Abstract
Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Streptococcus, GAS) is an exclusively human pathogen that causes a wide range of diseases. We have identified two novel proteins, Spy1094 and Spy1370, which show sequence similarity with peptidoglycan deacetylases (PGDAs) from other streptococcal species like S. pneumoniae and S. iniae, that represent important virulence factors. Recombinant Spy1094 and Spy1370 were active at a wide pH range (pH 4.0–9.0) and showed metal ion-dependence, with the highest activities observed in the presence of Mn2+, Mg2+and Zn2+. The enzymes showed typical Michaelis–Menten saturation kinetics with the pseudo-substrate GlcNAc3. Binding affinities for rSpy1094 and rSpy1370 were high (Km = 2.2 ± 0.9 μM and 3.1 ± 1.1 μM, respectively), but substrate turnover was low (Kcat = 0.0075/s and 0.0089/s, respectively) suggesting that peptidoglycan might not be the preferred target for deacetylation. Both enzymes were expressed during bacterial growth.
1. Introduction
Streptococcus pyogenes, or Group A Streptococcus (GAS), is a Gram-positive bacterium that exclusively infects humans and causes a wide range of diseases. These range from mild throat and skin diseases such as pharyngitis, tonsillitis and impetigo, to severe, life-threatening invasive diseases including necrotising fasciitis (‘flesh-eating disease’) and toxic shock syndrome [1,2,3,4]. If untreated, pharyngitis/tonsillitis can result in post-streptococcal autoimmune diseases such as acute rheumatic fever, rheumatic heart disease and acute glomerulonephritis [5,6,7]. It is estimated that S. pyogenes is responsible for approximately 500,000 deaths, globally, each year [8].
The success of S. pyogenes as a major human pathogen can be attributed to the production of a large arsenal of virulence factors, including spreading factors (e.g., DNases, lipases, hyaluronidase, streptokinase), immunopathogenic factors (superantigens) and immune evasion factors (e.g., C5a peptidase, SpyCEP, streptococcal inhibitor of complement) [9,10,11,12,13].
S. pyogenes is normally resistant to lysozyme and lysosomal enzymes found in human phagocytes, and this was shown to be mediated by modification of the peptidoglycan (PG) cell wall [14]. PG consists of long glycan chains crosslinked by short peptides. The glycan structure is a heteropolymer made up of alternating N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) residues that are linked β-1→4. As a strategy to evade innate immunity and to control autolysins, many pathogenic bacteria modify PG by deacetylation. Peptidoglycan N-deacetylases (PGDAs) hydrolyse the amide bonds of the 2-N-acetyl groups of GlcNAc or MurNAc residues, resulting in increased resistance to lysozyme, a muramidase that cleaves the bond between GlcNAc and MurNAc in the glycan strands [15,16]. Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) produces a PG N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase (SpPgdA), a metalloenzyme that accepts GlcNAc3 as a substrate [17]. A pgdA gene deletion mutant showed increased susceptibility to lysozyme and reduced virulence in an intraperitoneal mouse model [18]. Orthologues of PgdA have also been discovered in other important pathogens such as Streptococcus suis [19], Bacillus subtilis [20] and Listeria monocytogenes [21].
Deacetylation has also been observed in Staphylococcus epidermidis, where a metal-dependent deacetylase (IcaB) recognises and modifies bacterial biofilms. Bacteria associated with biofilms show decreased susceptibility to antibiotic treatment and attacks by the innate immune response. Poly-β-1,6-N-acetyl-d-glucosamine (PNAG), also referred to as polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA), is an exopolysaccharide that forms the extracellular matrix of some bacterial biofilms [22]. IcaB recognises and modifies PNAG, a process that is minimised in icaB gene deletion mutants, leading to impaired biofilm formation and colonisation of the bacteria (Vuong et al., 2004). An orthologue of IcaB has been described in Streptococcus iniae and named polysaccharide deacetylase of S. iniae (Pdi) [23]. Notably, both IcaB and Pdi show some sequence homology with PgdA enzymes, and were shown to also contribute to lysozyme resistance.
Peptidoglycan- or exopolysaccharide-specific deacetylases have not been reported in S. pyogenes. Here, we describe the identification and characterisation of two putative PGDAs from S. pyogenes (Spy1094 and Spy1370) that both accept GlcNAc3 as a substrate and might represent orthologues of PdgA and Pdi.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatic Analysis
Amino acid sequences were compared using Blastp at the National Center of Biotechnology Information (NCBI) (available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 1 July 2021)). The blastp (protein–protein BLAST algorithm) was used with the BLOSUM62 matrix to search the non-redundant protein sequences database. Prediction of signal peptidase sequences was performed using the SignalP-5.0 server (available online: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/ (accessed on 1 July 2021)).
