Advances in the Treatment of Enterovirus-D68 and Rhinovirus Respiratory Infections
Abstract
1. Background
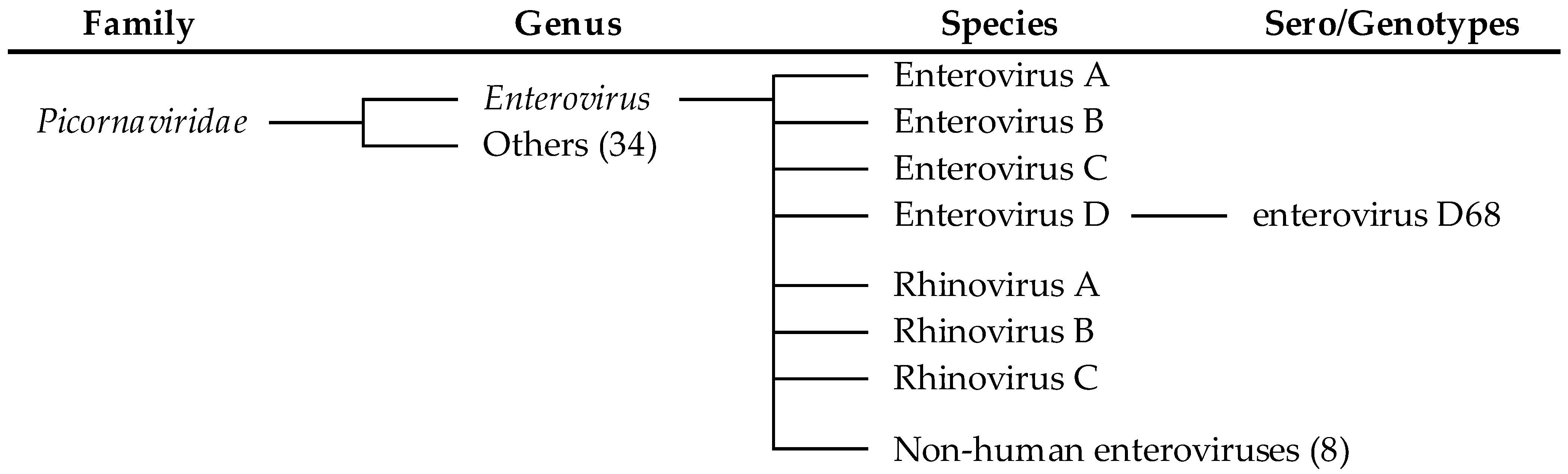
2. Enterovirus Classification
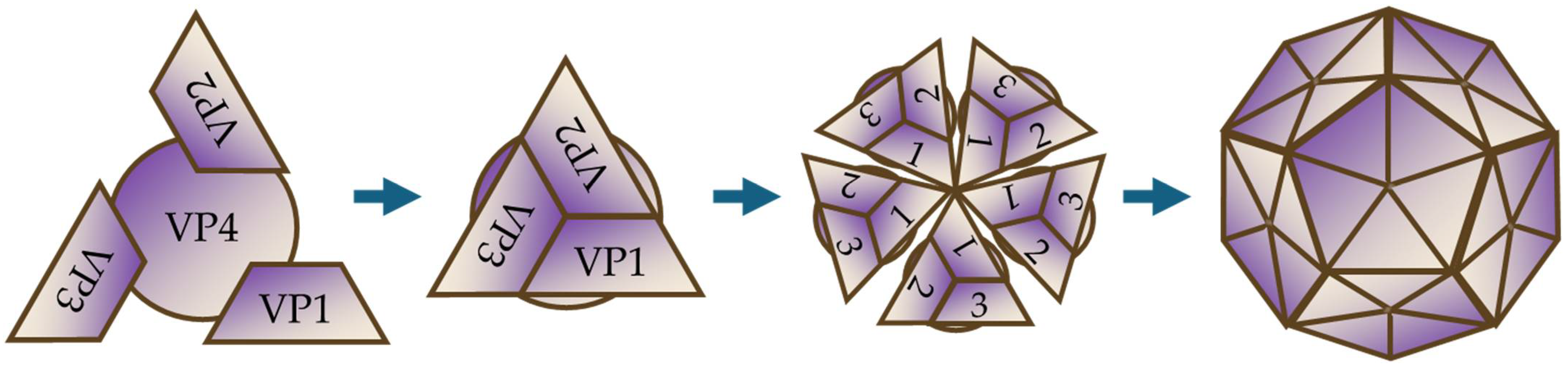
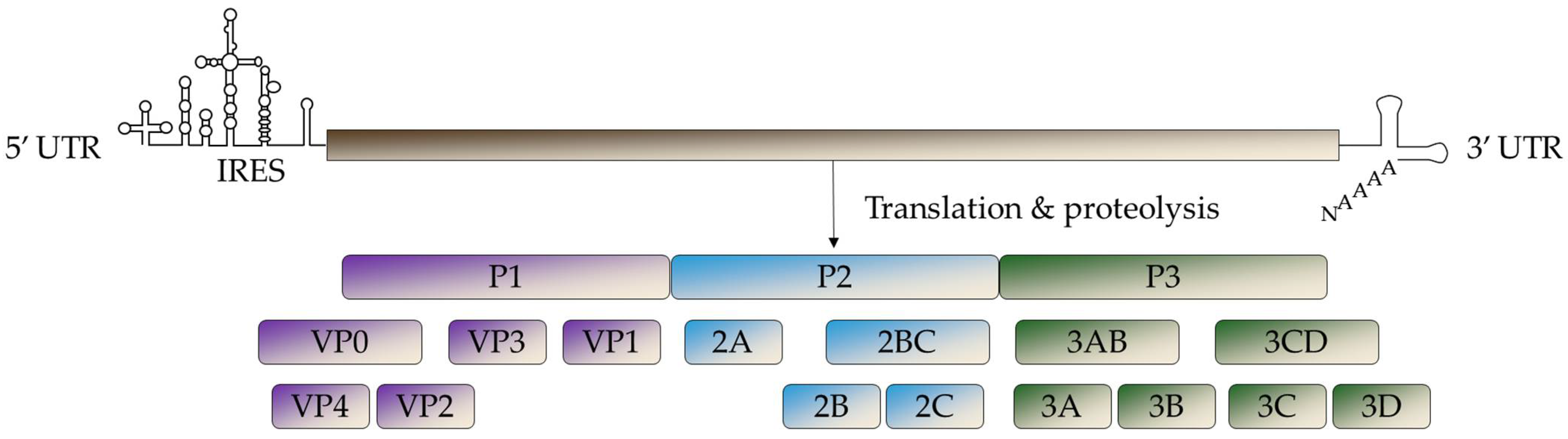
3. Virological Characteristics
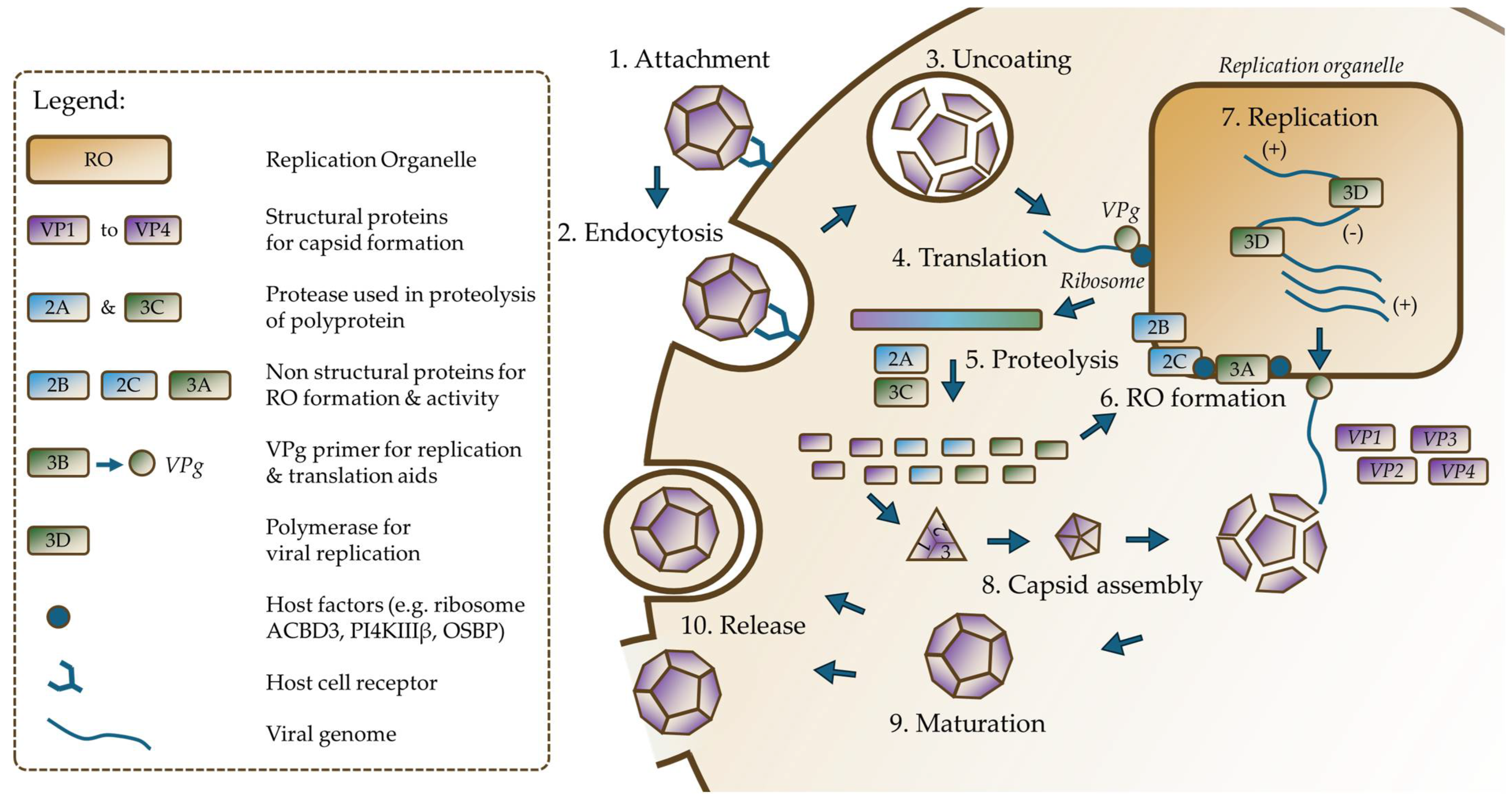
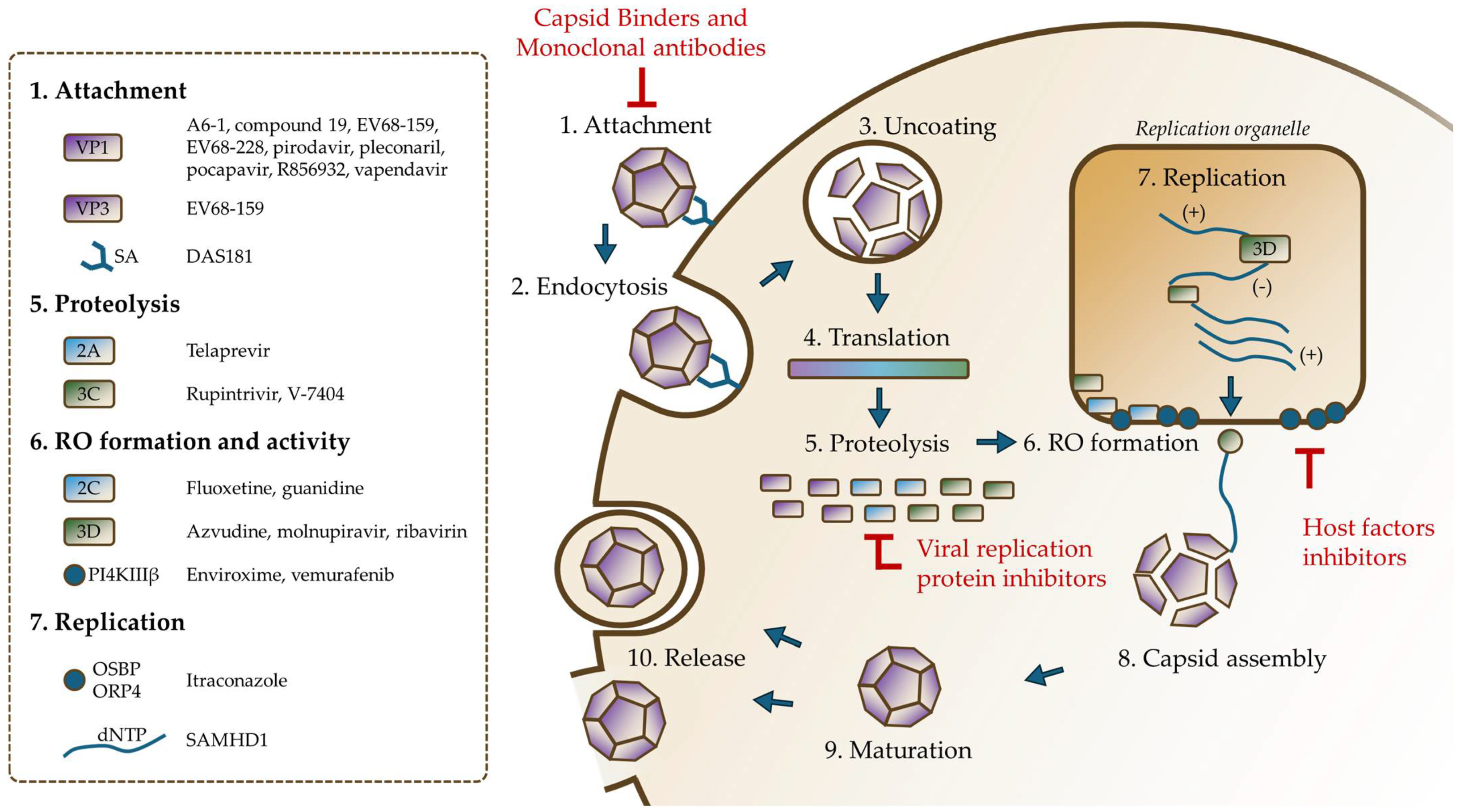
4. Replicative Cycle
5. Current Strategies in Enterovirus Antiviral Research
5.1. Experimental Models
5.2. Broad-Spectrum and Adaptable Treatments
6. Emerging Antiviral Candidates for RV-D68 and RVs
6.1. Capsid Binders
6.1.1. Pleconaril
6.1.2. Pirodavir and Vapendavir
6.1.3. Pocapavir
6.1.4. R856932
6.1.5. Quinoline Derivative Compound 19
6.2. Viral Replication Protein Inhibitors
6.2.1. Telaprevir—2A Protease Inhibitor
6.2.2. Guadinine Hydrochloride and Fluoxetine—2C Protein Inhibitors
6.2.3. Rupintrivir and V-7404—3C Protease Inhibitors
6.2.4. Azvudine—3D Polymerase Inhibitor
6.2.5. Ribavirin—Guanosine Nucleoside Analog
6.2.6. Molnupiravir and EIDD-1931
6.3. Host Factors Antiviral
6.3.1. SAMHDI
6.3.2. Enviroxime and Vemurafenib—Pi4kiiiβ Inhibitor
6.3.3. CRT0066101, CRT0066051 and XX-050—Protein Kinase D Inhibitor
6.3.4. Itraconazole—OSBP Inhibitor
6.3.5. DAS181—Inhibitors Targeting the Cell Surface Sialic Acid Receptors
6.4. Antibodies
6.4.1. Human Antibodies
6.4.2. Non-Human Antibodies
6.5. Vaccines
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, Z.; Khamrin, P.; Maneekarn, N.; Kumthip, K. Epidemiology of Enterovirus Genotypes in Association with Human Diseas Es. Viruses 2024, 16, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messacar, K. Overview of Enterovirus Infections. Available online: https://www.merckmanuals.com/en-ca/professional/infectious-diseases/enteroviruses/overview-of-enterovirus-infections (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Halabi, K.C.; Stockwell, M.S.; Alba, L.; Vargas, C.; Reed, C.; Saiman, L. Mobile Surveillance for Acute Respiratory Infection/Influenza-like Illness in the Community (MoSAIC) Study Team Clinical and Socioeconomic Burden of Rhinoviruses/Enteroviruses in the Community. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2022, 16, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICTV Report Consortium Picornaviridae. Available online: https://ictv.global/report/chapter/picornaviridae/picornaviridae/enterovirus (accessed on 23 February 2025).
