Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Atmospheric Duct Interference Detection and Mitigation in TD-LTE Networks †
Abstract
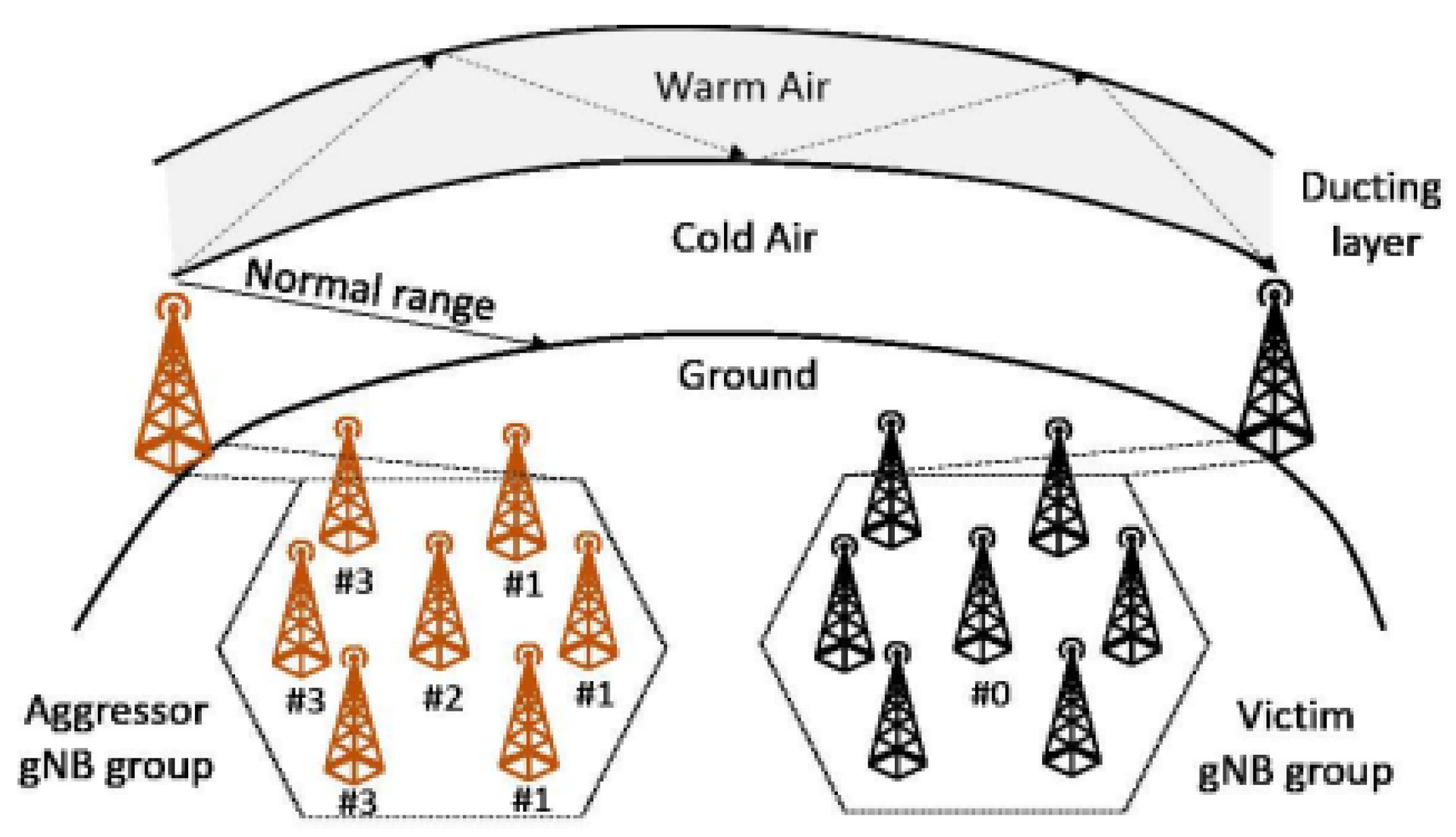
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Signal Processing Approach to Mitigate ADI
2.2. Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches to Mitigate ADI
2.3. Hybrid Approaches to Mitigate ADI
2.4. Other Approaches to Mitigate ADI
2.5. Overview of Existing Mitigation Approaches
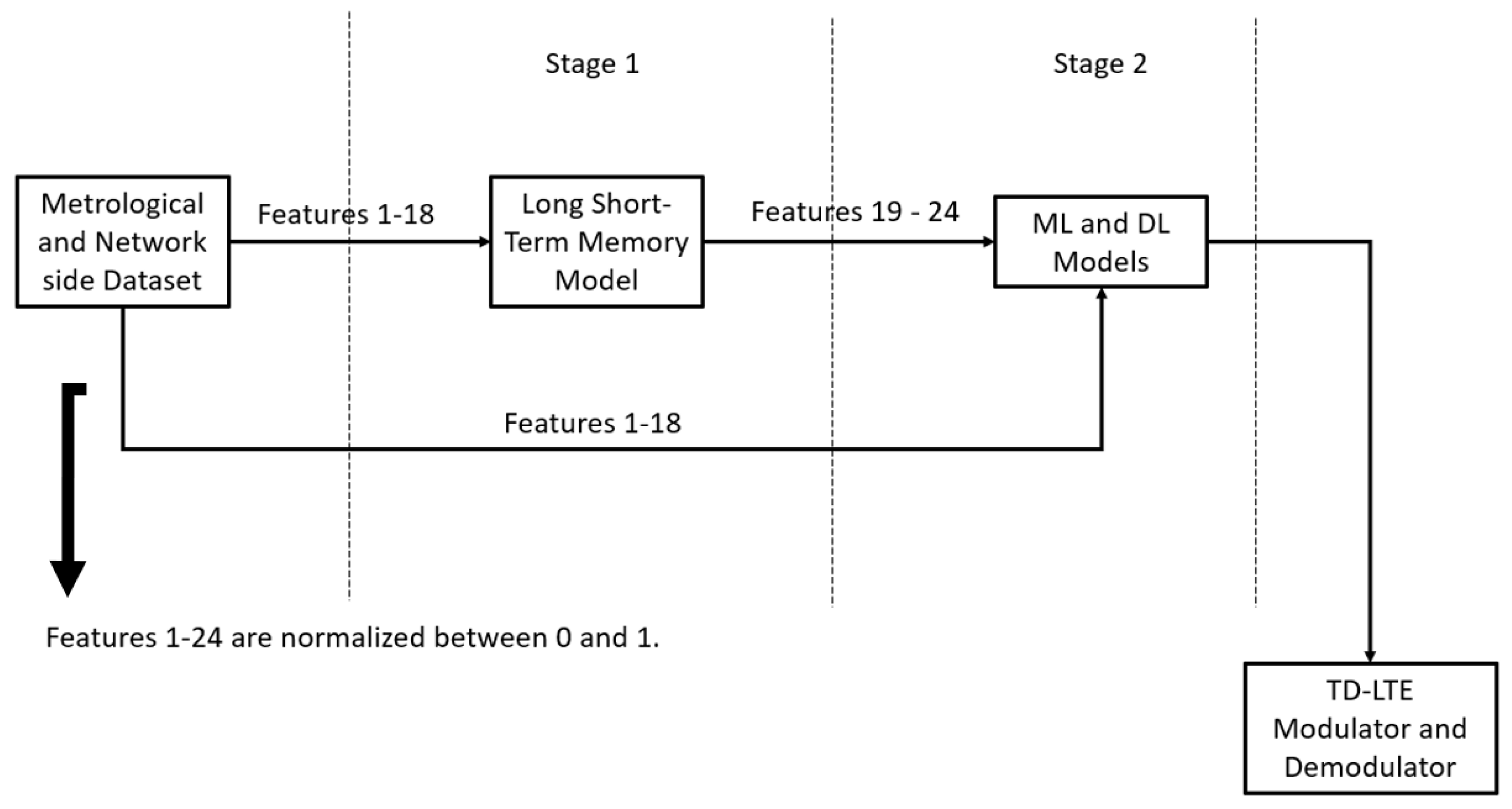
3. Methodology
3.1. Atmospheric Duct Interference Prediction
3.2. Atmospheric Duct Interference Mitigation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. The Results of the ADI Prediction Models
4.1.1. The Evaluation Parameters of the ML- and DL-Based ADI Models
4.1.2. The Evaluation Parameters of the ML and DL Classifier-Based Prediction Model
4.1.3. The Evaluation Parameters of the Cascaded ML and DL Classifier-Based Prediction Model
4.2. The Results of the ADI Mitigation Models
4.2.1. The Results of the GB Classifier-Based ADI Mitigation System
4.2.2. The Results of the LSTM Classifier-Based ADI Mitigation System
4.2.3. The Results of the CNN Classifier-Based ADI Mitigation System
4.2.4. The Results of the ODGB Classifier-Based ADI Mitigation System
4.2.5. The Results of the SGD Classifier-Based ADI Mitigation System
4.2.6. The Results of the HGB Classifier-Based ADI Mitigation System
4.2.7. Discussion: Comparative Analysis of the Six ADI Mitigation Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, F.; Pan, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, G.Y. Atmospheric Ducting Effect in Wireless Communications: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Commun. Inf. Netw. 2021, 6, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolovskiy, S.; Schreiner, W.; Zeng, Z.; Hunt, D.; Lin, Y.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H. Observation, Analysis, and Modeling of Deep Radio Occultation Signals: Effects of Tropospheric Ducts and Interfering Signals. Radio Sci. 2014, 49, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Sun, T.; Hu, H.; Xu, H.; Yang, Y.; Harjula, I.; Koucheryavy, Y. Analysis and Prediction of 100 Km-Scale Atmospheric Duct Interference in TD-LTE Networks. J. Commun. Inf. Netw. 2017, 2, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Q. Modeling Low Elevation GPS Signal Propagation in Maritime Atmospheric Ducts. J. Atmospheric Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2012, 80, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson. An Overview of Remote Interference Management. Available online: https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2019/9/overview-of-remote-interference-management (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Wei, T.; Feng, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.-X.; Ge, N.; Lu, J. Hybrid Satellite-Terrestrial Communication Networks for the Maritime Internet of Things: Key Technologies, Opportunities, and Challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 8910–8934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dialog Axiata PLC. 4G Mobile Broadband Coverage Area. Available online: https://www.dialog.lk/support/coverage (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Peralta, E.; Levanen, T.; Mäenpää, M.; Yuk, Y.; Pedersen, K.; Nielsen, S.; Valkama, M. Remote Interference Management in 5G New Radio: Methods and Performance. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, Z.; Guo, X.; Wu, J.; Cao, Y.; Qu, T.; Xue, J. Estimation of Co-Channel Interference between Cities Caused by Ducting and Turbulence. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 024102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, E.; Maenpaa, M.; Levanen, T.; Yuk, Y.; Pedersen, K.; Nielsen, S.; Valkama, M. Reference Signal Design for Remote Interference Management in 5G New Radio. In Proceedings of the 2019 European Conference on Networks and Communications (EuCNC), Valencia, Spain, 18–21 June 2019; pp. 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, L.; Guo, J.; Shen, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Atmospheric Duct Interference Identification and Avoidance in NR TDD Network. In Signal and Information Processing, Networking and Computers; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; Volume 1188, pp. 276–284. ISBN 978-981-97-2123-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, G.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Xie, T. Monitoring and Avoidance of Atmospheric Duct on Interference Optimization in TD-LTE System. In Signal and Information Processing, Networking and Computers; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 473, pp. 36–45. ISBN 978-981-10-7520-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, X.; Xin, Y. Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network to Recognize LTE Uplink Interference. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Marrakesh, Morocco, 15–18 April 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhou, T.; Xu, H.; Yang, Y. A Random Forest-Based Prediction Method of Atmospheric Duct Interference in TD-LTE Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.-H.; Liu, J.-X.; Zuo, J.-L.; Ding, W.-B.; Shen, A.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.-D.; Luo, F. Recognition and Optimization of Atmospheric Duct in TD-LTE System Based on Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Intl Conf on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications, Big Data & Cloud Computing, Sustainable Computing & Communications, Social Computing & Networking (ISPA/BDCloud/SocialCom/SustainCom), Exeter, UK, 17–19 December 2020; pp. 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Guo, X.; Wu, Z.; Wu, J.; Wu, T.; Zhao, K.; Qu, T.; Linghu, L. Using Multi-Source Real Landform Data to Predict and Analyze Intercity Remote Interference of 5G Communication with Ducting and Troposcatter Effects. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Samiee, A.; Zhou, T.; Jalali, B. Deep Learning Interference Cancellation in Wireless Networks. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, Z. Analysis of the Co-Channel Interference Caused by Atmospheric Duct and Tropospheric Scattering. In Proceedings of the 2018 12th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory (ISAPE), Hangzhou, China, 3–6 December 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, J.; Haider, A.; Ali, R.; Kim, A. Machine Learning for Physical Layer in 5G and beyond Wireless Networks: A Survey. Electronics 2021, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, T.; Xu, T.