Coordinated Slip Ratio and Yaw Moment Control for Formula Student Electric Racing Car
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Racing Parameters and Conditions
2.1. Racing Parameters
2.2. Analysis of Working Conditions
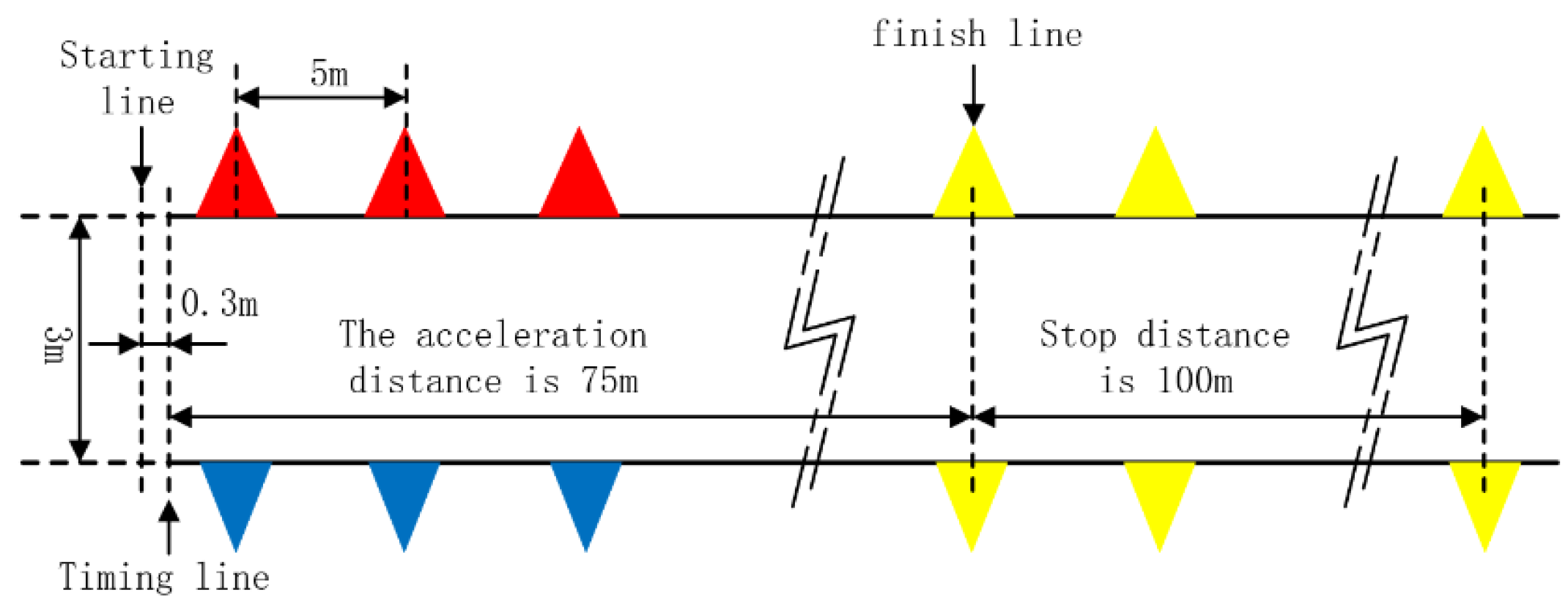
2.2.1. Straight-Line Acceleration Condition
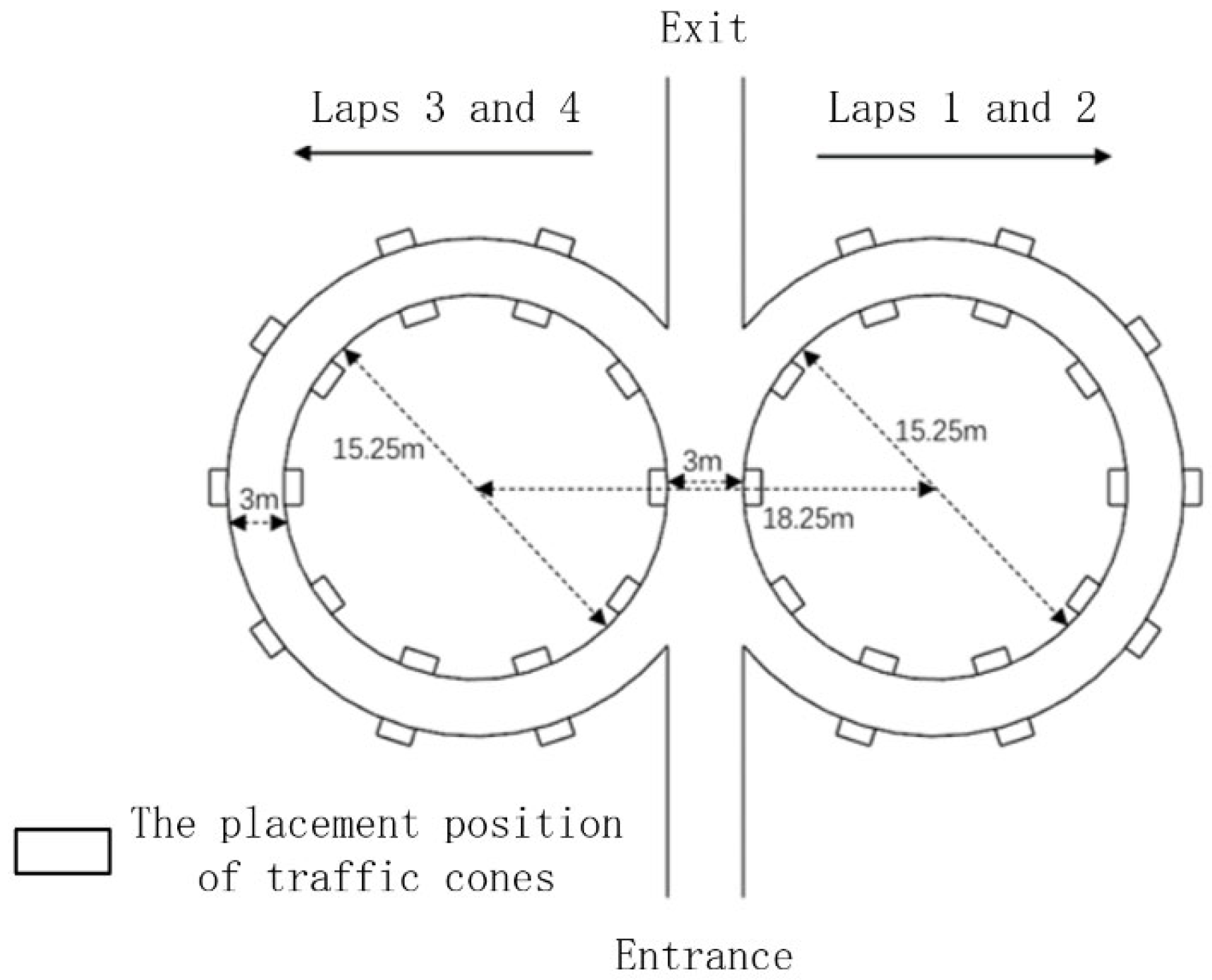
2.2.2. Figure-Eight Loop Condition
3. Model Construction
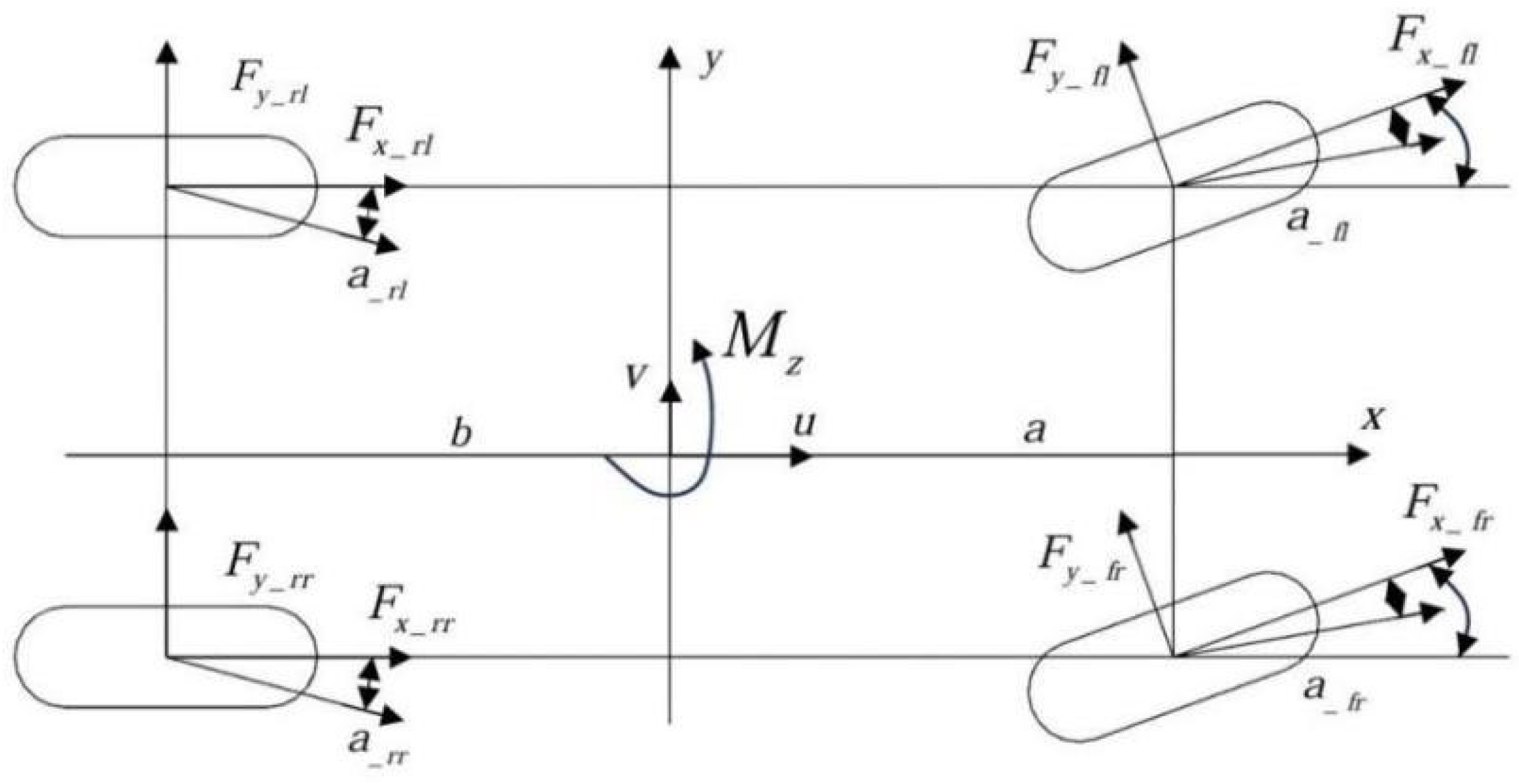
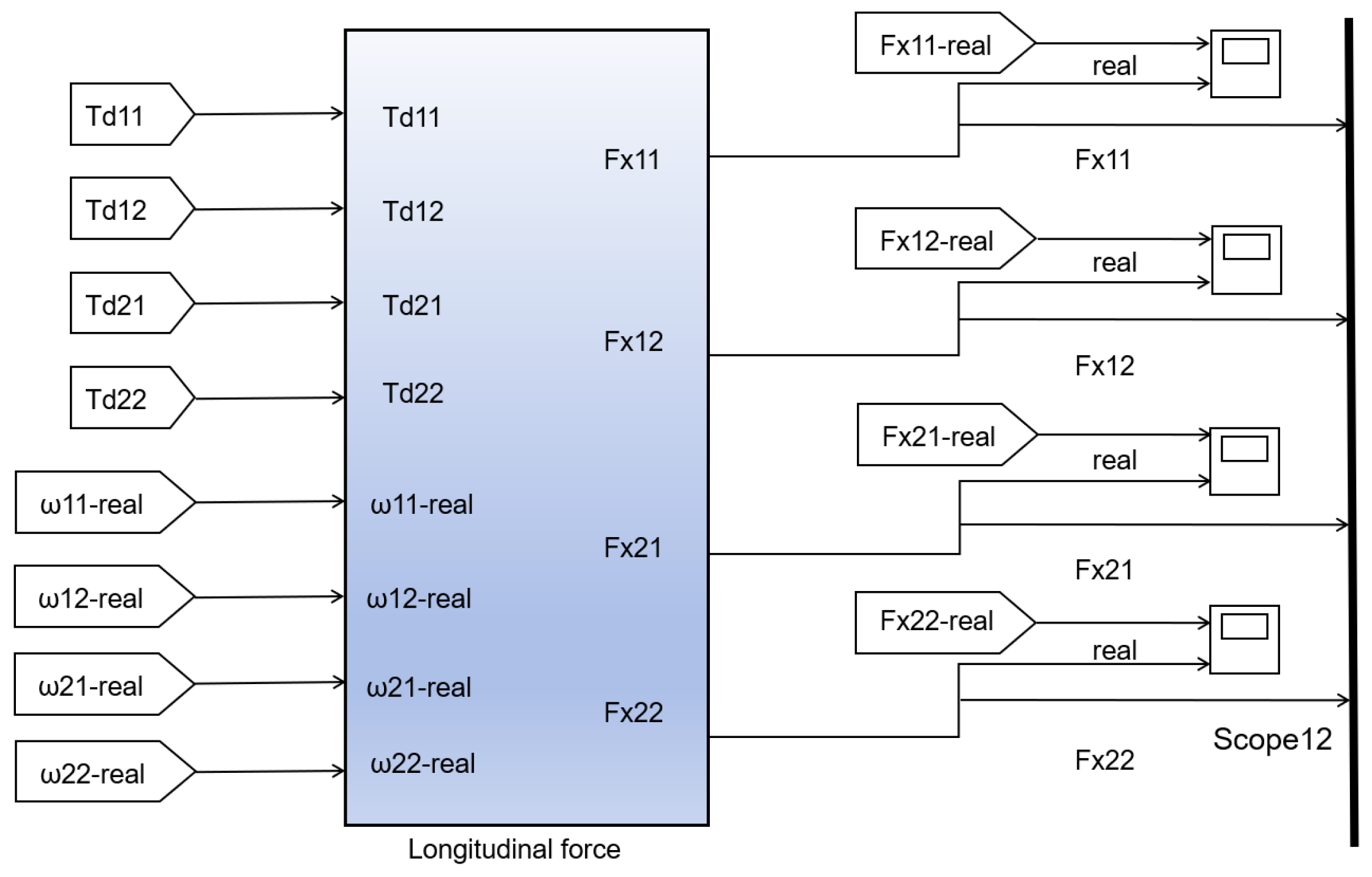
3.1. Estimation Model
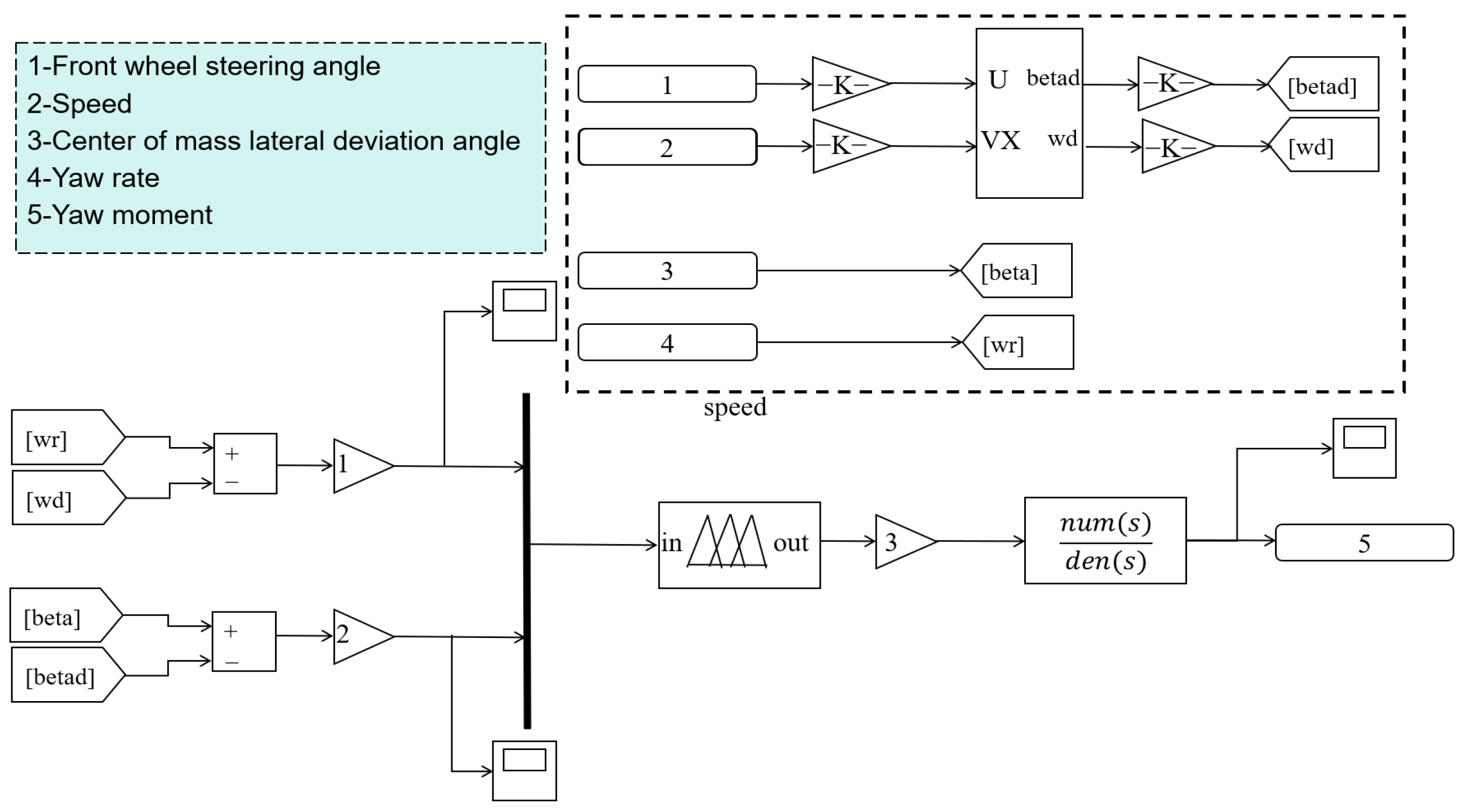
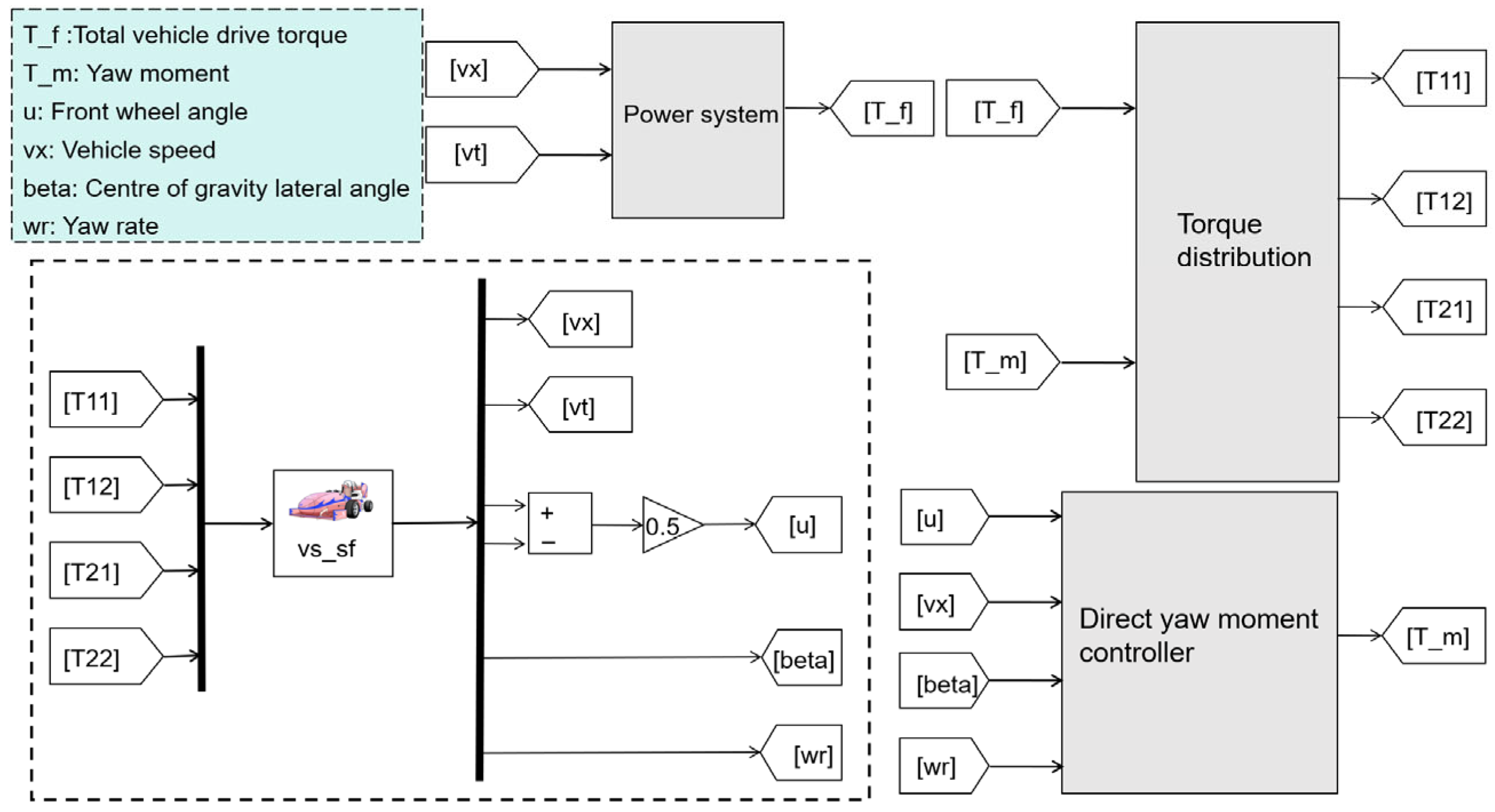
3.2. Drive Control Strategy Model
3.2.1. Straight-Line Acceleration Condition
3.2.2. Figure-Eight Loop Condition
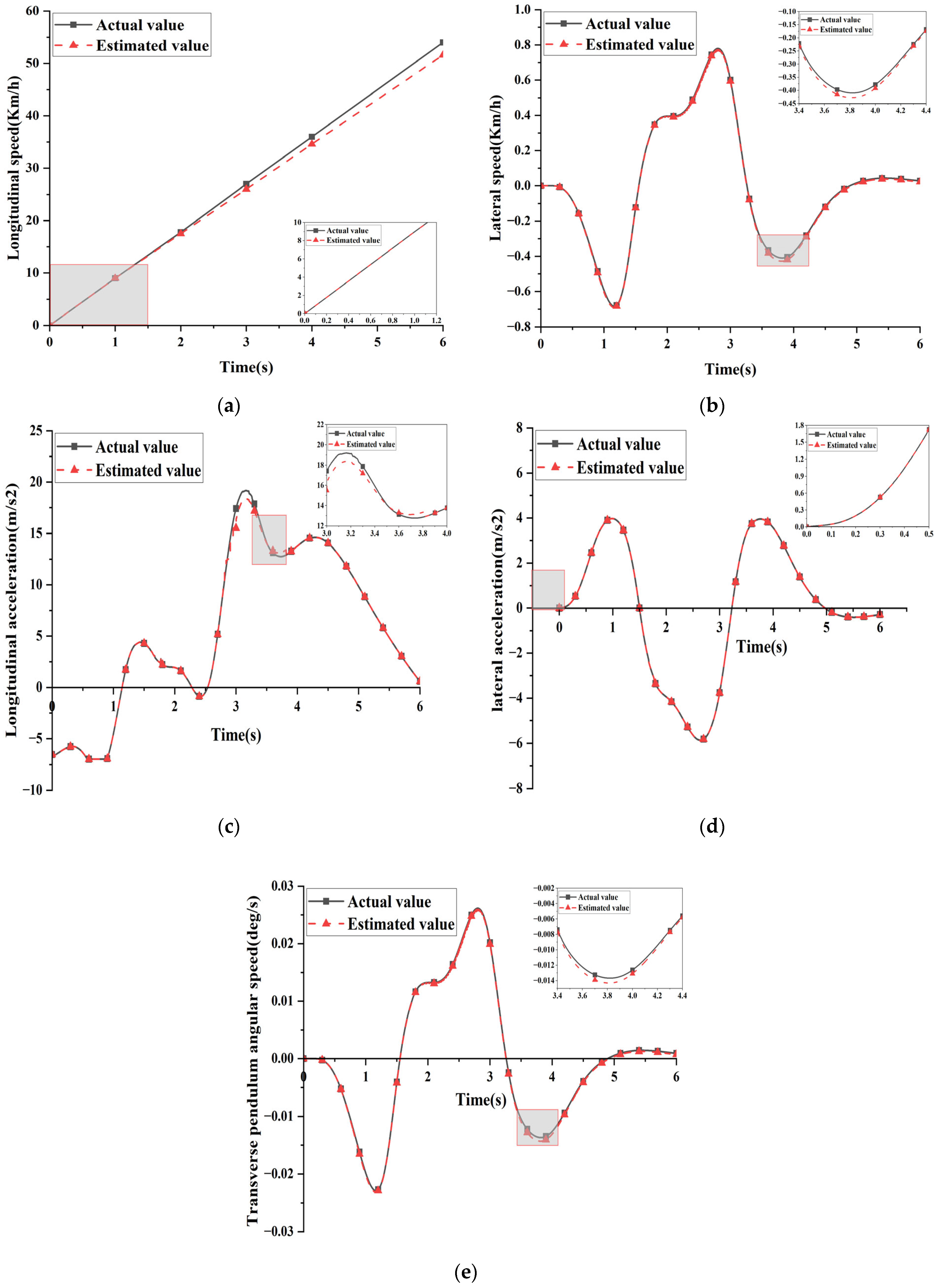
4. Validation of State Estimation
4.1. Straight-Line Acceleration Condition
4.2. Figure-Eight Loop Condition
5. Simulation Result
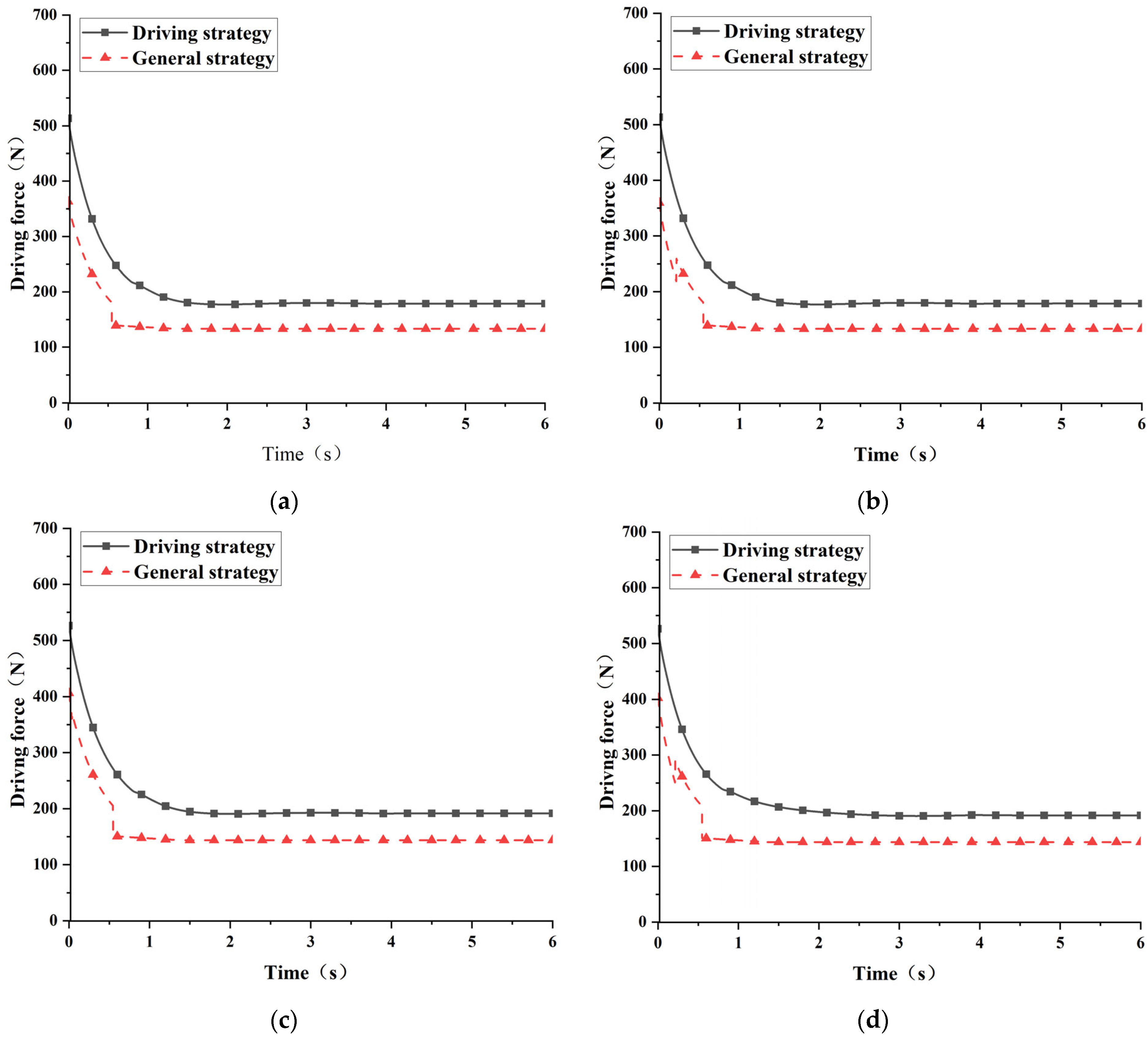
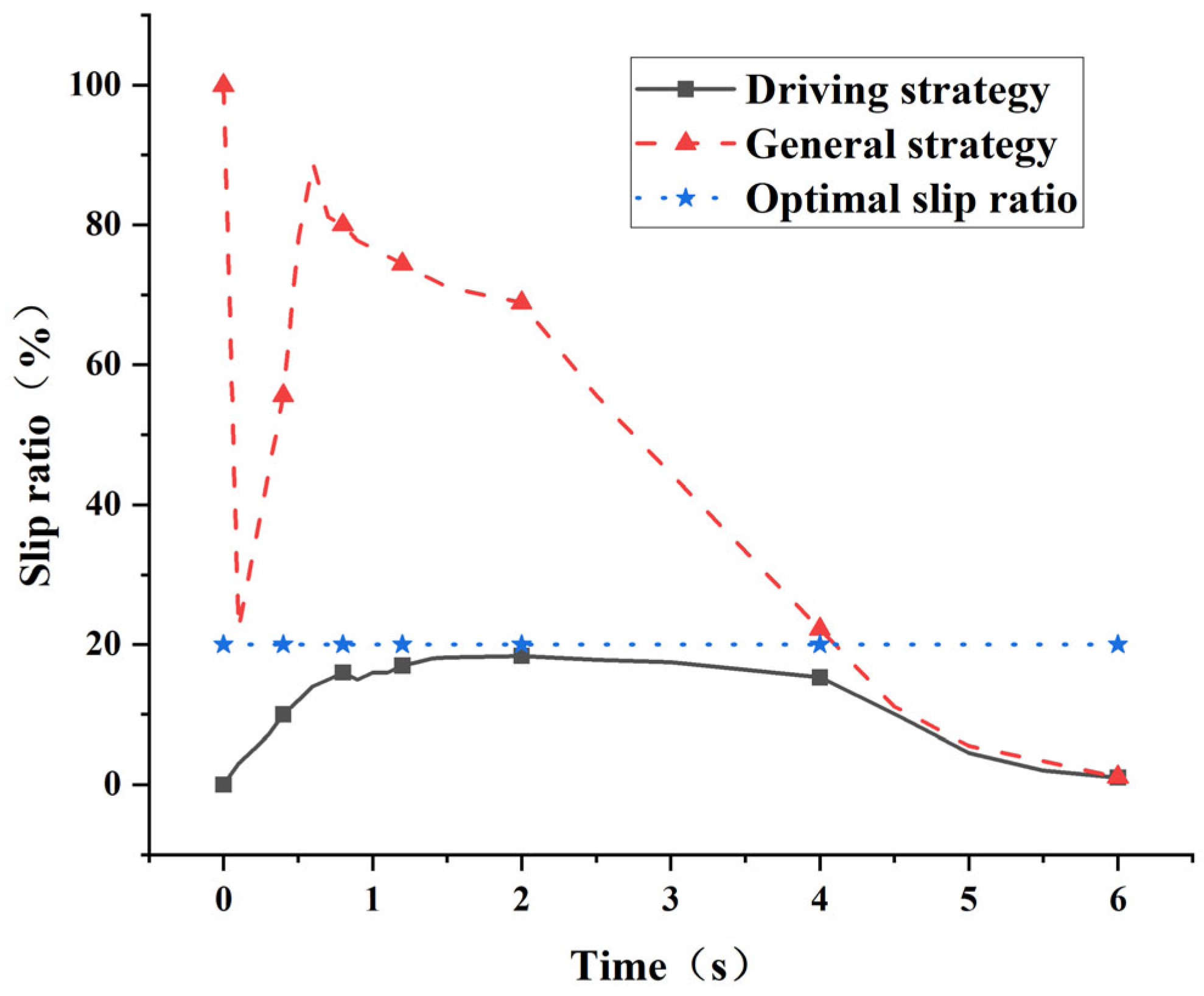
5.1. Straight-Line Acceleration Condition
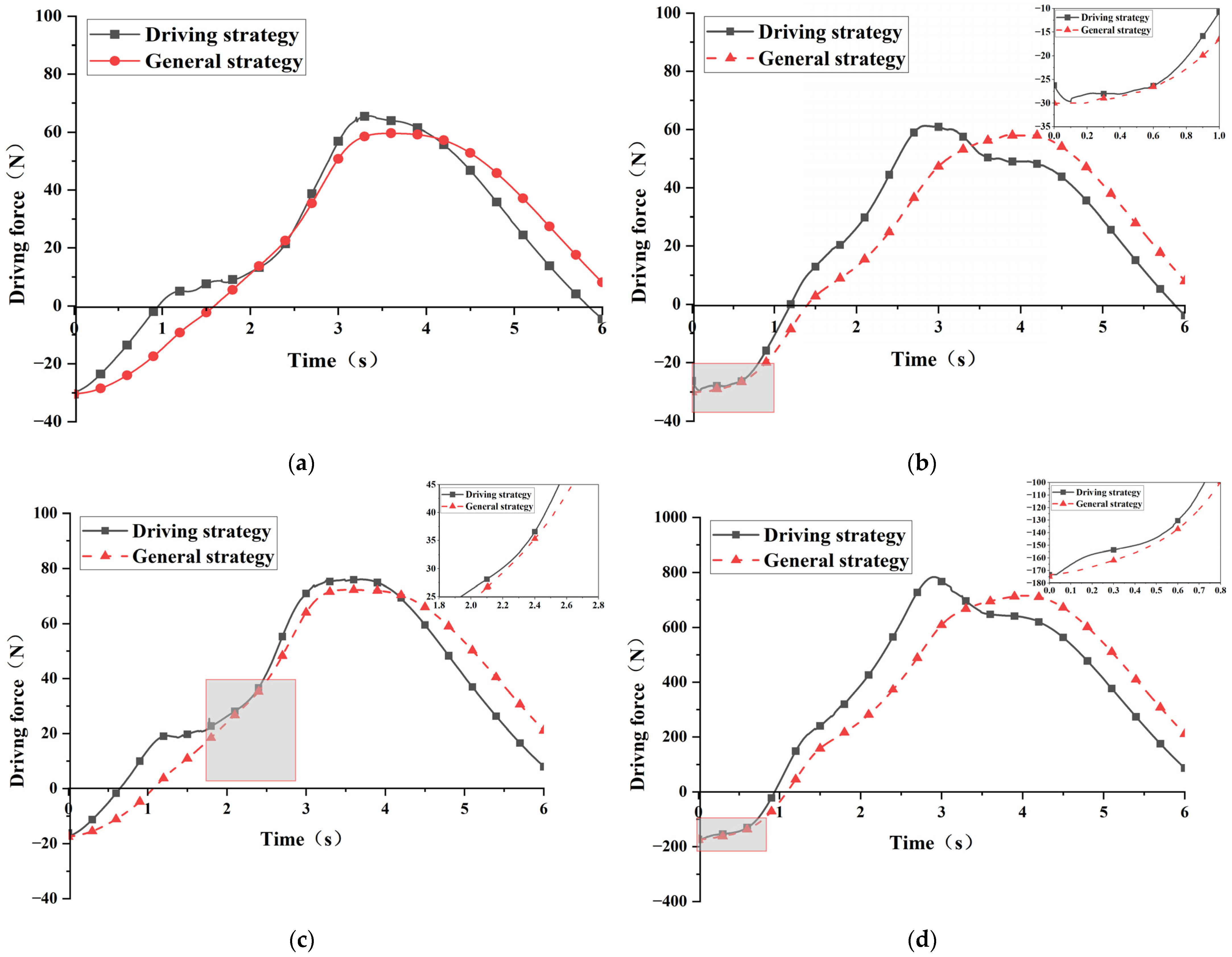
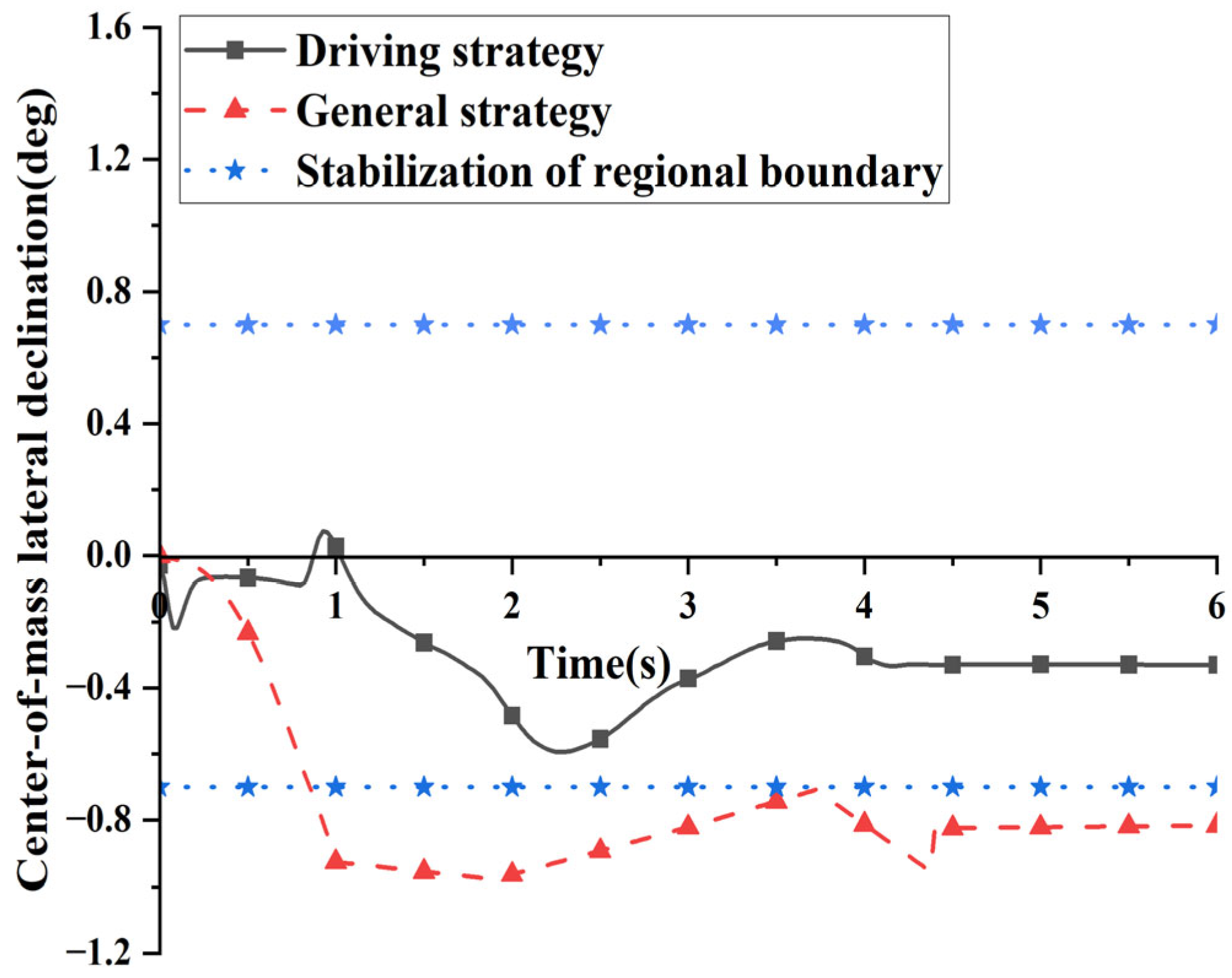
5.2. Figure-Eight Loop Condition
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niu, S.; Yu, H.; Niu, S.; Jian, L. Power loss analysis and thermal assessment on wireless electric vehicle charging technology: The over-temperature risk of ground assembly needs attention. Appl. Energy 2020, 275, 