Abstract
Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis (BRIC) stands as a rare genetic contributor to cholestasis, aligning itself within the spectrum of inherited intrahepatic cholestasis syndromes, such as progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Manifesting in infancy or early adulthood, BRIC is marked by recurrent episodes of jaundice accompanied by intense pruritus, enduring from weeks to years across the lifespan. Normal gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) levels are a characteristic laboratory finding. Initially considered unlikely to progress to chronic liver disease or cirrhosis, some reports suggest BRIC may evolve into a continuous and progressive form of cholestasis. Moreover, these recurrent cholestatic episodes significantly impact quality of life, and certain mutations elevate the risk of hepatobiliary malignancy. Between episodes, histological findings of centrilobular cholestasis and abnormal laboratory parameters revert to normal, potentially obviating the need for liver biopsy. This review focuses on the genetic aspects of BRIC, its pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and prognosis. Additionally, it outlines triggering factors and available treatment options.
1. Introduction
Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis (BRIC) is a genetically determined, autosomal recessive disorder [1,2]. It was first described by Summerskill and Walshe in 1959 as a cause of jaundice [3]. Characterized by recurrent episodes of jaundice, pruritus, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and steatorrhea, BRIC manifests symptoms that can mimic a malignant condition, leading to weight loss [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. However, BRIC is a benign clinical entity, as between the episodes, patients experience good clinical condition with normal laboratory values and histologic findings in liver histology. This return to normality is typical of BRIC. The attacks can last for weeks to years, presenting with cholestatic laboratory profiles and abnormal histopathology. Despite its characterization as a benign syndrome, BRIC carries the risk of developing a permanent form of cholestasis in some reports [10,11].
During attacks, liver biopsy specimens reveal intrahepatic non-inflammatory cholestasis and hyperplasia of Kupffer cells [12,13]. Elevated levels of serum conjugated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) are observed, while serum gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) levels and transaminases remain normal or only slightly increased [12,13]. It is noteworthy that normality in serum GGT values, contrasting with an abnormal biochemical liver profile, should raise the clinical suspicion of BRIC. This review aims to explore the genetic aspects of BRIC, its triggering factors, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment options.
2. Literature Search
On 18 September 2023, we conducted a literature search using the term “benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis” in the PubMed database. The search yielded 24 case reports, 38 systematic/narrative reviews, and 2 guidelines published in the English language between 2013 and 2023.
3. History and Epidemiology of Cholestatic Syndromes: BRIC and PFIC
BRIC, formerly known as Summerskill–Walshe–Tygstrup syndrome [3], made its debut in medical literature during the latter half of the 20th century, with awareness limited to a minority of clinicians. In 1959, Summerskill and Walshe initially reported two unrelated patients from the United Kingdom with recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis [3]. Subsequently, in 1960, Tygstrup detailed a similar condition in two distantly related 15-year-old boys in a Faroe Islands village, with disease onset occurring within the first two years of life, marked by cholestasis confirmed through liver biopsy and direct cholangiography [4]. By 1969, Tygstrup and Jensen added five new cases of intermittent intrahepatic cholestasis in young males from the Faroe Islands to the literature. Exacerbations were characterized by intense pruritus and jaundice, with disease-free intervals showing no clinical or biochemical abnormalities. Remission episodes lasted for months or even years [5]. A 1999 follow-up by Tygstrup et al. revealed that none of the patients had progressed to chronic liver disease, and with increasing age, episodes of cholestasis tended to diminish. One patient, aged 25 with 16 episodes lasting about 6 months each, underwent a liver transplant, after which no further episodes were recorded one-year post-transplantation [6].
In the contemporary era of remarkable medical advances, particularly in the fields of genetics and molecular medicine, the incidence of BRIC is on the rise. The global incidence is estimated at approximately 1 in 50,000 to 100,000 people [7]. While the exact prevalence of BRIC remains unknown, it is less common than the related cholestatic disorder progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) [7]. Intrahepatic cholestasis symptoms may manifest in infancy and early adulthood, with the mean age at diagnosis typically ≤20 years old in reported cases. Notably, 10–15% of cases with marked cholestasis in the pediatric population are attributed to PFIC, constituting 10% of liver transplant candidates in infancy [8]. Sex differences are not significant, as males and females are affected at the same ratio [7].
BRIC, along with PFIC types 1 and 2, has been reported in diverse racial groups, including Northern and Mediterranean Europe, Africa, North and South America, and Japan. PFIC3 has been documented in Western European, White, and North African Arabic populations. A family history of cholestatic disease is present in 50% of patients suffering from cholestasis, although sporadic cases have also been described [9].
4. Genetic Aspects of BRIC and PFIC
BRIC, PFIC, and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) are disorders affecting similar genes and associated with intrahepatic cholestasis, collectively considered as part of the group of intrahepatic cholestasis syndromes. However, they exhibit differences in their prognoses and outcomes [1,2,3,14].
BRIC is further categorized into two subtypes: BRIC1 and BRIC2, resulting from mutations in ATP8B1 and ABCB11 genes, respectively [7,15]. Mutations in SLC51A have also been reported in BRIC patients [16]. All affected genes lead to decreased bile salt (BS) secretion. BRIC has been considered an autosomal recessive disorder. However, several studies have demonstrated that heterozygous variants in ATP8B1 or ABCB11 genes can cause BRIC, raising the possibility of haploinsufficiency [17,18,19,20].