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H. FNN-Based Prediction of Wireless Channel with Atmospheric Duct. In Proceedings of the ICC 2021—IEEE International Conference on Communications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.; Esswie, A.; Lei, D.; Harrebek, J.; Yuk, Y.; Selvaganapathy, S.; Helmers, H. Advancements in 5G New Radio TDD Cross Link Interference Mitigation. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feilong, Z. Forming Interference of Atmospheric Duct in 5G and Avoid Method. Chin. J. Radio Sci. 2021, 36, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinc, E.; Akan, O. Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications with Ducting Layer. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, J.; Gong, S. Modeling on Multi-eigenpath Channel in Marine Atmospheric Duct. Radio Sci. 2009, 44, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, X.; Shi, Q.; Hong, M.; Fu, X.; Sidiropoulos, N.D. Learning to Optimize: Training Deep Neural Networks for Interference Management. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 5438–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, R. Support Vector Machine—Introduction to Machine Learning Algorithms. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/support-vector-machine-introduction-to-machine-learning-algorithms-934a444fca47/ (accessed on 25 May 2025).
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W. Research Challenges and Opportunities of UAV Millimeter-Wave Communications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2019, 26, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y. Integrated Terrestrial-Satellite Communication Networks and Services. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2020, 27, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, T.; Hu, H. A Traceable Approach to Remote Interference Management for New Radio. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Shanghai, China, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Approach | Year | Detection Methodology | Accuracy | Network |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peralta et al. [10] | 2019 | Fast Fourier transform | Detection probability: 0.900 False alarm probability: 0.002 | 5G New Radio (FR1) |
| Peralta et al. [8] | 2021 | Remote interference reference signal design | 18 dB SNR for comb 1 and 2, 13 dB SNR for comb 4. | 5G New Radio (FR1 and FR2) |
| Guo et al. [11] | 2024 | Guard period adjustment based on remote interference | 5–7 dB SNR reduction | 5G New Radio (FR1 and FR2) |
| Shen et al. [12] | 2017 | ADI mitigation systems based on the TD-LTE reference signals | Power: 1–2 dB SNR reduction, Elevation angle: 5–10 dB SNR reduction, Antenna height: 3–4 dB SNR reduction | TD-LTE Networks |
| Approach | Year | Detection Methodology | Train Accuracy | Test Accuracy | Network |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ren et al. [13] | 2019 | CNN | - | 0.856 | LTE/Wi-Fi |
| Sun et al. [14] | 2017 | Random Forest | - | 0.650 (4000 samples), 0.680 (10,000 samples), 0.700 (20,000 samples) | TD-LTE |