- Mammas, I.; Drysdale, S.; Theodoridou, M.; Greenough, A.; Spandidos, D. Viruses, Vaccinations and RSV: Exploring Terminology in Paediatric Virology. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.C.; Wells, A.I.; Ciomperlik-Patton, J.; Myerburg, M.M.; Yang, L.; Konopka-Anstadt, J.; Coyne, C.B. Respiratory and Intestinal Epithelial Cells Exhibit Differential Susceptibility and Innate Immune Responses to Contemporary EV-D68 Isolates. eLife 2021, 10, e66687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.; Dutilh, G.; Reist, J.; Bingisser, R.; Egli, A.; Heininger, U. Clinical Presentation of Enterovirus D68 in a Swiss Pediatric Universi Ty Center. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2024, 43, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodcroft, E.B.; Dyrdak, R.; Andrés, C.; Egli, A.; Reist, J.; García Martínez De Artola, D.; Alcoba Flórez, J.; Niesters, H.G.M.; Antón, A.; Poelman, R.; et al. Evolution, Geographic Spreading, and Demographic Distribution of Enter Ovirus D68. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 18, e1010515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm-Hansen, C.C.; Midgley, S.E.; Fischer, T.K. Global Emergence of Enterovirus D68: A Systematic Review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e64–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monto, A.S. Epidemiology of Viral Respiratory Infections. Am. J. Med. 2002, 112, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gern, J.E. The ABCs of Rhinoviruses, Wheezing, and Asthma. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7418–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, T.E.; Marley, A.-M.; Baxter, N.; Christie, S.N.; O’Neill, H.J.; Elborn, J.S.; Coyle, P.V.; Kidney, J.C. Respiratory Viral Infection in Exacerbations of COPD. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.L.; Pattemore, P.K.; Sanderson, G.; Smith, S.; Lampe, F.; Josephs, L.; Symington, P.; O’Toole, S.; Myint, S.H.; Tyrrell, D.A.J.; et al. Community Study of Role of Viral Infections in Exacerbations of Asthma in 9–11 Year Old Children. BMJ 1995, 310, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wark, P.A.B.; Johnston, S.L.; Moric, I.; Simpson, J.L.; Hensley, M.J.; Gibson, P.G. Neutrophil Degranulation and Cell Lysis Is Associated with Clinical Severity in Virus-Induced Asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 19, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grissell, T.V.; Powell, H.; Shafren, D.R.; Boyle, M.J.; Hensley, M.J.; Jones, P.D.; Whitehead, B.F.; Gibson, P.G. Interleukin-10 Gene Expression in Acute Virus-Induced Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arden, K.E.; Chang, A.B.; Lambert, S.B.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P.; Mackay, I.M. Newly Identified Respiratory Viruses in Children with Asthma Exacerbation Not Requiring Admission to Hospital. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 1458–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, P.; Message, S.D.; Kebadze, T.; Parker, H.L.; Kon, O.M.; Johnston, S.L. An Experimental Model of Rhinovirus Induced Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbations: A Pilot Study. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, P.; Message, S.D.; Gielen, V.; Contoli, M.; Gray, K.; Kebadze, T.; Aniscenko, J.; Laza-Stanca, V.; Edwards, M.R.; Slater, L.; et al. Experimental Rhinovirus Infection as a Human Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, S.A.; Petrich, A.; Hamid, J.S.; Mertz, D.; Richardson, S.E.; Smieja, M. Clinical Severity of Rhinovirus/Enterovirus Compared to Other Respiratory Viruses in Children. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2014, 8, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Sarmiento, J.; Corrales, S.C.; Obando, E.; Amin, J.; Bastidas Goyes, A.; Barrera Lopez, P.A.; Bernal Ortiz, N. Factors Associated with Severe Acute Respiratory Infections Due to Rhinovirus/Enterovirus Complex in Children and Their Comparison with Those of Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Arch. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2021, 10, e115548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggen, J.; Thibaut, H.J.; Strating, J.R.P.M.; Van Kuppeveld, F.J.M. The Life Cycle of Non-Polio Enteroviruses and How to Target It. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Harvala, H.; Hovi, T.; Knowles, N.J.; Lindberg, A.M.; Oberste, M.S.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Reuter, G.; Skern, T.; et al. Recommendations for the Nomenclature of Enteroviruses and Rhinoviruses. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoelen, I.; Moës, E.; Lemey, P.; Mostmans, S.; Wollants, E.; Lindberg, A.M.; Vandamme, A.-M.; Van Ranst, M. Analysis of the Serotype and Genotype Correlation of VP1 and the 5′ Noncoding Region in an Epidemiological Survey of the Human Enterovirus B Species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Filipe, I.C.; Guedes, M.S.; Zdobnov, E.M.; Tapparel, C. Enterovirus D: A Small but Versatile Species. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffret, M.-L.; Polston, P.M.; Razafindratsimandresy, R.; Bessaud, M.; Heraud, J.-M.; Delpeyroux, F. Whole Genome Sequencing of Enteroviruses Species A to D by High-Throughput Sequencing: Application for Viral Mixtures. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Füzik, T.; Moravcová, J.; Kalynych, S.; Plevka, P. Structure of Human Enterovirus 70 and Its Inhibition by Capsid-Binding Compounds. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0060422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevka, P.; Perera, R.; Yap, M.L.; Cardosa, J.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. Structure of Human Enterovirus 71 in Complex with a Capsid-Binding Inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Wang, K.; Zhao, K.; Hua, S.-C.; Du, J. The Structure, Function, and Mechanisms of Action of Enterovirus Non-Structural Protein 2C. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 615965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.D.; Semler, B.L. Bridging IRES Elements in mRNAs to the Eukaryotic Translation Apparatus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Gene Regul. Mech. 2009, 1789, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslin, C.; Mac Kain, A.; Bessaud, M.; Blondel, B.; Delpeyroux, F. Recombination in Enteroviruses, a Multi-Step Modular Evolutionary Process. Viruses 2019, 11, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden, L.; Wolthers, K.C.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M. Replication and Inhibitors of Enteroviruses and Parechoviruses. Viruses 2015, 7, 4529–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchta, D.; Füzik, T.; Hrebík, D.; Levdansky, Y.; Sukeník, L.; Mukhamedova, L.; Moravcová, J.; Vácha, R.; Plevka, P. Enterovirus Particles Expel Capsid Pentamers to Enable Genome Release. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melia, C.E.; Peddie, C.J.; De Jong, A.W.M.; Snijder, E.J.; Collinson, L.M.; Koster, A.J.; Van Der Schaar, H.M.; Van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Bárcena, M. Origins of Enterovirus Replication Organelles Established by Whole-Cell Electron Microscopy. mBio 2019, 10, e00951-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Musharrafieh, R.; Zheng, M.; Wang, J. Enterovirus D68 Antivirals: Past, Present, and Future. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 1572–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalam, N.; Balasubramaniam, V.R.M.T. Emerging Therapeutics in the Fight Against EV-D68: A Review of Current Strategies. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2024, 18, e70064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhy, D.A.; Giddings, T.H.; Kirkegaard, K. Remodeling the Endoplasmic Reticulum by Poliovirus Infection and by Individual Viral Proteins: An Autophagy-Like Origin for Virus-Induced Vesicles. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8953–8965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, M.; Cheng, A.; Wen, X.; Ou, X.; Mao, S.; Gao, Q.; Sun, D.; Jia, R.; Yang, Q.; et al. Enterovirus Replication Organelles and Inhibitors of Their Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galitska, G.; Jassey, A.; Wagner, M.A.; Pollack, N.; Miller, K.; Jackson, W.T. Enterovirus D68 Capsid Formation and Stability Requires Acidic Compartments. mBio 2023, 14, e0214123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owusu, I.A.; Quaye, O.; Passalacqua, K.D.; Wobus, C.E. Egress of Non-Enveloped Enteric RNA Viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmikangas, S.; Laiho, J.E.; Kalander, K.; Laajala, M.; Honkimaa, A.; Shanina, I.; Oikarinen, S.; Horwitz, M.S.; Hyöty, H.; Marjomäki, V. Detection of Viral −RNA and +RNA Strands in Enterovirus-Infected Cells and Tissues. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, A.A.; Semler, B.L. Translation and Host Cell Shutoff. In Human Enterovirus Infections; Rotbart, H.A., Ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 113–133. ISBN 978-1-68367-272-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.-C.; Weng, K.-F.; Chang, S.-C.; Lin, J.-Y.; Huang, P.-N.; Shih, S.-R. Development of Antiviral Agents for Enteroviruses. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshaghi, A.; Duvvuri, V.R.; Isabel, S.; Banh, P.; Li, A.; Peci, A.; Patel, S.N.; Gubbay, J.B. Global Distribution and Evolutionary History of Enterovirus D68, with Emphasis on the 2014 Outbreak in Ontario, Canada. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messacar, K.; Abzug, M.J.; Dominguez, S.R. 2014 Outbreak of Enterovirus D68 in North America. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benschop, K.S.; Albert, J.; Anton, A.; Andrés, C.; Aranzamendi, M.; Armannsdóttir, B.; Bailly, J.-L.; Baldanti, F.; Baldvinsdóttir, G.E.; Beard, S.; et al. Re-Emergence of Enterovirus D68 in Europe after Easing the COVID-19 Lockdown, September 2021. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2100998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ren, L.; Luo, M.; Li, A.; Gong, C.; Chen, M.; Yu, X.; Wu, J.; Deng, Y.; Huang, F. Enterovirus D68-Associated Severe Pneumonia, China, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 916–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongpan, I.; Wanlapakorn, N.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Linsuwanon, P.; Theamboonlers, A.; Payungporn, S.; Poovorawan, Y. Prevalence and Phylogenetic Characterization of Enterovirus D68 in Pediatric Patients with Acute Respiratory Tract Infection in Thailand. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 69, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallow, M.M.; Mendy, M.P.; Barry, M.A.; Diagne, M.M.; Sagne, S.N.; Tall, F.; Diouf, J.B.N.; Ndiaye, N.K.; Kiori, D.; Sy, S.; et al. Real-Time Enterovirus D68 Outbreak Detection through Hospital Surveillance of Severe Acute Respiratory Infection, Senegal, 2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, A.; Schuffenecker, I.; Casalegno, J.-S.; Josset, L.; Valette, M.; Armand, N.; Dhondt, P.B.; Escuret, V.; Lina, B. Enterovirus D68 Nosocomial Outbreak in Elderly People, France, 2014. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, e61–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.M.; Zhang, Y.; Scheuermann, R.H. Epidemiology and Sequence-Based Evolutionary Analysis of Circulating Non-Polio Enteroviruses. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.C.; Winn, A.; Moline, H.L.; Scobie, H.M.; Midgley, C.M.; Kirking, H.L.; Adjemian, J.; Hartnett, K.P.; Johns, D.; Jones, J.M.; et al. Increase in Acute Respiratory Illnesses Among Children and Adolescents Associated with Rhinoviruses and Enteroviruses, Including Enterovirus D68—United States, July-September 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunnill, M.; Eshaghi, A.; Damodaran, L.; Nagra, S.; Gharouni, A.; Braukmann, T.; Clark, S.; Peci, A.; Isabel, S.; Banh, P.; et al. Inferring Enterovirus D68 Transmission Dynamics from the Genomic Data of Two 2022 North American Outbreaks. Npj Viruses 2024, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, Q.X.T.; Hoang, P.T.; Ho, P.T.; Ayun, R.Q.; Lee, T.K.; Lee, S. Potential Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents: A Key Arsenal Against Newly Emerging and Reemerging Respiratory RNA Viruses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devries, M.K.; Bochkov, Y.A.; Evans, M.D.; Gern, J.E.; Jackson, D.J. Recent Clinical Isolates of Enterovirus D68 Have Increased Replication and Induce Enhanced Epithelial Immune Response Compared to the Protot Ype Fermon Strain. Viruses 2023, 15, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, T.K.; Simmonds, P.; Harvala, H. The Importance of Enterovirus Surveillance in a Post-Polio World. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e35–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, C.G.; Nickerson, C.A.; Coyne, C.B. A Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Model To Study Enterovirus Infection of Polarized Intestinal Epithelial Cells. mSphere 2016, 1, e00030-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basta, H.A.; Ashraf, S.; Sgro, J.-Y.; Bochkov, Y.A.; Gern, J.E.; Palmenberg, A.C. Modeling of the Human Rhinovirus C Capsid Suggests Possible Causes for Antiviral Drug Resistance. Virology 2014, 448, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, C.; Aguayo, E.; Rodriguez, M.; Lee, G.; Jordan, R.; Cihlar, T.; Birkus, G. Multiple Classes of Antiviral Agents Exhibit In Vitro Activity against Human Rhinovirus Type C. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Sanden, S.M.G.; Sachs, N.; Koekkoek, S.M.; Koen, G.; Pajkrt, D.; Clevers, H.; Wolthers, K.C. Enterovirus 71 Infection of Human Airway Organoids Reveals VP1-145 as a Viral Infectivity Determinant. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, A.; Depla, J.A.; Mulder, L.A.; Karelehto, E.; Brouwer, L.; Kruiswijk, L.; Vieira De Sá, R.; Meijer, A.; Evers, M.M.; Van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; et al. Enterovirus D68 Infection in Human Primary Airway and Brain Organoids: No Additional Role for Heparan Sulfate Binding for Neurotropism. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01694-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xatzipsalti, M.; Papadopoulos, N.G. Cellular and Animals Models for Rhinovirus Infection in Asthma. In Contributions to Microbiology; Sjöbring, U., Taylor, J.D., Eds.; KARGER: Basel, Switzerland, 2007; pp. 33–41. ISBN 978-3-8055-8332-9. [Google Scholar]
