Efficacy and Safety of Rescue Treatment with Plasma Exchange in Patients with Acute Inflammatory Neurological Disorders: A Single Center Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Objective
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Subjects
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Plasma Exchange
2.6. Defining Effectiveness
2.7. Defining Adverse Events
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Features
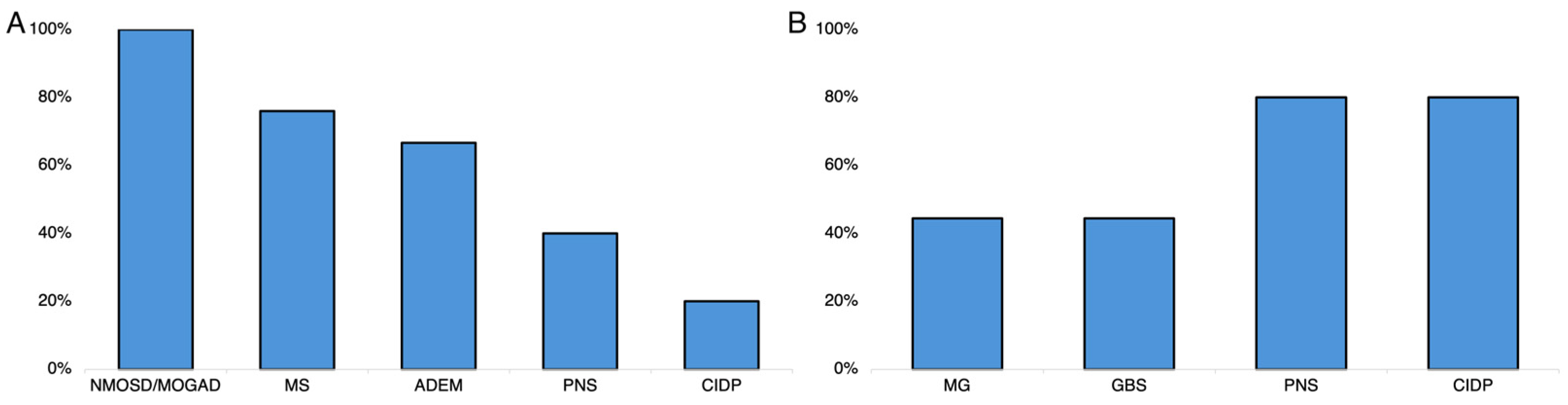
3.2. Effectiveness Analyses
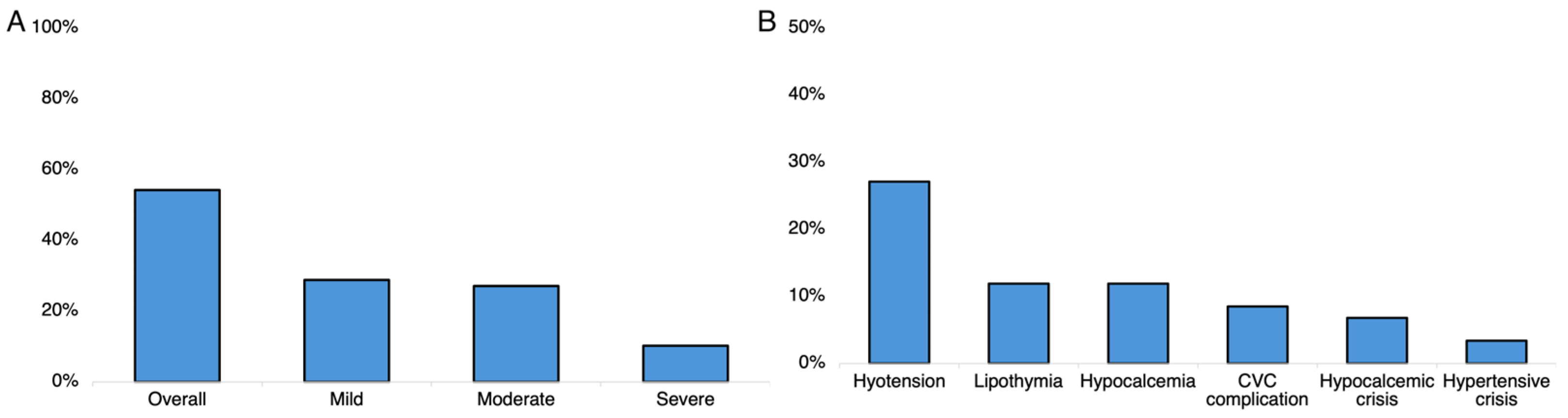
3.3. Safety Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. TPE in MS
4.2. TPE in NMOSD/MOGAD and ADEM
4.3. TPE in MG
4.4. TPE in Acquired Polyneuropathies
4.5. TPE in Stiff Person Syndrome
4.6. Predictors of TPE Effectiveness
4.7. TPE before Obtaining a Definite Diagnosis
4.8. TPE Safety
4.9. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacob, S.; Mazibrada, G.; Irani, S.R.; Jacob, A.; Yudina, A. The Role of Plasma Exchange in the Treatment of Refractory Autoimmune Neurological Diseases: A Narrative Review. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021, 16, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecher, M.E. Plasma exchange: Why we do what we do. J. Clin. Apher. 2002, 17, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, H.C.; Hartung, H.P.; Hetzel, G.R.; Stüve, O.; Kieseier, B.C. Plasma exchange in neuroimmunological disorders: Part 1: Rationale and treatment of inflammatory central nervous system disorders. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, H.C.; Hartung, H.P.; Hetzel, G.R.; Stüve, O.; Kieseier, B.C. Plasma exchange in neuroimmunological disorders: Part 2. Treatment of neuromuscular disorders. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, I.; Chaudhry, V.; So, Y.T.; Cantor, F.; Cornblath, D.R.; Rae-Grant, A. Evidence-based guideline update: Plasmapheresis in neurologic disorders: Report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2011, 76, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly-Smith, L.; Alquist, C.R.; Aqui, N.A.; Hofmann, J.C.; Klingel, R.; Onwuemene, O.A.; Patriquin, C.J.; Pham, H.P.; Sanchez, A.P.; Schneiderman, J.; et al. Guidelines on the Use of Therapeutic Apheresis in Clinical Practice—Evidence-Based Approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: The Ninth Special Issue. J. Clin. Apher. 2023, 38, 77–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.A.C. Randomised trial of plasma exchange, intravenous immunoglobulin, and combined treatments in Guillain-Barre syndrome. Lancet 1997, 349, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, A.A.; De Seze, J.; Jacob, A.; Reddel, S.; Yudina, A.; Tan, K. Comparison of IVIg and TPE efficacy in the treatment of neurological disorders: A systematic literature review. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2023, 16, 17562864231154306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stoian, A.; Șerban, G.; Bajko, Z.; Andone, S.; Mosora, O.; Bălașa, A. Therapeutic plasma exchange as a first-choice therapy for axonal Guillain-Barré syndrome: A case-based review of the literature (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van der Meché, F.; Schmitz, P.; Dutch Guillain–Barré Study Group. A Randomized Trial Comparing Intravenous Immune Globulin and Plasma Exchange in Guillain–Barré Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, H.