Deducing Energy Consumer Behavior from Smart Meter Data †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- separate disaggregation data analyses from data representations;
- use open standard interfaces to exchange data (i.e., ZigBee and RESTful web interfaces) in a seamless way;
- provide a unique and shared database for appliance signatures and disaggregated results;
- improve the aggregated data quality by detecting and fixing its errors;
- combine the consumptions of several homes to detect appliance usage patterns.
- provide natural language reports about the user behavior to relevant stakeholders (hospitals, companies, etc.).
2. State of the Art
3. Background
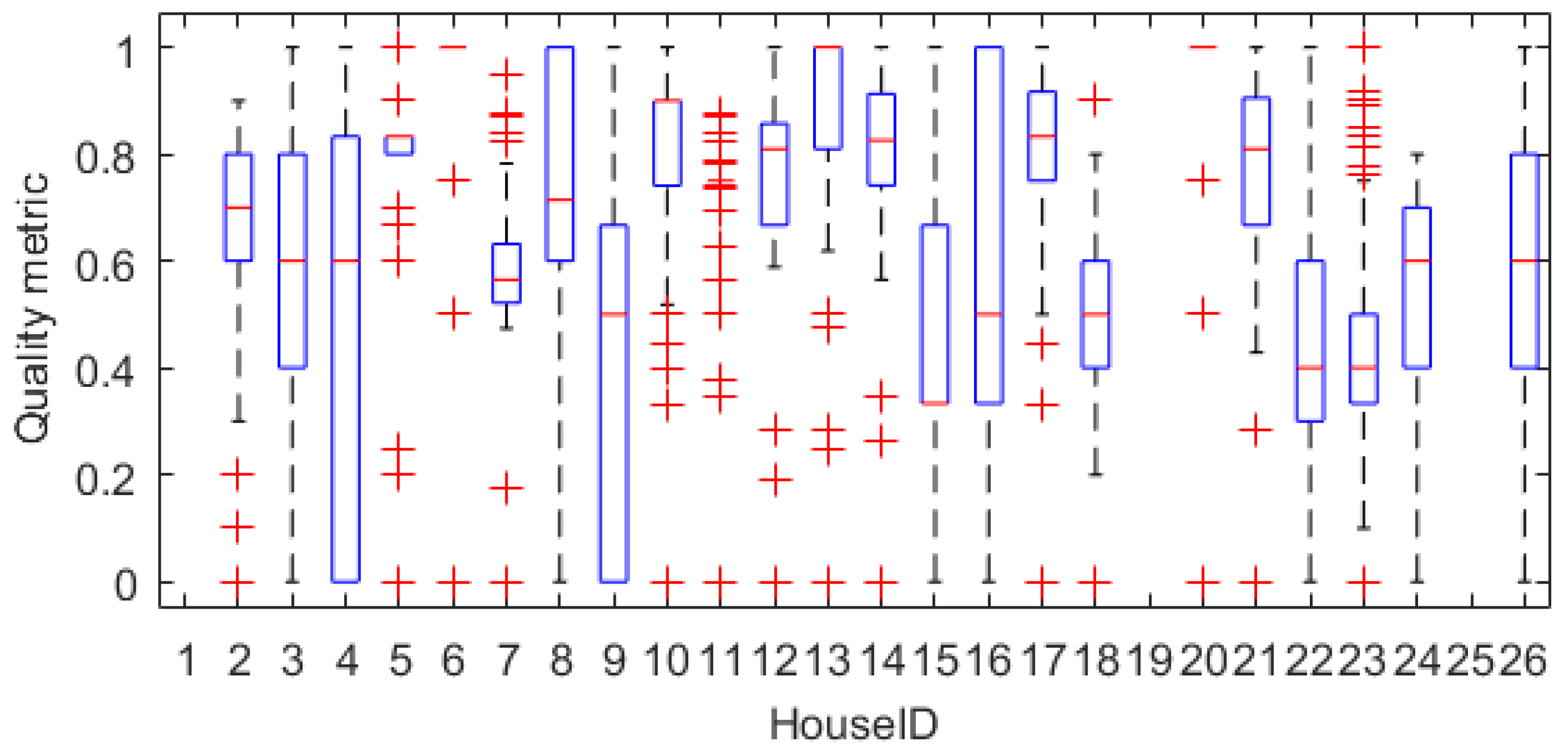
3.1. Quality Check
3.2. Gap Filling
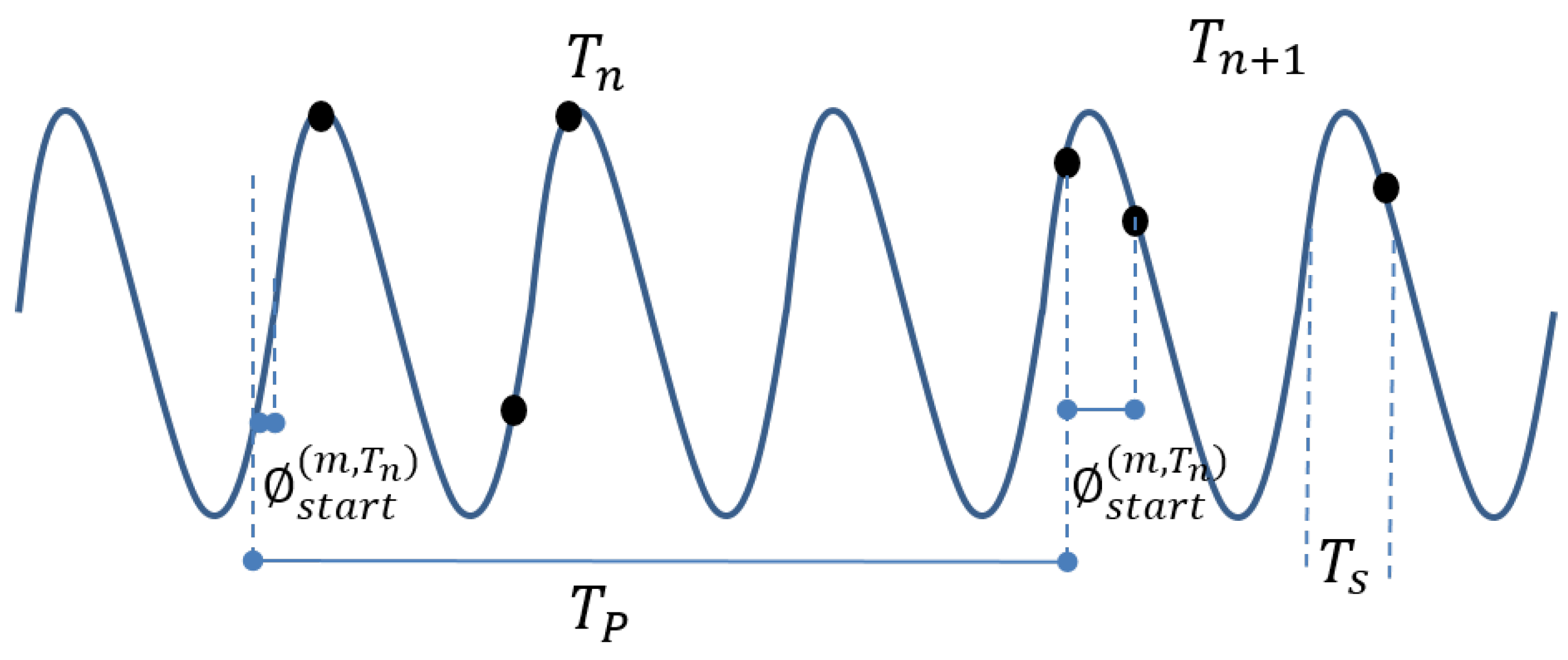
3.3. Load Disaggregation Algorithm
3.4. Outcome Refinement
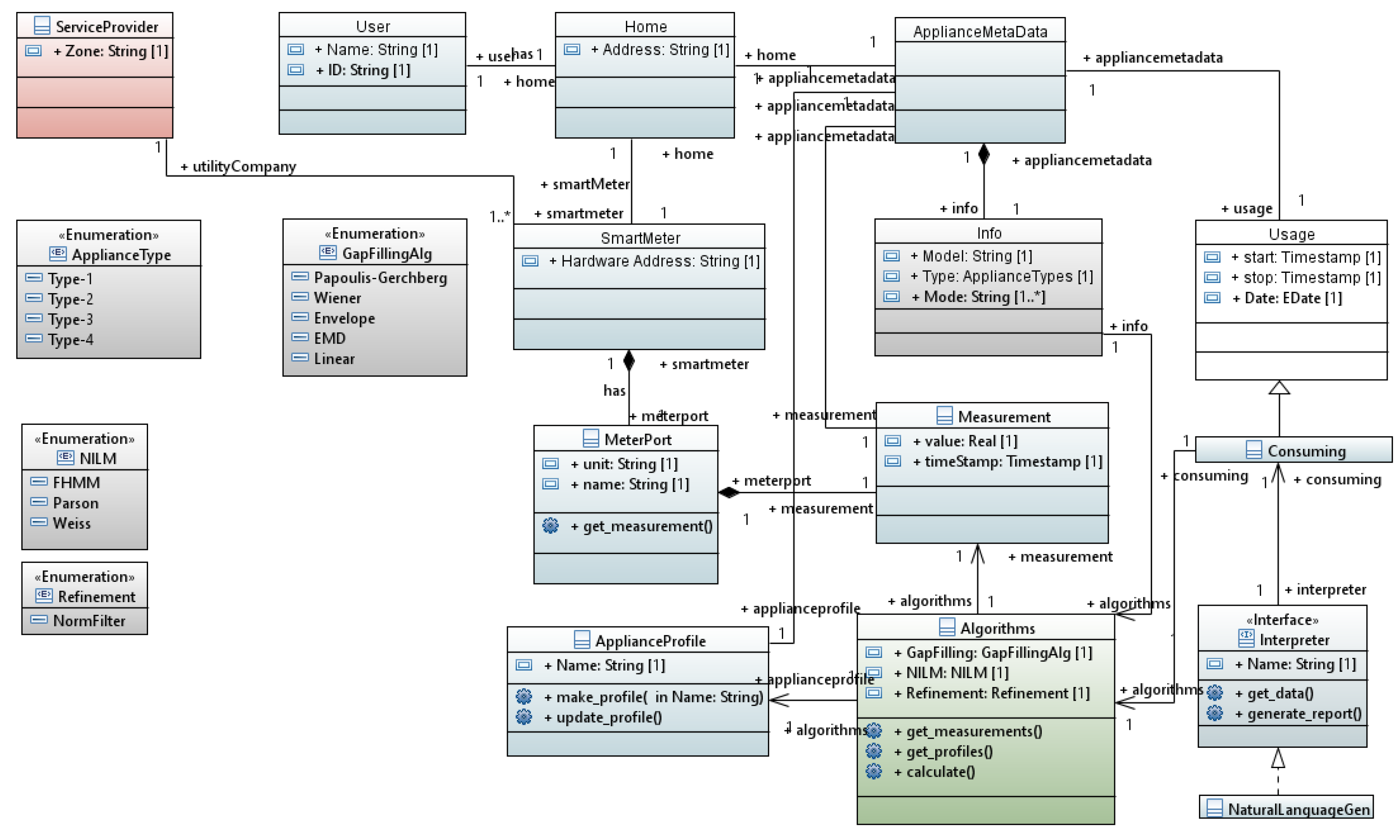
3.5. Data Representation
3.5.1. Modeling
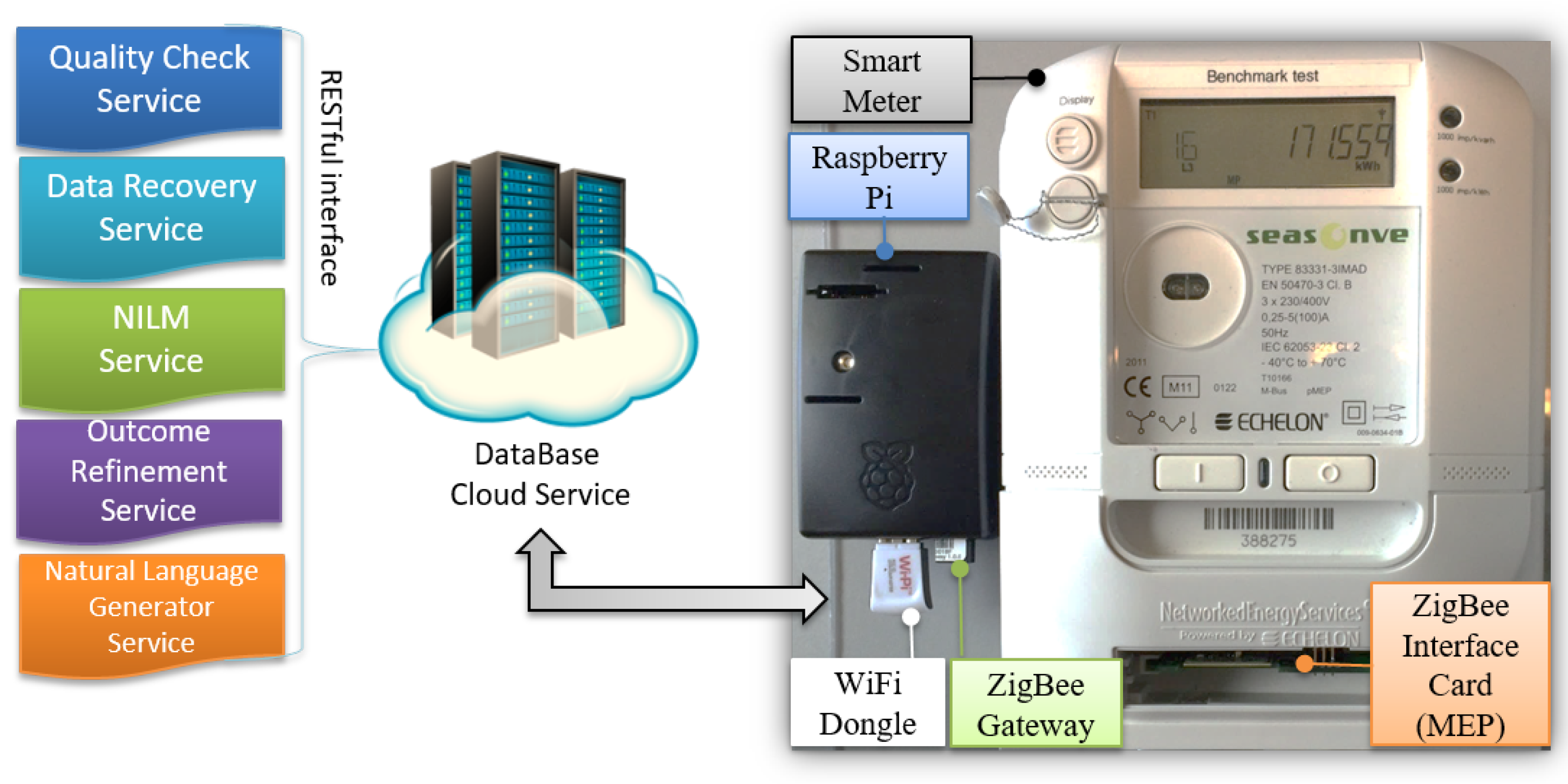
3.5.2. Interfaces
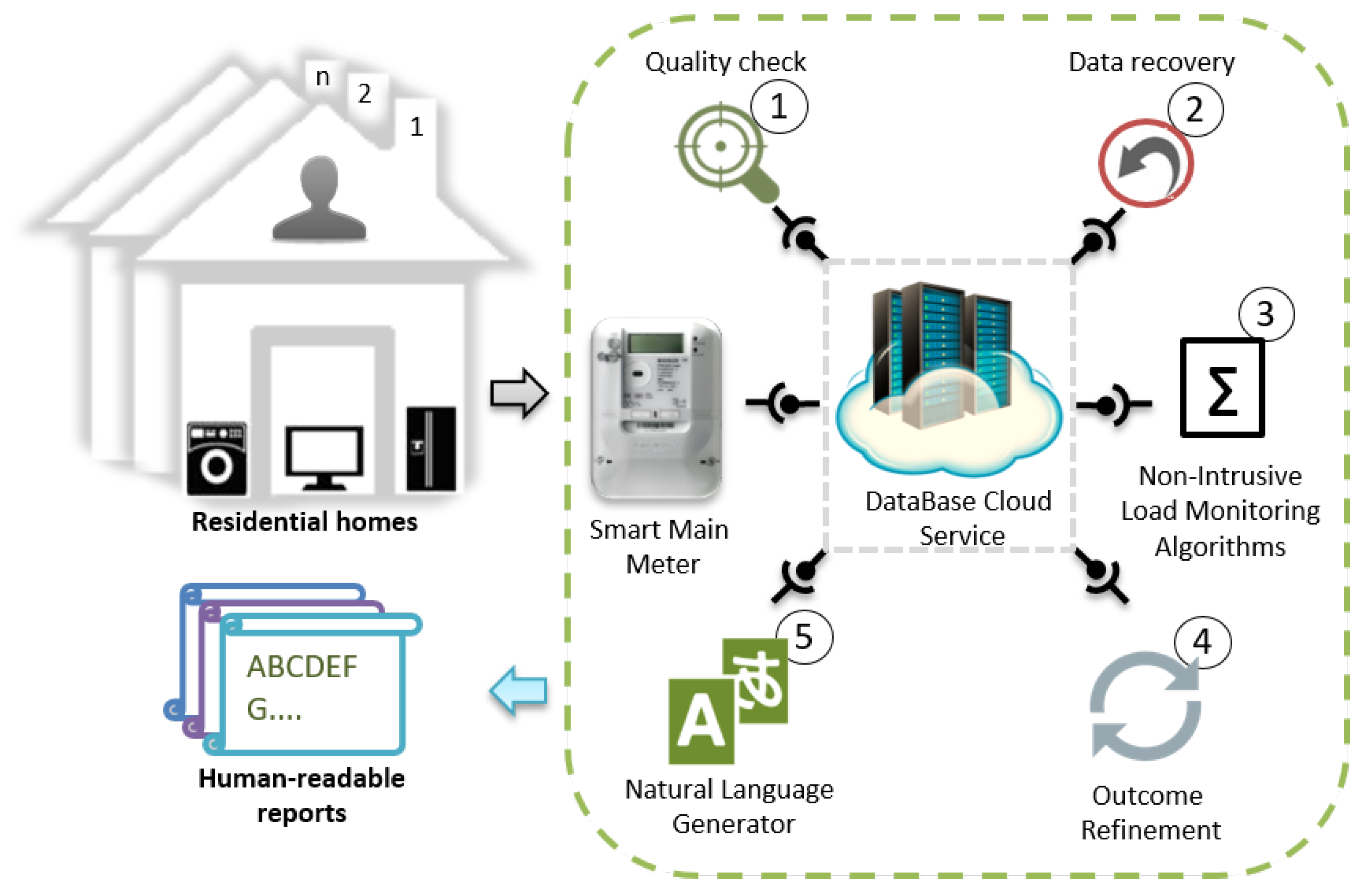
4. Proposed Framework
4.1. Data Quality Service
4.1.1. Sample availability
4.1.2. Activity
