Scalable Energy Management Model for Integrating V2G Capabilities into Renewable Energy Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Energy Communities and Smart Charging Integration
1.2. Energy Management Algorithms
1.2.1. Rule-Based Methods
- Rule-based methods become increasingly complex as more objectives are added since each new objective can double the size of the decision tree [30]. To manage this, objectives can be prioritized and structured hierarchically. Alternatively, decision trees can be generated using more advanced automated methods. For instance, Huo et al. [33] developed a technique to derive decision trees from MILP models, while Ruddick et al. [34] proposed a machine learning-based approach for constructing interpretable decision trees.
- Need for qualitative decisions and actions, based on differences in input data and variable states. Referring to the example provided by Alirezaei et al. [31], it could be considered to distribute the PV energy surplus between the BESS and the EV rather than charging only the EV. Van der Kam et al. [35] proposed distributing the load between two EVs connected to the same POD, assigning priority values based on estimated parking time and residual Depth of Discharge. Alternatively, fuzzy logic controllers can manage uncertainties by making adaptive decisions based on external factors, thereby enhancing flexibility and decision-making under fluctuating conditions [36].
- Dependence on real-time data and limited forecasting capabilities. Rule-based methods usually rely on actual data, and decision-making based on short-term forecasts is generally not implemented [30]. Consequently, they are typically less effective than optimization-based methods but can still be useful when forecast data are unavailable.
1.2.2. Optimization-Based Methods
- PV power production throughout the day. Forecasts of PV generation can be obtained using Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) or specialized APIs. The latter is particularly suitable for scalable models that must be applied across various contexts and geographic locations.
- Building and residential energy consumption. This is a critical factor in a robust optimization algorithm. To obtain reliable forecasts, historical consumption and weather data can be used to train an ANN. Luo et al. [52] proposed a multi-ANN framework, training a distinct network with each historical data cluster. In addition, Long Short-Term Memory networks are widely used due to their proven performance in time series forecasting, as shown by Kim et al. [53] in their proposed hybrid framework.
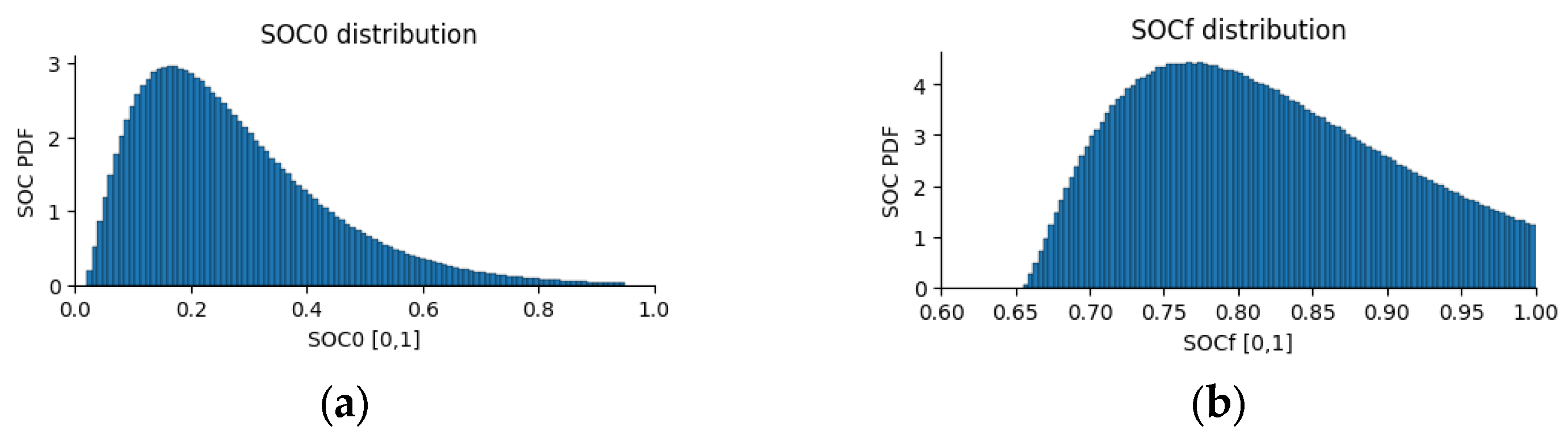
- User behavior in predicting EV charging events. The integration of EVs within an energy community is key and represents an additional opportunity for optimization. Therefore, it is necessary to forecast likely charging events during the day, in addition to user constraints that must be respected to ensure satisfactory charging conditions [54]. Extensive research based on dataset analysis has been conducted to identify and forecast clustered EV charging patterns [55,56]. For simulation purposes, Monte Carlo random sampling can be used to generate EV power demand throughout the day [43,57].
1.3. Contributions
- Lack of comprehensive and scalable models for integrating EV charging flexibility into RECs. Most current approaches do not scale with the number of locations or account for diverse internal characteristics. Our model offers a modular and scalable framework at a small scale for different REC configurations.
- Focus primarily on economic benefits and cost savings. In addition, the proposed model emphasizes technical objectives, such as reducing the REC’s dependency on the MV grid, avoiding unconventional battery usage, and respecting user-specific charging requirements.
- Reliance on single-method approaches in most current literature. In contrast, our solution introduces a hybrid control framework that combines global optimization-based scheduling with local rule-based balancing strategies. This hybrid structure ensures both robustness and feasibility for real-time operations.
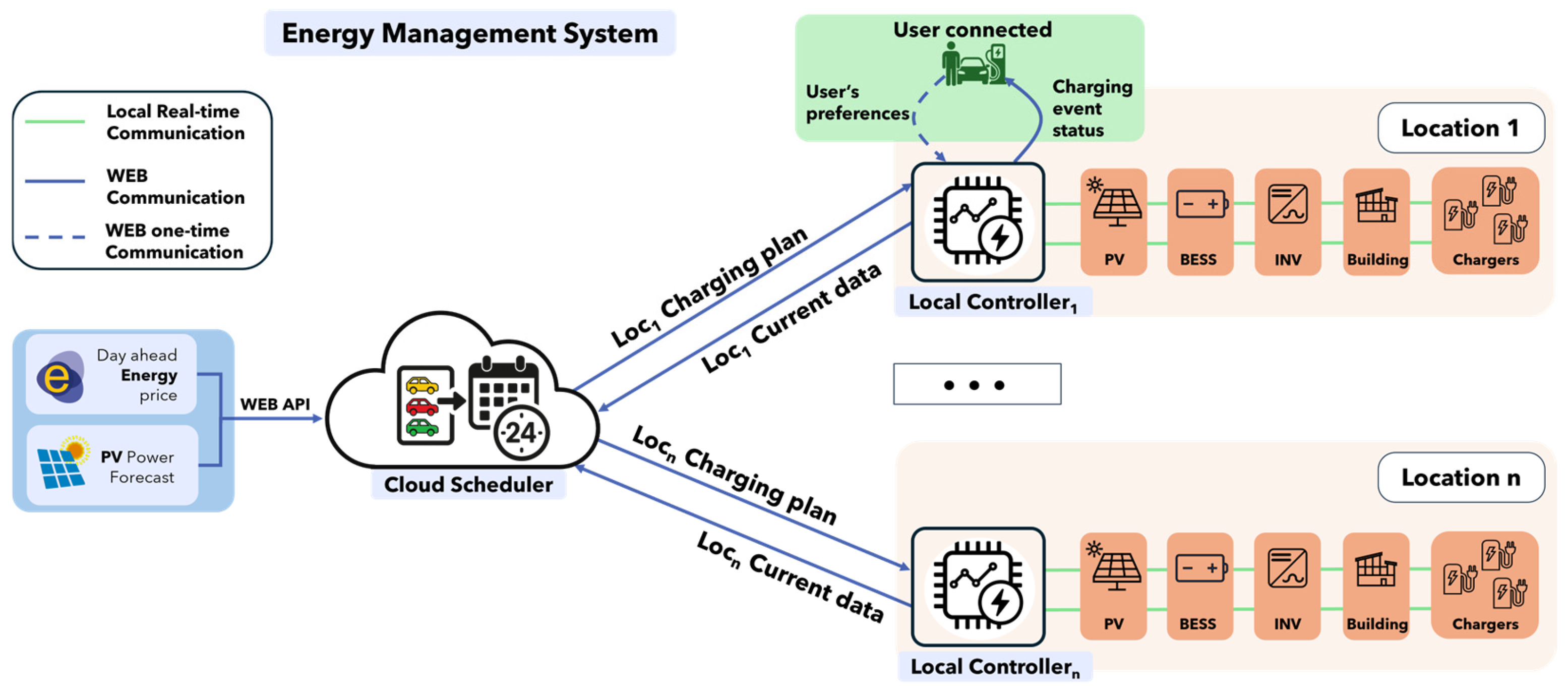
2. Materials and Methods
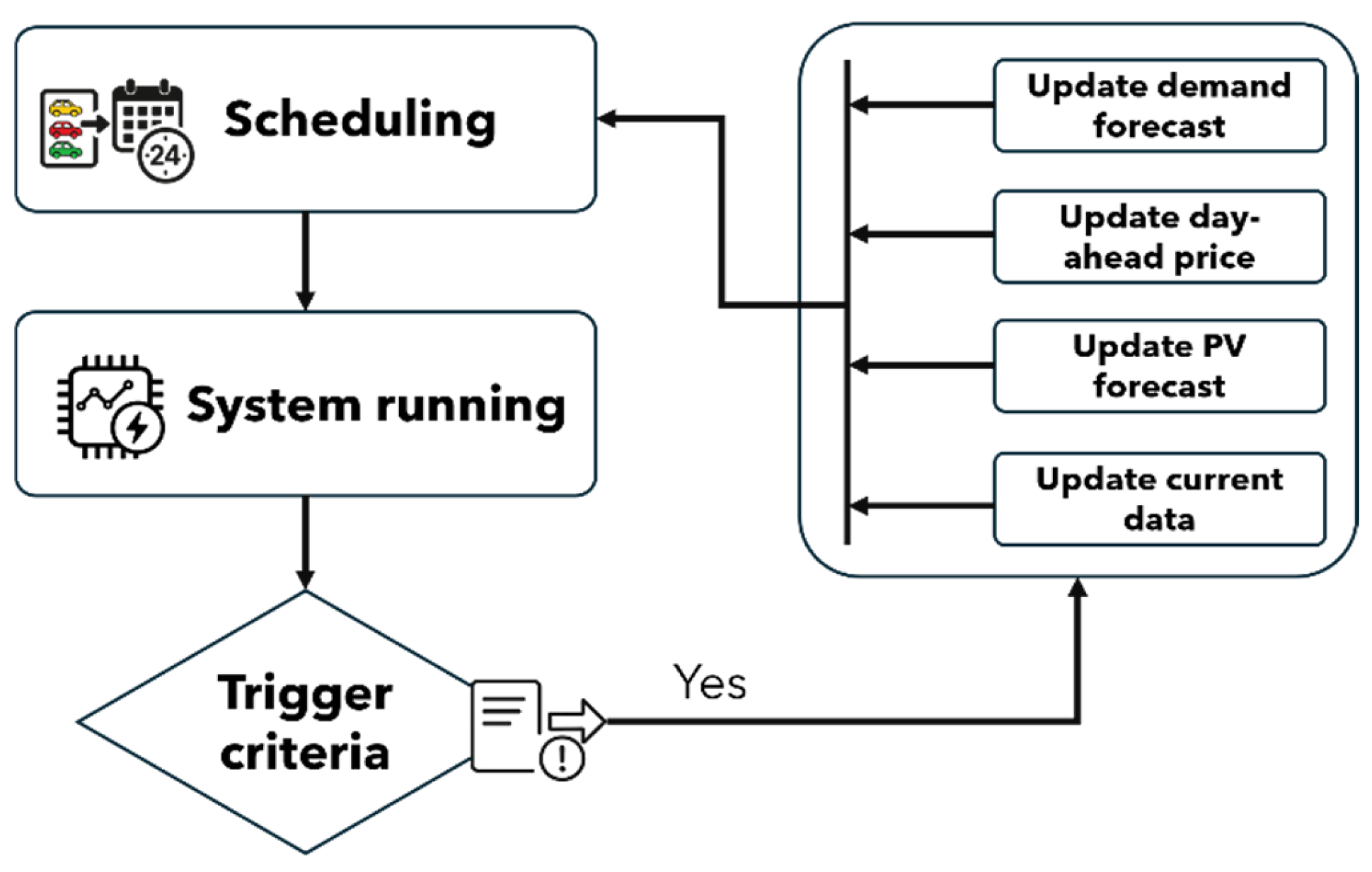
- Cloud Scheduler—Based on a MILP formulation, the scheduler, once triggered by one of the REC’s locations, computes globally optimal EV and BESS charging schedules according to user needs, flexibility, and battery aging penalties. It also incorporates PV power forecasts from the Forecast.Solar API [59], day-ahead electricity prices from the ENTSO-E API [60] to evaluate grid energy costs for the community and potential incentives, and computes building power forecasts for the next 24 h, as discussed in Section 2.3.