-C.; Haupt, W.F.; Kloss, T.M.; Rosenow, F.; Philipp, T.; Koeppen, S.; Vietorisz, A. A Preliminary, Randomized, Multicenter Study Comparing Intravenous Immunoglobulin, Plasma Exchange, and Immune Adsorption in Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Eur. Neurol. 2001, 46, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Gao, Q.; Xiao, K.; Tian, D.; Hu, W.; Han, Z. Efficacy of therapies in the treatment of Guillain-Barre syndrome: A network meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, E27351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandawat, A.; Kaminski, H.J.; Cutter, G.; Katirji, B.; Alshekhlee, A. Comparative analysis of therapeutic options used for myasthenia gravis. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, D.; Nabavi Nouri, M.; Ng, E.; Nwe, P.; Bril, V. Comparison of IVIg and TPE in patients with myasthenia gravis. Neurology 2011, 76, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Chauhan, V.D.; Mills, D.; Johal, N.J.; Tan, M.; Matthews, R.; Keh, R.; Lilleker, J.B.; Gosal, D.; Sharaf, N. Therapeutic plasma exchange in neurological disorders: Experience from a tertiary neuroscience centre. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2019, 58, 102654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabally, Y.A. Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy: Current Therapeutic Approaches and Future Outlooks. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2024, 13, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Cabre, P.; Carroll, W.; Chitnis, T.; De Seze, J.; Fujihara, K.; Greenberg, B.; Jacob, A.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. Neurology 2015, 85, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Banwell, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Marignier, R.; Kim, H.J.; Brilot, F.; Flanagan, E.P.; Ramanathan, S.; Waters, P.; Tenembaum, S.; Graves, J.S.; et al. Diagnosis of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease: International MOGAD Panel proposed criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, D.B.; Wolfe, G.I.; Benatar, M.; Evoli, A.; Gilhus, N.E.; Illa, I.; Kuntz, N.; Massey, J.M.; Melms, A.; Murai, H.; et al. International consensus guidance for management of myasthenia gravis: Executive summary. Neurology 2016, 87, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Asbury, A.K.; Cornblath, D.R. Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 27, S21–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society—First Revision. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2010, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ill, A.B. The environment and disease: Association or causation? Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1965, 58, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Graus, F.; Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Antoine, J.G.; Desestret, V.; Dubey, D.; Giometto, B.; Irani, S.R.; Joubert, B.; Leypoldt, F.; et al. Updated Diagnostic Criteria for Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chia, N.H.; McKeon, A.; Dalakas, M.C.; Flanagan, E.P.; Bower, J.H.; Klassen, B.T.; Dubey, D.; Zalewski, N.L.; Duffy, D.; Pittock, S.J.; et al. Stiff person spectrum disorder diagnosis, misdiagnosis, and suggested diagnostic criteria. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2023, 10, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Broderick, J.P.; Adeoye, O.; Elm, J. Evolution of the Modified Rankin Scale and Its Use in Future Stroke Trials. Stroke 2017, 48, 2007–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muppidi, S.; Wolfe, G.I.; Conaway, M.; Burns, T.M. MG-ADL: Still a relevant outcome measure. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983, 33, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleyweg, R.P.; Van Der Meché, F.G.A.; Schmitz, P.I.M. Interobserver agreement in the assessment of muscle strength and functional abilities in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Muscle Nerve 1991, 14, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, G.; Waller, J.L.; Voeks, J.H.; Howard, V.J.; Jauch, E.C.; Lees, K.R.; Nichols, F.T.; Rahlfs, V.W.; Hess, D.C. A Simple, Assumption-Free, and Clinically Interpretable Approach for Analysis of Modified Rankin Outcomes. Stroke 2012, 43, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggi, A.; Antozzi, C.; Baggi, F.; Leonardi, M.; Maggi, L.; Mantegazza, R. Validity, reliability, and sensitivity to change of the myasthenia gravis activities of daily living profile in a sample of Italian myasthenic patients. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1927–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, G.; Herbelin, L.; Nations, S.; Foster, B.; Bryan, W.; Barohn, R. Myasthenia gravis activities of daily living profile. Neurology 1999, 52, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0. 2017. Available online: https://www.meddra.org/ (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Brusaferri, F.; Candelise, L. Steroids for multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. J. Neurol. 2000, 247, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebst, C.; Reising, A.; Kielstein, J.T.; Hafer, C.; Stangel, M. Plasma Exchange Therapy in Steroid-Unresponsive Relapses in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Blood Purif. 2009, 28, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blechinger, S.; Ehler, J.; Bsteh, G.; Winkelmann, A.; Leutmezer, F.; Meister, S.; Santer, A.; Hecker, M.; Berger, T.; Rommer, P.; et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange in steroid-refractory multiple sclerosis relapses. A retrospective two-center study. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2021, 14, 1756286420975642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, M.; König, F.; McClelland, R.; Brück, W.; Morales, Y.; Bitsch, A.; Panitch, H.; Lassmann, H.; Weinshenker, B.; Rodriguez, M.; et al. Relation between humoral pathological changes in multiple sclerosis and response to therapeutic plasma exchange. Lancet 2005, 366, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiter, I.; Gahlen, A.; Borisow, N.; Fischer, K.; Wernecke, K.; Wegner, B.; Hellwig, K.; Pache, F.; Ruprecht, K.; Havla, J.; et al. Neuromyelitis optica: Evaluation of 871 attacks and 1153 treatment courses. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnan, M.; Valentino, R.; Debeugny, S.; Merle, H.; Fergé, J.-L.; Mehdaoui, H.; Cabre, P. Short delay to initiate plasma exchange is the strongest predictor of outcome in severe attacks of NMO spectrum disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, C. Evidence-based guideline update: Plasmapheresis in neurologic disorders. Neurology 2011, 77, 294–300. [Google Scholar]
