Cardiac Amyloidosis: Diagnostic Tools for a Challenging Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology
3. Clinical Features
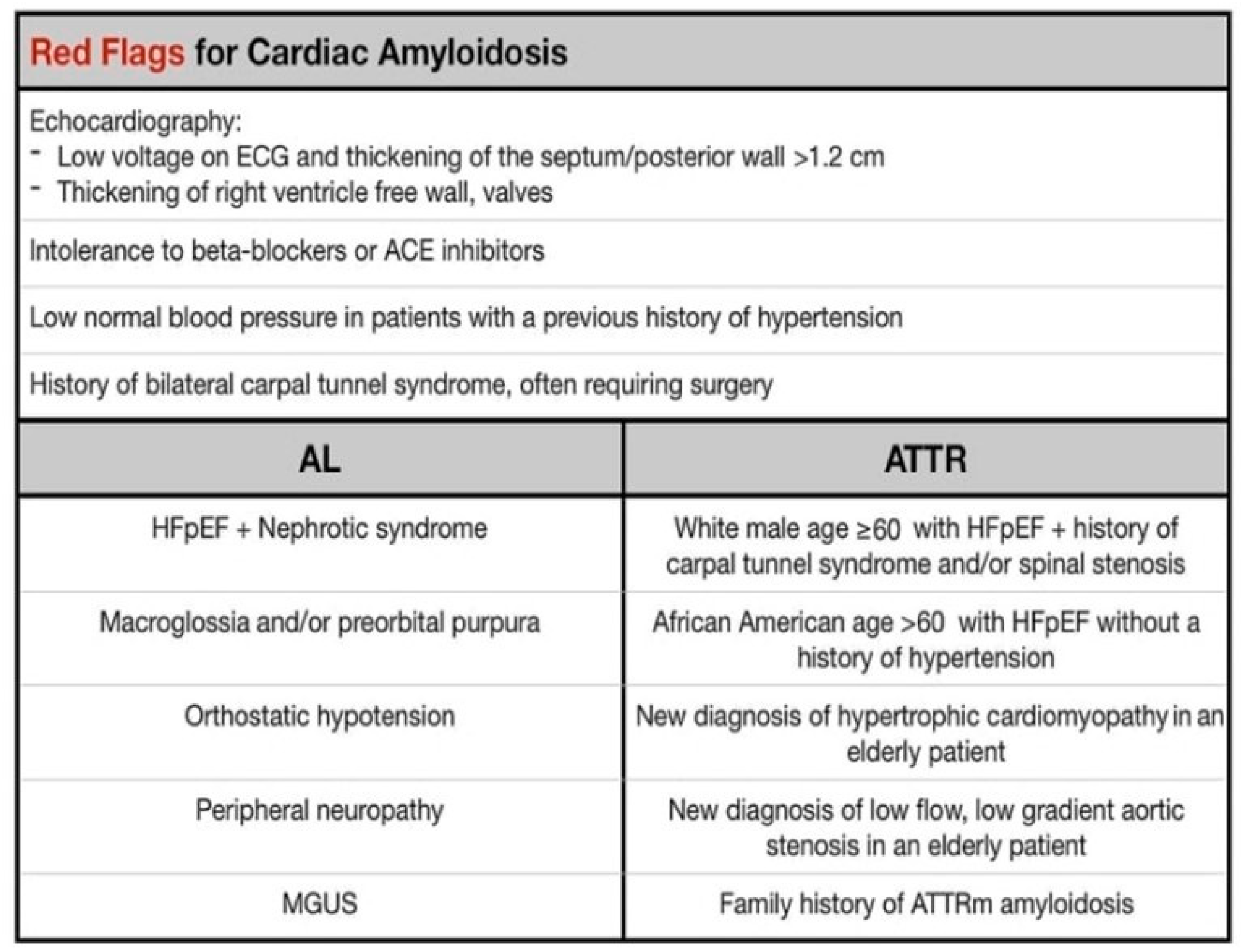
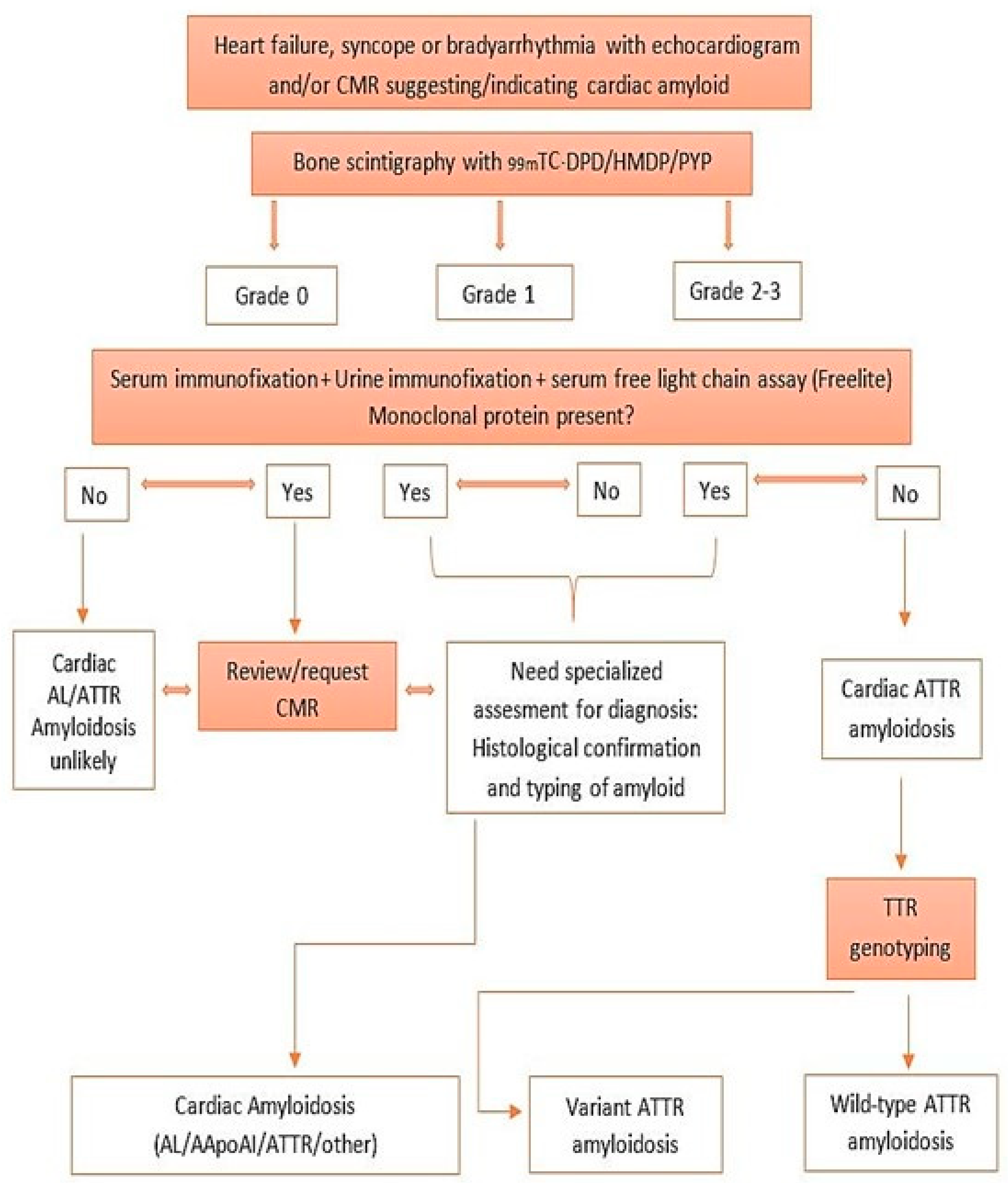
4. Diagnosis and Evaluation of Cardiac Amyloidosis
5. Biomarkers
6. Genetic Testing
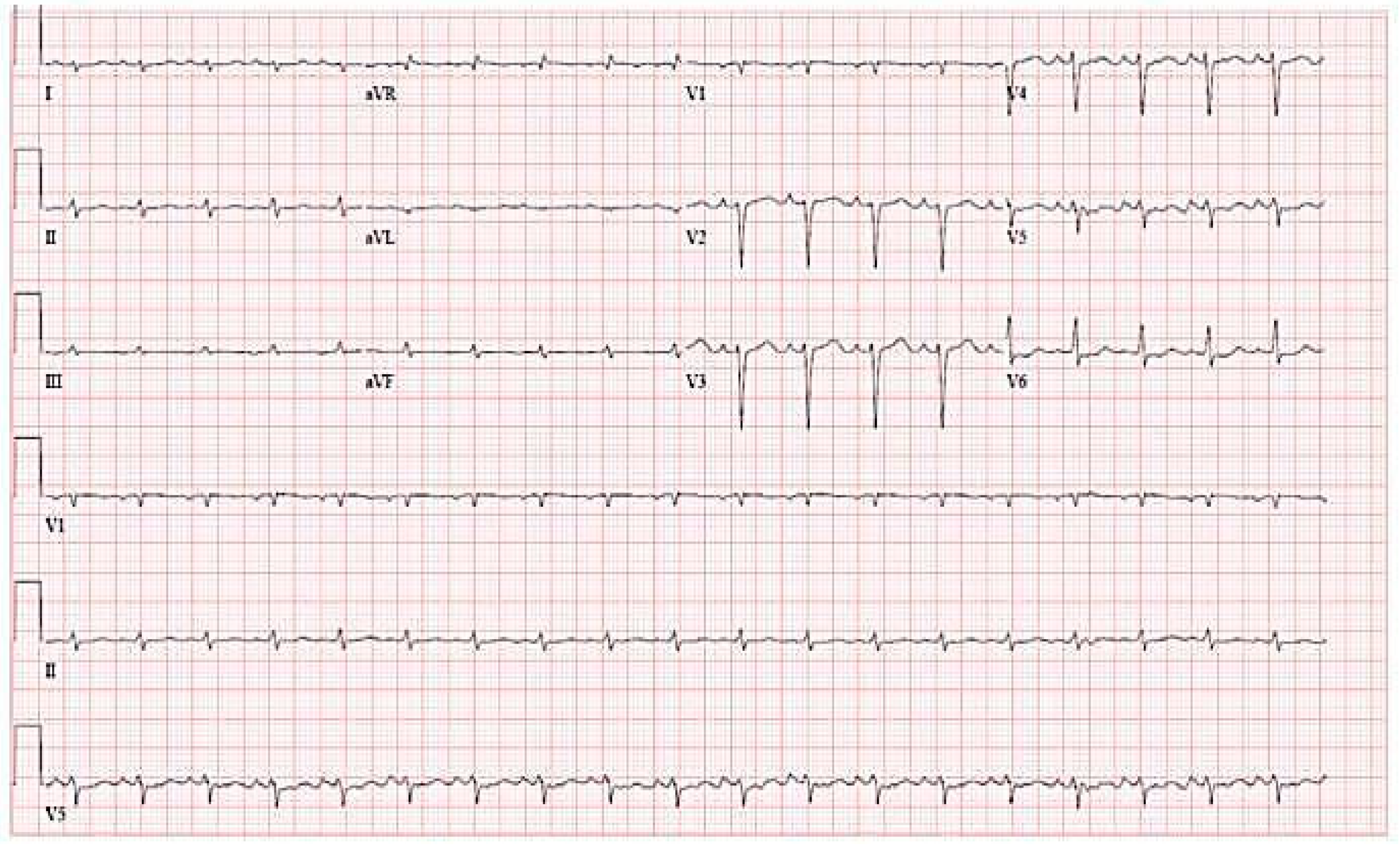
7. Electrocardiography
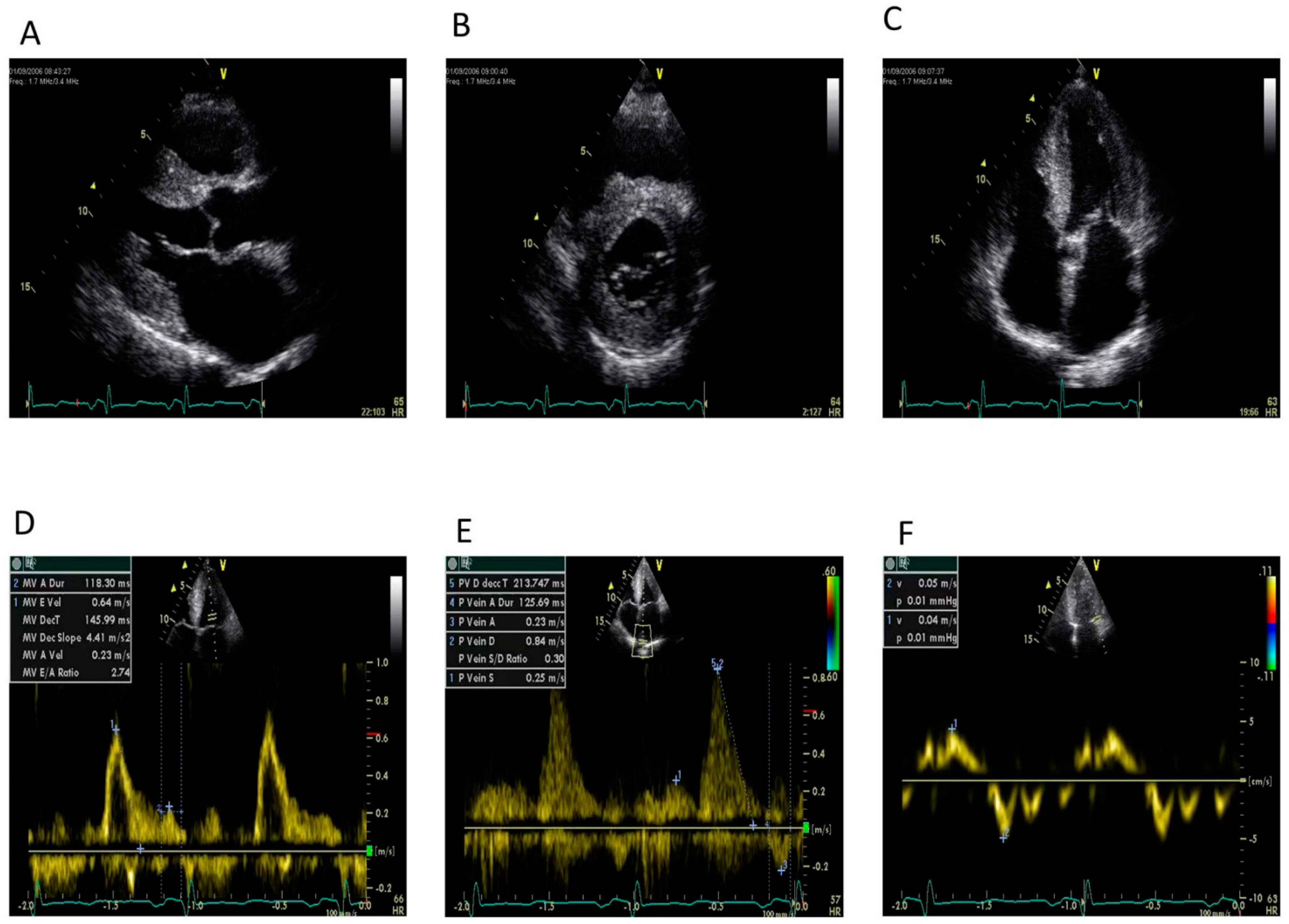
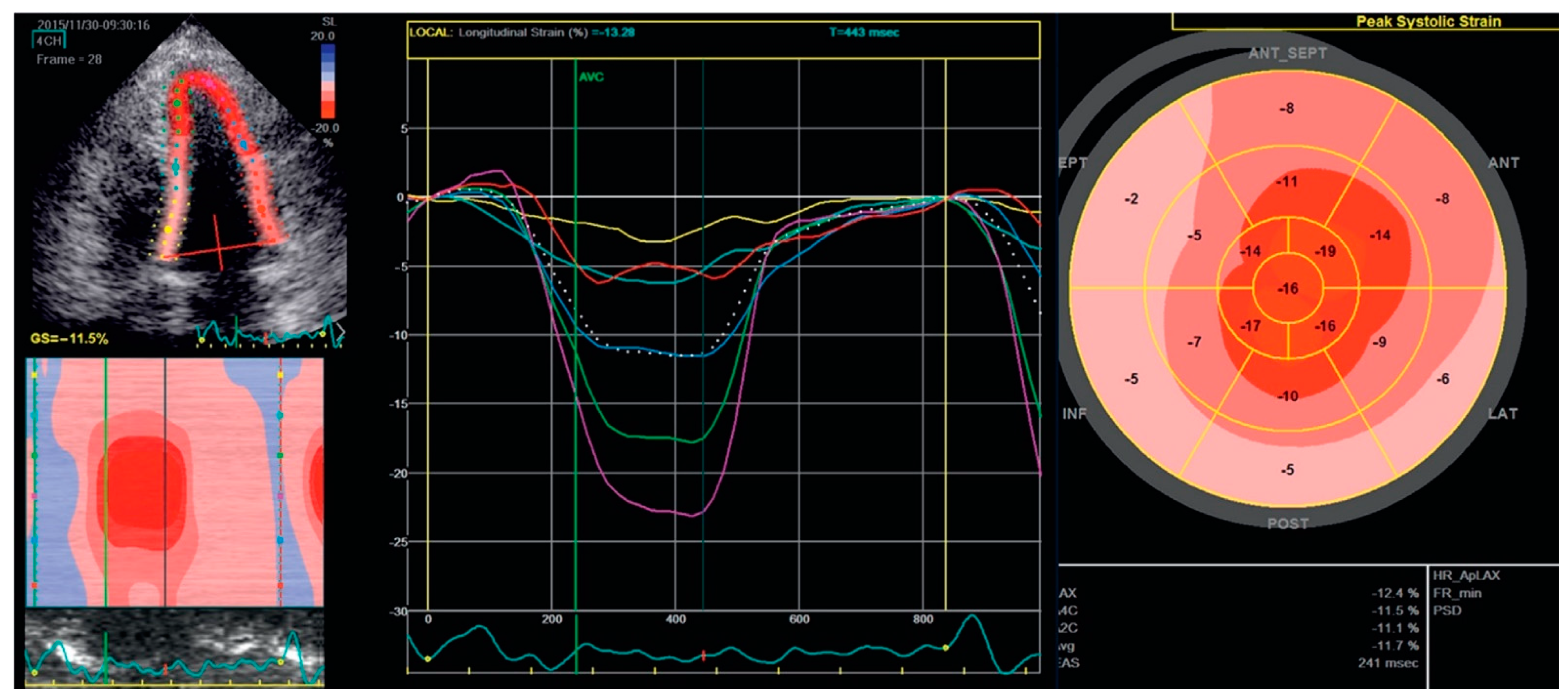
8. Echocardiography
9. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance
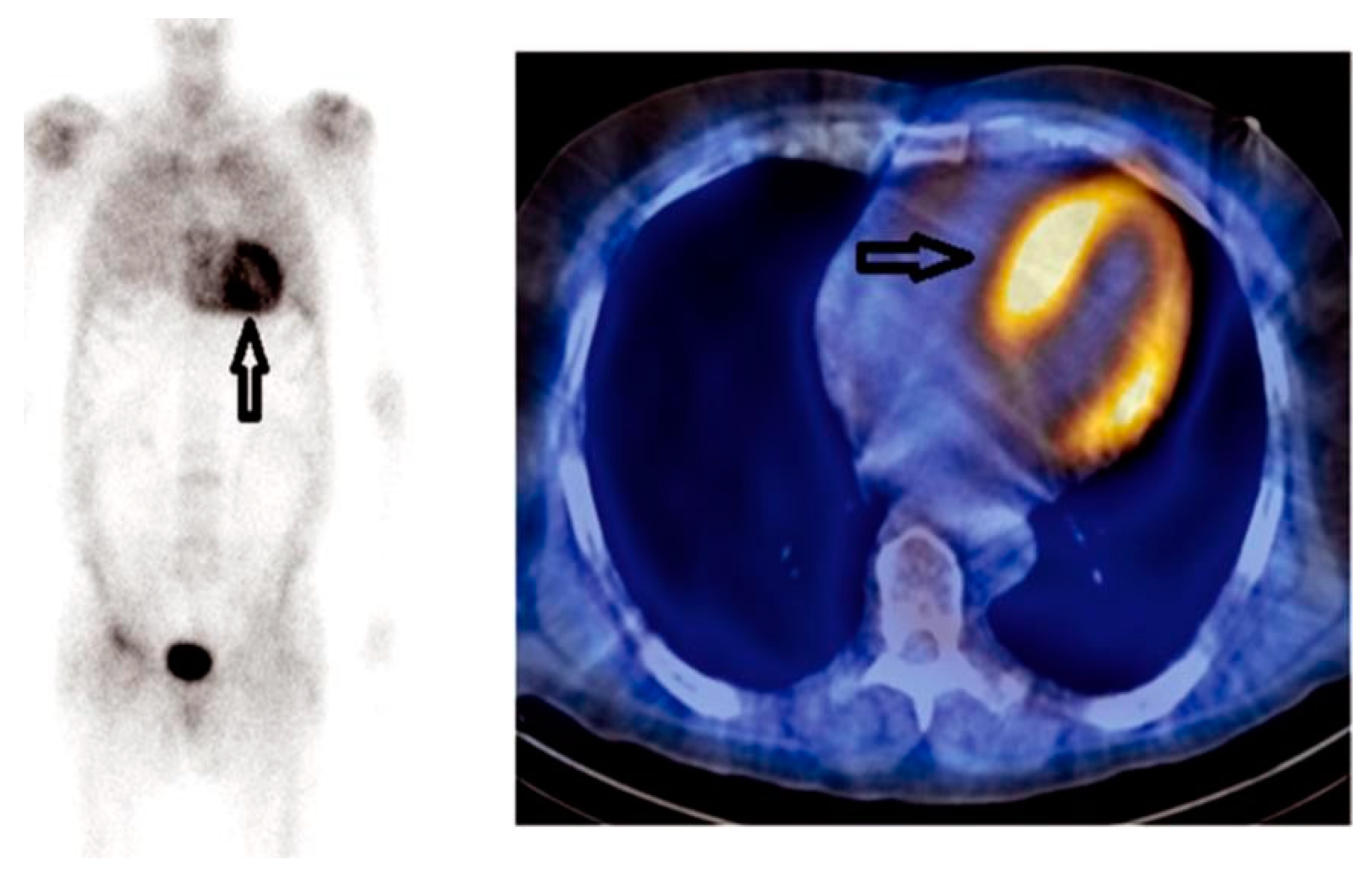
10. Radionuclide Imaging
11. Tissue Biopsy
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merlini, G.; Bellotti, V. Molecular mechanisms of amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, D.B.; Cookson, L.M.; Berges, A.C.; Barton, S.V.; Lane, T.; Ritter, J.M.; Fontana, M.; Moon, J.C.; Pinzani, M.; Gillmore, J.D.; et al. Therapeutic Clearance of Amyloid by Antibodies to Serum Amyloid P Component. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sipe, J.D.; Benson, M.D.; Buxbaum, J.N.; Ikeda, S.; Merlini, G.; Saraiva, M.J.; Westermark, P. Nomenclature 2014: Amyloid fibril proteins and clinical classification of the amyloidosis. Amyloid 2014, 21, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.S.; Elliott, P.; Comenzo, R.; Semigran, M.; Rapezzi, C. Addressing Common Questions Encountered in the Diagnosis and Management of Cardiac Amyloidosis. Circulation 2017, 135, 1357–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyle, R.A.; Linos, A.; Beard, C.M.; Linke, R.P.; Gertz, M.A.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Kurland, L.T. Incidence and natural history of primary systemic amyloidosis in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1950 through 1989. Blood 1992, 79, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quock, T.P.; Yan, T.; Chang, E.; Guthrie, S.; Broder, M.S. Epidemiology of AL amyloidosis: A real-world study using US claims data. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sperry, B.W.; Ikram, A.; Hachamovitch, R.; Valent, J.; Vranian, M.N.; Phelan, D.; Hanna, M. Efficacy of Chemotherapy for Light-Chain Amyloidosis in Patients Presenting With Symptomatic Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 2941–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J.P.; Hanna, M. Cardiac amyloidosis: An update on diagnosis and treatment. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2017, 84 (Suppl. 3), 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubrey, S.W.; Cha, K.; Anderson, J.; Chamarthi, B.; Reisinger, J.; Skinner, M.; Falk, R.H. The clinical features of immunoglobulin light-chain (AL) amyloidosis with heart involvement. QJM 1998, 91, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekijima, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Tokuda, T.; Ikeda, S.-I. Familial Transthyretin Amyloidosis; Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Eds.; University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993–2017; Updated 26 January 2012. Available online: https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.ccmain.ohionet.org/books/NBK1194/ (accessed on 16 November 2017).
- Vermeer, A.M.C.; Janssen, A.; Boorsma, P.C.; Mannens, M.M.A.M.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Christiaans, I. Transthyretin amyloidosis: A phenocopy of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Amyloid 2017, 24, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siddiqi, O.K.; Ruberg, F.L. Cardiac amyloidosis: An update on pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 28, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhi, S.; Quarta, C.C.; Milandri, A.; Lorenzini, M.; Gagliardi, C.; Manuzzi, L.; Bacchi-Reggiani, M.L.; Leone, O.; Ferlini, A.; Russo, A.; et al. Atrial fibrillation in amyloidotic cardiomyopathy: Prevalence, incidence, risk factors and prognostic role. Amyloid 2015, 22, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, E.T.; Jorge, A.J.L.; Souza CVJunior Andrade, T.R. Cardiac amyloidosis and its new clinical phenotype: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2017, 109, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Ando, Y.; Beirão, J.M.; Coelho, T.; Gertz, M.A.; Gillmore, J.D.; Hawkins, P.N.; Lousada, I.; Suhr, O.B.; Merlini, G. Expert consensus recommendations to improve diagnosis of ATTR amyloidosis with polyneuropathy. J Neurol. 