2.2. Generation of Recombinant Spy1370 and Spy1094
The spy1370 and spy1094 open reading frames (ORFs) of S. pyogenes SF370 (ATCC 700294) were amplified without the regions encoding the predicted N-terminal lipid anchor sequence from genomic DNA. PCR (30 cycles) was performed with iProof polymerase (BioRad) at an annealing temperature of 53 °C, using primers spy1370-BamHI.fw (gcggatccaatcgttggaaactaaacg)/spy1370-XhoI.rev (ccgctcgagttactgatgcgcatagag) or spy1094-BamHI.fw (ggatcctatttatatcaagggtctaac)/spy1094-EcoRI.rev (gaattcttatggttccattgtttg), and subsequently cloned into the pBC vector. After confirmation by Sanger DNA-sequencing, the gene fragments were cloned into the pET32a-3c expression vector which generates thioredoxin fusion proteins with a highly specific 3c-virus protease recognition site between the inserted gene and the thioredoxin tag [24]. Plasmids were transformed into Novagen E. coli BL21 (DE3)pLysS (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Cultures were grown at 30 °C and protein expression was induced for 3–4 h after adding 0.1 mM isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The fusion proteins were purified on Ni2+-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni2+-NTA) sepharose (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. The thioredoxin tag was removed after cleavage with 3c protease by re-applying it onto a Ni2+-NTA column, as described previously [24]. The purified recombinant enzymes were analysed on 12.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gels. The protein concentrations were determined by reading the optical density (OD280) using a Nanodrop spectrophotometer and corrected with the specific extinction coefficients. The recombinant proteins were aliquoted and stored at −80 °C immediately after purification.
2.3. Biochemical Assays
The standard reaction mix contained 50 mM Bis-Tris pH 7.0, 5 μM MgCl2, 100 nM recombinant enzyme and 35 μM GlcNAc3 (Sigma-Aldrich) as the substrate. After incubation for 1 h at 37 °C, 50 μL of 0.4 M borate buffer, pH 9.0 was added. To label free amines, 2 mg fluorescamine/mL (Sigma-Aldrich) in dimethylformamide (DMF) was added. The reaction mix was incubated for 10 min at room temperature before the reaction was stopped with the addition of 150 μL of DMF/H2O (1:1). Fluorescence was measured in a Perkin-Elmer Ensight multimode plate reader with excitation/emission wavelengths of 360 nm and 460 nm, respectively. The production of free amine was quantified with a glucosamine standard (Sigma-Aldrich). Michaelis–Menten curve fitting using non-linear regression was performed using GraphPad Prism version 7.03 software.
Analysis of pH and metal dependence was carried out with 100 nM recombinant enzyme and 35 μM GlcNAc3 at 37 °C. Bis-Tris buffer was replaced by citrate buffer for analysis at pH 4.0 to pH 6.0. To analyse metal-dependency of the enzymes, the 100 mM EDTA was added to the recombinant proteins to remove the bound metals. EDTA was removed by dialysing the proteins against PBS before 5 μM of NiSO4, ZnCl2, CaCl2, MgCl2, MnCl2, or FeCl2. was added. Reactions were measured in triplicates.
2.4. Generation of Enzyme-Specific Antibodies
Next, 100 μg of either rSpy1094 or rSpy1370 were mixed 1:1 with incomplete Freund’s adjuvant (Sigma-Aldrich) in a total volume of 1 mL and injected subcutaneously into a New Zealand White rabbit, followed by two booster immunisations on days 14 and 28. Immune serum was collected on day 42. Pre-immune serum (PIS) was collected before immunisation. All animal work was carried out in the Vernon Jansen Unit (VJU) at the University of Auckland according to ARRIVE guidelines and approved by the University of Auckland Animal Ethics Committee (approved code: R2173, approved date: 30 May 2019).
2.5. Western-Blot Analysis
S. pyogenes strain SF370 (serotype M1) was grown in Brain Heart Infusion broth (Bacto) at 37 °C without shaking. Samples were taken after 3 h (OD600 = 0.4), 8 h (OD600 = 1.1) and 24 h (OD600 = 1.2). Bacterial cells from 50 mL of culture were pelleted by centrifugation (4500× g for 15 min), resuspended in 5 mL of PBS, and sonicated 4× for 30 s using a QSonica Q700 sonicator. Then, 5 μL of the lysate was loaded onto a 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel. Cell culture supernatant (5 μL) was loaded onto the gel directly without concentrating. The protein gels were blotted onto Biotrace nitrocellulose membranes (Biolab, Singapore), blocked with 5% milk/TBS-T for 1 h at room temperature and incubated with either anti-rSpy1094 or anti-rSpy1370 serum from immunised rabbits at 1:1000 dilution. Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H + L) secondary antibody conjugated with horse radish peroxidase (HRP) (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) was used at 1:1000 dilution. The blots were developed using ECL Detection Reagent (Biolab, Singapore) and visualised on a BioRad ChemiDoc imaging system.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification of Peptidoglycan Deacetylases in S. pyogenes
PGDAs have been identified in several bacterial pathogens, but have not yet been reported in S. pyogenes. Using the amino acid sequence of the two previously characterised PGDAs, S. pneumoniae PdgA and S. iniae Pdi, we searched the whole genome of the S. pyogenes SF370 reference strain. S. pneumoniae PdgA showed 35% identity and 55% similarity with the uncharacterised gene product Spy1370, whereas S. iniae Pdi showed 72% identity and 85% similarity with Spy1094. Next, we used the putative S. pyogenes PGDA sequences to search the genomes of other streptococci. We found that Spy1370 is related to S. iniae PgdA (48% identity, 69% similarity), and most closely to putative PGDAs in Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis (68% identity, 82% similarity), Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus (60% identity, 72% similarity), and Streptococcus agalactiae (60% identity, 77% similarity). Spy1094 is most closely related to S. iniae Pdi and putative deacetylases from S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis (75% identity, 84% similarity), Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus (67% identity, 80% similarity) and Streptococcus mutans (57% identity, 70% similarity).