4.2. Gap Filling Service
4.2.1. Papoulis-Gerchberg Algorithm
4.2.2. Wiener Filling Algorithm
4.2.3. Spatio-Temporal Filling Algorithm
4.2.4. Envelope Filling Algorithm
4.2.5. Empirical Mode Decomposition Filling Algorithm
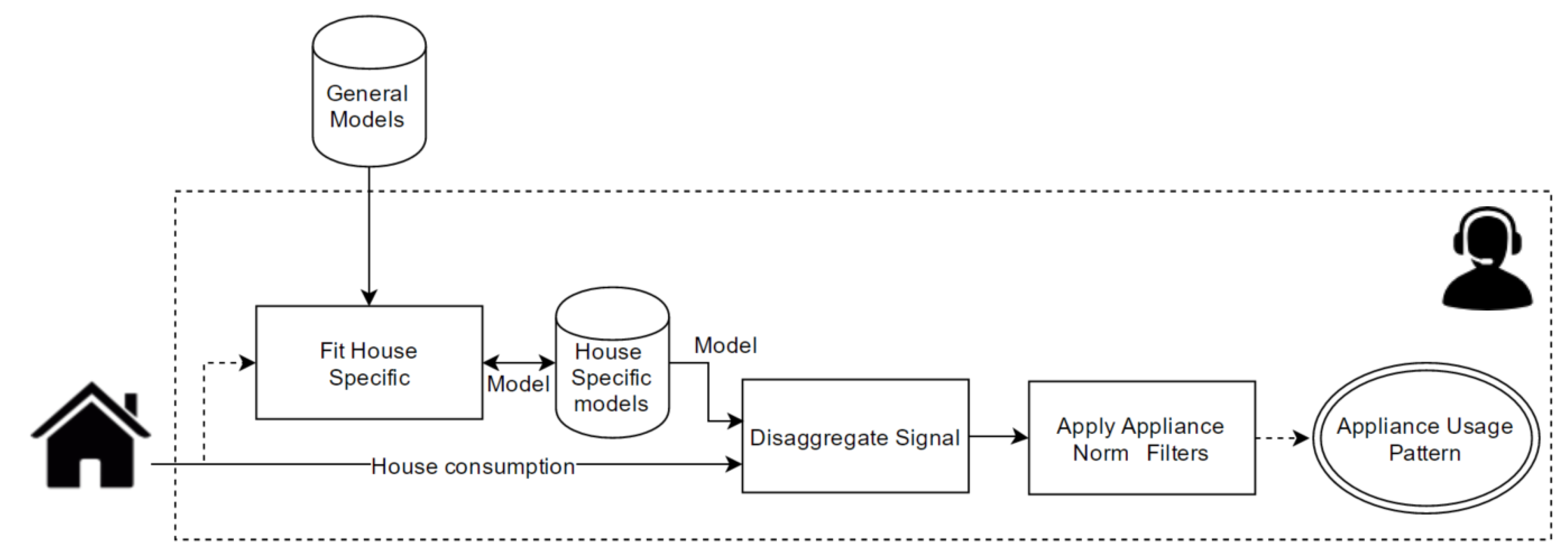
4.3. Load Disaggregation Algorithm (LDA)
4.3.1. Concepts and Challenges
- Type-1: Appliances that only have 2 states corresponding to ON/OFF. This could be a lamp or a water boiler.
- Type-2: These are appliances with multiple states. The appliance in this category can be modeled as a finite state machine. Many modern devices such as TV’s, computers and washing machines fall in this category.
- Type-3: These appliances are referred to as “Continuously Variable Devices”. These devices have a variable power draw and is impossible to model as a finite state machine. This could be appliances like power drills, and dimmer lights. These are by far the hardest for the NILM algorithms to detect.
- Type-4: These are a special kind of appliances that are always ON and consume energy at a constant rate. Such devices could be smoke detectors and burglary alarms.