- Local Controller—Each location is equipped with a local controller, which is responsible for monitoring local assets, handling user requests, and triggering an optimization process when one of the criteria discussed in Section 2.3 is met. For real-world applications, a user interface can be integrated to provide feedback on the EV charging status. Once a new optimization is triggered, the Local Controller sends current data to the Cloud Scheduler, including asset characteristics, current SOC values, and user preferences, and receives back the optimized charging schedule. It also ensures adherence to the planned power flows and handles forecast errors using real-time corrections. It communicates with the inverter, BESS, and charging stations to effectively manage energy flow. A Comprehensive description is provided in Section 2.4.
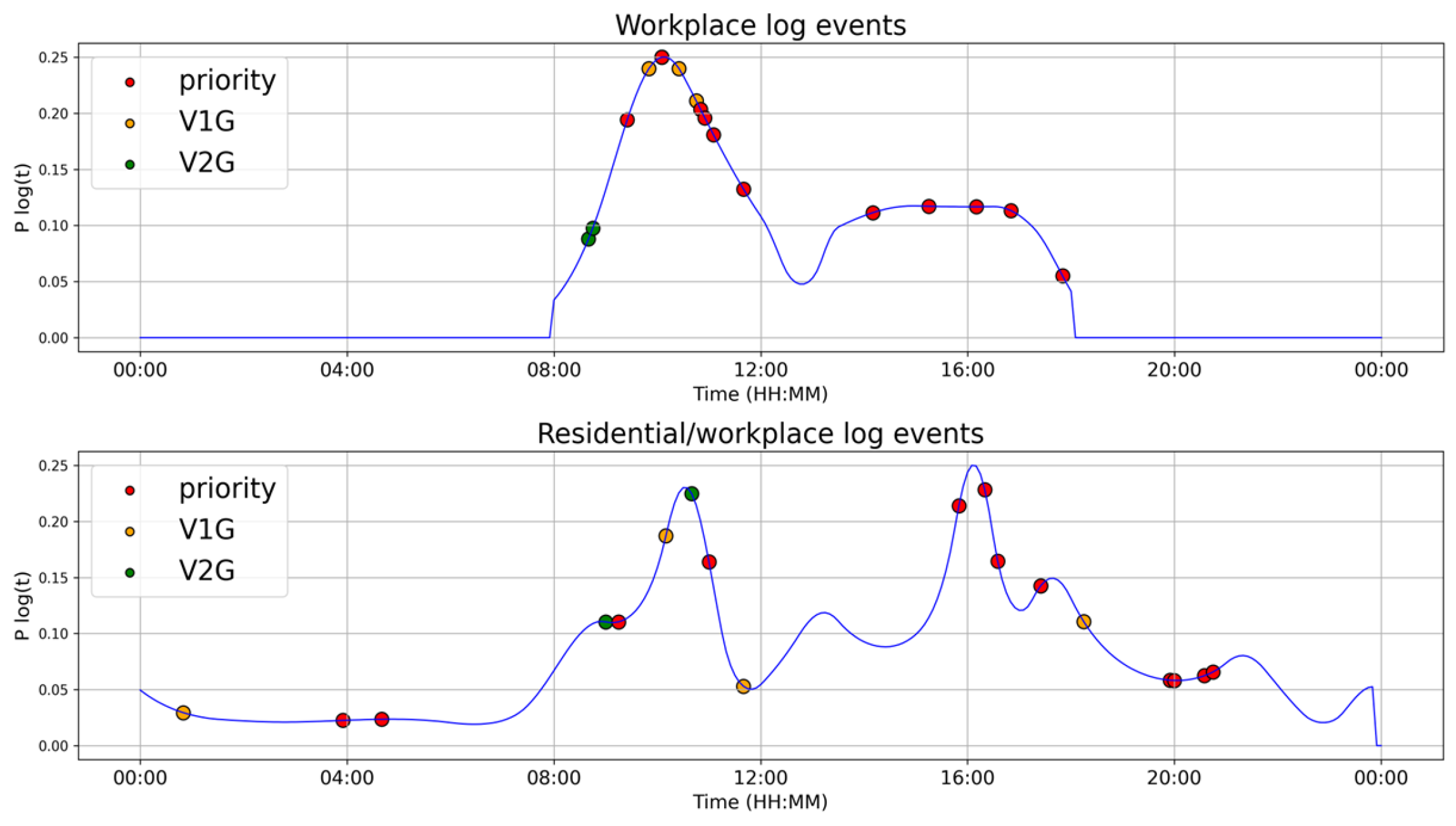
2.1. Simulated Timeframe of Charging Events
- Workplace area: characterized by defined opening and closing hours, with a high probability peak in the early morning and a second relaxed peak after the lunch break. No charging events are expected during weekends or on public holidays.
- Mixed residential/workplace area: characterized by a more evenly distributed probability throughout the day, with higher arrival rates in the evening.
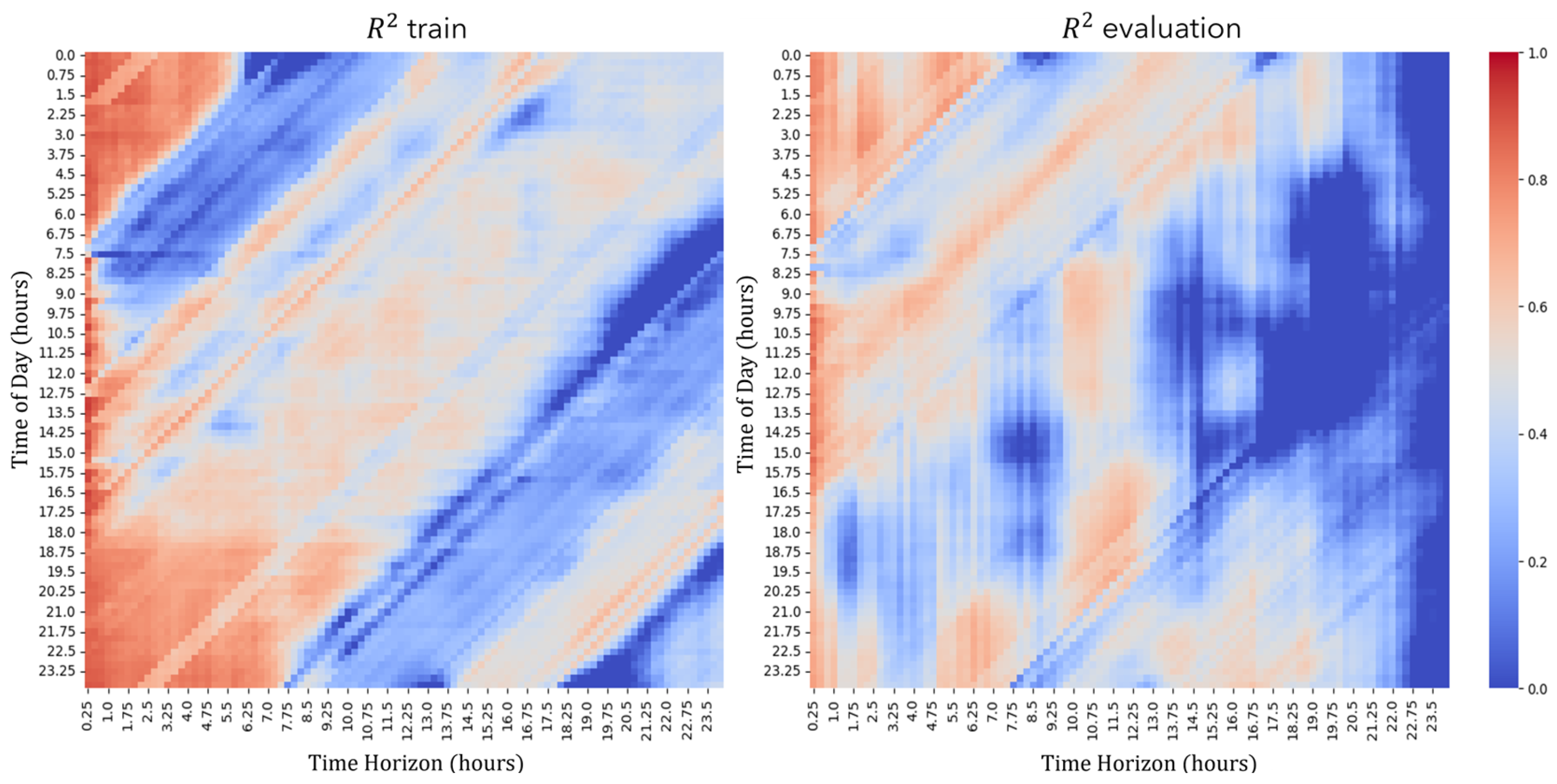
2.2. Building Power Forecast
Training and Evaluation
2.3. Day-Ahead Optimization Problem
- A new EV charging session begins.
- An EV charging session ends earlier than the estimated departure time.
- The integral of power prediction error over time exceeds a defined threshold from the last optimization process (30 kWh in the analyzed case study).
