Froin’s Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature and the Addition of Two New Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
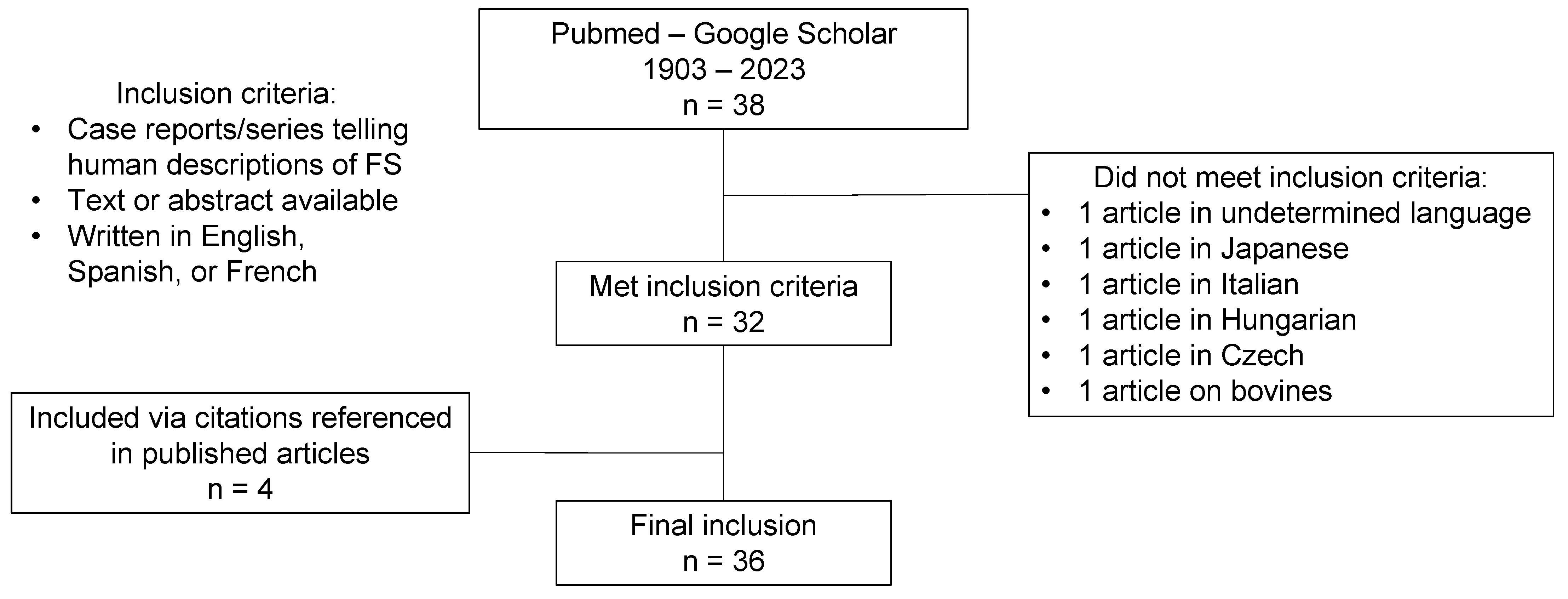
2. Materials and Methods
3. Two New Clinical Cases
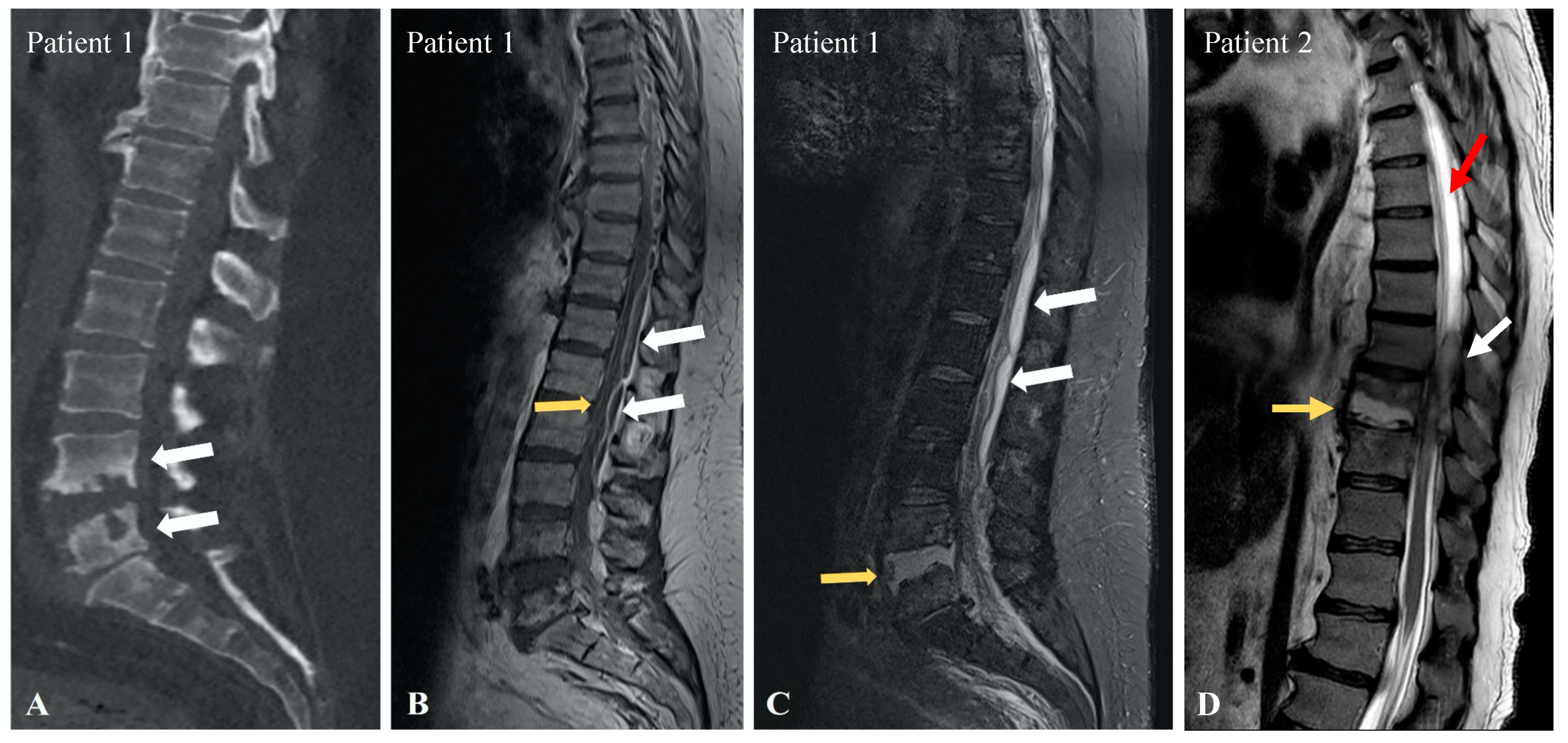
3.1. Patient 1
3.2. Patient 2
4. Discussion
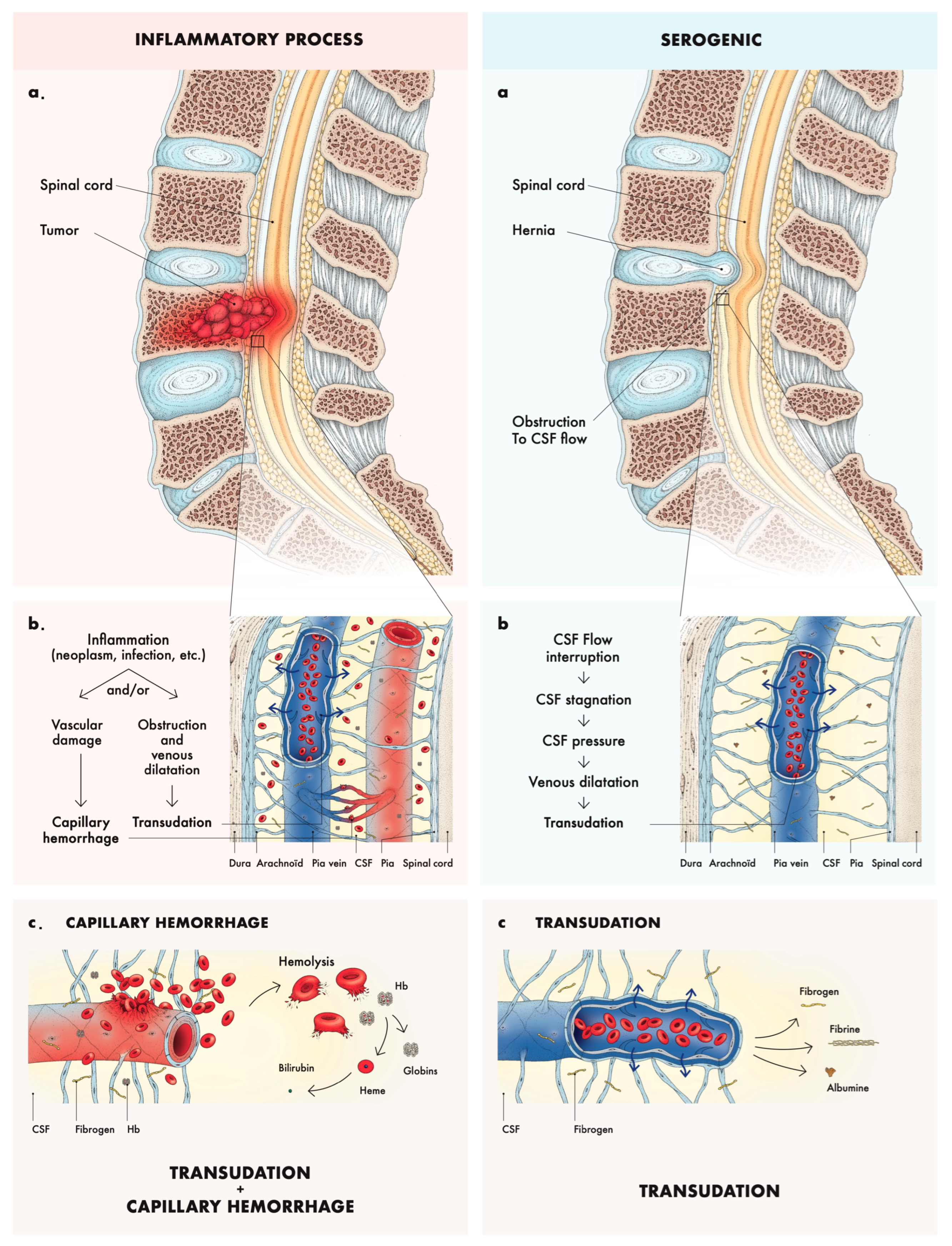
4.1. Pathophysiology and Etiologies
4.2. Clinical Features
4.3. Workup
4.4. Outcomes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Froin, G. Inflammations méningées avec réactions chromatique, fibrineuse et cytologique du liquide céphalo-rachidien. Gaz. Hôp. 1903, 76, 1005–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield, J.G. Original Papers: On Froin’s syndrome, and its relation to allied conditions in the cerebrispinal fluid. J. Neurol. Psychopathol. 1921, 2, 105–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olukoga, A.O.; Bolodeoku, J.; Donaldson, D. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis in clinical diagnosis. J. Clin. Pathol. 1997, 50, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millian, G.; Chiray, F. Méningite à pneumocoques. Xanthochromie du liquide céphalo-rachidien. Bull. Soc. Anat. Paris 1902, 4, 550–552. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, F.; Miller, B. On differentiation of coloured cerebrospinal fluids. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1936, 191, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, F.J. Yellow spinal fluid its origin and significance. Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1923, 10, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.H. Fluid dynamics of cerebrospinal fluid flow in perivascular spaces. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B. Cerebrospinal fluid pressure changes in response to coughing. Brain A J. Neurol. 1976, 99, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohee, K.; Sekar, V.; Williams, S.; Goulding, P. An unusual cause of raised CSF protein. Pract. Neurol. 2013, 13, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garispe, A.; Naji, H.; Dong, F.; Arabian, S.; Neeki, M. Froin’s Syndrome Secondary to Traumatic and Infectious Etiology. Cureus 2019, 11, e6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Owji, S.C.; Pakravan, M.; Charoenkijkajorn, C.; Lee, A.G. Papilledema from Froin Syndrome due to a Myxopapillary Ependymoma. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2023, 43, e161–e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, S.; Adams, W.M.; Corkhill, R.A. Froin’s syndrome revisited, 100 years on. Pseudo-Froin’s syndrome on MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2008, 63, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomfield, I.G.; Johnston, I.H.; Bilston, L.E. Effects of proteins, blood cells and glucose on the viscosity of cerebrospinal fluid. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1998, 28, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, N.; Montelius, R.; Holtz, A.; Mouwitz, L.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Coagulation of cerebrospinal fluid--the Nonne-Froin sign. Pract. Neurol. 2013, 13, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, A.; Sivakumar, K.; Yacoub, H. Froin Syndrome, a Rare Complication of Multiple Myeloma. Neurologist 2021, 26, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, A.T.; Fricker, G.P.; Crook, T.W. A Case of a 4-Year-Old Female with a Primary Spinal Malignancy Presenting with Froin’s Syndrome. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2018, 53, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dancel, R.; Shaban, M. Images in clinical medicine. Froin’s syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, I.; Temel, M.; Kokoglu, S.; Boyraz, O.; Karadas, O.; Odabasi, Z. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis presenting with acute motor axonal neuropathy. Indian. J. Cancer 2022, 59, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saga, T.; Ishihara, T.; Kanagawa, M. Meningeal infiltration of malignant lymphoma presenting with Froin’s syndrome. Rinsho Ketsueki 2017, 58, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Noake, J.R.; Shepherd, A.; Smith, W.R. Melanomatous Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis masquerading as Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Acute Med. 2010, 9, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljevak, J.; Poljaković, Z.; Adamec, I.; Habek, M. Glioblastoma multiforme presenting as Froin’s syndrome: A new face of an old foe. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2014, 114, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, S.; Kotani, A.; Takimoto, T.; Yoshino, A.; Katayama, Y. Acute aggravation of subdural fluid collection associated with dural metastasis of malignant neoplasms: Case report and review of the literature. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2014, 31, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koton, Y.; Bisharat, N. Nonne-Froin sign. QJM 2017, 110, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fries, F.L.; Kleiser, B.; Schwarz, P.; Tieck, M.P.; Laichinger, K.; Mengel, A.; Ziemann, U.; Kowarik, M.C. Diagnosis of Froin’s Syndrome by Parallel Analysis of Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt and Lumbar Cerebrospinal Fluid in a Patient with Cervical Spinal Stenosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-K.; Kim, M.