) (n = 39) | Late (>24 Months) (n = 58) | Total (n = 156) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monomicrobial | 42 (71%) | 27 (69%) | 45 (78%) | 114 |
| Polimicrobial | 2 (3%) | 2 (5%) | 2 (3%) | 6 |
| Negative culture PJI | 15 (25%) | 10 (26%) | 11 (19%) | 36 (23%) |
| With previously antibiotic treatment | 10 (67%) | 6 (60%) | 4 (36%) | 20 (56%) |
| No. of isolates | 47 | 31 | 48 | 126 |
| MDR | 16 (34%) | 12 (39%) | 12 (25%) | 40 (32%) |
| GPC | 31 (66%) | 23 (74%) | 32 (67%) | 86 |
| CoNS* | 14 | 16 | 12 | 42 |
| S. aureus | 11 | 2 | 6 | 19 |
| S. lugdunensis | 1 | 1 | 4 | 6 |
| S. pneumoniae | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Beta-hemolític Streptococci | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| S. agalactiae (Group B) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| S. dysgalactiae (Group C) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| S. equi zooepidemicu (Group C) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Streptococcus viridans group | 1 | 2 | 5 | 8 |
| Enterococcus faecalis. | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| GPB | 0 | 0 | 1 (2%) | 1 |
| Listeria monocytogenes | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| GNB | 10 (21%) | 1 (3%) | 6 (13%) | 17 |
| Enterobacteriaceae | 9 | 1 | 5 | 15 |
| B. melitensis | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| P. aeruginosa | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Anaerobes | 6 (13%) | 7 (23%) | 9 (19%) | 22 |
| C. acnes | 4 | 6 | 9 | 19 |
| F. magna | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Gemella spp. | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | TOTAL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knee PJI | 9 (39%) | 21 (68%) | 11 (33%) | 21 (70%) | 18 (46%) | 80 |
| S. epidermidis | 1 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 4 | |
| S. aureus | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| C.acnes | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Enterobacteriacee | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| Hip PJI | 13 (57%) | 10 (32%) | 17 (52%) | 7 (23%) | 19 (49%) | 10 |
| S. epidermidis | 2 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 | |
| S. aureus | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| C.acnes | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | |
| Enterobacteriacee | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 * | 3 | |
| Shoulder PJI | 1 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (15%) | 2 (7%) | 2 (5%) | 66 |
| S. epidermidis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. aureus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| C.acnes | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| Enterobacteriacee | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| TOTAL PJI | 23 | 31 | 33 | 30 | 39 | 156 |
| Meticiline | Fluoroquinolones | Rifampicin | Third Generation Cephalosporins * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Staphylococcus aureus (n = 19) | 3 (16%) (SARM) | 7 (37%) | 0 | - |
| ConS (n = 42) | 31 (74%) | 24 (57%) | 6 (14%) | - |
| Enterobacteriaceae (n = 15) | - | 3 (20%) | - | 6 (40%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henriquez, L.; Uribarri, A.; Beguiristain, I.; Sancho, I.; Ezpeleta Baquedano, C.; Portillo, M.E. Microbiological Profile and Resistance Patterns in Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Regional Multicenter Study in Spain. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16070142
Henriquez L, Uribarri A, Beguiristain I, Sancho I, Ezpeleta Baquedano C, Portillo ME. Microbiological Profile and Resistance Patterns in Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Regional Multicenter Study in Spain. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(7):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16070142
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenriquez, Lucia, Ander Uribarri, Iñaki Beguiristain, Ignacio Sancho, Carmen Ezpeleta Baquedano, and Maria Eugenia Portillo. 2025. "Microbiological Profile and Resistance Patterns in Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Regional Multicenter Study in Spain" Microbiology Research 16, no. 7: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16070142
APA StyleHenriquez, L., Uribarri, A., Beguiristain, I., Sancho, I., Ezpeleta Baquedano, C., & Portillo, M. E. (2025). Microbiological Profile and Resistance Patterns in Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Regional Multicenter Study in Spain. Microbiology Research, 16(7), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16070142