- Every 7 h, a regular update is performed to maintain scheduling accuracy.
2.3.1. Optimization Variables
- Power exchange with EVs with local BESS and with a local low voltage grid for a location .
- SOC evolution over time for EVs and for BESSs .
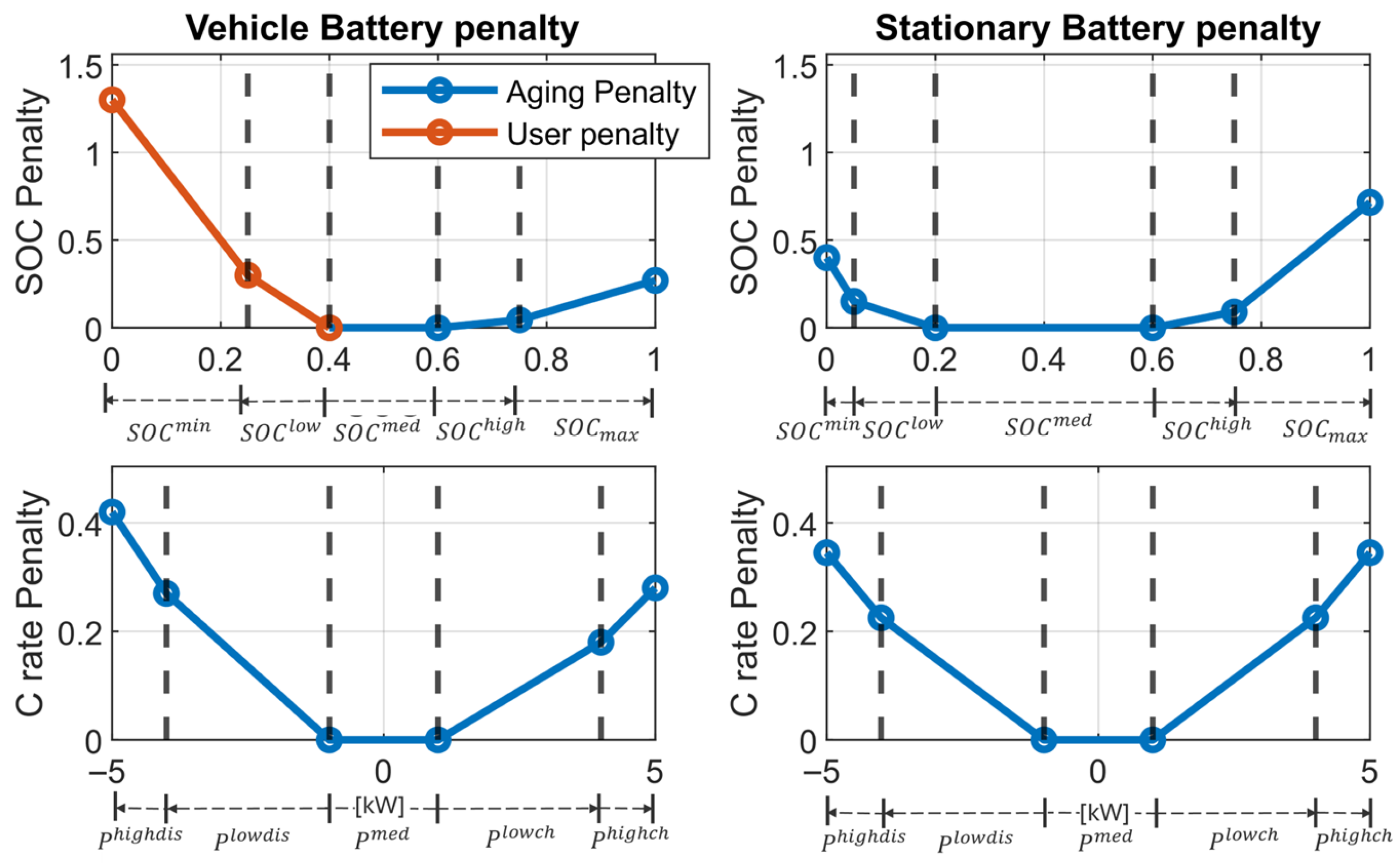
- Sub-optimization variables are defined to enable custom piecewise linear cost functions for aging penalties, which ensure that the optimization problem remains linear, avoiding the need for non-linear optimization methods. Specifically, for each EV and BESS, a set of five variables is defined for Power (; ; ; ; ) and SOC (; ; ; ). These sub-variables are restricted to a limited range within the domain of the main variables and are designed to penalize the extreme values of power and SOC. The constraints linking each auxiliary variable to its respective main counterpart are described in Section 2.3.2 (see Equation (12)). The structure of the custom cost function and the range definitions for each auxiliary variable are illustrated in Section 2.3.3.
- Global power exchanged between the community and MV grid , as well as its positive and negative components, and , respectively.
- Power derivative variables for EVs , BESSs , and grid defined in positive semi-continuous space.
2.3.2. Problem Constraints
- Power balance constraint for ensuring that energy supply equals demand at each time step for every location:
- SOC evolution constraint to ensure physical consistency between the power and corresponding SOC values. It is defined as:
- Inverter maximum power constraints. When transferring power between the DC and AC lines via an inverter, the maximum deliverable power must be accounted for. Accordingly, DC-side power flows at each location are constrained within technically feasible limits, defined by the inverter’s rated capacities (; ):
- User flexibility constraints applied to the vehicle charging processes. These constraints reflect the user’s preference for the desired charging behavior. For a vehicle , it may include V1G user constraint,
- Sub-Constraints applied to sub-optimization variables. These constraints ensure that the sum of the sub-variables equals the corresponding main variable. For an EV, they are defined as:
- Positive constraint formulation for power derivative variables. For the grid power is defined as
- Power-sign constraint. Finally, for the entire community, a global constraint is imposed to ensure that the positive and negative components are mutually exclusive. The following constraint is therefore introduced:
2.3.3. Cost Function
- Energy cost function () for minimizing energy costs based on day-ahead energy prices () established by the Transmission System Operator. Using an energy price profile for a specific market zone not only results in cost savings but also contributes to achieving an hourly demand-supply balance within the REC price zone [63,64]. Energy cost function is defined as:
- Incentive cost penalties for reducing energy exchanges with the MV grid while high incentives for shared energy within RECs are available. It also contributes to enhancing the energy community’s independence from centralized generation, as well as active energy exchange between producers and consumers within the LV local grid. Incentives price profile () is computed in function of day-ahead price market as illustrated in Table 1. The penalty term is computed using the following relation:where the second term clearly identifies the absolute value of the grid load. Since the definition of shared power involves several non-linear terms that scale with the number of locations (see Equation (1)), the incentive cost formulation does not directly include it, but implicitly encourages its use by penalizing MV grid exchanges when high sharing incentives are available.
- Aging penalty functions to limit critical battery usage. These functions aim to limit both excessive power levels and extreme SOC values, thereby reducing cycle and calendar aging effects for both EVs and BESSs. Aging penalties are applied through sub-variable weighting, resulting in a global piecewise linear cost profile. Cycle and calendar penalties for EVs are defined as
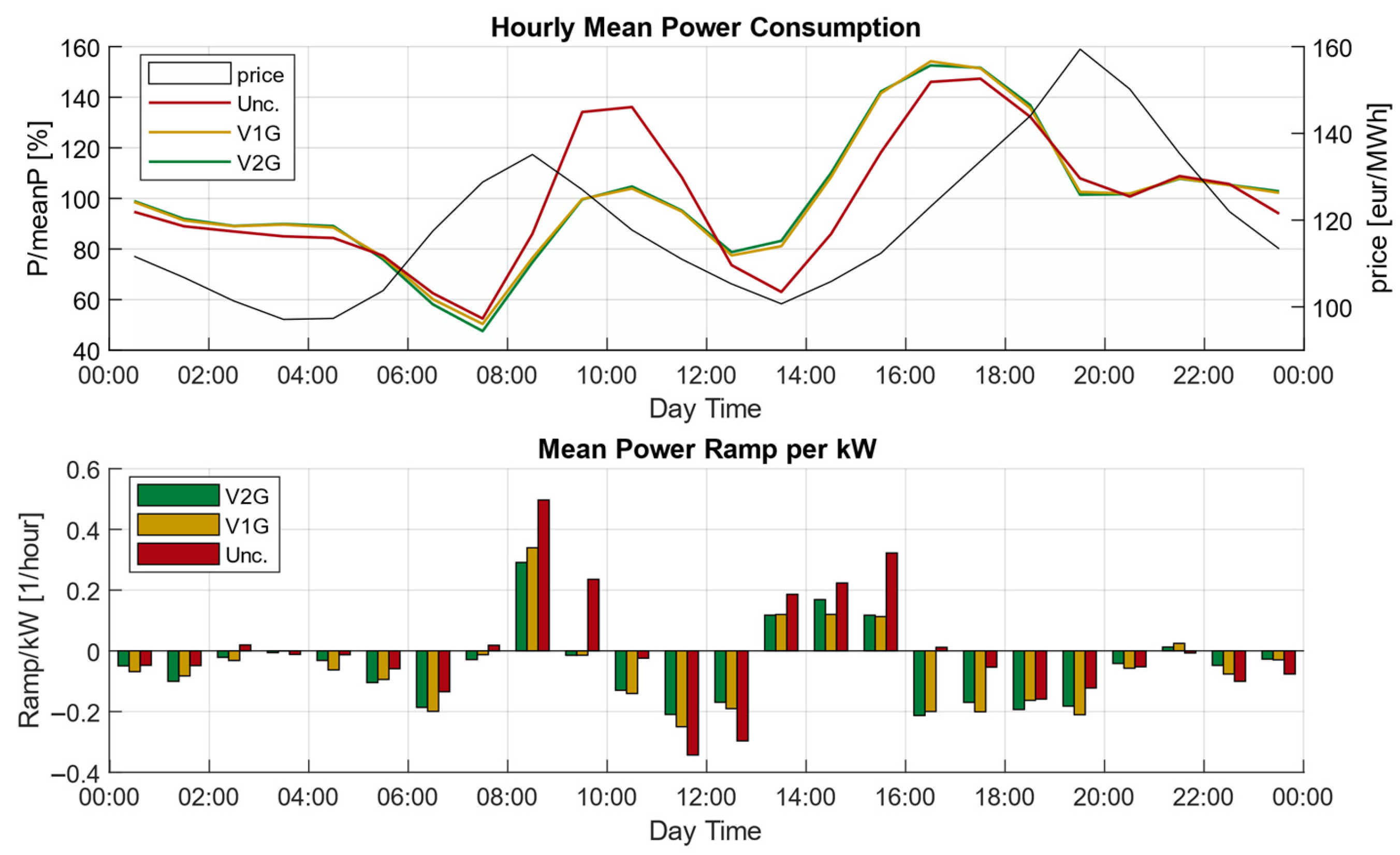
- Power ramp penalty to avoid excessive and rapid variations in the optimized power profile over time. This formulation is applied to both the charging/discharging power of EVs and BESSs, ensuring smooth and stable solutions. Additionally, it is applied to the global power exchanged with the MV grid, thereby reducing sudden fluctuations in the REC grid power exchange. This approach enhances the REC’s ramping flexibility with respect to centralized and external load generation, leveraging the dynamic capabilities provided by V2G and storage systems [49,67] and contributing to a more stable power demand over time.