| Shen et al. [15] | 2020 | CNN | 0.990 | 0.977 | TD-LTE |
| Zhou et al. [3] | 2017 | SVM KNN | - | 0.680 (10,000 samples), 0.720 (40,000 samples) 2. 0.700 (10,000 samples), 0.710 (40,000 samples) | TD-LTE |
| Yang et al. [16] | 2021 | LSTM | - | 0.984 | 5G (FR1) |
| Approach | Year | Methodology | Results | Network |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peralta et al. [10] | 2019 | Remote Interference Management Reference Signal (RIM-RS) | Detection probability: 0.900 False alarm probability: 0.002 | 5G New Radio (FR1) |
| Zhou et al. [17] | 2020 | DSP, LSTM, and CNN | Symbol error rate is reduced from 0.37618 to 0.0003 | QAM-OFDM |
| Zhou et al. [3] | 2017 | Adjustment of the Guard period | - | TD-LTE |
| Sun et al. [14] | 2017 | Adjustment of the Guard period | - | TD-LTE |
| Target Classes | Min Value | Max Value |
|---|---|---|
| Class A | −112.00 dB | |
| Class B | −116.00 dB | −112.01 dB |
| Class C | −120.00 dB | −116.01 dB |
| Class D | −124.00 dB | −120.01 dB |
| Class E | −128.00 dB | −124.01 dB |
| Class F | −128.01 dB |
| Base Station | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|
| Palali | 80.08 | 9.79 |
| Karainagar | 79.86 | 9.71 |
| Kandarodai | 80.01 | 9.75 |
| Jaffna | 80.00 | 9.66 |
| Manipai | 79.99 | 9.72 |
| Alaweddy | 80.01 | 9.77 |
| Kankasanthure | 80.03 | 9.81 |
| Nallur | 80.03 | 9.67 |
| Chawakachcheri | 80.16 | 9.65 |
| Kodikamam | 80.22 | 9.68 |
| Model | SGD Classifier | Gradient Boosting Classifier | Optimized Distributed Gradient Boosting Classifier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scaler | Standard Scaler | Min-Max Scaler | Min-Max Scaler |
| Algorithm | SVM: Linear | Random Forest | Random Forest |
| Dataset shuffled | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Estimators | - | 100 | 100 |
| Max-Depth | - | 2 | 2 |
| Max-Features | - | 2 | 2 |
| Loss | MSE | MSE | MSE |
| Iterations | 1000 | - | - |
| Kernel | Linear | - | - |
| Other features | Macro-average | Macro-average | Macro-average |
| Classifiers | Classifier in Stage 1 | Classifier in Stage 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | LSTM | SDG |
| 2 | LSTM | GB |
| 3 | LSTM | XGB |
| 4 | LSTM | LSTM |
| 5 | LSTM | CNN |
| Target Classes | Min Value | Max Value |
|---|---|---|
| Class A | −112.00 dB | |
| Class B | −116.00 dB | −112.01 dB |
| Class C | −120.00 dB | −116.01 dB |
| Class D | −124.00 dB | −120.01 dB |
| Class E | −128.00 dB | −124.01 dB |
| Class F | −128.01 dB |
| Config. ID | Conventional Configuration Approach | Extended Configuration Approach | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWPTS | GP | UPPTS | DWPTS | GP | UPPTS | |
| C1 | 3 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 8 | 1 |
| C2 | 3 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 2 |
| C3 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 3 | 1 |
| C4 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 2 |
| C5 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 2 | 1 |
| C6 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 2 |
| C7 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| C8 | 11 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 2 |