Spy1370 and Spy1094 are found in a wide range of S. pyogenes strains and are highly conserved with 91–100% and 94–100% amino acid identity, respectively. Both proteins contain a N-terminal hydrophobic region, but no predicted signal peptidase cleavage site. This suggests that the proteins are anchored in the bacterial membrane.
3.2. Biochemical Analysis of Spy1094 and Spy1370
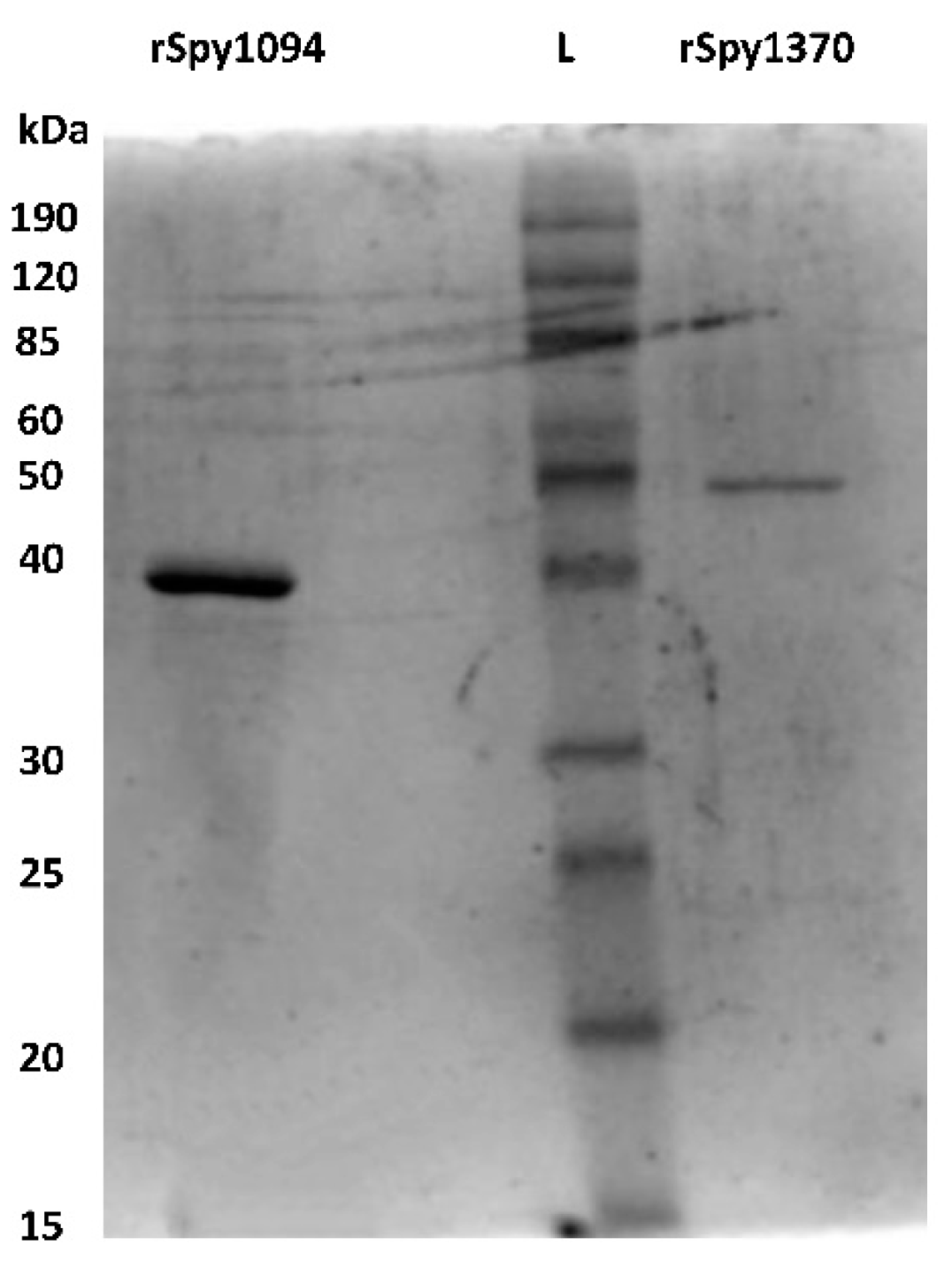
Spy1094 and Spy1370, without the predicted N-terminal membrane anchor sequences (amino acids 1 to 33 in Spy1094, and 1 to 24 in Spy1370), were expressed in Escherichia coli as thioredoxin fusion proteins and purified by metal chelate affinity chromatography (IMAC). After removal of the thioredoxin with 3c protease, the proteins showed an estimated purity of >90% on an SDS-PAGE gel (Figure 1). The molecular weight (MW) for recombinant Spy1094 (rSpy1094) was estimated at ~38 kDa, which is slightly higher than the theoretical molecular weight of 32,584.24 daltons. The MW for rSpy1370 was estimated at 50 kDa, which is higher than the theoretical MW of 45,666.84 daltons. The final yield for rSpy1094 and rSpy1370 per litre of E. coli culture was 1.9 mg and 0.7 mg, respectively.