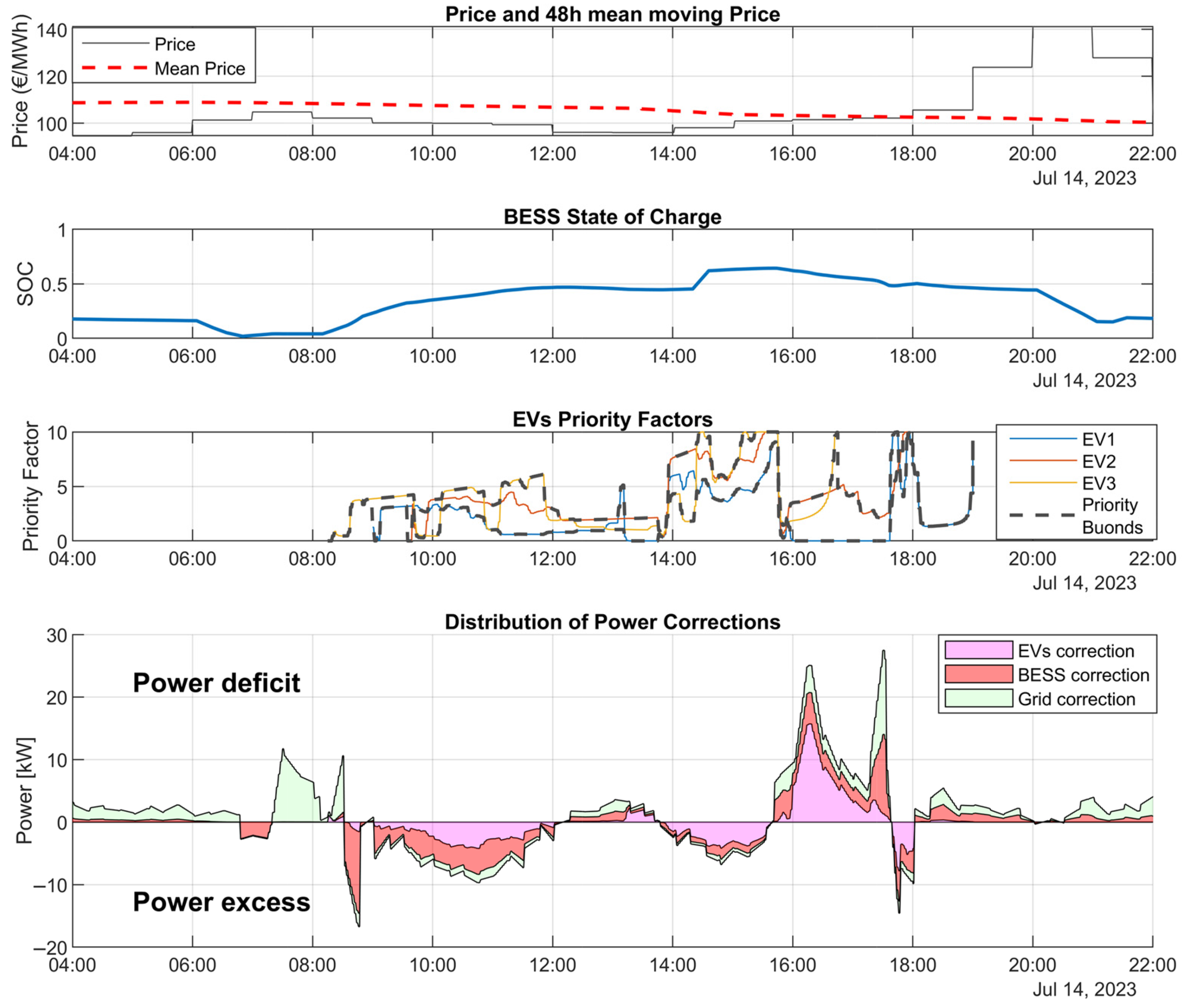
2.4. Rule-Based Decision Algorithm
- EVs’ availability to compensate for power fluctuations is based on a priority function ), following the approach proposed by Van der Kam et al. [35]. This function correlates the urgency of charging with the estimated remaining charging time ( and the expected parking duration (see Equation (21)). is computed (see Equation (22)) as the ratio between the remaining energy required by the user and the exponentially weighted average of the mean charging power () (see Equation (23)).
- BESS weight coefficient is instead computed based on its SOC and the maximum exploitable charging or discharging power (, ). According to the two described scenarios, it is defined as follows:
- Grid weight coefficient is computed based on the comparison between the current electricity price () and the average price () over a centered 48 h window. Depending on the scenario, it is defined as
3. Results
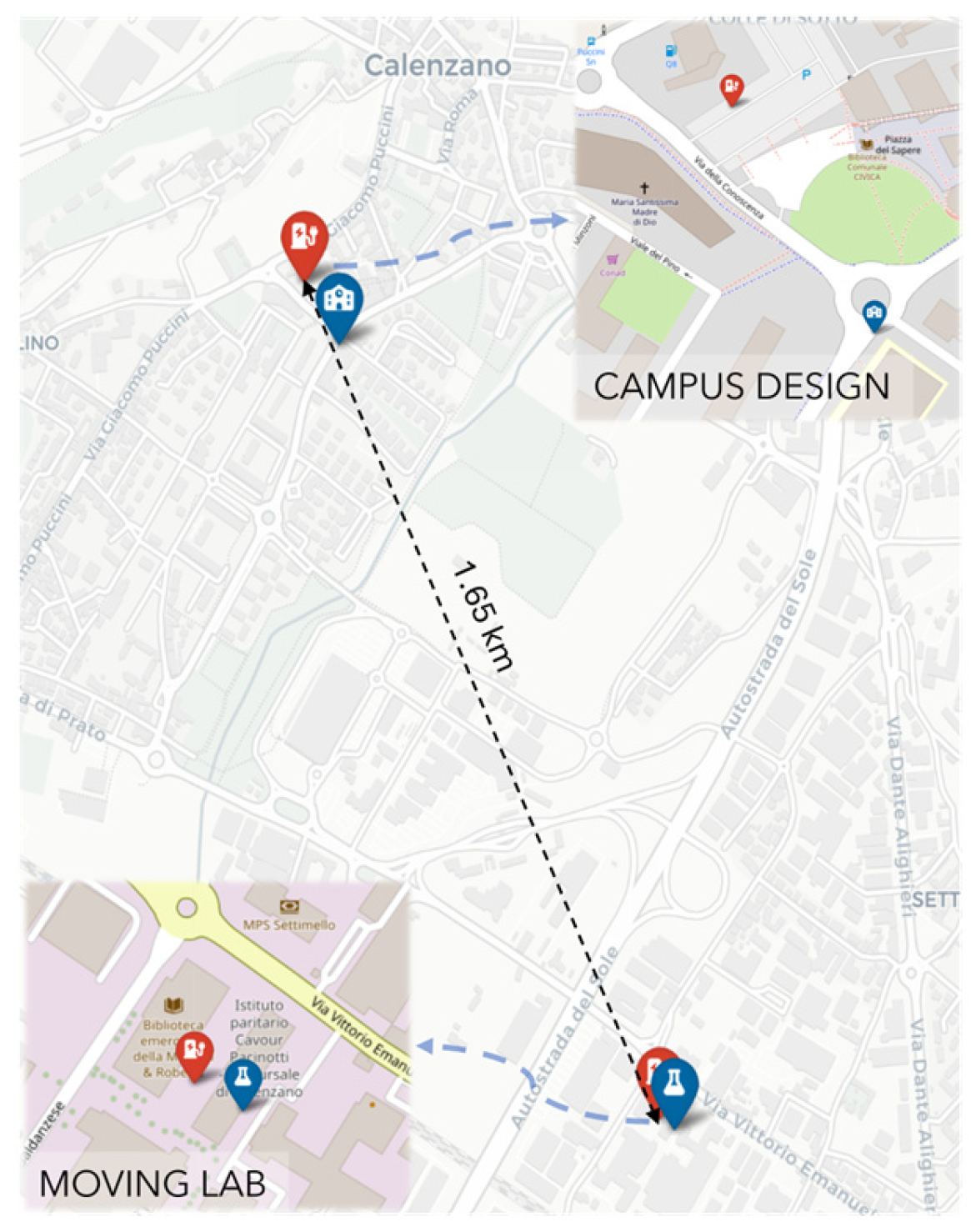
3.1. Analyzed Case Study
- MOVING LAB—A facility accessible exclusively to University of Florence members. It features three charging points, a PV power system, and a battery storage system. Additionally, it hosts the building of the Department of Industrial Engineering laboratories, which is characterized by high energy consumption and peak periods, making it an ideal setting for testing energy management models.
- CAMPUS DESIGN AREA—Situated on public land near the University’s Faculty of Design, it involves six public charging points located in a mixed residential and workplace area.