PFIC is a distinct family of inherited cholestatic syndromes of autosomal recessive origin, categorized into PFIC1, PFIC2, and PFIC3. PFIC1 and PFIC2 result from mutations in ATP8B1 (chromosome 18q21-22), encoding a defective familial intrahepatic cholestasis 1 protein (FIC1), and mutations in ABCB11 (FIC2) (chromosome 2q24), encoding a defective bile salt export pump protein (BSEP), respectively [16].
Interestingly, similar genes are implicated in BRIC1 and PFIC1, as well as among BRIC2 and PFIC2 patients [1,2]. Despite both BRIC1 and PFIC1 stemming from mutations in ATP8B1, there is substantial differentiation in gene expression, resulting in major clinical and prognostic differences between the two entities. BRIC1 is characterized by recurrent episodes of intrahepatic cholestasis, while PFIC1 progresses to a chronic state of cholestasis. This chronic cholestasis may lead to chronic lesions observed in liver biopsy, progressing from lobular fibrosis to cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease. Consequently, patients with PFIC1 or PFIC2 may ultimately require liver transplantation, whereas those with BRIC1 or BRIC2 usually experience a benign course [1,2,14]. Similar distinctions exist between BRIC2 and PFIC2, as PFIC2 carries a 15% risk of cirrhosis progressing to hepatocellular carcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma [1]. PFIC3, characterized by mutations in ABCB4, which encodes the multi-drug-resistant 3 protein (MDR3). MDR3 acts as a floppase, thus catalyzing the movement of phospholipids from the inner to the outer leaflet of the canalicular membrane. Unlike BRIC1, BRIC2, PFIC1 and PFIC2, in PFIC3, serum gamma-glutamyl transferase levels are elevated [10]. Other genes, including SLC51A, ATP8B1, NR1H4, and MYO5B have also been reported to be affected in PFIC [1,10] (Figure 1). Mutations in the TJP2 [21], Mtm1 [22], PKLR and UGT1A genes [23] have also been associated with BRIC.
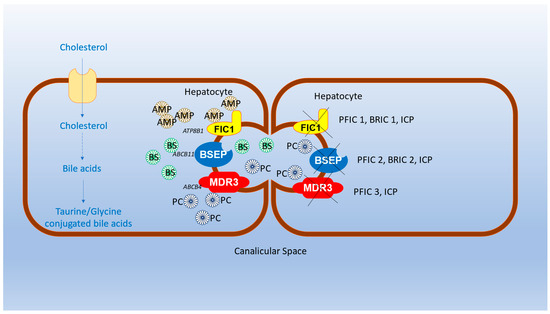
Figure 1.
Pathogenesis of BRIC1 and 2, PFIC-1, 2 and 3 and ICP: Familial intrahepatic cholestasis protein 1 (FIC1 protein) is a flippase that helps in the movement of aminophospholipids; phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine from the outer to the inner space of the plasma membrane; dysfunction of FIC1 results in PFIC1, BRIC1 and ICP. The bile salt exporter pump (BSEP) exports bile acids—cholesterol’s catabolism products—from hepatocytes to the bile canaliculus; Defective BSEP underlies the pathogenesis of PFIC2, BRIC2 and ICP. Multidrug resistance protein 3 is a floppase involved in transporting phosphatidylcholine from the inner to the outer leaflet of the canalicular membrane. PFIC 3 and ICP result in a nonfunctional MDR3 protein. Genetic mutations in ATP8B1, ABCB11, and ABCB4 genes result in the impaired function of FIC1, BSEP and MDR3, respectively. ABCB4 gene: ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 4, ABCB11 gene: ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 11, AMP: aminophospholipids, ATP8B1 gene: ATPase phospholipid transporting 8B1, BRIC: benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis, BSs: bile salts, BSEP: bile salt export pump protein, FIC: familial intrahepatic cholestasis, ICP: intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, MDR3: multi-drug-resistant 3 protein, PC: phosphatidylcholine, PFIC: progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis.
The BSEP, a member of the adenosino-triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family, utilizes ATP to transport substrates, such as taurocholate and other BSs [24,25,26]. Genetic variability is present, evidenced by various mutations in aforementioned genes [18,19,27,28,29,30,31]. New mutations in ATP8B1, ABCB11, and SLC51A genes have recently been reported [15,18,19,27,28,29,30]. Notably, over 100 mutations in ABCB11 have been described, with more than 50% being non-sense mutations [28,29,30,31,32].
In summary, BRIC and PFIC share mutations in similar genes contributing to intrahepatic cholestasis. However, the severity of the diseases varies, with some mutations resulting in milder conditions like BRIC1 and BRIC2, while others, as seen in PFIC1 and PFIC2, lead to more severe clinical entities that may necessitate liver transplantation or even result in death.
5. Pathophysiology of BRIC
Bile formation and outflow play a pivotal role in maintaining health. The hepatocytes produce bile acids, primarily cholic acid, and chenodeoxycholic acid, which are then conjugated with taurine or glycine to form more soluble bile salts. These bile salts are subsequently secreted into the duodenum, where some are re-absorbed into the portal circulation, establishing an enterohepatic circulation. The liver produces approximately 200 mg to 600 mg of bile acids daily [1,26].
BSEP, located on hepatocytes, is essential for the secretion of bile salts into the bile canaliculi, the interspace between hepatocytes. Disruption in this secretion results in the accumulation of bile salts in the canaliculi, leading to impaired bile outflow and intrahepatic cholestasis. In BRIC, the hallmark of pathophysiology is the accumulation of bile salts, particularly in the bile canaliculi. Although the exact mechanisms of intrahepatic cholestasis remain largely unknown, several hypotheses have been proposed.
