Sudden Cardiac Death in Biventricular Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: A New Undescribed Variant of the MYH6 Gene
Abstract
1. Introduction
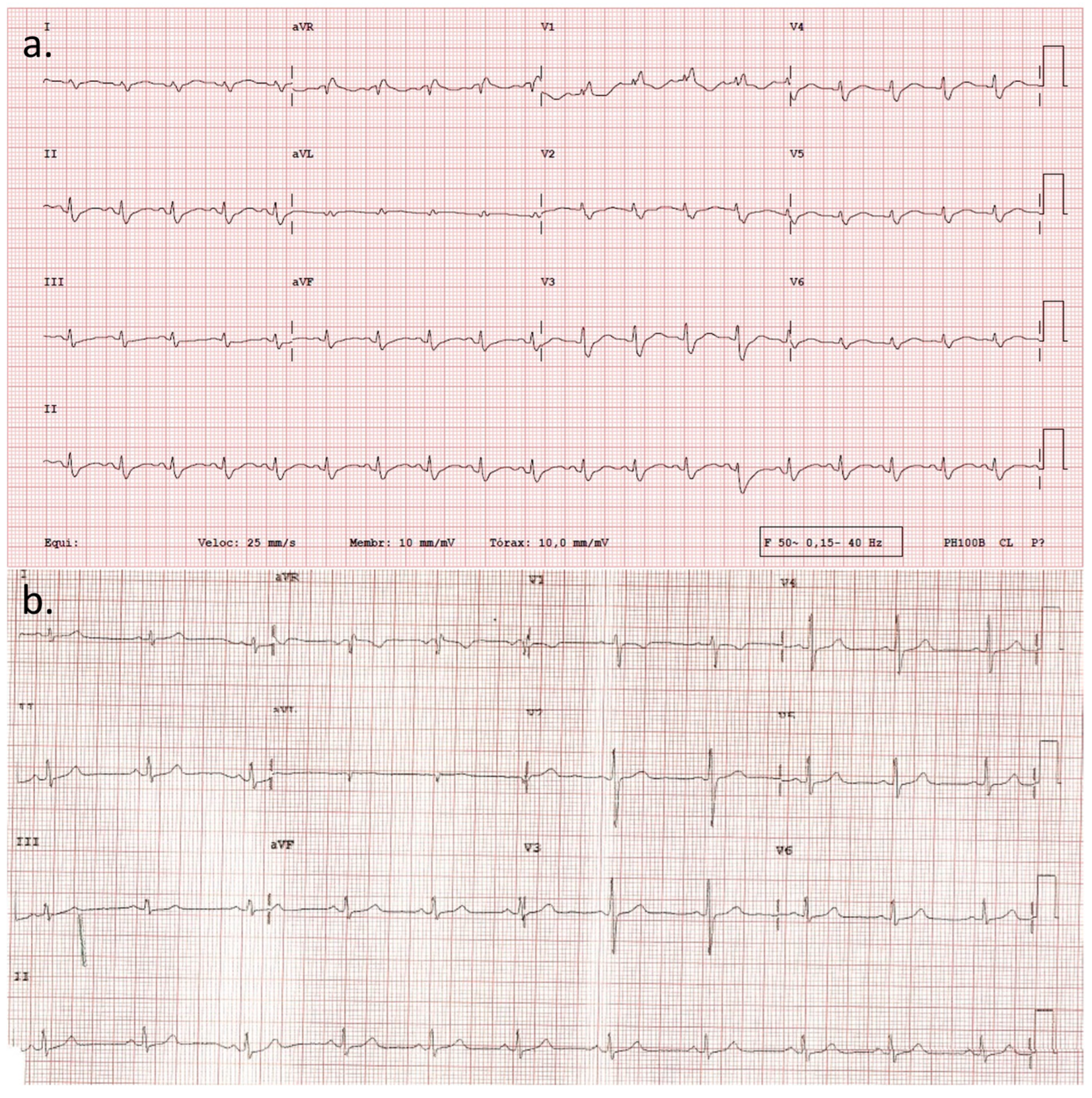
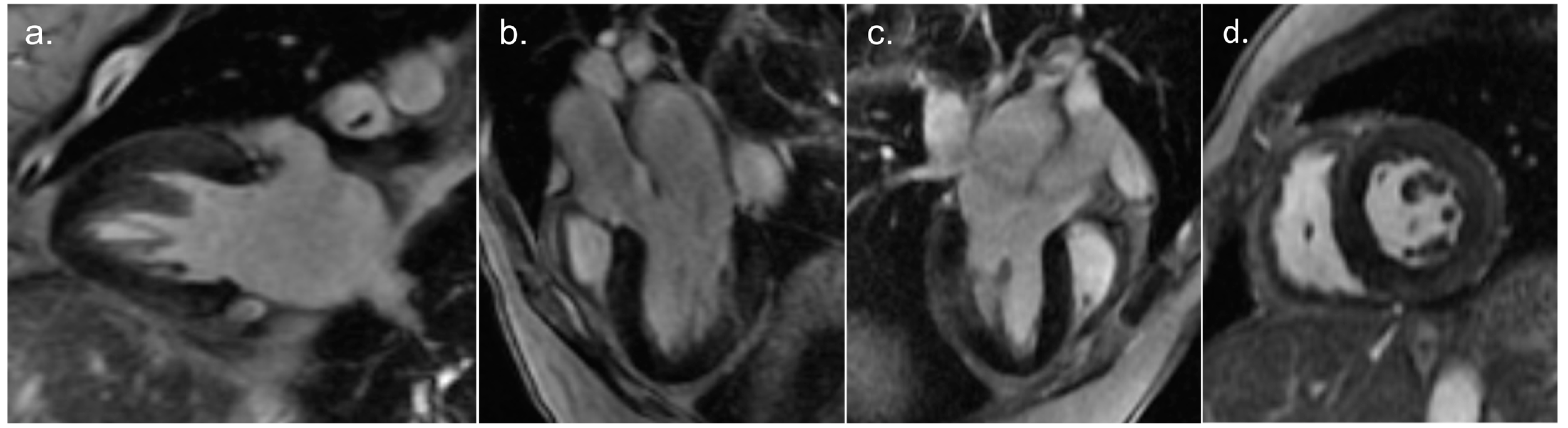
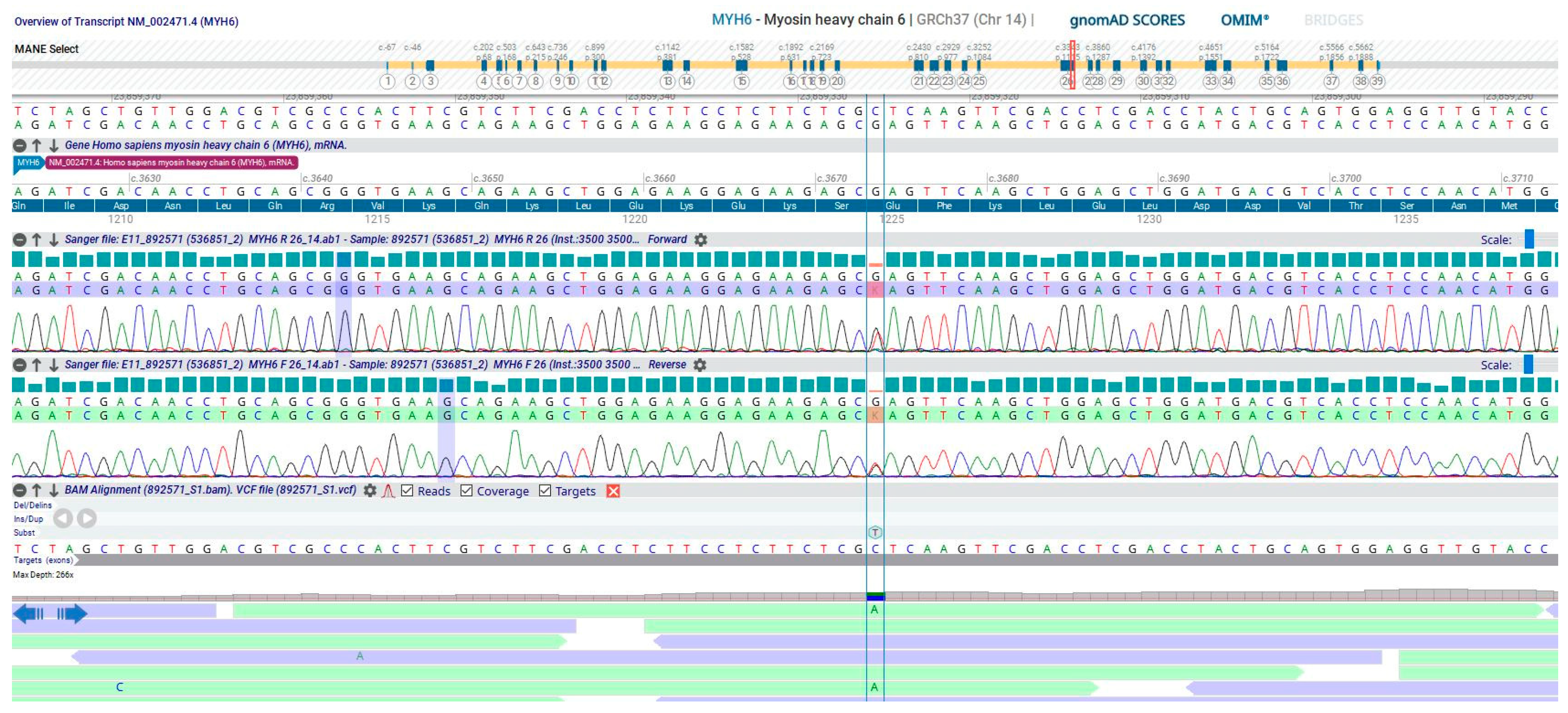
2. Detailed Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corrado, D.; Perazzolo Marra, M.; Zorzi, A.; Beffagna, G.; Cipriani, A.; Lazzari, M.; Migliore, F.; Pilichou, K.; Rampazzo, A.; Rigato, I.; et al. Diagnosis of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: The Padua criteria. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 319, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrado, D.; Basso, C. Arrhythmogenic left ventricular cardiomyopathy. Heart 2022, 108, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerull, B.; Brodehl, A. Insights Into Genetics and Pathophysiology of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2021, 18, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.M.; Green, K.J. Desmosomes in the Heart: A Review of Clinical and Mechanistic Analyses. Cell Commun. Adhes. 2014, 21, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerull, B.; Heuser, A.; Wichter, T.; Paul, M.; Basson, C.T.; McDermott, D.A.; Lerman, B.B.; Markowitz, S.M.; Ellinor, P.T.; MacRae, C.A.; et al. Mutations in the desmosomal protein plakophilin-2 are common in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 1162–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodehl, A.; Rezazadeh, S.; Williams, T.; Munsie, N.M.; Liedtke, D.; Oh, T.; Ferrier, R.; Shen, Y.; Jones, S.J.; Stiegler, A.L.; et al. Mutations in ILK, encoding integrin-linked kinase, are associated with arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Transl. Res. 2019, 208, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Genga, M.F.; Cuenca, S.; Ferro, M.D.; Zorio, E.; Salgado-Aranda, R.; Climent, V.; Padrón-Barthe, L.; Duro-Aguado, I.; Jiménez-Jáimez, J.; Hidalgo-Olivares, V.M.; et al. Truncating FLNC Mutations Are Associated With High-Risk Dilated and Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2440–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodehl, A.; Hedde, P.N.; Dieding, M.; Fatima, A.; Walhorn, V.; Gayda, S.; Šarić, T.; Klauke, B.; Gummert, J.; Anselmetti, D.; et al. Dual Color Photoactivation Localization Microscopy of Cardiomyopathy-associated Desmin Mutants. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16047–16057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protonotarios, A.; Brodehl, A.; Asimaki, A.; Jager, J.; Quinn, E.; Stanasiuk, C.; Ratnavadivel, S.; Futema, M.; Akhtar, M.M.; Gossios, T.D.; et al. The Novel Desmin Variant p.Leu115Ile Is Associated With a Unique Form of Biventricular Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Can. J. Cardiol. 