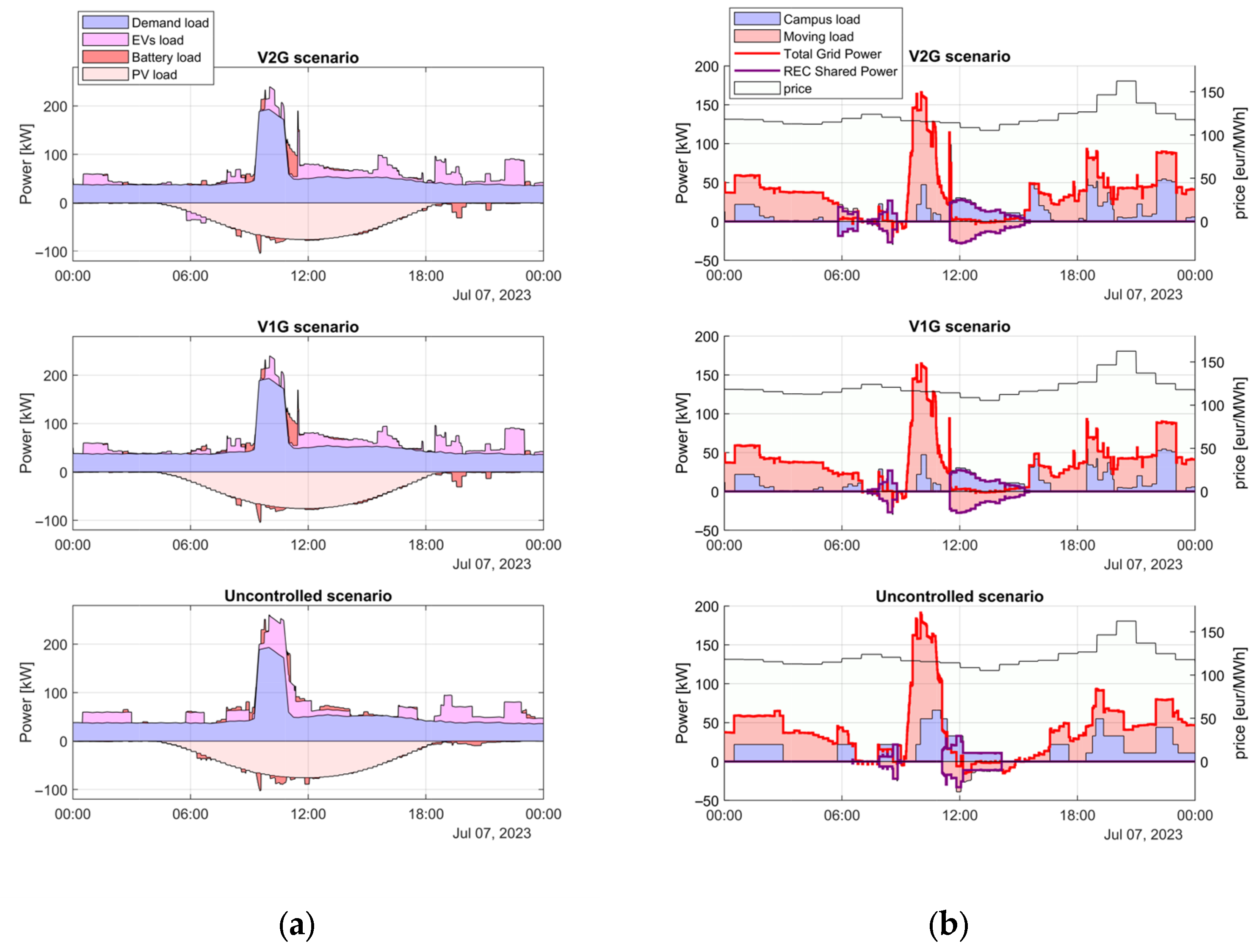
- V1G scenario: All users allow unidirectional charging flexibility.
- V2G scenario: All users allow bidirectional charging flexibility.
- Uncontrolled charging scenario: All users belong to the priority class (see Table 2); EVs are charged at the maximum available power as soon as they are plugged in, without offering any form of flexibility in the charging process.
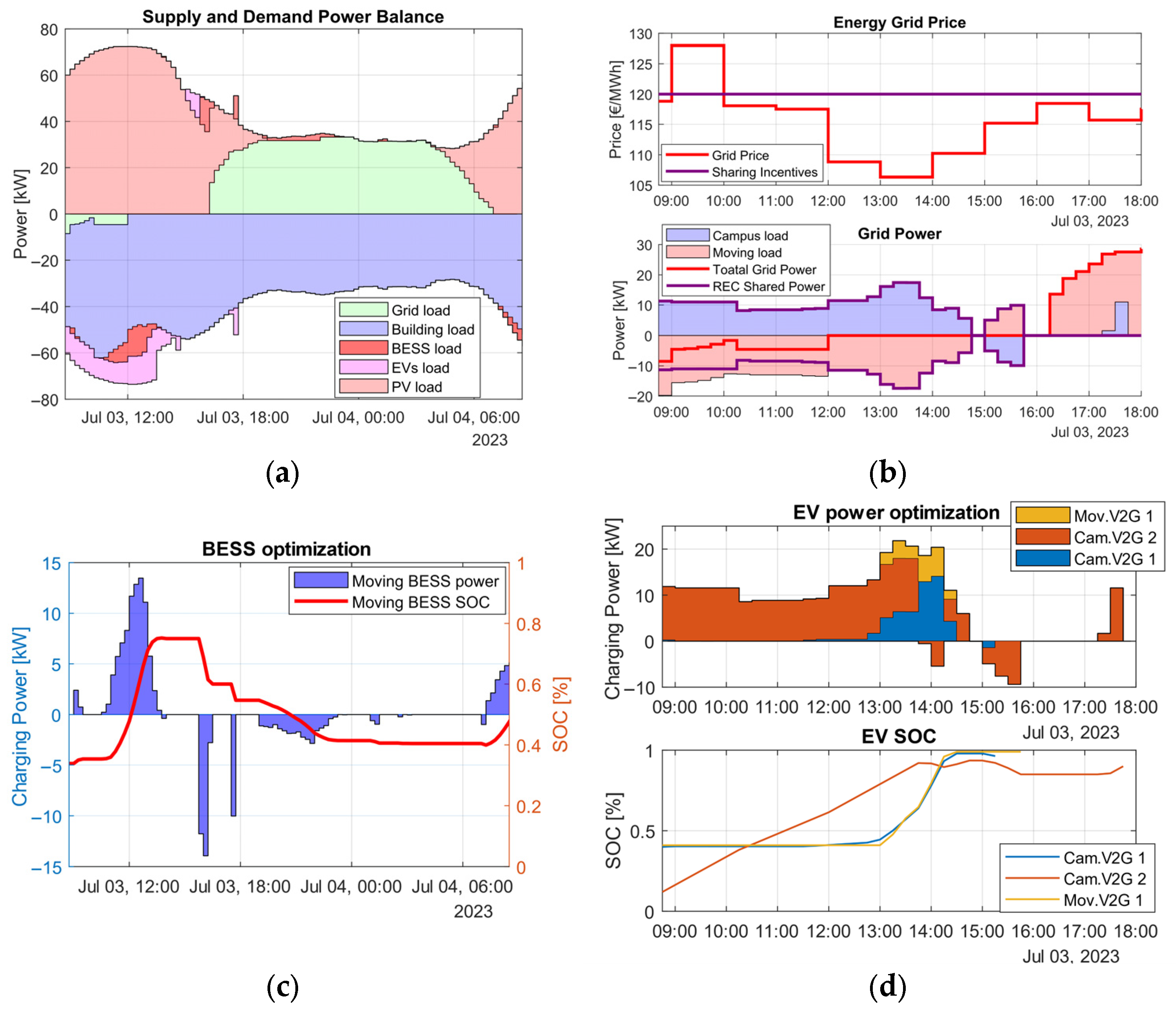
3.2. MILP Optimization Results
3.3. Rule-Based Algorithm Results
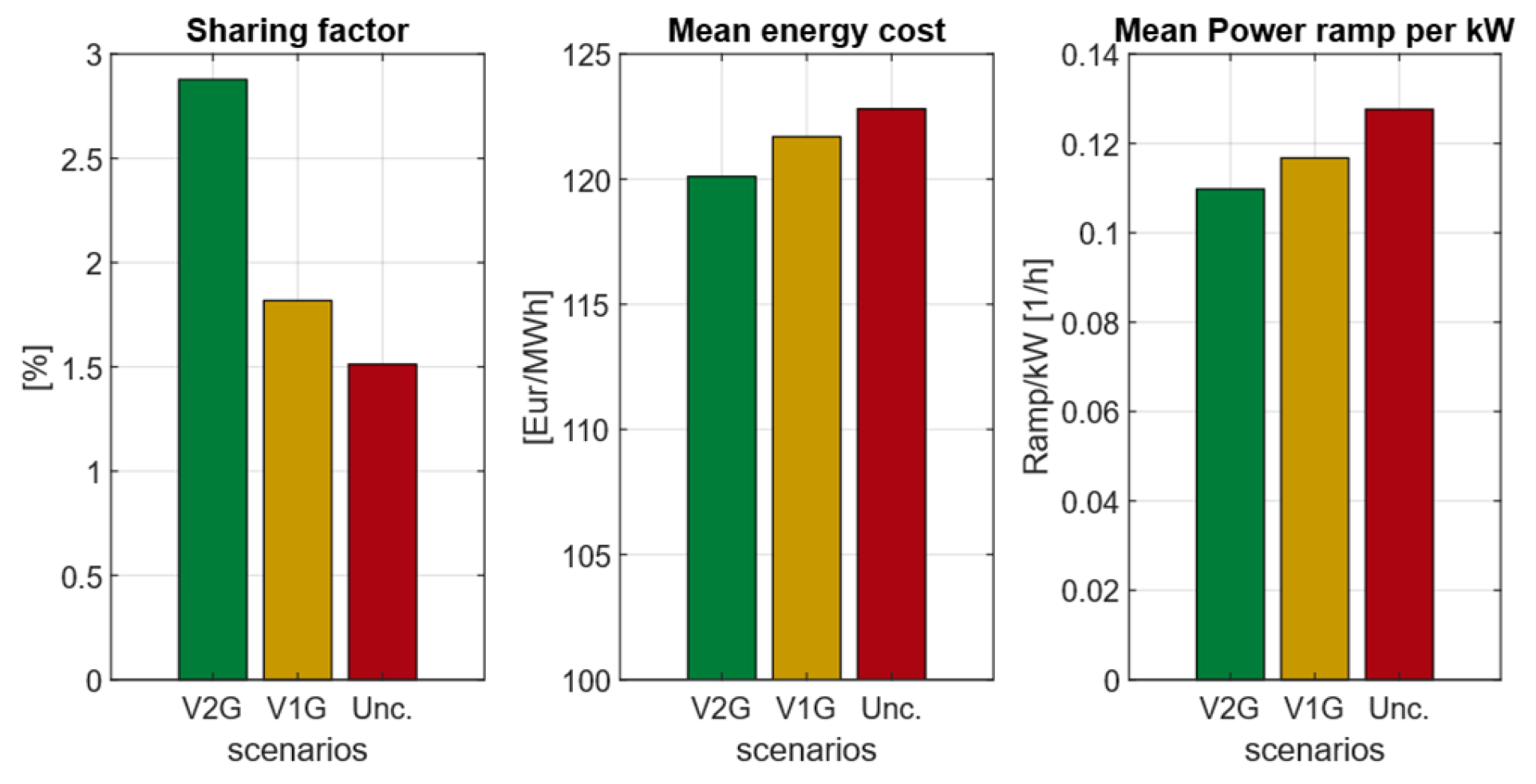
3.4. Comprehensive Results and KPI Analysis
3.4.1. Impact on Grid Peak Mitigation and Energy Cooperation
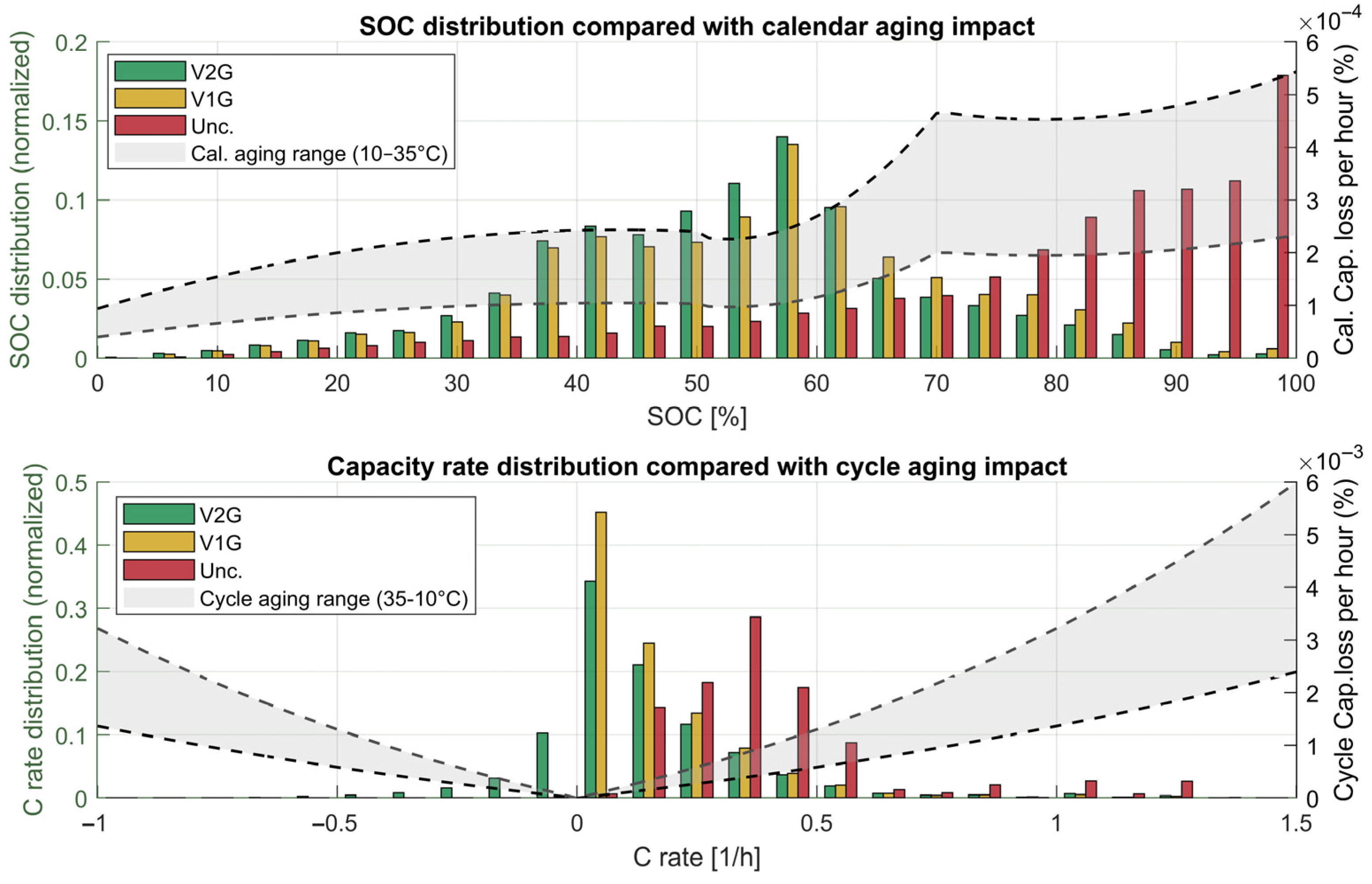