In BRIC1, it is suggested that reduced levels or impaired function of FIC1 lead to decreased plasma membrane stability. FIC1, a flippase, is involved in the translocation of various phospholipids across the membrane, contributing to membrane asymmetry and stability. Flippases, as type 4 P-ATPase efflux enzymes, facilitate the movement of phospholipids from the outer to the inner leaflet of the canalicular membrane, maintaining membrane stability. Conversely, floppases move phosphatidylcholine in the opposite direction, from the inner to the outer leaflet of the canalicular membranes. In other words, flippases and floppases are enzymes that participate in the movement of phospholipids in the inner and outer leaflets, contributing to the charge gradient of canalicular membranes [33].
In BRIC-2, the impaired function of BSEP results in decreased elimination of bile salts, leading to their accumulation in hepatocytes and bile canaliculi [26,33,34]. BSEP is the primary transporter of bile salts in the bile canaliculi, and its defect results in intrahepatic cholestasis [26,33,34]. The rigid and detergent-stable membrane of the canaliculi may be compromised by the impaired FIC1 in BRIC1, contributing to intrahepatic cholestasis. Overall, these disruptions in bile salt transport and membrane stability collectively contribute to the pathophysiology of BRIC [33].
6. Triggering Factors for BRIC
Various factors have been identified as potential triggers for exacerbations of BRIC, including hormonal influences, infections, and drugs (Table 1). Hormonal changes, such as in pregnancy and oral contraceptive drug administration, have been linked to BRIC, particularly during the initial two trimesters [33,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. Pregnancy, in particular, may act as a triggering factor, especially during the first two trimesters. This can pose a diagnostic challenge when BRIC presents for the first time during pregnancy, requiring differential diagnosis from ICP), viral hepatitis, acute fatty liver of pregnancy, drugs, pre-eclampsia with hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets (HELLP) syndrome, and neoplasms [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. However, most hepatic diseases related to pregnancy typically emerge in the third trimester or the later part of the second trimester [33]. Laboratory findings specific to viral hepatitis, pre-eclampsia, and HELLP syndrome aid in their exclusion. Imaging studies of the liver can reveal acute fatty liver of pregnancy and neoplasms. The association between BRIC and pregnancy or oral contraceptive drugs may involve hormonal factors, possibly implicating estrogen levels [33]. It is suggested that estrogen levels could modulate the function of bile salt transporters, such as BSEPs. Estrogens may impact BSEPs’ function by inhibiting the farsenoid X receptor (FXR), a transcription factor via which BSEP is postulated to be involved in the excretion of bile salts [33].
Beyond pregnancy and oral contraceptive drug use, thyroid dysfunction has been linked to triggering BRIC episodes, with recent reports associating hyperthyroidism with BRIC [43]. Additionally, hypothyroidism has been proposed as an extra-hepatic manifestation of BRIC rather than a direct triggering factor [33].
Infections, particularly those involving Gram-negative bacteria and their lipopolysaccharides (LPS), are considered potential triggers for BRIC. LPS can induce pro-inflammatory cytokine production from Kupffer cells, leading to the downregulation of canalicular bile salt transporters and predisposing individuals to intrahepatic cholestasis [33]. Viral diseases, including influenza and SARS-CoV-2 infections, have also been associated with BRIC attacks [33,44].
While the association of BRIC with drug administration, especially antibiotics, has been rarely reported, it is important to note that antibiotics are often prescribed in the context of infection, making it challenging to establish a definite causal relationship between antibiotics and BRIC episodes. Furthermore, antibiotics appear to contribute to only a minority of the infrequent cases where exacerbation of BRIC is attributed to drugs [33].
7. Clinical Presentation of BRIC
The defining clinical manifestations of BRIC encompass jaundice accompanied by intense pruritus. Additional symptoms, including anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss, may also manifest. BRIC1 can present with pancreatitis, diarrhea, and hearing loss, attributed to the expression of mutated ATP8B1 in the pancreas, intestines, and cochlear cells, respectively. Cholelithiasis has been reported in BRIC2 [33,45,46,47,48].
The onset of the first BRIC attack typically occurs in childhood or early adolescence, although cases can present in infancy or adulthood. The disease follows a course marked by exacerbations lasting from weeks to months or even several years. During symptom-free intervals, which may extend for months to several years, patients experience good health. Table 1 provides details on BRIC cases and their characteristics over the past decade. Liver biopsy abnormalities are observed only during the attacks, with intrahepatic cholestasis resolving during asymptomatic intervals [33,45,46,47,48]. A distinctive feature is the absence of progression to cirrhosis, setting BRIC apart from PFIC. While BRIC generally has a favorable prognosis, its repetitive cholestatic episodes can significantly impact quality of life. It is important to note that any deficiency in BSEP heightens the risk of hepatobiliary malignancy, estimated at a 15% lifetime risk [14]. Despite not progressing to advanced liver disease, BRIC underscores the importance of regular monitoring and management to mitigate the impact on the patient’s well-being.
8. Diagnosis of BRIC
In 1999, Luketic and Shiffman proposed six criteria for diagnosing BRIC, which included cholestasis with intense pruritus, at least two episodes of jaundice with asymptomatic intervals, laboratory findings of intrahepatic cholestasis, normal intra-hepatic and extra-hepatic bile ducts on imaging, a liver biopsy consistent with centrilobular cholestasis during attacks, and the absence of other known causes of cholestasis [9]. While these criteria have been helpful, they are somewhat dated. Advances in technology, particularly next-generation sequencing (NGS), now allow for genetic confirmation of BRIC [49,50,51,52,53,54]. Genetic information, obtained through NGS, has the potential to obviate the need for a liver biopsy in certain cases.
