Infection Frequency and Allelic Variants of Toxoplasma gondii in Wildlife from the Panama Canal Zone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Permission to Access Resources
2.2. Geographic Area Studied
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. DNA Extraction and Quantification
2.5. Detection of T. gondii DNA in Tissue Samples from Wild Animals
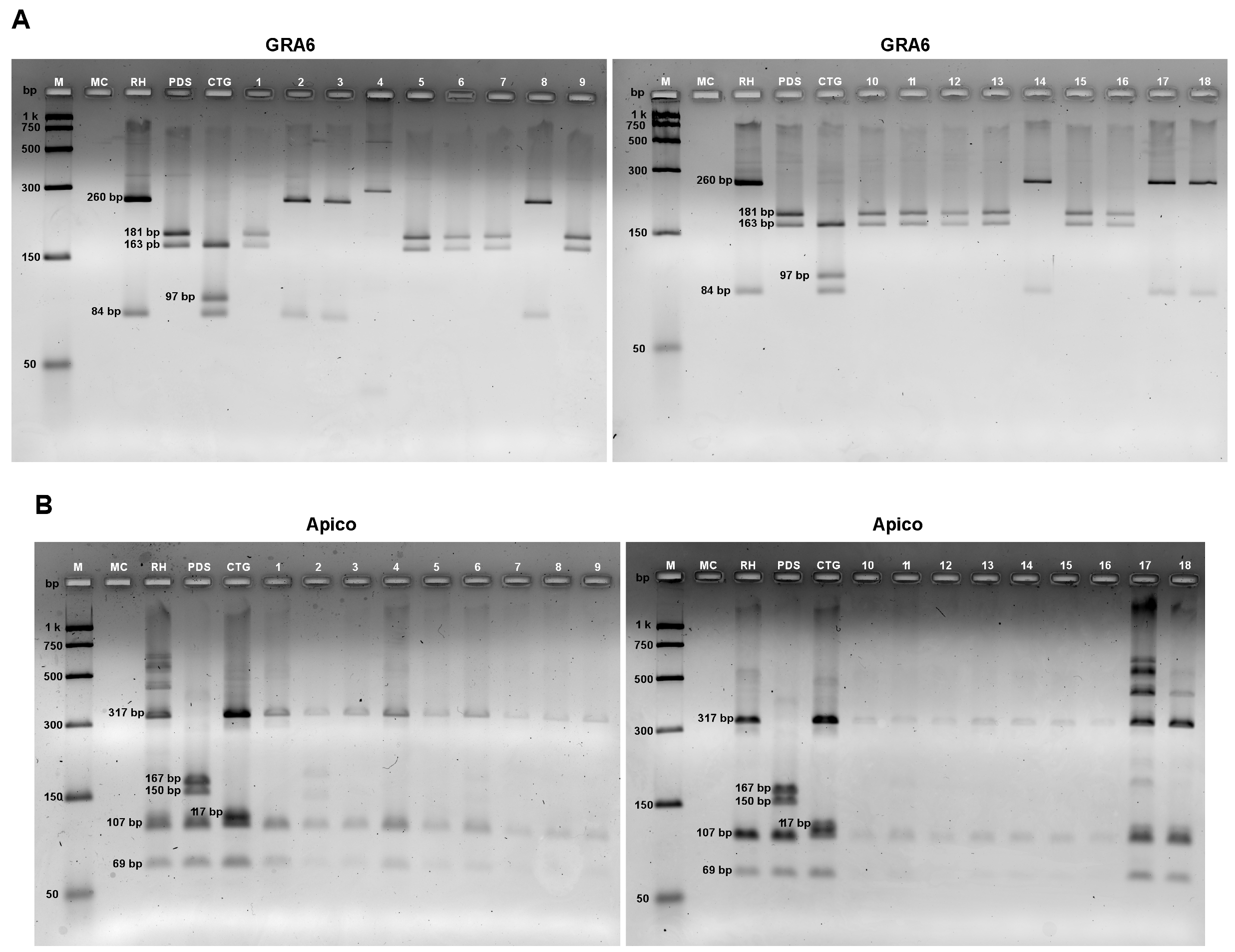
2.6. Allelic Variants of T. gondii Determined by Multilocus PCR-RFLP Markers
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Frequency of T. gondii Infection in Different Classes of Wild Animals
3.2. Frequency of T. gondii Infection in Five Organs from Different Classes of Wild Animal
3.3. Allelic Profiles of T. gondii in Tissues Samples from Wild Animals
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehmann, T.; Marcet, P.L.; Graham, D.H.; Dahl, E.R.; Dubey, J.P. Globalization and the population structure of Toxoplasma gondii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11423–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Frenkel, J.K. Cyst-Induced Toxoplasmosis in Cats. J. Protozool. 1972, 19, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Miller, N.L.; Frenkel, J.K. Toxoplasma gondii life cycle in cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1970, 157, 1767–1770. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Black, M.W.; Boothroyd, J.C. Lytic cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Advances in the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, V.; Teymurzadeh, S.; Karimi, G.; Nasiri, M. Molecular detection of Toxoplasma gondii in snakes. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 169, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, C.P.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Man. Parasitology 1988, 100, 500–501. [Google Scholar]
- Omata, Y.; Umeshita, Y.; Murao, T.; Kano, R.; Kamiya, H.; Kudo, A.; Masukata, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Maeda, R.; Saito, A.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii does not persist in goldfish (Carassius auratus). J. Parasitol. 2005, 91, 1496–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Mann, T.; Striepen, B.; Beckers, C.J.; Roos, D.S.; Murray, J.M. Daughter cell assembly in the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.; Dubey, J.P. Biology of toxoplasmosis. In Toxoplasmosis: A Comprehensive Clinical Guide; Joynson, D.H.M., Wreghitt, T.G., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lindsay, D.S.; Speer, C.A. Structures of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites, bradyzoites, and sporozoites and biology and development of tissue cysts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, L.D.; Khan, A.; Ajioka, J.W.; Rosenthal, B.M. Genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and humans. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2749–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, D.K.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma gondii comprises three clonal lineages: Correlation of parasite genotype with human disease. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibley, L.D.; Ajioka, J.W. Population structure of Toxoplasma gondii: Clonal expansion driven by infrequent recombination and selective sweeps. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 62, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, D.K.; Honoré, S.; Derouin, F.; Sibley, L.D. Determination of genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii strains isolated from patients with toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1411–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, L.D.; Boothroyd, J.C. Virulent strains of Toxoplasma gondii comprise a single clonal lineage. Nature 1992, 359, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzenberg, D.; Bañuls, A.L.; Su, C.; Dumètre, A.; Demar, M.; Carme, B.; Dardé, M.L. Genetic diversity, clonality and sexuality in Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carme, B.; Bissuel, F.; Ajzenberg, D.; Bouyne, R.; Aznar, C.; Demar, M.; Bichat, S.; Louvel, D.; Bourbigot, A.M.; Peneau, C.; et al. Severe acquired toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent adult patients in French Guiana. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4037–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Gennari, S.M.; Sundar, N.; Vianna, M.C.; Bandini, L.M.; Yai, L.E.; Kwok, C.H.; Suf, C. Diverse and atypical genotypes identified in Toxoplasma gondii from dogs in São Paulo, Brazil. J. Parasitol. 2007, 93, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Sundar, N.; Gennari, S.M.; Minervino, A.H.; Farias, N.A.; Ruas, J.L.; dos Santos, T.R.; Cavalcante, G.T.; Kwok, O.C.; Su, C. Biologic and genetic comparison of Toxoplasma gondii isolates in free-range chickens from the northern Pará state and the southern state Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil revealed highly diverse and distinct parasite populations. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 143, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo Ferreira, A.; Vitor, R.W.A.; Gazzinelli, R.T.; Melo, M.N. Genetic analysis of natural recombinant Brazilian Toxoplasma gondii strains by multilocus PCR-RFLP. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2006, 6, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Jordan, C.; Muccioli, C.; Vallochi, A.L.; Rizzo, L.V.; Belfort, R., Jr.; Vitor, R.W.; Silveira, C.; Sibley, L.D. Genetic divergence of Toxoplasma gondii strains associated with ocular toxoplasmosis, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, T.; Graham, D.H.; Dahl, E.R.; Bahia-Oliveira, L.M.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P. Variation in the structure of Toxoplasma gondii and the roles of selfing, drift, and epistatic selection in maintaining linkage disequilibria. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2004, 4, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fábrega, L.; Restrepo, C.M.; Torres, A.; Smith, D.; Chan, P.; Pérez, D.; Cumbrera, A.; Caballero, E.Z. Frequency of Toxoplasma gondii and Risk Factors Associated with the Infection in Stray Dogs and Cats of Panama. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, C.; Villalobos-Cerrud, D.; Borace, J.; Fábrega, L.; Norero, X.; Sáez-Llorens, X.; Moreno, M.T.; Restrepo, C.M.; Llanes, A.; Quijada, R.M.; et al. Epidemiological Aspects of Maternal and Congenital Toxoplasmosis in Panama. Pathogens 2021, 10, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengifo-Herrera, C.; Pile, E.; García, A.; Pérez, A.; Pérez, D.; Nguyen, F.K.; de la Guardia, V.; McLeod, R.; Caballero, Z. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in domestic pets from metropolitan regions of Panama. Parasite 2017, 24, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, R.; Cedeño, I.; de Escobar, C.; Fuentes, I. Increased urban seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infecting swine in Panama. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 153, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Syabri, I.; Kho, Y. An Introduction to Spatial Data Analysis. Geogr. Anal. 2006, 38, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, J.L.; Grover, C.M.; Pouletty, P.; Boothroyd, J.C. Direct and sensitive detection of a pathogenic protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii, by polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 1787–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelloux, H.; Dupouy-Camet, J.; Derouin, F.; Aboulker, J.P.; Raffi, F.; Bio-Toxo Study Group. A multicentre prospective study for the polymerase chain reaction detection of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in blood samples from 186 AIDS patients with suspected toxoplasmic encephalitis. AIDS 1997, 11, 1888–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohlfeld, P.; Daffos, F.; Costa, J.M.; Thulliez, P.; Forestier, F.; Vidaud, M. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis with a polymerase-chain-reaction test on amniotic fluid. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Zhang, X.; Dubey, J.P. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii by multilocus PCR-RFLP markers: A high resolution and simple method for identification of parasites. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, T.; Blackston, C.R.; Parmley, S.F.; Remington, J.S.; Dubey, J.P. Strain typing of Toxoplasma gondii: Comparison of antigen-coding and housekeeping genes. J. Parasitol. 2000, 86, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazaeli, A.; Carter, P.E.; Darde, M.L.; Pennington, T.H. Molecular typing of Toxoplasma gondii strains by GRA6 gene sequence analysis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigg, M.E.; Ganatra, J.; Boothroyd, J.C.; Margolis, T.P. Unusual Abundance of Atypical Strains Associated with Human Ocular Toxoplasmosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Su, C.; German, M.; Storch, G.A.; Clifford, D.B.; Sibley, L.D. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii strains from immunocompromised patients reveals high prevalence of type I strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5881–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T-Test GraphPad Prism Version 6.1 for Windows; GraphPad Software Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016.