4.3.2. Features
4.3.3. Learning Strategy
4.3.4. Challenges
4.3.5. Recognition Methods
Factorial Hidden Markov Models
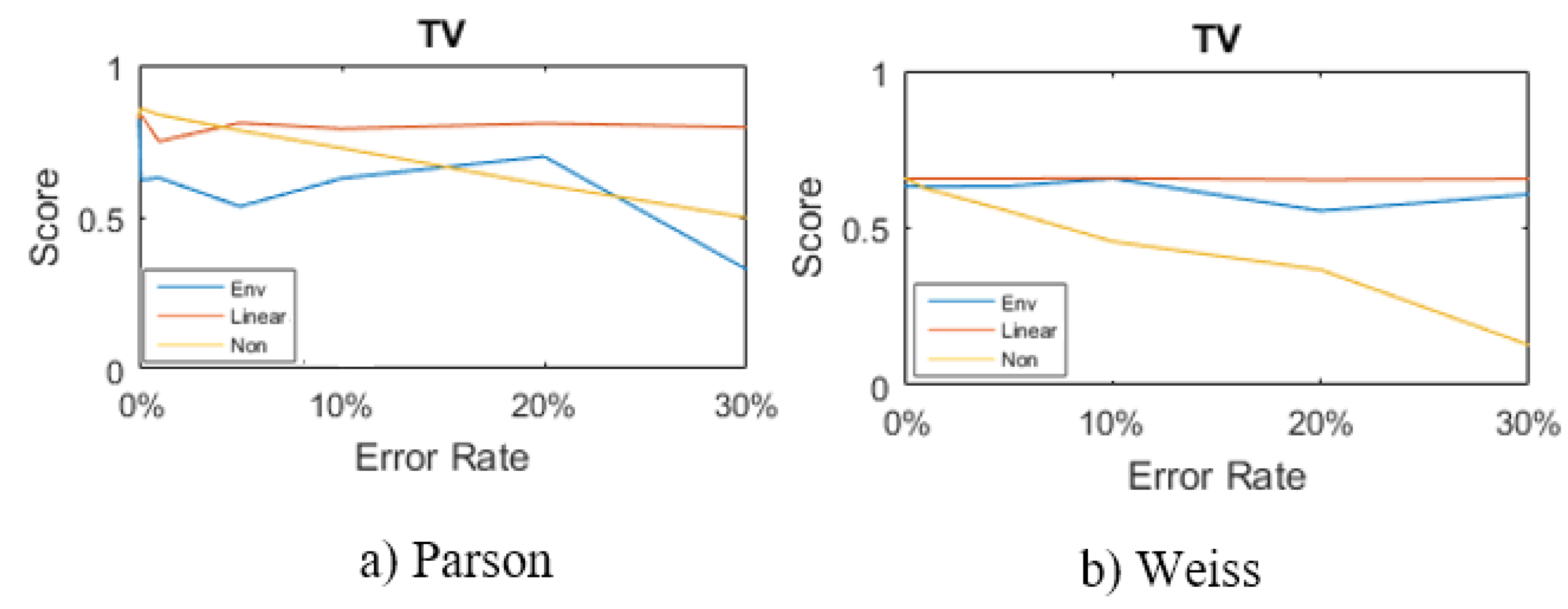
Parson
Weiss
4.4. Outcome Refinement Service
The Methodology
4.5. Data Representation Service
[let I: Sequence (InstanceSpecification) = model . eAllContents (InstanceSpecification)] [if (I. classifier ->at(i). name = ’User ’)] [I->at(i). name /] [let iUser : Integer = i] [for (it : NamedElement | I->at(iUser). clientDependency . supplier)] [it. name /] living in ..... [it. clientDependency . supplier . eAllContents (LiteralString).value ->sep(’from ’,’ to ’,’.’)/] ...
5. Experimental Validation
5.1. Quality Check
5.2. Data Recovery
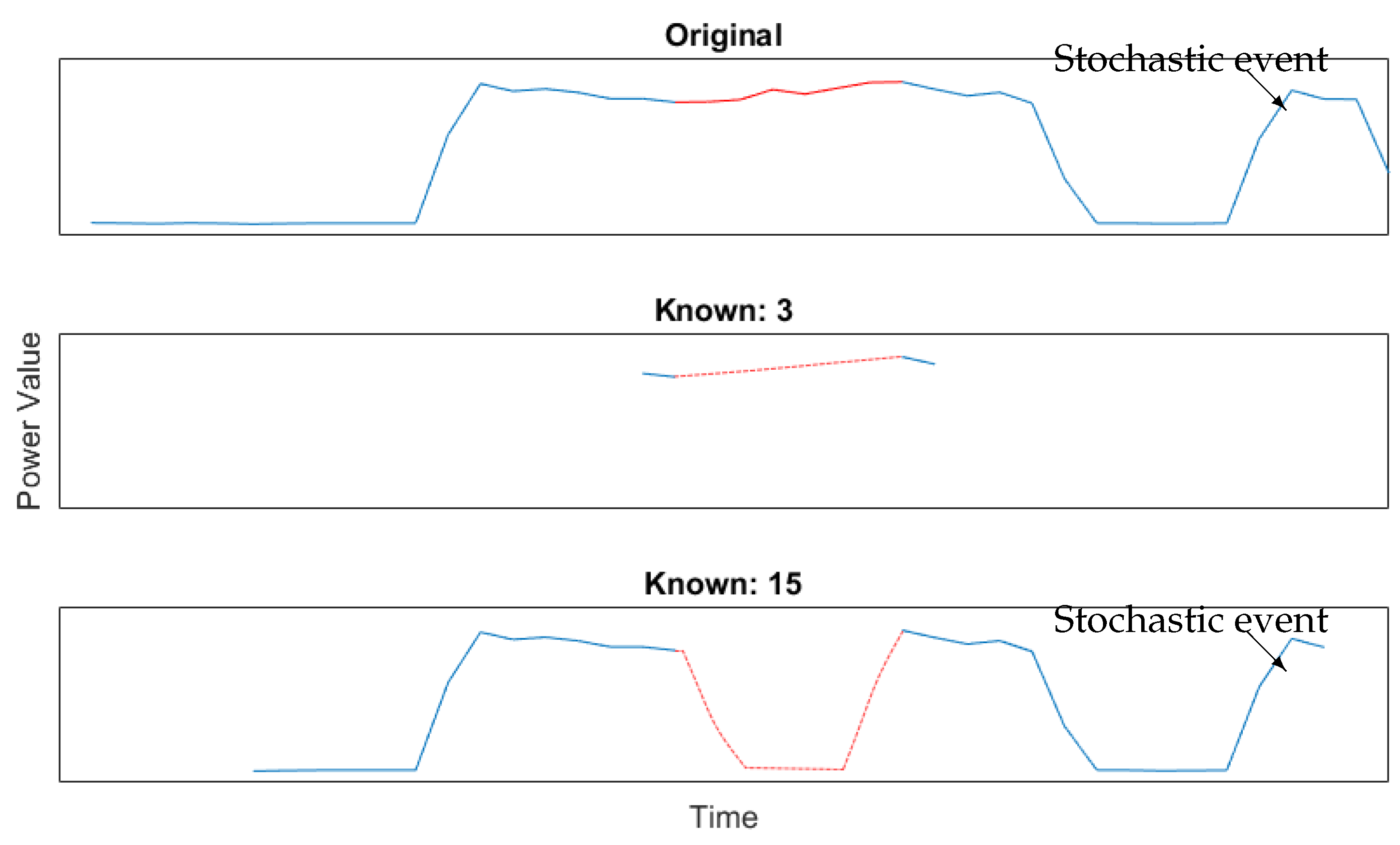
5.2.1. Post and Prior Knowledge
5.2.2. SmartHG Dataset Reconstruction
Sample Comparison
Frequency Comparison
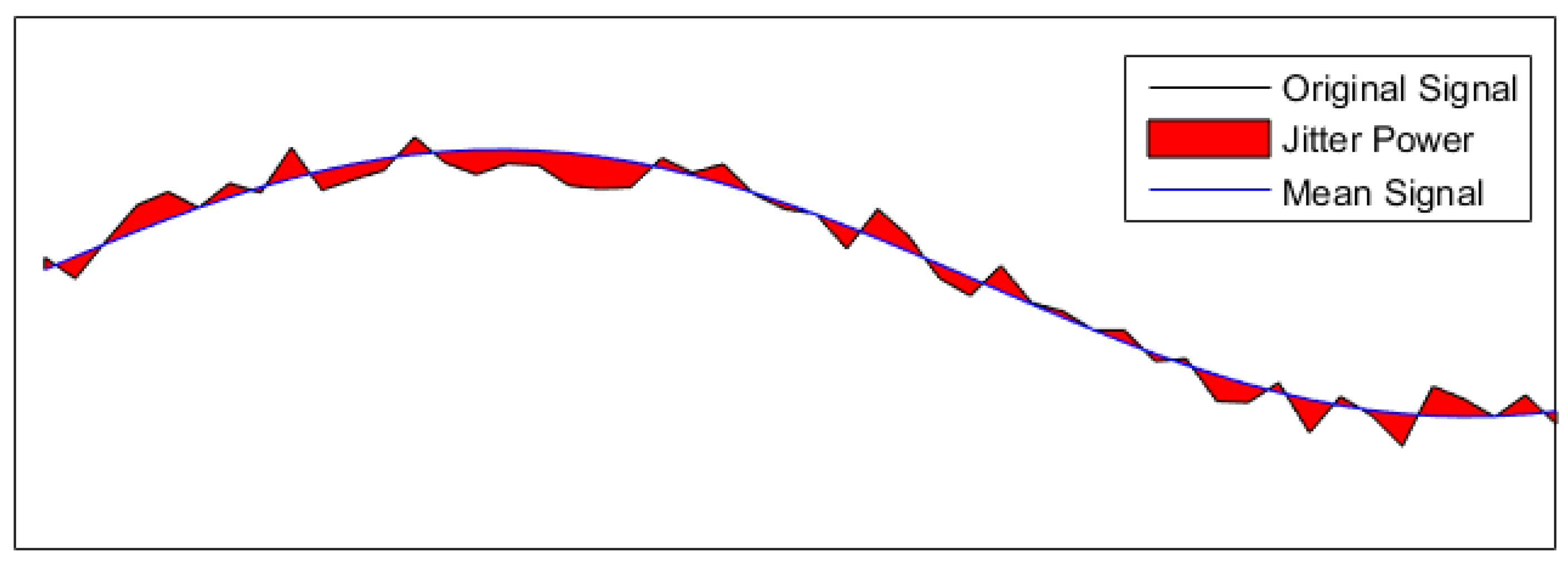
Jitter Comparison
5.3. Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM) Algorithms
5.4. Outcome Refinement
Results
5.5. NLP and Report Generation
“Peter (User ID: 123) living in XYZ (Home ID: 2) was watching TV from 18:00 to 20:45 on 1 May 2015”.
“CompanyA (Service provider of Zone: 4321) ran algorithm named: Norm Filter on Smart Meters: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and detects that the TV was ON from 06:00 to 09:00 on Monday, 4 May 2015”.
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ABI Research. Smart Electricity Meters to Total 780 Million in 2020. Available online: http://abiresearch.com/press/smart-electricity-meters-to-total-780-million-in-2 (accessed on 1 December 2015).
- Green Tech Media. What Will Drive Investment in the Next 60 Million Smart Meters? Available online: greentechmedia.com (accessed on 1 March 2016).
- European Commission. Benchmarking Smart Metering Deployment in the EU-27 with a Focus on Electricity. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/ (accessed on 1 June 2014).
- Depuru, S.; Wang, L.; Devabhaktuni, V. Smart Meters for Power Grid: Challenges, Issues, Advantages and Status. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2736–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, T.; Mari, F.; Melatti, I.; Salvo, I.; Tronci, E.; Gruber, J.K.; Hayes, B.; Prodanovic, M.; Elmegaard, L. User Flexibility Aware Price Policy Synthesis for Smart Grids. In Proceedings of the 2015 Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design, Funchal, Portugal, 26–28 August 2015; pp. 478–485. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, R.; Tørring, N.; Danielsen, B.; Hansen, M.; Pedersen, E. Towards an App Platform for Data Concentrators. In Proceedings of the IEEE ISGT Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 February 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Trung, K.N.; Zammit, O.; Dekneuvel, E.; Nicolle, B.; Nguyen Van, C.; Jacquemod, G. An Innovative Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring System for Commercial and Industrial Application. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Communications, Hanoi, Vietnam, 10–12 October 2012; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Sun, Y.; Deng, D.J.; Vinel, A.; Zhang, Y. Wireless Big Data Computing in Smart Grid. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, H.G.C.P.; Perera, P.H.; Godaliyadda, G.M.R.I.; Ekanayake, M.P.B.; Ekanayake, J.B. Residential Appliance Monitoring Based on Low Frequency Smart Meter Measurements. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Miami, FL, USA, 2–5 November 2015; pp. 878–884. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen, S.A.; Jacobsen, R.H.; Terkelsen, A.F. DB&A: An Open Source Web Service for Meter Data Management. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Service-Oriented System Engineering, Oxford, UK, 29 March–2 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Batra, N.; Kelly, J.; Parson, O.; Dutta, H.; Knottenbelt, W.; Rogers, A.; Singh, A.; Srivastava, M. NILMTK: An Open Source Toolkit for Non-intrusive Load Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Future Energy Systems, Cambridge, UK, 1–13 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Beckel, C.; Kleiminger, W.; Cicchetti, R.; Staake, T.; Santini, S. The ECO Data Set and the Performance of Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, Memphis, TN, USA, 3–6 November 2014; pp. 