| Parameters | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scaler | Min-Max Scaler | Min-Max Scaler | Min-Max Scaler |
| Dataset shuffled | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Estimators | 125 | 135 | 145 |
| Criterion | Friedman MSE | Squared Error | Friedman MSE |
| Max-Depth | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Max-Features | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| Loss | Log loss | Log loss | Log loss |
| Minimum sample leaf | 4 | 3 | 5 |
| Minimum sample split | 3 | 5 | 3 |
| Minimum weight fraction leaf | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.20 |
| Maximum depth | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Average | Macro-average | Macro-average | Macro-average |
| Learning rate | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 |
| Parameters | LSTM Model 1 | LSTM Model 2 | LSTM Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Time series | Time series | Time series |
| Encoder | Label encoder | Label encoder | Label encoder |
| Optimizer | Adam | Adam | Adam |
| Loss | Log loss | Log loss | Log loss |
| Activation | Tanh | ReLu | ReLu |
| Recurrent activation | Sigmoid | Sigmoid | Tanh |
| Dropout | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.20 |
| Recurrent dropout | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.15 |
| Input layer | 18 neurons | 18 neurons | 18 neurons |
| Hidden layer 1–3 | 20 neurons | 22 neurons | 24 neurons |
| Hidden layer 4–6 | 22 neurons | 24 neurons | 20 neurons |
| Output layer | 6 neurons | 6 neurons | 6 neurons |
| Learning rate | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 |
| Parameters | CNN Model 1 | CNN Model 2 | CNN Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Shuffled | Shuffled | Shuffled |
| Encoder | One Hot encoder | One Hot encoder | One Hot encoder |
| Optimizer | Adam | Adam | Adam |
| Loss | Log loss | Log loss | Log loss |
| Input layer | 18 neurons, ReLu | 18 neurons, ReLu | 18 neurons, Tanh |
| Hidden layer 1 | 18 neurons, ReLu | 20 neurons, ReLu | 20 neurons, Tanh |
| Hidden layer 2 | 20 neurons, Sigmoid | 22 neurons, Tanh | 24 neurons, Sigmoid |
| Hidden layer 3 | 18 neurons, ReLu | 20 neurons, ReLu | 20 neurons, Tanh |
| Hidden layer 4 | 20 neurons, Sigmoid | 22 neurons, Tanh | 24 neurons, Sigmoid |
| Hidden layer 5 | 18 neurons, ReLu | 20 neurons, ReLu | 20 neurons, Tanh |
| Hidden layer 6 | 20 neurons, Sigmoid | 22 neurons, Tanh | 24 neurons, Sigmoid |
| Output layer | 6 neurons, Sigmoid | 6 neurons, Tanh | 6 neurons, Tanh |
| Learning rate | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 |
| Parameters | ODGB Model 1 | ODGB Model 2 | ODGB Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scaler | Min-Max Scaler | Min-Max Scaler | Min-Max Scaler |
| Dataset shuffled | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Gamma | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| Max depth | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| Minimum child weight | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Max delta step | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| Sampling method | Uniform | Gradient-based | Uniform |
| Lamda | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Tree method | Auto | Exact | Auto |
| Process type | Default | Update | Default |