-W. Pseudo-Froin’s syndrome, xanthochromia with high protein level of cerebrospinal fluid. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2014, 67, S58–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carteyron, A.S.; Saint-Lézer, A.; Damoo, B.; Ondzé, B. Froin’s syndrome dissemination from temporal horn entrapment after stereotactic needle biopsy. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 176, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decramer, T.; Wouters, A.; Kiekens, C.; Theys, T. Froin Syndrome After Spinal Cord Injury. World Neurosurg. 2019, 127, 490–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.A.; Doppman, J.L.; Patronas, N.J.; Nieman, L.K.; Chrousos, G.P. Do Glucocorticoids Cause Spinal Epidural Lipomatosis? When Endocrinology and Spinal Surgery Meet. Trends Endocrinol. Metabolism. 2000, 11, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotmongkol, V.; Wanitpongpun, C.; Phuttharak, W.; Khamsai, S. Intramedullary Conus Medullaris Tuberculoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2021, 13, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, K.; Adhikari, S.; Basnyat, B. Froin’s syndrome associated with spinal tuberculosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 11, e228367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantese, C.E.; Lubini, R. Froin’s syndrome with tuberculosis myelitis and spinal block. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2022, 68, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindarajan, R.; Khan, T. Froin’s syndrome: An uncommon mimicker of Guillain-Barre syndrome. Eur. Spine J. 2012, 21, 1674–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Moscote-Salazar, L.R.; Joaquim, A.F.; Alcala-Cerra, G.; Agrawal, A.; Calderon-Miranda, W.G. Froin’s Syndrome Mimicking Guillain-Barre Syndrome in a Patient with Spinal Epidural Abscess. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2019, 14, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaldo, M.P.A.; Garcia, D.V.; Arrabal, E.G. Froin’s syndrome secondary to epidural abscess. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2022, 35, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K.; Mahalingam, R.; Shimek, C.; Marcoux, H.L.; Wellish, M.; Tyler, K.L.; Gilden, D. Profound cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis and Froin’s Syndrome secondary to widespread necrotizing vasculitis in an HIV-positive patient with varicella zoster virus encephalomyelitis. J. Neurol. Sci. 1998, 159, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, P.; Hall, J.P.; Jhaveri, M.; Dafer, R.M. Cerebral Vasculopathy and Spinal Arachnoiditis: Two Rare Complications of Ventriculitis Post Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Cureus 2020, 12, e12241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiersma, D. A remarkable case of pachymeningitis hypertrophica presenting spinal block and Froin’s syndrome. J. Neurol. Psychopathol. 1928, 8, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morren, J.; Salgado, E. Not an Ordinary Dry Spinal Tap: Froin’s Syndrome in an Unusual Case of Neurosarcoidosis (P05.207). Neurology 2013, 80, P05.207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokahmetoglu, G.; Aksu, R.; Biçer, C.; Bayram, A. Incidental Finding of Froin Syndrome during Spinal Anesthesia in a 72-Year-Old Patient. J. Pain Relief 2014, 3, 158. Available online: https://avesis.erciyes.edu.tr/yayin/1a2e9f66-a630-4a99-baf3-73f2c2820978/incidental-finding-of-froin-syndrome-during-spinal-anesthesia-in-a-72-year-oldpatient (accessed on 6 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Laviv, Y.; Kasper, B.S.; Kasper, E.M. Vascular hyperpermeability as a hallmark of phacomatoses: Is the etiology angiogenesis comparable with mechanisms seen in inflammatory pathways? Part I: Historical observations and clinical perspectives on the etiology of increased CSF protein levels, CSF clotting, and communicating hydrocephalus: A comprehensive review. Neurosurg. Rev. 2018, 41, 957–968. [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhammer, F.; Bartos, A.; Egg, R.; Gilhus, N.E.; Giovannoni, G.; Rauer, S.; Sellebjerg, F. Guidelines on routine cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Report from an EFNS task force. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luoma, K.; Raininko, R.; Nummi, P.; Luukkonen, R. Is the signal intensity of cerebrospinal fluid constant? Intensity measurements with high and low field magnetic resonance imagers. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1993, 11, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conly, J.M.; Ronald, A.R. Cerebrospinal fluid as a diagnostic body fluid. Am. J. Med. 1983, 75, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Causes of Froin’s Syndrome | References |
|---|---|
| Neoplasia (33%) | |
| Spinal ependymoma | [11,12,14] |
| Multiple myeloma | [15] |
| Primary central nervous system tumors | [16,17,18] |