- Vermillion, M.S.; Dearing, J.; Zhang, Y.; Adney, D.R.; Scheuermann, R.H.; Pekosz, A.; Tarbet, E.B. Animal Models of Enterovirus D68 Infection and Disease. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e00833-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, N.W.; Walton, R.P.; Edwards, M.R.; Aniscenko, J.; Caramori, G.; Zhu, J.; Glanville, N.; Choy, K.J.; Jourdan, P.; Burnet, J.; et al. Mouse Models of Rhinovirus-Induced Disease and Exacerbation of Allergic Airway Inflammation. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singanayagam, A.; Glanville, N.; Walton, R.P.; Aniscenko, J.; Pearson, R.M.; Pinkerton, J.W.; Horvat, J.C.; Hansbro, P.M.; Bartlett, N.W.; Johnston, S.L. A Short-Term Mouse Model That Reproduces the Immunopathological Features of Rhinovirus-Induced Exacerbation of COPD. Clin. Sci. Lond. Engl. 1979 2015, 129, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, M.; Jackson, D.J.; Swieboda, D.; Guedán, A.; Tsourouktsoglou, T.-D.; Ching, Y.M.; Radermecker, C.; Makrinioti, H.; Aniscenko, J.; Bartlett, N.W.; et al. Host DNA Released by NETosis Promotes Rhinovirus-Induced Type-2 Allergic Asthma Exacerbation. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traub, S.; Nikonova, A.; Carruthers, A.; Dunmore, R.; Vousden, K.A.; Gogsadze, L.; Hao, W.; Zhu, Q.; Bernard, K.; Zhu, J.; et al. An Anti-Human ICAM-1 Antibody Inhibits Rhinovirus-Induced Exacerbations of Lung Inflammation. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanville, N.; McLean, G.R.; Guy, B.; Lecouturier, V.; Berry, C.; Girerd, Y.; Gregoire, C.; Walton, R.P.; Pearson, R.M.; Kebadze, T.; et al. Cross-Serotype Immunity Induced by Immunization with a Conserved Rhinovirus Capsid Protein. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombo, I.M.; Lukashev, A.N.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Berthet, N.; Maganga, G.D.; Durand, P.; Arnathau, C.; Boundenga, L.; Ngoubangoye, B.; et al. African Non-Human Primates Host Diverse Enteroviruses. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sestak, K. Non-Human Primate Models of Enteric Viral Infections. Viruses 2018, 10, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.-W.; Sun, M.; Guo, L.; Wang, J.-J.; Song, J.; Li, J.-Q.; Li, H.-Z.; Ning, R.-T.; Yang, Z.-N.; Fan, H.-T.; et al. Nasal Infection of Enterovirus D68 Leading to Lower Respiratory Tract Pathogenesis in Ferrets (Mustela Putorius Furo). Viruses 2017, 9, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Z.; Dai, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Gao, Z.; Meng, F. Medicinal Chemistry Strategies toward Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents to Prevent next Pandemics. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 271, 116442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, M.; Lo, C.-W.; Einav, S. Preparing for the next Viral Threat with Broad-Spectrum Antivirals. J. Clin. Invest. 2023, 133, e170236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderlinden, E.; Vrancken, B.; Van Houdt, J.; Rajwanshi, V.K.; Gillemot, S.; Andrei, G.; Lemey, P.; Naesens, L. Distinct Effects of T-705 (Favipiravir) and Ribavirin on Influenza Virus Replication and Viral RNA Synthesis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6679–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraghty, R.J.; Aliota, M.T.; Bonnac, L.F. Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Strategies and Nucleoside Analogues. Viruses 2021, 13, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Schoggins, J.W.; Diamond, M.S. Shared and Distinct Functions of Type I and Type III Interferons. Immunity 2019, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kejriwal, R.; Evans, T.; Calabrese, J.; Swistak, L.; Alexandrescu, L.; Cohen, M.; Rahman, N.; Henriksen, N.; Charan Dash, R.; Hadden, M.K.; et al. Development of Enterovirus Antiviral Agents That Target the Viral 2C Protein. ChemMedChem 2023, 18, e202200541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobinska, G.; Pilpel, Y.; Nowak, M.A. Evolutionary Safety of Lethal Mutagenesis Driven by Antiviral Treatment. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Kim, C.; Kim, D.; Song, J.-H.; Choi, M.; Choi, K.; Kang, M.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, J.S.; et al. Synergistic Antiviral Activity of Gemcitabine and Ribavirin against Enteroviruses. Antiviral Res. 2015, 124, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sheng, J.; Fokine, A.; Meng, G.; Shin, W.-H.; Long, F.; Kuhn, R.J.; Kihara, D.; Rossmann, M.G. Structure and Inhibition of EV-D68, a Virus That Causes Respiratory Illness in Children. Science 2015, 347, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, F.G.; Herrington, D.T.; Coats, T.L.; Kim, K.; Cooper, E.C.; Villano, S.A.; Liu, S.; Hudson, S.; Pevear, D.C.; Collett, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Pleconaril for Treatment of Colds Due to Picornaviruses in Adults: Results of 2 Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trials. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, K. FDA Panel Rejects Common Cold Treatment. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, F.G.; Andries, K.; Janssen, P.A. Safety and Efficacy of Intranasal Pirodavir (R77975) in Experimental Rhinovirus Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1992, 36, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, F.G.; Hipskind, G.J.; Woerner, D.H.; Eisen, G.F.; Janssens, M.; Janssen, P.A.; Andries, K. Intranasal Pirodavir (R77,975) Treatment of Rhinovirus Colds. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, A.; Galabov, S.; Galabov, A.S. Antiviral Activity in Vitro of Double Combinations of Enteroviral Inhibitors. Acta Virol. 2024, 68, 12361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdani, S.M.; Kim, H.S.; Orvedahl, A.; John, A.O.; Said, A.; Simpson, K. Successful Treatment of Fulminant Neonatal Enteroviral Myocarditis in Monochorionic Diamniotic Twins with Cardiopulmonary Support, Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Pocapavir. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2017-224133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Real-Hohn, A.; Blaas, D. Rhinovirus Inhibitors: Including a New Target, the Viral RNA. Viruses 2021, 13, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, S.; Cao, R.; Li, X.; He, X.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Cheng, T.; Li, H.; et al. Discovery and Optimization of Quinoline Analogues as Novel Potent Antivirals against Enterovirus D68. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 14792–14808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Musharrafieh, R.; Wang, J. A Novel Capsid Binding Inhibitor Displays Potent Antiviral Activity against Enterovirus D68. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1952–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biota Pharmaceuticals, Inc. A Phase 2, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Dose-Ranging Study of Vapendavir in Moderate to Severe Asthmatic Adults with Symptomatic Human Rhinovirus Infection. Clinical Trials for Eudract_number:2014-001785-95. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=eudract_number:2014-001785-95 (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- NCT06149494; RCT of Vapendavir in Patients with COPD and Human Rhinovirus/Enterovirus Upper Respiratory Infection. Altesa Biosciences, Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06149494 (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- China Daily Domestically Developed Drug Joins Virus Battle. Available online: https://english.nmpa.gov.cn/2022-08/15/c_797867.htm (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dai, Q.; Yang, X.; Guo, X.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Cao, R.; et al. Molnupiravir and Its Active Form, EIDD-1931, Show Potent Antiviral Activity against Enterovirus Infections In Vitro and In Vivo. Viruses 2022, 14, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) First Oral Antiviral for COVID-19, Lagevrio (Molnupiravir); MHRA: London, UK, 2021.