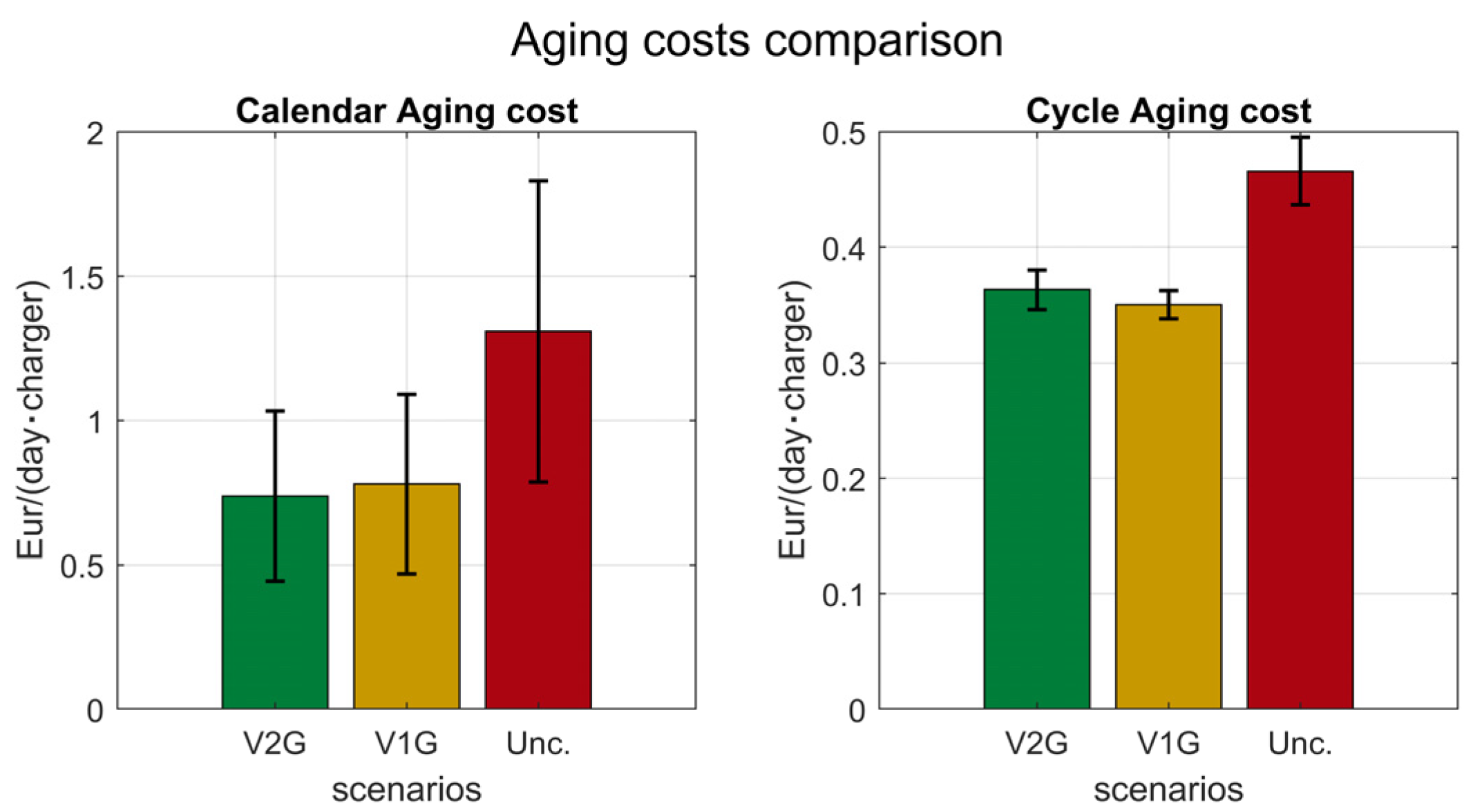
3.4.2. EV Batteries Degradation Impact
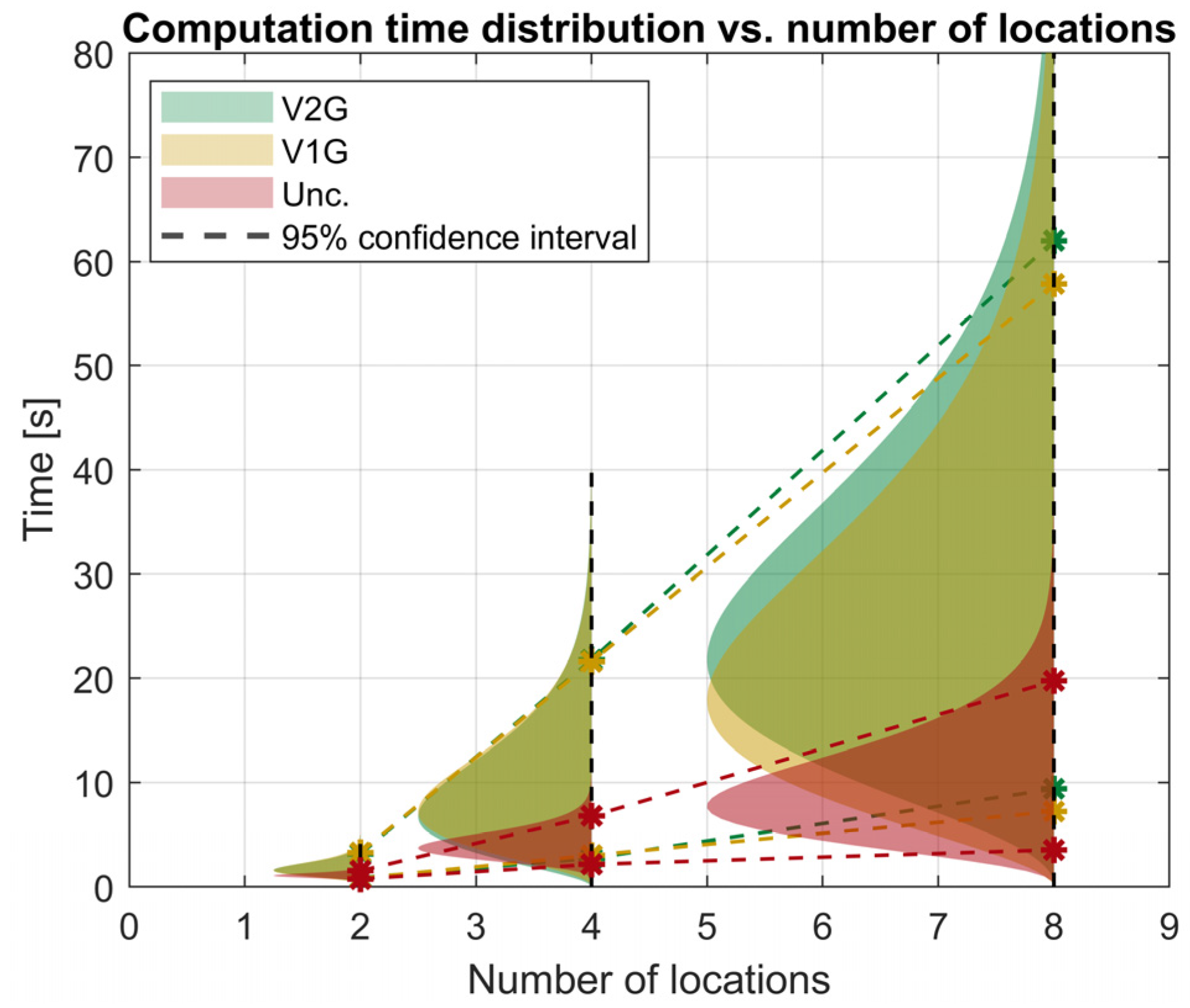
3.5. Scalability Analysis
4. Discussion
- Adoption of decentralized coordination models to improve model computation efficiency in a large-scale configuration.
- Comprehensive evaluation of optimization performance, considering both the impact of data quality across different REC configurations and EV usage patterns, and the influence of key model parameters, such as SOC and Capacity rate thresholds.
- Deployment on a real-world demonstrator, which implies managing the lack of data regarding vehicle and user preferences as well as real-time API communication.