- Rødgaard, A.; Nielsen, F.C.; Djurup, R.; Somnier, F.; Gammeltoft, S. Acetylcholine receptor antibody in myasthenia gravis: Predominance of IgG subclasses 1 and 3. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1987, 67, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Foettinger, F.; Pilz, G.; Wipfler, P.; Harrer, A.; Kern, J.M.; Trinka, E.; Moser, T. Immunomodulatory Aspects of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in Neurological Disorders—A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehndiratta, M.M.; Hughes, R.A.; Pritchard, J. Plasma exchange for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2017, CD003906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doorn, P.A.; Ruts, L.; Jacobs, B.C. Clinical features, pathogenesis, and treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevret, S.; Hughes, R.A.; Annane, D. Plasma exchange for Guillain-Barré syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2017, CD001798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codron, P.; Cousin, M.; Subra, J.; Pautot, V.; Letournel, F.; Verny, C.; Cassereau, J. Therapeutic plasma exchange in chronic dysimmune peripheral neuropathies: A 10-year retrospective study. J. Clin. Apher. 2017, 32, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.L.; Darnell, J.C.; Bender, A.; Francisco, L.M.; Bhardwaj, N.; Darnell, R.B. Tumor-specific killer cells in paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1321–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahra, S.; Yates, S.G.; Joseph, D.; De Simone, N.; Burner, J.D.; Sarode, R. Role of plasma exchange in stiff person syndrome. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2019, 58, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnan, M.; Cabre, P. Plasma Exchange in Severe Attacks of Neuromyelitis Optica. Mult. Scler. Int. 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, T.; Inoue, S.; Takagi, Y.; Shimomura, T.; Sagami, Y.; Katayama, S.; Eguchi, Y.; Watase, K.; Miyamoto, M.; Minakata, T. Adverse Events in Therapeutic Apheresis: A Single Center Survey of Various Therapies. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2010, 14, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malchesky, P.S.; Koo, A.P.; Skibinski, C.I.; Hadsell, A.T.; Rybicki, L.A. Apheresis Technologies and Clinical Applications: The 2007 International Apheresis Registry. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2010, 14, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingele, M.; Allmendinger, C.; Thieme, S.; Baerens, L.; Fliser, D.; Jan, B. Therapeutic apheresis within immune-mediated neurological disorders: Dosing and its effectiveness. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| TPE Indication | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Definite diagnosis | 45 (76.3) |
| MS attack | 20 (44.4) |
| MG crisis | 9 (20) |
| GBS | 9 (20) |
| CIDP | 3 (6.6) |
| PNSs | 2 (4.4) |
| MOGAD | 1 (2.2) |
| SPS | 1 (2.2) |
| Diagnosis unknown | 14 (23.7) |
| Acute myelitis or encephalomyelitis | 9 (64.3) |
| Subacute or chronic polyneuropathy | 5 (35.7) |
| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Women, n (%) | 36 (61) |
| Age at disease onset, y, median (IQR) | 43 (30–62) |
| Age at diagnosis, y, median (IQR) | 45 (31–64) |
| TPE as first-line rescue therapy, n (%) | 19 (32.2) |
| Age at TPE initiation y, median (IQR) | 52 (41–65) |
| Time from acute symptom to TPE, d, median (IQR) | 26 (14–60) |
| Number of TPE cycles, median (IQR) | 5 (5–9) |
| At least two HA, n (%) | 13 (22) |
