A Unique Case of Bilateral Thalamic High-Grade Glioma in a Pediatric Patient with LI-Fraumeni Syndrome: Case Presentation and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
Case Presentation
2. Methods
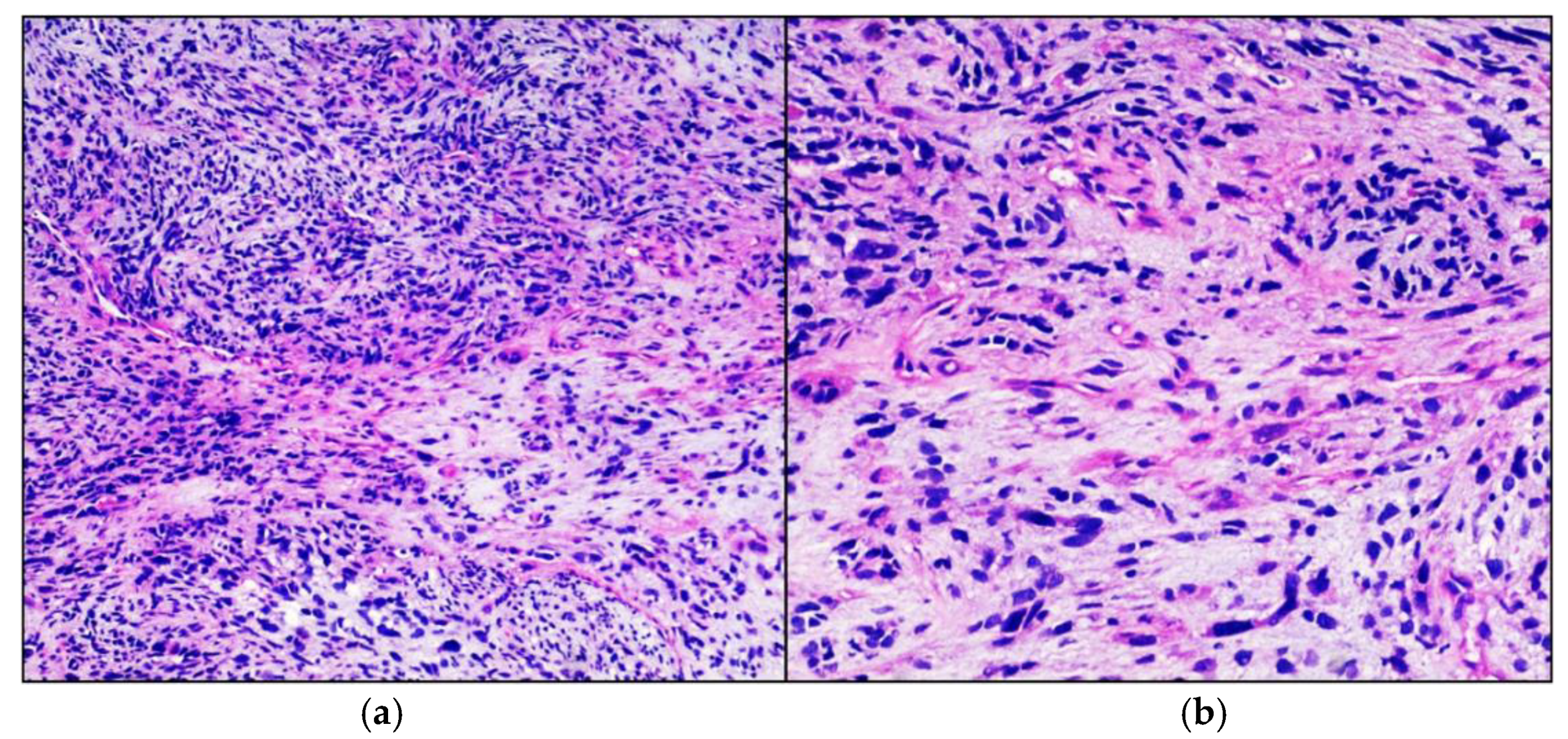
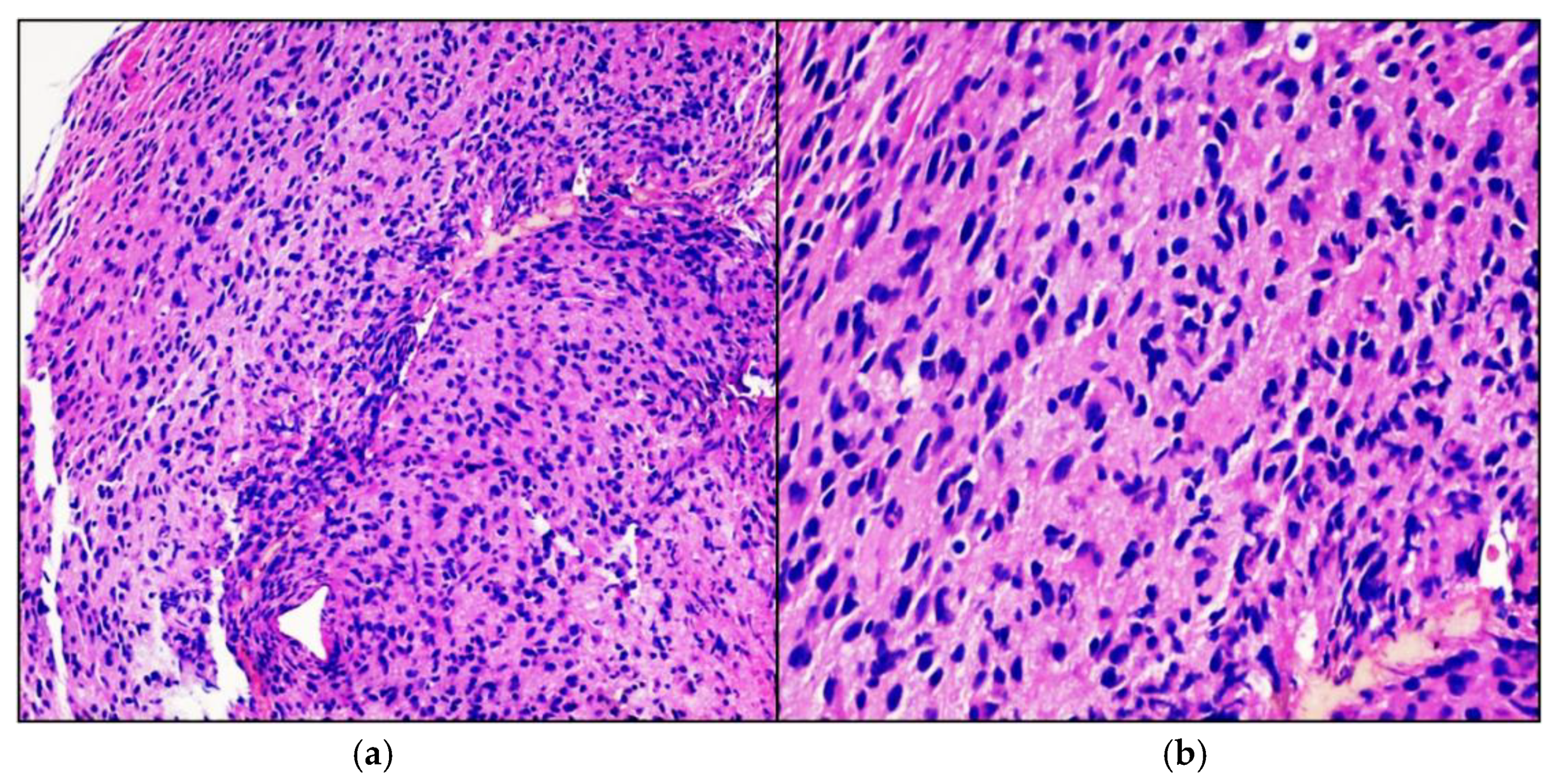
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, A.; Flemming, K.; McInnes, E.; Oliver, S.; Craig, J. Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research: ENTREQ. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2012, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, E.A.L.; Hilz, S.; Gupta, R.; Cadwell, C.; Ramani, B.; Hofmann, J.; Kline, C.N.; Banerjee, A.; Reddy, A.; Oberheim Bush, N.A.; et al. Gliomas arising in the setting of Li-Fraumeni syndrome stratify into two molecular subgroups with divergent clinicopathologic features. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cárdenas, J.M.; Zambrano, A.K.; Guevara-Ramírez, P.; Guerrero, S.; Runruil, G.; López-Cortés, A.; Torres-Yaguana, J.P.; Armendáriz-Castillo, I.; Pérez-Villa, A.; Yumiceba, V.; et al. A deep analysis using panel-based next-generation sequencing in an Ecuadorian pediatric patient with anaplastic astrocytoma: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 31, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zureick, A.H.; McFadden, K.A.; Mody, R.; Koschmann, C. Successful treatment of a TSC2-mutant glioblastoma with everolimus. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e227734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, L.A.; Shafi, G. TSC1/2 mutations as markers of response to everolimus in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A case study. Indian J. Cancer 2019, 56, 274–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaeli, O.; Tabori, U. Pediatric High Grade Gliomas in the Context of Cancer Predisposition Syndromes. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2018, 61, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mody, R.J.; Wu, Y.M.; Lonigro, R.J.; Cao, X.; Roychowdhury, S.; Vats, P.; Frank, K.M.; Prensner, J.R.; Asangani, I.; Palanisamy, N.; et al. Integrative clinical sequencing in the management of refractory or relapsed cancer in youth. JAMA 2015, 314, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, D.W.; Roy, A.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Scollon, S.; Bergstrom, K.; Kerstein, R.A.; Gutierrez, S.; Petersen, A.K.; Bavle, A.; et al. Diagnostic yield of clinical tumor and germline whole-exome sequencing for children with solid tumors. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Walsh, M.F.; Wu, G.; Edmonson, M.N.; Gruber, T.A.; Easton, J.; Hedges, D.; Ma, X.; Zhou, X.; Yergeau, D.A.; et al. Germline mutations in predisposition genes in pediatric cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2336–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.; Zelley, K.; Nichols, K.E.; Garber, J. Li-Fraumeni Syndrome. In GeneReviews®; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tinat, J.; Bougeard, G.; Baert-Desurmont, S.; Vasseur, S.; Martin, C.; Bouvignies, E.; Caron, O.; Bressac-de Paillerets, B.; Berthet, P.; Dugast, C.; et al. 2009 version of the Chompret criteria for li Fraumeni syndrome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, e108–e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, M.; Goldgar, D.E.; Sodha, N.; Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P.; Hainaut, P.; Eeles, R.A. Li-Fraumeni and Related Syndromes: Correlation between Tumor Type, Family Structure, and TP53 Genotype. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6643–6650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bougeard, G.; Renaux-Petel, M.; Flaman, J.M.; Charbonnier, C.; Fermey, P.; Belotti, M.; Gauthier-Villars, M.; Stoppa-Lyonnet, D.; Consolino, E.; Brugières, L. Revisiting Li-Fraumeni syndrome from TP53 mutation carriers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broniscer, A.; Hwang, S.N.; Chamdine, O.; Lin, T.; Pounds, S.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Chi, L.; Shurtleff, S.; Allen, S.; Gajjar, A.; et al. Bithalamic gliomas may be molecularly distinct from their unilateral high-grade counterparts. Brain Pathol. 2018, 28, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, N.; Arivazhagan, A.; Bhat, D.I.; Arvinda, H.R.; Mahadevan, A.; Santosh, V.; Devi, B.I.; Sampath, S.; Chandramouli, B.A. Stereotactic biopsy of brainstem lesions: Techniques, efficacy, safety, and disease variation between adults and children: A single institutional series and review. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2014, 5, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquenazi, Y.; Moussazadeh, N.; Link, T.W.; Link, T.W.; Hovinga, K.E.; Reiner, A.S.; DiStefano, N.M.; Brennan, C.; Gutin, P.; Tabar, V. Thalamic Glioblastoma: Clinical Presentation, Management Strategies, and Outcomes. Neurosurgery 2018, 83, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carai, A.; Mastronuzzi, A.; de Benedictis, A.; Messina, R.; Cacchione, A.; Miele, E.; Randi, F.; Esposito, G.; Trezza, A.; Colafati, G.S.; et al. Robot-assisted stereotactic biopsy of Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma: A single centre experience. World Neurosurg. 