2021, 268, 2109–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorbala, S.; Ando, Y.; Bokhari, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Falk, R.H.; Ferrari, V.A.; Fontana, M.; Gheysens, O.; Gillmore, J.D.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; et al. ASNC/AHA/ASE/EANM/HFSA/ISA/SCMR/SNMMI expert consensus recommendations for multimodality imaging in cardiac amyloidosis: Part 1 of 2-evidence base and standardized methods of imaging. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 2065–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladini, G.; Campana, C.; Klersy, C.; Balduini, A.; Vadacca, G.; Perfetti, V.; Perlini, S.; Obici, L.; Ascari, E.; d’Eril, G.M.; et al. Serum N-terminal probrain natriuretic peptide is a sensitive marker of myocardial dysfunction in AL amyloidosis. Circulation 2003, 107, 2440–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechalekar, A.D.; Gillmore, J.D.; Wassef, N.; Lachmann, H.J.; Whelan, C.; Hawkins, P.N. Abnormal N-terminal fragment of brain natriuretic peptide in patients with light chain amyloidosis without cardiac involvement at presentation is a risk factor for development of cardiac amyloidosis. Haematologica 2011, 96, 1079–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Z.W.; Tian, Z.; Kang, L.; Chen, T.B.; Fang, L.G.; Cheng, K.A.; Zeng, Y.; Fang, Q. Electrocardiographic and echocardiographic features of patients with primary cardiac amyloidosis. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2010, 38, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murtagh, B.; Hammill, S.C.; Gertz, M.A.; Kyle, R.A.; Tajik, A.J.; Grogan, M. Electrocardiographic findings in primary systemic amyloidosis and biopsy- proven cardiac involvement. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, J.D.; Gaasch, W.H.; McAdam, K.P. Amyloid cardiomyopathy: Characterization by a distinctive voltage/mass relation. Am. J. Cardiol. 1982, 49, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.A.; Comenzo, R.; Falk, R.H.; Fermand, J.P.; Hazenberg, B.P.; Hawkins, P.N.; Merlini, G.; Moreau, P.; Ronco, P.; Sanchorawala, V.; et al. Definition of organ involvement and treatment response in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis (AL): A consensus opinion from the 10th International Symposium on Amyloid and Amyloidosis, Tours, France, 18-22 April 2004. Am. J. Hematol. 2005, 79, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto-Garcia, L.; Reeder, G.S.; Kyle, R.A.; Wood, D.L.; Seward, J.B.; Naessens, J.; Offord, K.P.; Greipp, P.R.; Edwards, W.D.; Tajik, A.J. Echocardiographic findings in systemic amyloidosis: Spectrum of cardiac involvement and relation to survival. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1985, 6, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buss, S.J.; Emami, M.; Mereles, D.; Korosoglou, G.; Kristen, A.V.; Voss, A.; Schellberg, D.; Zugck, C.; Galuschky, C.; Giannitsis, E.; et al. Longitudinal left ventricular function for prediction of survival in systemic light-chain amyloidosis: Incremental value compared with clinical and biochemical markers. J Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koyama, J.; Ray-Sequin, P.A.; Falk, R.H. Longitudinal myocardial function assessed by tissue velocity, strain, and strain rate tissue Doppler echocardiography in patients with AL (primary) cardiac amyloidosis. Circulation 2003, 107, 2446–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, D.; Collier, P.; Thavendiranathan, P.; Popović, Z.B.; Hanna, M.; Plana, J.C.; Marwick, T.H.; Thomas, J.D. Relative apical sparing of longitudinal strain using two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography is both sensitive and specific for the diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis. Heart 2012, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldrini, M.; Cappelli, F.; Chacko, L.; Restrepo-Cordoba, M.A.; Lopez-Sainz, A.; Giannoni, A.; Aimo, A.; Baggiano, A.