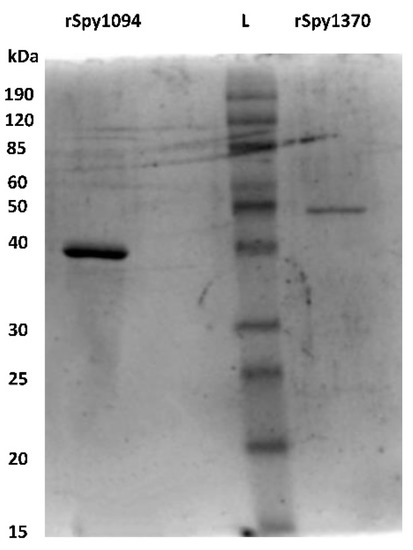
Figure 1.
Purified recombinant Spy1094 and rSpy1370. The proteins were expressed in E. coli as thioredoxin fusion proteins and purified by immobilised metal chelate affinity chromatography (IMAC) using an NTA-Ni2+ resin. Thioredoxin was cleaved-off with 3c protease and removed by passing the solution over NTA-Ni2+ again. The purified proteins were run on a 12.5% SDS PAGE gel and have an estimated purity of >90%.
Biochemical assays were initially carried out with 100 nM recombinant protein and 35 µM GlcNAc3 as a substrate at 37 °C and pH 7.0 in accordance to the protocol described for SpPgdA [17]. The release of free amines as a result of deacetylation was measured via a reaction with fluorescamine.
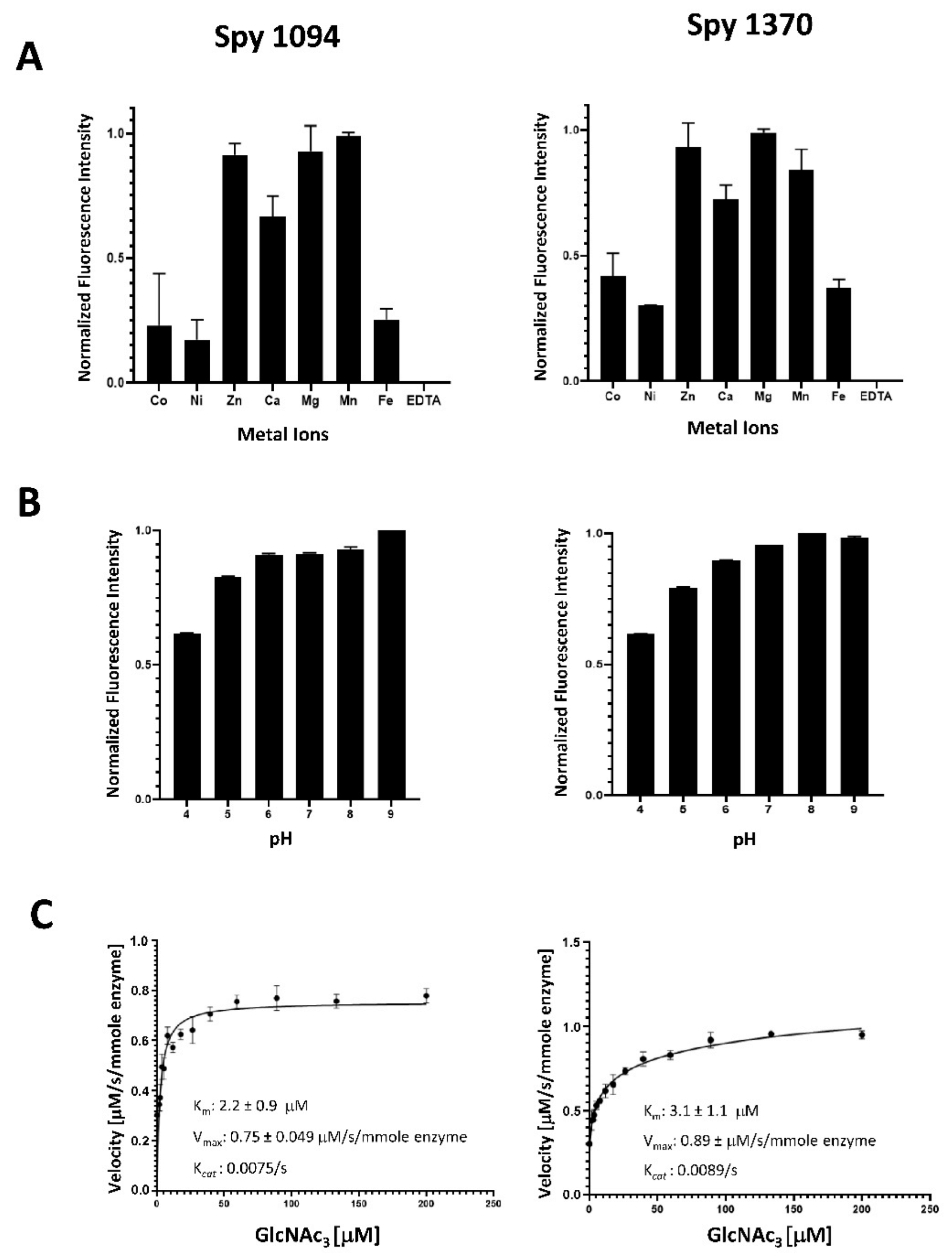
We first tested metal dependence of rSpy1370 and rSpy1094 using a range of metal ions previously assessed for other peptidoglycan deacetylases after removing naturally bound metal ions with 100 mM EDTA. Addition of EDTA abolished all rSpy1094 and rSpy1370 function, confirming their dependence on metal ions (Figure 2A).
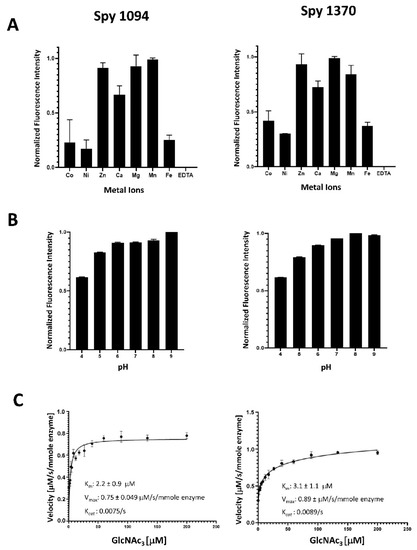
Figure 2.
Biochemical analysis of rSpy1094 and rSpy1370. Metal requirement, pH range and enzyme kinetics of rSpy1094 (left) and rSpy1370 (right) were determined by measuring the release of free amines from the pseudo-substrate GlcNAc3. (A) Deacetylation of 35 μM GlcNAc3 with 100 nM enzyme was measured using a range of divalent cations at pH 7.0 at 37 °C. (B) Deacetylation of 35 μM GlcNAc3 with 100 nM enzyme was measured at a pH range of 4.0–9.0 at 37 °C in the presence of 5 µM MgCl2. (C) The Vmax and Km values for deacetylation of the GlcNAc3 were obtained by velocity measurements with different concentrations of substrate and calculated using GraphPad Prism version 7.03 software. Experiments were carried out in triplicates. Bar graphs show the average ± standard deviation.
