Railway Fastener Defect Detection Model Based on Dual Attention and MobileNetv3
Abstract
1. Introduction
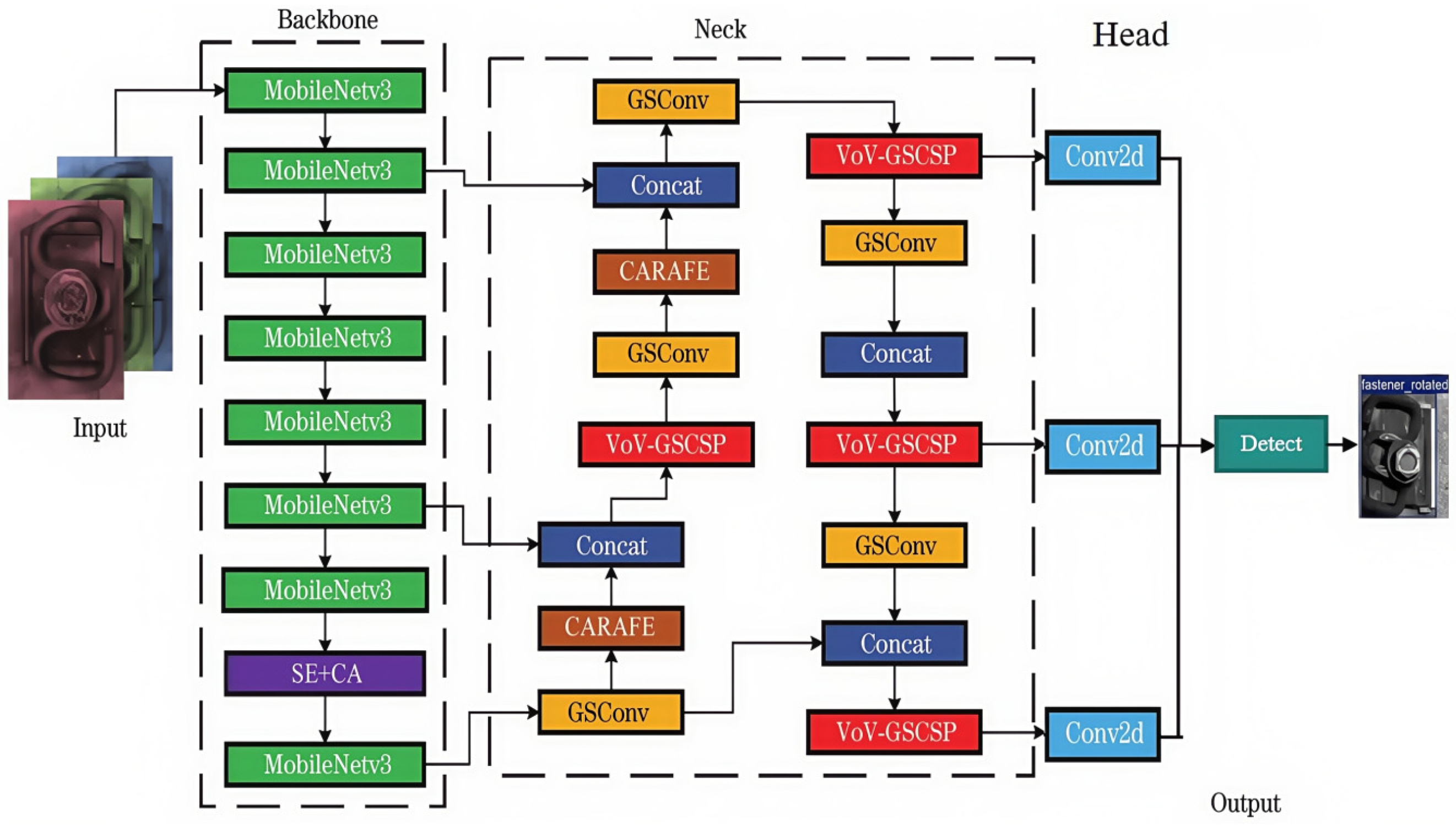
2. YOLOv5 Improvement
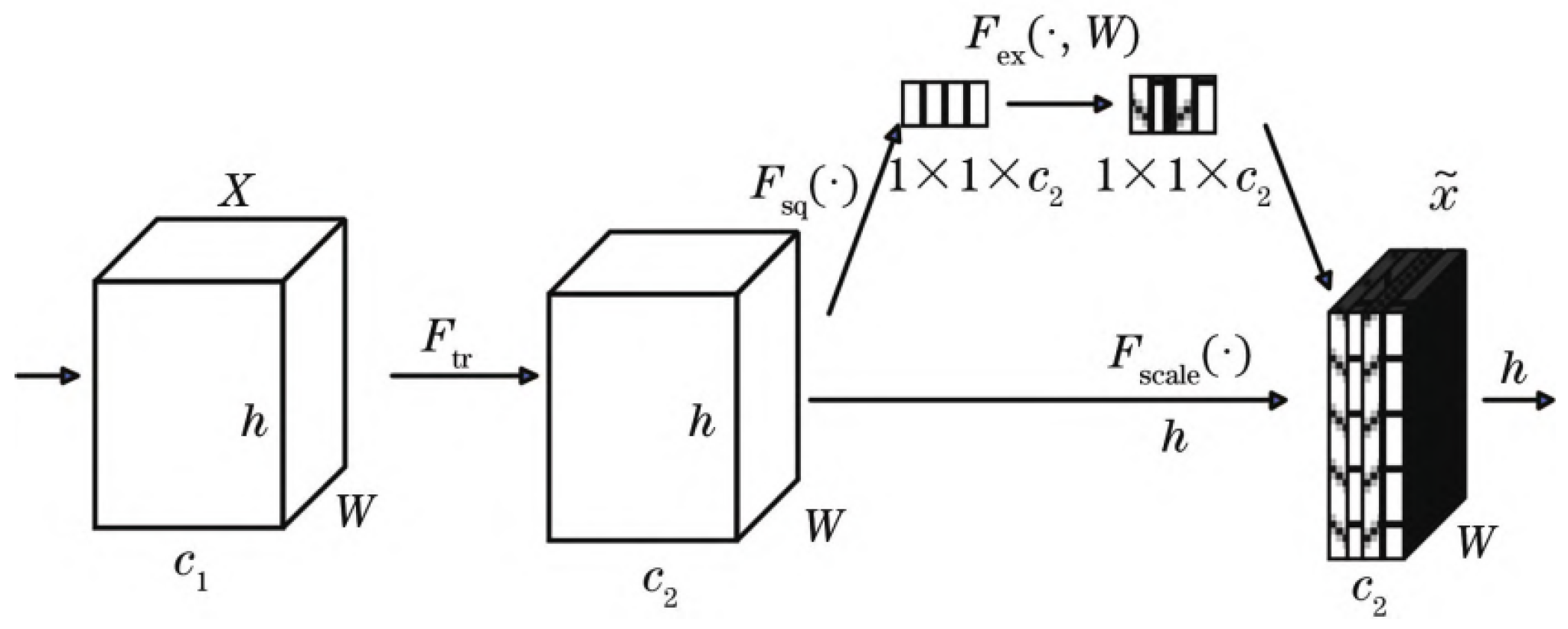
2.1. Attentional Mechanisms
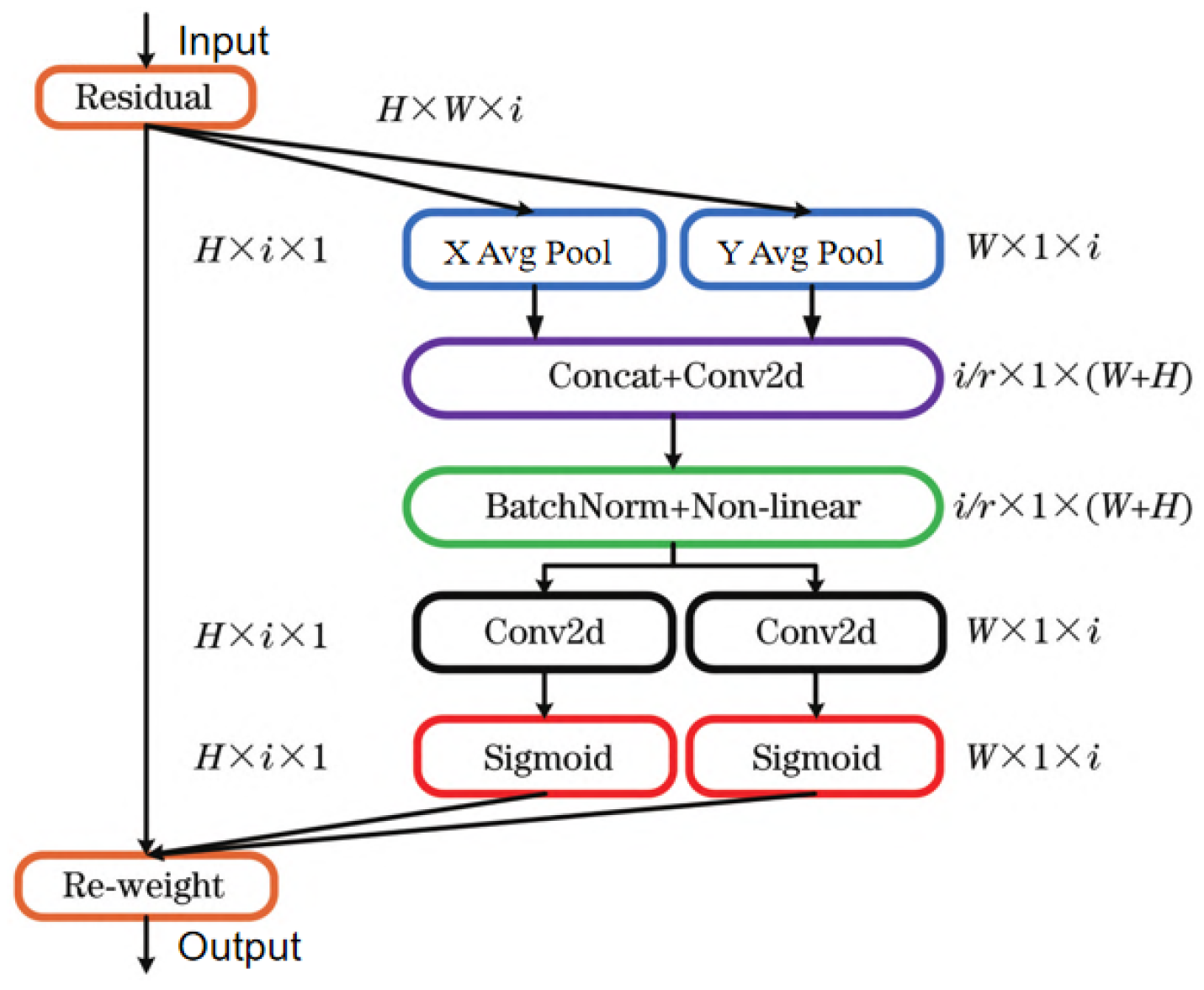
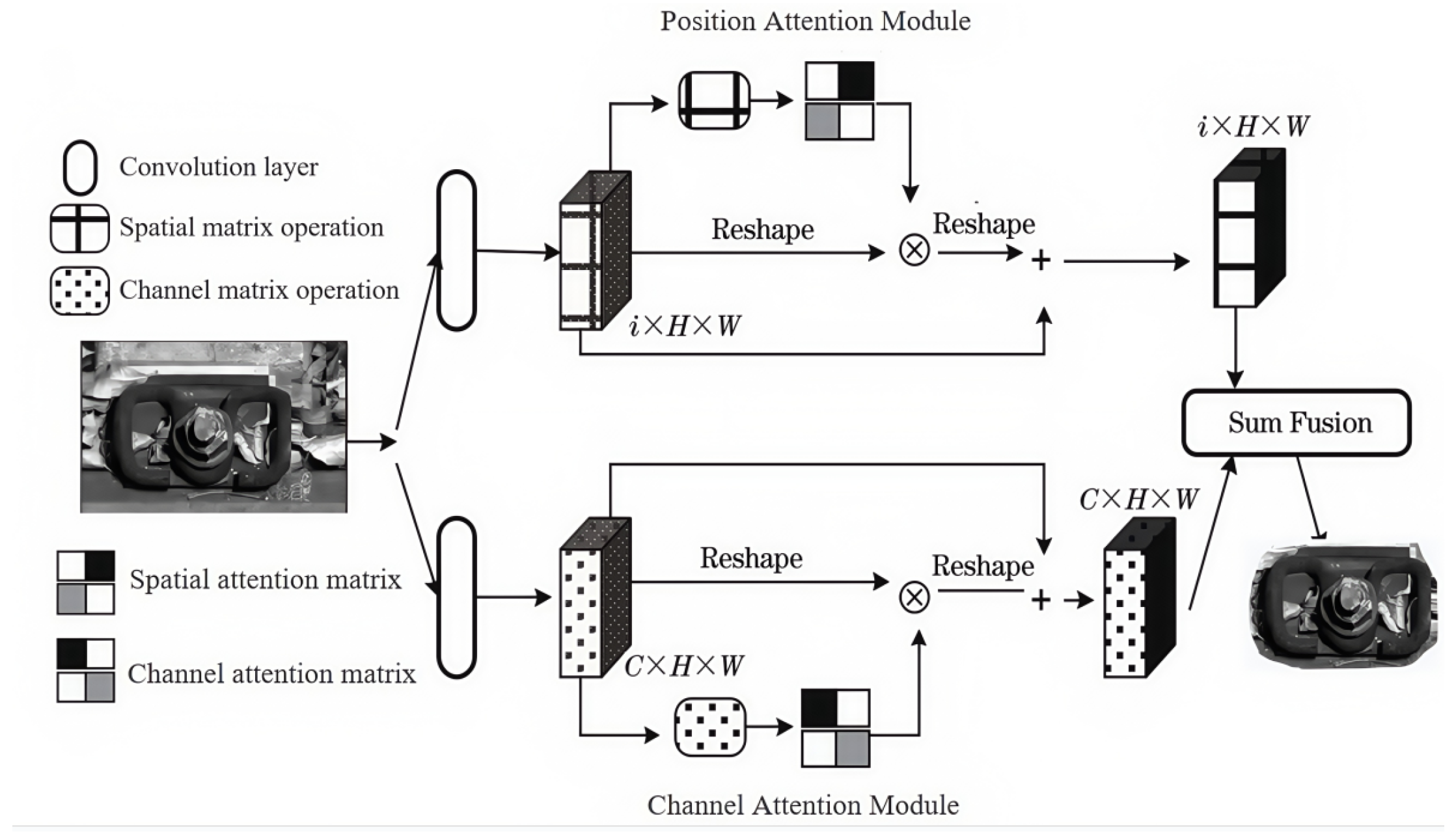
2.2. Dual Attention Mechanism
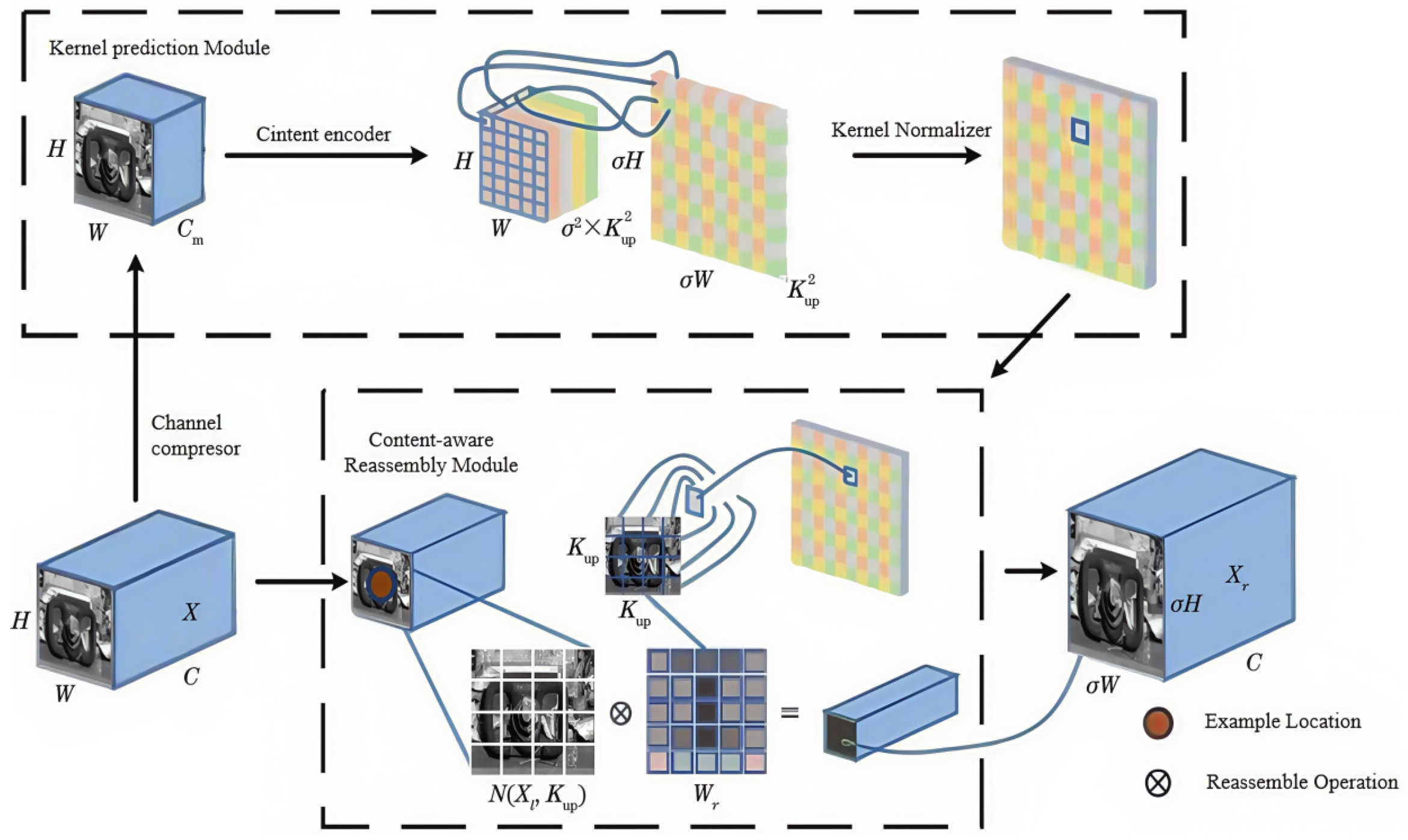
2.3. Application of Lightweight Upsampling Operator CARAFE
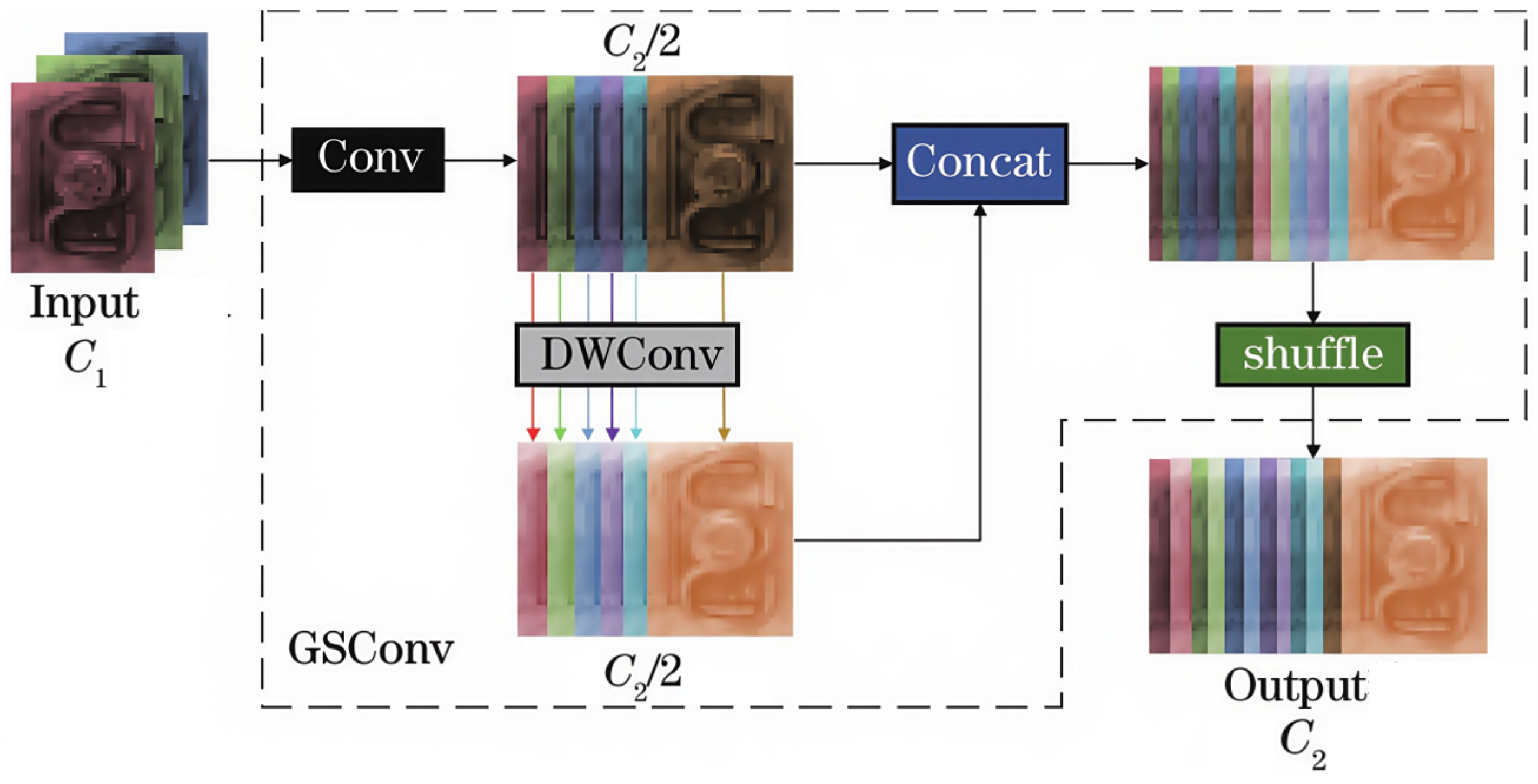
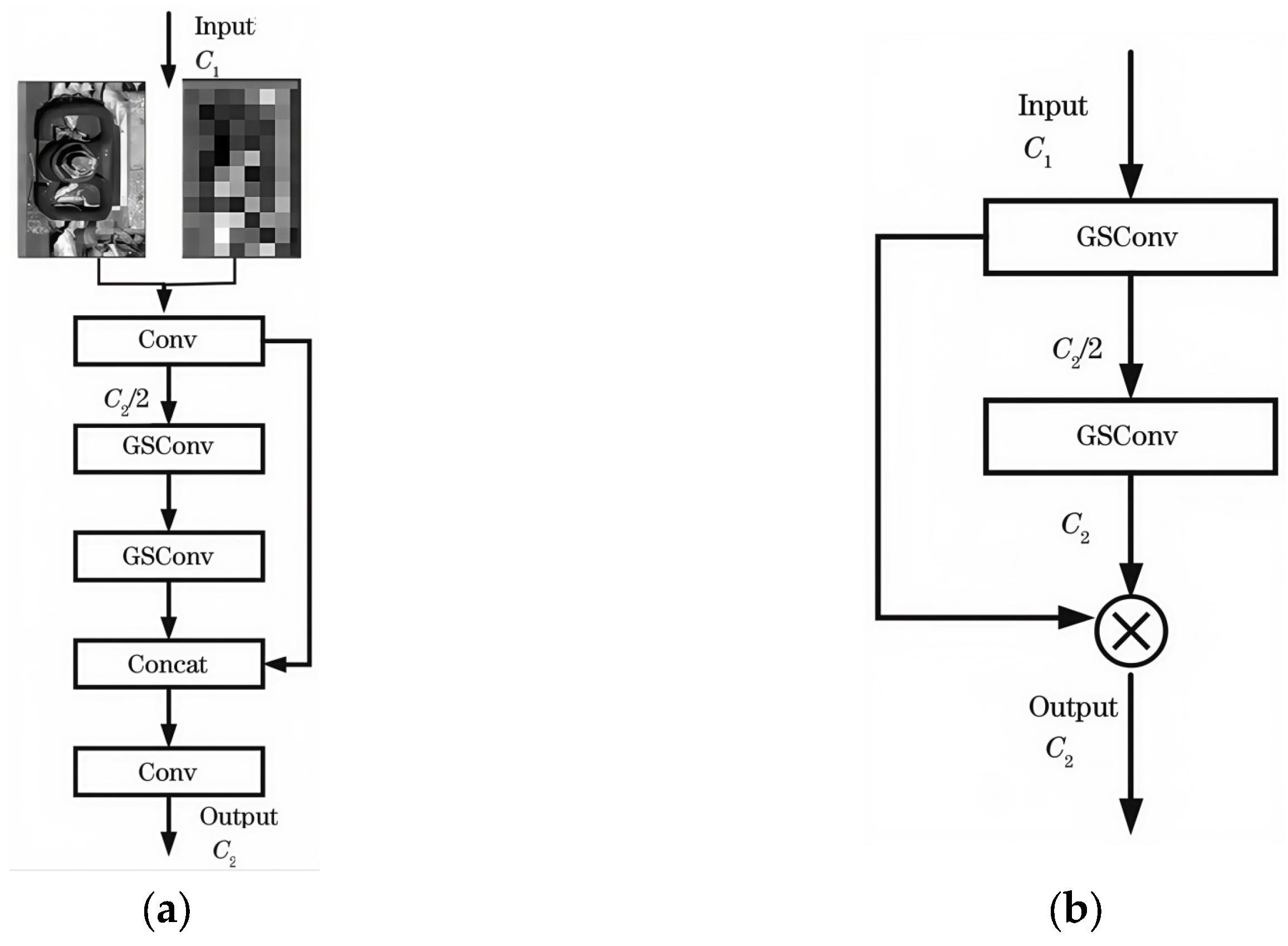
2.4. Lightweight Integration of MobileNetV3 Backbone with GSSN Architecture
3. Dataset Preparation and Experimental Setup
3.1. Dataset Preparation and Environment Setup
3.2. Training Parameters and Evaluation Metrics
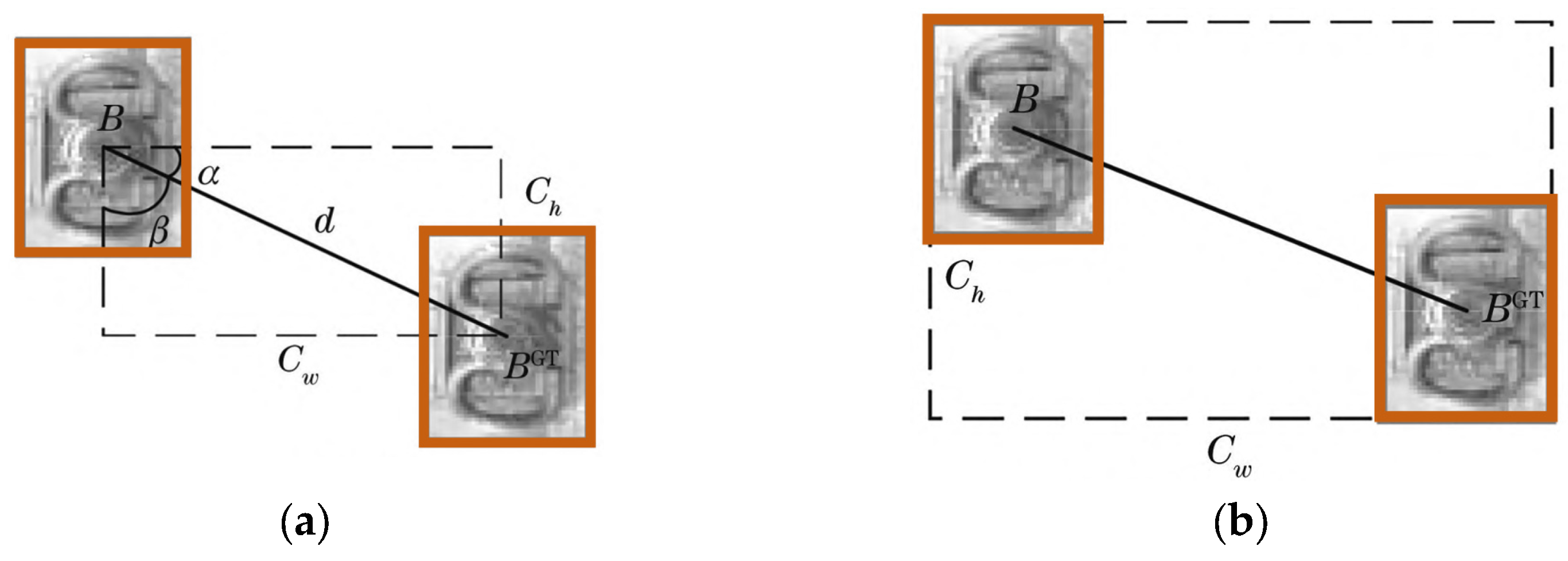
3.3. Coordinate Loss Function Configuration
4. Experimental Results Analysis
4.1. Model Training Results
4.2. Comparative Experiments on Improvement Points
4.3. Ablation Experiments
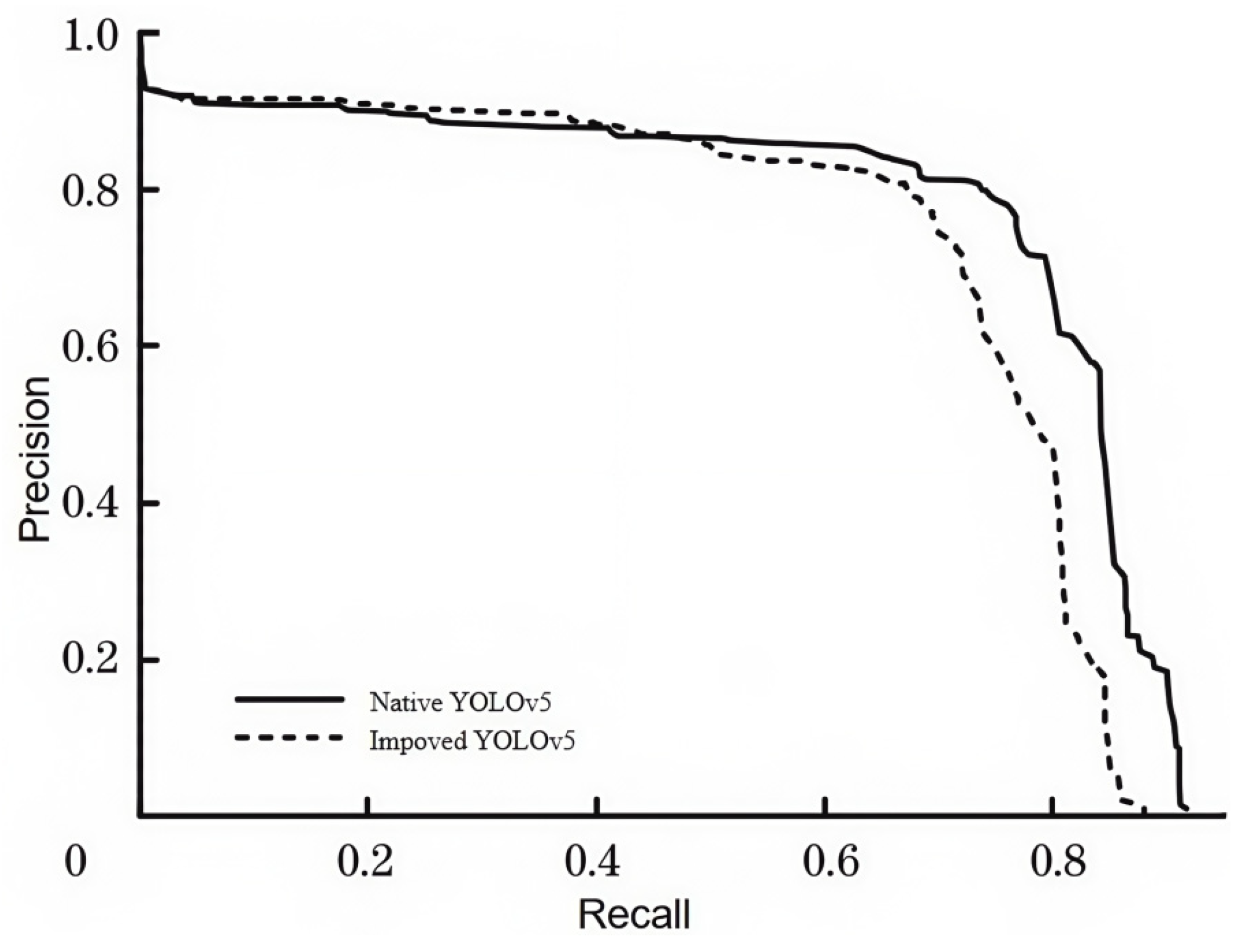
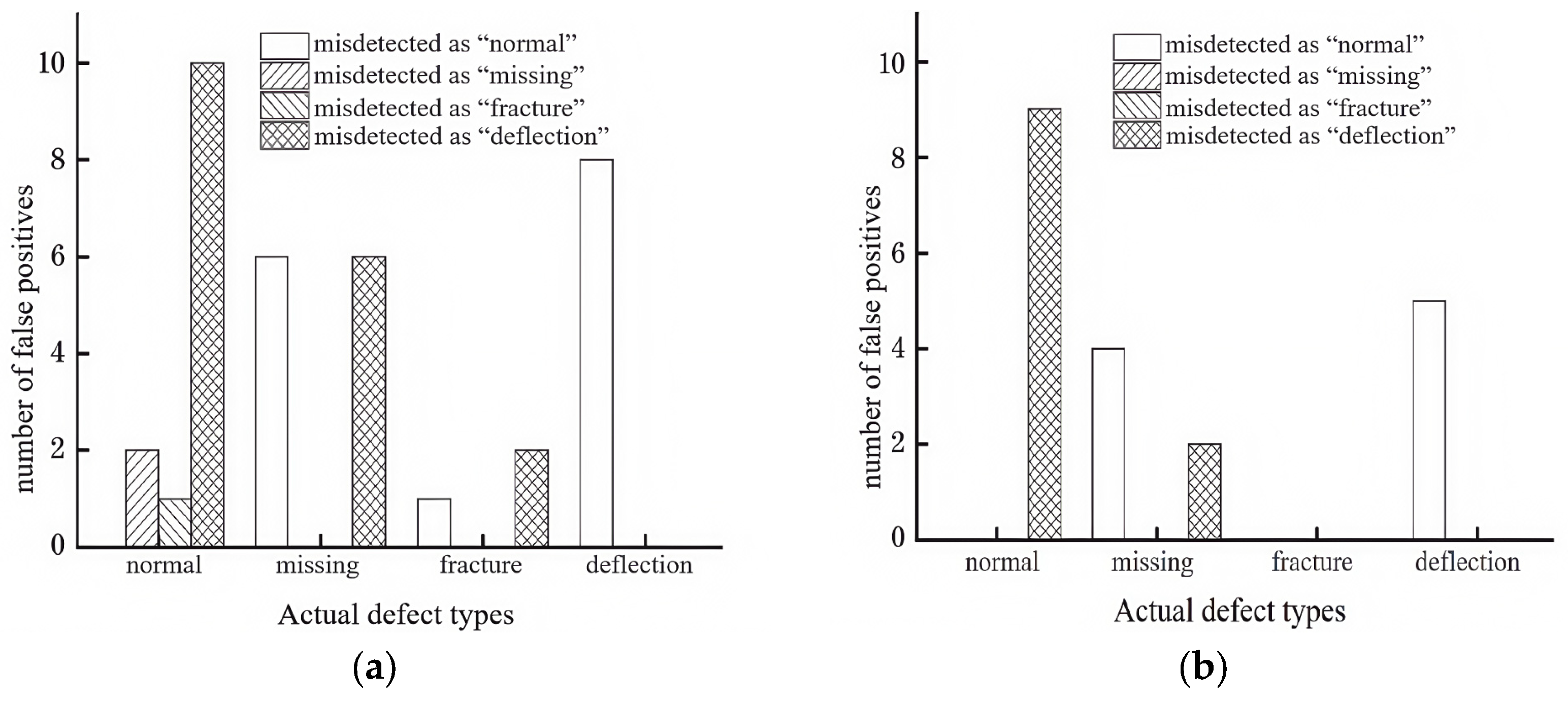
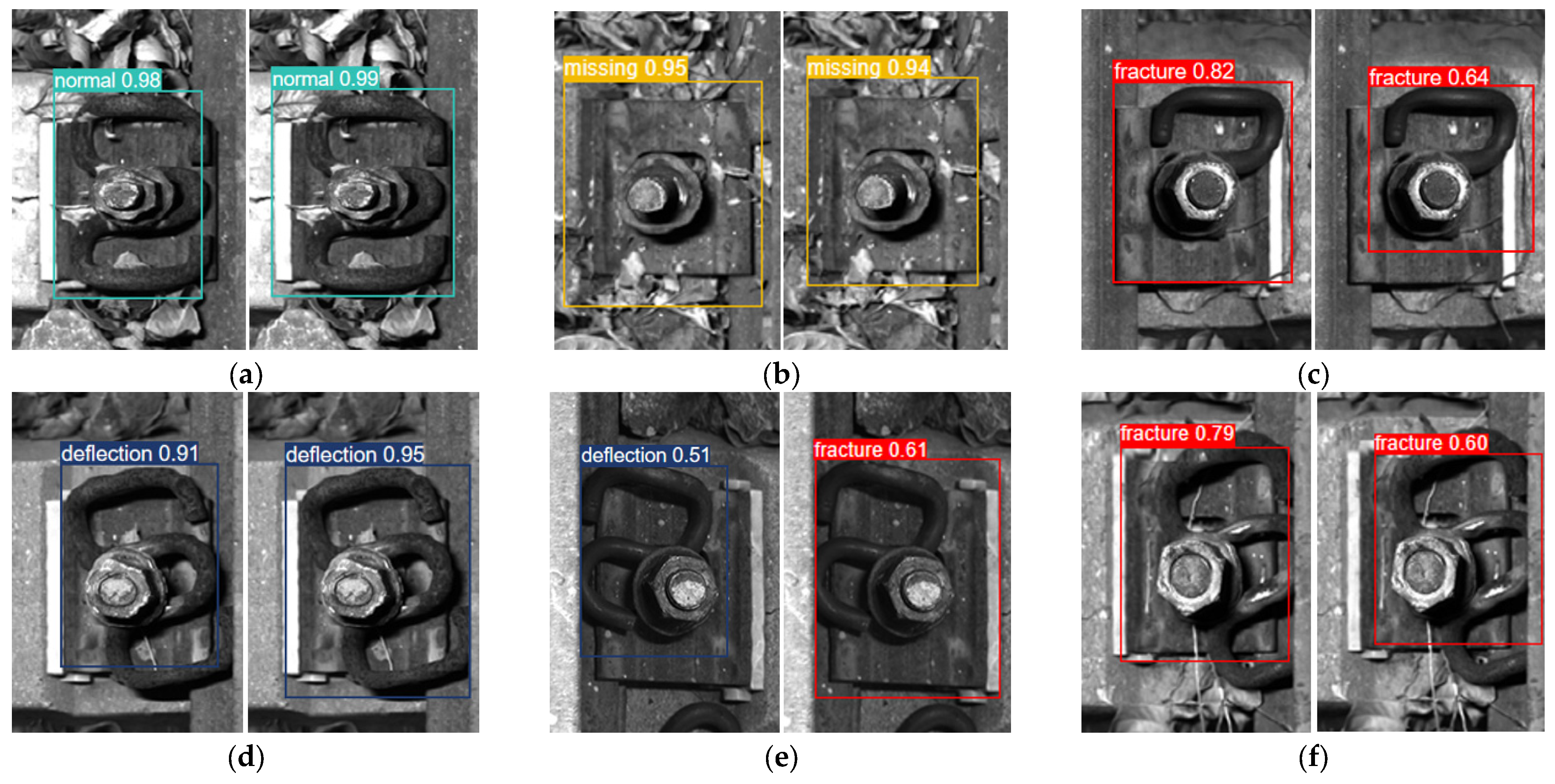
4.4. Results and Analysis of Rail Fastener Defect Recognition
