A Pilot Study: The Effect of CPAP Intervention on Sleep Architecture and Cognition in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants Inclusion
2.2. Cognitive Assessment
2.3. Video-Polysomnography (V-PSG) and Sleep Architecture
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
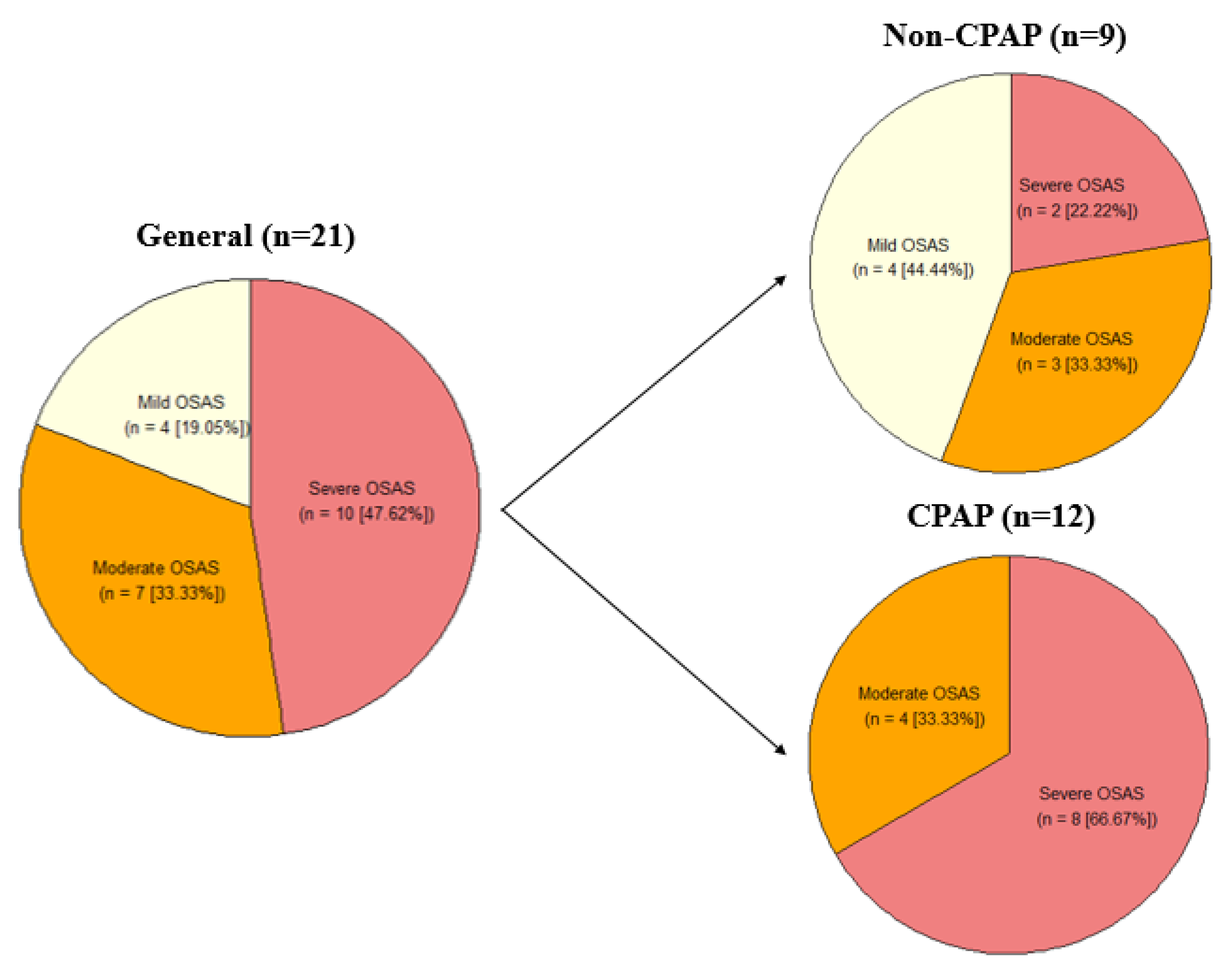
3.1. Demographic Description of the CPAP and Non-CPAP Groups
3.2. CPAP Results
Longitudinal Cognitive Status
3.3. Effect of Sleep in Cognitive Progression
4. Discussion
4.1. Cognitive Progression in the Full Cohort
4.2. Impact of the CPAP on Cognitive Progression
4.3. Effect of Sleep Parameters on Cognitive Progression
4.4. Glymphatic System and Sleep-Cognition Relationships
4.5. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiao, B.; Li, R.; Zhou, H.; Qing, K.; Liu, H.; Pan, H.; Lei, Y.; Fu, W.; Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; et al. Neural biomarker diagnosis and prediction to mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease using EEG technology. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mayer, G.; Frohnhofen, H.; Jokisch, M.; Hermann, D.M.; Gronewold, J. Associations of sleep disorders with all-cause MCI/dementia and different types of dementia—Clinical evidence, potential pathomechanisms and treatment options: A narrative review. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1372326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thipani Madhu, M.; Balaji, O.; Kandi, V.; Ca, J.; Harikrishna, G.V.; Metta, N.; Mudamanchu, V.K.; Sanjay, B.G.; Bhupathiraju, P. Role of the Glymphatic System in Alzheimer’s Disease and Treatment Approaches: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e63448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hussain, R.; Graham, U.; Elder, A.; Nedergaard, M. Air pollution, glymphatic impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 2023, 46, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekanayake, A.; Peiris, S.; Ahmed, B.; Kanekar, S.; Grove, C.; Kalra, D.; Eslinger, P.; Yang, Q.; Karunanayaka, P. A Review of the Role of Estrogens in Olfaction, Sleep and Glymphatic Functionality in Relation to Sex Disparity in Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 2024, 39, 15333175241272025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, Z.; Jordan, J.D.; Zhang, Q. Early life adversity as a risk factor for cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2023, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Heutz, R.; Claassen, J.; Feiner, S.; Davies, A.; Gurung, D.; Panerai, R.B.; Heus, R.; Beishon, L.C. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2023, 43, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, Q.; Coury, R.; Tang, W. Prediction of conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease and simultaneous feature selection and grouping using Medicaid claim data. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Matuskova, V.; Veverova, K.; Jester, D.J.; Matoska, V.; Ismail, Z.; Sheardova, K.; Horakova, H.; Cerman, J.; Laczó, J.; Andel, R.; et al. Mild behavioral impairment in early Alzheimer’s disease and its association with APOE and BDNF risk genetic polymorphisms. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Astara, K.; Tsimpolis, A.; Kalafatakis, K.; Vavougios, G.D.; Xiromerisiou, G.; Dardiotis, E.; Christodoulou, N.G.; Samara, M.T.; Lappas, A.S. Sleep disorders and Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology: The role of the Glymphatic System. A scoping review. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2024, 217, 111899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhu, J. Glymphatic system: An emerging therapeutic approach for neurological disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1138769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Voumvourakis, K.I.; Sideri, E.; Papadimitropoulos, G.N.; Tsantzali, I.; Hewlett, P.; Kitsos, D.; Stefanou, M.; Bonakis, A.; Giannopoulos, S.; Tsivgoulis, G.; et al. The Dynamic Relationship between the Glymphatic System, Aging, Memory, and Sleep. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Örzsik, B.; Palombo, M.; Asllani, I.; Dijk, D.J.; Harrison, N.A.; Cercignani, M. Higher order diffusion imaging as a putative index of human sleep-related microstructural changes and glymphatic clearance. Neuroimage 2023, 274, 120124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M.J.; Liao, Y.; Thiyagarajan, M.; O’Donnell, J.; Christensen, D.J.; Nicholson, C.; Iliff, J.J.; et al. Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 2013, 342, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tarasoff-Conway, J.M.; Carare, R.O.; Osorio, R.S.; Glodzik, L.; Butler, T.; Fieremans, E.; Axel, L.; Rusinek, H.; Nicholson, C.; Zlokovic, B.V.; et al. Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015, 11, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, E.; Levine, K.S.; Han, J.; Iwaki, H.; Koretsky, M.J.; Kuznetsov, N.; Faghri, F.; Solsberg, C.W.; Schuh, A.; Jones, L.; et al. Sleep disturbances as risk factors for neurodegeneration later in life. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oliver, C.; Li, H.; Biswas, B.; Woodstoke, D.; Blackman, J.; Butters, A.; Drew, C.; Gabb, V.; Harding, S.; Hoyos, C.M.; et al. A systematic review on adherence to continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) treatment for obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) in individuals with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Sleep Med. Rev. 2024, 73, 101869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, K.C.; Lozano, A.J.; Morris, J.; Moelter, S.T.; Ji, W.; Vallabhaneni, V.; Wang, Y.; Chi, L.; Davis, E.M.; Cheng, C.; et al. Predictors of Adherence to Continuous Positive Airway Pressure in Older Adults With Apnea and Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2023, 78, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ke, S.; Luo, T.; Ding, Y.; Tang, C.-J.; Jie, Z.; Shen, J.Z.; Wu, D.; Du, Y. Does Obstructive sleep apnea mediate the risk of cognitive impairment by expanding the perivascular space? Sleep Breath. 2025, 29, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; Koundal, S.; Al Bizri, E.; Chen, X.; Gursky, Z.; Dai, F.; Lim, A.; Heerdt, P.; Kipnis, J.; Tannenbaum, A.; et al. Continuous positive airway pressure increases CSF flow and glymphatic transport. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e170270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C.G. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 479–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Weaver, T.E.; Grunstein, R.R. Adherence to continuous positive airway pressure therapy: The challenge to effective treatment. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Duff, K.; Suhrie, K.R.; Hammers, D.B.; Dixon, A.M.; King, J.B.; Koppelmans, V.; Hoffman, J.M. Repeatable battery for the assessment of neuropsychological status and its relationship to biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2023, 37, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, W.T.; Huang, H.T.; Hung, H.Y.; Lin, S.Y.; Hsu, W.H.; Lee, F.Y.; Kuan, Y.C.; Lin, Y.T.; Hsu, C.R.; Stettler, M.; et al. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Reduces Plasma Neurochemical Levels in Patients with OSA: A Pilot Study. Life 2023, 13, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grimmer, T.; Riemenschneider, M.; Förstl, H.; Henriksen, G.; Klunk, W.E.; Mathis, C.A.; Shiga, T.; Wester, H.J.; Kurz, A.; Drzezga, A. Beta amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease: Increased deposition in brain is reflected in reduced concentration in cerebrospinal fluid. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liguori, C.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Izzi, F.; Nuccetelli, M.; Bernardini, S.; Schillaci, O.; Mercuri, N.B.; Placidi, F. Sleep apnoeas may represent a reversible risk factor for amyloid-β pathology. Brain 2017, 140, e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, G.-H.; Gao, M.; Chen, N.-H.; Toh, C.H.; Hsu, J.-L.; Wu, K.-Y.; Huang, C.-M.; Lin, C.-M.; et al. Effects of sleep on the glymphatic functioning and multimodal human brain network affecting memory in older adults. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 30, 1717–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L.; Howard, M.E.; Barnes, M. Cognition and daytime functioning in sleep-related breathing disorders. Prog. Brain Res. 2011, 190, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, D.A.; Shin, K.J.; Park, K.M. Glymphatic system dysfunction in obstructive sleep apnea evidenced by DTI-ALPS. Sleep Med. 2022, 89, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamagata, K.; Andica, C.; Takabayashi, K.; Saito, Y.; Taoka, T.; Nozaki, H.; Kikuta, J.; Fujita, S.; Hagiwara, A.; Kamiya, K.; et al. Association of MRI Indices of Glymphatic System With Amyloid Deposition and Cognition in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer Disease. Neurology 2022, 99, e2648–e2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ren, L.; Wang, K.; Shen, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, R. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy on neurological and functional rehabilitation in Basal Ganglia Stroke patients with obstructive sleep apnea: A prospective multicenter study. Medicine 2019, 98, e16344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bubu, O.M.; Andrade, A.G.; Umasabor-Bubu, O.Q.; Hogan, M.M.; Turner, A.D.; de Leon, M.J.; Ogedegbe, G.; Ayappa, I.; Jean-Louis, G.G.; Jackson, M.L.; et al. Obstructive sleep apnea, cognition and Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review integrating three decades of multidisciplinary research. Sleep. Med. Rev. 2020, 50, 101250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Richards, K.C.; Gooneratne, N.; Dicicco, B.; Hanlon, A.; Moelter, S.; Onen, F.; Wang, Y.; Sawyer, A.; Weaver, T.; Lozano, A.; et al. CPAP adherence may slow 1-year cognitive decline in older adults with mild cognitive impairment and apnea. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2019, 67, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancoli-Israel, S.; Palmer, B.W.; Cooke, J.R.; Corey-Bloom, J.; Fiorentino, L.; Natarajan, L.; Liu, L.; Ayalon, L.; He, F.; Loredo, J.S. Cognitive effects of treating obstructive sleep apnea in Alzheimer’s disease: A randomized controlled study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, J.R.; Ayalon, L.; Palmer, B.W.; Loredo, J.S.; Corey-Bloom, J.; Natarajan, L.; Liu, L.; Ancoli-Israel, S. Sustained use of CPAP slows deterioration of cognition, sleep, and mood in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and obstructive sleep apnea: A preliminary study. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajoie, A.C.; Lafontaine, A.L.; Kimoff, R.J.; Kaminska, M. Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Neurodegenerative Disorders: Current Evidence in Support of Benefit from Sleep Apnea Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Djonlagic, I.; Guo, M.; Matteis, P.; Carusona, A.; Stickgold, R.; Malhotra, A. First night of CPAP: Impact on memory consolidation attention and subjective experience. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fernandes, M.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Manfredi, N.; Placidi, F.; Nuccetelli, M.; Izzi, F.; Camedda, R.; Bernardini, S.; Schillaci, O.; Mercuri, N.B.; et al. Nocturnal Hypoxia and Sleep Fragmentation May Drive Neurodegenerative Processes: The Compared Effects of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Periodic Limb Movement Disorder on Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 88, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, C.; Mercuri, N.B.; Izzi, F.; Romigi, A.; Cordella, A.; Sancesario, G.; Placidi, F. Obstructive Sleep Apnea is Associated With Early but Possibly Modifiable Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers Changes. Sleep 2017, 40, zsx011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, O.C.; van der Werf, Y.D. The Sleeping Brain: Harnessing the Power of the Glymphatic System through Lifestyle Choices. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Scullin, M.K.; Bliwise, D.L. Is cognitive aging associated with levels of REM sleep or slow wave sleep? Sleep 2015, 38, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Song, Y.; Blackwell, T.; Yaffe, K.