Disaggregated Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Impairs Bactericidal Activity and Bacterial Phagocytosis by Human Neutrophils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Culture Media
2.2. Characterization of H. pylori BF Formation In Vitro
2.3. Preparation of Disaggregated H. pylori BF
2.4. Staphylococcus aureus
2.5. Interaction of Human Neutrophils with Disaggregated H. pylori BF
2.6. Determination of Phagocytic Cells by Optical Microscopy
2.7. Viability of S. aureus
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
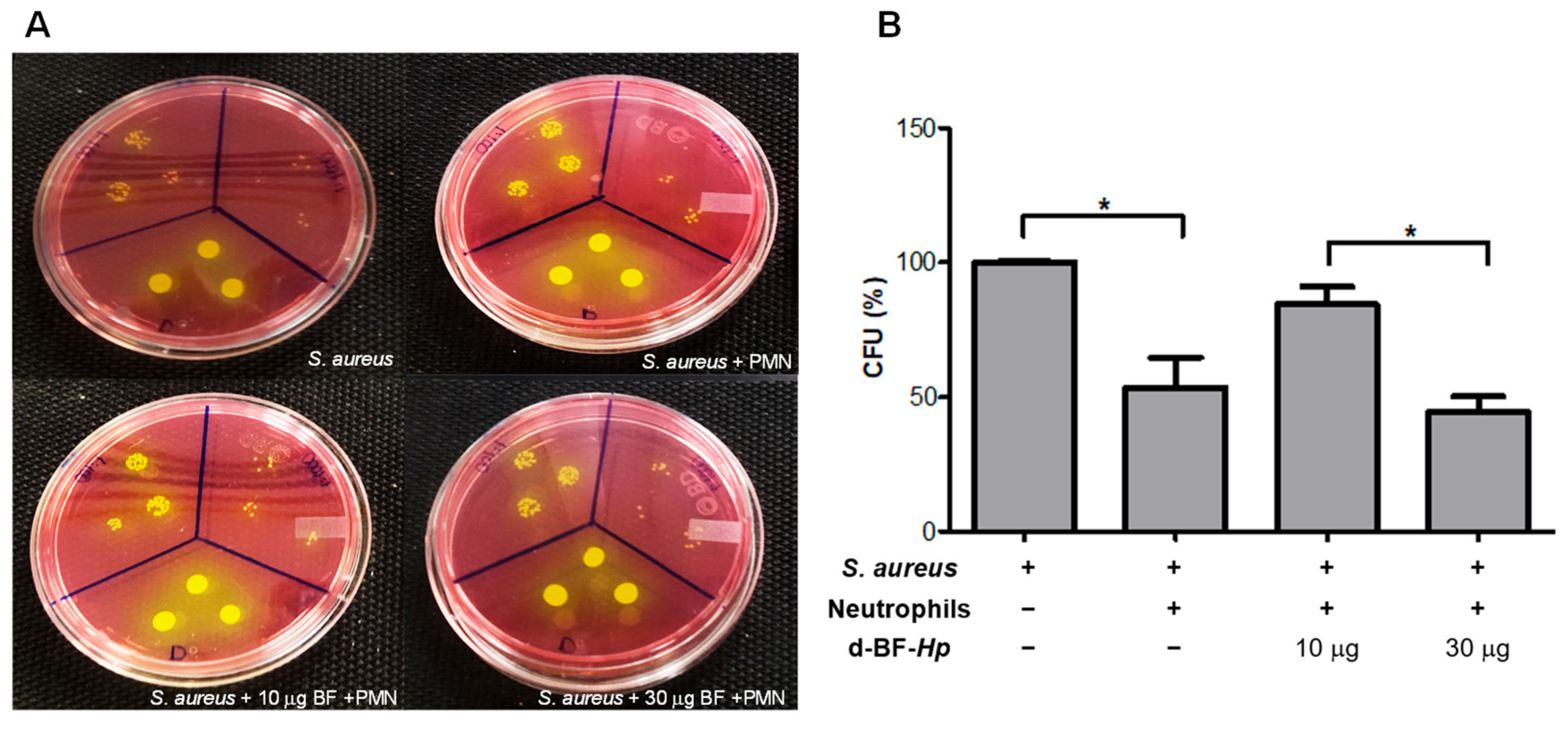
3.1. Disaggregated BF H. pylori Increase S. aureus Survival in Human Neutrophils
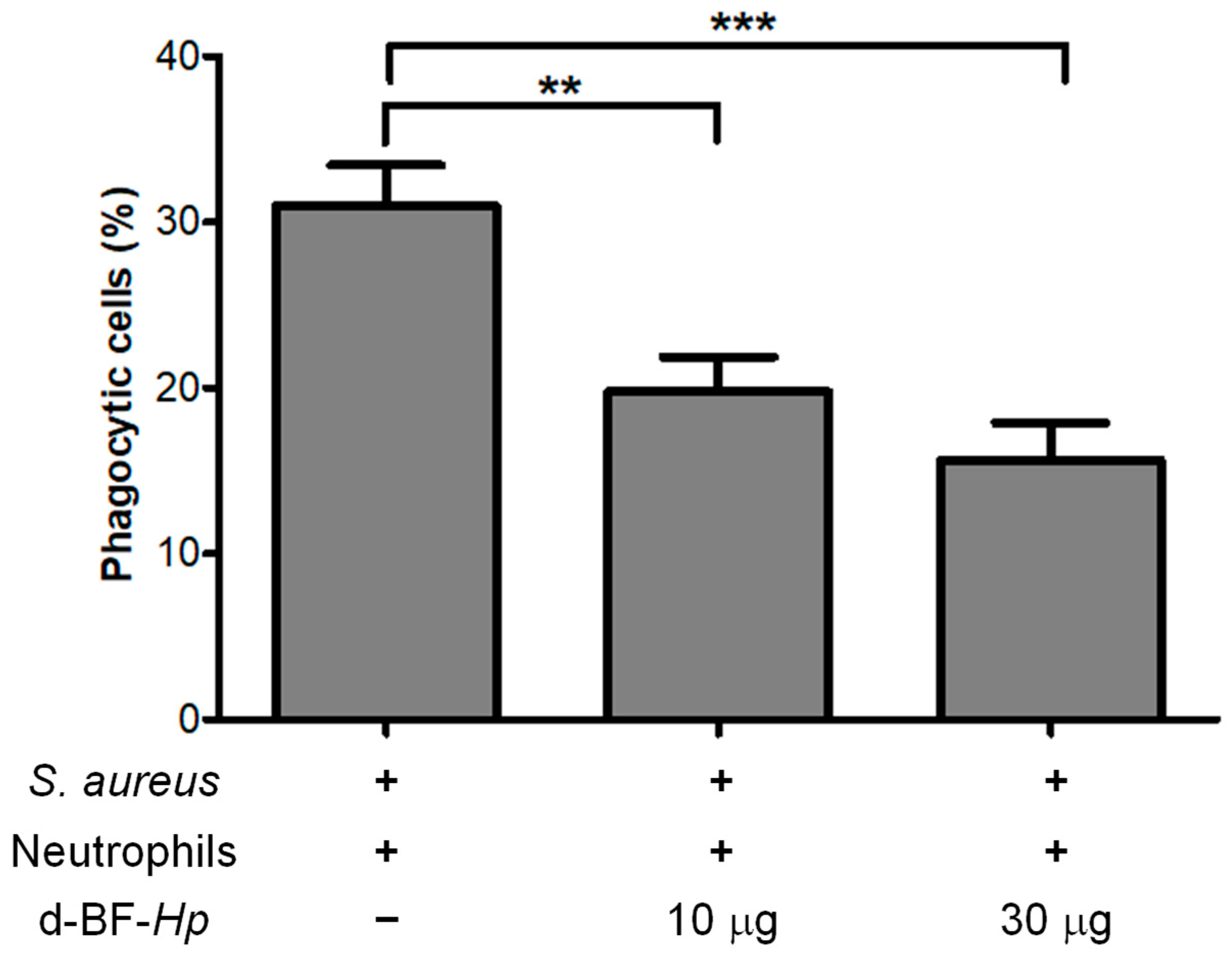
3.2. Disaggregated H. pylori BF Reduces the Phagocytosis Rate of S. aureus by Neutrophils
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BB | Brucella broth |
| BF | Biofilm |
| BHI | Brain–heart infusion broth |
| BHIA | Brain–heart infusion agar |
| CFU | Colony-forming Units |
| d-BF-Hp | Disaggregated H. pylori biofilm |
| MSA | Mannitol Salt Agar |
| NETs | Neutrophil Extracellular Traps |
| PAMPs | Pathogen-associated Molecular Patterns |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 |
References
- Li, N.; Xie, C.; Lu, N.H. Transforming growth factor-β: An important mediator in Helicobacter pylori-associated pathogenesis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Xie, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Chan, M.T.V.; Wu, W.K.K.; Chen, H. Host Cell Antimicrobial Responses against Helicobacter pylori Infection: From Biological Aspects to Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzaheed. Helicobacter pylori Oncogenicity: Mechanism, Prevention, and Risk Factors. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 3018326. [CrossRef]
- Fauzia, K.A.; Effendi, W.I.; Alfaray, R.I.; Malaty, H.M.; Yamaoka, Y.; Mifthussurur, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Biofilm Formation in Helicobacter pylori. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.L.; Hassanbhai, A.M.; Chen, H.Y.; Huang, Z.Y.; Lin, T.L.; Wu, S.H.; Ho, B. Proteomannans in biofilm of Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504. Helicobacter 2011, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżek, P.; Grande, R.; Migdał, P.; Paluch, E.; Gościniak, G. Biofilm Formation as a Complex Result of Virulence and Adaptive Responses of Helicobacter pylori. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yao, H.; Zhao, X.; Ge, C. Biofilm Formation and Control of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria. Molecules 2023, 28, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherr, T.D.; Hanke, M.L.; Huang, O.; James, D.B.; Horswill, A.R.; Bayles, K.W.; Fey, P.D.; Torres, V.J.; Kielian, T. Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms Induce Macrophage Dysfunction Through Leukocidin AB and Alpha-Toxin. mBio 2015, 6, e01021-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Berends, E.T.M.; Zheng, X.; Hill, P.J.; Chan, R.; Torres, V.J.; Wozniak, D.J. Leukocidins and the Nuclease Nuc Prevent Neutrophil-Mediated Killing of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00372-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fakhrany, O.M.; Elekhnawy, E. Helicobacter pylori in the post-antibiotics era: From virulence factors to new drug targets and therapeutic agents. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieni, A.; Barresi, V.; Rigoli, L.; Fedele, F.; Tuccari, G.; Caruso, R.A. Morphological and Cellular Features of Innate Immune Reaction in Helicobacter pylori Gastritis: A Brief Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacha, D.; Walha, M.; Ben Slama, S.; Ben Romdhane, H.; Bouraoui, S.; Bellil, K.; Lahmar, A. Chronic gastritis classifications. Tunis Med. 2018, 96, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aristotelous, A.C. Biofilm neutrophils interactions under hypoxia: A mathematical modeling study. Math. Biosci. 2022, 352, 108893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschfeld, J. Dynamic interactions of neutrophils and biofilms. J. Oral. Microbiol. 2014, 6, 26102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codolo, G.; Coletta, S.; D’Elios, M.M.; de Bernard, M. HP-NAP of Helicobacter pylori: The Power of the Immunomodulation. Front. Immunol 2022, 13, 944139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A. Microtiter dish biofilm formation assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 47, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 7, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Salud. Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-210-SSA1-2014, Productos y Servicios. Métodos de Prueba Microbiológicos. Determinación de Microorganismos Indicadores. Determinación de Microorganismos Patógenos. Available online: https://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle_popup.php?codigo=5398468 (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Curtiellas-Piñol, V.; Ventura-Juárez, J.; Ruiz-Baca, E.; Romo-Lozano, Y. Morphological changes and phagocytic activity during the interaction of human neutrophils with Sporothrix schenckii: An in vitro model. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 129, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Montelongo, J.H.; Medina-Ramírez, I.E.; Romo-Lozano, Y.; González-Gutiérrez, A.; Macías-Díaz, J.E. Development of nano-antifungal therapy for systemic and endemic mycoses. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichard, A.; Khuu, L.; Whitmore, L.C.; Irimia, D.; Allen, L.H. Helicobacter pylori-infected human neutrophils exhibit impaired chemotaxis and a uropod retraction defect. Front. Immunol 2022, 13, 1038349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirit, I.S.; Peek, R.M., Jr. Decoding the ability of Helicobacter pylori to evade immune recognition and cause disease. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 101470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wu, D.; Cui, G.; Lee, K.H.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chua, E.G.; Chen, Z. Association between biofilm formation and structure and antibiotic resistance in H. pylori. Infect. Drug Resist. 2024, 17, 2501–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Burmølle, M.; Hentzer, M.; Haagensen, J.A.J.; Hougen, H.P.; Calum, H.; Madsen, K.G.; Moser, C.; Molin, S.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa tolerance to tobramycin, hydrogen peroxide and polymorphonuclear leukocytes is quorum-sensing dependent. Microbiology 2005, 151, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiam, H.R.; Wong, S.L.; Wagner, D.D.; Waterman, C.M. Cellular mechanisms of NETosis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 36, 191–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzato, C.; Torres, J.; Kasamatsu, E.; Camorlinga-Ponce, M.; Bravo, M.M.; Canzian, F.; Kato, I. Potential Role of Biofilm Formation in the Development of Digestive Tract Cancer