A Vehicle Routing Optimization Framework of a Property City Based on an Intelligent Algorithm and Its Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
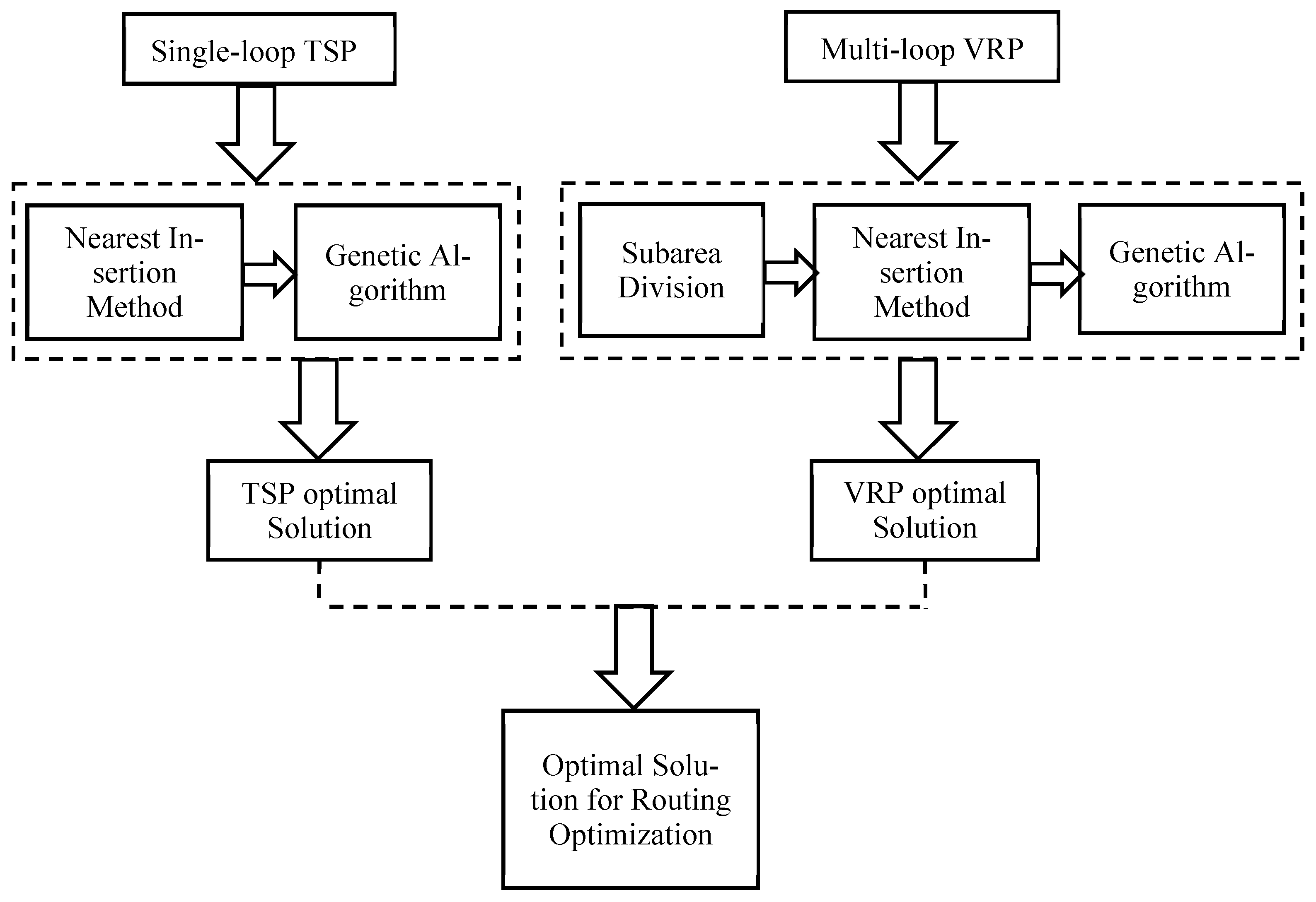
2. Analysis Framework
2.1. Single-Area and Multi-Area Transportation
2.2. Overall Analysis Framework Design
3. Basic Principles