Both rSpy1094 and rSpy1370 showed highest activity in the presence of Mg2+, Mn2+ and Zn2+, followed by Ca2+ (about 65% activity for rSpy1094 and 70% activity for rSpy1370). The lowest activity was seen with Ni2+, Co2+, and Fe2+ (<50% activity). This was similar to the metal requirement for B. subtilis PdaC, which was reported to be mostly active in the presence of Mn2+, followed by Ca2+, Mg2+, and Zn2+. The lowest activity was observed with Ni2+ [20]. Differences in metal requirements were reported for other peptidoglycan deacetylases. S. epidermidis IcaB showed maximum enzymatic activity with Co2+, followed by Zn2+ and Mn2+ (>50% activity), but was less active with Ni2+, Ca2+ and Fe2+ (<50% activity) [25]. S. pneumoniae PdgA was also reported to show maximum activity in the presence of Co2+, but was only moderately active (<20%) with Zn2+, Mn2+, Ni2+ and Fe2+ and weakly active (<10%) with Cu2+ and Cd2+. S. pneumoniae PdgA was inactive in the presence of Cu2+ or Mg2+ [17]. The most surprising finding was the strong activity of rSpy1370 in the presence of Mg2+, a reaction condition in which S. pneumoniae PdgA is completely inactive. However, the two proteins share only 35% amino acid identity, suggesting some marked differences in the metal binding site (s). Notably, B. subtilis PdaC was approximately 50% active with Mg2+ when compared to Mn2+ [20]. A better insight into the metal requirements might emerge in the future with the structural analysis of additional peptidoglycan deacetylases.