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ruzzelli, A.G.; Nicolas, C.; Schoofs, A.; O’Hare, G.M.P. Real-Time Recognition and Profiling of Appliances through a Single Electricity Sensor. In Proceedings of the 7th Annual IEEE Communications Society Conference on Sensor, Mesh and Ad Hoc Communications and Networks (SECON), Boston, MA, USA, 21–25 June 2010; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.; Elafoudi, G.; Stankovic, L.; Stankovic, V. Non-intrusive appliance load monitoring using low-resolution smart meter data. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Venice, Italy, 3–6 November 2014; pp. 535–540. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, B.; Hu, Y.C. Load disaggregation using harmonic analysis and regularized optimization. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Signal Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Hollywood, CA, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO19157 Geographic Information & Data Quality; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pastorello, G.; Agarwal, D.; Papale, D.; Samak, T.; Trotta, C.; Ribeca, A.; Poindexter, C.; Faybishenko, B.; Gunter, D.; Hollowgrass, R.; et al. Observational Data Patterns for Time Series Data Quality Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 10th International Conference on e-Science ( e-Science ’14), Sao Paulo, Brazil, 20–24 October 2014; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Moghtaderi, A.; Borgnat, P.; Flandrin, P. Gap-Filling by the empirical mode decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Kyoto, Japan, 25–30 March 2012; pp. 3821–3824. [Google Scholar]
- Manolakis, D.; Ingle, V. Applied Digital Signal Processing: Theory and Practice; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.; Guan, Y.L.; Chen, S. Modeling and analysis of noise effects on broadband power-line communications. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2005, 20, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, G.H. Power Line Filter for Transient and Continuous Noise Suppression. U.S. Patent 4,698,721, 6 October 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Meijer, M.; Vullings, L.; Bulens, J.; Rip, F.; Boss, M.; Hazeu, G.; Storm, M. Spatial Data Quality and a Workflow Tool. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simader, A.M.; Kluger, B.; Neumann, N.K.N.; Bueschl, C.; Lemmens, M.; Lirk, G.; Krska, R.; Schuhmacher, R. QCScreen: A software tool for data quality control in LC-HRMS based metabolomics. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, R.; Mikkelsen, S.A. Infrastructure for Intelligent Automation Services in the Smart Grid. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2014, 76, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burden, H.; Heldal, R. Natural Language Generation from Class Diagrams. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Model-Driven Engineering, Verification and Validation, Wellington, New Zealand, 17 October 2011; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 8402:1994 Quality Management and Quality Assurance—Vocabulary; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Object Management Group. Unified Modeling Language, (Version 2.5); Object Management Group: Needham, MA, USA, 2013; Available online: http://uml.org (accessed on 15 March 2017).
- Eclipse. Acceleo. Available online: http://eclipse.org/acceleo/ (accessed on 15 March 2016).
- Ebeid, E.; Rotger-Griful, S.; Mikkelsen, S.A.; Jacobsen, R.H. A Methodology to Evaluate Demand Response Communication Protocols for the Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communication Workshop (ICCW), London, UK, 8–12 June 2015; pp. 2012–2017. [Google Scholar]