- Environmental assessment of the proposed model. By enhancing grid performance and preventing excessive battery usage, the model significantly affects local generation needs, renewable self-consumption, and battery lifespan, which are key factors for environmental sustainability. Future iterations may integrate custom cost functions that explicitly address the environmental targets.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EV | Electric Vehicle |
| RES | Renewable Energy Source |
| V1G | Vehicle-one-Grid or Unidirectional Smart Charging |
| V2G | Vehicle-to-Grid or Bidirectional Smart Charging |
| REC | Renewable Energy Community |
| RED | Renewable Energy Directive |
| LV | Low Voltage |
| MV | Medium Voltage |
| POD | Point-of-Delivery |
| GSE | Gestore dei Servizi Energetici |
| MILP | Mixed-Integer Linear Programming |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| EMS | Energy Management System |
| BESS | Battery Energy Storage System |
| SOC | State of Charge |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| KPI | Key Performance Indicator |
| Shared power [kW]. | |
| Power fed/consumed by a community’s member [kW]. | |
| / | Full/(EV event) time optimization horizon. |
| t | Time step within optimization horizon. |
| / | Power exchanged with EV/BESS [kW]. |
| / | SOC value of EV/BESS. |
| Power value defined below a −4 Capacity rate threshold of EV/BESS [kW]. | |
| Power value defined within [−4:−1] Capacity rate range of EV/BESS [kW]. | |
| Power value defined within [−1: 1] Capacity rate range of EV/BESS [kW]. | |
| Power value defined within [1: 4] Capacity rate range of EV/BESS [kW]. | |
| / | Power value defined over a 4 Capacity rate threshold of EV/BESS [kW]. |
| / | SOC value defined below 0.2/0.05 threshold of EV/BESS. |
| / | SOC value defined within [0.2:0.4]/[0.05:0.2] range of EV/BESS. |
| / | SOC value defined within [0.4:0.6]/[0.2:0.6] range of EV/BESS. |
| / | SOC value defined within [0.6:0.8] range of EV/BESS. |
| / | SOC value defined over 0.8 threshold of EV/BESS. |
| / | Target SOC/departure time for an EV. |
| / | Battery available capacity for an EV/BESS [kWh]. |
| / | Power fed/consumed by the REC [kW] |
| // | Abs. value of the time derivative of power for EV/BESS/REC [kW/h]. |
| / | Forecasted PV/Building load [kW]. |
| / | Maximum charging power of the charger/EV [kW]. |
| Binary variable representing power direction with MV grid substation. | |
| / | Energy cost function and associated coefficient (grid price) [€/h]/[€/kWh]. |
| / | Incentive penalty and associated coefficient (sharing incentives) [€/h]/[€/kWh]. |
| / | Cycle and calendar penalties for an EV [€/h]. |
| / | Power ramp penalty and associated coefficient [€/h]/[€/kWh]. |
| Priority function of an EV. | |
| Exponential weighted average of EV charging power [kW]. | |
| // | Correction weight coefficients for EV/BESS/LV Grid. |
| // | Power adjustment applied to EV/BESS/LV Grid [kW]. |
| Sharing factor: ratio between LV energy shared and MV energy exchanged. | |
| Comprehensive mean energy cost including incentives [€/kWh]. | |
| Mean power ramp normalized over MV grid exchange [1/h]. | |
| / | Capacity fade caused by Calendar/Cycle Aging. |
| Cost associated with EV battery degradation. |
Appendix A
| Weighted Cost Component | Parameter | Value [€/MWh] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRID | EV | BESS | ||
| Energy cost | [0; 0.265] | |||
| Incentive cost | [0.08; 0.12] | |||
| Power ramp | 0.025 | 0.005 | 0.005 | |
| Cycle aging | ||||
| Calendar aging | 0.4 | 0.5 | ||
| 0.2 | 0.1 | |||
| 0.03 | 0.04 | |||
| 0.09 | 0.18 | |||
References
- Ritchie, H.; Rosado, P.; Roser, M. Breakdown of Carbon Dioxide, Methane and Nitrous Oxide Emissions by Sector. Our World Data 2020. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/emissions-by-sector (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Ritchie, H. Sector by Sector: Where Do Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From? Our World Data 2020. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/ghg-emissions-by-sector (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Trends in Electric Light-Duty Vehicles—Global EV Outlook 2023—Analysis. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2023/trends-in-electric-light-duty-vehicles (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Jones, C.B.; Lave, M.; Vining, W.; Garcia, B.M. Uncontrolled Electric Vehicle Charging Impacts on Distribution Electric Power Systems with Primarily Residential, Commercial or Industrial Loads. Energies 2021, 14, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jenn, A. Impact of Electric Vehicle Charging Demand on Power Distribution Grid Congestion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2317599121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemtarghi, A.; Mallik, A.; Chen, Y. Dynamic Pricing Strategy for Electric Vehicle Charging Stations to Distribute the Congestion and Maximize the Revenue. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 158, 109946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Meyboom, J.; Bauer, P.; Qin, Z. Techno-Economic Analysis of Energy Storage Systems Integrated with Ultra-Fast Charging Stations: A Dutch Case Study. eTransportation 2025, 24, 100411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Garrido, A.; González-Pérez, M.; Asensio, F.J.; Cortes-Borray, A.F.; Santos-Mugica, M.; Vicente-Figueirido, I. Hierarchical Control for Collaborative Electric Vehicle Charging to Alleviate Network Congestion and Enhance EV Hosting in Constrained Distribution Networks. Renew. Energy 2024, 230, 120823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyyamani Sunddararaj, S.; Rangarajan, S.S.; Nallusamy, S.; Collins, E.R.; Senjyu, T. A Brief Survey on Important Interconnection Standards for Photovoltaic Systems and Electric Vehicles. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempton, W.; Tomić, J. Vehicle-to-Grid Power Fundamentals: Calculating Capacity and Net Revenue. J. Power Sources 2005, 144, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Greenblatt, J.B.; MacDougall, P.; Saxena, S.; Jayam Prabhakar, A. Quantifying the Benefits of Electric Vehicles on the Future Electricity Grid in the Midwestern United States. Appl. Energy 2020, 270, 115174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashgi Shishvan, N.; Qin, J.; Guo, Z. Electric Vehicles’ Potential for Smoothing Daily Load Profile Considering Mobility Needs and Solar Output. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2025, 43, 101761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Qi, S.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S. Potential Co-Benefit Effect Analysis of Orderly Charging and Discharging of Electric Vehicles in China. Energy 2021, 226, 120352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amertet, S.; Gebresenbet, G. Hybridized Renewable Energy for Smart Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Systems. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2024, 42, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Transport in Europe. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/indicators/greenhouse-gas-emissions-from-transport (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Ahmed, S.; Ali, A.; Ciocia, A.; D’Angola, A. Technological Elements behind the Renewable Energy Community: Current Status, Existing Gap, Necessity, and Future Perspective—Overview. Energies 2024, 17, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ali, A.; D’Angola, A. A Review of Renewable Energy Communities: Concepts, Scope, Progress, Challenges, and Recommendations. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Directive (EU) 2018/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 December 2018 on the Promotion of the Use of Energy from Renewable Sources (Recast) (Text with EEA Relevance); Official Journal of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018; Volume 328. [Google Scholar]
- Gianaroli, F.; Preziosi, M.; Ricci, M.; Sdringola, P.; Ancona, M.A.; Melino, F. Exploring the Academic Landscape of Energy Communities in Europe: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 451, 141932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatti, M.; Moncecchi, M.; Gabba, M.; Chiesa, A.; Bovera, F.; Merlo, M. Energy Communities Design Optimization in the Italian Framework. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comunità Energetiche Rinnovabili. Available online: https://www.gse.it/servizi-per-te/autoconsumo/gruppi-di-autoconsumatori-e-comunita-di-energia-rinnovabile/comunit%C3%A0-energetiche-rinnovabili (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Taromboli, G.; Campagna, L.; Bergonzi, C.; Bovera, F.; Trovato, V.; Merlo, M.; Rancilio, G. Renewable Energy Communities: Frameworks and Implementation of Regulatory, Technical, and Social Aspects Across EU Member States. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkovski, B.; Gjorgievski, V.Z.; Markovski, B.; Cundeva, S.; Markovska, N. A Framework for Shared EV Charging in Residential Renewable Energy Communities. Renew. Energy 2024, 231, 120897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncecchi, M.; Meneghello, S.; Merlo, M. A Game Theoretic Approach for Energy Sharing in the Italian Renewable Energy Communities. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.; Hossain, M.J.; Nawazish Ali, S.M.; Sharma, V. An Efficient P2P Energy Trading Platform Based on Evolutionary Games for Prosumers in a Community. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 34, 101074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanvettor, G.G.; Casini, M.; Giannitrapani, A.; Paoletti, S.; Vicino, A. Optimal Management of Energy Communities Hosting a Fleet of Electric Vehicles. Energies 2022, 15, 8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.C.; Pinheiro, M.D. Energy Communities and Electric Mobility as a Win–Win Solution in Built Environment. Energies 2024, 17, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, G.; Brusco, G.; Menniti, D.; Pinnarelli, A.; Polizzi, G.; Sorrentino, N.; Vizza, P.; Burgio, A. How Smart Metering and Smart Charging May Help a Local Energy Community in Collective Self-Consumption in Presence of Electric Vehicles. Energies 2020, 13, 4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhoff, S.; Wagner, H.; Werth, O.; Gerlach, J.; Breitner, M.H.; Engel, B. Electric Mobility Integration in Energy Communities: Trending Topics and Future Research Directions. In Proceedings of the 5th E-Mobility Power System Integration Symposium (EMOB 2021), Berlin, Germany, 27 September 2021; Volume 2021, pp. 196–204. [Google Scholar]
