Sliding Mode Thrust Control Strategy for Electromagnetic Energy-Feeding Shock Absorbers Based on an Improved Gray Wolf Optimizer
Abstract
1. Introduction
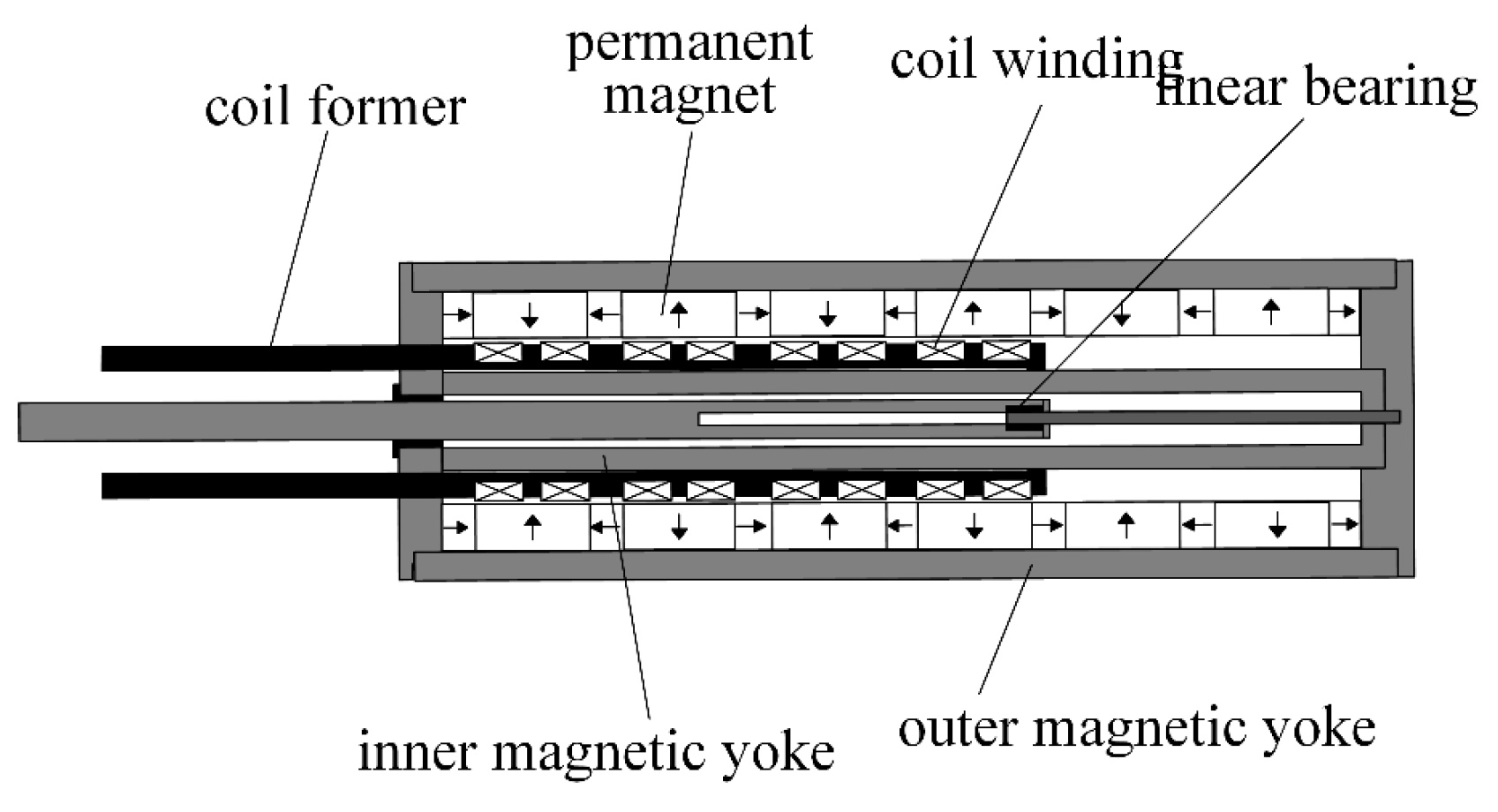
2. Mathematical Model of the Electromagnetic Energy-Feeding Shock Absorber
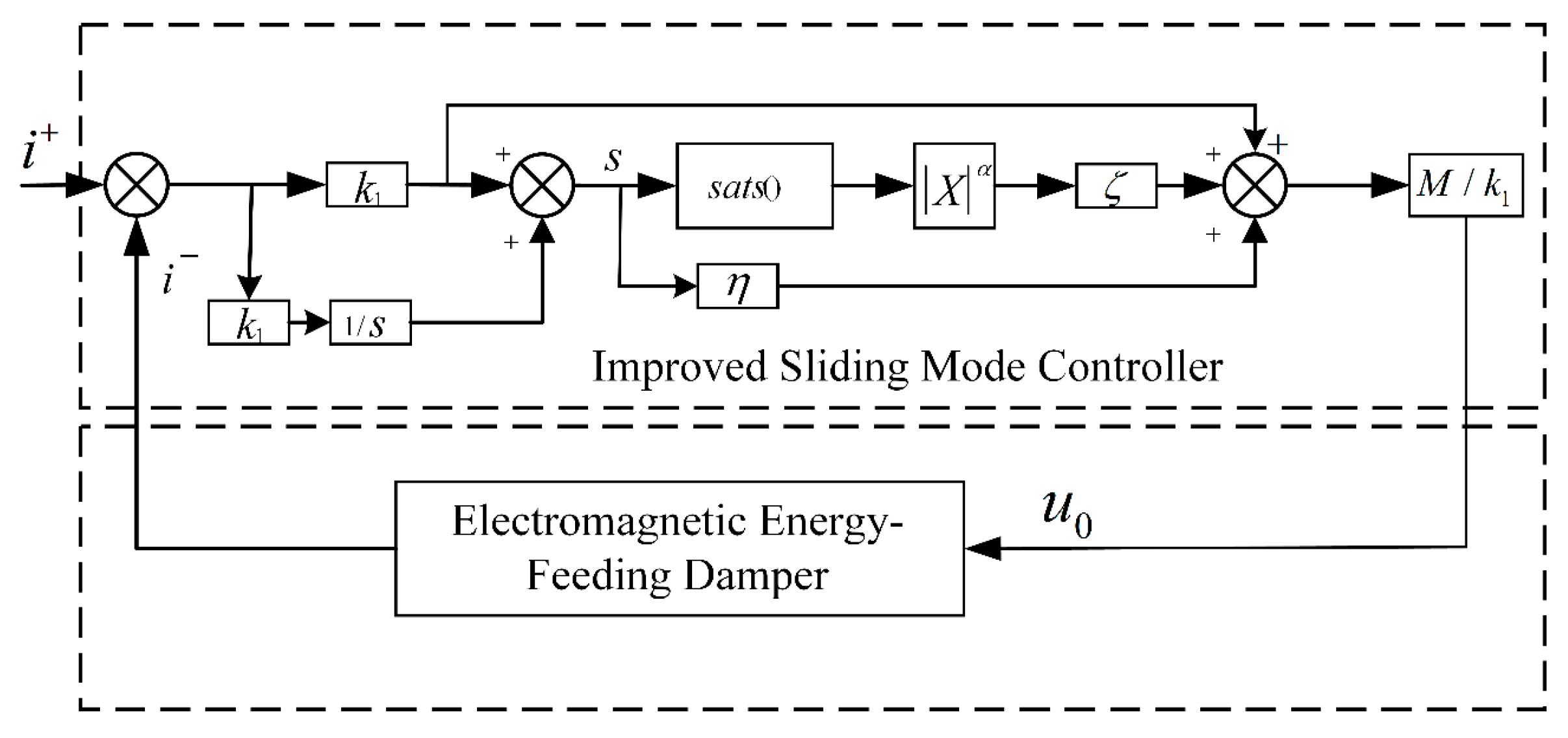
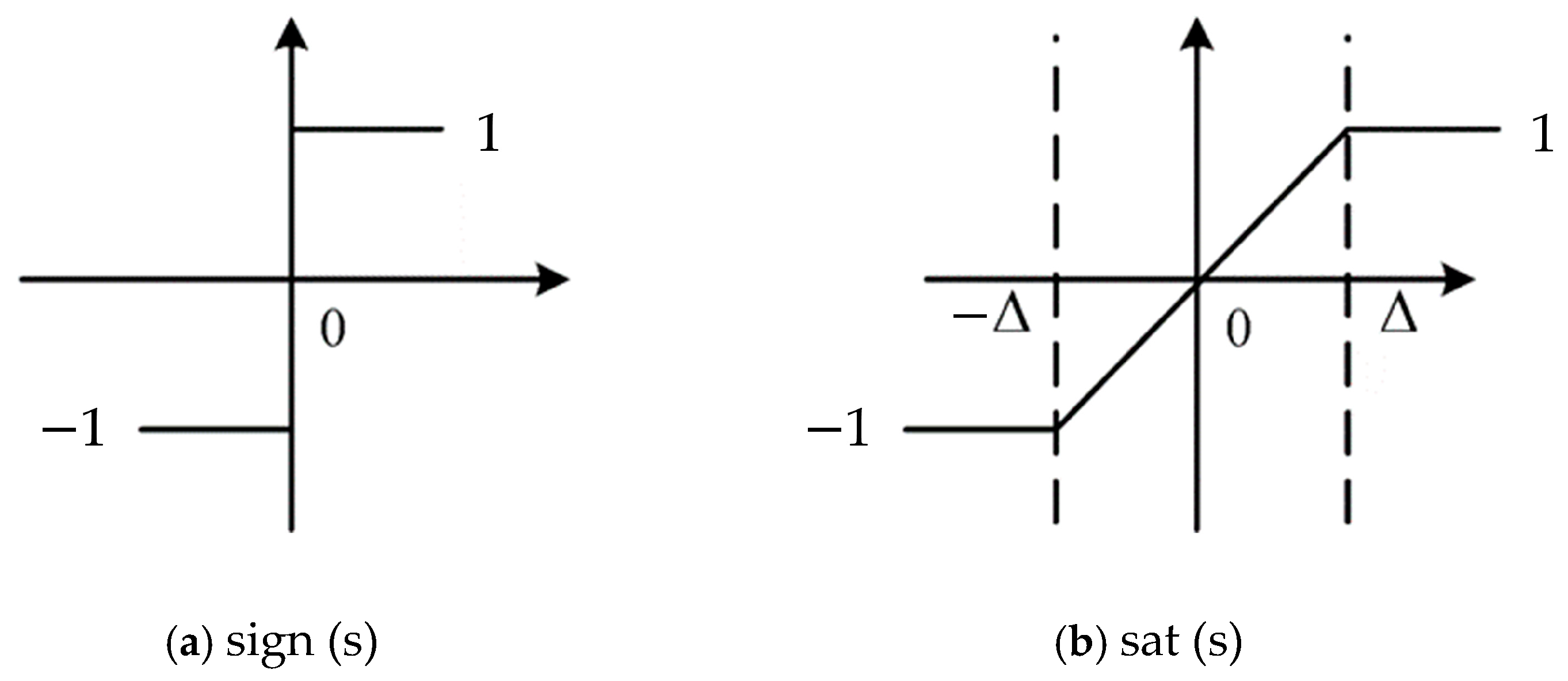
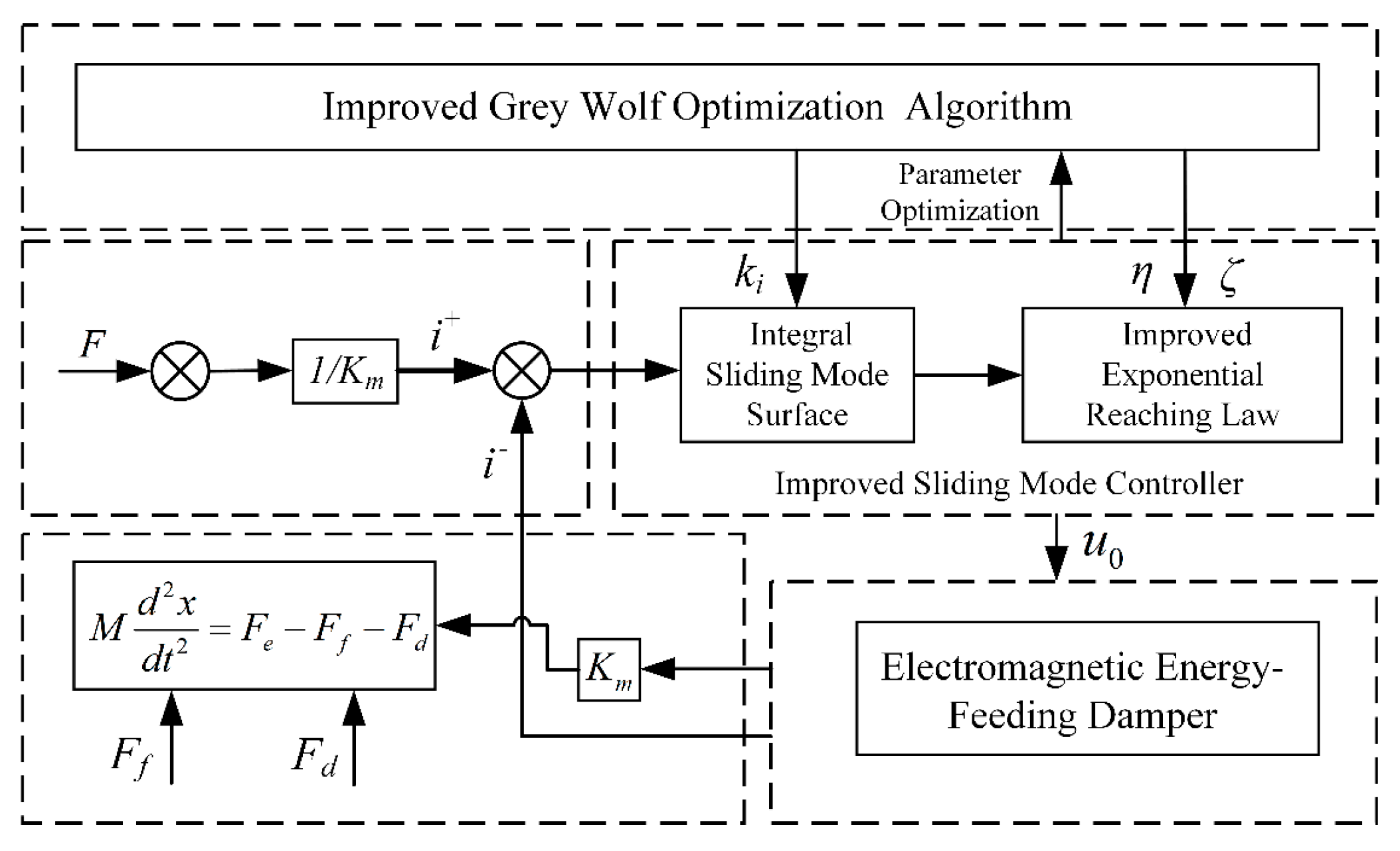
3. Improved Sliding Mode Thrust Controller Design
Stability Analysis
4. Improved Gray Wolf Optimizer Design
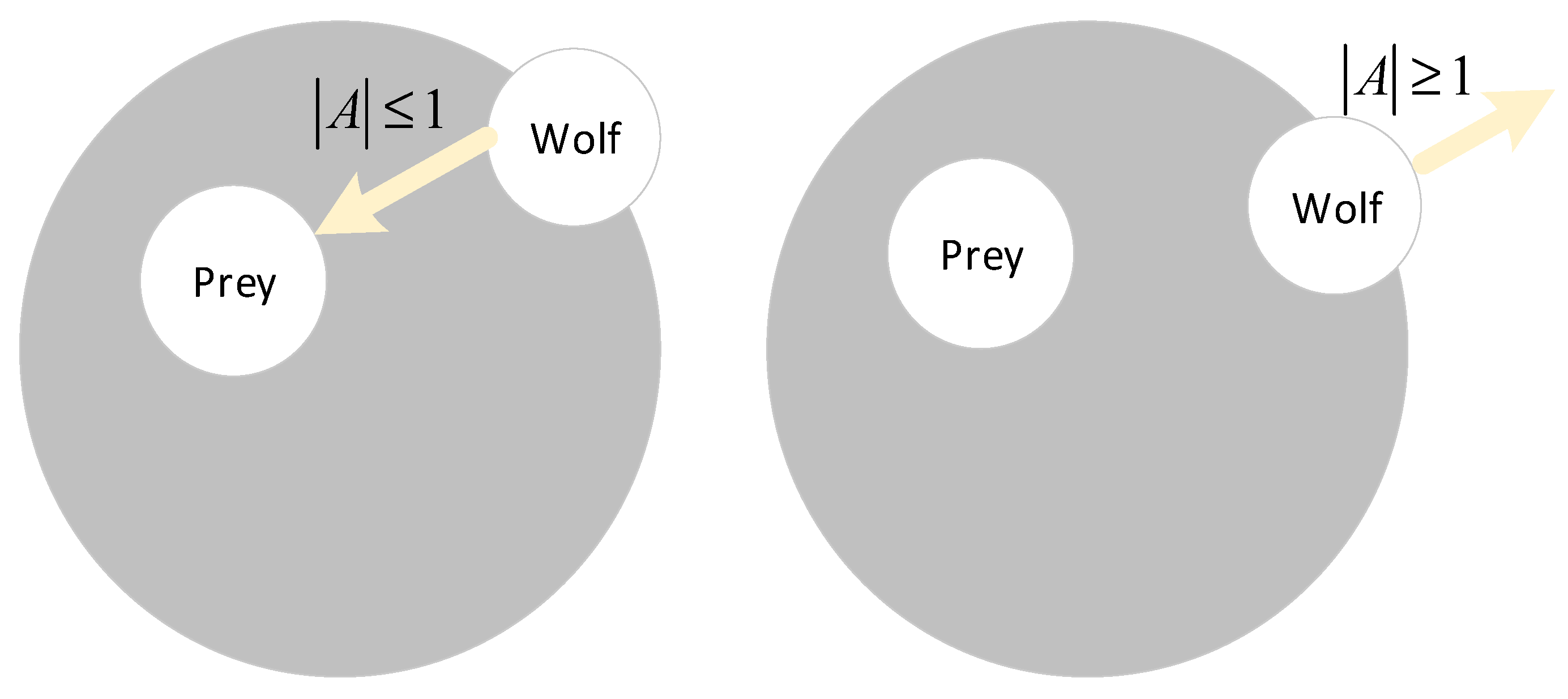
4.1. Basic Principles of the Gray Wolf Optimizer
4.2. Improved Gray Wolf Optimization Fitness Function Analysis
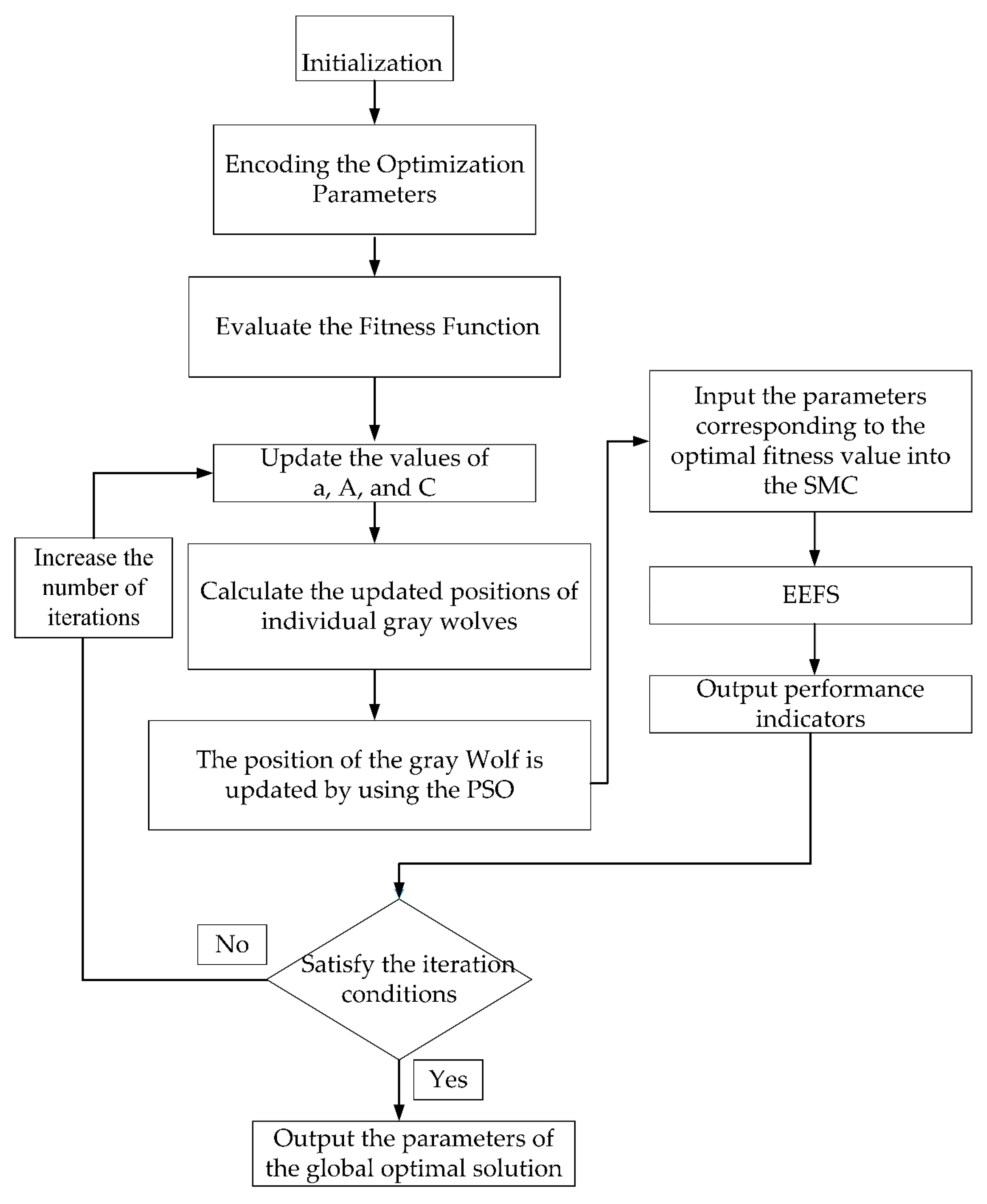
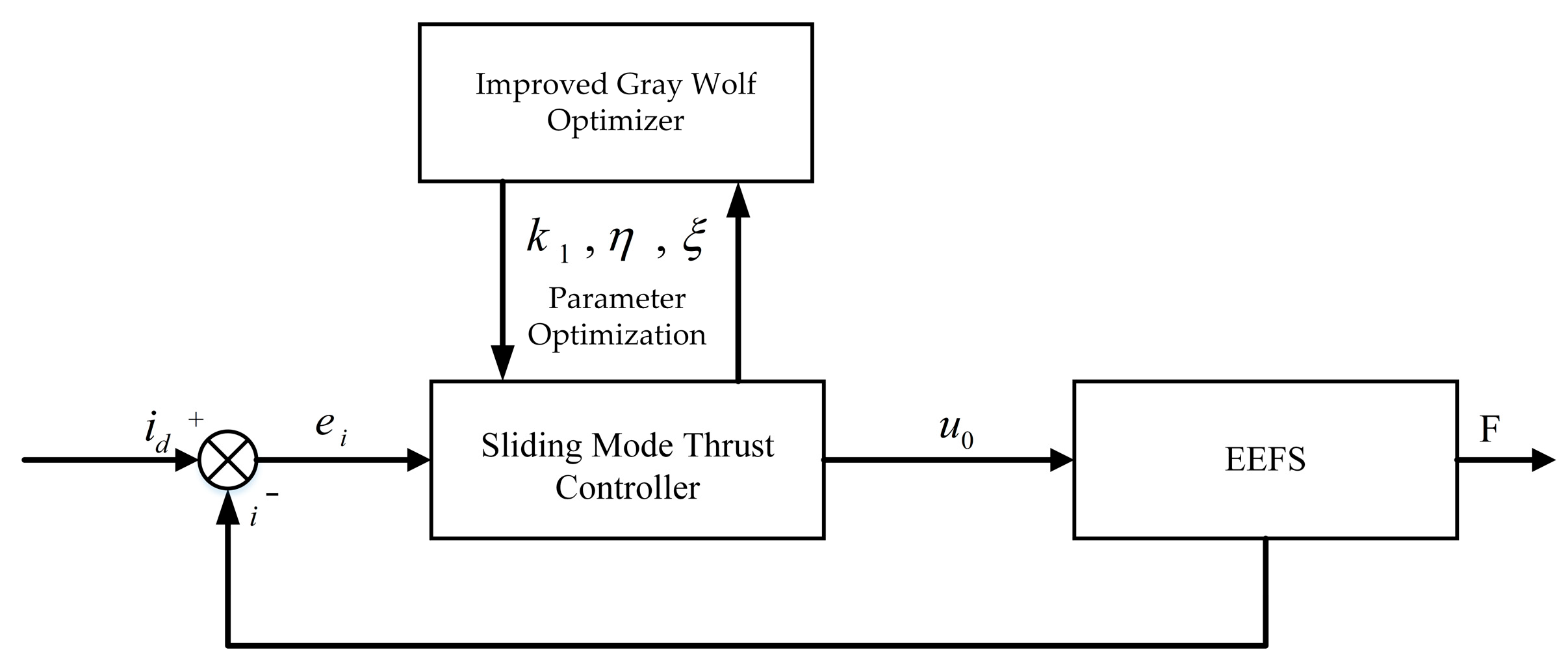
5. Design of a Sliding Mode Thrust Tracking Method Based on Improved Gray Wolf Optimization Algorithm
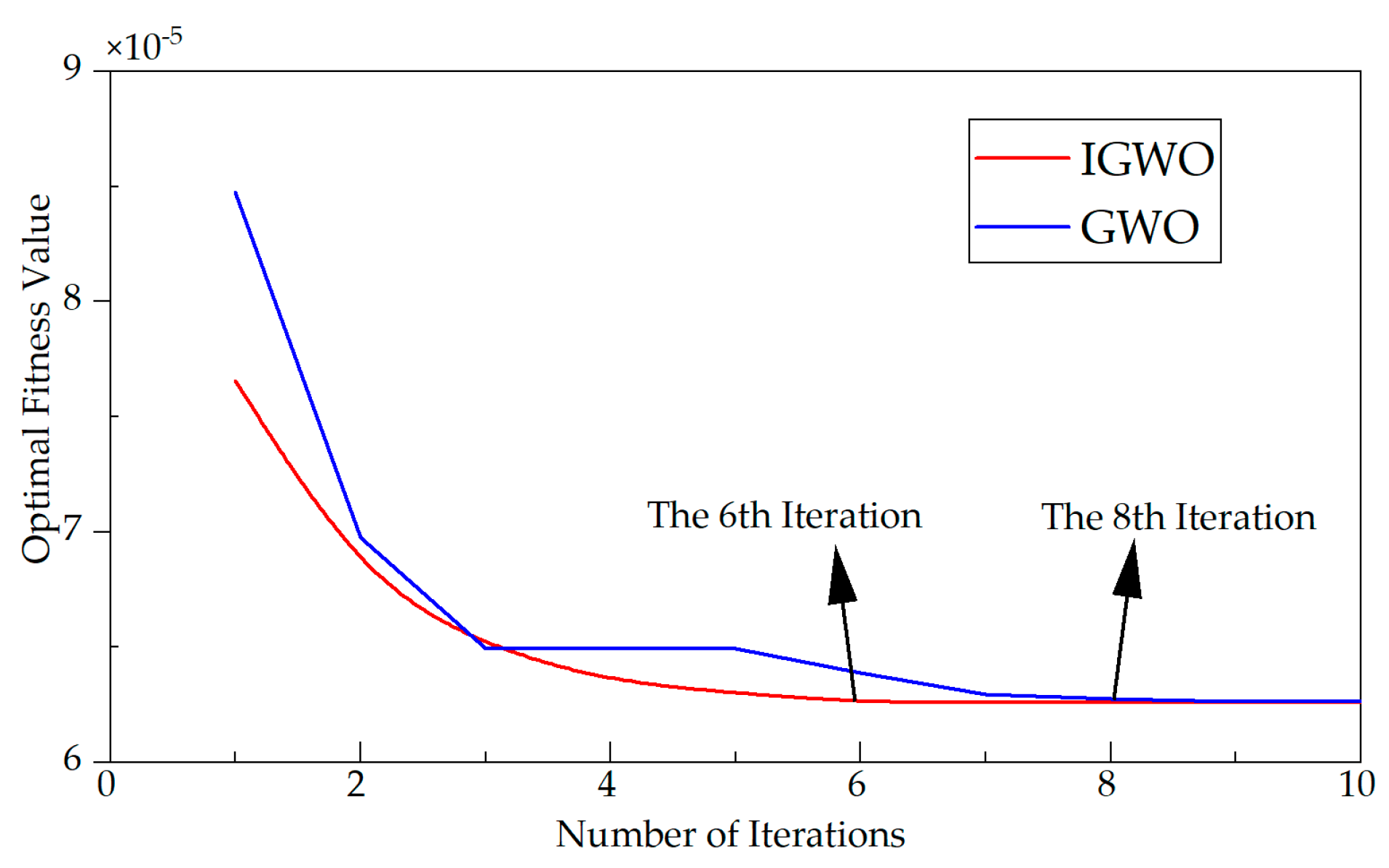
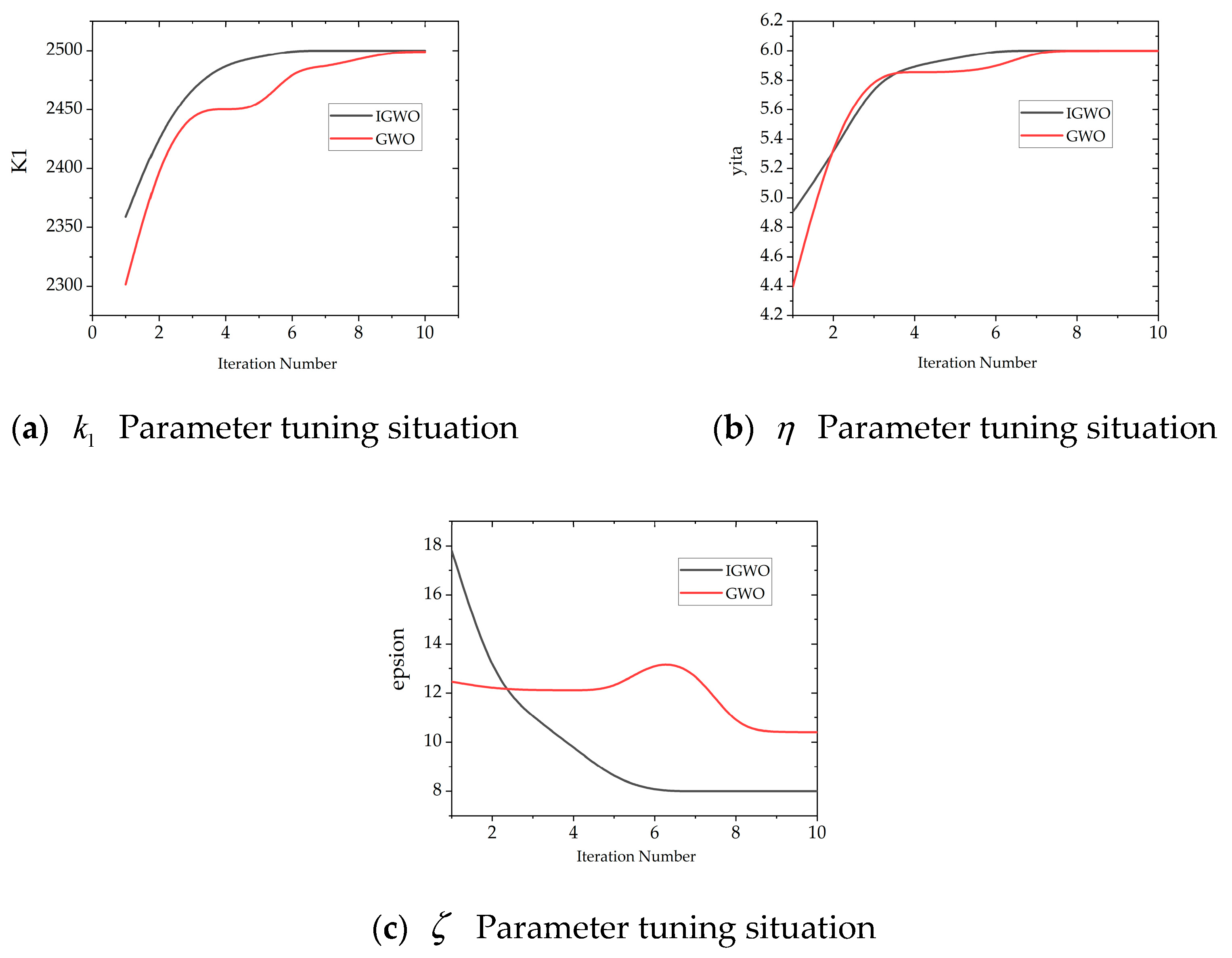
6. Simulation Analysis of Sliding Mode Thrust Controller Based on Improved Gray Wolf Optimization Algorithm
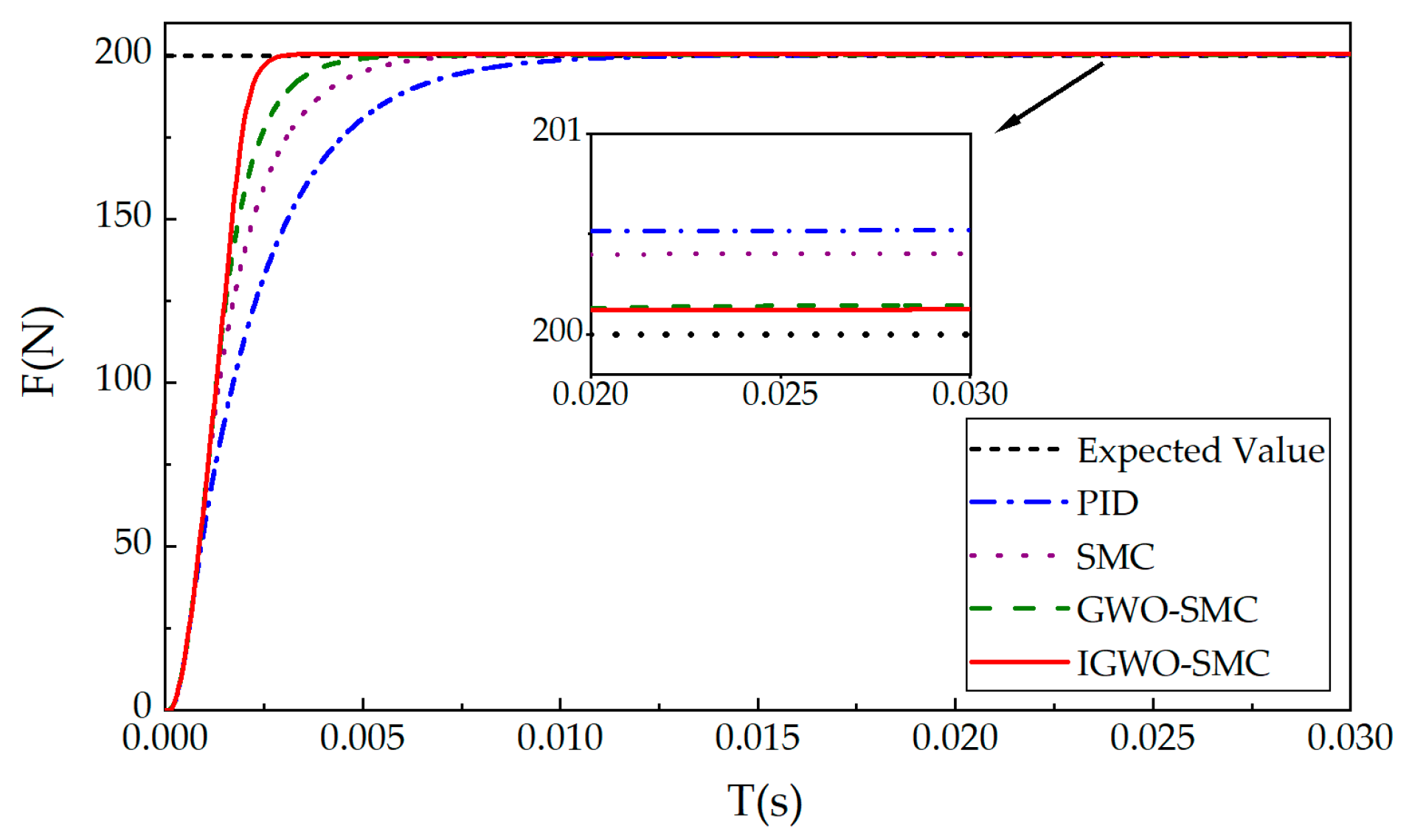
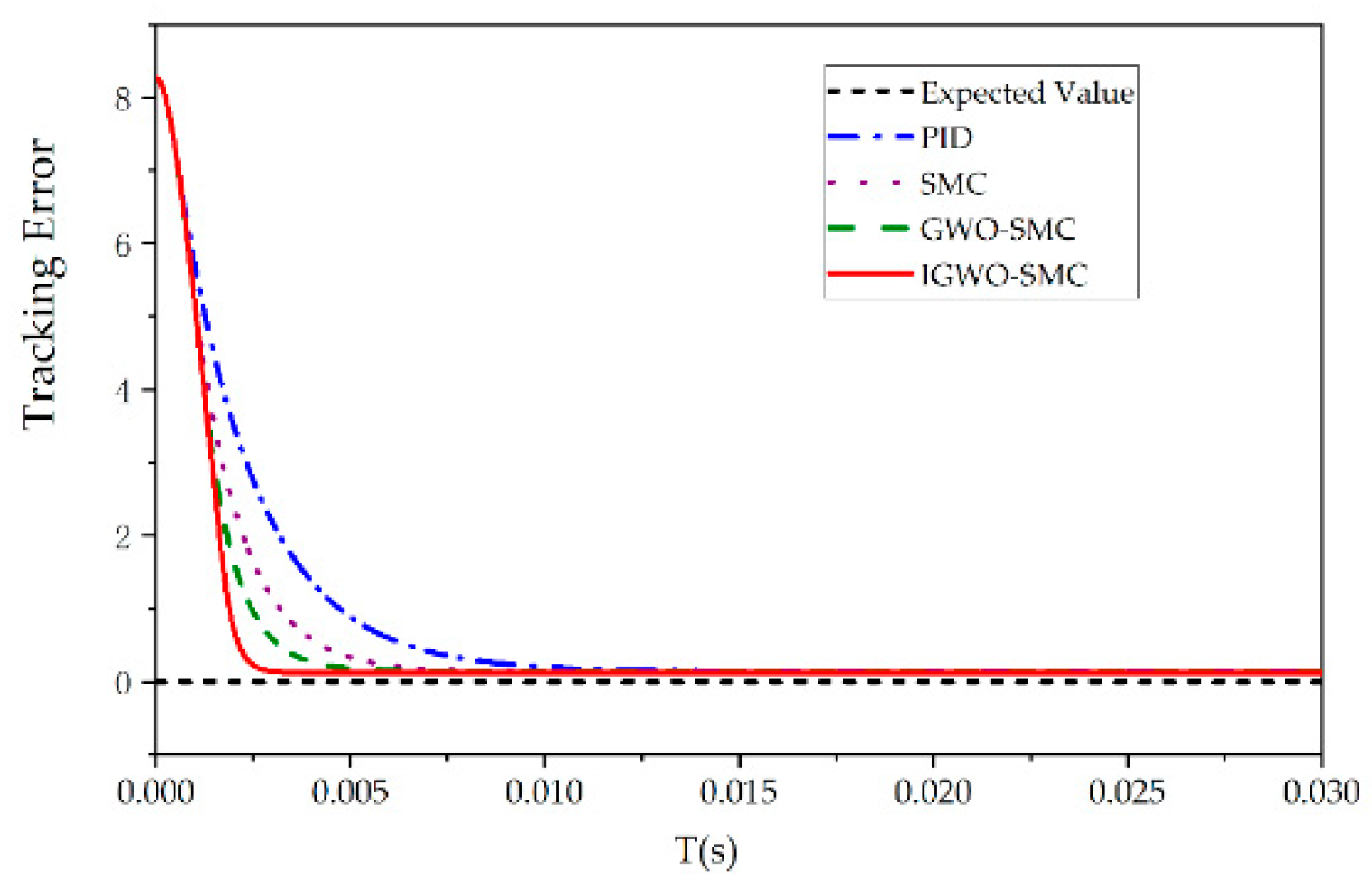
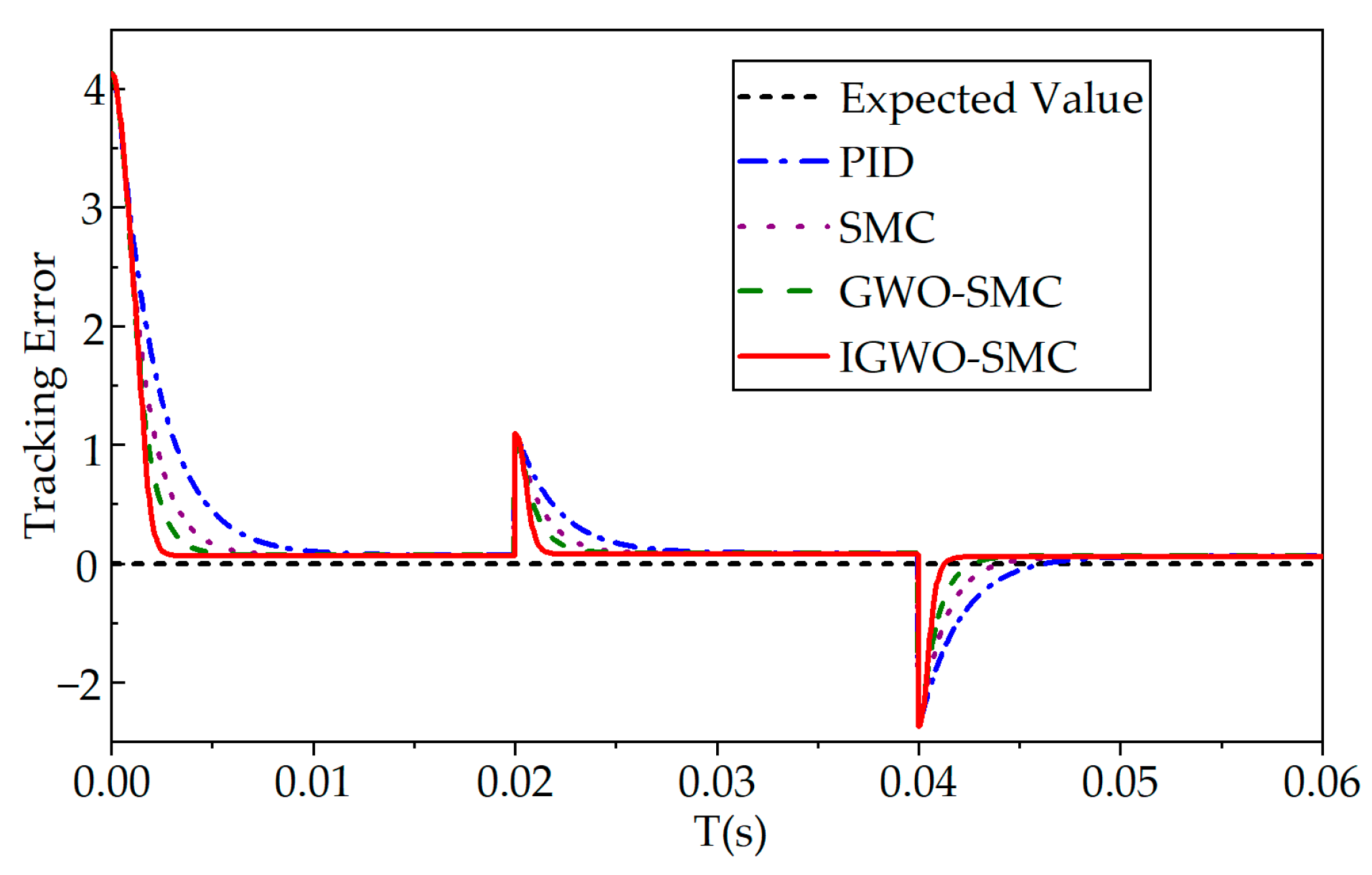
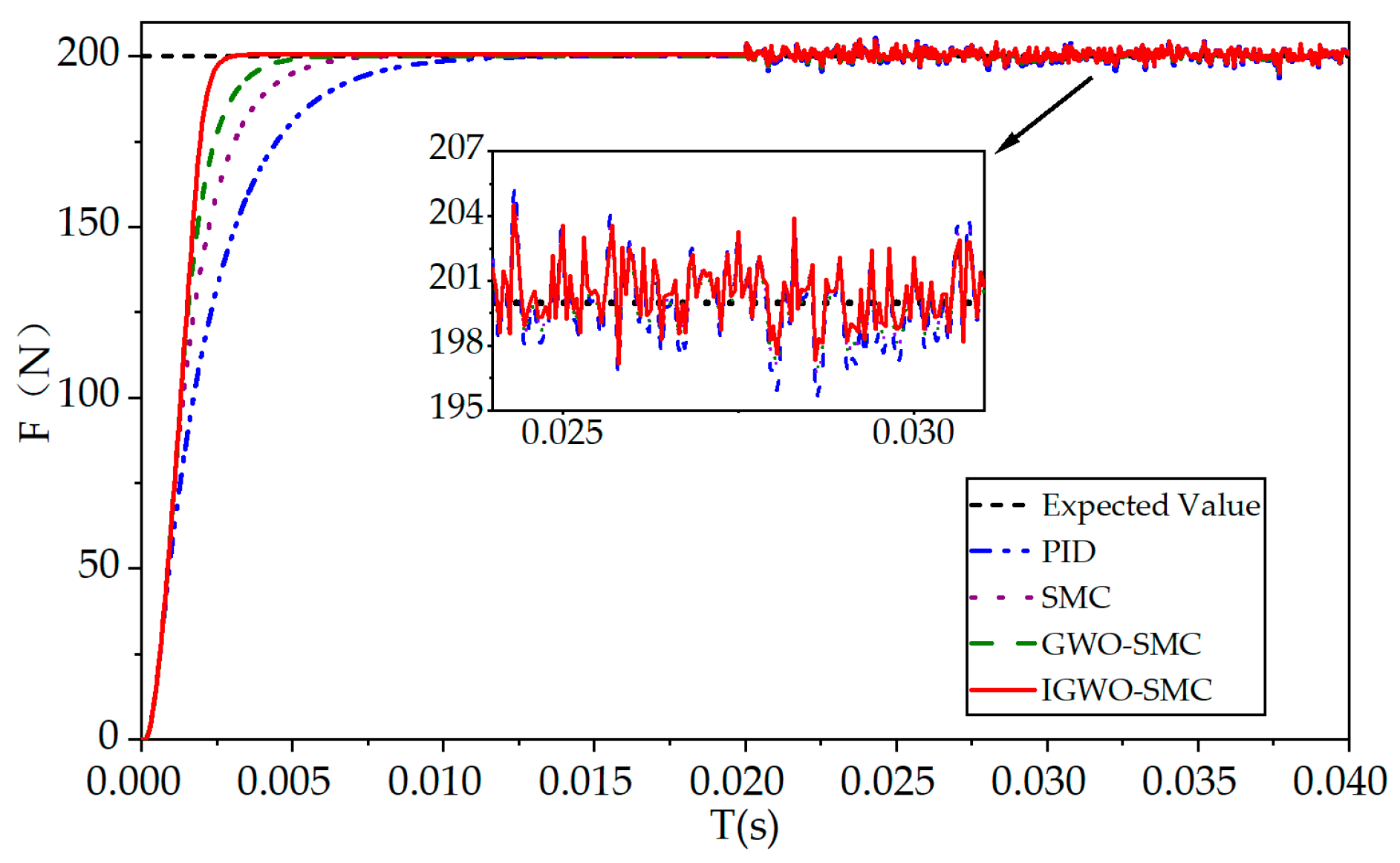
6.1. Step Response Condition Analysis
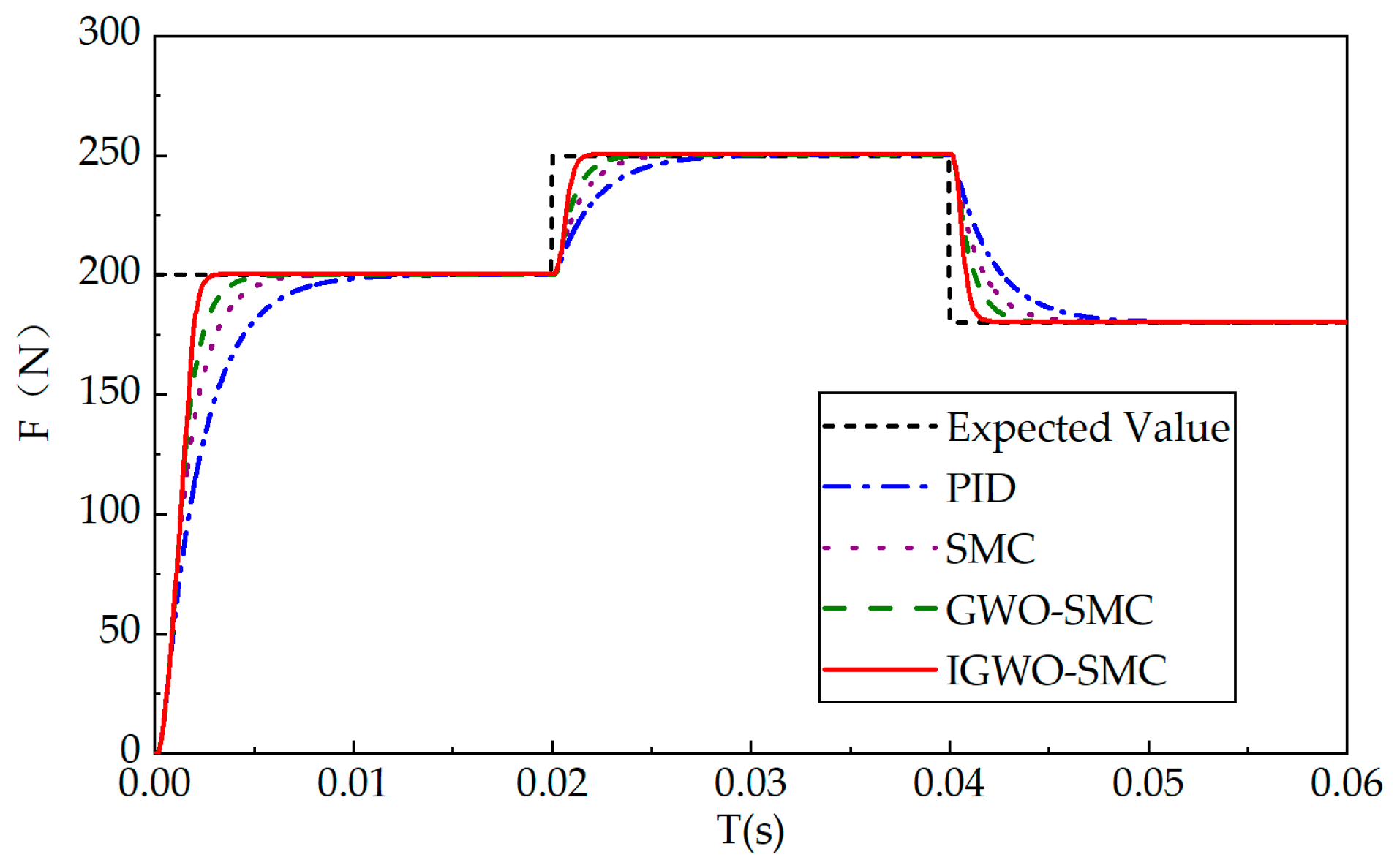
