Microbiological Surveillance and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Observations on Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis in an Outpatient German Reference Center
Abstract
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Diagnosis
2.3. Standardized Sample Handling
2.4. Evaluation of Microbial Spectrum and Resistance Profile
2.5. Treatment Regimens
2.6. Ethical Approval
2.7. Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Distribution of Peritonitis Episodes
3.3. Spectrum of Causative Bacteria
3.4. Changes in the Pathogenic Spectrum over Time
3.5. Resistance Profiles
3.6. Multi-Drug-Resistant and Atypical Pathogens
| Antibiotics | Microorganisms [s (r)] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | Staphylococcus epidemidis | Streptococcus spp. | Enterococcus spp. | Enterobacter cloacae | Escherichia coli | Klebsiella spp. | Serratia marcescens | Acinetobacter spp. | |
| Penicillines | |||||||||
| Penicillin G | 2 (2) | 0 (3) | 3 (0) | NT | NT | NT | 0 (2) | NT | NT |
| Ampicillin | 4 (3) | 1 (3) | 5 (0) | 1 (1) | 0 (1) | 0 (5) | 0 (1) | 0 (2) | 0 (2) |
| Ampicillin/Sulbactam | 9 (0) | 4 (1) | 2 (0) | 1 (1) | 0 (1) | 2 (3) | 1 (0) | 0 (1) | 1 (0) |
| Piperacillin/Tazobactam | 6 (0) | 3 (1) | 3 (0) | 1 (1) | 5 (0) | 3 (0) | 3 (0) | 0 (1) | 1 (0) |
| Oxacillin | 9 (0) | 4 (1) | 1 (1) | NT | NT | NT | NT | 1 (1) | NT |
| Cephalosporines | |||||||||
| Cefazolin (1) 1 | 4 (0) | 3 (1) | 1 (0) | NT | NT | NT | NT | 0 (1) | NT |
| Cefuroxim (2) 1 | 11 (0) | 6 (1) | 5 (0) | 0 (2) | NT | 3 (2) | NT | 0 (1) | 1 (0) |
| Ceftriaxon (3a) 1 | 5 (0) | 3 (1) | 5 (0) | 0 (2) | 5 (0) | 2 (0) | 2 (0) | 0 (1) | 0 (1) |
| Ceftazidim (3b) 1 | 2 (0) | 1 (1) | 3 (0) | 0 (1) | 5 (0) | 3 (1) | 3 (0) | 1 (1) | 1 (2) |
| Cefepim (4) 1 | 1 (0) | 1 (1) | 1 (0) | NT | 4 (0) | NT | 2 (0) | 0 (1) | 0 (1) |
| Carbapenemes | |||||||||
| Imipinem | 6 (0) | 2 (1) | 2 (0) | 1 (1) | 1 (0) | 5 (0) | 1 (0) | 1 (1) | 2 (0) |
| Meropenem | 8 (0) | 3 (1) | 2 (0) | 0 (1) | 5 (0) | 5 (0) | 3 (0) | 0 (1) | 3 (0) |
| Chinolone | |||||||||
| Ciprofloxacin | 7 (0) | 5 (1) | 2 (1) | 1 (0) | 5 (0) | 4 (1) | 3 (0) | 1 (0) | 3 (0) |
| Levofloxacin | 10 (0) | 7 (0) | 6 (0) | 1 (0) | 5 (0) | 2 (1) | 2 (0) | 0 (1) | 2 (0) |
| Glykopeptides | |||||||||
| Vancomycin | 9 (0) | 5 (0) | 4 (0) | 2 (0) | NT | NT | NT | 1 (0) | NT |
| Aminoglykosides | |||||||||
| Gentamicin | 11 (1) | 7 (0) | 1 (2) | 1 (1) | 5 (0) | 5 (0) | 3 (0) | 1 (0) | 3 (0) |