- ZigBee Alliance. ZigBee. Available online: www.zigbee.org (accessed on 1 December 2016).
- Ferreira, P.J.S.G. Interpolation and the discrete Papoulis-Gerchberg algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 2596–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.; Neves, A.; Marques, J.S.; Sanches, J. The Papoulis-Gerchberg Algorithm with Unknown Signal Bandwidth. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Image Analysis and Recognition (ICIAR 2006) Part I, Póvoa de Varzim, Portugal, 18–20 September 2006; Campilho, A., Kamel, M.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 436–445. [Google Scholar]
- Rune Heick. P-G Algorithm. Available online: https://github.com/RuneHeick/SpecialeAppendix/tree/master/P-G%20Algo (accessed on 1 April 2016).
- Thomson, D.; Lanzerotti, L.; Maclennan, C. Interplanetary magnetic field: Statistical properties and discrete modes. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 15941–15962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rune Heick. Weiner Gap Filter Algorithm. Available online: https://github.com/RuneHeick/SpecialeAppendix/tree/\master/SSA%20Algo (accessed on 15 March 2016).
- Kondrashov, D.; Ghil, M. Spatio-temporal filling of missing points in geophysical data sets. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2006, 13, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rune Heick. Spatio-Temporal Filling Algorithm. Available online: https://github.com/RuneHeick/SpecialeAppendix/tree/\master/SSA%20Algo (accessed on 15 March 2016).
- Rune Heick. Envelope Filling Algorithm. Available online: https://github.com/RuneHeick/SpecialeAppendix/tree/master/\Env%20Algo (accessed on 15 March 2016).
- Rune Heick. Empirical Mode Decomposition Filling Algorithm. Available online: https://github.com/RuneHeick/SpecialeAppendix/tree/master/Emd%20Algo (accessed on 15 March 2016).
- Bonino, D.; Corno, F.; Russis, L.D. Home energy consumption feedback: A user survey. Energy Build. 2012, 47, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoha, A.; Gluhak, A.; Imran, M.A.; Rajasegarar, S. Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Approaches for Disaggregated Energy Sensing: A Survey. Sensors 2012, 12, 16838–16866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, D.; Ng, W.S.; Liew, A.C. Neural-network-based signature recognition for harmonic source identification. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2006, 21, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.N.; Robertson, T.; Kientz, J.A.; Reynolds, M.S.; Abowd, G.D. At the Flick of a Switch: Detecting and Classifying Unique Electrical Events on the Residential Power Line (Nominated for the Best Paper Award). In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp 2007), Innsbruck, Austria, 16–19 September 2007; Krumm, J., Abowd, G.D., Seneviratne, A., Strang, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 271–288. [Google Scholar]
- Ghahramani, Z.; Jordan, M.I. Factorial Hidden Markov Models. Mach. Learn. 1997, 29, 245–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolter, J.Z.; Jaakkola, T. Approximate Inference in Additive Factorial HMMs with Application to Energy Disaggregation. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS-12), La Palma, Canary Islands, Spain, 21–23 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, M.; Helfenstein, A.; Mattern, F.; Staake, T. Leveraging smart meter data to recognize home appliances. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), Lugano, Switzerland, 19–23 March 2012; pp. 190–197. [Google Scholar]
- Parson, O.; Ghosh, S.; Weal, M.; Rogers, A. Non-intrusive load monitoring using prior models of general appliance types. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Toronto, ON, Canada, 22–26 July 2012; pp. 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- Rune Heick. Detailed results from the disaggregation of TV’s in Case study. Available online: https://github.com/RuneHeick/SpecialeAppendix/tree/master/Case%20Study%20Plot (accessed on 15 March 2016).
