Species of the Genera Neopestalotiopsis and Alternaria as Dominant Pathogen Species Attacking Mastic Trees (Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Fungal Isolation
2.2. Colony Morphology and Microscopy Observation
2.3. Application of Koch’s Postulates
2.4. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
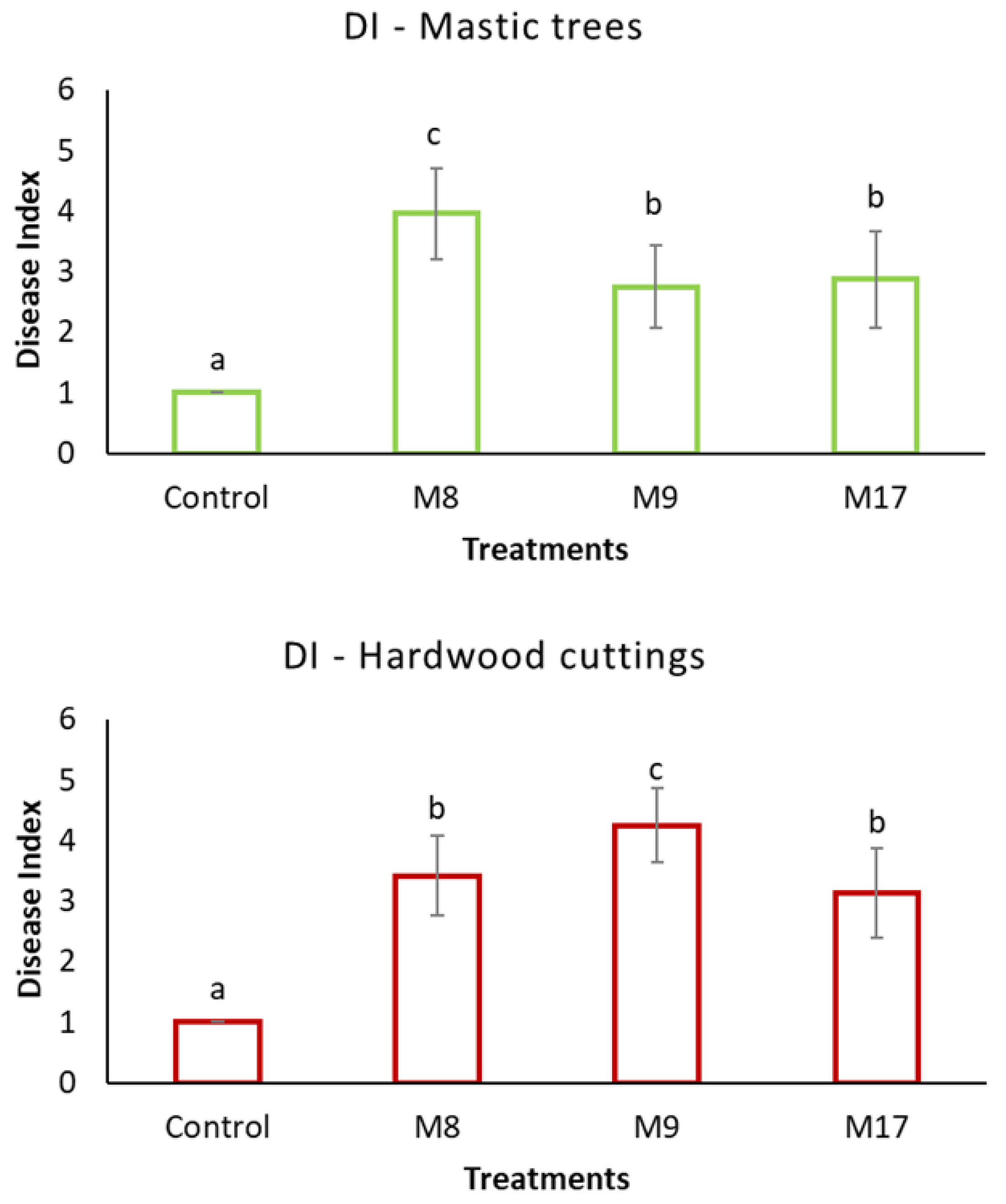
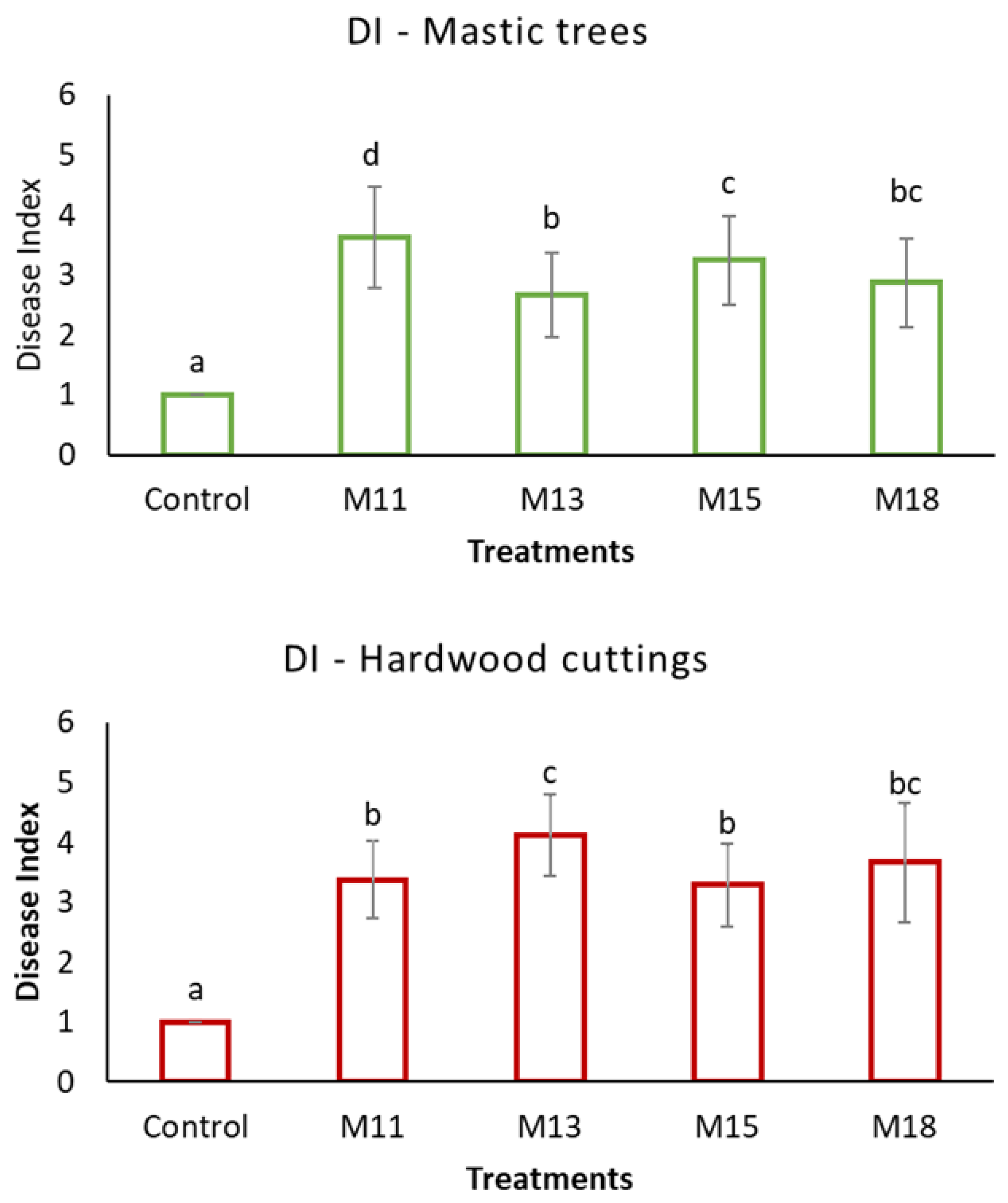
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Browicz, K. Pistacia lentiscus cv. Chia (Anacardiaceae) on Chios Island. Plant Syst. Evol. 1987, 155, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belles, C.; Sachtouri, C. Mastiha Island; Aegeas: Chios, Greece, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Paraschos, S.; Mitakou, S.; L Skaltsounis, A. Chios Gum Mastic: A Review of its Biological Activities. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2292–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soulaidopoulos, S.; Tsiogka, A.; Chrysohoou, C.; Lazarou, E.; Aznaouridis, K.; Doundoulakis, I.; Tyrovola, D.; Tousoulis, D.; Tsioufis, K.; Vlachopoulos, C.; et al. Overview of Chios Mastic Gum (Pistacia lentiscus) Effects on Human Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljubuncic, P.; Song, H.; Cogan, U.; Azaizeh, H.; Bomzon, A. The effects of aqueous extracts prepared from the leaves of Pistacia lentiscus in experimental liver disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoudaki, C.; Krsek, M.; Rodger, A. Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Activity of the Essential Oil and the Gum of Pistacia lentiscus Var. Chia. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7681–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiatis, P.; Melliou, E.; Skaltsounis, A.-L.; Chinou, I.; Mitaku, S. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of the Essential Oils of Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assimopoulou, A.; Zlatanos, S.; Papageorgiou, V. Antioxidant activity of natural resins and bioactive triterpenes in oil substrates. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyridopoulou, K.; Tiptiri-Kourpeti, A.; Lampri, E.; Fitsiou, E.; Vasileiadis, S.; Vamvakias, M.; Bardouki, H.; Goussia, A.; Malamou-Mitsi, V.; Panayiotidis, M.I.; et al. Dietary mastic oil extracted from Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia suppresses tumor growth in experimental colon cancer models. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachi, V.K.; Mikropoulou, E.V.; Gkiouvetidis, P.; Siafakas, K.; Argyropoulou, A.; Angelis, A.; Mitakou, S.; Halabalaki, M. Traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Chios mastic gum (Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia, Anacardiaceae): A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 254, 112485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huwez, F.U.; Thirlwell, D.; Cockayne, A.; Ala’Aldeen, D.A.A. Mastic Gum Kills Helicobacter pylori. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, P.; Bono, L.; Leone, E.; Bona, S.; Carretto, E.; Perversi, L. Bactericidal Activity of Pistacia lentiscus Mastic Gum Against Helicobacter pylori. J. Chemother. 2001, 13, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotirios, P.; Prokopios, M.; Sofia, M.; Kalliopi, P.; Antonios, K.; Petros, M.; Andreas, M.; Dionyssios, S.; Alexios-Leandros, S. In Vitro and In Vivo Activities of Chios Mastic Gum Extracts and Constituents against Helicobacter pylori. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabos, K.J.; Sfika, E.; Vlatta, L.J.; Giannikopoulos, G. The effect of mastic gum on Helicobacter pylori: A randomized pilot study. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, T.; Okimoto, T.; Kuwano, M. Chemical Composition of the Essential Oil of Mastic Gum and their Antibacterial Activity Against Drug-Resistant Helicobacter pylori. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect 2014, 4, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmuely, H.; Domniz, N.; Yahav, J. Non-pharmacological treatment of Helicobacter pylori. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 7, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachi, V.K.; Mikropoulou, E.V.; Dimou, S.; Dionysopoulou, M.; Argyropoulou, A.; Diallinas, G.; Halabalaki, M. Chemical Profiling of Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia Resin and Essential Oil: Ageing Markers and Antimicrobial Activity. Processes 2021, 9, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigling, M.; Fraatz, M.A.; Trögel, S.; Sun, J.; Zorn, H.; Zhang, Y. Aroma Investigation of Chios Mastic Gum (Pistacia lentiscus Variety Chia) Using Headspace Gas Chromatography Combined with Olfactory Detection and Chiral Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13420–13429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Chios Mastiha Growers Association (CGMA)—The Association of the Mastiha Producers. Available online: https://www.gummastic.gr/en/itemlist/category/26-home-gr (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- European Pharmacopoeia. Herbal Drugs and Herbal Drug Preparations; European Pharmacopoeia 9.0.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2017; p. 1430. [Google Scholar]
- Zografou, P.; Linos, A.; Hagidimitriou, M. Genetic diversity among different genotypes of Pistacia lentiscus var. chia (mastic tree). In Proceedings of the XIV GREMPA Meeting on Pistachios and Almonds, Athens, Greece, 1 January 2010; CIHEAM: Zaragoza, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- İsfendiyaroğlu, M. Propagation of Mastic Tree: From Seed to Tissue Culture. In Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, İzmir, Turkey, 2–4 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gali, Z.I. Incidences of Fungal Leaf Diseases on Mastic Shrubs in Libya. Int. J. Res. 2017, 5, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göre, M.E.; Parlak, S.; Aydın, M.H. Pestalotiopsis guepinii newly reported to cause dieback on Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia in Turkey. Plant Path. 2010, 59, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziros, G.T.; Karpouzis, A.; Lagopodi, A.L. Alternaria alternata as the cause of decline and necrosis on olive tree cuttings in Greece. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2021, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.H. Single Spore Isolation. Iowa Acad. Sci. 1930, 37, 151–159. Available online: https://scholarworks.uni.edu/pias/vol37/iss1/29 (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols a Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, M.; Peever, T.L.; Pryor, B.M. An expanded multilocus phylogeny does not resolve morphological species within the small-spored Alternaria species complex. Mycologia 2009, 101, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woudenberg, J.H.C.; Seidl, M.F.; Groenewald, J.Z.; de Vries, M.; Stielow, J.B.; Thomma, B.P.H.J.; Crous, P.W. Alternaria section Alternaria: Species, formae speciales or pathotypes? Saprobic and Phytopathogenic Dothideomycetes. Stud. Mycol. 2015, 82, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crous, P.W.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Risède, J.-M.; Simoneau, P.; Hywel-Jones, N.L. Calonectria species and their Cylindrocladium anamorphs: Species with sphaeropedunculate vesicles. Scopus 2004, 50, 415–430. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-20144389253&partnerID=40&md5=e6e40aed3e3969c5d7434f767b79e065 (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Testempasis, S.I.; Kamou, N.N.; Papadakis, E.-N.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Karaoglanidis, G.S. Conventional vs. organic vineyards: Black Aspergilli population structure, mycotoxigenic capacity and mycotoxin contamination assessment in wines, using a new Q-TOF MS-MS detection method. Food Control 2022, 136, 108860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Guo, L.-D.; Cai, L.; Chukeatirote, E.; Wu, W.P.; Sun, X.; Crous, P.W.; Bhat, D.J.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Bahkali, A.H.; et al. A multi-locus backbone tree for Pestalotiopsis, with a polyphasic characterization of 14 new species. Fungal Divers. 2012, 56, 95–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Guo, L.-D.; Chukeatirote, E.; Bahkali, A.H.; Hyde, K.D. Pestalotiopsis—Morphology, phylogeny, biochemistry and diversity. Fungal Divers. 2011, 50, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiong, F.; Lu, Q.; Hao, X.; Zheng, M.; Wang, L.; Li, N.; Ding, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Diversity of Pestalotiopsis-like Species Causing Gray Blight Disease of Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis) in China, Including two Novel Pestalotiopsis Species, and Analysis of Their Pathogenicity. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2548–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.-Q.; Deng, H.-Y.; Yang, X.-L.; Shi, B.-Z.; Zhang, J.-Z. Oleanane-Type Triterpenoids from the Endophytic Fungus Pestalotiopsis clavispora Isolated from the Chinese Mangrove Plant Bruguiera sexangula. Helv. Chim. Acta 2011, 94, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill Pérez, C.F.; Daletos, G.; Liu, Z.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Polyketides from the Mangrove-derived fungal endophyte Pestalotiopsis clavispora. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 2078–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alade, G.O.; Moody, J.O.; Bakare, A.G.; Awotona, O.R.; Adesanya, S.; Lai, D.; Debbab, A.; Proksch, P. Metabolites from endophytic fungus; Pestalotiopsis clavispora isolated from Phoenix reclinata leaf. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 4, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, M.; Aguado, A.; De los Santos, B. First report of root and crown rot caused by Pestalotiopsis clavispora (Neopestalotiopsis clavispora) on strawberry in Spain. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, V.G.; Meneguzzi, N.G.; Ibañez, J.M.; Lattar, T.E.; Kirschbaum, D.S. First Report of Neopestalotiopsis clavispora Causing Root and Crown Rot on Strawberry Plants in Argentina. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigillo, L.; Ruocco, M.; Gualtieri, L.; Pane, C.; Zaccardelli, M. First report of Neopestalotiopsis clavispora causing crown rot in strawberry in Italy. J. Plant Path. 2020, 102, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machín, A.; González, P.; Vicente, E.; Sánchez, M.; Estelda, C.; Ghelfi, J.; Silvera-Pérez, E. First Report of Root and Crown Rot Caused by Neopestalotiopsis clavispora on Strawberry in Uruguay. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarotto, M.; Muniz, M.F.B.; Poletto, T.; Dutra, C.B.; Blume, E.; Harakawa, R.; Poletto, I. First Report of Pestalotiopsis clavispora Causing Leaf Spot of Carya illinoensis in Brazil. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.C.; Domingues, J.L.; Santos, R.F.; Spósito, M.B.; Santos, A.; Novaes, Q.S. First Report of Neopestalotiopsis clavispora Causing Leaf Spot on Macadamia in Brazil. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.R.; Liu, B.S.; Sun, B.B. First Report of Leaf Blotch Caused by Pestalotiopsis clavispora on Rosa chinensis in China. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wei, J.G.; Huang, R.S.; Wei, J.F.; Luo, J.T.; Yang, X.H.; Yang, X.B. First Report of Ring Spot on Kadsura coccinea Caused by Neopestalotiopsis clavispora in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrero, C.; Castaño, R.; Avilés, M. First Report of Pestalotiopsis clavispora (Neopestalotiopsis clavispora) Causing Canker and Twig Dieback on Blueberry Bushes in Spain. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Zhao, J.; Qiao, G.H.; Liu, J.; Tan, X. First report of leaf blight caused by Alternaria alternata on Platanus acerifolia in China. Plant Dis. 2022, 0, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farr, D.F.; Rossman, A.Y. Fungal Databases, U.S. National Fungus Collections, ARS, USDA. 2019. Available online: https://nt.ars-grin.gov/fungaldatabases (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Hameed, Z.L.; Lahuf, A.A.; Jasim, M.T.; Mohsen, H.M.; Kadim, B.J.; Saleh, S.A.; Mohamed, A.F. First Report of Alternaria Alternata Causing Brown Leaf Spot on Apricot (Prunus Armeniaca) in Karbala Province of Iraq. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference for Agricultural and Sustainability Sciences, Babil, Iraq, 4–5 October 2021; Volume 910, p. 012080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezra, D.; Shulhani, R.; Bar Ya’akov, I.; Harel-Beja, R.; Holland, D.; Shtienberg, D. Factors Affecting the Response of Pomegranate Fruit to Alternaria alternata, the Causal Agent of Heart Rot. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smagulova, A.; Uakhit, R.; Kiyan, V. First Record of Alternaria alternata Causing Necrosis of Thuja (Thuja occidentalis) in Kazakhstan. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagogianni, C.S.; Tjamos, E.C.; Antoniou, P.P.; Tsitsigiannis, D.I. First Report of Alternaria alternata as the Causal Agent of Alternaria Bud and Blossom Blight of Olives. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teviotdale, B.L.; Viveros, M.; Pryor, B.; Adaskaveg, J.E. First Report of Alternaria Leaf Spot of Almond Caused by Species in the Alternaria alternata Complex in California. Plant Dis. 2001, 85, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenneker, M.; Pham, K.T.K.; Woudenberg, J.H.C.; Thomma, B.P.H.J. First Report of Alternaria arborescens Species Complex Causing Leaf Blotch and Associated Premature Leaf Drop of ‘Golden Delicious’ Apple Trees in the Netherlands. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, K.; Fourrier-Jeandel, C.; Armitage, A.D.; Boutigny, A.-L.; Crépet, M.; Caffier, V.; Gnide, D.C.; Shiller, J.; Le Cam, B.; Giraud, M.; et al. Identification and pathogenicity of Alternaria species associated with leaf blotch disease and premature defoliation in French apple orchards. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namsi, A.; Gargouri, S.; Rabaoui, A.; Mokhtar, N.; Takrouni, M.L.; Moretti, A.; Masiello, M.; Touil, S.; Dieb, L.; Werbrouck, S.P.O. First Report of Leaf Blight Caused by Alternaria mali and A. arborescens on Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera) in Tunisia. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
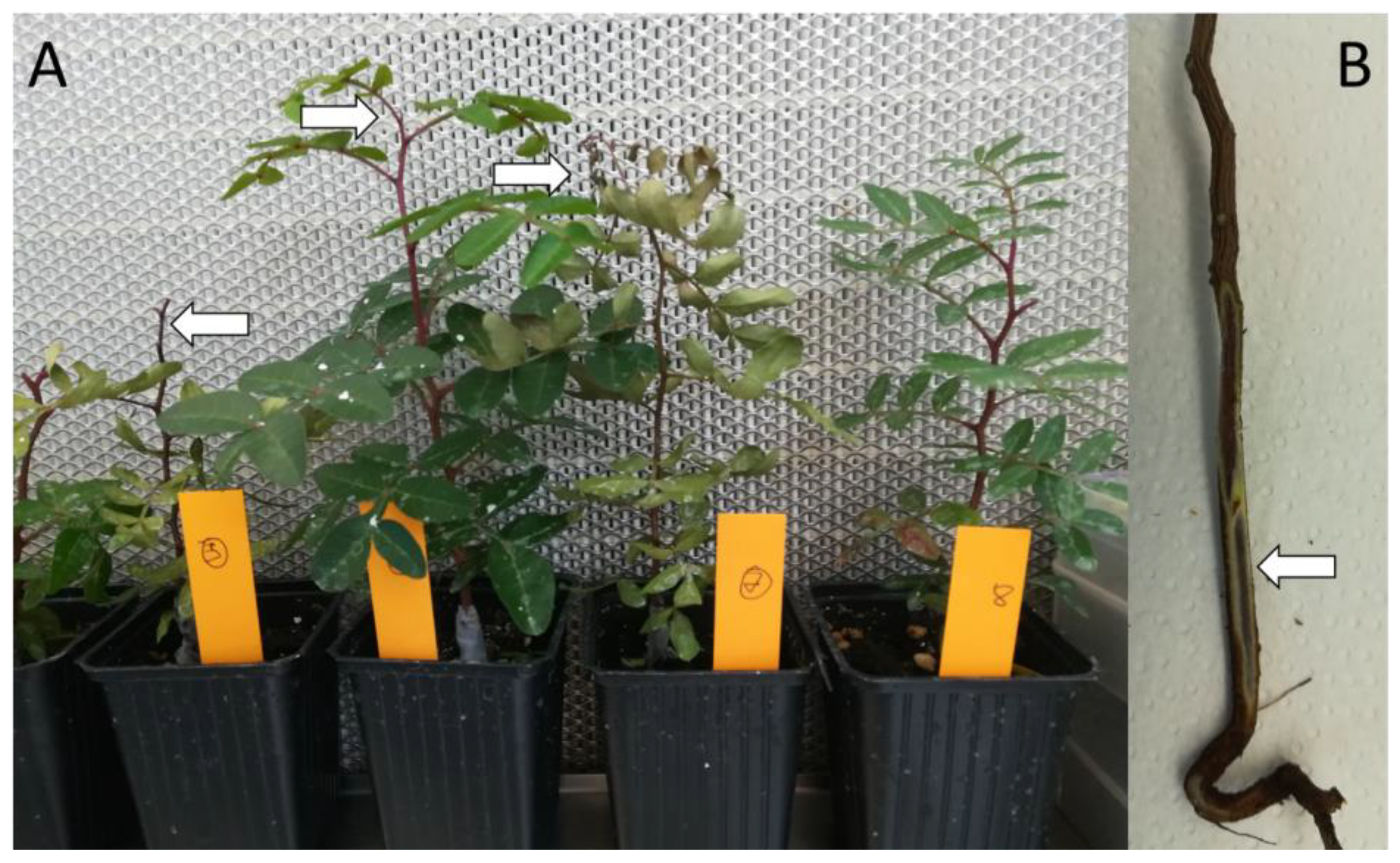
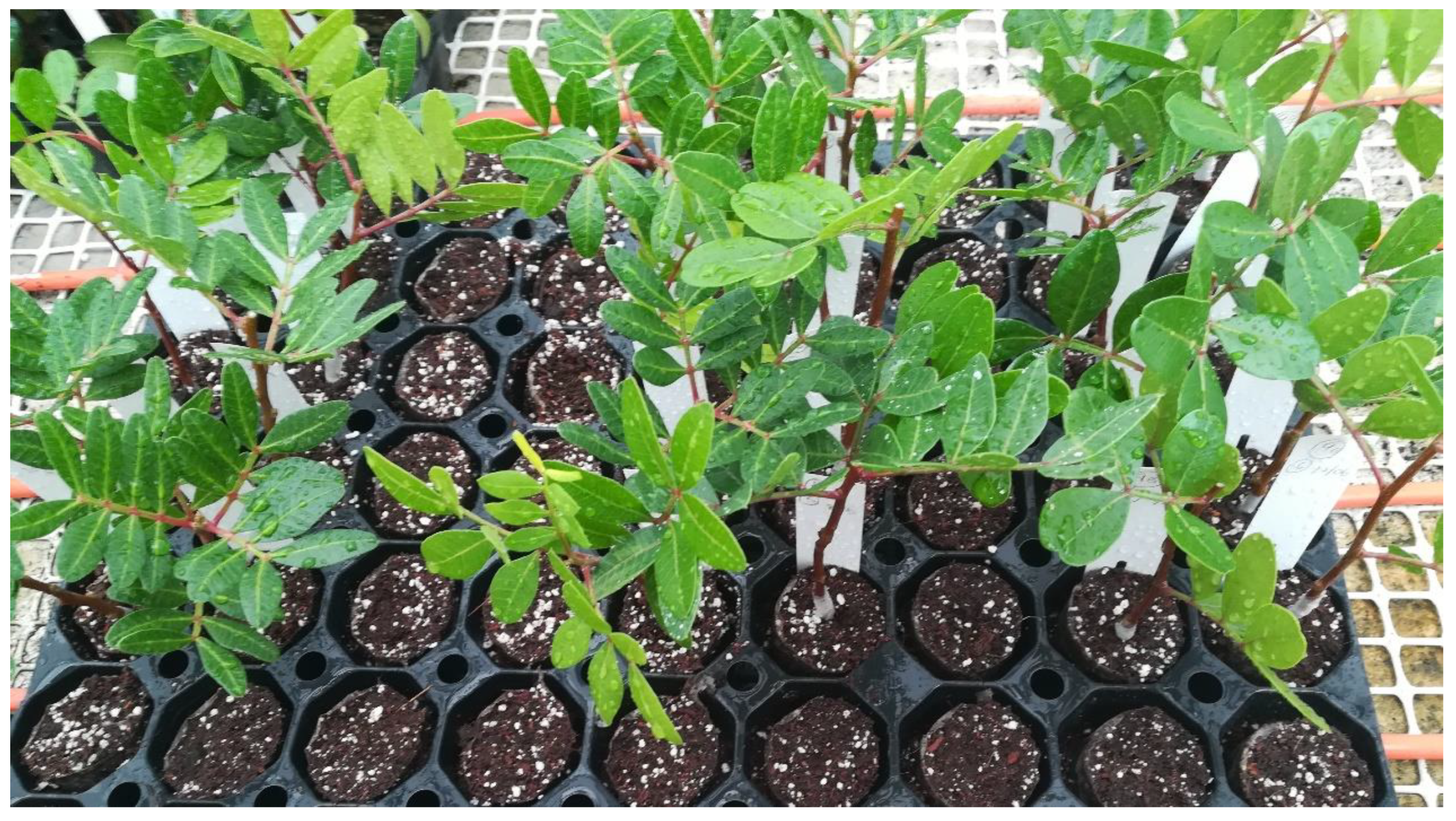
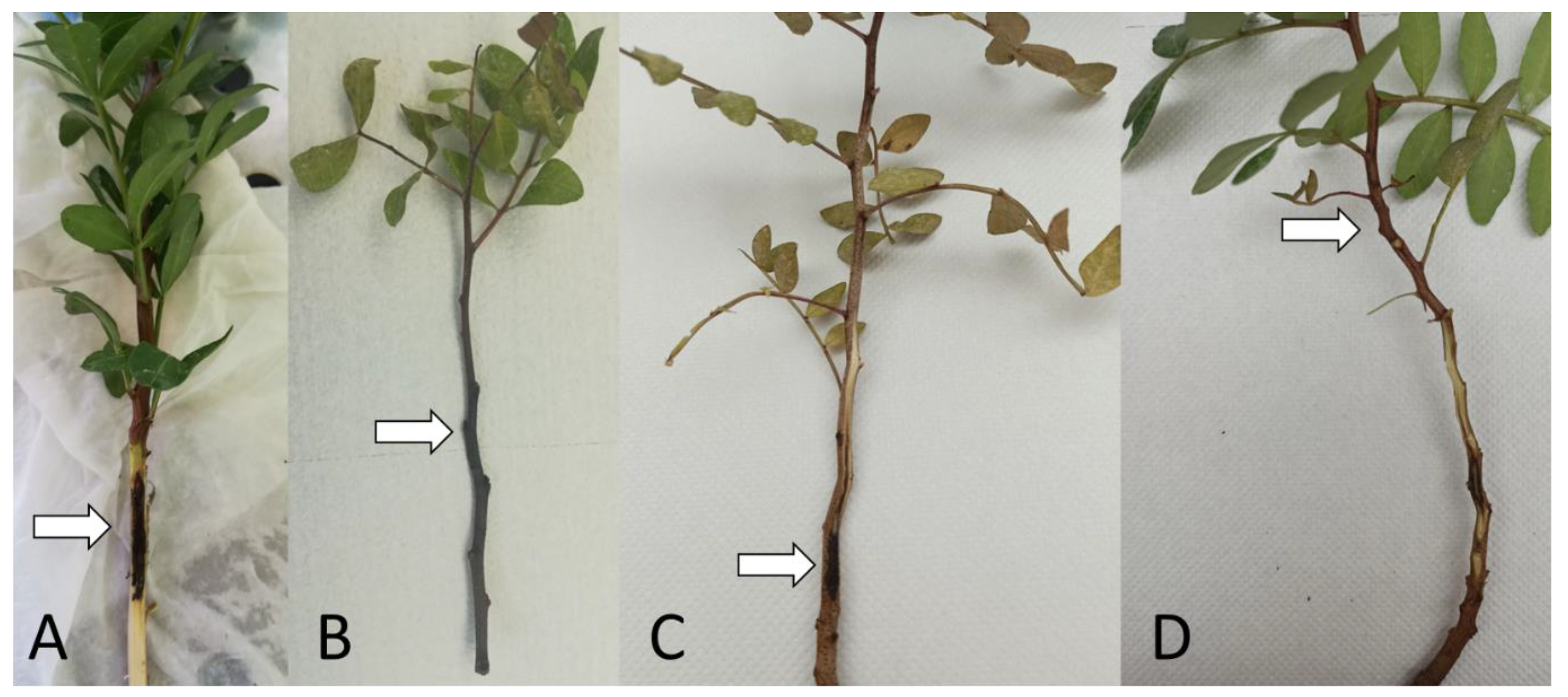
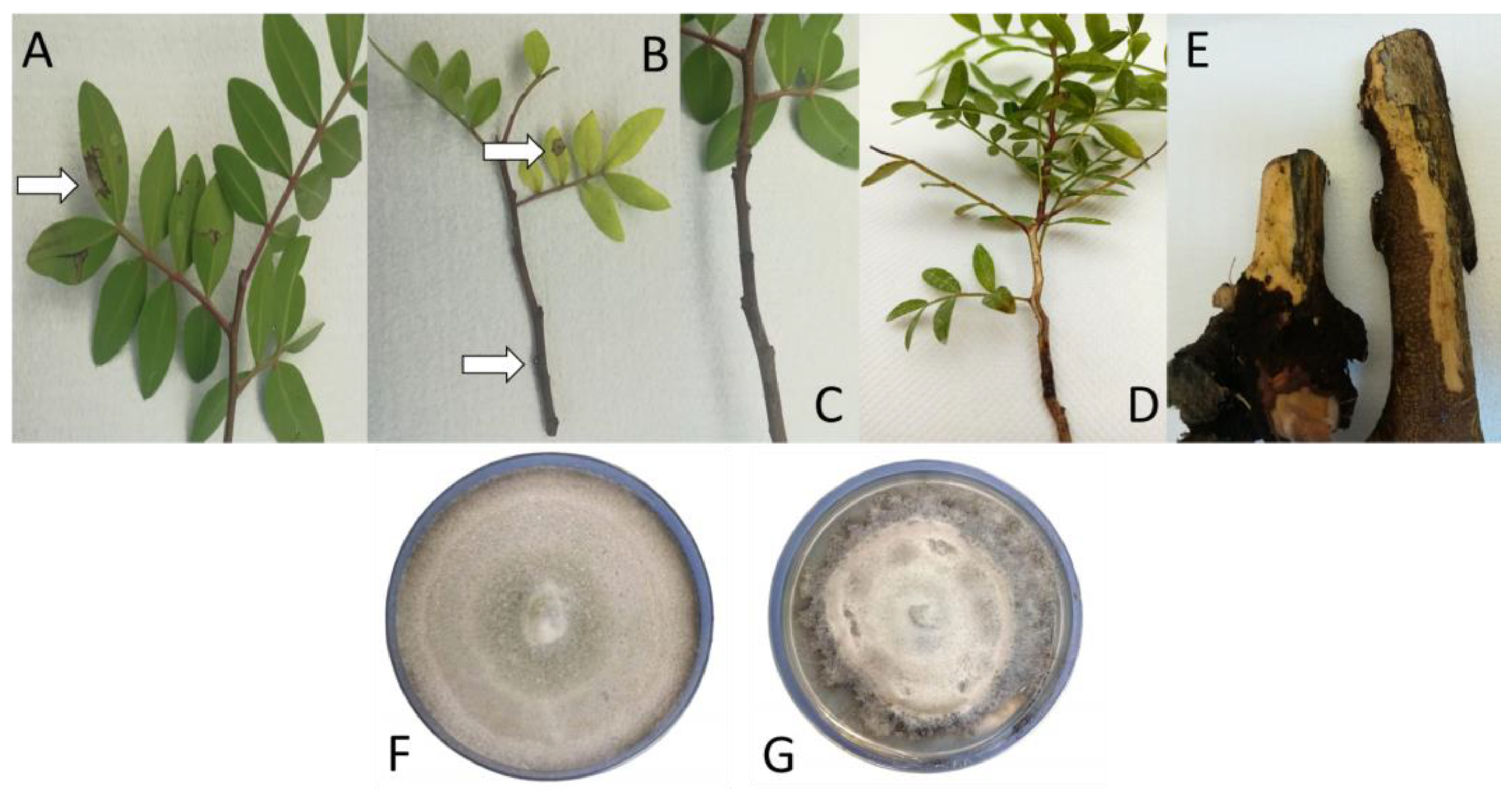






| Isolate Information | Accession Numbers | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolate Number | Fungal Species | Host, Tissue | Location | Date | ITS | β-tubulin | Alta-1 | EndoPG | Histone |
| M8 | Neopestalotiopsis clavispora | Cuttings, necrotized buds | Nursery of CMGA | May 2019 | OP783346 | OP897766 | n. a. | n. a. | n. a. |
| M9 | Alternaria arborescens | Cuttings, necrotized buds | Nursery of CMGA | May 2019 | OP783347 | n. a. | OP817016 | OP817018 | n. a. |
| M11 | Neopestalotiopsis clavispora | Mastic tree, wood rots on bark | Field, Chios Island (38°14′07″ Ν 25°57′38″ Ε) | August 2019 | OP895136 | OP897767 | n. a. | n. a. | n. a. |