Both rSpy1094 and rSpy1370 were active over a wide pH range (pH 6.0–9.0) (Figure 2B), similar to other peptidoglycan deacetylases. Both enzymes were also active at pH 5.0 and pH 4.0, but with reduced activity (about 80% and 60%, respectively). S. pneumoniae PdgA has a reported pH optimum at pH 9.0 [17], whereas S. epidermidis IcaB showed maximum activity at pH 8.0 [25]. Like rSpy1370, IcaB was slightly less active at pH 6.0, whereas the Bacillus cereus bc1960 peptidoglycan deacetylase was shown to be optimally active at pH 6.0 [26]. Our results suggest that Spy1094 and Spy1370 are active at all physiologically relevant pH conditions.
rSpy1094 and rSpy1370 showed typical Michaelis–Menten saturation kinetics with similar Km values of 2.2 ± 0.9 μM (rSpy1094) and 3.1 ± 1.1 μM (rSpy1370), Vmax of 7.5 ± 0.49 μM/s/mmole enzyme (rSpy1094) and 8.9 ± 0.65 μM/s/mmole enzyme (rSpy1370) and Kcat values of 0.0075/s (rSpy1094) and 0.0089/s (rSpy1370) (Figure 2C). These were substantially different from the kinetics reported for SpPdgA (Km = 3.8 ± 0.5 mM; Vmax = 0.055 ± 0.003 μM/s and Kcat of 0.55/s) [17]. Other bacterial deacetylases also had reported Km values in the low mM range. However, there were also substantial differences in the substrate turn-over rates. IcaB from Staphylococcus epidermidis had a very low Kcat of 0.0007/s when GlcNAc3 was used as a substrate [25]. It should be noted that IcaB was found to play a role in S. epidermidis biofilm formation by deacetylating polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA), a GlcNAc polymer. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis deacetylase Rv1096 had a Kcat of 0.099/s when peptidoglycan was used as a substrate. Rv1096 is a peptidoglycan deacetylase that contributes to lysozyme resistance [27]. The length of the GlcNAc oligomer and the location of the substrate binding site relative to the catalytic site might both play a role in substrate turn-over. Analysis of the Spy1094 and Spy1370 protein structures might shed further light on this. GlcNAc is part of a variety of carbohydrate polymers and therefore it is also possible that peptidoglycan is not the actual substrate of Spy1094 and Spy1370. We are currently in the process of generating gene deletion mutants which will allow us to analyse lysozyme sensitivity, which is generally decreased by the deacetylation of peptidoglycan.