It is important to note that serum conjugated bilirubin and ALP levels are typically significantly elevated in BRIC, in contrast to serum transaminase levels and GGT, which remain normal or only mildly increased. The divergence between ALP and GGT levels can serve as a diagnostic clue for BRIC [34]. However, it is worth mentioning that PFIC and the recently described ubiquitin-specific protease 53 (USP53) disease also exhibit normal or mildly elevated levels of serum GGT [45,50,51,52]. USP53 disease, appearing in early infancy to adolescence, manifests as intrahepatic cholestasis and has been associated with hearing loss in animal models. While the cholestasis in USP53 disease may be relapsing, it can progress to chronic liver disease with fibrosis [51,55,56,57]. Consequently, genetic testing becomes crucial in differentiating between BRIC, PFIC, and USP53 disease, enabling a more personalized evaluation of patients’ prognosis.
Notably, genetic sequencing may identify mutations in ATP8B1 and ABCB11 genes, but it does not provide information about their functional impact. Although the discovery of mutations may support a diagnosis of BRIC or PFIC, understanding the activity of these mutated genes is paramount due to the significant differences in prognosis and monitoring approaches for BRIC and PFIC. Early detection is essential, especially since PFIC may necessitate liver transplantation. To address the limitations of genetic sequencing, alternative techniques have emerged to evaluate gene function, such as in vitro mutagenesis. However, in vitro mutagenesis is technically demanding and time-consuming [58,59].
Mizutani et al. proposed an alternative method to assess ATP8B1 deficiency in BRIC1 or PFIC1 using human peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages (HMDMs). They found that ATP8B1 is expressed in HMDMs and is associated with the polarization of HMDMs into M2 macrophages through treatment with interleukin-10 (IL-10). Flow cytometry analysis demonstrated a significant reduction in M2 macrophage markers, CD14 and CD163, in PFIC1, but only a slight reduction in BRIC1 [54]. M2 macrophages, known for their anti-inflammatory effects, secrete cytokines like IL-10, moderating the host response to inflammatory stimuli. This reduction in host response protects against overactive reactions, contributing to homeostasis. Conversely, M1 macrophages, associated with inflammation, secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, potentially contributing to cholestatic chronic liver injury. The diminished or dysfunctional M2 macrophages in PFIC1 may account for chronic inflammation, liver tissue damage, cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease [59].
In summary, the evolution of sophisticated molecular techniques allows for easier differentiation between BRIC and PFIC, even in the early stages of these inherited cholestatic disorders.
9. Treatment Options and Future Challenges in BRIC
Several compounds have been utilized to alleviate symptoms in BRIC, with varying degrees of success. Anti-histamine drugs, though limited in efficacy for pruritus, do not address the underlying cholestasis-induced pruritus pathogenesis [57]. Opioids, believed to play a role in cholestasis-induced pruritus by acting on the mu-opioid receptor, have led to the exploration of opioid antagonists, such as intravenous naloxone or oral naltrexone. While providing substantial relief, caution is warranted in severe liver disease, and the issue of opioid withdrawal syndrome restricts their use [60].
Cholestyramine and ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) are commonly employed in BRIC treatment. Cholestyramine, a non-absorbable polystyrene, binds bile acids (BAs) in the gut lumen, inhibiting their re-absorption by approximately 90%, thereby reducing BA levels [60,61]. Rifampin, acting on the pregnane X receptor (PXR), exhibits anti-pruritic effects in cholestasis but requires vigilant liver function monitoring due to the potential for drug-induced liver injury [26,62,63,64]. UDCA, a dihydroxy bile acid, alters the bile acids pool to a more hydrophilic mixture, and its favorable safety profile has contributed to its increased use, even during pregnancy [2,21,25,27,28,37,65].
Combination therapies, such as cholestyramine (4 g daily) with UDCA (15–20 g daily) and rifampicin, have been explored in non-responsive BRIC cases [15,18,19,24,44,60]. Endoscopic nasobiliary drainage is a well-established method of biliary decompression where the distal end of the drain is placed in the common bile duct and the proximal end emerges out through the nose. Pruritus and jaundice often resolve following drainage. The intervention is minimal, and the effects may be long-lasting even if the drainage is left for short time and was only placed once. For individuals not tolerating nasobiliary drainage, a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) may be implanted and two nasobiliary tubes placed through the PEG into the left and right hepatic ducts. Both methods have the advantage of the real-time monitoring of drainage status. A reduction in bile acid levels was determined, and they became normalized shortly after the placement of the tubes [66,67,68,69]. Hemodialysis with specific filters has been attempted with encouraging outcomes in certain cases [61,70,71].
Fibrates, such as fenofibrate, inhibit bile acid synthesis and enhance bile excretion, potentially offering a management option for BRIC [57]. Obeticholic acid, an FXR agonist, is FDA-approved for the treatment of primary biliary cholangitis in patients non-responding to UDCA in doses 5–10 mg daily [57]. However, due to its common complication of pruritus, it has not been widely used in inherited cholestasis disorders. It is noteworthy that, as shown in Table 1, obeticholic acid has not been administered in any BRIC case during the last 10 years.
Recent discoveries of ileal bile acid transport (IBAT) inhibitors, like odevixibat and maralixibat, approved by the FDA for Alagille syndrome treatment, present additional options for BRIC patients [72,73].