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasap, A.; Paitekul, P.; Noraphaiphipaksa, N.; Kanchanomai, C. Analysis of the fatigue performance of elastic rail clip. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 92, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellaswamy, C.; Krishnasamy, M.; Balaji, L.; Dhanalakshmi, A.; Ramesh, R. Optimized Railway Track Health Monitoring System Based on Dynamic Differential Evolution Algorithm. Measurement 2020, 152, 107332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiwald, D.; Fass, U.; Litschke, H. Railcheck system: Automated optoelectronic inspection of rail systems. Eisenbahningenieur 1998, 7, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Application of German RAILCHECK photoelectric automatic rail detection system in track inspection vehicles. Harbin Railw. Technol. 2001, 4, 3. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Stella, E.; Mazzeo, P.; Nitti, M.; Cicirelli, G.; Distante, A.; D’Orazio, T. Visual recognition of missing fastening elements for railroad maintenance. In Proceedings of the IEEE 5th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Washington, DC, USA, 6 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Min, Y.; Yin, C.; Cheng, T.; Xiao, B.; Yue, B.; Li, X. A Real Time Detection Method of Track Fasteners Missing of Railway Based on Machine Vision. Int. J. Perform. Eng. 2018, 14, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibert, X.; Patel, V.M. Sequential Score Adaptation with Extreme Value Theory for Robust Railway Track Inspection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gibert, X.; Patel, V.M.; Chellappa, R. Deep Multitask Learning for Railway Track Inspection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wei, D.; Jia, L.; Li, Y. Railway Track Fastener Defect Detection Based on Image Processing and DeepLearning Techniques: A Comparative Study. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 80, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, H.C.; Chakraborty, K. Cascade learning embedded vision inspection of rail fastener by using a fault detection IoT vehicle. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wei, D.; Suo, D.; Jia, L.; Li, Y. Multi-Target Defect Identification for Railway Track Line Based on Image Processing and Improved YOLOv3 Model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 61973–61988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiy, Y.; Shi, D.X.; Qiao, Z.T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, S. A survey on recent advances in few-shot object detection. Chin. J. Comput. 2023, 46, 1753. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.W.; Liu, Z.G.; Wang, H.R.; Nunez, A.; Han, Z. Automatic defect detection of fasteners on the catenary support device using deep convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Zhou, J.P.; Tan, X.; Lin, J.; Tian, L.; Wang, H. Lightweight YOLOv5 detection algorithm for low-altitude micro UAV. J. Optoelectron. 2024, 35, 641–649. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.02640. [Google Scholar]
- Hegbste, V.; Legler, T.; Ruskowski, M. Federated ensemble YOLOv5: A better generalized object detection algorithm. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.17829. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E.H. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:1709.01507. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.B.; Zhou, D.Q.; Feng, J.S. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.02907v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, D.F.; Meng, J.J.; Qi, W.Z. Rail fastener defect detection based on dual attention and GSSN lightweighting. J. Comput. Eng. 2025, 51, 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chou, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3[EB/OL]. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.D.; Han, Z.Q.; Xu, H.Y.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, K. YOLOv3-Lite: A lightweight crack detection network for aircraft structure based on depthwise separable convolution. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.02357. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.C.; Jiao, H.N.; Yang, J.; Zeng, H.F. Garbage image classification algorithm based on improved MobileNet v2. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Eng. Sci.) 2021, 55, 1490. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Chang, M.; Xie, L.; Xu, W.; Chen, N. PSG-Yolov5: A Paradigm for Traffic Sign Detection and Recognition Algorithm Based on Deep Learning. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Li, J.; Wei, H.B.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Ren, Q. Slim-neck by GSConv: A better design paradigm of detector architectures for autonomous vehicles. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.02424v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.N. A parallel implementation of computing mean average precision. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.09504v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevorgyan, Z. SIoU loss: More powerful learning for bounding box regression. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Types | Normal | Missing | Fracture | Deflection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 2680 | 1356 | 1211 | 1253 |
| Hyperparameter Name | Hyperparameter Value |
|---|---|
| Input Image Size | 640 × 640 |
| Initial Learning Rate | 0.005 |
| Training Epochs | 300 |
| Warmup Learning Rate Momentum | 0.937 |
| Bounding Box Localization Loss Coefficient | 0.05 |
| Classification Loss Coefficient | 0.5 |
| Confidence Loss Coefficient | 0.5 |
| Mosaic Data Augmentation Ratio | 1 |
| Batch Size Normalization Value | 16 |
| Backbone | P/% | R/% | AmAP/% | GPU Memory Usage (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSPDarkNet (Baseline) | 89.9 | 92.3 | 94.5 | 4.53 |
| ShuffleNetv2 | 75.6 | 85.0 | 87.8 | 3.49 |
| MobileNetv2 | 75.8 | 92.2 | 88.0 | 3.95 |
| MobileNetv3 (Proposed) | 76.3 | 95.6 | 88.3 | 3.70 |
| Attention Mechanisms | P/% | R/% | AmAP/% | GPU Memory Usage (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE (Original) | 89.9 | 92.3 | 94.5 | 4.53 |
| CBAM | 92.9 | 94.4 | 97.3 | 4.92 |
| Dual Attention (Neck) | 90.7 | 92.9 | 94.8 | 4.50 |
| Dual Attention (Backbone, Ours) | 95.9 | 96.3 | 98.9 | 4.45 |