| Number of HA, mean ± SD | 1.39 ± 1 |
| Number of TPE cycles per HA (95% CI) | 5.4 (4.1–7.1) |
| Positive testing for serum antibodies, n (%) | 17 (28.8) |
| AChR | 8 (47) |
| MuSK | 1 (5.9) |
| Antigangliosides | 2 (11.8) |
| Hu | 1 (5.9) |
| Yo | 1 (5.9) |
| MAG | 1 (5.9) |
| MOG | 1 (5.9) |
| Titin | 1 (5.9) |
| GAD | 1 (5.9) |
| Diagnosis | Female n (%) | Age at TPE, y | Days to TPE | No. TPE Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 18/25 (72) | 42 (31–47) | 46 (14–75) | 5 (5–6) |
| MG | 7/9 (77.8) | 63 (52–69) | 25 (8–41) | 6 (4–15) |
| GBS | 3/9 (33.3) | 65 (59–67) | 17 (15–21) | 5 (5–10) |
| CIDP | 1/4 (20) | 69 (64–70) | 51 (22–151) | 16 (5–33) |
| PNSs | 3/5 (60) | 46 (38–72) | 26 (26–94) | 5 (5–5) |
| ADEM | 1/3 (33.3) | 54 (49–60) | 29 (22–43) | 5 (4–6) |
| NMOSD/MOGAD | 2/2 (100) | 35 (26–44) | 17 (15–18) | 8 (7–10) |
| p | 0.09 * | <0.0001 | 0.09 | 0.35 |
| Predictors | B | aOR | 95% CI for aOR | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | −0.15 | 0.86 | 0.22 | 3.4 | 0.83 |
| Age < 50 y at TPE | 1.51 | 4.5 | 0.97 | 20.9 | 0.054 |
| TPE as first-line therapy | 1.70 | 5.5 | 0.96 | 31.6 | 0.056 |
| Positive serum antibody | 1.87 | 6.5 | 1.01 | 40.1 | 0.045 |
| ≥5 TPE sessions | 0.65 | 1.6 | 0.37 | 6.6 | 0.54 |
| mRS score before TPE | 0.39 | 1.48 | 0.70 | 3.20 | 0.31 |
| Predictors | B | aOR | 95% CI for aOR | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 0.31 | 1.36 | 0.4 | 4.65 | 0.62 |
| Age < 50 y at TPE | −0.17 | 0.85 | 0.26 | 2.76 | 0.78 |
| TPE as first-line therapy | 0.26 | 1.29 | 0.37 | 4.47 | 0.69 |
| ≥5 TPE sessions | 1.76 | 5.79 | 1.67 | 20.1 | 0.006 |
| mRS score before TPE | −0.68 | 0.51 | 0.25 | 1.04 | 0.063 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iacono, S.; Schirò, G.; Salemi, G.; Scirè, E.; Aridon, P.; Melfa, M.; Andolina, M.; Sorbello, G.; Calì, A.; Brighina, F.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rescue Treatment with Plasma Exchange in Patients with Acute Inflammatory Neurological Disorders: A Single Center Experience. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 761-775. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16040056
Iacono S, Schirò G, Salemi G, Scirè E, Aridon P, Melfa M, Andolina M, Sorbello G, Calì A, Brighina F, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rescue Treatment with Plasma Exchange in Patients with Acute Inflammatory Neurological Disorders: A Single Center Experience. Neurology International. 2024; 16(4):761-775. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16040056
Chicago/Turabian StyleIacono, Salvatore, Giuseppe Schirò, Giuseppe Salemi, Elisabetta Scirè, Paolo Aridon, Michele Melfa, Michele Andolina, Gabriele Sorbello, Andrea Calì, Filippo Brighina, and et al. 2024. "Efficacy and Safety of Rescue Treatment with Plasma Exchange in Patients with Acute Inflammatory Neurological Disorders: A Single Center Experience" Neurology International 16, no. 4: 761-775. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16040056
APA StyleIacono, S., Schirò, G., Salemi, G., Scirè, E., Aridon, P., Melfa, M., Andolina, M., Sorbello, G., Calì, A., Brighina, F., D’Amelio, M., & Ragonese, P. (2024). Efficacy and Safety of Rescue Treatment with Plasma Exchange in Patients with Acute Inflammatory Neurological Disorders: A Single Center Experience. Neurology International, 16(4), 761-775. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16040056