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Redline, S.; Stone, K.L.; Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Study Group. Relationships between sleep stages and changes in cognitive function in older men: The MrOS Sleep Study. Sleep 2015, 38, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lo, J.C.; Groeger, J.A.; Cheng, G.H.; Dijk, D.J.; Chee, M.W. Self-reported sleep duration and cognitive performance in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2016, 17, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Dai, R.; Zhang, T. Associations Between Total Sleep Duration and Cognitive Function Among Middle-Aged and Older Chinese Adults: Does Midday Napping Have an Effect on It? Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nelson, K.L.; Davis, J.E.; Corbett, C.F. Sleep quality: An evolutionary concept analysis. Nurs. Forum 2022, 57, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barami, K. Cerebral venous overdrainage: An under-recognized complication of cerebrospinal fluid diversion. Neurosurg. Focus 2016, 41, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleadhill, I.C.; Schwartz, A.R.; Schubert, N.; Wise, R.A.; Permutt, S.; Smith, P.L. Upper airway collapsibility in snorers and in patients with obstructive hypopnea and apnea. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 143, 1300–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellman, A.; Genta, P.R.; Owens, R.L.; Edwards, B.A.; Sands, S.A.; Loring, S.H.; White, D.P.; Jackson, A.C.; Pedersen, O.F.; Butler, J.P. Test of the Starling resistor model in the human upper airway during sleep. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 117, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Vinitsky, H.S.; Sun, Q.; Stæger, F.F.; Sigurdsson, B.; Mortensen, K.N.; Lilius, T.O.; Nedergaard, M. Increased glymphatic influx is correlated with high EEG delta power and low heart rate in mice under anesthesia. Sci Adv. 2019, 5, eaav5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Penzel, T.; Möller, M.; Becker, H.F.; Knaack, L.; Peter, J.-H. Effect of Sleep Position and Sleep Stage on the Collapsibility of the Upper Airways in Patients with Sleep Apnea. Sleep 2001, 24, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, S.A.; Beatty, C.; Thomson, L.D.J.; Wong, A.M.; Edwards, B.A.; Hamilton, G.S.; Joosten, S.A. A review of supine position related obstructive sleep apnea: Classification, epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment. Sleep Med. Rev. 2023, 72, 101847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.D.; Chen, G.Y.; Lo, H.M. Effect of different recumbent positions on spectral indices of autonomic modulation of the heart during the acute phase of myocardial infarction. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.L.; Chen, G.Y.; Kuo, C.D. Comparison of effect of 5 recumbent positions on autonomic nervous modulation in patients with coronary artery disease. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Muppidi, S.; Gupta, P.K.; Vernino, S. Reversible right vagal neuropathy. Neurology 2011, 77, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cheng, K.P.; Brodnick, S.K.; Blanz, S.L.; Zeng, W.; Kegel, J.; Pisaniello, J.A.; Ness, J.P.; Ross, E.; Nicolai, E.N.; Settell, M.L.; et al. Clinically-derived vagus nerve stimulation enhances cerebrospinal fluid penetrance. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.J.; Lee, H.P.; Kim, M.S.; Park, Y.J.; Go, H.J.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, S.P.; Chae, J.H.; Lee, C.T. The effect of total sleep deprivation on cognitive functions in normal adult male subjects. Int. J. Neurosci. 2001, 109, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilcher, J.J.; McClelland, L.E.; DeWayne, D.; Henk, M.; Jaclyn, H.; Thomas, B.; Wallsten, S.; McCubbin, J.A. Language performance under sustained work and sleep deprivation conditions. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2007, 78, B25–B38. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, R.; Alderman, E.; Javadi, A.H.; Tamminen, J. A systematic and meta-analytic review of the impact of sleep restriction on memory formation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 167, 105929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, E.C.; Fang, E.; Gooley, J.J. Effects of total sleep deprivation on divided attention performance. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nedergaard, M.; Goldman, S.A. Glymphatic failure as a final common pathway to dementia. Science 2020, 370, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Menon, R.N.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Sreedharan, S.E.; Sarma, P.S.; Kumari, R.S.; Kesavadas, C.; Sasi, D.; Lekha, V.S.; Justus, S.; Unnikrishnan, J.P. Do quantified sleep architecture abnormalities underlie cognitive disturbances in amnestic mild cognitive impairment? J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 67, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Features | Non-CPAP (n = 9) | CPAP (n = 12) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yrs | 79 (72–81) | 74 (60–78) | 0.010 |
| Sex | 1.000 | ||
| Females | 6 (66.67%) | 9 (75.00%) | |
| Males | 3 (33.33%) | 3 (25.00%) | |
| Education, yrs | 12 (5–18) | 9 (2–20) | 0.327 |
| Neurocognitive Test/Assessment | Score T0 (Baseline) (Mean ± SD) | Score T1 (12 Months) (Mean ± SD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDR | 0.64 ± 0.36 | 0.71 ± 0.37 | 0.223 |
| MMSE | 22.67 ± 5.35 | 20.71 ± 5.51 | <0.001 |
| RBANS Total | 66.24 ± 14.77 | 64.24 ± 15.48 | <0.001 |
| RBANS IMI | 65.05 ± 15.50 | 61.29 ± 15.25 | <0.001 |
| RBANS LL | 17.90 ± 5.51 | 16.50 ± 6.07 | <0.001 |
| RBANS SM | 7.24 ± 4.33 | 6.33 ± 4.82 | 0.001 |
| RBANS VSPI | 85.89 ± 19.38 | 87.95 ± 17.08 | 0.056 |
| RBANS FC | 16.65 ± 2.66 | 17.10 ± 1.92 | 0.365 |
| RBANS LO | 13.00 ± 4.24 | 13.05 ± 4.05 | 0.031 |
| RBANS LNGI | 74.21 ± 19.12 | 77.68 ± 16.45 | <0.001 |
| RBANS PN | 7.84 ± 2.14 | 8.58 ± 1.71 | 0.016 |
| RBANS SF | 11.71 ± 5.58 | 11.38 ± 5.16 | <0.001 |
| RBANS ATI | 69.42 ± 18.14 | 69.11 ± 18.59 | <0.001 |
| RBANS DDS | 4.86 ± 1.28 | 4.48 ± 1.33 | 0.005 |
| RBANS IDS | 2.82 ± 2.83 | 4.47 ± 1.55 | 0.768 |
| RBANS C | 21.00 ± 14.15 | 20.00 ± 14.86 | <0.001 |
| RBANS DMI | 64.75 ± 19.35 | 57.30 ± 19.49 | 0.003 |
| RBANS LR | 1.10 ± 1.67 | 1.33 ± 2.20 | 0.003 |
| RBANS LRe | 14.90 ± 4.38 | 14.50 ± 2.70 | 0.349 |
| RBANS SR | 2.57 ± 2.77 | 1.86 ± 2.41 | 0.002 |