3.3. Expression of Spy1094 and Spy1370 during S. pyogenes Growth in Culture
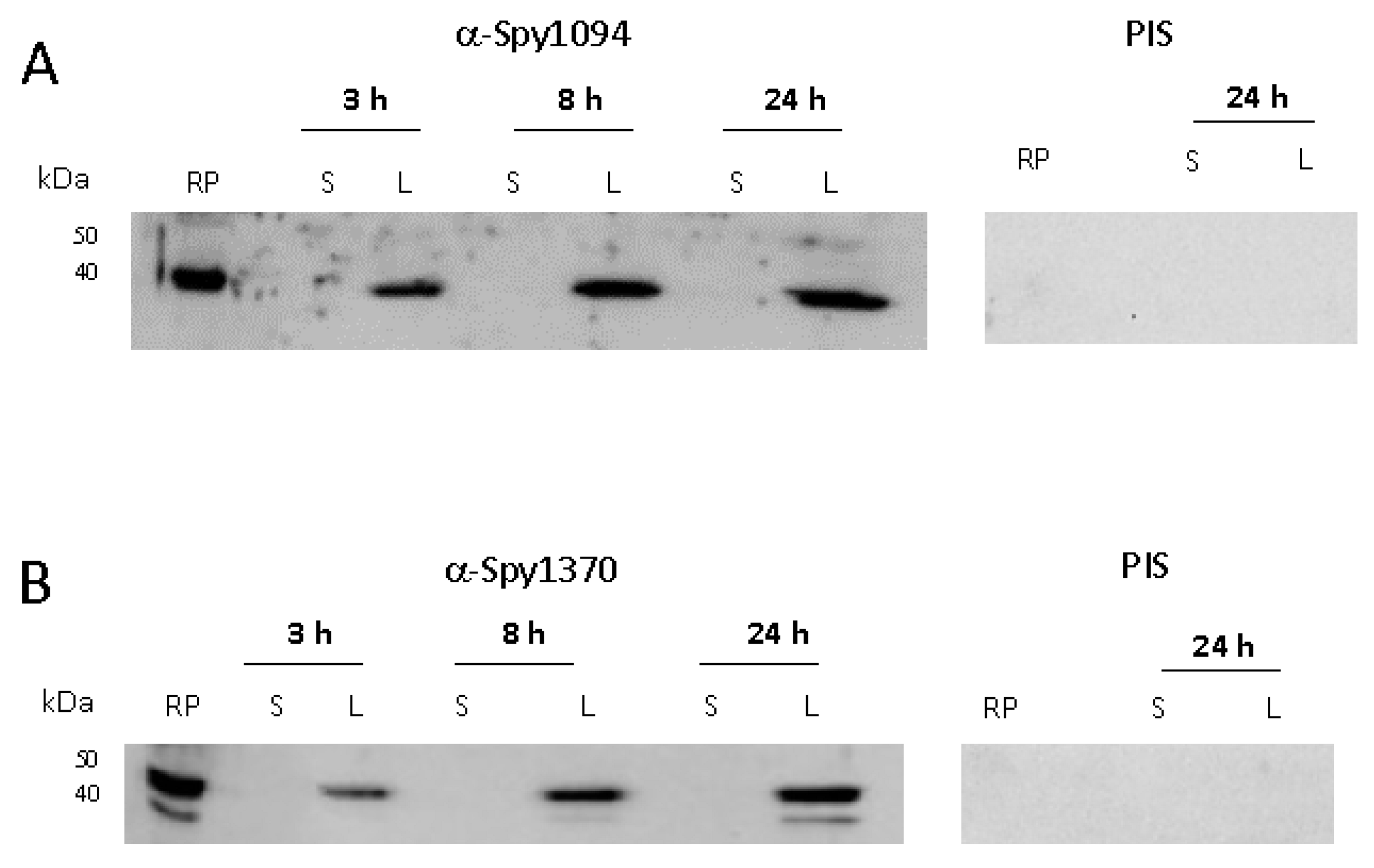
Neither the enzyme kinetics and pH range nor the metal requirement revealed any substantial differences between rSpy1094 and rSpy1370, suggesting that the proteins might be redundant. Therefore, we investigated whether the two enzymes are produced during different growth phases which might also reflect their expression at different stages of infection. S. pyogenes was grown to early exponential phase (3 h, OD600 = 0.4), late exponential phase (8 h, OD600 = 1.1) and stationary phase (24 h, OD600 = 1.2). Sonicated bacterial lysate and culture supernatant were analysed by Western blot with specific serum raised against rSpy1094 or rSpy1370 in rabbits (Figure 3 and Supplementary Figure S1). Both proteins were expressed during all growth phases, again suggesting that the enzymes might be redundant. No protein was found in the cell culture supernatant, confirming their predicted location within the bacterial cell.
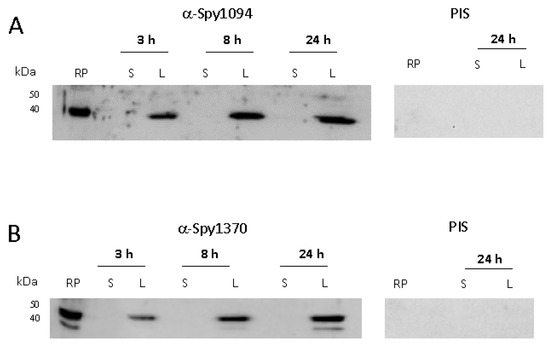
Figure 3.
Expression of Spy1094 and Spy1370 during in vitro bacterial growth. S. pyogenes strain SF370 (serotype M1) was grown in BHI broth for 3 h (OD600 = 0.4), 8 h (OD600 = 1.1) and 24 h (OD600 = 1.2) at 37 °C without shaking. Sonicated bacterial lysate (L) and cell culture supernatant (S) were analysed by Western blot using specific antibodies raised against the purified recombinant proteins in rabbits; 2 μg of recombinant protein (RP) was loaded as a control. PIS, pre-immune serum. (A) Spy1094. (B) Spy1370.
4. Conclusions
We successfully generated soluble recombinant forms of the two putative S. pyogenes deacetylases, Spy1094 and Spy1370, and analysed their activity using the pseudo-substrate GlcNAc3. Although we found specific deacetylation of GlcNAc3, our results suggest that either longer GlcNAc oligomers are required to achieve full enzymatic activity, or that the enzymes are specific for other GlcNAc containing carbohydrate polymers.