| Oxazolidinone | |||||||||
| Linezolid | 8 (0) | 5 (0) | 2 (0) | 2 (0) | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT |
| Total (n) 2 | 14 | 7 | 12 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 3 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| APD | Automated peritoneal dialysis |
| CAPD | Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis |
| ISPD | International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis |
| IP | Intraperitoneal |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| MRSE | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis |
| MRGN | Multi-resistant Gram-negative pathogens |
| PD | Peritoneal dialysis |
| spp. | Species |
| VRE | Vancomycin-resistant enterococci |
References
- Robinski, M.; Mau, W.; Wienke, A.; Girndt, M. The Choice of Renal Replacement Therapy (CORETH) Project: Dialysis Patients’ Psychosocial Characteristics and Treatment Satisfaction. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2017, 32, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, A.; Richter, S.; Kalk, P.; Stieger, P.; Woitas, R.P.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C.; Albert, C. Analysis of a Nurse-Provided on-Call Peritoneal Dialysis Support in an Outpatient Reference Care Centre. BMC Nurs. 2024, 23, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, A.; Richter, S.; Woitas, R.P.; Hinkel, U.P.; Stieger, P.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C.; Albert, C. Baxter Physioneal, Extraneal, Nutrineal (PEN) and Dianeal Solution Bags Can Be Accidentally Connected to Fresenius Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Extensions in a Non-Sterile Manner. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfae067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.K.-T.; Chow, K.M.; Cho, Y.; Fan, S.; Figueiredo, A.E.; Harris, T.; Kanjanabuch, T.; Kim, Y.-L.; Madero, M.; Malyszko, J.; et al. ISPD Peritonitis Guideline Recommendations: 2022 Update on Prevention and Treatment. Periton Dialysis Int. 2022, 42, 110–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellit, T.H.; Owens, R.C.; McGowan, J.E.; Gerding, D.N.; Weinstein, R.A.; Burke, J.P.; Huskins, W.C.; Paterson, D.L.; Fishman, N.O.; Carpenter, C.F.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America Guidelines for Developing an Institutional Program to Enhance Antimicrobial Stewardship. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, M.; Waters, G.P.; Verger, C. Peritoneal Dialysis Associated Peritonitis Rate—Validation of a Simplified Formula. Bull. Dial. Domic. 2021, 4, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchimol, E.I.; Smeeth, L.; Guttmann, A.; Harron, K.; Moher, D.; Petersen, I.; Sørensen, H.T.; von Elm, E.; Langan, S.M.; Committee, R.W. The REporting of Studies Conducted Using Observational Routinely-Collected Health Data (RECORD) Statement. PloS Med. 2015, 12, e1001885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 0-387-95457-0. [Google Scholar]
- Eckmann, C.; Isenmann, R.; Kujath, P.; Pross, A.; Rodloff, A.C.; Schmitz, F.-J. Calculated Parenteral Initial Treatment of Bacterial Infections: Intra-Abdominal Infections. GMS Infect. Dis. 2020, 8, Doc13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Solache, M.; Rice, L.B. The Enterococcus: A Model of Adaptability to Its Environment. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00058-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitterer, D.; Latus, J.; Pöhlmann, C.; Alscher, M.D.; Kimmel, M. Microbiological Surveillance of Peritoneal Dialysis Associated Peritonitis: Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of a Referral Center in GERMANY over 32 Years. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piraino, B.; Bernardini, J.; Brown, E.; Figueiredo, A.; Johnson, D.W.; Lye, W.-C.; Price, V.; Ramalakshmi, S.; Szeto, C.-C. ISPD Position Statement on Reducing the Risks of Peritoneal Dialysis–Related Infections. Perit. Dial. Int. 2011, 31, 614–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofteridis, D.P.; Valachis, A.; Perakis, K.; Maraki, S.; Daphnis, E.; Samonis, G. Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis: Clinical Features and Predictors of Outcome. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e489–e493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Esch, S.; Krediet, R.T.; Struijk, D.G. 32 Years’ Experience of Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis in a University Hospital. Periton Dialysis Int. 2014, 34, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, K.; Shen, H.; Feng, S. Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis Caused by Gram-Negative Organisms: Ten-Years Experience in a Single Center. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.C.M.L.; Hernandes, R.T.; Montelli, A.C.; Monteiro, A.C.M.; Barbosa, T.A.; Camargo, C.H.; Ferreira, A.M.; Mondelli, A.L.; de Lourdes Ribeiro de Souza da Cunha, M.; Barretti, P. Clinical and Microbiological Factors Predicting Outcomes of Nonfermenting Gram-Negative Bacilli Peritonitis in Peritoneal Dialysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunke, C.M.; Brier, M.E.; Golper, T.A. Outcomes of Single Organism Peritonitis in Peritoneal Dialysis: Gram Negatives versus Gram Positives in the Network 9 Peritonitis Study. Kidney Int. 1997, 52, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.R.; Madonia, C.; Rascon-Pacheco, R.A. Improved Patient/Technique Survival and Peritonitis Rates in Patients Treated with Automated Peritoneal Dialysis When Compared to Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis in a Mexican PD Center. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, S76–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubu, M.; Matsui, M.; Uemura, T.; Morimoto, K.; Eriguchi, M.; Samejima, K.; Akai, Y.; Tsuruya, K. Relationship between Initial Peritoneal Dialysis Modality and Risk of Peritonitis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.-N.; Lo, K.-Y.; Tong, G.M.W.; Chan, S.-F.; Lo, M.-W.; Mak, S.-K.; Wong, A.K.M. Prevention of Fungal Peritonitis with Nystatin Prophylaxis in Patients Receiving CAPD. Perit. Dial. Int. J. Int. Soc. Perit. Dial. 2007, 27, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitrungphaiboon, T.; Puapatanakul, P.; Chuengsaman, P.; Tiskajornsiri, K.; Halue, G.; Siribamrungwong, M.; Matayart, S.; Chongthanakorn, K.; Poonvivatchaikarn, U.; Boonyakrai, C.; et al. Intraperitoneal Cefepime Monotherapy Versus Combination Therapy of Cefazolin Plus Ceftazidime for Empirical Treatment of CAPD-Associated Peritonitis: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Noninferiority, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahav, D.; Paul, M.; Fraser, A.; Sarid, N.; Leibovici, L. Efficacy and Safety of Cefepime: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, S.W.Y.; Chen, L.; Woo, A.Y.H.; Ng, D.M.H.; Wong, J.K.W.; Chow, K.M.; Runnegar, N.; Johnson, D.W.; Li, P.K.-T. Stability and Compatibility of Antibiotics in Peritoneal Dialysis Solutions. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Tang, X.; Dong, W.; Sun, N.; Yuan, W. A Review of Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus aureus and Its Regulation Mechanism. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahlen, S.D. Serratia Infections: From Military Experiments to Current Practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 755–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, E.; Canney, M.; McCormick, B.; Brown, P.; Biyani, M.; Zimmerman, D. Predictors of Serum Vancomycin Levels in Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis. Perit. Dial. Int. 2023, 43, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, E.; Canney, M.; McCormick, B.; Ramsay, T.; Biyani, M.; Brown, P.A.; Zimmerman, D. The Association Between Serum Vancomycin Level and Clinical Outcome in Patients With Peritoneal Dialysis Associated Peritonitis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 2646–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J. Pathogenic Spectrum and Risk Factors of Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
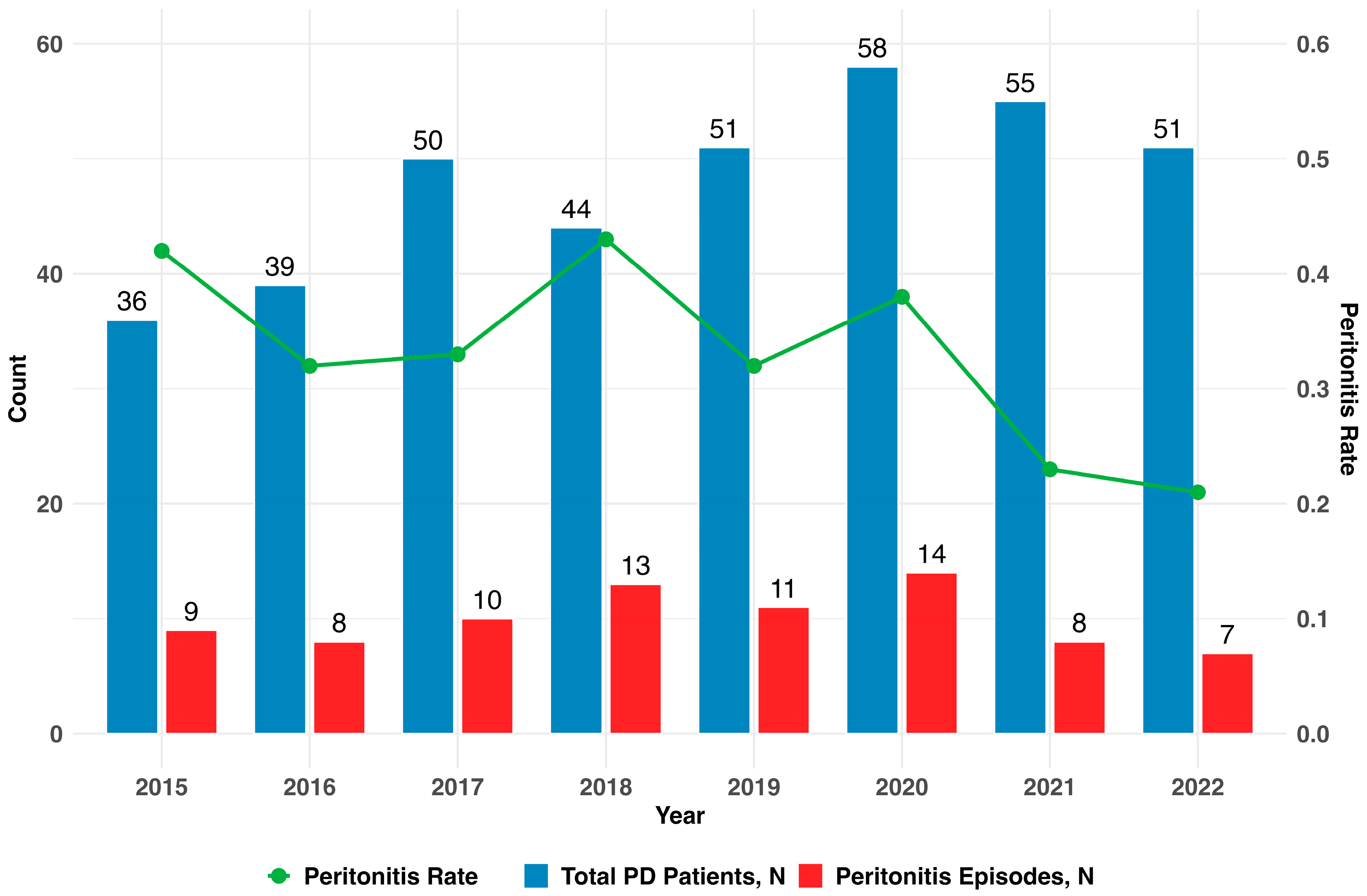
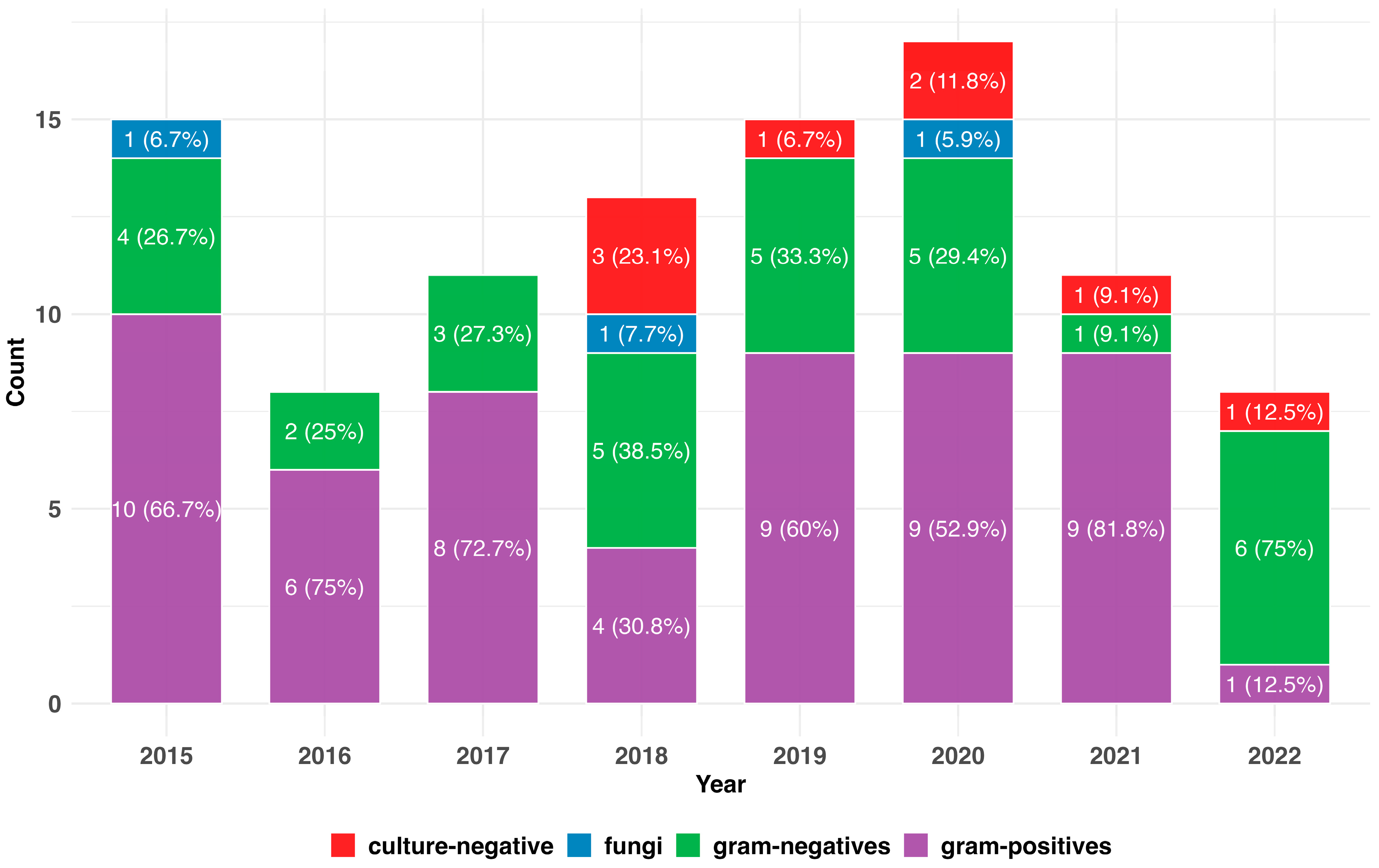
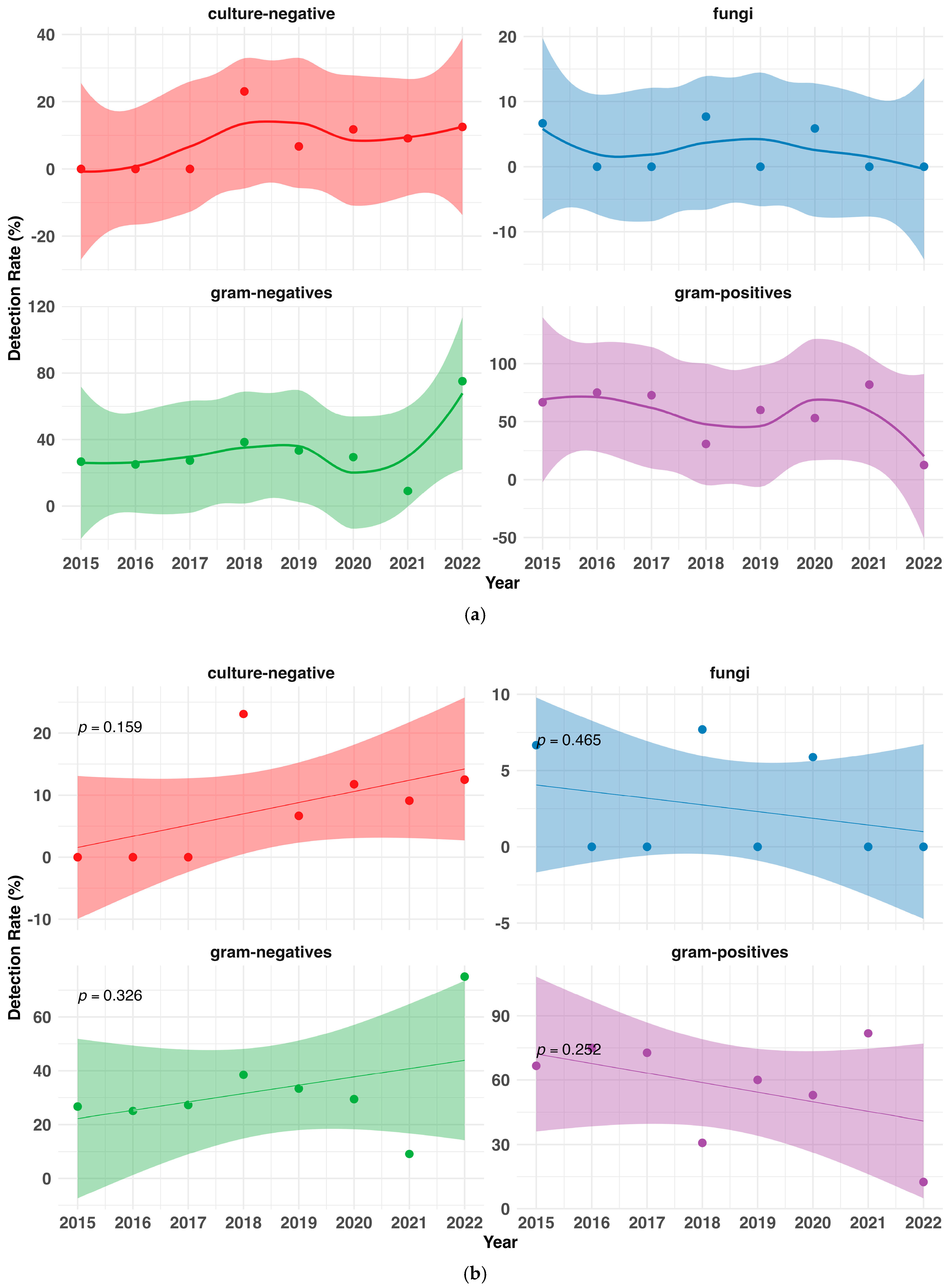
| Total PD patients during timeframe, N | 129 |
| Most recent PD modality (APD:CAPD:IPD) | 79:39:11 |
| Sex (Male; Female) | 82; 47 |
| Age at PD initiation, Median (25–75 CI), years | 69 (55–78) |
| Age at first peritonitis episode, Median (25–75 CI), years | 73 (62–79) |
| Time from PD initiation to first peritonitis episode, Median (25–75 CI), months | 13 (4–24) |
| Relapsing peritonits, N (%) | 3 (3.75) |
| Recurrent peritonitis, N (%) | 3 (3.75) |
| Repeat peritonits, N (%) | 8 (10.0) |
| Tunnel affection, N (%) | 6 (7.5) |
| Peritonitis associated modality switch, N (%) * | 14 (17.5) |
| Died in hospital related to peritonitis, N (%) | 2 (2.5) |
| Microorganism | N (%) | Family | Potential Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-Positives | 56 (56.57) | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus | 14 (14.14) | Staphylococcaceae | upper respiratory tract and skin microbiota |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 7 (7.07) | Staphylococcaceae | typically skin microbiota, less commonly the mucosal microbiota |
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus | 6 (6.06) | Staphylococcaceae | skin microbiota |
| Enterococcus faecialis | 4 (4.04) | Enterococcaceae | physiologic gastrointestinal tracts microbiota |
| Streptococcus mitis | 4 (4.04) | Streptococcaceae | human mouth, throat, and upper respiratory tract microbiota |