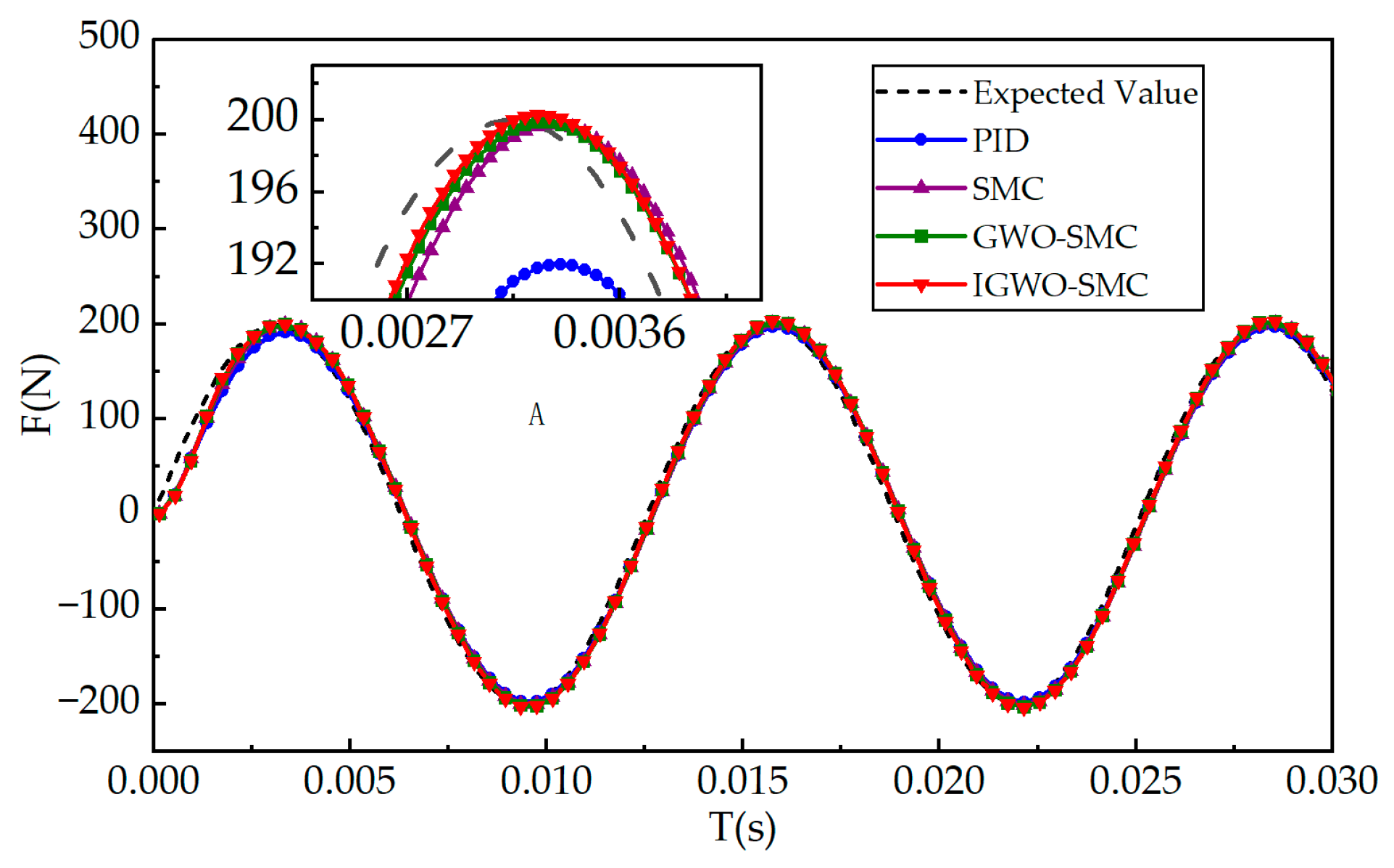
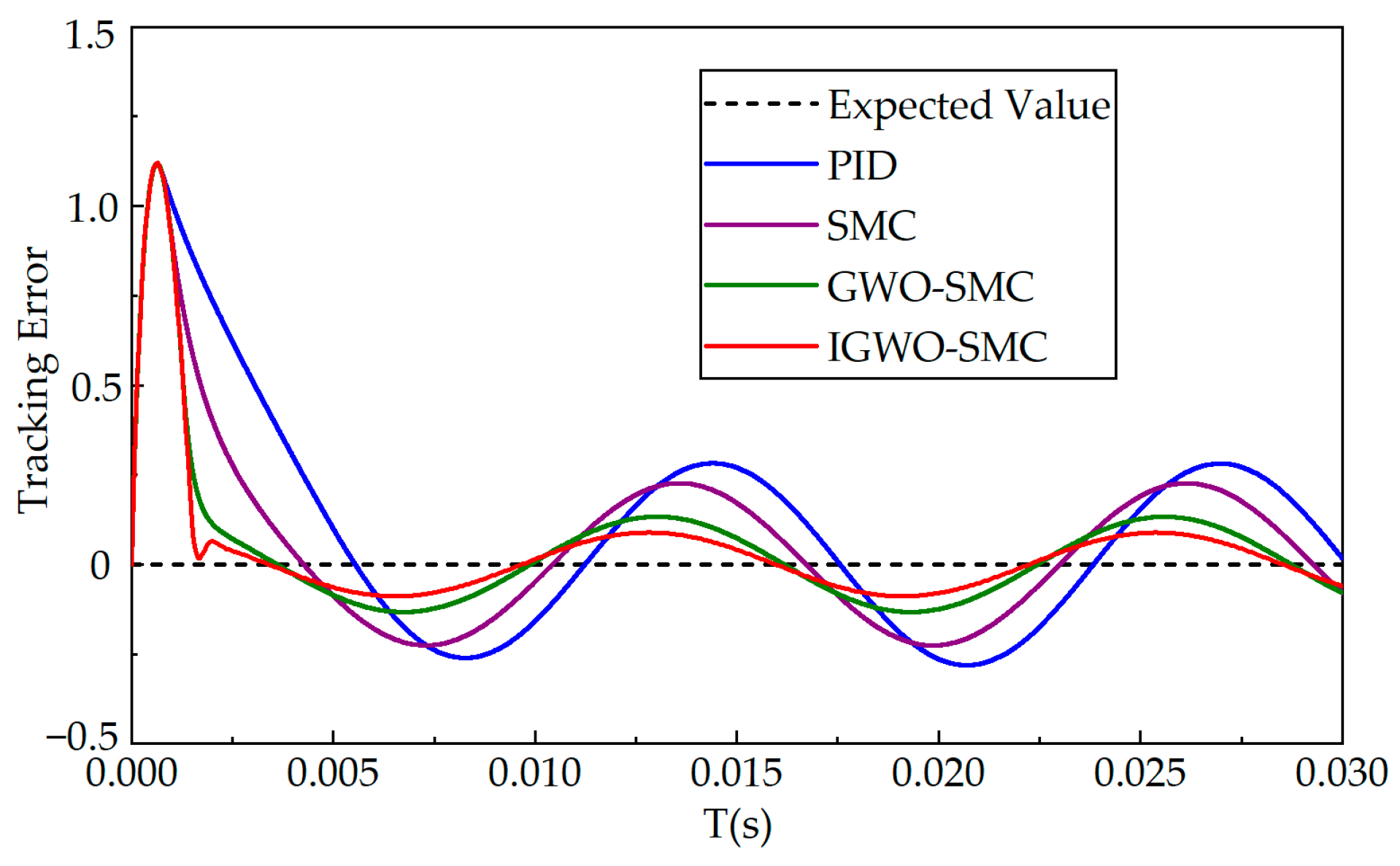
6.2. Sinusoidal Condition Analysis
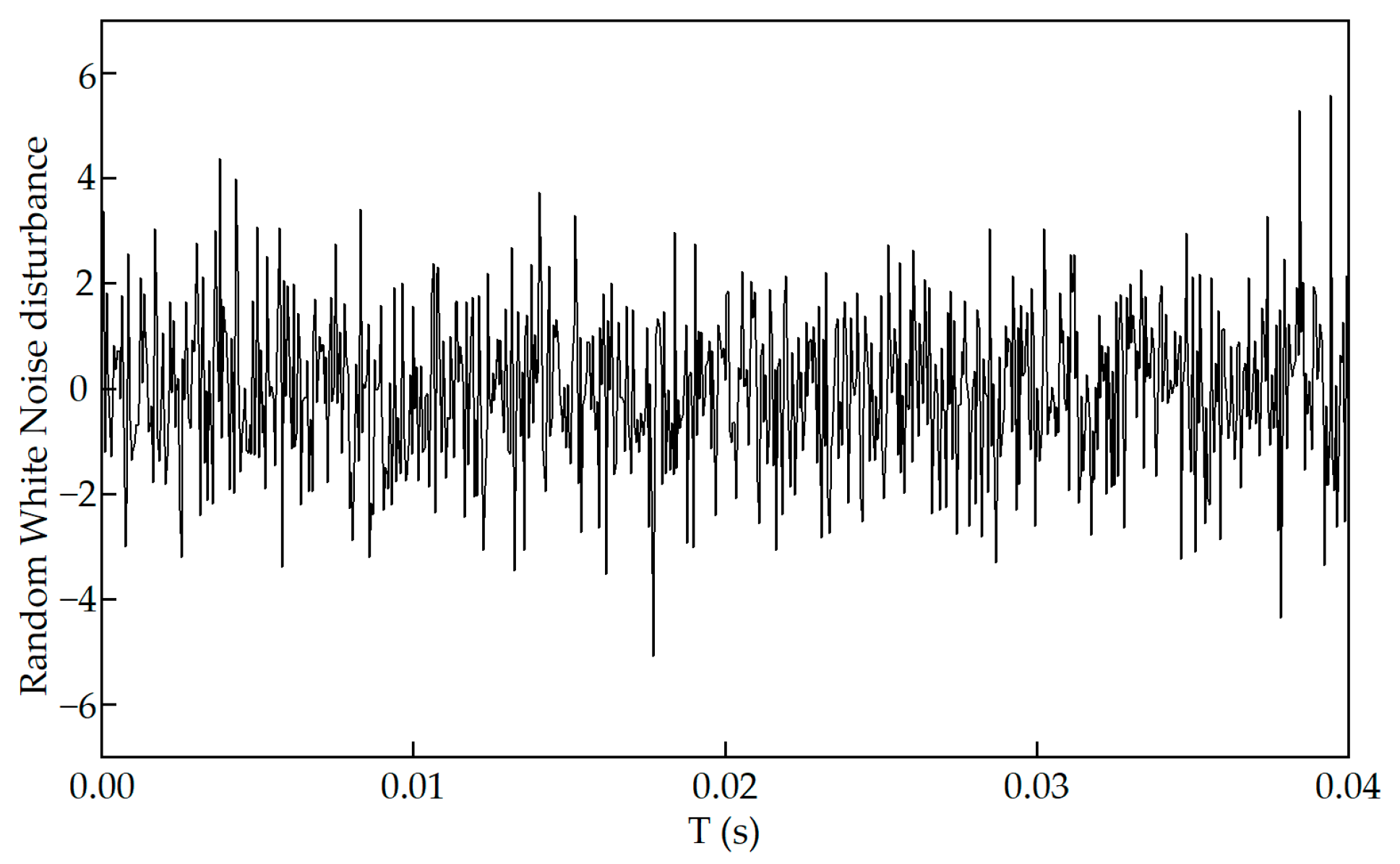
6.3. Noise Disturbance Analysis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibrahim, B.; Abdelkader, H.; Hartani, M.A.; Kayisli, K. Optimization of Sliding Mode Control for Doubly Fed Induction Generator Systems Using Particle Swarm and Grey Wolf Algorithms. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2024, 52, 1782–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, B.; Ge, W.; Tan, C.; Sun, B. Analysis and experimental study on servo dynamic stiffness of electromagnetic linear actuator. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 169, 108587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Jing, X. A comprehensive review on vibration energy harvesting: Modelling and realization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskys, A. A Combined Controller for Closed-Loop Control Systems Affected by Electromagnetic Interference. Sensors 2024, 24, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangxu, X.; Xiaodong, Y. Research on PMSM Control Based on ADRC, Shanghai Dianji Unversity (China); Mingo New Motor Electric Control Research Institute (China): Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-San Lázaro, R.; Mendoza-Bautista, K.J.; Fuentes-Aguilar, R.Q.; Chairez, I. State-restricted adaptive control of a multilevel rotating electromagnetic mechanical flexible device using electromagnetic actuators. ISA Trans. 2024, 155, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, W.; Zong, X.; Zhang, W. Optimal Control Model of Electromagnetic Interference and Filter Design in Motor Drive System. Electronics 2025, 14, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, A.A.; Fekry, M.; El-Bardini, M.; El-Nagar, A.M. Deep reinforcement learning-based adaptive fuzzy control for electro-hydraulic servo system. Neural Comput. Appl. 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Chen, Y.; Hong, X.; Luo, H.; Chen, G. Research on Path-Following Technology of a Single-Outboard-Motor Unmanned Surface Vehicle Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning and Model Predictive Control Algorithm. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K. A finite-time speed control method for permanent magnet synchronous motor drives based on sliding mode control and estimation theory. Electr. Eng. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B. Adaptive super-twisting fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control with ESO for high-pressure electro-pneumatic servo valve. Control. Eng. Pract. 2023, 134, 105483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lin, H.; Li, B. Sliding-Mode Clamping Force Control of Electromechanical Brake System Based on Enhanced Reaching Law. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19506–19515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Friction compensation control of electromechanical actuator based on neural network adaptive sliding mode. Sensors 2021, 21, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, V.; Shah, D. Parameter optimization of reaching law based sliding mode control by computational intelligence techniques. In International Conference on Soft Computing and its Engineering Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 88–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ayinalem, A.Z.; Kassie, T.A. PSO Tuned Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Controller for Trajectory Tracking Control of an Articulated Robot. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2025, 2025, 1171569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Pan, Z.; Yang, G.; Chen, C.; Xu, F.; Zhu, B. An adaptive robust sliding mode control strategy based on radial basis function neural networks for the magnetorheological semi-active suspension. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2025, 239, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, X. Path planning and tracking control of orchard wheel mower based on BL-ACO and GO-SMC. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 228, 109696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, O.M.; Fareh, R.; Tawfik, H.; Sinan, S.; Khadraoui, S.; Bettayeb, M. Optimized Power Rate Sliding Mode Control for a Robot Manipulator Using Genetic Algorithms. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2024, 22, 3166–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soreng, B.; Pradhan, R. Optimal controller design for an islanded microgrid during load change. Int. J. Grid Util. Comput. 2021, 12, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Choi, S.B. Clamping force control based on dynamic model estimation for electromechanical brakes. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2018, 232, 2000–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lu, J.; Tan, C.; Tian, M.; Dong, G. Adaptive Non-Singular Terminal Sliding Mode Control Method for Electromagnetic Linear Actuator. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Prieto, J.A. Adaptive finite time smooth nonlinear sliding mode tracking control for surface vessels with uncertainties and disturbances. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 279, 114474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Lin, H.; Li, B. Chattering-Free Sliding-Mode Control for Electromechanical Actuator with Backlash Nonlinearity. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2017, 2017, 6150750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadi, A.; Motlagh, M.M. Optimal control of DC motor using grey wolf optimizer algorithm. Tech. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2014, 4, 373–379. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Nie, G.; Li, Y. Optimal Trajectory Planning for Minimizing Base Disturbance of a Redundant Space Robot with IQPSO. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2022, 2022, 3398810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, G.; Kumar, V. Spotted hyena optimizer: A novel bio-inspired based metaheuristic technique for engineering applications. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 48–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, Q.; Mao, W.; Liu, S.; Dou, Z.; Liu, G. Hybrid Particle Swarm and Grey Wolf Optimizer and its application