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Whelan, C.; et al. Multiparametric Echocardiography Scores for the Diagnosis of Cardiac Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tendler, A.; Helmke, S.; Teruya, S.; Alvarez, J.; Maurer, M.S. The myocardial contraction fraction is superior to ejection fraction in predicting survival in patients with AL cardiac amyloidosis. Amyloid 2015, 22, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Naharro, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, E.; Corovic, A.; Mirelis, J.G.; Baksi, A.J.; Moon, J.C.; Garcia-Pavia, P.; Gillmore, J.D.; Hawkins, P.N.; Fontana, M. High Prevalence of Intracardiac Thrombi in Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1733–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Edwards, W.D.; Oh, J.K.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Grogan, M.; Martinez, M.W.; Syed, I.S.; Hughes, D.A.; Lust, J.A.; Jaffe, A.S.; et al. Intracardiac thrombosis and embolism in patients with cardiac amyloidosis. Circulation 2007, 116, 2420–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellavia, D.; Pellikka, P.A.; Dispenzieri, A.; Scott, C.G.; Al-Zahrani, G.B.; Grogan, M.; Pitrolo, F.; Oh, J.K.; Miller, F.A., Jr. Comparison of right ventricular longitudinal strain imaging, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion, and cardiac biomarkers for early diagnosis of cardiac involvement and risk stratification in primary systematic (AL) amyloidosis: A 5-year cohort study. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 13, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rapezzi, C.; Lorenzini, M.; Longhi, S.; Milandri, A.; Gagliardi, C.; Bartolomei, I.; Salvi, F.; Maurer, M.S. Cardiac amyloidosis: The great pretender. Heart Fail. Rev. 2015, 20, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damy, T.; Maurer, M.S.; Rapezzi, C.