| Coagulase negative Staphylococci | 2 (2.02) | Staphylococcaceae | physiologic skin flora |
| Staphylococcus capitis | 2 (2.02) | Staphylococcaceae | skin and nasal microbiota |
| Streptococcus agalacitae | 2 (2.02) | Streptococcaceae | gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract microbiota |
| Streptococcus dysgalactiae ssp. equisimilis | 2 (2.02) | Streptococcaceae | gastroinetstinal and genital tract, less commonly the skin flora. |
| Streptococcus salivarius | 2 (2.02) | Streptococcaceae | the oral cavity and upper respiratory tract |
| Actinomyces neuii | 1 (1.01) | Actinomycetaceae | vaginal microbiota |
| Bacillus cereus | 1 (1.01) | Bacillaceae | found in earth and soil |
| Brevibacterium casei | 1 (1.01) | Brevibacteriaceae | raw milk and cheese manufacturing |
| Coyrnebacterium spp. | 1 (1.01) | Corynebacteriaceae | upper respiratory tract and skin microbiota |
| Enterococcus spp. | 1 (1.01) | Enterococcaceae | gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract microbiota |
| Listeria monozytogenes | 1 (1.01) | Listeriaceae | gastrointestinal, contaminated drinking water or food |
| Micrococcus luteus | 1 (1.01) | Micrococcaceae | found in soil, dust, water and air, and as part of the microbiota of the mammalian skin |
| Norcadia | 1 (1.01) | Nocardiaceae | oral microflora |
| Staphylococcus hominis | 1 (1.01) | Staphylococcaceae | human and animal skin |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | 1 (1.01) | Streptococcaceae | respiratory tract, sinuses, and nasal cavity |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | 1 (1.01) | Streptococcaceae | skin microbiota |
| Gram-negatives | 31 (31.31) | ||
| Escherichia coli | 9 (9.09) | Enterobacteriaceae | gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 5 (5.05) | Enterobacteriaceae | gastrointestinal microbiota |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | 4 (4.04) | Enterobacteriaceae | opportunistic and gastrointestinal origin |
| Serratia marcescens | 3 (3.03) | Yersiniaceae | ubiquitous in soil, water, animals and plants |
| Acinetobacter baumanii | 2 (2.02) | Moraxellaceae | hospital environments; environmental soil and water samples |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 3 (3.03) | Enterobacteriaceae | mouth, skin, and intestinal microbiota |
| Acinetobacter pittii | 1 (1.01) | Moraxellaceae | skin and upper respiratory tract |
| Bacteroides uniforms | 1 (1.01) | Bacteroidaceae | lower intestinal tract microbiota |