In summary, gaining a deeper understanding of the molecular pathways involving FIC1 and BSEP in both healthy individuals and BRIC patients is crucial. Exploring the biosynthesis and various factors influencing FIC1 and BSEP at the transcriptional and translational levels may provide insights into this clinically benign yet troublesome entity. Continued research and the development of targeted therapies hold promise for improving the management of BRIC in the future.

Table 1.
BRIC cases reported in the past 10 years and their characteristics.
Table 1.
BRIC cases reported in the past 10 years and their characteristics.
| Author/Year | Age y.o. | Number of Attacks | Sex | BRIC-1/ BRIC-2 | Triggering Factor | Treatment | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moghadamrad et al., 2013 [74] | 44 | Unknown | F | BRIC-2 | Gastroenteritis | None | |
| Oldakowska Jedynak et al., 2014 [71] | 14 | Unknown | M | BRIC-1 | Skin infection or tetracycline | None | |
| Kumar et al., 2016 [34] | 27 | >10 | M | BRIC 1 | Unknown | UDCA | |
| Schreiner et al., 2019 [75] | 16 | Unknown | M | BRIC-2 | Pharyngitis | UDCA | |
| Dold et al., 2019 [67] | 51 | 1 | F | BRIC 2 | Unknown | Nasobillary Drainage + Percutaneous Transgastral Biliodigestive Diversion | |
| Sohn et al., 2019 [26] | 6 | 3 | F | BRIC 1 | Unknown | Phenylbutyrate and Rifampicin | |
| Fotoulaki et al., 2019 [30] | 27 months | 1 | F | BRIC 2+ PFIC 2 | Cystitis | UDCA + Liver Transplantation after 5 years | |
| Halawi et al., 2020 [43] | 37 | 7 | F | BRIC-1 | Hyperthyroidism | UDCA + Thyroxine | |
| Arthur et al., 2020 [76] | 27 | 2 | F | BRIC-2 | Pregnancy | None | |
| Piazzolla et al., 2020 [19] | 29 | Unknown | M | BRIC-1 | Unknown | UDCA 15 mg/Kg + Cholestyramine 8 g/d | |
| Salyani et al., 2020 [63] | 21 | 4 | M | Unnknown | Skin abscess in 2 prior attacks | Rifampicin 150 mg × 2/d | |
| Schoneich et al., 2020 [70] | 24 | Unknown | Unknown | BRIC-1 | No | Dialysis | Resistant to Cholestyramine + Steroids + Rifampicin |
| Ayyash et al., 2021 [37] | 29 | 2 related to ICP | F | Unknown | Pregnancy | UDCA 600 mg × 2/d | Fetal Death at 36 weeks of gestation |
| Akbulut et al., 2021 [15] | 16 | >10 | M | BRIC-2 | Unknown | UDCA 20 mg/Kg/d + Cholestyramine 4 g/d | |
| Provenzano et al., 2021 [47] | 35 | 1 | F | BRIC 1 | Pregnancy | Childbirth | |
| Kornitzer et al., 2021 [21] | 15 | >10 | F | BRIC 1 | Unknown | UDCA | |
| Kalaranjini et al., 2021 [25] | 12 | >10 | M | BRIC-2 | Fever | UDCA | |
| Gupta et al., 2021 [2] | 26 | 3 | M | Unknown | Methamphetamine use | UDCA | |
| Chen et al., 2021 [27] | 34 | >10 | M | BRIC-1 | Pharyngitis | UDCA | |
| Koukoulioti et al., 2021 [61] | 47 | >10 | M | BRIC-1 | Unknown | Dialysis | Resistant to drugs on dialysis for many years |
| Bing et al., 2022 [20] | 17 | 1 | M | BRIC-1 | Unknown | UDCA Glycyrrhizin + Glucocorticoids + Dialysis | |
| Calhan et al., 2022 [44] | 59 | Unknown | M | Unknown | COVID-19 | UDCA + Cholestyramine + Rifampicin | |
| Miura et al., 2022 [24] | 16 | 1 | F | Unknown | Unknown | UDCA 300 mg/d + Cholestyramine 4 g/d | |
| Suzuki et al., 2022 [18] | 17 | Unknown | M | BRIC 1 | Unknown | UDCA/Prednisolone/Rifampicin 450 mg/day |
Abbreviations: d, daily; F, vemale; ICP, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy; M, male; UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid; y.o., years old.
