Abstract
In order to more effectively design the structure of vehicle ISD (Inerter Spring Damper) suspension system using the inerter, this paper proposed a design method using a fractional-order electrical network structure of a mechatronic inerter for fractional-order electrical network components, according to the characteristics that the external electrical network of a mechatronic inerter can simulate the corresponding mechanical network structure equivalently. First, the 1/4 dynamic model of the suspension is constructed. The improved Oustaloup filtering algorithm is used to simulate fractional calculus, and the fractional order components are simulated. Then, the simulation model of the vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension is established. In order to simplify the electrical network, one resistance, one fractional inductance and one fractional capacitance are limited in the design of the fractional electrical network at the outer end of the mechatronic inerter. The structure-immittance approach is used to obtain two general layouts of all possible structures of three elements. At the same time, the optimal fractional electrical network structure and parameters are obtained by combining the optimization algorithm. The simulation results verify the performance of the fractional ISD suspension with the optimized structure, which can provide a new idea for the structural design of a fractional-order electrical network applied in vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension.
1. Introduction
The proposition of the inerter [1] breaks through the inherent structure of the existing suspension system “spring damper” parallel connection, and forms a new suspension structure system. This suspension, consisting of spring, damper and inerter elements, is called ISD suspension. Scholars all over the world have adopted many methods to realize the inerter [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9], and after the application of the inerter, the performance potential of the vibration isolation system has also been expanded to include aircraft [10], trains [11], buildings [12], bridges [13], etc. The structural design of ISD suspension plays an important role in meeting various performance indicators of vehicles. The question of how to design the structure of ISD suspension has attracted the attention of scholars at home and abroad.
Common ISD suspension structure design methods include the structure approach, the immitance approach and the structure-immitance approach. The structure approach [14] limits the number of components in the suspension, and integrates them into parameter optimization according to the feasible range of component parameters. The disadvantage is that the arrangement and combination method has a huge workload, which makes it difficult to cover a wide range of mechanical networks, and it is easy to omit structures with excellent performance. The immitance approach [15] replaces the suspension structure with a fixed form of impedance or admittance expression, uses the parameter optimization method to optimize the solution and finally realizes it passively through network synthesis. The suspension component parameters obtained by the immitance approach often do not conform to the routine, which is not conducive to engineering realization. The structure-immitance approach [16] can be used to express the structure with a predetermined number of elements with a general impedance expression. However, the structural complexity of a pure mechanical network is high, which has affected the engineering design of ISD suspension. The mechatronic inerter [17] is a device coupled by a mechanical inerter and a rotating motor. The external circuit impedance of the mechatronic inerter can be used to simulate the target mechanical impedance to achieve the passive structure design of complex mechanical network, overcome the space limitation of pure mechanical network suspension structure and expand the design idea of suspension system structure. However, for the electrical network at the outer end of the mechatronic inerter, the increase of the order of its impedance transfer function will bring higher performance improvement [18], and at the same time, the difficulty of network integration will also increase greatly. For example, the bicubic impedance transfer function requires no more than 13 elements to realize passively [19], and its structure is complex.
In the structural design of the suspension system, fractional calculus theory has also been commonly used [20,21,22,23], and its feasibility has also been verified [24,25], indicating that the fractional-order function can more accurately describe the dynamic characteristics of complex systems than the integral-order function. Using fractional-order electrical network elements to replace the original integer-order electrical network at the outer end of the mechatronic inerter can effectively avoid the high complexity of pure integer order network structures. However, the structural design of fractional-order electrical networks in vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension has not been reported yet, and in the design of a fractional-order vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension, a simple and clear fractional-order electrical network structure is essential. Therefore, this paper will use the structure-immitance approach to study the optimal design of the fractional-order electrical network structure for a vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension. The content layout of the rest of this paper is as follows.
First, in Section 2, the definition and algorithm realization of fractional calculus are introduced, and the equivalent realization relationship between fractional electrical components and fractional mechanical components are analyzed. In Section 3, a quarter suspension dynamic simulation model is established, and fractional-order electrical components are used in the design of the electrical network, and the structure-immitance approach is used to design the electrical network structure. Then, in Section 4, the electrical network structure and parameters of the suspension system are obtained through optimization. Finally, in Section 5, the dynamic performance of the optimized fractional-order ISD suspension is evaluated by comparison, and some conclusions are made in Section 6.