2021, 37, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Jiménez, F.J.; Carriel, V.; Brodehl, A.; Alaminos, M.; Campos, A.; Schirmer, I.; Milting, H.; Abril, B.; Álvarez, M.; López-Fernández, S.; et al. Novel Desmin Mutation p.Glu401Asp Impairs Filament Formation, Disrupts Cell Membrane Integrity, and Causes Severe Arrhythmogenic Left Ventricular Cardiomyopathy/Dysplasia. Circulation 2018, 137, 1595–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ayala, J.M.; Ortiz-Genga, M.; Gomez-Milanes, I.; Lopez-Cuenca, D.; Ruiz-Espejo, F.; Sanchez-Munoz, J.J.; Oliva-Sandoval, M.J.; Monserrat, L.; Gimeno, J.R. A mutation in the Z-line Cypher/ZASP protein is associated with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Clin. Genet. 2015, 88, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, J.-M.; Fellmann, F.; Bhuiyan, Z.A.; Rotman, S.; Pruvot, E.; Schläpfer, J. ACTN2 variant associated with a cardiac phenotype suggestive of left-dominant arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Hear. Case Rep. 2020, 6, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Riele, A.S.J.; Agullo-Pascual, E.; James, C.A.; Leo-Macias, A.; Cerrone, M.; Zhang, M.; Lin, X.; Lin, B.; Rothenberg, E.; Sobreira, N.L.; et al. Multilevel analyses of SCN5A mutations in arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy suggest non-canonical mechanisms for disease pathogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiso, N.; Stephan, D.A.; Nava, A.; Bagattin, A.; Devaney, J.M.; Stanchi, F.; Larderet, G.; Brahmbhatt, B.; Brown, K.; Bauce, B.; et al. Identification of mutations in the cardiac ryanodine receptor gene in families affected with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy type 2 (ARVD2). Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zwaag, P.A.; van Rijsingen, I.A.; Asimaki, A.; Jongbloed, J.D.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Wiesfeld, A.C.; Cox, M.G.; van Lochem, L.T.; de Boer, R.A.; Hofstra, R.M.; et al. Phospholamban R14del mutation in patients diagnosed with dilated cardiomyopathy or arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: Evidence supporting the concept of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmerman, H.; Jones, L. Phospholamban: Protein Structure, Mechanism of Action, and Role in Cardiac Function. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 921–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarta, G.; Syrris, P.; Ashworth, M.; Jenkins, S.; Alapi, K.Z.; Morgan, J.; Muir, A.; Pantazis, A.; McKenna, W.J.; Elliott, P.M. Mutations in the Lamin A/C gene mimic arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, L.; Mavroidis, M.; Psarras, S.; Capetanaki, Y.; Lattanzi, G. Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle Disorders Caused by Mutations in Genes Encoding Intermediate Filament Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merner, N.D.; Hodgkinson, K.A.; Haywood, A.F.; Connors, S.; French, V.M.; Drenckhahn, J.