| RBANS FR | 5.86 ± 5.08 | 5.48 ± 5.71 | 0.003 |
| Neuropsychological Test/Assessment | Non-CPAP (n = 9) | CPAP (n = 12) | p-Value | Confidence Interval (95%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 (12 Months)–T0 (Baseline) (Mean ± SD) | T1 (12 Months)–T0 (Baseline) (Mean ± SD) | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||
| CDR | 0.06 ± 0.17 | 0.08 ± 0.19 | 0.838 | −0.214 | 0.173 |
| MMSE | −3.78 ± 2.54 | −0.58 ± 3.42 | 0.016 | 1.071 | 6.967 |
| RBANS Total | −6.38 ± 7.73 | 1.89 ± 9.09 | 0.028 | 2.320 | 20.104 |
| RBANS IMI | −4.78 ± 9.96 | −3.00 ± 14.52 | 0.229 | −4.153 | 18.659 |
| RBANS LL | −2.56 ± 4.10 | −0.45 ± 4.91 | 0.589 | 0.160 | 8.700 |
| RBANS SM | −0.78 ± 2.91 | −1.00 ± 4.59 | 0.495 | −2.480 | 5.217 |
| RBANS VSPI | −6.11 ± 14.83 | 9.40 ± 20.59 | 0.119 | −2.529 | 29.632 |
| RBANS FC | −1.11 ± 2.09 | 1.73 ± 2.97 | 0.010 | 0.820 | 4.275 |
| RBANS LO | −0.33 ± 2.74 | 0.40 ± 4.81 | 0.988 | −3.812 | 3.756 |
| RBANS LNGI | 2.44 ± 12.27 | 4.40 ± 15.68 | 0.177 | −3.563 | 22.073 |
| RBANS PN | 0.67 ± 1.41 | 0.80 ± 1.99 | 0.643 | −1.129 | 1.846 |
| RBANS SF | −1.67 ± 2.69 | 0.67 ± 4.10 | 0.045 | 0.348 | 7.167 |
| RBANS ATI | −1.38 ± 6.80 | 0.45 ± 8.49 | 0.834 | −8.081 | 10.044 |
| RBANS DDS | −0.33 ± 0.87 | −0.42 ± 0.79 | 0.961 | −0.893 | 0.849 |
| RBANS IDS | 2.00 ± 3.16 | 1.33 ± 4.27 | 0.151 | −2.719 | 0.338 |
| RBANS C | −3.38 ± 6.07 | 0.73 ± 6.31 | 0.135 | −1.379 | 12.846 |
| RBANS DMI | −18.00 ± 13.87 | 1.18 ± 15.52 | 0.064 | 0.167 | 27.458 |
| RBANS LR | −0.44 ± 0.88 | 0.75 ± 2.18 | 0.326 | −0.658 | 0.304 |
| RBANS LRe | −2.67 ± 3.43 | 1.45 ± 4.95 | 0.145 | −0.584 | 4.757 |
| RBANS SR | −0.78 ± 1.09 | −0.67 ± 1.87 | 0.211 | −0.466 | 2.298 |
| RBANS FR | −0.67 ± 4.09 | −0.17 ± 4.93 | 0.802 | −3.980 | 5.165 |
| Sleep Stages | Sleep Quality | Sleep Position | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | N3 | REM | TST | SE | W | ST | RST | ||
| Δ MMSE | p-value | 0.038 | 0.022 | 0.879 | 0.856 | 0.673 | 0.655 | 0.023 | 0.011 |
| r | −0.41 | 0.51 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.01 | −0.02 | −0.44 | 0.56 | |
| Δ RBANS Total | p-value | 0.415 | 0.299 | 0.766 | 0.055 | 0.090 | 0.094 | 0.549 | 0.076 |
| r | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.35 | 0.29 | −0.29 | −0.10 | 0.35 | |
| Δ RBANS IMI | p-value | 0.106 | 0.977 | 0.044 | 0.014 | 0.038 | 0.048 | 0.420 | 0.966 |
| r | 0.32 | −0.17 | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.29 | −0.27 | 0.25 | −0.12 | |
| Δ RBANS LL | p-value | 0.393 | 0.628 | 0.015 | 0.024 | 0.036 | 0.041 | 0.705 | 0.866 |
| r | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.40 | 0.36 | −0.35 | 0.12 | −0.02 | |
| Δ RBANS SM | p-value | 0.106 | 0.865 | 0.294 | 0.038 | 0.118 | 0.148 | 0.329 | 0.877 |
| r | 0.35 | −0.17 | 0.20 | 0.39 | 0.26 | −0.23 | 0.28 | −0.07 | |
| Δ RBANS LO | p-value | 0.928 | 0.249 | 0.985 | 0.214 | 0.294 | 0.360 | 0.041 | 0.002 |
| r | −0.08 | 0.28 | −0.13 | 0.10 | 0.07 | −0.06 | −0.43 | 0.54 | |
| Δ RBANS LNGI | p-value | 0.280 | 0.509 | 0.682 | 0.098 | 0.183 | 0.194 | 0.579 | 0.679 |
| r | 0.42 | −0.04 | −0.27 | 0.31 | 0.27 | −0.26 | 0.26 | −0.03 | |