- Su, C.; Shwab, E.K.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Dubey, J.P. Moving towards an integrated approach to molecular detection and identification of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 2010, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convention on Biological Diversity United Nations. Panama—Main Details. Biodiversity Facts. Status and Trends of Biodiversity, Including Benefits from Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Available online: https://www.cbd.int/countries/profile/?country=pa#facts (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Carrillo, J.D.; Faurby, S.; Silvestro, D.; Zizka, A.; Jaramillo, C.; Bacon, C.D.; Antonelli, A. Disproportionate extinction of South American mammals drove the asymmetry of the Great American Biotic Interchange. PNAS 2020, 117, 26281–26287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Mammalogists (ASM). The Mammal Diversity Database. Available online: https://www.mammaldiversity.org/index.html (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- de Oliveira, T.G.; Fox-Rosales, L.A.; Ramírez-Fernández, J.D.; Cepeda-Duque, J.C.; Zug, R.; Sanchez-Lalinde, C.; Oliveira, M.J.R.; Marinho, P.H.D.; Bonilla-Sánchez, A.; Marques, M.C.; et al. Ecological modeling, biogeography, and phenotypic analyses setting the tiger cats’ hyperdimensional niches reveal a new species. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, F.A. A Field Guide to the Mammals of Central America and Southeast Mexico, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, R.J.; Harmsen, B.J.; Valdes, B.; Pomilla, C.; Doncaster, C.P. Food habits of sympatric jaguars and pumas across a gradient of human disturbance. J. Zool. 2010, 280, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwab, E.K.; Zhu, X.Q.; Majumdar, D.; Pena, H.F.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. Geographical patterns of Toxoplasma gondii genetic diversity revealed by multilocus PCR-RFLP genotyping. Parasitology 2014, 141, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, L.; Ariey, F.; Gouilh, M.A.; Dardé, M.L.; Hamidović, A.; Letourneur, F.; Prugnolle, F.; Mercier, A. A unique Toxoplasma gondii haplotype accompanied the global expansion of cats. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela-Moreno, L.F.; Méndez-Cruz, S.T.; Rico-Torres, C.P.; Cedillo-Peláez, C.; Correa, D.; Caballero-Ortega, H. SAG3 Toxoplasma gondii cloning reveals unexpected fivefold infection in the blood of feral cats in the Mexican Caribbean. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.K.; Sweeny, A.R.; Lovallo, M.J.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Kwok, O.C.; Jiang, T.; Su, C.; Grigg, M.E.; Dubey, J.P. Seroprevalence, isolation and co-infection of multiple Toxoplasma gondii strains in individual bobcats (Lynx rufus) from Mississippi, USA. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, M.; Cabezón, O.; Dubey, J.P.; Almería, S.; Ribas, M.P.; Escobar, L.E.; Ramos, B.; Medina-Vogel, G. Toxoplasma gondii infection in wild mustelids and cats across an urban-rural gradient. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, T.F.; Parentoni, R.N.; Vilela, L.R.; Nety, T.F.L.; de Jesus Pena, H.F. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in mammals, birds and reptiles at the zoological-botanical park in Joāao Pessoa, Paraíba, Brazil. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2017, 84, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, J. Las noches y los días de la iguana. Rev. Américas 1987, 359–363. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, P.L. The iguana, Iguana iguana iguana (L). Herpetologica 1950, 6, 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, D.I.; Rey, D.I.; Hyde, D. La Biología De La Iguana Verde; Fundación Pro Iguana Verde, Instituto de Investigaciones Tropicales Smithsonian: Balboa, Panama, 1987. [Google Scholar]