2. Equivalent Realization of Fractional Passive Network Elements
Fractional calculus has the basic operator , among which, α is limited to real numbers, t and t0 are the upper and lower bounds of the operator. The unified definition of fractional calculus operator [26] is:
There are many definitions of fractional calculus. This paper adopts the Grünwald–Letnikow [26] fractional calculus definition. The Grünwald–Letnikow of the α derivative of a given function f(t) is defined as:
where [·] means taking the nearest integer. At the same time, in order to ensure the approximation effect at the frequency band boundary and ensure that the transfer function is regular, the improved Oustaloup filtering algorithm [27] is considered to approximate fractional calculus. The mathematical model of the improved Oustaloup filter is:
where N is the filter order, γ is the fractional order, ω’k and ωk are zero point and the pole, respectively. ωh and ωb are the upper and lower limits of frequency bands, respectively. In general, the weighting parameters b = 10, d = 9. In this paper, the filter frequency band is (10−3, 103) rad/s. The larger the filter order, the higher the approximation accuracy. In this frequency band, the fifth order Oustaloup filtering effect has met the accuracy requirements, so the selection order is five.
In the new mechanical and electrical analogy, the spring and the inductance, the damper and the resistance, and the inerter and capacitance are similar, respectively [28]. According to the above fractional definition and approximation method, the impedance expression of fractional network elements (including mechanical network and electrical network) is obtained by using the form of pull transform, with excitation force as the input and corresponding speed as the output, as shown in Table 1, where s is the Laplace variable, α and β are fractional orders.

Table 1.
Impedance expression of fractional network elements.
3. Model Construction of Vehicle Mechatronic ISD Suspension System
3.1. The Ball-Screw Mechatronic Inerter
A mechatronic inerter is considered in this paper, which is formed by coupling a ball-screw inerter with a rotary motor. Its structural diagram is shown in Figure 1. The relative linear motion of the two ends of the mechanical inerter can be converted into the rotary motion of the motor. The inductor, resistor and capacitor in the electrical network at the outer end of the rotary motor can equivalently simulate the spring, damper, and inerter in the mechanical network structure.
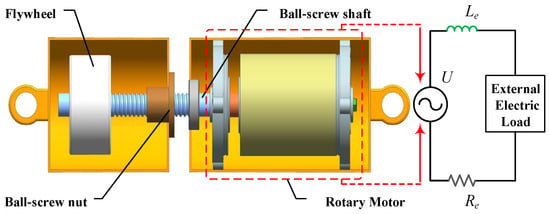
Figure 1.
The schematic of ball-screw mechatronic inerter.
3.2. Mechatronic ISD Suspension Structure Layout
The quarter suspension model is a typical vibration model of vehicle suspension system, which is a basic dynamic model for studying its vertical performance. In this paper, a quarter vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension dynamics model is established, as shown in Figure 2. Based on a mature vehicle model, Table 2 illustrates the parameters for the model.
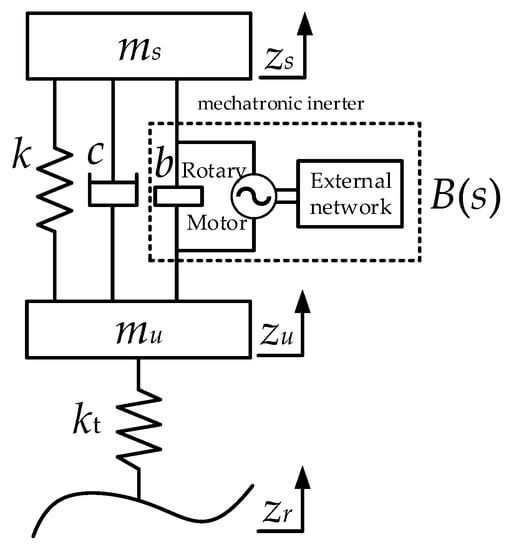
Figure 2.
A quarter vehicle suspension model.

Table 2.
Parameters of quarter vehicle suspension model.