- Nazari, S.; Borrelli, F.; Stefanopoulou, A. Electric Vehicles for Smart Buildings: A Survey on Applications, Energy Management Methods, and Battery Degradation. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 1128–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alirezaei, M.; Noori, M.; Tatari, O. Getting to Net Zero Energy Building: Investigating the Role of Vehicle to Home Technology. Energy Build. 2016, 130, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cao, S. Energy Flexibility Investigation of Advanced Grid-Responsive Energy Control Strategies with the Static Battery and Electric Vehicles: A Case Study of a High-Rise Office Building in Hong Kong. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 199, 111888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Bouffard, F.; Joós, G. Decision Tree-Based Optimization for Flexibility Management for Sustainable Energy Microgrids. Appl. Energy 2021, 290, 116772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, J.; Ramirez Camargo, L.; Putratama, M.A.; Messagie, M.; Coosemans, T. TreeC: A Method to Generate Interpretable Energy Management Systems Using a Metaheuristic Algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 309, 112756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kam, M.; van Sark, W. Smart Charging of Electric Vehicles with Photovoltaic Power and Vehicle-to-Grid Technology in a Microgrid; A Case Study. Appl. Energy 2015, 152, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, A.; Lachheb, A.; El Amraoui, L. Optimizing Efficiency of Vehicle-to-Grid System with Intelligent Management and ANN-PSO Algorithm for Battery Electric Vehicles. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 226, 109936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, H.U.R.; Subramaniam, U.; Waqar, A.; Farhan, B.S.; Kotb, K.M.; Wang, S. Energy Cost Optimization of Hybrid Renewables Based V2G Microgrid Considering Multi Objective Function by Using Artificial Bee Colony Optimization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 62076–62093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobana, S.; Praghash, K.; Ramya, G.; Rajakumar, B.R.; Binu, D. Integrating Renewable Energy in Electric V2G: Improved Optimization Assisting Dispatch Model. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 7917–7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltamaly, A.M. Optimal Dispatch Strategy for Electric Vehicles in V2G Applications. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 3161–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulla, A.; Jadhav, H.T. Optimal Scheduling of Vehicle-to-Grid Power Exchange Using Particle Swarm Optimization Technique. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2022, 44, 687–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, H.I.; Rashed, G.I.; Yang, B.; Yang, J. Optimal Electric Vehicle Charging and Discharging Scheduling Using Metaheuristic Algorithms: V2G Approach for Cost Reduction and Grid Support. J. Energy Storage 2024, 90, 111816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, M.; Beenish, H. Efficient V2G Model on Smart Grid Power Systems Using Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2019 1st Global Power, Energy and Communication Conference (GPECOM), Nevsehir, Turkey, 12–15 June 2019; pp. 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Fang, B.; Deng, J. Multi-Objective Optimization Strategy for Distribution Network Considering V2G-Enabled Electric Vehicles in Building Integrated Energy System. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2020, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, S.M.; Khan, H.A.; Sohaib, S.; Hashmi, A.M. Optimized Power Dispatch for Smart Building and Electric Vehicles with V2V, V2B and V2G Operations. Energies 2023, 16, 4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhoseini, P.; Ghaffarzadeh, N. Economic Battery Sizing and Power Dispatch in a Grid-Connected Charging Station Using Convex Method. J. Energy Storage 2020, 31, 101651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, H.; Ranjbar, H.; Fattaheian-Dehkordi, S.; Moeini-Aghtaie, M.; Ehsan, M.; Shahidehpour, M. Transactive Energy Management of V2G-Capable Electric Vehicles in Residential Buildings: An MILP Approach. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 13, 1734–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, R.; Steen, D.; Wikner, E.; Tuan, L.A. Optimal V2G Scheduling of an EV With Calendar and Cycle Aging of Battery: An MILP Approach. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 10497–10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterakis, N.G.; Erdinç, O.; Bakirtzis, A.G.; Catalão, J.P.S. Optimal Household Appliances Scheduling Under Day-Ahead Pricing and Load-Shaping Demand Response Strategies. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2015, 11, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Che, L.; Wang, L.; Madawala, U.K. Game-Theory Based V2G Coordination Strategy for Providing Ramping Flexibility in Power Systems. Energies 2020, 13, 5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Qin, J.; Li, F.; Yu, X.; Kang, Y. Game Theoretic-Based Distributed Charging Strategy for PEVs in a Smart Charging Station. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksan, F.; Suresh, V.; Janik, P. Optimal Capacity and Charging Scheduling of Battery Storage through Forecasting of Photovoltaic Power Production and Electric Vehicle Charging Demand with Deep Learning Models. Energies 2024, 17, 2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.J.; Oyedele, L.O.; Ajayi, A.O.; Akinade, O.O.; Owolabi, H.A.; Ahmed, A. Feature Extraction and Genetic Algorithm Enhanced Adaptive Deep Neural Network for Energy Consumption Prediction in Buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 131, 109980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-Y.; Cho, S.-B. Predicting Residential Energy Consumption Using CNN-LSTM Neural Networks. Energy 2019, 182, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreft, M.; Brudermueller, T.; Fleisch, E.; Staake, T. Predictability of Electric Vehicle Charging: Explaining Extensive User Behavior-Specific Heterogeneity. Appl. Energy 2024, 370, 123544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.N.; Kütt, L.; Lehtonen, M.; Millar, R.J.; Püvi, V.; Rassõlkin, A.; Demidova, G.L. Travel Activity Based Stochastic Modelling of Load and Charging State of Electric Vehicles. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tayarani, M.; Gao, O. An Activity-Based Travel and Charging Behavior Model for Simulating Battery Electric Vehicle Charging Demand. Energy 2022, 258, 124938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Tao, S.; He, K.; Lu, M.; Xie, B.; Yang, B.; Sun, Y. V2G Multi-Objective Dispatching Optimization Strategy Based on User Behavior Model. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 739527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XL-CONNECT|On Demand Multi-Directional Charging Solutions for Electric Vehicles. Available online: https://xlconnect.eu/ (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Kohl, K. Homepage [Forecast.Solar]. Available online: https://forecast.solar/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Transparency Platform. Available online: https://newtransparency.entsoe.eu/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Innocenti, E.; Berzi, L.; Kociu, A.; Pugi, L.; Delogu, M. Planning of Smart Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles: An Italian Case Study. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Industrial Engineering and Automation ISIEA 2024, Bolzano, Italy, 19–21 June 2024; ISBN 978-3-031-70465-9. [Google Scholar]
- De Angelis, F.; Boaro, M.; Fuselli, D.; Squartini, S.; Piazza, F.; Wei, Q. Optimal Home Energy Management Under Dynamic Electrical and Thermal Constraints. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day Ahead Market. Available online: https://www.etpa.nl/knowledge-base/markets/day-ahead-market (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Eicke, A.; Ruhnau, O.; Hirth, L. Electricity Balancing as a Market Equilibrium: An Instrument-Based Estimation of Supply and Demand for Imbalance Energy. Energy Econ. 2021, 102, 105455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, P.; Jossen, A. Calendar and Cycle Aging of Commercial NCA Lithium-Ion Cells. Meet. Abstr. 2016, MA2016-02, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, P.; Schuster, S.F.; Wilhelm, J.; Travi, J.; Hauser, A.; Karl, R.C.; Jossen, A. Calendar Aging of Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagropoulos, S.I.; Bakirtzis, A.G. Optimal Bidding Strategy for Electric Vehicle Aggregators in Electricity Markets. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 4031–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP) Algorithms—MATLAB & Simulink. Available online: https://it.mathworks.com/help/optim/ug/mixed-integer-linear-programming-algorithms.html (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Shoja, S. On Complexity Certification of Branch-and-Bound Methods for MILP and MIQP with Applications to Hybrid MPC. Licentiate’s Thesis, Linkoping University Electronic Press, Linkoping, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Purewal, J.; Liu, P.; Hicks-Garner, J.; Soukazian, S.; Sherman, E.; Sorenson, A.; Vu, L.; Tataria, H.; Verbrugge, M.W. Degradation of Lithium Ion Batteries Employing Graphite Negatives and Nickel–Cobalt–Manganese Oxide + Spinel Manganese Oxide Positives: Part 1, Aging Mechanisms and Life Estimation. J. Power Sources 2014, 269, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ma, P.; Wang, M.; Fang, B.; Zhang, M. A Hierarchical Strategy for Multi-Objective Optimization of Distribution Network Considering DGs and V2G-Enabled EVs Integration. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 869844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, A.; Pourakbari-Kasmaei, M.; Jasinski, M.; Lehtonen, M.; Leonowicz, Z. A Hybrid Decentralized Stochastic-Robust Model for Optimal Coordination of Electric Vehicle Aggregator and Energy Hub Entities. Appl. Energy 2021, 304, 117708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümrükcü, E.; Klemets, J.R.A.; Suul, J.A.; Ponci, F.; Monti, A. Decentralized Energy Management Concept for Urban Charging Hubs With Multiple V2G Aggregators. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 2367–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour-Saatloo, A.; Pezhmani, Y.; Mirzaei, M.A.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Zare, K.; Marzband, M.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A. Robust Decentralized Optimization of Multi-Microgrids Integrated with Power-to-X Technologies. Appl. Energy 2021, 304, 117635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| RES Plant Size [Pls] | Incentive [€/MWh] | Min Value Incentive [€/MWh] | Max Value Incentive [€/MWh] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pls < 200 kWp | .) | 80 | 120 |
| 200 ≤ Pls ≤ 600 kWp | .) | 70 | 110 |
| Pls > 600 kWp | .) | 60 | 100 |
| User Type | Description | SOC Target | Parking Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Priority | |||
| Full charge | Charges at maximum power | Not required | Not required | |
| Partial charge | Charges to a specific SOC at maximum power | Required | Not required | |
 | V1G | Allows modular charging | Optional | Required |
 | V2G | Allows bidirectional charging | Optional | Required |
| Feature | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Time signature | Minute of the day | |
| Boolean flag indicating if the current day is a holiday | |||
| Boolean flag indicating if the next day is a holiday | |||
| Normalized day of the week (0/8 to 8/8) | |||
| Cosine of the minute of the day | |||
| Cosine of the day of the year | |||
| Short-term data | Previous 12 h of power sampled at 15-min intervals | ||
| Output | Next 24 h forecasted power sampled at 15-min intervals | ||
| Hyperparameters | Values | Best Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Activation function | [Relu, Leaky Relu] | Leaky Relu |
| Number of hidden layers | [1, 2, 4] | 2 |
| Learning rate | [1 × 10−2, 1 × 10−3, 1 × 10−4] | 1 × 10−4 |
| Problem Constraints | N. | Cost Function Parts | N. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power balance | Energy cost | 1 | ||
| SOC evolution | ||||
| Inverter maximum power | Incentive penalty | 1 | ||
| User | V1G | |||
| Priority | Aging penalty | |||
| SOC target | ||||
| Sub-constraints definition | Power ramp penalty | |||
| Power derivative definition | 1 | |||
| Positive grid power definition | 1 | |||
| Moving Lab | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Value | |
| Charging point power | [22, 22, 22] | kWp |
| PV power | 100 | kWp |
| BESS capacity | 50 | kWh |
| Building mean power | 50 | kW |
| Campus Design | ||
| Parameter | Value | |
| Charging point power | [22, 22, 22, 22, 11, 11] | kWp |
| Loc. | Buildings | Chargers |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 9 |
| 4 | 2 | 18 |
| 8 | 4 | 36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pezzati, N.; Innocenti, E.; Berzi, L.; Delogu, M. Scalable Energy Management Model for Integrating V2G Capabilities into Renewable Energy Communities. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16080450
Pezzati N, Innocenti E, Berzi L, Delogu M. Scalable Energy Management Model for Integrating V2G Capabilities into Renewable Energy Communities. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(8):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16080450
Chicago/Turabian StylePezzati, Niccolò, Eleonora Innocenti, Lorenzo Berzi, and Massimo Delogu. 2025. "Scalable Energy Management Model for Integrating V2G Capabilities into Renewable Energy Communities" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 8: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16080450
APA StylePezzati, N., Innocenti, E., Berzi, L., & Delogu, M. (2025). Scalable Energy Management Model for Integrating V2G Capabilities into Renewable Energy Communities. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(8), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16080450