| Molecular Markers | External and Internal Primers | Internal PCR Product Size | Restriction Enzymes | Conditions of Enzymatic Restriction | Band Size (bp) after Enzymatic Digestion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAG1 (Chr. VIII) | Fext:GTTCTAACCACGCACCCTGAG Rext2:AAGAGTGGGAGGCTCTGTGA Fs2:CAATGTGCACCTGTAGGAAGC R:GTGGTTCTCCGTCGGTGTGAG | 390 pb | Sau96I + HaeII | 37 °C 1 h. 2.5% gel. | I: 334, 56 II/III: 293, 97 | Grigg et al. (2001) [35] |
| alt.SAG2 (Chr. VIII) | F:GGAACGCGAACAATGAGTTT R:GCACTGTTGTCCAGGGTTTT Fa:ACCCATCTGCGAAGAAAACG Ra:ATTTCGACCAGCGGGAGCAC | 546 pb | HinfI + Taq I | 37 °C 30 min, 65 °C 30 min. 2.5% gel. | I: 350, 175 II: 350, 120 III: 360, 175 | Khan et al. (2005) [36] C. Su et al. (2006) [37] |
| SAG3 (Chr. XII) | F:CAACTCTCACCATTCCACCC R:GCGCGTTGTTAGACAAGACA P43S2:TCTTGTCGGGTGTTCACTCA P43AS2:CACAAGGAGACCGAGAAGGA | 225 pb | NciI | 37 °C 1 h. 2.5% gel. | I: 100, 60 II: 220 III: 180, 60 | Grigg et al. (2001) [35] |
| GRA6 (Chr. X) | F:ATTTGTGTTTCCGAGCAGGT R:GCACCTTCGCTTGTGGTT F-1:TTTCCGAGCAGGTGACCT R1x:TCGCCGAAGAGTTGACATAG | 344 pb | MseI | 37 °C 1 h. 2.5% gel. | I: 260, 84 II: 181, 163 III: 163, 97, 84 | Fazaeli et al. (2000) [34] Khan et al. (2005) [36] C. Su et al. (2006) [38] |
| Apico (Plastid) | Apico-Fext:TGGTTTTAACCCTAGATTGTGG Apico -Rext: AAACGGAATTAATGAGATTTGAA Apico-F: TGCAAATTCTTGAATTCTCAGTT Apico-R: GGGATTCGAACCCTTGATA | 640 pb | AflII + DdeI | 37 °C 1 h. 3% gel. | I: 317, 107, 69 II: 167, 150, 107, 69 III: 317, 117, 107, 69 | C. Su et al. (2006) [38] |
| No. (%) (95% CI) of Positive Samples | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Total Samples | No. Total Positive | No. Total Birds | No. Total Mammals | No. Total Reptiles | ||||
| 221 | 145 (65.6%) (58.94–71.85) | 122 | 82 (67.2%) (58.13–75.44) | 77 | 54 (70.12%) (58.62–80.03) | 22 | 12 (54.5%) (32.21–75.61) | |
| Organs analyzed | ||||||||
| Brain | 146 | 50 (34.24%) (22.60–42.55) | 77 | 25 (32.46%) (22.23–44.10) | 56 | 22 (39.28%) (26.50–53.25) | 13 | 3 (23.07%) (5.04–53.81) |
| Liver | 146 | 48 (32.87%) (25.34–41.13) | 77 | 25 (32.46%) (22.23–44.10) | 56 | 20 (35.71%) (23.36–49.64) | 13 | 3 (23.07%) (5.04–53.81) |
| Heart | 146 | 46 (31.50%) (24.08–39.71) | 77 | 23 (29.87%) (19.97–41.38) | 56 | 20 (35.71%) (23.36–49.64) | 13 | 3 (23.07%) (5.04–53.81) |
| Lung | 146 | 55 (37.67%) (29.79–46.06) | 77 | 25 (32.46%) (22.23–44.10) | 56 | 17 (30.35%) (18.78–44.10) | 13 | 6 (46.15%) (19.22–74.87) |
| S. muscle | 146 | 47 (32.19%) (24.71–40.42) | 77 | 24 (31.16%) (21.09–42.74) | 56 | 20 (35.71%) (23.36–49.64) | 13 | 3 (23.07%) (5.04–53.81) |
| Total | 730 | 246 (33.69%) (30.27–37.26) | 385 | 122 (31.68%) (27.07–36.59) | 280 | 99 (35.35%) (29.76–41.27) | 65 | 18 (27.69%) (17.31–40.19) |
| CI = Confidence Interval | ||||||||
| No. | Code | Species | Animal Type | Diet | Behavior | Tissue | Allelic Profiles of Five Genes of T. gondii | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAG1 | alt. SAG2 | SAG3 | GRA6 | Apico | |||||||