to clustering optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 101, 107061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessi, R.; Rezk, H.; Bouallègue, S. Grey wolf optimization based tuning of terminal sliding mode controllers for a quadrotor. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 68, 2265–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Controller | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| PID | 5.2 | 2.1 | 0.05 |
| Controller | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| SMC | 2.5 | 6.0 | 8.5 |
| GWO-SMC | 2.379453 | 5.979515 | 8.241134 |
| IGWO-SMC | 2.4950169 | 5.99691083 | 8.618871 |
| System Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Numerical Values | 2.885 Kg | 7.765 mH | 6.4 Ω |
| Controller | Rise Time/s | Settling Time/s |
|---|---|---|
| PID | 0.0048 | 0.0081 |
| SMC | 0.0034 | 0.0053 |
| GWO-SMC | 0.0026 | 0.0039 |
| IGWO-SMC | 0.002 | 0.0025 |
| Controller | Maximum Error/N | Average Error/N |
|---|---|---|
| PID | 1.23 | 0.28 |
| SMC | 1.22 | 0.26 |
| GWO-SMC | 1.20 | 0.17 |
| IGWO-SMC | 1.19 | 0.12 |
| Controller | Maximum Error /N | Average Error/N |
|---|---|---|
| PID | 7.73 | 3.18 |
| SMC | 6.51 | 2.77 |
| GWO-SMC | 5.32 | 2.31 |
| IGWO-SMC | 4.85 | 2.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Lu, J.; Ge, W.; Xie, X.; Tan, C.; Zhang, H. Sliding Mode Thrust Control Strategy for Electromagnetic Energy-Feeding Shock Absorbers Based on an Improved Gray Wolf Optimizer. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16070366
Zhang W, Lu J, Ge W, Xie X, Tan C, Zhang H. Sliding Mode Thrust Control Strategy for Electromagnetic Energy-Feeding Shock Absorbers Based on an Improved Gray Wolf Optimizer. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(7):366. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16070366
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenqiang, Jiayu Lu, Wenqing Ge, Xiaoxuan Xie, Cao Tan, and Huichao Zhang. 2025. "Sliding Mode Thrust Control Strategy for Electromagnetic Energy-Feeding Shock Absorbers Based on an Improved Gray Wolf Optimizer" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 7: 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16070366
APA StyleZhang, W., Lu, J., Ge, W., Xie, X., Tan, C., & Zhang, H. (2025). Sliding Mode Thrust Control Strategy for Electromagnetic Energy-Feeding Shock Absorbers Based on an Improved Gray Wolf Optimizer. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(7), 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16070366