3.1. TSP Model and Nearest Insertion Method
3.2. VRP Model and Its Solution
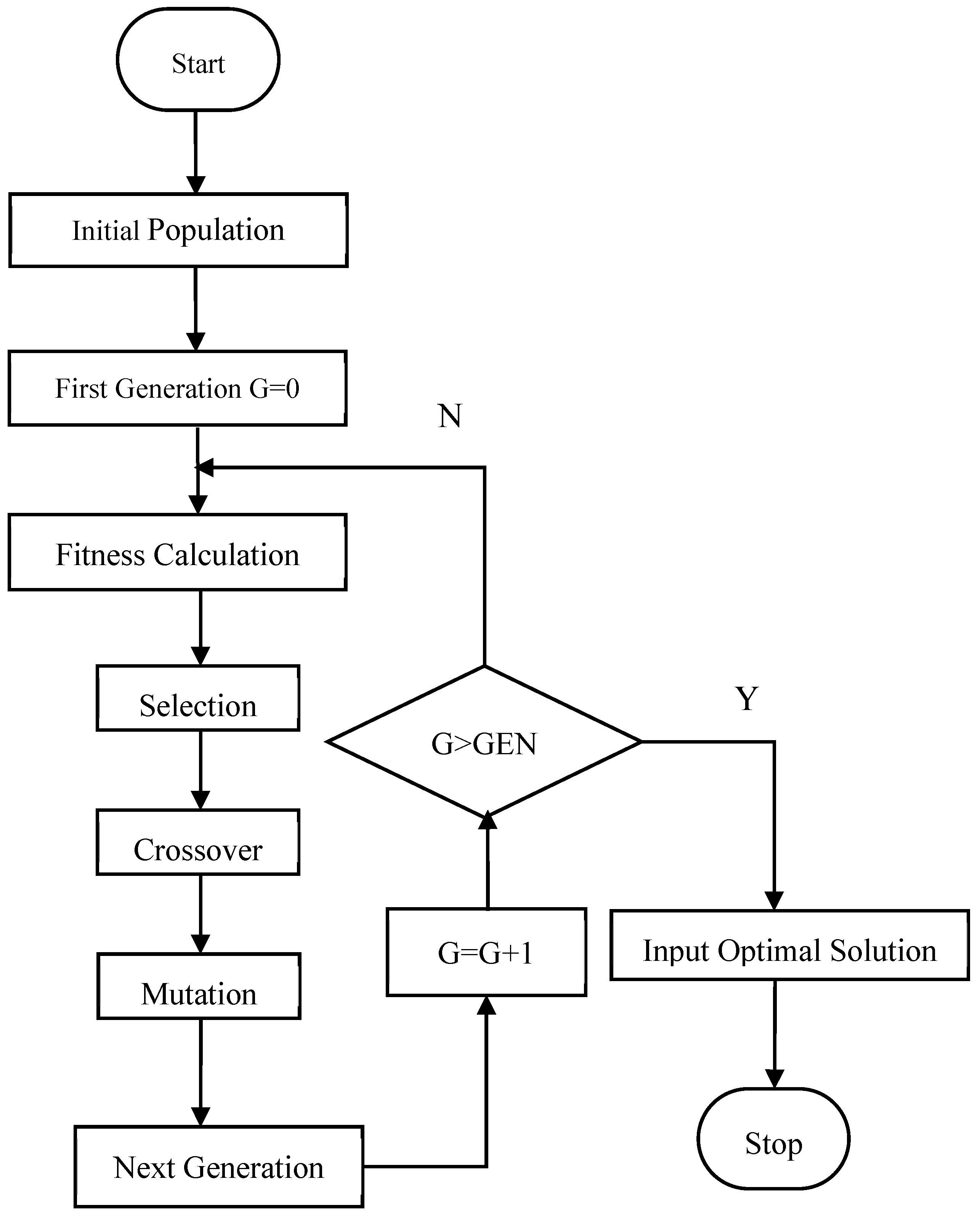
3.3. Genetic Algorithm
4. Example Analysis
4.1. Data Collection
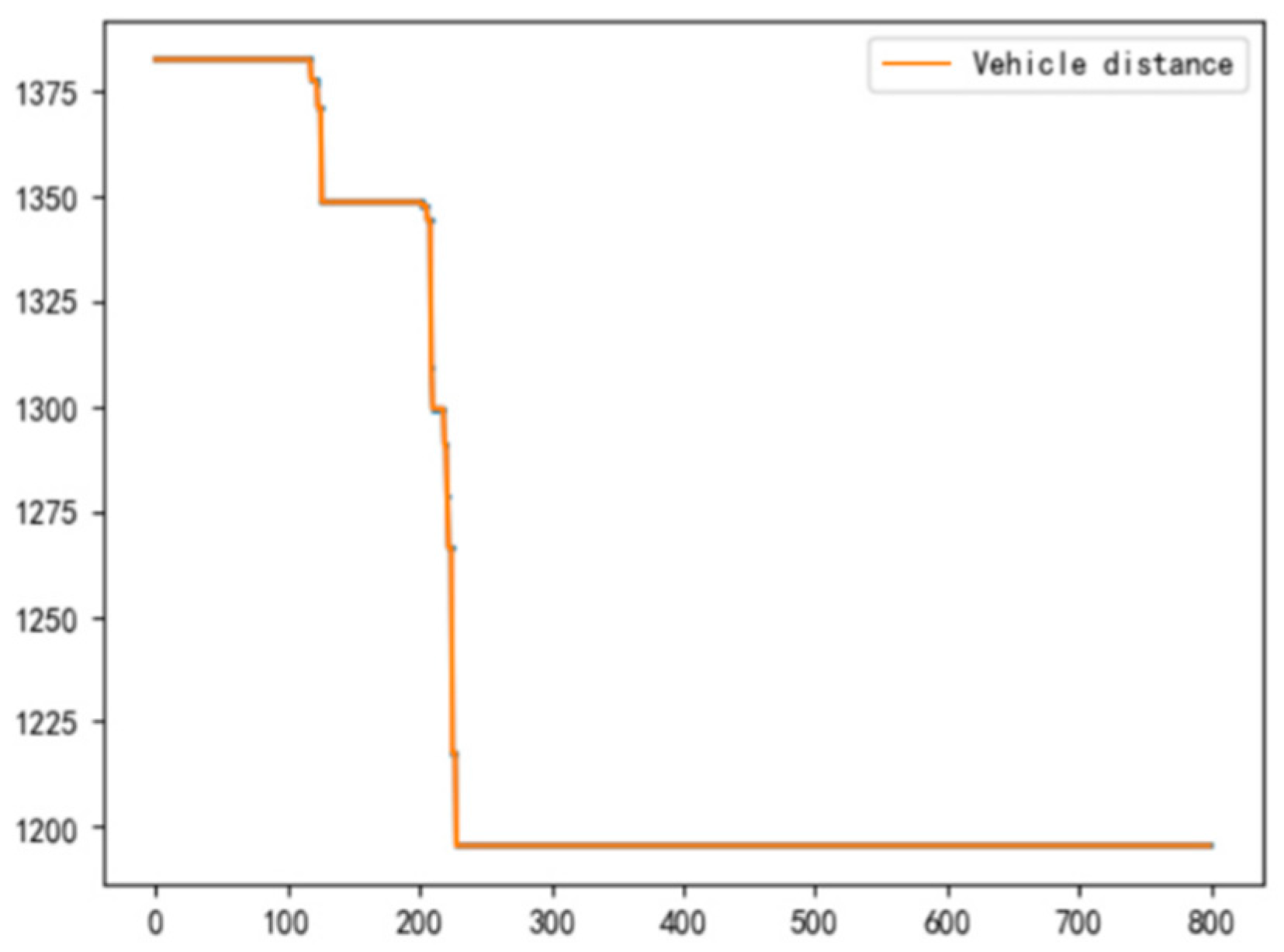
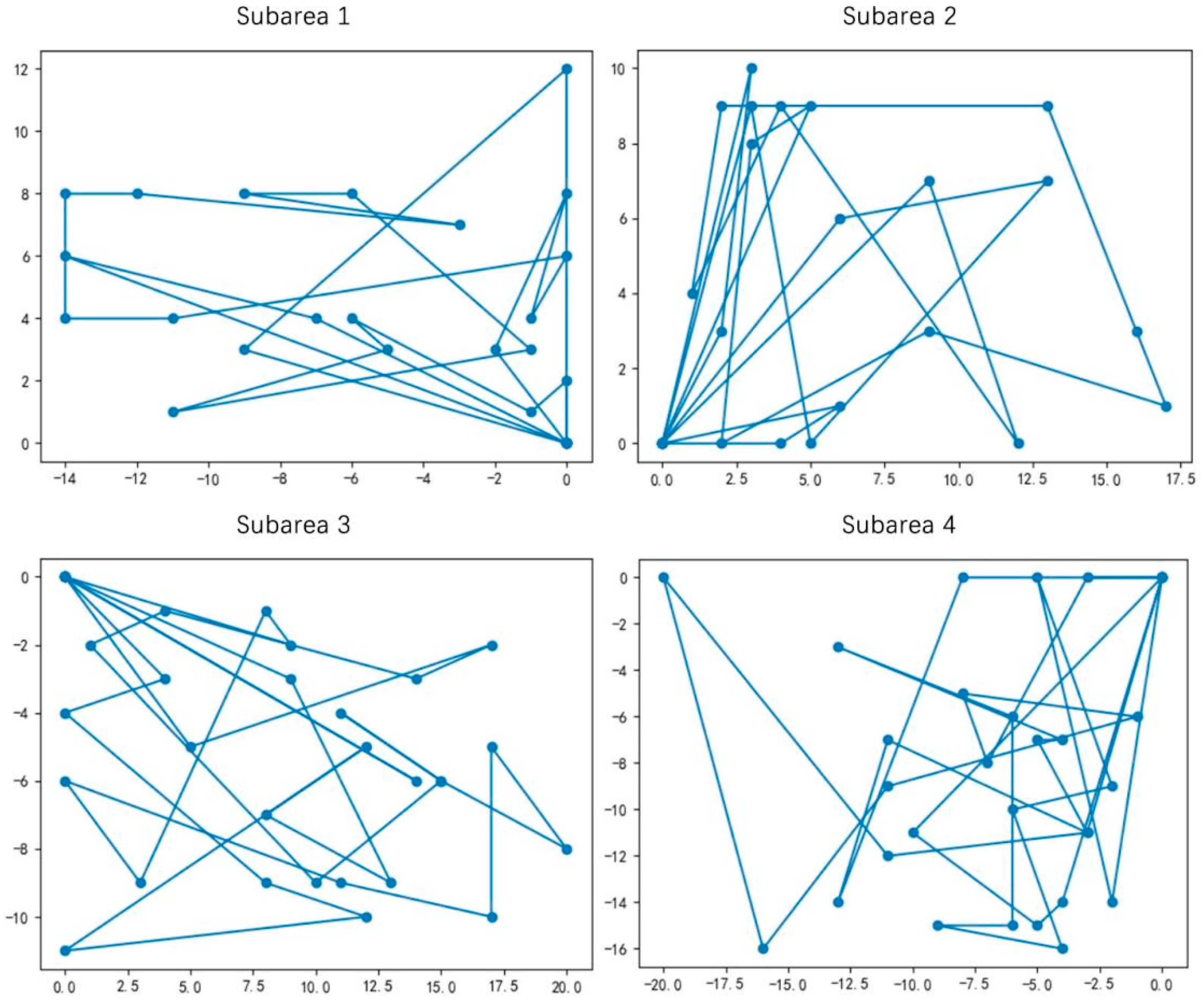
4.2. Optimization Analysis of Single-Area Vehicle Transportation
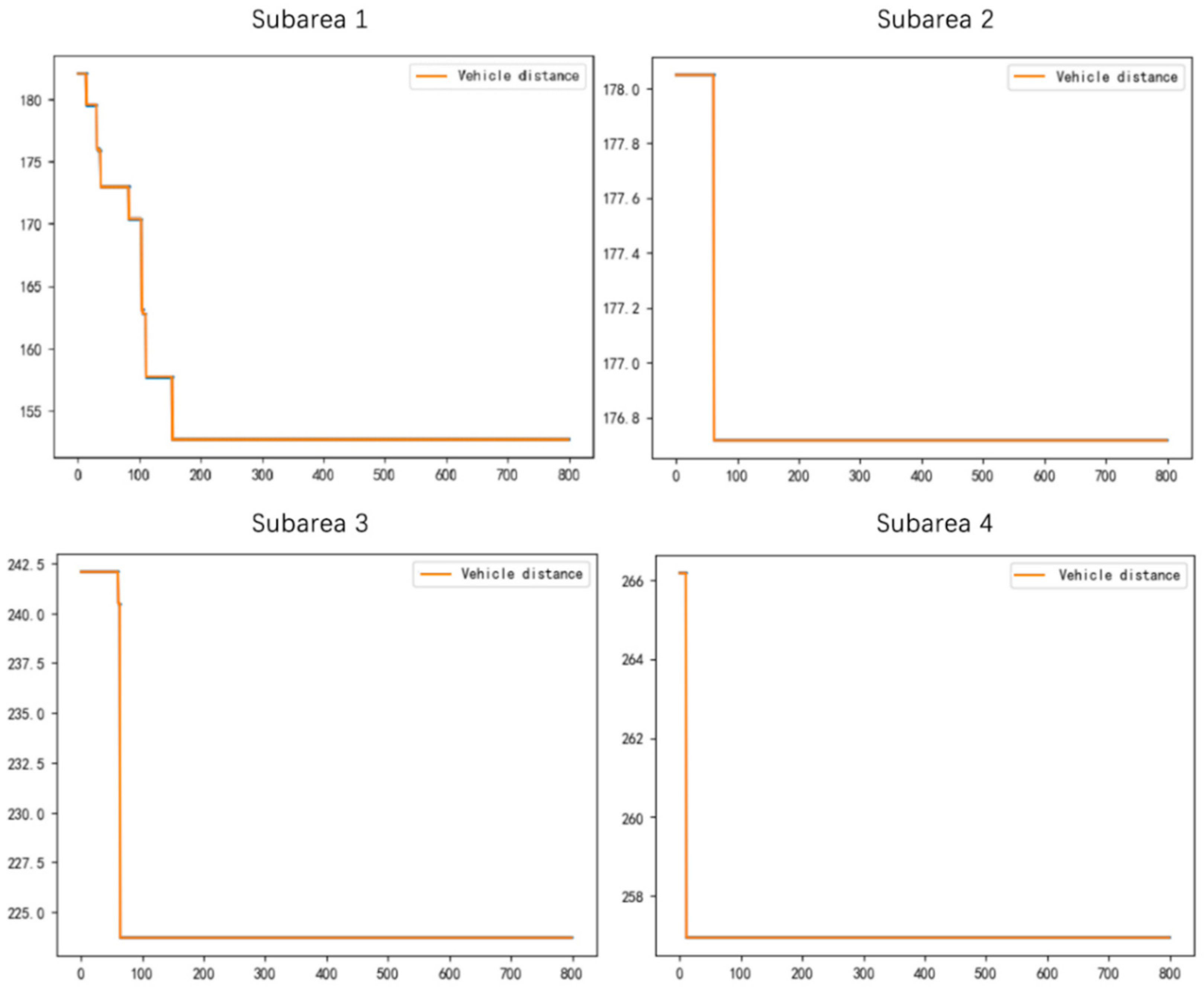
4.3. Multi-Area Vehicle Transportation Optimization Analysis
4.4. Comparative Analysis of Vehicle Transportation Costs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niu, G. Hengqin property city mode to achieve intelligent empowerment. People Daily Online, 8 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Tu, K.; Chiang, T. Establish a customer property service strategy framework. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2021, 25, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Tan, Y.; Lin, H. Review on the model of property city under the background of urban governance modernization. Housing Real Est. 2023, 9, 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, T.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, X.; Wen, F. Theory and practice of property city--Research on innovative mode of urban governance in Hengqin New District. SSAP 2021, 35–62. Available online: https://xiaoshuo.qq.com/detail/1054865401 (accessed on 21 October 2025).