| 1 | 135 | Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris | Mammal | Herbivorous | Terrestrial | Liver | II/III | II | I | II | I |
| 2 | 135 | Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris | Mammal | Herbivorous | Terrestrial | Brain | I | II | I | I | I |
| 3 | 103 | Tamandua mexicana | Mammal | Myrmecophage | A/T | S. muscle | _ | II | II | I | I |
| 4 | 139 | Dasypus novemcinctus | Mammal | M/F | Terrestrial | Brain | II/III | II | I | und | I |
| 5 | 141 | Dasypus novemcinctus | Mammal | M/F | Terrestrial | Heart | _ | II | II | II | I |
| 6 | 128 | Potus flavus | Mammal | Omnivore | Arboreal | Liver | II/III | II | II | II | I |
| 7 | 128 | Potus flavus | Mammal | Omnivore | Arboreal | Lung | II/III | II | II | II | I |
| 8 | 111 | Saguinus geoffroyi | Mammal | Omnivore | Arboreal | Brain | II/III | II | II | I | I |
| 9 | 98 | Potus flavus | Mammal | Omnivore | Arboreal | Brain | II/III | II | II | II | I |
| 10 | 159 | Potos flavus | Mammal | Omnivore | Arboreal | Liver | I | II | II | II | I |
| 11 | 107 | Nyctidromus albicolis | Bird | Insectivore | A/T | Eye | II/III | II | II | II | I |
| 12 | 150 | Piaya cayana | Bird | Omnivore | Arboreal | Liver | II/III | II | II | II | I |
| 13 | 150 | Piaya cayana | Bird | Omnivore | Arboreal | Lung | I | II | II | II | I |
| 14 | 153 | Buteo platypterus | Bird | Carnivorous | Arboreal | S. muscle | II/III | II | II | I | I |
| 15 | 153 | Buteo platypterus | Bird | Carnivorous | Arboreal | Liver | II/III | II | II | II | I |
| 16 | 167 | Turdus grayi | Bird | Omnivore | Arboreal | Lung | I | II | I | II | I |
| 17 | 142 | Iguana iguana | Reptile | Omnivore | Arboreal | Lung | II/III | II | II | I | III |
| 18 | 142 | Iguana iguana | Reptile | Omnivore | Arboreal | Heart | II/III | II | I | I | III |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henríquez-Carrizo, E.; Cruz, H.; Jurado, A.; Smith, D.; Villalobos-Cerrud, D.; Fábrega, L.; de la Guardia, C.; Cano, R.; Correa, R.; Frías, E.; et al. Infection Frequency and Allelic Variants of Toxoplasma gondii in Wildlife from the Panama Canal Zone. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 2035-2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040136
Henríquez-Carrizo E, Cruz H, Jurado A, Smith D, Villalobos-Cerrud D, Fábrega L, de la Guardia C, Cano R, Correa R, Frías E, et al. Infection Frequency and Allelic Variants of Toxoplasma gondii in Wildlife from the Panama Canal Zone. Microbiology Research. 2024; 15(4):2035-2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040136
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenríquez-Carrizo, Evelyn, Hector Cruz, Alessandra Jurado, Diorene Smith, Delba Villalobos-Cerrud, Lorena Fábrega, Carolina de la Guardia, Ryan Cano, Ricardo Correa, Edy Frías, and et al. 2024. "Infection Frequency and Allelic Variants of Toxoplasma gondii in Wildlife from the Panama Canal Zone" Microbiology Research 15, no. 4: 2035-2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040136
APA StyleHenríquez-Carrizo, E., Cruz, H., Jurado, A., Smith, D., Villalobos-Cerrud, D., Fábrega, L., de la Guardia, C., Cano, R., Correa, R., Frías, E., García, A. A., Ríos, N., Sandoval, N., Martínez Torres, A. O., Castillo-Pimentel, A., & Caballero E., Z. (2024). Infection Frequency and Allelic Variants of Toxoplasma gondii in Wildlife from the Panama Canal Zone. Microbiology Research, 15(4), 2035-2047. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15040136