| M13 | Alternaria alternata | Mastic tree, necrotic twigs, and branches, necrotic buds | Field, Chios Island (38°13′42″ Ν 26°00′17″ Ε) | November 2021 | OP895138 | n. a. | OP897762 | OP897764 | n. a. |
| M15 | Neopestalotiopsis clavispora | Mastic tree, necrotic twigs, and branches, necrotic buds | Field, Chios Island (38°14′31″ Ν 26°01′01″ Ε) | November 2021 | OP895137 | OP897768 | n. a. | n. a. | n. a. |
| M17 | Alternaria alternata | Mastic tree, necrotic twigs, and branches with discolorations, leaves with spots | Field, Chios Island (38°12′13″ Ν 25°59′59″ Ε) | November 2021 | OP783348 | n. a. | OP817017 | OP817019 | n. a. |
| M18 | Alternaria alternata/ A. tenuissima | Mastic tree, necrotic twigs, and branches with discolorations, leaves with spots | Field, Chios Island (38°12′13″ Ν 25°59′59″ Ε) | November 2021 | OP895139 | n. a. | OP897763 | OP897765 | OP897769 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamou, N.N.; Testempasis, S.; Lagopodi, A.L. Species of the Genera Neopestalotiopsis and Alternaria as Dominant Pathogen Species Attacking Mastic Trees (Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia). Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 104-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010010
Kamou NN, Testempasis S, Lagopodi AL. Species of the Genera Neopestalotiopsis and Alternaria as Dominant Pathogen Species Attacking Mastic Trees (Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia). Microbiology Research. 2023; 14(1):104-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamou, Nathalie N., Stefanos Testempasis, and Anastasia L. Lagopodi. 2023. "Species of the Genera Neopestalotiopsis and Alternaria as Dominant Pathogen Species Attacking Mastic Trees (Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia)" Microbiology Research 14, no. 1: 104-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010010
APA StyleKamou, N. N., Testempasis, S., & Lagopodi, A. L. (2023). Species of the Genera Neopestalotiopsis and Alternaria as Dominant Pathogen Species Attacking Mastic Trees (Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia). Microbiology Research, 14(1), 104-115. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres14010010