The dynamic Laplace equation of the suspension model is shown in Equation (5):
where k, kt, and c are spring stiffness, tire stiffness, and the damping coefficient, respectively, ms and mu are the sprung mass and the unsprung mass, respectively. zs, zu and zr are the vertical displacements of the sprung mass, the unsprung mass, and road roughness, respectively, and Zs, Zu and Zr are their Laplace transforms, respectively. B(s) is the impedance expression of the mechatronic inerter, which is shown as follows [17]:
where b is the inertance of the ball-screw mechatronic inerter, P is the pitch of the ball-screw mechanism, ke is the induced electromotive force coefficient of the rotary motor, kt is the thrust coefficient of the rotary motor. Km is the electromechanical parameter conversion coefficient of the ball-screw mechatronic inerter, which is taken as 7056 HN/m in this paper. Ze(s) is the impedance expression of the external electrical network of the rotary motor. The fractional-order external electrical network of the mechatronic inerter includes resistor(s), fractional-order capacitor(s) and fractional-order inductor(s). In order to simplify the electrical network, the number of resistors, fractional capacitors and fractional inductors is limited to one in the optimal design. Eight structures of the three element arrangement are summarized using the structure-immittance approach, and two general structures are used for general expression, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
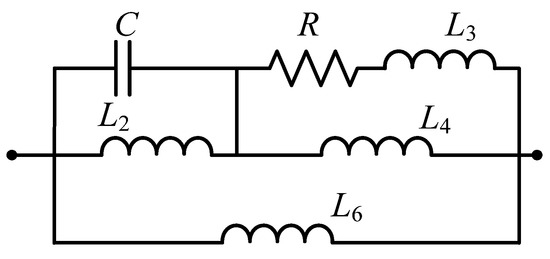
Figure 3.
General structure of Y1(s).
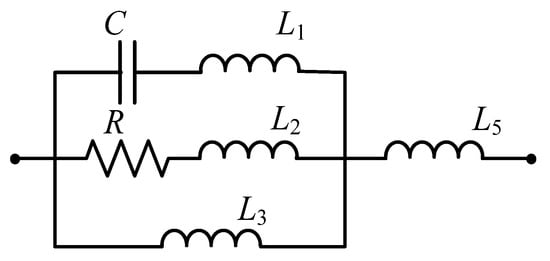
Figure 4.
General structure of Y2(s).
The impedance transfer function expressions of the two general structures in Figure 3 and Figure 4 are, respectively, as follows:
where L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, and L6 are fractional-order inductors, R and C are the resistor and the fractional-order capacitor, respectively. α and β are the fractional-order inductance order and the fractional-order capacitance order, respectively. In the Y1 (s) structure, at least three of L2, 1/L3, L4 and L6 are zero, and in the Y2 (s) structure, at least three of 1/L1, 1/L2, L3 and 1/L5 are zero. For example, in Figure 3, when L3, L4 and L6 are zero, it is a structure in which a fractional-order inductor is connected in parallel with a fractional-order capacitor, and then connected in series with a resistor. In Figure 4, when 1/L2, 1/L3 and 1/L5 are zero, it is a fractional-order capacitor in series with a fractional-order inductor, and then in parallel with a resistor.
4. Parameter Optimization Design
4.1. Pattern Search Optimization Algorithm
In this paper, the pattern search method [29] is used for the optimization design of the suspension system. As a general algorithm for solving the optimal value of a function, the greatest advantage of pattern search method is that it does not need to use the derivative of the objective optimization function in the algorithm program of pattern search method. Therefore, pattern search method can effectively solve the optimization problems of non-derivative functions and complex derivative functions. The specific steps of pattern search method are shown in Figure 5.
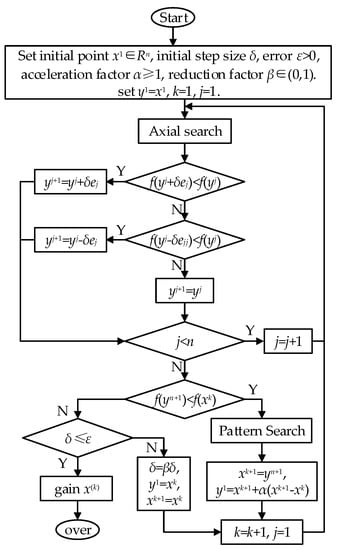
Figure 5.
Pattern search optimization algorithm.
