Molecular Analysis of the Microbial Guild Fixing Nitrogen in Ricefield Soils in Missouri
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ricefields and Soil Sampling
2.2. Direct Extraction of DNA
2.3. PCR Amplification of nifH Genes
2.4. Cloning, Fingerprinting, and Sequencing of PCR Amplicons
3. Results
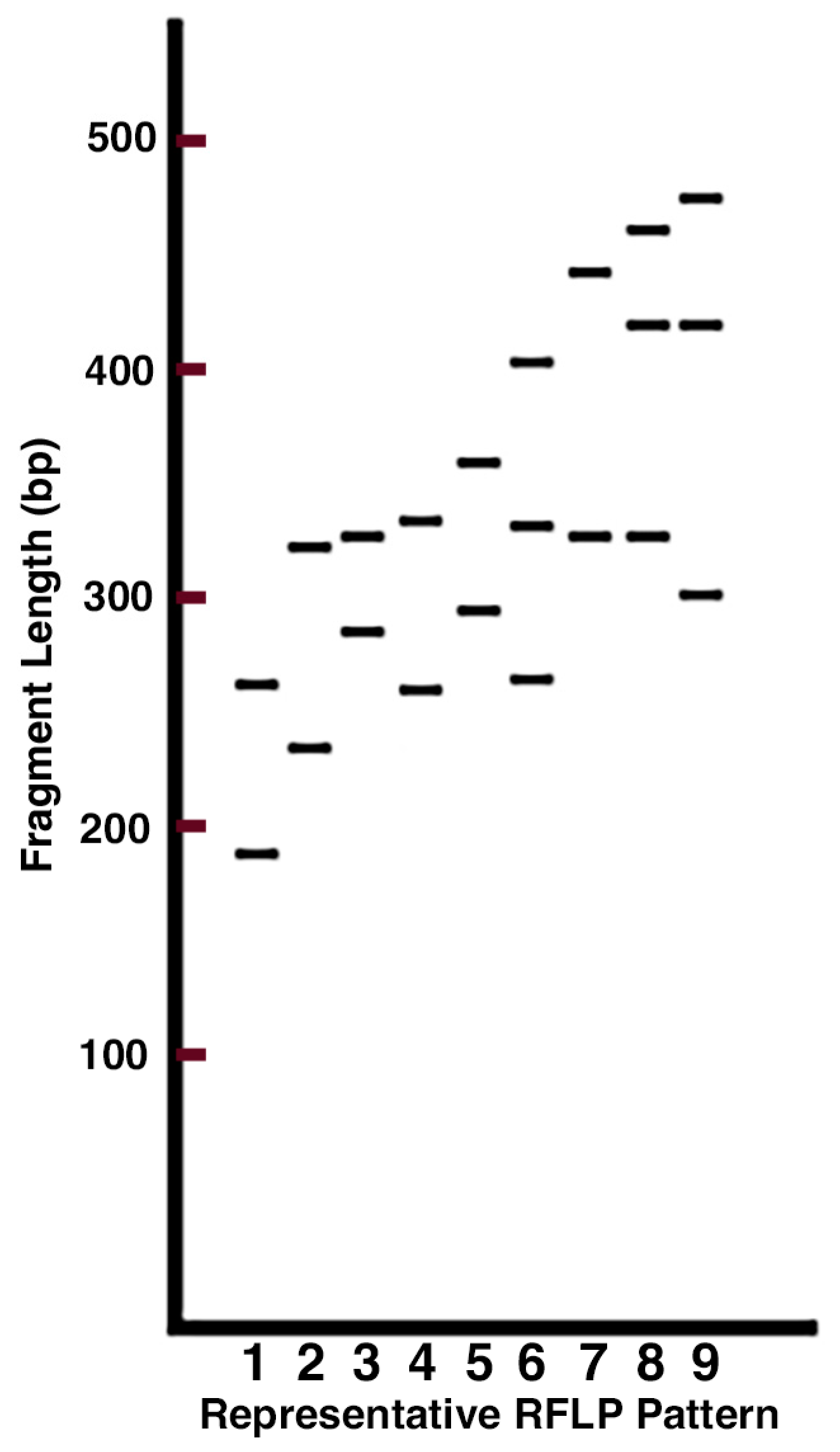
3.1. Extraction and Fingerprinting
3.2. Phylogenetic Analyses of nifH Clones
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muthayya, S.; Sugimoto, J.D.; Montgomery, S.; Maberly, G.F. An overview of global rice production, supply, trade, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1324, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkishore, S.K.; Vignesh, N.S.; Doraisamy, P.; Maheswari, M. Methane emission from rice ecosystems: 100 years of research. Ecoscan 2015, 9, 181–193. [Google Scholar]
- Roger, P.A.; Watanabe, I. Technologies for utilizing biological nitrogen fixation in wetland rice: Potentialities, current usage, and limiting factors. Fert. Res. 1986, 9, 39–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, P.A.; Kulassoriya, S.A. Blue-Green Algae and Rice; International Rice Research Institute: Manila, Philippines, 1980; 112p. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, A.T.M.A.; Kennedy, I.R. Prospects and potentials for systems of biological nitrogen fixation in sustainable rice production. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2004, 39, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herridge, D.F.; Peoples, M.B.; Boddey, R.M. Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil 2008, 311, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-F.; Buckley, D.H. Evidence for the functional significance of diazotroph community structure in soil. ISME J. 2009, 3, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladha, J.K.; Tirol-Padre, A.; Reddy, C.K.; Cassman, K.G.; Verma, S.; Powlson, D.S.; van Kessel, C.; Richter, D.B.; Chakraborty, D.; Pathak, H. Global nitrogen budgets in cereals: A 50-year assessment for maize, rice, and wheat production systems. Nature Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladha, J.K.; Pathak, H.; Krupnik, T.J.; Six, J.; van Kessel, C. Efficiency of fertilizer in cereal production: Retrospects and prospects. Adv. Agron. 2005, 87, 85–156. [Google Scholar]
- Stokstad, E. The nitrogen fix. Science 2016, 353, 1225–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlool, B.B.; Ladha, J.K.; Garrity, D.P.; George, T. Biological nitrogen fixation for sustainable agriculture: A perspective. Plant Soil 1992, 141, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, P.A.; Ladha, J.K. Biological nitrogen fixation in wetland rice fields: Estimation and contribution to nitrogen balance. Plant Soil 1992, 141, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.C.; Smith, K.L. Soil microbial diversity and the sustainability of agricultural soils. In The Significance and Regulation of Soil Biodiversity; Collins, H.P., Robertson, G.P., Klug, M.J., Eds.; Kluwer: Rijn, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Roger, P.A. Biological nitrogen fixation and its management in wetland rice cultivation. Fert. Res. 1995, 42, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, C.E.; Ophel-Keller, K.; Doube, B.M.; Gupta, V.V.S.R. Biodiversity of soil microbial communities in agricultural systems. Biodiv. Conserv. 1996, 5, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wartiainen, I.; Eriksson, T.; Zheng, W.; Rasmussen, U. Variation in the active diazotrophic community in rice paddy—nifH PCR-DGGE analysis of rhizosphere and bulk soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 39, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mårtensson, L.; Díez, B.; Wartiainen, I.; Zheng, W.; El-Shehawy, R.; Rasmussen, U. Diazotrophic diversity, nifH gene expression and nitrogenase activity in a rice paddy field in Fujian, China. Plant Soil 2009, 325, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyarudin; Rusmana, I.; Lestari, Y. Metagenomic of actinomycetes based on 16S rRNA of nifH genes in soil and roots of four Indonesian rice cultivars using PCR-DGGE. HAYATI J. Biosci. 