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Karayal, O.N.; Mundayat, R.; Suhr, O.B.; Kristen, A.V. Clinical, ECG and echocardiographic clues to the diagnosis of TTR-related cardiomyopathy. Open Heart 2016, 3, e000289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maceira, A.M.; Joshi, J.; Prasad, S.K.; Moon, J.C.; Perugini, E.; Harding, I.; Sheppard, M.N.; Poole-Wilson, P.A.; Hawkins, P.N.; Pennell, D.J. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in cardiac amyloidosis. Circulation 2005, 111, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, T.; Jambhekar, K.; Shaikh, R.; Lensing, S.; Viswamitra, S. Utility of the inversion scout sequence (TI scout) in diagnosing myocardial amyloid infiltration. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 29, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fontana, M.; Pica, S.; Reant, P.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Treibel, T.A.; Banypersad, S.M.; Maestrini, V.; Barcella, W.; Rosmini, S.; Bulluck, H.; et al. Prognostic Value of Late Gadolinium Enhancement Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Cardiac Amyloidosis. Circulation 2015, 132, 1570–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelsberg, H.; Mahrholdt, H.; Deluigi, C.C.; Yilmaz, A.; Kispert, E.M.; Greulich, S.; Klingel, K.; Kandolf, R.; Sechtem, U. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in clinically suspected cardiac amyloidosis: Noninvasive imaging compared to endomyocardial biopsy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Syed, I.S.; Glockner, J.F.; Feng, D.; Araoz, P.A.; Martinez, M.W.; Edwards, W.D.; Gertz, M.A.; Dispenzieri, A.; Oh, J.K.; Bellavia, D.; et al. Role of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in the detection of cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2010, 3, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.A.; Kim, H.W.; Shah, D.; Fine, N.; Kim, K.Y.; Wendell, D.C.; Al-Jaroudi, W.; Parker, M.; Patel, M.; Gwadry-Sridhar, F.; et al. CMR imaging with rapid visual T1 assessment predicts mortality in patients suspected of cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruberg, F.L.; Appelbaum, E.; Davidoff, R.; Ozonoff, A.; Kissinger, K.V.; Harrigan, C.; Skinner, M.; Manning, W.J. Diagnostic and prognostic utility of cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in light-chain cardiac amyloidosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 103, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Austin, B.A.; Tang, W.H.; Rodriguez, E.R.; Tan, C.; Flamm, S.D.; Taylor, D.O.; Starling, R.C.; Desai, M.Y. Delayed hyper-enhancement magnetic resonance imaging provides incremental diagnostic and prognostic utility in suspected cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2009, 2, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontana, M. Systemic Amyloidosis by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. Ph.D. Thesis, UCL University College London, London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Banypersad, S.M.; Moon, J.C.; Whelan, C.; Hawkins, P.N.; Wechalekar, A.D. Updates in cardiac amyloidosis: A review. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hutt, D.F.; Quigley, A.M.; Page, J.; Hall, M.L.; Burniston, M.; Gopaul, D.; Lane, T.; Whelan, C.J.; Lachmann, H.J.; Gillmore, J.D.; et al. Utility and limitations of 3,3-diphosphono-1,2- propanodicarboxylic acid scintigraphy in systemic amyloidosis. Eur Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 15, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappelli, F.; Gallini, C.; Di Mario, C.; Costanzo, E.N.; Vaggelli, L.; Tutino, F.; Ciaccio, A.; Bartolini, S.; Angelotti, P.; Frusconi, S.; et al. Accuracy of 99mTc-Hydroxymethylene diphosphonate scintigraphy for diagnosis of transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2019, 26, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galat, A.; Rosso, J.; Guellich, A.; Van Der Gucht, A.; Rappeneau, S.; Bodez, D.; Guendouz, S.; Tissot, C.M.; Hittinger, L.; Dubois-Randé, J.L.; et al. Usefulness of (99m)Tc-HMDP scintigraphy for the etiologic diagnosis and prognosis of cardiac amyloidosis. Amyloid 2015, 22, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillmore, J.D.; Maurer, M.S.; Falk, R.H.; Merlini, G.; Damy, T.; Dispenzieri, A.; Wechalekar, A.D.; Berk, J.L.; Quarta, C.C.; Grogan, M.; et al. Nonbiopsy Diagnosis of Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Circulation 2016, 133, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, N.M.; Arruda-Olson, A.M.; Dispenzieri, A.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Gertz, M.A.; Kyle, R.A.; Swiecicki, P.L.; Scott, C.G.; Grogan, M. Yield of noncardiac biopsy for the diagnosis of transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 113, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Gucht, A.; Cottereau, A.S.; Abulizi, M.; Guellich, A.; Blanc-Durand, P.; Israel, J.M.; Galat, A.; Plante-Bordeneuve, V.; Dubois-Randé, J.L.; Bodez, D.; et al. Apical sparing pattern of left ventricular myocardial 99mTc-HMDP uptake in patients with transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2017, 25, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Migliaccio, M.G.; Iodice, F.; Di Mauro, M.; Iannuzzi, A.; Pacileo, R.; Caiazza, M.; Esposito, A. Cardiac Amyloidosis: Diagnostic Tools for a Challenging Disease. Cardiogenetics 2021, 11, 111-121. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11030012
Migliaccio MG, Iodice F, Di Mauro M, Iannuzzi A, Pacileo R, Caiazza M, Esposito A. Cardiac Amyloidosis: Diagnostic Tools for a Challenging Disease. Cardiogenetics. 2021; 11(3):111-121. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleMigliaccio, Marco Giuseppe, Franco Iodice, Marco Di Mauro, Angela Iannuzzi, Roberta Pacileo, Martina Caiazza, and Augusto Esposito. 2021. "Cardiac Amyloidosis: Diagnostic Tools for a Challenging Disease" Cardiogenetics 11, no. 3: 111-121. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11030012
APA StyleMigliaccio, M. G., Iodice, F., Di Mauro, M., Iannuzzi, A., Pacileo, R., Caiazza, M., & Esposito, A. (2021). Cardiac Amyloidosis: Diagnostic Tools for a Challenging Disease. Cardiogenetics, 11(3), 111-121. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11030012