-D.; Kupprion, C.; Ramadanova, K.; Thierfelder, L.; McKenna, W.; et al. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Type 5 Is a Fully Penetrant, Lethal Arrhythmic Disorder Caused by a Missense Mutation in the TMEM43 Gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 82, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padrón-Barthe, L.; Villalba-Orero, M.; Gómez-Salinero, J.M.; Domínguez, F.; Román, M.; Larrasa-Alonso, J.; Ortiz-Sánchez, P.; Martínez, F.; López-Olañeta, M.; Bonzón-Kulichenko, E.; et al. Severe Cardiac Dysfunction and Death Caused by Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Type 5 Are Improved by Inhibition of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β. Circulation 2019, 140, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfatah, N.; Chen, R.; Duff, H.J.; Seifer, C.M.; Buffo, I.; Huculak, C.; Clarke, S.; Clegg, R.; Jassal, D.S.; Gordon, P.M.; et al. Characterization of a Unique Form of Arrhythmic Cardiomyopathy Caused by Recessive Mutation in LEMD2. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2019, 4, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.M.; Schulz-Menger, J.; Holmvang, G.; Kramer, C.M.; Carbone, I.; Sechtem, U.; Kindermann, I.; Gutberlet, M.; Cooper, L.T.; Liu, P.; et al. Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Nonischemic Myocardial Inflammation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 3158–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S.; Minobe, W.; Bristow, M.R.; Leinwand, L.A. Myosin Heavy Chain Isoform Expression in the Failing and Nonfailing Human Heart. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, V.; Chambers, A.P.; Nadal-Ginard, B. Cardiac alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain genes are organized in tandem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 2626–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, J.; Loughna, S. Heavy and light roles: Myosin in the morphogenesis of the heart. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 1221–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Daya, A.; Sater, A.K.; Wells, D.E.; Mohun, T.J.; Zimmerman, L.B. Absence of heartbeat in the Xenopus tropicalis mutation muzak is caused by a nonsense mutation in cardiac myosin myh6. Dev. Biol. 2009, 336, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmara, E.; Garshasbi, M. Whole-exome sequencing identifies R1279X of MYH6 gene to be associated with congenital heart disease. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2018, 18, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anfinson, M.; Fitts, R.H.; Lough, J.W.; James, J.M.; Simpson, P.M.; Handler, S.S.; Mitchell, M.E.; Tomita-Mitchell, A. Significance of α-Myosin Heavy Chain (MYH6) Variants in Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome and Related Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowles, N.E.; Jou, C.J.; Arrington, C.B.; Kennedy, B.J.; Earl, A.; Matsunami, N.; Meyers, L.L.; Etheridge, S.P.; Saarel, E.V.; Bleyl, S.B.; et al. Exome analysis of a family with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome identifies a novel disease locus. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2015, 167, 2975–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalazan, B.; Mol, D.; Darbar, F.A.; Ornelas-Loredo, A.; Al-Azzam, B.; Chen, Y.; Tofovic, D.; Sridhar, A.; Alzahrani, Z.; Ellinor, P.; et al. Association of Rare Genetic Variants and Early-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Ethnic Minority Individuals. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, L.; Ingles, J.; Turner, C.; Kilborn, M.; Bagnall, R.D.; Semsarian, C. Exome sequencing identifies a novel mutation in the MYH6 gene in a family with early-onset sinus node dysfunction, ventricular arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest. Hear. Case Rep. 2015, 1, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, T.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xian, J.; Geng, X.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.; Yang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Lin, Y. Young and early-onset dilated cardiomyopathy with malignant ventricular arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death induced by the heterozygous LDB3, MYH6, and SYNE1 missense mutations. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2021, 26, e12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubattu, S.; Bozzao, C.; Pennacchini, E.; Pagannone, E.; Musumeci, B.M.; Piane, M.; Germani, A.; Savio, C.; Francia, P.; Volpe, M.; et al. A Next-Generation Sequencing Approach to Identify Gene Mutations in Early- and Late-Onset Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Patients of an Italian Cohort. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carniel, E.; Taylor, M.R.; Sinagra, G.; Di Lenarda, A.; Ku, L.; Fain, P.R.; Boucek, M.M.; Cavanaugh, J.; Miocic, S.; Slavov, D.; et al. α-Myosin Heavy Chain. Circulation 2005, 112, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.; Painter, T.; Li, R.; Siegfried, J.D.; Li, D.; Norton, N.; Hershberger, R.E. Rare Variant Mutations in Pregnancy-Associated or Peripartum Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2010, 121, 2176–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vershinina, T.; Fomicheva, Y.; Muravyev, A.; Jorholt, J.; Kozyreva, A.; Kiselev, A.; Gordeev, M.; Vasichkina, E.; Segrushichev, A.; Pervunina, T.; et al. Genetic Spectrum of Left Ventricular Non-Compaction in Paediatric Patients. Cardiology 2020, 145, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.; Hoorntje, E.T.; Riele, A.S.J.M.T.; Tichnell, C.; van der Heijden, J.F.; Tandri, H.; Berg, M.P.v.D.; Jongbloed, J.D.H.