2017, 101, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedictis, A.; Trezza, A.; Carai, A.; Genovese, E.; Procaccini, E.; Messina, R.; Randi, F.; Cossu, S.; Esposito, G.; Palma, P.; et al. Robot-assisted procedures in pediatric neurosurgery. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 42, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Sun, M.H. Stereotactic biopsy for brainstem lesion: Comparison of approaches and reports of 10 cases. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2011, 74, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellaretti, M.; Reyns, N.; Touzet, G.; Dubois, F.; Gusmão, S.; Pereira, J.L.; Blond, S. Stereotactic biopsy for brainstem tumors: Comparison of trans-cerebellar with transfrontal approach. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2012, 90, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, I.F.; Finkelstein, S.D.; Woods, J.; Burnham, J.; Holmes, E.J.; Hamilton, R.L.; Yates, A.J.; Boyett, J.M.; Finlay, J.L.; Sposto, R. Children’s Cancer Group. Expression of P53 and prognosis in children with malignant gliomas. N. Eng. J. Med. 2002, 346, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, J.M.; Spreadborough, A.; Greaves, M.J.; Birch, J.M.; Varley, J.M.; Scott, D. The relationship between radiation-induced G(1) arrest and chromosome aberrations in Li-Fraumeni fibroblasts with or without germline TP53 mutations. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 85, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaeli, O.; Tabori, U.; Schiffman, J.D.; Naumer, A.; Kohlmann, W.; Evans, D.G.; Forde, C.; Hoffman, L.M.; Rednam, S.P.; Maxwell, K.N.; et al. Gliomas in the context of Li-Fraumeni Syndrome—An international cohort. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.K.; Kim, M.M.; Chen, P.; Furman, F.; Julin, C.M.; Israel, M.A. The intrinsic radioresistance of glioblastoma-derived cell lines is associated with a failure of p53 to induce p21(BAX) expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14453–14458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhukova, N.; Ramaswamy, V.; Remke, M.; Martin, D.C.; Castelo-Branco, P.; Zhang, C.H.; Fraser, M.; Tse, K.; Poon, R.; Shih, D.J. WNT