- Bauer, L.; Manganaro, R.; Zonsics, B.; Strating, J.R.P.M.; El Kazzi, P.; Lorenzo Lopez, M.; Ulferts, R.; van Hoey, C.; Maté, M.J.; Langer, T.; et al. Fluoxetine Inhibits Enterovirus Replication by Targeting the Viral 2C Protein in a Stereospecific Manner. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messacar, K.; Sillau, S.; Hopkins, S.; Otten, C.; Wilson-Murphy, M.; Wong, B.; Santoro, J.; Treister, A.; Tokhie, H.; Torres, A.; et al. 1901. Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of Fluoxetine as an Antiviral for Enterovirus D68 Associated Acute Flaccid Myelitis: A Retrospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, S546–S547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, B.L.; Evans, W.J.; Smee, D.F.; Van Wettere, A.J.; Tarbet, E.B. Evaluation of Antiviral Therapies in Respiratory and Neurological Disease Models of Enterovirus D68 Infection in Mice. Virology 2019, 526, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.B.; Walsh, E.E.; Hruska, J.F.; Betts, R.F.; Hall, W.J. Ribavirin Treatment of Experimental Respiratory Syncytial Viral Infection. A Controlled Double-Blind Study in Young Adults. JAMA 1983, 249, 2666–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, V.; Sousa, F.H.; Stevens, C.; Barlow, P.G. Antiviral Therapeutic Approaches for Human Rhinovirus Infections. Future Virol. 2018, 13, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyström, K.; Waldenström, J.; Tang, K.-W.; Lagging, M. Ribavirin: Pharmacology, Multiple Modes of Action and Possible Future Perspectives. Future Virol. 2019, 14, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoden, E.; Zhang, M.; Nix, W.A.; Oberste, M.S. In Vitro Efficacy of Antiviral Compounds against Enterovirus D68. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7779–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, F.G.; Turner, R.B.; Gwaltney, J.M.; Chi-Burris, K.; Gersten, M.; Hsyu, P.; Patick, A.K.; Smith, G.J.; Zalman, L.S. Phase II, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Studies of Ruprintrivir Nasal Spray 2-Percent Suspension for Prevention and Treatment of Experimentally Induced Rhinovirus Colds in Healthy Volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3907–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musharrafieh, R.; Ma, C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Diesing, J.M.; Marty, M.T.; Wang, J. Validating Enterovirus D68-2Apro as an Antiviral Drug Target and the Discovery of Telaprevir as a Potent D68-2Apro Inhibitor. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e02221-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, J.; Rudy, M.J.; Leser, J.S.; Tan, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Clarke, P.; Tyler, K.L. Telaprevir Treatment Reduces Paralysis in a Mouse Model of Enterovirus D68 Acute Flaccid Myelitis. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0015623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankam, M.K.; Burns, J.M.; Collett, M.S.; Corrado, M.L.; Hincks, J.R. A Phase 1 Study of the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Single and Multiple Oral Doses of V-7404 in Healthy Adult Volunteers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e01029-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedán, A.; Swieboda, D.; Charles, M.; Toussaint, M.; Johnston, S.L.; Asfor, A.; Panjwani, A.; Tuthill, T.J.; Danahay, H.; Raynham, T.; et al. Investigation of the Role of Protein Kinase D in Human Rhinovirus Replication. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00217-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCT05016687; First-in-Human Clinical Trial Evaluating CUR-N399 in Healthy Volunteers. Curovir AB: Kalmar, Sweden, 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05016687 (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Salvatore, M.; Satlin, M.J.; Jacobs, S.E.; Jenkins, S.G.; Schuetz, A.N.; Moss, R.B.; Van Besien, K.; Shore, T.; Soave, R. DAS181 for Treatment of Parainfluenza Virus Infections in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients at a Single Center. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjuki, H.; Mishin, V.P.; Chesnokov, A.P.; De La Cruz, J.A.; Fry, A.M.; Villanueva, J.; Gubareva, L.V. An Investigational Antiviral Drug, DAS181, Effectively Inhibits Replication of Zoonotic Influenza A Virus Subtype H7N9 and Protects Mice from Lethality. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Meijer, A.; Froeyen, M.; Zhang, L.; Thibaut, H.J.; Baggen, J.; George, S.; Vernachio, J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Leyssen, P.; et al. Antiviral Activity of Broad-Spectrum and Enterovirus-Specific Inhibitors against Clinical Isolates of Enterovirus D68. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7782–7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.D.; Monto, A.S.; DeLong, D.C.; Exelby, A.; Bryan, E.R.; Srivastava, S. Controlled Trial of Enviroxime against Natural Rhinovirus Infections in a Community. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1985, 27, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smee, D.F.; Evans, W.J.; Nicolaou, K.C.; Tarbet, E.B.; Day, C.W. Susceptibilities of Enterovirus D68, Enterovirus 71, and Rhinovirus 87 Strains to Various Antiviral Compounds. Antiviral Res. 2016, 131, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCT05677347; Phase 1, Single and Repeat Dose Study to Assess Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics (PK) of GSK3923868 in Participants with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). GlaxoSmithKline: London, UK, 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05677347?rank=1 (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- NCT04585009; Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of GSK3923868 Inhalation Powder in Healthy Participants and Stable Asthmatics. GlaxoSmithKline: London, UK, 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04585009?rank=1 (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- NCT05398198; Efficacy and Safety of GSK3923868 Inhalation Powder, During Experimental Human Rhinovirus Infection in Participants With Mild Asthma. GlaxoSmithKline: London, UK, 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05398198 (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Shim, A.; Song, J.-H.; Kwon, B.-E.; Lee, J.-J.; Ahn, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Rhee, K.-J.; Chang, S.-Y.; Cha, Y.; Lee, Y.-S.; et al. Therapeutic and Prophylactic Activity of Itraconazole against Human Rhinovirus Infection in a Murine Model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strating, J.R.P.M.; van der Linden, L.; Albulescu, L.; Bigay, J.; Arita, M.; Delang, L.; Leyssen, P.; van der Schaar, H.M.; Lanke, K.H.W.; Thibaut, H.J.; et al. Itraconazole Inhibits Enterovirus Replication by Targeting the Oxysterol-Binding Protein. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 600–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCT04908800; A Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of KRP-A218 in Healthy Subjects. Kyorin Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04908800 (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Z.; Huan, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W. SAMHD1 Inhibits Multiple Enteroviruses by Interfering with the Interaction between VP1 and VP2 Proteins. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0062021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laajala, M.; Zwaagstra, M.; Martikainen, M.; Nekoua, M.P.; Benkahla, M.; Sane, F.; Gervais, E.; Campagnola, G.; Honkimaa, A.; Sioofy-Khojine, A.-B.; et al. Vemurafenib Inhibits Acute and Chronic Enterovirus Infection by Affecting Cellular Kinase Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase Type IIIβ. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00552-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Guo, L.; Li, H.; Song, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Fan, H.; Huang, X.; et al. A Novel Neutralizing Antibody Specific to the DE Loop of VP1 Can Inhibit EV-D68 Infection in Mice. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2018, 201, 2557–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, M.R.; Fu, J.; Kose, N.; Williamson, L.E.; Bombardi, R.; Setliff, I.; Georgiev, I.S.; Klose, T.; Rossmann, M.G.; Hurst, B.L.; et al. Human Antibodies Neutralize Enterovirus D68 and Protect against Infection and Paralytic Disease. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaba4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCT06444048; Phase 1, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Safety and Tolerability of an Enterovirus D68-Specific Monoclonal Antibody in Healthy Adults. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID): Hamilton, MO, USA, 2025. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06444048 (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Pevear, D.C.; Tull, T.M.; Seipel, M.E.; Groarke, J.M. Activity of Pleconaril against Enteroviruses. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 2109–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abzug, M.J.; Michaels, M.G.; Wald, E.; Jacobs, R.F.; Romero, J.R.; Sánchez, P.J.; Wilson, G.; Krogstad, P.; Storch, G.A.; Lawrence, R.; et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Pleconaril for the Treatment of Neonates With Enterovirus Sepsis. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2016, 5, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feil, S.C.; Hamilton, S.; Krippner, G.Y.; Lin, B.; Luttick, A.; McConnell, D.B.; Nearn, R.; Parker, M.W.; Ryan, J.; Stanislawski, P.C.; et al. An Orally Available 3-Ethoxybenzisoxazole Capsid Binder with Clinical Activity against Human Rhinovirus. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Torres, S.; Myers, A.L.; Klatte, J.M.; Rhoden, E.E.; Oberste, M.S.; Collett, M.S.; McCulloh, R.J. First Use of Investigational Antiviral Drug Pocapavir (V-073) for Treating Neonatal Enteroviral Sepsis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsen, C. P58 An Antiviral Dilemma—Reflections on the Pocapavir Predicament. In Proceedings of the Abstracts form the Neonatal and Paediatric Pharmacy Conference 2023; BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.: Cheshire, UK, 2024; pp. A38–A39. [Google Scholar]
- Magden, J.; Kääriäinen, L.; Ahola, T. Inhibitors of Virus Replication: Recent Developments and Prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 66, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. INCIVEK® (Telaprevir) Tablets, for Oral Use; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yao, F.; Xue, G.; Xu, Y.; Niu, J.; Cui, M.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Lu, A.; Zhong, J.; et al. Antiviral Effects of Simeprevir on Multiple Viruses. Antiviral Res. 2019, 172, 104607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, G.-C.; Yang, J.; Sun, X.; Wu, W.; Qiu, Y.; Shu, T.; Zhao, X.; Yin, L.; et al. Human Enterovirus Nonstructural Protein 2CATPase Functions as Both an RNA Helicase and ATP-Independent RNA Chaperone. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, K.L. Rationale for the Evaluation of Fluoxetine in the Treatment of Enterovirus D68-Associated Acute Flaccid Myelitis. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulferts, R.; Van Der Linden, L.; Thibaut, H.J.; Lanke, K.H.W.; Leyssen, P.; Coutard, B.; De Palma, A.M.; Canard, B.; Neyts, J.; Van Kuppeveld, F.J.M. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Fluoxetine Inhibits Replication of Human Enteroviruses B and D by Targeting Viral Protein 2C. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1952–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixon, A.M.; Clarke, P.; Tyler, K.L. Evaluating Treatment Efficacy in a Mouse Model of Enterovirus D68–Associated Paralytic Myelitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gofshteyn, J.; Cárdenas, A.M.; Bearden, D. Treatment of Chronic Enterovirus Encephalitis With Fluoxetine in a Patient With X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 64, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patick, A.K.; Binford, S.L.; Brothers, M.A.; Jackson, R.L.; Ford, C.E.; Diem, M.D.; Maldonado, F.; Dragovich, P.S.; Zhou, R.; Prins, T.J.; et al. In Vitro Antiviral Activity of AG7088, a Potent Inhibitor of Human Rhinovirus 3C Protease. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 2444–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Yang, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Huan, C.; Wang, S.; Chang, J.; Zhang, W. The Pyrimidine Analog FNC Potently Inhibits the Replication of Multiple Enteroviruses. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00204-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, G.L.; Esteban-Mur, R.; Rustgi, V.; Hoefs, J.; Gordon, S.C.; Trepo, C.; Shiffman, M.L.; Zeuzem, S.; Craxi, A.; Ling, M.-H.; et al. Interferon Alfa-2b Alone or in Combination with Ribavirin for the Treatment of Relapse of Chronic Hepatitis C. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te, H.S.; Randall, G.; Jensen, D.M. Mechanism of Action of Ribavirin in the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 3, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Crotty, S.; Cameron, C.E.; Andino, R. RNA Virus Error Catastrophe: Direct Molecular Test by Using Ribavirin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6895–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyssen, P.; Balzarini, J.; De Clercq, E.; Neyts, J. The Predominant Mechanism by Which Ribavirin Exerts Its Antiviral Activity In Vitro against Flaviviruses and Paramyxoviruses Is Mediated by Inhibition of IMP Dehydrogenase. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruuskanen, O.; Waris, M.; Kainulainen, L. Treatment of Persistent Rhinovirus Infection with Pegylated Interferon A2a and Ribavirin in Patients with Hypogammaglobulinemia. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2014, 58, 1784–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheahan, T.P.; Sims, A.C.; Zhou, S.; Graham, R.L.; Pruijssers, A.J.; Agostini, M.L.; Leist, S.R.; Schäfer, A.; Dinnon, K.H.; Stevens, L.J.; et al. An Orally Bioavailable Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in Human Airway Epithelial Cell Cultures and Multiple Coronaviruses in Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabb5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Molnupiravir: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggins, S.A.; Mahboubi, B.; Schinazi, R.F.; Kim, B. SAMHD1 Functions and Human Diseases. Viruses 2020, 12, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguette, N.; Sobhian, B.; Casartelli, N.; Ringeard, M.; Chable-Bessia, C.; Ségéral, E.; Yatim, A.; Emiliani, S.; Schwartz, O.; Benkirane, M. SAMHD1 Is the Dendritic- and Myeloid-Cell-Specific HIV-1 Restriction Factor Counteracted by Vpx. Nature 2011, 474, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Schaar, H.M.; van der Linden, L.; Lanke, K.H.W.; Strating, J.R.P.M.; Pürstinger, G.; de Vries, E.; de Haan, C.A.M.; Neyts, J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M. Coxsackievirus Mutants That Can Bypass Host Factor PI4KIIIβ and the Need for High Levels of PI4P Lipids for Replication. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 1576–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, G.R.V.; Burke, J.E. Novel Roles of Phosphoinositides in Signaling, Lipid Transport, and Disease. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2020, 63, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillpotts, R.J.; Jones, R.W.; Delong, D.C.; Reed, S.E.; Wallace, J.; Tyrrell, D.A. The Activity of Enviroxime against Rhinovirus Infection in Man. Lancet Lond. Engl. 1981, 1, 1342–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sheng, J.; Baggen, J.; Meng, G.; Xiao, C.; Thibaut, H.J.; Van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Rossmann, M.G. Sialic Acid-Dependent Cell Entry of Human Enterovirus D68. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.D.; Shastri, M.D.; Vanka, S.K.; Jha, N.K.; Dureja, H.; Gupta, G.; Chellappan, D.K.; Oliver, B.G.; Dua, K.; Walters, E.H. Targeting Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1) to Reduce Rhinovirus-Induced Acute Exacerbations in Chronic Respiratory Diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Whiteman, S.C.; Sethi, S.K.; Allen, J.T.; Knight, R.A.; Spiteri, M.A. Expression of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in Nasal Epithelial Cells of Atopic Subjects: A Mechanism for Increased Rhinovirus Infection? Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 121, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krug, P.W.; Wang, L.; Shi, W.; Kong, W.-P.; Moss, D.L.; Yang, E.S.; Fisher, B.E.; Morabito, K.M.; Mascola, J.R.; Kanekiyo, M.; et al. EV-D68 Virus-like Particle Vaccines Elicit Cross-Clade Neutralizing Antibodies That Inhibit Infection and Block Dissemination. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Dai, W.; Xie, J.; Ye, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, Q.; Gong, S.; et al. Enterovirus D68 Virus-like Particles Expressed in Pichia Pastoris Potently Induce Neutralizing Antibody Responses and Confer Protection against Lethal Viral Infection in Mice. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Dai, W.; Liu, Q.; Xiong, P.; Wang, S.; Geng, L.; Gong, S.; Huang, Z. A Mouse Model of Enterovirus D68 Infection for Assessment of the Efficacy of Inactivated Vaccine. Viruses 2018, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, P.; Liu, Q.; Gong, S.; Geng, L.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Z. A Virus-like Particle Vaccine Confers Protection against Enterovirus D68 Lethal Challenge in Mice. Vaccine 2018, 36, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.C.; Wang, W.; Pletneva, L.M.; Rajagopala, S.V.; Tan, Y.; Hartert, T.V.; Boukhvalova, M.S.; Vogel, S.N.; Das, S.R.; Blanco, J.C.G. Enterovirus D-68 Infection, Prophylaxis, and Vaccination in a Novel Permissive Animal Model, the Cotton Rat (Sigmodon Hispidus). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCBI Datasets Kunming (KM) Strain—Enterovirus D68 Isolate RVL_KM201703 Polyprotein Gene, Partial Cds—MG991260. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/search/all/?term=MG991260 (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Behzadi, M.A.; Choi, A.; Duehr, J.; Feyznezhad, R.; Upadhyay, C.; Schotsaert, M.; Palese, P.; Nachbagauer, R. A Cross-Reactive Mouse Monoclonal Antibody against Rhinovirus Mediates Phagocytosis In Vitro. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Grady, M.; Bruner, P.J. Polio Vaccine. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-L.; Cheng, P.-Y.; Chin, C.-L.; Chuang, K.-T.; Lin, J.-Y.; Chang, N.; Pan, C.-K.; Lin, C.-S.; Pan, S.-C.; Chiang, B.-L. A Novel Mucosal Bivalent Vaccine of EV-A71/EV-D68 Adjuvanted with Polysaccharides from Ganoderma Lucidum Protects Mice against EV-A71 and EV-D68 Lethal Challenge. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, A.B.; Shen, E.Q.L.; Melendez, M.; Mishra, N.; Lipkin, W.I.; Racaniello, V.R. Cross-Reactive Antibody Responses against Nonpoliovirus Enteroviruses. mBio 2022, 13, e0366021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Nguyen, M.T.; Currier, M.G.; Jenkins, J.B.; Strobert, E.A.; Kajon, A.E.; Madan-Lala, R.; Bochkov, Y.A.; Gern, J.E.; Roy, K.; et al. A Polyvalent Inactivated Rhinovirus Vaccine Is Broadly Immunogenic in Rhesus Macaques. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyle, C.J.; Patel, N.D.; Edwards, M.R.; Shaw, S.; Johnston, S.L.; Shaw, S. Pre-Clinical Development of a Novel Cross-Protective Rhinovirus Vaccine. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 64, OA5461. [Google Scholar]
- APOLLO Therapeutics Pipeline—Status for All Assets Progressed into Full Development. Available online: https://www.apollotx.com/pipeline/ (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Vardavas, C.; Zisis, K.; Nikitara, K.; Lagou, I.; Marou, V.; Aslanoglou, K.; Athanasakis, K.; Phalkey, R.; Leonardi-Bee, J.; Fernandez, E.; et al. Cost of the COVID-19 Pandemic versus the Cost-Effectiveness of Mitigation Strategies in EU/UK/OECD: A Systematic Review. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e077602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, J.; Segura, J.; Shi, G.; Buchwald, J.; Roth, G.; Shen, T.J.; Wang, R.; Ji, X.; Fischer, E.R.; Moir, S.; et al. Inhibition of HIV-1 Release by ADAM Metalloproteinase Inhibitors. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1385775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyame, P.; Togami, A.; Yoshida, T.; Masunaga, T.; Begum, M.M.; Terasawa, H.; Monde, N.; Tahara, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. A Heterocyclic Compound Inhibits Viral Release by Inducing Cell Surface BST2/Tetherin/CD317/HM1.24. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Drug Class | Antiviral Compound | Virus Targeted | Protein Targeted | Stage of Development | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capsid Binders | |||||
| Pleconaril | RV, EV-D68 | VP1 | Phase II clinical trial for RV, Preclinical for EV-D68 | [79,80,81] | |
| Pirodavir | RV | VP1 | Phase II clinical trial | [82,83] | |
| Pocapavir (V-073) | RV | VP1 | Preclinical for RV and EV-D68, available for use in emergency treatment of severe neonatal EV-B infections | [84,85,86] | |
| Quinoline derivative: Compound 19 | EV-D68 | Hydrophobic pocket of VP1 | Preclinical | [87] | |
| R856932 (Tetrazole based) | EV-D68 | VP1 | Preclinical | [88] | |
| Vapendavir | RV | VP1 | Phase II clinical trial | [89,90] | |
| Viral replication protein inhibitors | |||||
| Azvudine (FNC *) | EV-D68 | 3D | Approved in China for indication other than EV or RV infection | [91] | |
| EIDD-1931, active form of molnupiravir | EV-D68 | 3D | EUA ** by FDA, approved in some countries for other infection than EV and RV | [92,93] | |
| Fluoxetine | EV-D68 | 2C | FDA approved for indication other than EV or RV infection | [94,95] | |
| Guanidine | EV-D68 | 2C | Preclinical | [96] | |
| Ribavirin | RV | 3D | FDA approved for indication other than EV or RV infection | [97,98,99] | |
| Rupintrivir (AG7088) | RV, EV-D68 | 3C | Phase II for RV | [100,101] | |
| Telaprevir | EV-D68 | 2A | FDA approved for indication other than EV or RV infection | [102,103] | |
| V-7404 | EV-D68 | 3C | Phase I | [104] | |
| Host factors inhibitors | |||||
| CRT0066101, CRT0066051 and XX-050 | RV | Protein Kinase D (PKD) | Preclinical | [105] | |
| CUR-N399 | RV | PI4KIIIβ | Phase I | [106] | |
| DAS181 | RV, EV-D68 | Sialic acid | Fast Track and Breakthrough Therapy designations by the FDA for indications other than EV or RV infection | [100,107,108] | |
| Enviroxime | RV, EV-D68 | PI4KIIIβ | Phase II for RV, preclinical for EV-D68 | [109,110,111] | |
| GSK3923868 | RV | PI4KIIIβ | Phase I | [112,113,114] | |
| Itraconazole | RV | OSBP, ORP4 | FDA approved for indication other than EV or RV infection | [115,116] | |
| KRP-A218 | RV | PI4KIIIβ | Phase I | [117] | |
| SAMHD1 *** | EV-D68 | Cellular deoxynucleotide triphosphate (dNTP) | Preclinical | [118] | |
| Vemurafenib | RV | PI4KIIIβ | FDA approved for indication other than EV or RV infection | [119] | |
| Antibodies | |||||
| A6-1 | EV-D68 | VP1 | Preclinical | [120] | |
| EV68-159 | EV-D68 | VP1, VP3 | Preclinical | [121] | |
| EV68-228 | EV-D68 | VP1 | Phase 1 | [121,122] | |
| 14C11 | RV | ICAM-1 | Preclinical | [66] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahajamanana, V.L.; Thériault, M.; Rabezanahary, H.; Sahnoun, Y.G.; Mallet, M.C.; Isabel, S.; Trottier, S.; Baz, M. Advances in the Treatment of Enterovirus-D68 and Rhinovirus Respiratory Infections. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030061
Rahajamanana VL, Thériault M, Rabezanahary H, Sahnoun YG, Mallet MC, Isabel S, Trottier S, Baz M. Advances in the Treatment of Enterovirus-D68 and Rhinovirus Respiratory Infections. Infectious Disease Reports. 2025; 17(3):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030061
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahajamanana, Vonintsoa L., Mathieu Thériault, Henintsoa Rabezanahary, Yesmine G. Sahnoun, Maria Christina Mallet, Sandra Isabel, Sylvie Trottier, and Mariana Baz. 2025. "Advances in the Treatment of Enterovirus-D68 and Rhinovirus Respiratory Infections" Infectious Disease Reports 17, no. 3: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030061
APA StyleRahajamanana, V. L., Thériault, M., Rabezanahary, H., Sahnoun, Y. G., Mallet, M. C., Isabel, S., Trottier, S., & Baz, M. (2025). Advances in the Treatment of Enterovirus-D68 and Rhinovirus Respiratory Infections. Infectious Disease Reports, 17(3), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030061