4.2. Optimization Results
To ensure vehicle ride comfort, the RMS (root-mean-square) values of the vehicle body acceleration, the suspension working space and the dynamic tire load are selected as evaluation indicators, and the traditional passive suspension is chosen as evaluation benchmark to establish the optimization objective function, as shown below:
where BA and BApas are the RMS values of the vehicle body acceleration of the suspension to be optimized and the traditional passive suspension, respectively, SWS and SWSpas are the RMS values of the suspension working space of the suspension to be optimized and the traditional passive suspension, respectively, and DTL and DTLpas are the RMS values of the dynamic tire load of the suspension to be optimized and the traditional passive suspension, respectively. BApas, SWSpas and DTLpas are calculated by a mature traditional passive suspension [30], and their performances have reached a high level, which are 1.3096 m·s−2, 0.0130 m and 900.4704 N, respectively. P represents the set of parameters to be optimized for the suspension system, including inertance b, damping coefficient c, fractional-order inductance coefficient Le, fractional-order capacitance coefficient Ce, resistance coefficient Re, fractional-order inductance order α, and fractional-order capacitance order β. Their constraints are as follows:
The optimized fractional-order electrical network structure is shown in Figure 6. This structure is the case when L2, 1/L3 and L6 are zero in Y1 (s) structure. Set the fractional-order inductance order α and the fractional-order capacitance order β to 1 for optimization, and get the integer-order ISD suspension system parameters. The optimization parameters of fractional-order ISD suspension and integral-order ISD suspension are shown in Table 3.
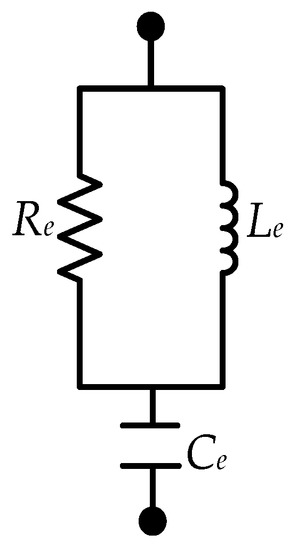
Figure 6.
The optimized fractional-order electrical network structure.

Table 3.
Optimization parameters.
5. Simulation Analysis
5.1. The Characteristics of Bode Diagram
Compared with the Bode diagram of the traditional passive suspension, Figure 7 shows the Bode diagram of vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension applying the optimized fractional-order electrical network structure.
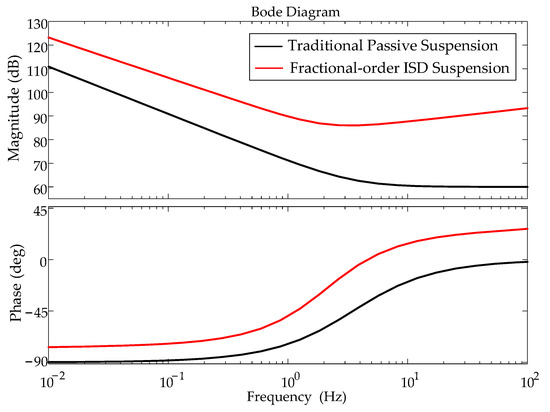
Figure 7.
Bode diagram comparison of two suspension systems.
It can be seen that for the fractional-order ISD suspension, in the low frequency range [10−2, 2] Hz, the optimized structure shape is similar to the spring. In the range [2,4] Hz, the structure shape is similar to the damper, and above 4 Hz, the optimized structure is similar to the inerter, which is the difference between the traditional passive suspension system and the optimized structure. The traditional suspension system composed of “spring damper” mechanical components cannot show inertia characteristics, which is the main factor limiting the performance improvement of the traditional suspension structure, and also the reason why the ISD suspension of vehicles containing the inerter has better vibration isolation performance.
5.2. Random Road Input
The random road input is selected as the road input model to study the advantages of the optimized fractional-order ISD suspension compared with the integral-order ISD suspension and the traditional passive suspension. The random road input model is as follows [31]:
where u, zr(t), w(t) and Gq(n0) are the vehicle speed, the vertical input displacement, the white noise with the mean value of 0, and the road roughness coefficient, respectively. Class C pavement is selected in this paper, and the pavement roughness coefficient is 2.56 × 10−4 m3. Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10 and Table 4 show the comparison of the RMS values of the vehicle body acceleration, the suspension working space and the dynamic tire load of the three suspension systems at a speed of 20 m/s.