activation by lithium abrogates TP53 mutation associated radiation resistance in medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Bernstein, A. p53 mutations increase resistance to ionizing radiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5742–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.S.; Wong, M.; Mayoh, C.; Kumar, A.; Tsoli, M.; Mould, E.; Tyrrell, V.; Khuong-Quang, D.A.; Pinese, M.; Gayevskiy, V. Brief Report: Potent clinical and radiological response to larotrectinib in TRK fusion-driven high-grade glioma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, M.; Mobark, N.A.; Balbaid, A.A.O.; Alanazi, F.A.; Aljabarat, W.A.R.; Bakhsh, E.A.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Abedalthagafi, M. Regression of ETV6-NTRK3 Infantile Glioblastoma After First-Line Treatment with Larotrectinib. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerki, R.; Banerjee, A.; Zamorski, A. HGG-15. Successful treatment of an ntrk-fusion positive infantile glioblastoma with larotrectinib, a targeted trk inhibitor. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21 (Suppl. 2), ii89–ii90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, M.; Vasudevaraja, V.; Serrano, J.; DeLorenzo, M.; Malinowski, S.; Blandin, A.F.; Pages, M.; Ligon, A.H.; Dong, F.; Meredith, D.M. Molecular and clinicopathologic features of gliomas harboring NTRK fusions. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, R.; Boichard, A.; Kato, S.; Sicklick, J.K.; Bazhenova, L.; Kurzrock, R. Analysis of NTRK Alterations in Pan-Cancer Adult and Pediatric Malignancies: Implications for NTRK-Targeted Therapeutics. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambella, A.; Senetta, R.; Collemi, G.; Vallero, S.G.; Monticelli, M.; Cofano, F.; Zeppa, P.; Garbossa, D.; Pellerino, A.; Rudà, R. NTRK Fusions in Central Nervous System Tumors: A Rare, but Worthy Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Reference | No. | IDH Mutation Status | Age and Sex | Other Cancers | Family History | Brain Tumor Histology | Location | Follow Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sloan et al. [2] | 1 | Wildtype | 4, Male | None | Negative | Glioblastoma | Thalamus | 2 months |
| 2 | Wildtype | 6, Male | None | Negative | Glioblastoma | Cerebral hemisphere | 12 months | |