115344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Dang, M.; Chang, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, R.; Ma, J. Hierarchical driving force allocation strategy for 4-WID electric vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2023, 237, 2484–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Wang, C.; Hou, Y.; Hou, R.; Ming Mok, Y.; Zhang, X. Two-level optimal torque distribution for handling stability control of a four hub-motor independent-drive electric vehicle under various adhesion conditions. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2023, 237, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, W.; Xiang, C.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Torque coordinated control of four in-wheel motor independent-drive vehicles with consideration of the safety and economy. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 9604–9618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y. Multi-perspective evaluation of a novel powertrain integrating series-parallel and power-split modes: An ultra-rapid hierarchical control approach. Mech. Mach. Theory 2025, 210, 106034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, Z. Design of Hierarchical Control System for Dual-steering of Multi-wheel Distributed Electric Drive Vehicles. Automot. Eng. 2021, 43, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Vali, R.A.; Allahverdizadeh, F.; Behnamgol, V. Fixed-time dynamic control allocation for the distribution of braking forces in a vehicle ESC system. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 22009–22037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, D.; Wong, K.P.; Huang, W. Model predictive control allocation based on adaptive sliding mode control strategy for enhancing the lateral stability of four-wheel-drive electric vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2024, 238, 1514–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Quan, X.; Ma, F.; Liu, G.; Zheng, X.; Yu, M. Stability control for a four-wheel-independent-drive electric vehicle based on model predictive control. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2021, 5, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Yue, M.; Shangguan, J.; Guo, L.; Zhao, J. Integrated control method for path tracking and lateral stability of distributed drive electric vehicles with extended Kalman filter–based tire cornering stiffness estimation. J. Vib. Control 2024, 30, 2582–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, R.; Zhang, R.; Wen, J. Stability control strategy for in-wheel-motor-drive electric vehicle based on dspace. Mechatron. Syst. Control 2020, 48, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhwar, P. Application of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Electric Vehicle. Indian J. Des. Eng. 2024, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.Q.; Jia, Q.; Gao, R. Research on the Adaptive PID speed control method for Hub Motors. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 4979824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabari, M.; Rad, A. Optimization of speed control and reduction of torque ripple in switched reluctance motors using metaheuristic algorithms based PID and FOPID controllers at the edge. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2025, 30, 1526–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.W.; Mohammed, A.S.; Noaman, S.F. An adaptive neuro-fuzzy with nonlinear PID controller design for electric vehicles. IFAC J. Syst. Control 2024, 27, 110238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.; Silva, L.; Eckert, J.J.; Yamashita, R.Y.; Lourenço, M.A. Parameter influence analysis in an optimized fuzzy stability control for a four-wheel independent-drive electric vehicle. Control Eng. Pract. 2022, 120, 115000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, B.; Fu, J.H. Research on Optimal Distribution Control Strategy of 4WID Electric Vehicle Torque. Mach. Des. Manuf. 2020, 12, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q. Wheel torque distribution optimization of four-wheel independent-drive electric vehicle for energy efficient driving. Control Eng. Pract. 2021, 111, 114779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Han, L.; Xin, H.; Xiang, C. Adaptive equivalent consumption minimisation strategy and dynamic control allocation-based optimal power management strategy for four-wheel drive hybrid electric vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2019, 233, 3125–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Li, E.; Peng, C. Research on the distribution strategy of longitudinal driving force of vehicle driven by 8 × 8 in-wheel motors. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2181, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Mahajan, M. Modeling and simulation of vehicle behavior for design and tuning of electronic differential for formula student vehicle. In Proceedings of the International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Charlotte, NC, USA, 21–24 August 2016; Volume 50138, p. V003T01A011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnane, M.; Nguyen, C.T.P.; Khoumsi, A.; Trovão, J.P.F. Real-time torque-distribution for dual-motor off-road vehicle using machine learning approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 4567–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimi, H.; Elgarouaz, M.; Lazrak, L.; El Daoudi, S. Experimental Validation of an Open Loop Drive Control of an Asynchronous Motor with the TMS320F28379D DSP Card and Speed Senser. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 105116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, D.; Ma’arif, A.; Maghfiroh, H.; Chotikunnan, P.; Rahmadhia, S.N. Design and application of PLC-based speed control for DC motor using PID with identification system and MATLAB tuner. Int. J. Robot. Control Syst. 2023, 3, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oubelaid, A.; Mohamed, N.; Rathore, R.S.; Bajaj, M.; Rekioua, T. Artificial Neural Networks-Based Torque Distribution for Riding Comfort Improvement of Hybrid Electric Vehicles. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 235, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zang, L.; Wang, S. Lateral Stability Control of Distributed Drive Electric Vehicle with Mechanical Elastic Wheel. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 58, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Driving stability control of four-wheel independent steering distributed drive electric vehicle with single-wheel steering failure. J. Mech. Eng. 2024, 60, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, H.; Tao, X.; Ding, Y.; Yu, B.; Bai, R. Driving Force Distribution and Control for Maneuverability and Stability of a 6WD Skid-Steering EUGV with Independent Drive Motors. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, K.; Li, Q.; Yang, J. An Optimal Hierarchical Control Strategy for 4WS-4WD Vehicles Using Nonlinear Model Predictive Control. Machines 2024, 12, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Ma, X.; Su, R.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C. Regenerative Braking of Electric Vehicles Based on Fuzzy Control Strategy. Processes 2023, 11, 2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