10. Conclusions
In conclusion, BRIC is characterized by recurrent episodes of intrahepatic cholestasis, yet it does not progress to cirrhosis. Clinicians should remain vigilant regarding this inherited disorder, particularly as it can be triggered by factors such as viral infections and pregnancy. A deeper understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of BRIC holds the promise of identifying potential therapeutic interventions in the near future. Molecular genetic testing emerges as a valuable tool for diagnosing this clinically benign entity. The critical differentiation between BRIC and PFIC is crucial, especially in the early stages of these conditions. As highlighted earlier, PFIC may necessitate liver transplantation, which is not required for BRIC. Thus, beyond traditional sequencing methods, novel techniques for assessing the residual function of ATP8B1 and ABCB11 could elucidate the distinctions between BRIC and PFIC at an early stage, facilitating accurate and timely diagnoses. Continued research and innovative diagnostic approaches will contribute to refining our understanding and management of BRIC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.V.G. and A.A.; methodology, E.V.G.; software, E.M.; validation, N.G.V. and E.M.; formal analysis, E.V.G. and V.S.; resources, E.V.G.; data curation, D.K.; writing—original draft preparation, E.V.G. and A.A.; writing—review and editing, V.S. and A.A.; visualization, E.M., N.G.V. and D.K.; supervision, A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data are created.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Henkel, S.A.; Squires, J.H.; Ayers, M.; Ganoza, A.; Mckiernan, P.; Squires, J.E. Expanding etiology of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Ali, I.A.; Abreo, E.; Gujju, V.; Hayat, M. The Mystery of Episodic Recurrent Jaundice in a Young Male: Cholestasis With a normal gamma-glutamyl Transferase. Cureus 2021, 13, e13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerskill, W.H.; Walshe, J.M. Benign recurrent intrahepatic “obstructive” jaundice. Lancet 1959, 2, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tygstrup, N. Intermittent possibly familial intrahepatic cholestatic jaundice. Lancet 1960, 275, 1171–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tygstrup, N.; Jensen, B. Intermittent intrahepatic cholestasis of unknown etiology in five young males from the Faroe Islands. Acta Med. Scand. 1969, 185, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tygstrup, N.; Steig, B.A.; Juijn, J.A.; Bull, L.N.; Houwen, R.H. Recurrent familial intrahepatic cholestasis in the Faeroe Islands. Phenotypic heterogeneity but genetic homogeneity. Hepatology 1999, 29, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2014, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, I.; Tadi, P. Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis. [Updated 3 July 2023]. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Luketic, V.A.; Shiffman, M.L. Bening Recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Clin. Liver Dis. 1999, 3, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ooteghem, N.A.; Klomp, L.W.; van Berge-Henegouwen, G.P.; Houwen, R.H. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis progressing to progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis: Low GGT cholestasis is a clinical continuum. J. Hepatol. 2002, 36, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Mil, S.W.; Klomp, L.W.; Bull, L.N.; Houwen, R.H. FIC1 disease: A spectrum of intrahepatic cholestatic disorders. Semin. Liver Dis. 2001, 21, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, R.; Suresh, N.; Sathiyasekeran, M.; Venkatakrishnan, L. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis Unravelling the paradox. Indian Pediatr. 2021, 58, 486–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Romero, R.; Morlan-Herrador, L.; Ros-Arnal, I.; Miramar, M.D.; Molera-Busons, C. Intrahepatic cholestasis, sometimes benign recurrent. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 44, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davit-Spraul, A.; Gonzales, E.; Baussan, C.; Jacquemin, E. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2009, 3, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbulut, U.E.; Randa, N.C.; Işık, İ.A.; Atalay, A. Beinign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis type 2 in a child. A case report and novel mutation. Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2021, 1, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the Management of Cholestatic Liver Diseases (2021). J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Umetsu, S.; Togawa, T.; Ito, K.; Kawabata, T.; Arinaga-Hino, T.; Tsumura, N.; Yasuda, R.; Mihara, Y.; Kusano, H.; et al. Clinicopathologic Features, Genetics, Treatment, and Long-Term Outcomes in Japanese Children and Young Adults with Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis: A Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Arinaga-Hino, T.; Sano, T.; Mihara, Y.; Kusano, H.; Mizuochi, T.; Togawa, T.; Ito, S.; Ide, T.; Kuwahara, R.; et al. Case Report: A Rare Case of Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 1 with a Novel Heterozygous Pathogenic Variant of ATP8B1. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 891659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzolla, M.; Castellaneta, N.; Novelli, A.; Agolini, E.; Cocciadiferro, D.; Resta, L.; Duda, L.; Barone, M.; Ierardi, E.; Di Leo, A. Nonsense variant of ATP8B1 gene in heterozygosis and benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis: A case report and review of the literature. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, H.; Li, Y.L.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Chang, B. Case Report: A Rare Heterozygous ATP8B1 Mutation in a BRIC1 Patient: Haploinsufficiency? Front. Med. 2022, 9, 897108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornitzer, G.A.; Alvarez, F. Case Report: A Novel Single Variant TJP2 Mutation in a Case of Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis. JPGN Rep. 2021, 2, e087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolczak, S.; Deshwar, A.R.; Aristegui, E.; Kamath, B.M.; Lawlor, M.W.; Andreoletti, G.; Volpatti, J.; Ellis, J.L.; Yin, C.; Dowling, J.J.; et al. Loss of Mtm1 causes cholestatic liver disease in a model of X-linked myotubular myopathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e166275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B.F. Case report: A rare case of pyruvate kinase deficiency and Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II with a novel pathogenic variant of PKLR and UGT1A1 mutation. Front Genet. 2023, 14, 1229271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, R.; Kawaoka, T.; Imamura, M.; Kosaka, M.; Johira, Y.; Shirane, Y.; Murakami, S.; Yano, S.; Amioka, K.; Naruto, K.; et al. Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 1 with Novel Nonsense Mutations in the ATP8B1 Gene. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2022, 16, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaranjini, K.V.; Glaxon, J.A.; Vasudevan, S.; Arunkumar, M.L. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis 2 deficiency in a child. Report from a tertiary care center in South India. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2021, 64 (Suppl. S1), S146–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, M.J.; Woo, M.H.; Seong, M.W.; Park, S.S.; Kang, G.H.; Moon, J.S.; Ko, J.S. Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 2 in Siblings with Novel ABCB11 mutations. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2019, 22, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wu, D.; Jiang, W.; Lei, T.; Lu, C.; Zhou, T. Case report: A novel homozygous variant identified in a Chinese patient with benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis type 1. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 705489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strautnieks, S.S.; Byrne, J.A.; Pawlikowska, L.; Cebecauerová, D.; Rayner, A.; Dutton, L.; Meier, Y.; Antoniou, A.; Stieger, B.; Arnell, H.; et al. Severe bile salt export pump deficiency: 82 different ABCB11 mutations in 109 families. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khabou, B.; Kallabi, F.; Abdelaziz, R.B.; Maaloul, I.; Aloulou, H.; Chehida, A.B.; Kammoun, T.; Barbu, V.; Boudawara, T.S.; Fakhfakh, F.; et al. Molecular and computational characterization of ABCB11 and ABCG5 variants in Tunisian patients with neonatal/infantile low-GGT intrahepatic cholestasis: Genetic diagnosis and genotype-phenotype correlation assessment. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2023; early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotoulaki, M.; Giza, S.; Jirsa, M.; Grammatikopoulos, T.; Miquel, R.; Hytiroglou, P.; Tsitouridis, I.; Knisely, A.S. Beyond an Obvious Cause of Cholestasis in a Toddler: Compound Heterozygosity for ABCB11 Mutations. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20182146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpechot, C.; Barbu, V.; Chazouillères, O.; Broué, P.; Girard, M.; Roquelaure, B.; Chrétien, Y.; Dong, C.; Lascols, O.; Housset, C.; et al. Genetic contribution of ABCC2 to Dubin Johnson syndrome and inherited cholestatic disorders. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonfeld, E.A.; Brown, R.S., Jr. Genetic causes of liver disease: When to suspect a genetic etiology, initial lab testing and the basics of management. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 103, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawi, A.; Ibrahim, N.; Bitar, R. Triggers of benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and its pathophysiology: A review of literature. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2021, 84, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Charaniya, R.; Ahuja, A.; Mittal, S.; Sahoo, R. Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis in a Young Adult. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, OD01-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.I.; Dönmez-Cakil, Y.; Szöllősi, D.; Stockner, T.; Chiba, P. The Bile Salt Export Pump: Molecular Structure, Study Models and Small-Molecule Drugs for the Treatment of Inherited BSEP Deficiencies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müllenbach, R.; Bennett, A.; Tetlow, N.; Patel, N.; Hamilton, G.; Cheng, F.; Chambers, J.; Howard, R.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Williamson, C. ATP8B1 mutations in British cases with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Gut 2005, 54, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.; Smith, N.; Keerthy, M.; Singh, A.; Shaman, M. Bening recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnancy. Fetal death at 36 weeks of gestation. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 6, 5086846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.D.; Sundaram, V.; Ayoub, W.S. Atypical causes of cholestasis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9418–9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sticova, E.; Jirsa, M.; Pawłowska, J. New insights in genetic cholestasis: From molecular mechanisms to clinical implications. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 2313675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Saxena, R. Pathophysiology and Diseases of the Proximal Pathways of the Biliary System. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2015, 139, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Woerd, W.L.; van Mil, S.W.; Stapelbroek, J.M.; Klomp, L.W.; van de Graaf, S.F.; Houwen, R.H. Familial cholestasis: Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis, benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 24, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C.G.; Geier, A. Effect of drug transporter pharmacogenetics on cholestasis. Expert. Opin. Drug. Metab. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 1533–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halawi, A.; Bitar, R.; Ibrahim, N. Hyperthyroidism as a potential trigger for benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. ACG Case Rep. J. 2020, 7, e00423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhan, T.; Yivli, E. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) as a potential trigger for benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e05557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroka, C.J.; Boyer, J.L. Biosynthesis and trafficking of the bile salt export pump, BSEP: Therapeutic implications of BSEP mutations. Mol. Aspects Med. 2014, 37, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, M.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Grison, S.; Lascols, O.; Fernandez, E.; Barbu, V. Clinical characteristics and genetic profiles of young and adult patients with cholestatic liver disease. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2019, 111, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, A.; Farina, A.; Seidenari, A.; Azzaroli, F.; Serra, C.; Della Gatta, A.; Zuffardi, O.; Giglio, S.R. Prenatal Noninvasive Trio-WES in a Case of Pregnancy Related Liver Disorder. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannoni, I.; Callea, F.; Bellacchio, E.; Torre, G.; De Ville De Goyet, J.; Francalanci, P. Genetics and Molecular Modeling of New Mutations of Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis in a Single Italian Center. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, M.C.; Hall, R.A.; Krawczyk, M.; Lammert, F. Genetic determinants of cholangiopathies: Molecular and systems genetics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togawa, T.; Sugiura, T.; Ito, K.; Endo, T.; Aoyama, K.; Ohashi, K.; Negishi, Y.; Kudo, T.; Ito, R.; Kikuchi, A.; et al. Molecular Genetic Dissection and Neonatal/Infantile Intrahepatic Cholestasis Using Targeted Next Generation Sequencing. J. Pediatr. 