| Coordinate Loss Functions | P/% | R/% | AmAP/% | GPU Memory Usage (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIoU (Original) | 89.9 | 92.3 | 94.5 | 4.53 |
| DIoU | 91.4 | 93.3 | 96.7 | 4.53 |
| GIoU | 96.0 | 95.2 | 97.7 | 4.53 |
| SIoU (Ours) | 96.1 | 95.8 | 97.7 | 4.53 |
| MobileNetv3 | GSSN | Dual Attention | CARAFE | SIoU | P/% | R/% | AmAP/% | GPU Memory Usage (GB) | Model Size/MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | √ | × | × | × | 83.5 | 92.9 | 92.3 | 3.74 | 9.1 |
| √ | × | √ | × | × | 77.8 | 88.7 | 88.7 | 3.24 | 6.9 |
| √ | × | × | × | √ | 75.4 | 90.9 | 88.6 | 3.31 | 7.5 |
| √ | × | × | √ | × | 83.3 | 92.4 | 92.3 | 3.74 | 9.1 |
| √ | √ | √ | × | × | 84.4 | 95.1 | 94.0 | 3.65 | 8.3 |
| √ | √ | × | × | √ | 88.4 | 89.8 | 95.2 | 3.74 | 9.1 |
| √ | √ | √ | × | √ | 88.9 | 95.5 | 96.1 | 3.65 | 8.3 |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 89.2 | 96.0 | 96.5 | 3.59 | 8.3 |
| Algorithm | P/% | R/% | mAP50/% | mAP 50–95/% | GPU Memory Usage (GB) | GFLOPs (G) | Param (M) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5m (Baseline) | 92.7 | 91.5 | 93.4 | 76.9 | 4.53 | 20.9 | 49.1 | 15.79 |
| Faster-RCNN | 81.4 | 83.0 | 82.8 | 71.5 | 6.95 | 112.1 | 131.5 | 9.21 |
| SSD | 83.1 | 84.4 | 84.7 | 71.9 | 5.25 | 34 | 90.2 | 10.12 |
| YOLOv3 | 90.9 | 91.8 | 92.4 | 74.3 | 5.85 | 61.6 | 156.4 | 9.93 |
| YOLOv4 | 92.1 | 91.9 | 92.8 | 75.7 | 5.92 | 69.6 | 195.1 | 11.83 |
| YOLOv4-tiny | 90.0 | 91.1 | 91.8 | 74.5 | 3.77 | 5.9 | 5.6 | 17.23 |
| Improved YOLOv5 | 96.1 | 95.2 | 96.5 | 77.6 | 3.65 | 6.5 | 37.3 | 17.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, D.; Meng, J.; Meng, G.; Shen, Y. Railway Fastener Defect Detection Model Based on Dual Attention and MobileNetv3. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090513
Lv D, Meng J, Meng G, Shen Y. Railway Fastener Defect Detection Model Based on Dual Attention and MobileNetv3. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(9):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090513
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Defang, Jianjun Meng, Gaoyang Meng, and Yanni Shen. 2025. "Railway Fastener Defect Detection Model Based on Dual Attention and MobileNetv3" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 9: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090513
APA StyleLv, D., Meng, J., Meng, G., & Shen, Y. (2025). Railway Fastener Defect Detection Model Based on Dual Attention and MobileNetv3. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(9), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090513