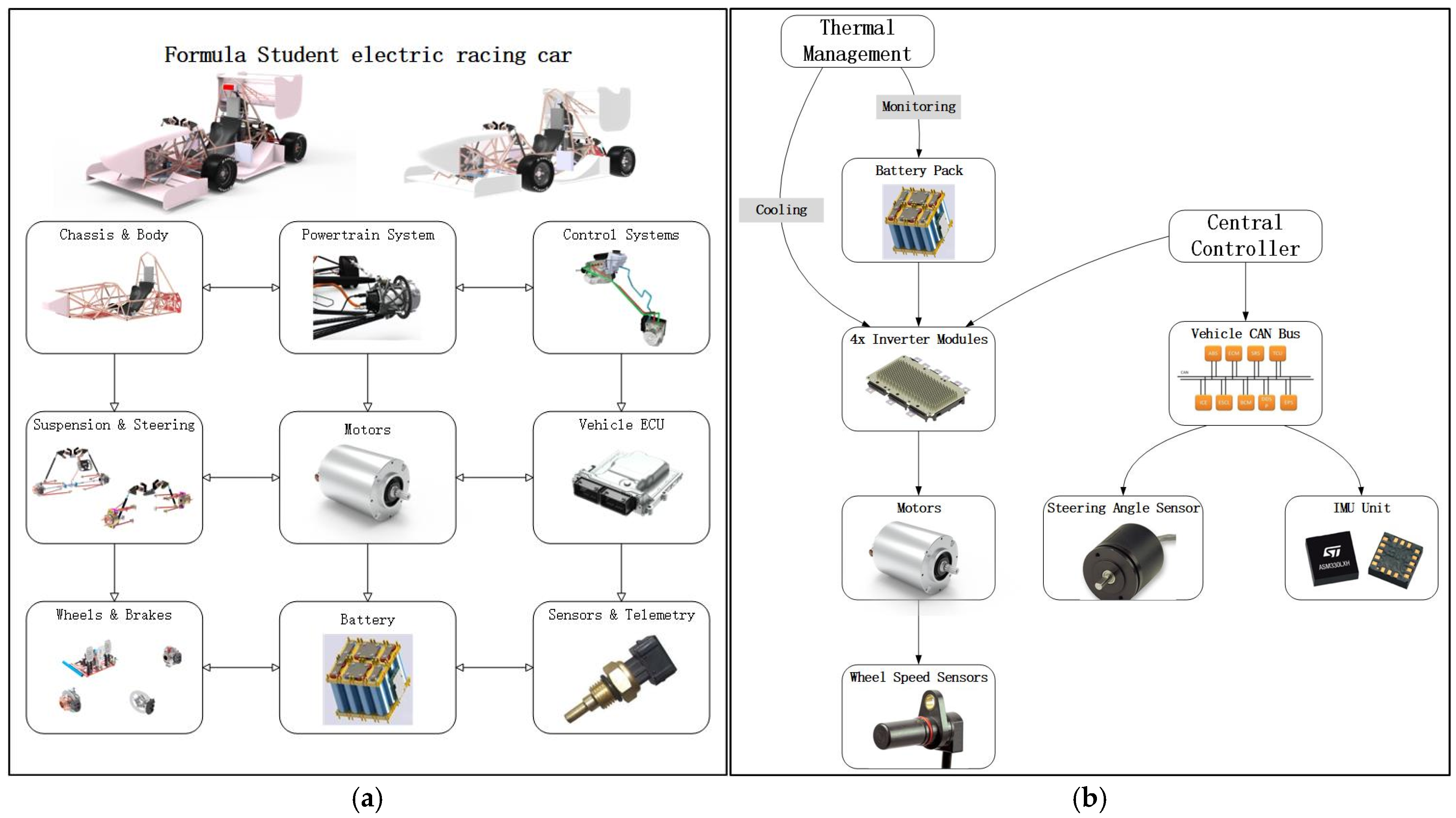

| Parameter Name | Unit | Value | Parameter Name | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle parameters | |||||
| Vehicle weight | kg | 250 | Wheelbase | mm | 1600 |
| Distance from center of mass to front axle | mm | 879.31 | Center of mass height | mm | 229.46 |
| Overall width | mm | 1402 | Overall height | mm | 1190 |
| Front wheelbase | mm | 1212 | Rear wheelbase | mm | 1212 |
| Spring loaded mass | kg | 150 | Front/rear load ratio | / | 48:52 |
| Windward area | m2 | 1.23 | Left/Right load ratio | / | 1:1 |
| Steering arm length | mm | 90 | Tire radius | mm | 205 |
| Front and rear tire width ratio | / | 1 | Steering ratio | / | 4:1 |
| Inclination angle of main pin | deg | 5 | Main pin rear camber angle | deg | 5 |
| Front wheel camber | deg | −5 | Front wheel front beam angle | deg | −5 |
| Motor parameters | |||||
| Motor mass | kg | 12 | Rated power | kW | 40 |
| Shaft length/mm | mm | 86 | Peak power | kW | 109 |
| Housing diameter/mm | mm | 228 | Continuous power | kW | 62 |
| Peak torque | N·m | 230 | Peak speed | rpm | 6000 |
| Continuous torque | N·m | 120 | Efficiency | % | 92–98 |
| Motor mass | kg | 12 | Rated power | kW | 40 |
| Shaft length | mm | 86 | Peak power | kW | 109 |
| Housing diameter | mm | 228 | Continuous power | kW | 62 |
| Battery parameters | |||||
| Battery pack size | mm3 | 474.6 × 618.2 × 168.4 | Battery pack-type | Serial connection | |
| Energy capacity | kWh | 7.84 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Y.; Kong, W.; Zang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, C.; Cui, S. Coordinated Slip Ratio and Yaw Moment Control for Formula Student Electric Racing Car. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16080421
Bai Y, Kong W, Zang L, Zhang W, Zhou C, Cui S. Coordinated Slip Ratio and Yaw Moment Control for Formula Student Electric Racing Car. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(8):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16080421
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Yuxing, Weiyi Kong, Liguo Zang, Weixin Zhang, Chong Zhou, and Song Cui. 2025. "Coordinated Slip Ratio and Yaw Moment Control for Formula Student Electric Racing Car" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 8: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16080421
APA StyleBai, Y., Kong, W., Zang, L., Zhang, W., Zhou, C., & Cui, S. (2025). Coordinated Slip Ratio and Yaw Moment Control for Formula Student Electric Racing Car. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(8), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16080421