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Hauer, R.N.W.; et al. Identification of sarcomeric variants in probands with a clinical diagnosis of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC). J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2018, 29, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Rao, M.; Guo, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Song, J. Sarcomere variants in arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: Pathogenic factor or bystander? Gene 2019, 687, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros-Domingo, A.; Saguner, A.M.; Magyar, I.; Bahr, A.; Akdis, D.; Brunckhorst, C.; Duru, F.; Berger, W. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: Implications of next-generation sequencing in appropriate diagnosis. Europace 2017, 19, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yan, L.; Kou, S.; Meng, J.; Lu, Z.; Lin, C.-P.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H. Generation and characterization of a Myh6-driven Cre knockin mouse line. Transgenic. Res. 2021, 30, 821–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, E.; Zhang, G.; Mu, L.; Ma, N.; Wang, T. Establishment of a human MYH6 compound heterozygous knockout hESC line to model cardiomyopathy and congenital heart defects by CRISPR/Cas9 system. Stem. Cell Res. 2021, 50, 102128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodehl, A.; Dieding, M.; Klauke, B.; Dec, E.; Madaan, S.; Huang, T.; Gargus, J.; Fatima, A.; Šaric, T.; Cakar, H.; et al. The Novel Desmin Mutant p.A120D Impairs Filament Formation, Prevents Intercalated Disk Localization, and Causes Sudden Cardiac Death. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia Brás, P.; Cardoso, I.; Viegas, J.; Antunes, D.; Rosa, S.A. Sudden Cardiac Death in Biventricular Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: A New Undescribed Variant of the MYH6 Gene. Cardiogenetics 2023, 13, 145-153. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics13040014
Garcia Brás P, Cardoso I, Viegas J, Antunes D, Rosa SA. Sudden Cardiac Death in Biventricular Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: A New Undescribed Variant of the MYH6 Gene. Cardiogenetics. 2023; 13(4):145-153. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics13040014
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia Brás, Pedro, Isabel Cardoso, José Viegas, Diana Antunes, and Sílvia Aguiar Rosa. 2023. "Sudden Cardiac Death in Biventricular Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: A New Undescribed Variant of the MYH6 Gene" Cardiogenetics 13, no. 4: 145-153. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics13040014
APA StyleGarcia Brás, P., Cardoso, I., Viegas, J., Antunes, D., & Rosa, S. A. (2023). Sudden Cardiac Death in Biventricular Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: A New Undescribed Variant of the MYH6 Gene. Cardiogenetics, 13(4), 145-153. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics13040014