| 3 | Wildtype | 11, Male | Osteosarcoma | Brain cancer (aunt); ovarian cancer (grandmother); rhabdomyosarcoma (uncle) | Anaplastic astrocytoma | Cerebral hemisphere | 8 months | |
| 4 | Wildtype | 6, Male | None | Negative | Glioblastoma | Cerebral hemisphere | 4 months | |
| García-Cárdenas et al. [3] | 5 | n.e * | 13, Female | None | Breast cancer (mother and maternal grandmother); brain cancer (two maternal uncles and two maternal cousins) | Anaplastic astrocytoma | Cerebral hemisphere | 17 months |
| Zureick et al. [4] | 6 | n.a. ** | 14, Male | n.a. ** | n.a. ** | Glioblastoma | Cerebral hemisphere | 33 months |
| Our case | 7 | Wildtype | 3, Male | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Ovarian cancer (great-grandmother); leukemia (cousin) | Glioblastoma | Thalamus bilateral | 4 months |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Messina, R.; Cazzato, G.; Perillo, T.; Stagno, V.; Blè, V.; Resta, M.; De Leonardis, F.; Santoro, N.; Signorelli, F.; Ingravallo, G. A Unique Case of Bilateral Thalamic High-Grade Glioma in a Pediatric Patient with LI-Fraumeni Syndrome: Case Presentation and Review of the Literature. Neurol. Int. 2021, 13, 175-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint13020017
Messina R, Cazzato G, Perillo T, Stagno V, Blè V, Resta M, De Leonardis F, Santoro N, Signorelli F, Ingravallo G. A Unique Case of Bilateral Thalamic High-Grade Glioma in a Pediatric Patient with LI-Fraumeni Syndrome: Case Presentation and Review of the Literature. Neurology International. 2021; 13(2):175-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint13020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleMessina, Raffaella, Gerardo Cazzato, Teresa Perillo, Vita Stagno, Valeria Blè, Mariachiara Resta, Francesco De Leonardis, Nicola Santoro, Francesco Signorelli, and Giuseppe Ingravallo. 2021. "A Unique Case of Bilateral Thalamic High-Grade Glioma in a Pediatric Patient with LI-Fraumeni Syndrome: Case Presentation and Review of the Literature" Neurology International 13, no. 2: 175-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint13020017
APA StyleMessina, R., Cazzato, G., Perillo, T., Stagno, V., Blè, V., Resta, M., De Leonardis, F., Santoro, N., Signorelli, F., & Ingravallo, G. (2021). A Unique Case of Bilateral Thalamic High-Grade Glioma in a Pediatric Patient with LI-Fraumeni Syndrome: Case Presentation and Review of the Literature. Neurology International, 13(2), 175-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint13020017