Peptidoglycan deacetylases have been found in many bacterial species and have an important role in host immune evasion by increasing susceptibility to lysozyme. Our results might provide a basis for the future development of specific treatment options against S. pyogenes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microbiolres13020025/s1, Figure S1: Expression of Spy1094 and Spy1370 during in vitro bacterial growth (the complete (uncropped) Western blot).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.P.; methodology, T.A. and A.H.J.K.; formal analysis, T.A.; investigation, T.A., J.M.S.L. and C.J.-Y.T.; data curation, T.A. and T.P.; writing—original draft preparation, T.A.; writing—review and editing, T.P., J.M.S.L. and C.J.-Y.T.; visualization, T.A. and T.P.; supervision, T.P., J.M.S.L. and C.J.-Y.T.; project administration, T.P.; funding acquisition, T.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by a Graduate Student Fund from the University of Auckland. J.M.L. is a New Zealand National Heart Foundation Senior Research Fellow. C.T. is an Auckland Medical Research Foundation Postdoctoral Research Fellow.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal work was carried out according to ARRIVE guidelines and approved by the University of Auckland animal ethics committee (approved code: R2173, approved date: 30 May 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or Supplementary Material.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Natalie Lorenz (University of Auckland) for assistance with calculating enzyme kinetics.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Botteaux, A.; Budnik, I.; Smeesters, P.R. Group A Streptococcus infections in children: From virulence to clinical management. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.W. Pathogenesis of group A streptococcal infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 470–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.L. Streptococcal toxic-shock syndrome: Spectrum of disease, pathogenesis, and new concepts in treatment. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1995, 1, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, D.L.; Bryant, A.E. Severe Group A Streptococcal Infections. In Streptococcus pyogenes: Basic Biology to Clinical Manifestations; Ferretti, J.J., Stevens, D.L., Fischetti, V.A., Eds.; The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center: Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, M.W. Streptococcus and rheumatic fever. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2012, 24, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.J.; Steer, A.C.; Smeesters, P.R.; Keeble, J.; Inouye, M.; Carapetis, J.; Wicks, I.P. Post-infectious group A streptococcal autoimmune syndromes and the heart. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 710–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, J.; Pedreanez, A. Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis: Analysis of the pathogenesis. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carapetis, J.R.; Steer, A.C.; Mulholland, E.K.; Weber, M. The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases. The Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, S.; Barnett, T.C.; Rivera-Hernandez, T.; Rohde, M.; Walker, M.J. Streptococcus pyogenes adhesion and colonization. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 3739–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.N.; Barnett, T.C.; Nizet, V.; Walker, M.J. Molecular insight into invasive group A streptococcal disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.J.; Shelburne, S.A.; Musser, J.M. Molecular mechanisms underlying group A streptococcal pathogenesis. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proft, T.; Fraser, J. Superantigens: Just like peptides only different. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 819–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proft, T.; Fraser, J.D. Streptococcal superantigens. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2007, 93, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, A.D.; Ranhand, J.M.; Cole, R.M. Degradation of group A streptococcal cell walls by egg-white lysozyme and human lysosomal enzymes. Infect. Immun. 1972, 6, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragunde, H.; Biarnes, X.; Planas, A. Substrate Recognition and Specificity of Chitin Deacetylases and Related Family 4 Carbohydrate Esterases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moynihan, P.J.; Sychantha, D.; Clarke, A.J. Chemical biology of peptidoglycan acetylation and deacetylation. Bioorg. Chem. 2014, 54, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, D.E.; Schuttelkopf, A.W.; MacRae, J.I.; van Aalten, D.M. Structure and metal-dependent mechanism of peptidoglycan deacetylase, a streptococcal virulence factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15429–15434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, W.; Tomasz, A. Peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase, a putative virulence factor in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 7176–7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Sekizaki, T.; Takamatsu, D.; de la Cruz Dominguez-Punaro, M.; Harel, J.; Bui, N.K.; Vollmer, W.; Gottschalk, M. Significant contribution of the pgdA gene to the virulence of Streptococcus suis. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 1120–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Sudiarta, I.P.; Kodama, T.; Fukushima, T.; Ara, K.; Ozaki, K.; Sekiguchi, J. Identification and characterization of a novel polysaccharide deacetylase C (PdaC) from Bacillus subtilis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9765–9776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boneca, I.G.; Dussurget, O.; Cabanes, D.; Nahori, M.A.; Sousa, S.; Lecuit, M.; Psylinakis, E.; Bouriotis, V.; Hugot, J.P.; Giovannini, M.; et al. A critical role for peptidoglycan N-deacetylation in Listeria evasion from the host innate immune system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branda, S.S.; Vik, S.; Friedman, L.; Kolter, R. Biofilms: The matrix revisited. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.J.E.; Aziz, R.K.; Locke, J.B.; Dahesh, S.; Nizet, V.; Buchanan, J.T. The novel polysaccharide deacetylase homologue Pdi contributes to virulence of the aquatic pathogen Streptococcus iniae. Microbiology 2010, 156, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proft, T.; Webb, P.D.; Handley, V.; Fraser, J.D. Two novel superantigens found in both group A and group C Streptococcus. Infect Immun. 2003, 71, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovskaya, V.; Poloczek, J.; Little, D.J.; Griffiths, H.; Howell, P.L.; Nitz, M. Functional characterization of Staphylococcus epidermidis IcaB, a de-N-acetylase important for biofilm formation. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 5463–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psylinakis, E.; Boneca, I.G.; Mavromatis, K.; Deli, A.; Hayhurst, E.; Foster, S.J.; Varum, K.M.; Bouriotis, V. Peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylases from Bacillus cereus, highly conserved proteins in Bacillus anthracis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30856–30863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, F.; Kang, J.; Zhang, W.; Deng, G.; Xin, Y.; Ma, Y. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv1096 protein: Gene cloning, protein expression, and peptidoglycan deacetylase activity. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).