| Pantonea agglomerans | 1 (1.01) | Enterobacteriaceae | commonly present on plant surfaces and animal or human feces |
| Pasteurella multocida | 1 (1.01) | Pasteurellaceae | domestic cats and dogs normal respiratory microbiota |
| Raoultella (Klebsiella) planticola | 1 (1.01) | Enterobacteriaceae | ubiquitous, may colonize plants, water, animals and humans |
| Fungi | 3 (3.03) | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 2 (2.02) | Saccharomycetacea | hospital environments; catheter surfaces |
| Candida spp. | 1 (1.01) | Saccharomycetaceae | hospital environments; catheter surfaces |
| Other | 9 (9.09) | ||
| culture-negative | 8 (8.08) | – | – |
| no data record | 1 (1.01) | – | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albert, A.; Richter, S.; Costello-Boerrigter, L.C.; Stieger, P.; Woitas, R.P.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C.; Albert, C. Microbiological Surveillance and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Observations on Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis in an Outpatient German Reference Center. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030049
Albert A, Richter S, Costello-Boerrigter LC, Stieger P, Woitas RP, Braun-Dullaeus RC, Albert C. Microbiological Surveillance and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Observations on Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis in an Outpatient German Reference Center. Infectious Disease Reports. 2025; 17(3):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbert, Annemarie, Stefan Richter, Lisa C. Costello-Boerrigter, Philipp Stieger, Rainer Peter Woitas, Rüdiger C. Braun-Dullaeus, and Christian Albert. 2025. "Microbiological Surveillance and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Observations on Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis in an Outpatient German Reference Center" Infectious Disease Reports 17, no. 3: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030049
APA StyleAlbert, A., Richter, S., Costello-Boerrigter, L. C., Stieger, P., Woitas, R. P., Braun-Dullaeus, R. C., & Albert, C. (2025). Microbiological Surveillance and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Observations on Peritoneal Dialysis-Associated Peritonitis in an Outpatient German Reference Center. Infectious Disease Reports, 17(3), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17030049