- Huang, Y.H.; Lee, P.C. Role of property management in service demands of elderly residents of apartment complexes. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2020, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.; Jiang, L.; Xu, Z.; Xu, J.; Herrera, F. Herrera, A linear programming method for multiple criteria decision making with probabilistic linguistic information. Inf. Sci. 2017, 415, 341–355. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, S.; Ye, A.; Su, W.; Chen, M.; Llopis-Albert, C. Llopis-Albert, Site evaluation of subsea tunnels with sightseeing function based on dynamic complex MARCOS method. Technol Forecast. Soc. 2024, 199, 123041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Su, W.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, S. Evaluation and selection model of community group purchase platform based on WEPLPA-CPT-EDAS method. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 172, 108573. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, P. Dynamic consensus of large group emergency decision-making under dual-trust relationship-based social network. Inf. Sci. 2022, 615, 58–89. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.; Chiclana, F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Herrera-Viedma, E. A bilateral negotiation mechanism by dynamic harmony threshold for group consensus decision making. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Li, D.; Yu, G. A general multi-attribute multi-scale decision making method based on dynamic LINMAP for property perceived service quality evaluation. Technol. Econ. Dev. Eco. 2020, 26, 1052–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Liu, L.; Hu, Q.; Zeng, S.; Hu, Z. A property perceived service quality evaluation method for public buildings based on multisource heterogeneous information fusion. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 122, 106070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzig, G.; Ramser, J. The truck dispatching problem. Manag. Sci. 1959, 10, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Ong, Y.; Heng, C.; Tan, P.; Zhang, N. City vehicle routing problem (city VRP): A review. IEEE T. Intell. Transp. 2015, 16, 1654–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassan, N. A reactive Tabu search for the vehicle routing problem. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2006, 57, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fang, M.; Chen, L.; Xu, G.; Du, Y.; Zhang, C. Reinforcement learning with multiple relational attention for solving vehicle routing problems. IEEE T. Cybern. 2021, 52, 11107–11120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Hao, Y.; Cao, J. Learning to traverse over graphs with a monte carlo tree search-based self-play framework. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 105, 104422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rodríguez, R.; Hernández-Aguirre, A. Simulation optimization for the vehicle routing problem with time windows using a Bayesian network as a probability model. Int. J Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2016, 85, 2505–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Fang, Y.; Yuan, J. Mutstion ant colony algorithm for multiple-depot multiple-types vehicle routing problems with shortest finfish time. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2011, 31, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Fernández, E.; Coello, C.; Troncoso, F. An adaptive evolutionary algorithm based on typical chess problems for tuning a chess evaluation function. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2012, 62, 306–317. [Google Scholar]
- Fayad, C.; Webb, P. Development of a hybrid crisp-fuzzy logic algorithm optimised by genetic algorithms for path-planning of an autonomous mobile robot. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2006, 17, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Guo, W.; Tickle, K. Solving the traveling salesman problem using cooperative genetic ant systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 5006–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applegate, D.; Bixby, R.; Vaek, C.; Cook, W. The Traveling Salesman Problem: A Computational Study; PUP: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bouhmala, N. A multilevel genetic algorithm for the traveling salesman problem. ENDM 2003, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, G.; Singh, A. Two evolutionary approaches with objective-specific variation operators for vehicle routing problem with time windows and quality of service objectives. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 134, 109964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutumlu, B.; Sarac, T. A mip model and a hybrid genetic algorithm for flexible job-shop scheduling problem with job-splitting. Comput. Oper. Res. 2023, 155, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.; Nguyen-Duy-Nhat, V.; Nguyen, H.; Shin, O. Ddpg-based optimization for zero-forcing transmission in uav-relay massive mimo networks. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2024, 4, 3386595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D. Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and Machine Learning; Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Talbi, H.; Draa, A.; Batouche, M. A new quantum-inspired genetic algorithm for solving the travelling salesman problem. IEEE 2004, 3, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Uthayasuriyan, A.; Hema, C.; Kavvin, U.; Mahitha, S.; Jeyakumar, G. A comparative study on genetic algorithm and reinforcement learning to solve the traveling salesman problem. RRCS 2023, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, I.; Baba Mohd, S.; Iksan, N. Applied genetic algorithm for solving rich VRP. Appl Artif Intell. 2014, 28, 957–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaira, G.; Kurasova, O. Genetic algorithm for vrp with constraints based on feasible insertion. Informatica 2014, 25, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, Q. A hybrid code genetic algorithm for vrp in public-private emergency collaborations. Int. J. simul. Model 2022, 21, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, D.; Stearns, R.; Lewis, P. An analysis of several heuristics for the traveling salesman problem. Siam. J. Comput. 1977, 6, 563–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cost Type | Unit Price |
|---|---|
| Running fuel consumption | 7.5 yuan/L |
| Fuel per kilometer | 0.5 L/km |
| Water price | 1.5 yuan/ton |
| Water per kilometer | 0.8 tons/km |
| Labor cost | 30 yuan/h |
| Time cost | 50 yuan/h |
| Solution Result | Nearest Insertion Method | Genetic Algorithm |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum mileage (km) | 135.2 | 119.5 |
| Oil consumption (L) | 67.6 | 59.8 |
| Time required (hours) | 6.7 | 5.8 |
| Water consumption (tons) | 108.1 | 95.6 |
| Items | Mileage (km) |
|---|---|
| Subarea 1 | 17.27 |
| Subarea 2 | 18.21 |
| Subarea 3 | 22.96 |
| Subarea 4 | 28.51 |
| Total area mileage | 86.95 |
| Items | Mileage (km) |
|---|---|
| Subarea 1 | 14.24 |
| Subarea 2 | 13.26 |
| Subarea 3 | 20.04 |
| Subarea 4 | 21.55 |
| Total area mileage | 69.10 |
| Solution Result | Nearest Insertion | Genetic Algorithm |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum mileage (km) | 87.0 | 69.1 |
| Oil consumption (L) | 43.5 | 29.9 |
| Time required (hours) | 4.3 | 3.3 |
| Water consumption (tons) | 69.6 | 55.3 |
| Algorithm Type | Number of Vehicles | Area Size of Operation | Number of Service Points | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 50 | 200 | |||
| TSP (single vehicle) | 1 vehicle | 10 km2 | 12.8~15.3 km | 38.5~45.2 km | 102.6~123.5 km |
| 50 km2 | 28.6~33.5 km | 85.7~98.3 km | 228.4~265.9 km | ||
| 200 km2 | 57.2~67.1 km | 171.3~196.7 km | 456.8~531.8 km | ||
| VRP (multiple vehicles) | 2 vehicles | 10 km2 | 8.3~10.5 km | 24.6~29.1 km | 65.8~78.3 km |
| 50 km2 | 18.5~22.3 km | 55.2~64.1 km | 146.8~172.5 km | ||
| 200 km2 | 37.0~44.5 km | 110.5~128.2 km | 293.6~345.0 km | ||
| 3 vehicles | 10 km2 | 6.5~8.2 km | 18.9~23.3 km | 50.2~61.4 km | |
| 50 km2 | 14.5~17.8 km | 42.5~51.3 km | 113.2~135.7 km | ||
| 200 km2 | 29.0~35.6 km | 85.0~102.6 km | 226.4~271.4 km | ||
| 5 vehicles | 10 km2 | 5.8~7.5 km | 15.3~19.6 km | 39.8~49.7 km | |
| 50 km2 | 12.8~16.1 km | 34.6~42.7 km | 90.5~112.3 km | ||
| 200 km2 | 25.6~32.2 km | 69.2~85.4 km | 181.0~224.6 km | ||
| Cost Type | Single-Area Cost | Multi-Area Cost | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nearest Insertion | Genetic Algorithm | Nearest Insertion | Genetic Algorithm | |
| Fuel cost | 507.0 | 448.1 | 326.3 | 259.1 |
| Water cost | 162.2 | 143.4 | 104.4 | 82.9 |
| Labor cost | 201.0 | 174.0 | 129.0 | 99.0 |
| Time cost | 335.0 | 290.0 | 215.0 | 165.0 |
| Total cost | 1205.2 | 1055.5 | 774.65 | 606.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Fang, K.; An, J.; Zuo, W.; Lin, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, L. A Vehicle Routing Optimization Framework of a Property City Based on an Intelligent Algorithm and Its Application. World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010025
Ye J, Fang K, An J, Zuo W, Lin Y, Lin J, Chen L. A Vehicle Routing Optimization Framework of a Property City Based on an Intelligent Algorithm and Its Application. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2026; 17(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Junhong, Kai Fang, Jingjing An, Wenjin Zuo, Yihang Lin, Jintao Lin, and Linfeng Chen. 2026. "A Vehicle Routing Optimization Framework of a Property City Based on an Intelligent Algorithm and Its Application" World Electric Vehicle Journal 17, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010025
APA StyleYe, J., Fang, K., An, J., Zuo, W., Lin, Y., Lin, J., & Chen, L. (2026). A Vehicle Routing Optimization Framework of a Property City Based on an Intelligent Algorithm and Its Application. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 17(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010025