2016, 171, 171–177.e1-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, L.N.; Ellmers, R.; Foskett, P.; Strautnieks, S.; Sambrotta, M.; Czubkowski, P.; Jankowska, I.; Wagner, B.; Deheragoda, M.; Thompson, R.J. Cholestasis due to USP53 Deficiency. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonfeld, E.A.; Brown, R.S., Jr. Genetic Testing in Liver Disease: What to order, in Whom, and When. Clin. Liver Dis. 2017, 21, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.E.; Choe, B.H.; Seo, A.N.; Bae, H.I.; Hwang, S.K. Early Diagnosis of ABCB11 Spectrum Liver Disorders by Next Generation Sequencing. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2017, 20, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, J.; de Waart, D.R.; Utsunomiya, K.; Duijst, S.; Mok, K.H.; Oude Elferink, R.P.; Bosma, P.J.; Paulusma, C.C. ATP8B1 and ATP11C: Two Lipid Flippases Important for Hepatocyte Function. Dig. Dis. 2015, 33, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, L.; Cheng, W.; Yan, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Jin, Y.; Hu, G.; Wang, C.; et al. Diagnostic yield and novel candidate genes by next generation sequencing in 166 children with intrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatol. Int. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Gong, J.Y.; Li, L.T.; Li, J.Q.; Zhang, M.H.; Lu, Y.; Xie, X.B.; Hong, Y.R.; Yu, Z.; et al. Low-GGT intrahepatic cholestasis associated with biallelic USP53 variants: Clinical, histological and ultrastructural characterization. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vij, M.; Sankaranarayanan, S. Biallelic Mutations in Ubiquitin-Specific Peptidase 53 (USP53) Causing Progressive Intrahepatic Cholestasis. Report of a Case With Review of Literature. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. Off. J. Soc. Pediatr. Pathol. Paediatr. Pathol. Soc. 2022, 25, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, D.E.; van der Mark, V.A.; Ho-Mok, K.S.; Oude Elferink, R.P.; Paulusma, C.C. Differential effects of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 1 and benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis type 1 mutations on canalicular localization of ATP8B1. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, A.; Sabu, Y.; Naoi, S.; Ito, S.; Nakano, S.; Minowa, K.; Mizuochi, T.; Ito, K.; Abukawa, D.; Kaji, S.; et al. Assessment of Adenosine Triphosphatase Phospholipid Transporting 8B1 (ATP8B1) Function in Patients With Cholestasis With ATP8B1 Deficiency by Using Peripheral Blood Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 5, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Woerd, W.L.; Houwen, R.H.; van de Graaf, S.F. Current and future therapies for inherited cholestatic liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koukoulioti, E.; Ziagaki, A.; Weber, S.N.; Lammert, F.; Berg, T. Long-Term Colestyramine Treatment Prevents Cholestatic Attacks in Refractory Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 1 Disease. Hepatology 2021, 74, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhebbi, H.; Peer-Zada, A.A.; Al-Hussaini, A.A.; Algubaisi, S.; Albassami, A.; AlMasri, N.; Alrusayni, Y.; Alruzug, I.M.; Alharby, E.; Samman, M.A.; et al. New paradigms of USP53 disease. Normal CG, cholestasis, BRIC, cholangiopathy and responsiveness to rifampicin. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 66, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salyani, A.; Barasa, L.; Rajula, A.; Ali, S.K. Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis (BRIC): An African Case Report. Case Rep. Gastrointest. Med. 2020, 10, 894293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgadottir, H.; Folvik, G.; Vesterhus, M. Improvement of cholestatic episodes in patients with benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis (BRIC) treated with rifampicin. A long-term follow-up. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 58, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagawa, T.; Orii, R.; Hirose, S.; Arase, Y.; Shiraishi, K.; Mizutani, A.; Tsukamoto, H.; Mine, T. Ursodeoxycholic acid stabilizes the bile salt export pump in the apical membranein MDCK II cells. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Sahoo, B.; Bihari, C. Endoscopic nasobiliary drainage: An effective treatment option for benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis(BRIC). BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr2016218874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dold, L.; Tschada, A.; Strassburg, C.P.; Weismüller, T.J. Percutaneous transgastral biliodigestive diversion as treatment option for benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakar, T.; Demir, M.; Gokturk, H.S.; Unler Kanat, A.G.; Parlakgumus, A.; Ozer, B.; Serin, E. Nasobiliary Drainage for Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis in Patients Refractory to Sandard Therapy. Clin. Investig. Med. 2016, 39, 27522. [Google Scholar]
- Appleby, V.J.; Hutchinson, J.M.; Davies, M.H. Safety and efficacy of long term nasobiliary drainage to treat intractable pruritus in cholestatic liver disease. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeneich, K.; Frimmel, S.; Koball, S. Successful treatment of a patient with benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis type 1 with albumin dialysis. Artif. Organs 2020, 44, 341–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ołdakowska-Jedynak, U.; Jankowska, I.; Hartleb, M.; Jirsa, M.; Pawłowska, J.; CzubChoudhury, A.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Sahoo, B.; Bihari Ckowski, P.; Krawczyk, M. Treatment of pruritus with Prometheus dialysis and absorption system in a patient with benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, E304–E308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntaha HS, T.; Munir, M.; Sajid, S.H.; Sarfraz, Z.; Sarfraz, A.; Robles-Velasco, K.; Sarfraz, M.; Felix, M.; Cherrez-Ojeda, I. Ileal Bile Acid Transporter Blockers for Cholestatic Liver Disease in Pediatric Patients with Alagille Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, B.M.; Stein, P.; Houwen, R.H.J.; Verkade, H.J. Potential of ileal bile acid transporter inhibition as a therapeutic target in Alagille syndrome and progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadamrad, S.; Montani, M.; Weimann, R.; De Gottardi, A. Cholestasis in a patient with gallstones and a normal gamma-glutamyl transferase. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2539–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiner, P.; Stieger, B.; McLin, V.; Rougemont, A.L.; Keitel, V.; Dröge, C.; Müllhaupt, B. A rare cause of cholestatic jaundice in a North African teenager. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 2036–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur Lorio, E.; Valadez, D.; Alkhouri, N.; Loo, N. Cholestasis in Benign Recurrent Intrahepatic Cholestasis 2. ACG Case Rep. J. 2020, 7, e00412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).