2015, 22, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Mishra, A.K. Comparative responses of diazotrophic abundance and community structure to the chemical composition of paddy soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wei, X.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Qin, H.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Ge, T.; Zhran, M.; et al. Diazotrophic community variation underlies differences in nitrogen fixation potential in paddy soils across a climatic gradient in China. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 81, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binarti, A.F.; Rusmana, I.; Wahyudi, A.T. Identification of nifD and nifH genes in methanotrophic bacteria from rice field. Ann. Bogorienses 2014, 18, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama, T.; Terakado-Tonooka, J.; Minamisawa, K. Exploration of bacterial N2-fixation systems in association with soil-grown sugarcane, sweet potato, and paddy rice: A review and synthesis. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 63, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.Y.; Peng, G.X.; Xu, P.Z.; Ai, S.Y.; Tang, S.H.; Zhang, G.X.; Zeng, F.Y. Diversity and high nitrogenase activity of endophytic diazotrophs isolated from Oryza rufipogon Griff. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrando, L.; Scavino, A.F. Strong shift in the diazotrophic endophytic bacterial community inhabiting rice (Oryza sativa) plants after flooding. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, fiv104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bishop, P.E.; Premakumar, R. Alternative nitrogen fixation systems. In Biological Nitrogen Fixation; Stacey, G., Burris, R.H., Evena, H.J., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 736–762. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porath, J.; Zehr, J.P. Detection and characterization of cyanobacterial nifH genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diallo, M.D.; Reinhold-Hurek, B.; Hurek, T. Evaluation of PCR primers for universal nifH gene targeting and for assessment of transcribed nifH pools in roots of Oryza longistaminata with and without low nitrogen input. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gaby, J.C.; Buckley, D.H. A comprehensive aligned nifH gene database: A multipurpose tool for studies of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Database 2014, 2014, bau001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehr, J.P.; McReynolds, L.A. Use of degenerate oligonucleotides for amplification of the nifH gene from the marine cyanobacterium Trichodesmium thiebautti. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 2522–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehr, J.P.; Mellon, M.T.; Hiorns, W.D. Phylogeny of cyanobacterial nifH genes: Evolutionary implications and potential applications to natural assemblages. Microbiology 1997, 43, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehr, J.P.; Mellon, M.T.; Zani, S. New nitrogen-fixing microorganisms detected in oligotrophic oceans by amplification of nitrogenase (nifH) genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3444–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthrong, S.T.; Yeager, C.M.; Gallegos-Graves, L.; Steven, B.; Eichorst, S.A.; Jackson, R.B.; Kuske, C.R. Nitrogen fertilization has a stronger effect on soil nitrogen-fixing bacterial communities than elevated atmospheric CO2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3103–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes Martiny, J.B.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Brown, J.H.; Colwell, R.K.; Fuhrman, J.A.; Green, J.L.; Horner-Devine, M.C.; Kane, M.; Krumins, J.A.; Kuske, C.R.; et al. Microbial biogeography: Putting microorganisms on the map. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneegurt, M.A.; Dore, S.Y.; Kulpa, C.F., Jr. Direct extraction of DNA from soils for studies in microbial ecology. Curr. Issues Molec. Biol. 2003, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, Y.-L.; Olson, B.H. Detection of low numbers of bacterial cells in soils and sediments by polymerase chain reaction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, T.; Suga, Y.; Yahiro, N.; Matsuguchi, T. Remarkable N2-fixing bacterial diversity detected in rice roots by molecular evolutionary analysis of nifH gene sequences. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 1414–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molec. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poly, F.; Monrozier, L.J.; Balle, R. Improvements in the RFLP procedure for studying the diversity of nifH genes in communities of nitrogen fixers in soil. Res. Microbiol. 2001, 152, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Héry, M.; Phillippot, L.; Mériaux, E.; Poly, F.; Le Roux, X.; Navarro, E. Nickel mine spoils revegetation attempts: Effect of pioneer plants on two functional bacterial communities involved in the N-cycle. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, X. Molecular diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria from the Tibetan Plateau, China. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 260, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, C.; Soni, R.; Jain, S.; Roy, S.; Goel, R. Diversification of nitrogen fixing bacterial community using nifH gene as a biomarker in different geographical soils of Western Indian Himalayas. J. Environ. Biol. 2010, 31, 553–556. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.H.; Tang, H.; Pu, L.J.; Sun, D.M.; Ma, J.Z.; Yu, M.; Duan, R.S. Diversity of nitrogenase (nifH) genes pool in soybean field soil after continuous and rotational cropping. J. Basic Microbiol. 2010, 50, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Das, B.; Tripathi, S.; Chakrabarti, K. nifH composition affecting nitrogen fixation in soil: Study in coastal saline region. J. Indian Soc. Coast. Agric. Res. 2015, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Calderoli, P.A.; Collavino, M.M.; Kraemer, F.B.; Morrás, H.J.M.; Aguilar, O.M. Analysis of nifH-RNA reveals phylotypes related to Geobacter and Cyanobacteria as important functional components of the N2-fixing community depending on depth and agricultural use of soil. Microbiol. Open 2017, 2017, 3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, Y.; Itoh, H.; Shiratori, Y.; Isobe, K.; Otsuka, S.; Senoo, K. Predominant by previously-overlooked prokaryotic drivers of reductive nitrogen transformation in paddy soils, revealed by metatranscriptomics. Microbes Environ. 2017, 32, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Masuda, Y.; Itoh, H.; Ushijima, N.; Shiratori, Y.; Senoo, K. Geomonas oryzae gen. nov., sp. nov., Geomonas edaphica sp. nov., Geomonas terrae sp. nov., four ferric-reducing bacteria isolated from paddy soil, and reclassification of three species of the genus Geobacter as members of the genus Geomonas gen. nov. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Su, Z.; Zhang, H. Community composition and co-occurrence patterns of diazotrophs along a soil profile in paddy fields of three soil types in China. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 82, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.-H.; Yang, S.; Tang, R.; Xie, C.-J.; Zhou, S.G. Genome analysis and description of three novel diazotrophs Geomonas species isolated from paddy soils. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 801462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Teng, Y.; Ren, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Kuramse, E.E. Variations of bacterial and diazotrophic community assemblies throughout the soil profile in distinct paddy soil types and their contributions to soil functionality. mSystems 2022, 7, e01047-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, W.; Pablo, G.P.; Jun, Y.; Danfeng, H. Abundance and diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in rhizosphere and bulk paddy soil under different duration of organic management. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bei, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhang, H.; Hao, J.; Qian, L.; Feng, Y.; Xie, Z. Unveiling of active diazotrophs in a flooded rice soil by combination of NanoSIMS and 15N2-DNA-stable isotope probing. Biol. Fert. Soils 2020, 56, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ma, K.; Lu, Y. Prevalence of betaproteobacterial sequences in nifH gene pools associated with roots of modern rice cultivars. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 57, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuever, J.; Rainey, F.A.; Widdel, F. Desulfovibrionales. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria, 2nd ed.; Brenner, D.J., Krieg, N.R., Staley, J.T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 2, Part C; pp. 922–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Piceno, Y.M.; Lovell, C.R. Stability in natural bacterial communities: I. nutrient addition effects on rhizosphere diazotroph assemblage composition. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 39, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piceno, Y.M.; Lovell, C.R. Stability in natural bacterial communities: II. Plant resource allocation effects in rhizosphere diazotroph assemblage composition. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 39, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, C.R.; Friez, M.J.; Longshore, J.W.; Bagwell, C.E. Recovery and phylogenetic analysis of nifH sequences from diazotrophic bacteria associated with dead aboveground biomass of Spartina alterniflora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 5308–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piromyou, P.; Greetatorn, T.; Teamtisong, K.; Tittabutr, P.; Boonkerd, N.; Teaumroong, N. Potential of rice stubble as a reservoir of bradyrhizobial inoculum in rice-legume crop rotation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 22, e01488-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.C.; Tiedje, J.M. Biogeography and degree of endemicity of fluorescent Pseudomonas strains in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5448–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.B.; Mills, A.L. Multi-scale variation in spatial heterogeneity for microbial community structure in an eastern Virginia agricultural field. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 44, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, P.; Buchheim, M.; Schneegurt, M. Molecular analysis of the microbial guild fixing nitrogen in ricefields. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Missouri Valley Branch of the American Society for Microbiology, Kansas City, MO, USA, 2–3 April 2003. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sawli, P.R.; Buchheim, M.A.; Schneegurt, M.A. Molecular Analysis of the Microbial Guild Fixing Nitrogen in Ricefield Soils in Missouri. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 841-849. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020054
Sawli PR, Buchheim MA, Schneegurt MA. Molecular Analysis of the Microbial Guild Fixing Nitrogen in Ricefield Soils in Missouri. Microbiology Research. 2024; 15(2):841-849. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020054
Chicago/Turabian StyleSawli, Prithi R., Mark A. Buchheim, and Mark A. Schneegurt. 2024. "Molecular Analysis of the Microbial Guild Fixing Nitrogen in Ricefield Soils in Missouri" Microbiology Research 15, no. 2: 841-849. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020054
APA StyleSawli, P. R., Buchheim, M. A., & Schneegurt, M. A. (2024). Molecular Analysis of the Microbial Guild Fixing Nitrogen in Ricefield Soils in Missouri. Microbiology Research, 15(2), 841-849. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres15020054