- Eclipse. Papyrus. Available online: https://eclipse.org/papyrus/ (accessed on 30 December 2016).



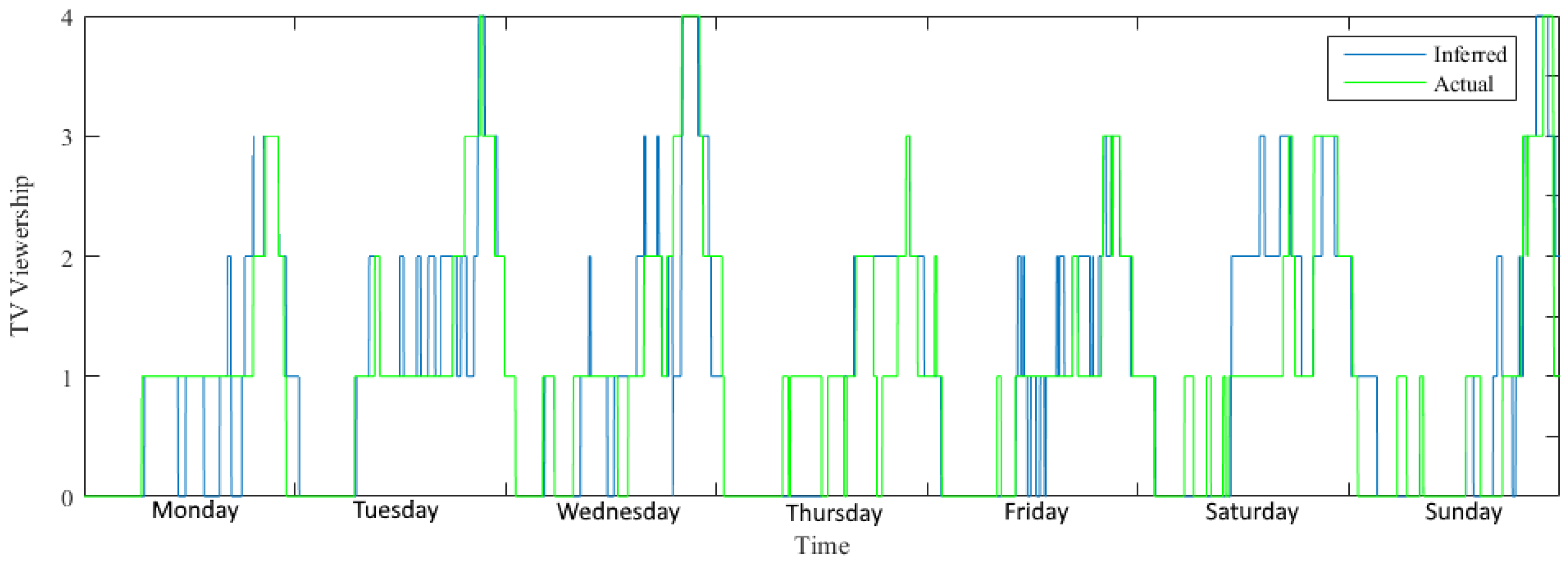


| Time of Day | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00–03 | 03–06 | 06–09 | 09–12 | 12–13 | 15–18 | 18–21 | 21–00 | ||
| Monday | Inferred | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.66 | 1.19 | 1.02 | 1.31 | 2.39 | 2.08 |
| True | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 0.68 | 1.28 | 2.49 | 1.72 | |
| Tuesday | Inferred | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 0.68 | 1.28 | 2.49 | 1.72 |
| True | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.39 | 0.88 | 0.73 | 1.24 | 2.23 | 2.26 | |
| Wednesday | Inferred | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.39 | 0.88 | 0.73 | 1.24 | 2.23 | 2.26 |
| True | 0.09 | 0.30 | 0.58 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 1.42 | 2.72 | 2.11 | |
| Thursday | Inferred | 0.09 | 0.30 | 0.58 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 1.42 | 2.72 | 2.11 |
| True | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.31 | 0.96 | 1.12 | 1.69 | 2.86 | 2.30 | |
| Friday | Inferred | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.31 | 0.96 | 1.12 | 1.69 | 2.86 | 2.30 |
| True | 0.10 | 0.18 | 0.66 | 0.91 | 0.74 | 1.65 | 3.17 | 2.35 | |
| Saturday | Inferred | 0.10 | 0.18 | 0.66 | 0.91 | 0.74 | 1.65 | 3.17 | 2.35 |
| True | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.95 | 0.77 | 1.39 | 1.36 | 2.26 | 2.10 | |
| Sunday | Inferred | 0.28 | 0.17 | 0.95 | 0.77 | 1.39 | 1.36 | 2.26 | 2.10 |
| True | 0.12 | 0.00 | 1.01 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 1.33 | 1.93 | 1.65 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebeid, E.; Heick, R.; Jacobsen, R.H. Deducing Energy Consumer Behavior from Smart Meter Data. Future Internet 2017, 9, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi9030029
Ebeid E, Heick R, Jacobsen RH. Deducing Energy Consumer Behavior from Smart Meter Data. Future Internet. 2017; 9(3):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi9030029
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbeid, Emad, Rune Heick, and Rune Hylsberg Jacobsen. 2017. "Deducing Energy Consumer Behavior from Smart Meter Data" Future Internet 9, no. 3: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi9030029
APA StyleEbeid, E., Heick, R., & Jacobsen, R. H. (2017). Deducing Energy Consumer Behavior from Smart Meter Data. Future Internet, 9(3), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi9030029