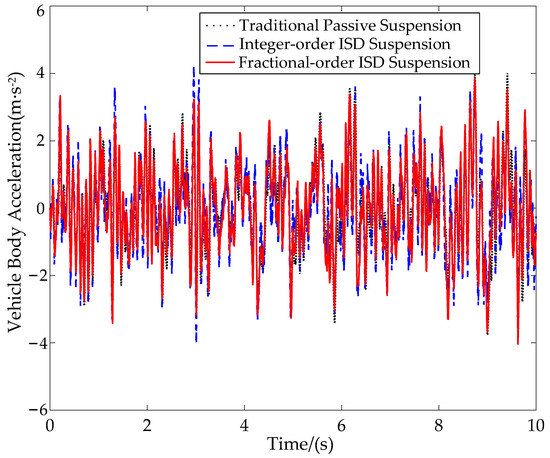
Figure 8.
Comparison of the vehicle body acceleration.
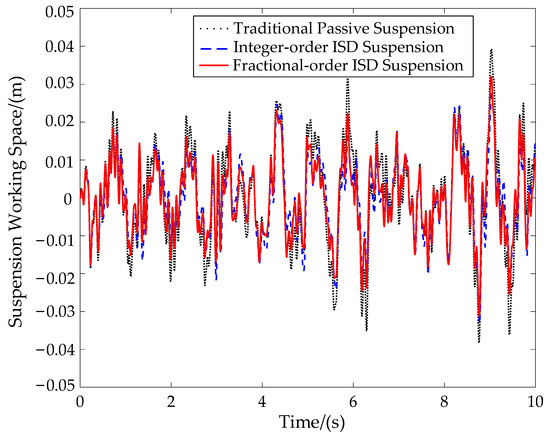
Figure 9.
Comparison of the suspension working space.
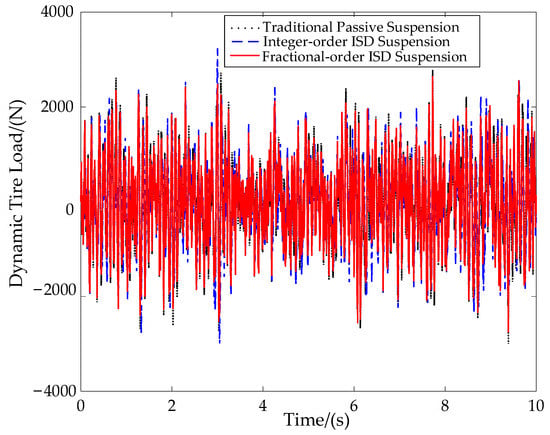
Figure 10.
Comparison of the dynamic tire load.

Table 4.
Comparison of performance indexes of three suspensions.
The optimization adopts multi-objective optimization, and the final optimization result is the best case of comprehensive improvement. From the data point of view, the RMS value of suspension working space has the best effect, and the other two indexes have also been improved. It can be seen that, compared with the traditional passive suspension, the RMS values of the vehicle body acceleration of the integral-order ISD suspension and the fractional-order ISD suspension are reduced by 3.44% and 4.12%, respectively. The RMS values of the suspension working space of the two suspensions are reduced by 22.31% and 23.08%, respectively. Furthermore, the RMS values of the dynamic tire load of the two suspensions are reduced by 2.73% and 5.31%, respectively, showing the advantages of the designed fractional-order electric network structure. It shows that the vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension with optimized fractional-order electrical network structure can further improve the vibration isolation performance of the suspension system.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, the optimal design of fractional-order electrical network for vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension is studied. An optimization design method of fractional-order electrical network for vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension is proposed by using the structure-immittance approach. The structural parameters of the fractional-order vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension are optimized by establishing a 1/4 dynamic model of the suspension. Through simulation comparison, the results show that the performance of the vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension system applying the fractional-order electrical network structure obtained by optimization design is further improved, which provides a reference for the structural design of fractional-order electrical network components based vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.H. and Y.S.; methodology, Y.Z.; software, J.H.; validation, X.Y.; formal analysis, Y.L.; investigation, Y.S.; writing—original draft preparation, J.H.; writing—review and editing, X.Y.; supervision, Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 52002156, 52072157 and 52008259, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant BK20200911.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Smith, M.C. Synthesis of mechanical networks: The inerter. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2002, 47, 1648–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K. The transmissibility of a vibration isolation system with ball-screw inerter based on complex mass. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control. 2018, 37, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Hu, N.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, Z. Modeling, design and experiments of a ball-screw inerter with mechanical diodes. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 504, 116121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Meng, X.; Shi, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L. Design and test of vehicle suspension system with inerters. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2014, 228, 2684–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, C.; Houghton, N.E.; Smith, M.C. Experimental Testing and Analysis of Inerter Devices. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2009, 131, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hong, M.; Lin, T. Design and testing a hydraulic inerter. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2011, 225, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shi, D.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Modeling and experimental tests of hydraulic electric inerter. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 2161–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenico, D.D.; Ricciardi, G.; Zhang, R. Optimal design and seismic performance of tuned fluid inerter applied to structures with friction pendulum isolators. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 132, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, J.Z.; Titurus, B.; Harrison, A. Model identification methodology for fluid-based inerters. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 106, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Howcroft, C.; Neild, S.A.; Jiang, J.Z. Using continuation analysis to identify shimmy-suppression devices for an aircraft main landing gear. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 408, 234–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liao, M.; Liao, B.; Su, W.; Chan, H. The performance improvements of train suspension systems with mechanical networks employing inerters. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2009, 47, 805–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, D.; Ricciardi, G. An enhanced base isolation system equipped with optimal tuned mass damper inerter (TMDI). Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 47, 1169–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Qiao, H.; De Domenico, D. Seismic protection of reinforced concrete continuous girder bridges with inerter-based vibration absorbers. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 164, 107526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C.; Wang, F. Performance benefits in passive vehicle suspensions employing inerters. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2004, 42, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Jiang, J.Z.; Neild, S.A.; Chen, L. Vehicle vibration suppression using an inerter-based mechatronic device. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2020, 234, 2592–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Sheng, X.; Jiang, J.Z.; Zhou, H.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z. Vibration suppression of bridges under moving loads using the structure-immittance approach. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 211, 106792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chan, H. Vehicle suspensions with a mechatronic network strut. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2011, 49, 811–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hsieh, M.; Chen, H. Stability and performance analysis of a full-train system with inerters. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2012, 50, 545–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Jiang, J.Z.; Wang, H.; Neild, S. Synthesis of essential-regular bicubic impedances. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2017, 45, 1482–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Shen, Y.; Xing, H.; Yang, S. Optimal control and parameters design for the fractional-order vehicle suspension system. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control. 2018, 37, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, R.; Xu, J.; Xu, F.; Zhang, B.; Dong, X. Fractional Modeling and Characteristic Analysis of Hydro-Pneumatic Suspension for Construction Vehicles. Processes 2021, 9, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Xing, W.; Wang, M.; Ma, W.; Chang, Y. Study on chaos of nonlinear suspension system with fractional-order derivative under random excitation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 152, 111300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Tai, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, N. Critical damping design method of vibration isolation system with both fractional-order inerter and damper. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 9, 1348–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Z.M.; Khanday, F.A. Analysis of Disordered Dynamics in Polymer Nanocomposite Dielectrics for the Realization of Fractional-Order Capacitor. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2021, 28, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman-White, W.; Kennedy, H.; Bodnar, R.; Lee, T. Adaptive Tuning of Large-Signal Resonant Circuits Using Phase-Switched Fractional Capacitance. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 64, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D. Definition and Calculation of Fractional Calculus. In Fractional Calculus and Fractional-Order Control; Zhang, Z., Jiang, H., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 31–35. ISBN 978-7-03-054398-1. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, D. Fractional Calculus Operators and Approximation of Systems. In Fractional Calculus and Fractional-Order Control; Zhang, Z., Jiang, H., Eds.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 115–121. ISBN 978-7-03-054398-1. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Hua, J.; Fan, W.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, L. Optimal design and dynamic performance analysis of a fractional-order electrical network-based vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 184, 109718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparo, M.G.; Papini, A.; Pasquali, A. Nonmonotone algorithms for pattern search methods. Numer. Algorithms 2001, 28, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.; Shi, D.; Yang, J. Improved design of dynamic vibration absorber by using the inerter and its application in vehicle suspension. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 361, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Cai, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Vehicle height and posture control of the electronic air suspension system using the hybrid system approach. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2016, 54, 328–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).