With Special Reference to Helicobacter pylori Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquant, G.; Grill, J.P.; Seksik, P. Impact of N-Acyl-Homoserine Lactones, Quorum Sensing Molecules, on Gut Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langereis, J.D.; Weiser, J.N. Shielding of a lipooligosaccharide IgM epitope allows evasion of neutrophil-mediated killing of an invasive strain of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. MBio 2014, 5, e01478-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoccia, D.; Ravaioli, S.; Mirzaei, R.; Bua, G.; Daglia, M.; Arciola, C.R. Interactions of neutrophils with the polymeric molecular components of the biofilm matrix in the context of implant-associated bone and joint infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, F.; Kazmi, S.U. Thin layer immunoassay: An economical approach to diagnose Helicobacter pylori infection in gastroduodenal ulcer disease patients of Pakistan, a comparative analysis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tovar-Robles, C.L.; Romo-Lozano, Y.; Cervantes-García, D.; González-Segovia, R. Disaggregated Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Impairs Bactericidal Activity and Bacterial Phagocytosis by Human Neutrophils. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060121
Tovar-Robles CL, Romo-Lozano Y, Cervantes-García D, González-Segovia R. Disaggregated Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Impairs Bactericidal Activity and Bacterial Phagocytosis by Human Neutrophils. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(6):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060121
Chicago/Turabian StyleTovar-Robles, Clara Lourdes, Yolanda Romo-Lozano, Daniel Cervantes-García, and Rodolfo González-Segovia. 2025. "Disaggregated Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Impairs Bactericidal Activity and Bacterial Phagocytosis by Human Neutrophils" Microbiology Research 16, no. 6: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060121
APA StyleTovar-Robles, C. L., Romo-Lozano, Y., Cervantes-García, D., & González-Segovia, R. (2025). Disaggregated Helicobacter pylori Biofilm Impairs Bactericidal Activity and Bacterial Phagocytosis by Human Neutrophils. Microbiology Research, 16(6), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16060121