| Δ RBANS PN | p-value | 0.216 | 0.683 | 0.893 | 0.235 | 0.379 | 0.390 | 0.153 | 0.410 |
| r | 0.49 | −0.32 | −0.19 | 0.25 | 0.21 | −0.21 | 0.46 | −0.30 | |
| Δ RBANS SF | p-value | 0.191 | 0.281 | 0.266 | 0.032 | 0.018 | 0.016 | 0.882 | 0.656 |
| r | 0.37 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.39 | −0.41 | 0.12 | −0.02 | |
| Δ RBANS ATI | p-value | 0.291 | 0.625 | 0.955 | 0.278 | 0.456 | 0.465 | 0.855 | 0.615 |
| r | 0.24 | 0.13 | −0.02 | 0.22 | 0.15 | −0.14 | −0.04 | 0.10 | |
| Δ RBANS DDS | p-value | 0.178 | 0.154 | 0.781 | 0.242 | 0.328 | 0.344 | 0.014 | 0.058 |
| r | −0.33 | 0.36 | −0.12 | −0.30 | −0.25 | 0.24 | −0.53 | 0.39 | |
| Δ RBANS C | p-value | 0.064 | 0.348 | 0.993 | 0.020 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.445 | 0.937 |
| r | 0.42 | 0.21 | −0.02 | 0.47 | 0.49 | −0.50 | 0.19 | −0.03 | |
| Δ RBANS DMI | p-value | 0.227 | 0.536 | 0.759 | 0.427 | 0.317 | 0.300 | 0.632 | 0.639 |
| r | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.29 | −0.31 | −0.04 | 0.04 | |
| Δ RBANS LR | p-value | 0.196 | 0.515 | 0.769 | 0.191 | 0.121 | 0.109 | 0.084 | 0.271 |
| r | 0.32 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.35 | −0.36 | 0.43 | −0.30 | |
| Δ RBANS SR | p-value | 0.181 | 0.360 | 0.079 | 0.019 | 0.055 | 0.073 | 0.776 | 0.216 |
| r | 0.40 | −0.10 | 0.45 | 0.51 | 0.40 | −0.37 | 0.24 | 0.05 | |
| Δ RBANS FR | p-value | 0.328 | 0.035 | 0.473 | 0.549 | 0.253 | 0.196 | 0.273 | 0.207 |
| r | 0.25 | 0.46 | −0.11 | 0.13 | 0.25 | −0.28 | −0.24 | 0.30 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frias, C.L.; Almeria, M.; Castejon, J.; Artero, C.; Caruana, G.; Elias-Mas, A.; Uscamaita, K.; Hawkins, V.; Ray, N.J.; Buongiorno, M.; et al. A Pilot Study: The Effect of CPAP Intervention on Sleep Architecture and Cognition in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Neurol. Int. 2025, 17, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17090147
Frias CL, Almeria M, Castejon J, Artero C, Caruana G, Elias-Mas A, Uscamaita K, Hawkins V, Ray NJ, Buongiorno M, et al. A Pilot Study: The Effect of CPAP Intervention on Sleep Architecture and Cognition in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Neurology International. 2025; 17(9):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17090147
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrias, Carmen L., Marta Almeria, Judith Castejon, Cristina Artero, Giovanni Caruana, Andrea Elias-Mas, Karol Uscamaita, Virginia Hawkins, Nicola J. Ray, Mariateresa Buongiorno, and et al. 2025. "A Pilot Study: The Effect of CPAP Intervention on Sleep Architecture and Cognition in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea" Neurology International 17, no. 9: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17090147
APA StyleFrias, C. L., Almeria, M., Castejon, J., Artero, C., Caruana, G., Elias-Mas, A., Uscamaita, K., Hawkins, V., Ray, N. J., Buongiorno, M., Cullell, N., & Krupinski, J. (2025). A Pilot Study: The Effect of CPAP Intervention on Sleep Architecture and Cognition in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Neurology International, 17(9), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint17090147