| Leptomeningeal involvement in hematological malignancy | [19] |
| Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in malignant melanoma | [20] |
| Glioblastoma | [21] |
| Solid tumors metastasis | [22,23] |
| Mechanic (27%) | |
| Degenerative stenosis | [12,24] |
| Herniation | [12] |
| Trauma | [10,25] |
| Iatrogenic (post cerebral stereotactic needle biopsy) | [26] |
| Spinal cord injury | [27] |
| Spinal epidural lipomatosis | [28] |
| Dermoid tumor | [12] |
| Infectious (27%) | |
| Tuberculosis meningitis, Pott disease, tuberculoma of the conus medullaris | [29,30,31] |
| Bacterial abscess | [32,33,34] |
| Varicella-zoster virus encephalitis | [10,35] |
| Vascular (6.5%) | |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage | [36] |
| Necrotizing vasculitis | [35] |
| Inflammatory (6.5%) | |
| Hypertrophic pachymeningitis | [37] |
| Neurosarcoïdosis | [38] |
| Symptoms of Froin’s Syndrome | Number of Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Paralysis/Paresis | 22 (64) |
| Back pain | 13 (38) |
| Confusion/Altered mental state | 8 (23) |
| Leg pain/Sciatica | 6 (17) |
| Headache | 6 (17) |
| Hypoesthesia/Anesthesia | 6 (17) |
| Urinary retention/Incontinence | 5 (14) |
| Visual loss | 1 (3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jacobs, L.; Delsaut, B.; Lamartine S. Monteiro, M.; Cambier, A.; Alcan, I.; Maillart, E.; Taghavi, M. Froin’s Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature and the Addition of Two New Cases. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 1112-1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050083
Jacobs L, Delsaut B, Lamartine S. Monteiro M, Cambier A, Alcan I, Maillart E, Taghavi M. Froin’s Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature and the Addition of Two New Cases. Neurology International. 2024; 16(5):1112-1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050083
Chicago/Turabian StyleJacobs, Lucas, Bertil Delsaut, Marta Lamartine S. Monteiro, Audrey Cambier, Ibrahim Alcan, Evelyne Maillart, and Maxime Taghavi. 2024. "Froin’s Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature and the Addition of Two New Cases" Neurology International 16, no. 5: 1112-1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050083
APA StyleJacobs, L., Delsaut, B., Lamartine S. Monteiro, M., Cambier, A., Alcan, I., Maillart, E., & Taghavi, M. (2024). Froin’s Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature and the Addition of Two New Cases. Neurology International, 16(5), 1112-1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16050083