| Max bin | 128 | 128 | 256 |
| Average | Macro-average | Macro-average | Macro-average |
| Learning rate | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 |
| Parameters | SGD Model 1 | SGD Model 2 | SGD Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scaler | Standard Scaler | Standard Scaler | Standard Scaler |
| Dataset shuffled | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Validation fraction | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Verbose | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Tolerance | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.003 |
| Fit Intercept | True | False | True |
| Alpha | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.003 |
| Penalty | L2 | L1 | L2 |
| Loss | Log loss | Log loss | Log loss |
| Maximum iterations | 900 | 800 | 750 |
| Kernel | Linear | Linear | Linear |
| Average | Macro-average | Macro-average | Macro-average |
| Learning rate | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 |
| Parameters | HGB Classifier 1 | HGB Classifier 2 | HGB Classifier 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scaler | Min-Max Scaler | Min-Max Scaler | Min-Max Scaler |
| Dataset shuffled | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Loss | Log loss | Log loss | Log loss |
| Maximum iteration | 125 | 150 | 175 |
| Maximum leaf nodes | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Minimum sample leaf | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| L2 regularization | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.25 |
| Maximum bins | 127 | 255 | 127 |
| Early slopping | Auto | Bool | Auto |
| Validation fraction | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| Tolerance | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.0025 |
| Average | Macro-average | Macro-average | Macro-average |
| Learning rate | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 | 0.001–0.048 |
| Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML models | Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test |
| KNN [8] | - | 0.670 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SVM [8] | - | 0.650 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SVM linear | 0.635 | 0.634 | 0.390 | 0.387 | 0.355 | 0.355 | 0.302 | 0.301 |
| SVM rbf | 0.686 | 0.672 | 0.665 | 0.623 | 0.485 | 0.463 | 0.508 | 0.478 |
| SVM polynomial | 0.677 | 0.668 | 0.706 | 0.682 | 0.467 | 0.451 | 0.487 | 0.465 |
| SVM sigmoid | 0.524 | 0.522 | 0.302 | 0.301 | 0.302 | 0.301 | 0.278 | 0.278 |
| Random forest [13] | - | 0.650 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Random forest M1 | 0.999 | 0.723 | 0.999 | 0.657 | 0.999 | 0.573 | 0.999 | 0.594 |
| Random forest M2 | 0.999 | 0.721 | 0.999 | 0.636 | 0.999 | 0.566 | 0.999 | 0.593 |
| LSTM [26] | - | 0.984 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| LSTM | 0.636 | 0.574 | 0.477 | 0.413 | 0.432 | 0.443 | 0.412 | 0.342 |
| CNN [15] | - | 0.856 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CNN [17] | 0.990 | 0.977 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CNN | 0.655 | 0.653 | 0.562 | 0.562 | 0.456 | 0.450 | 0.464 | 0.455 |
| Scenario One | Scenario Two | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classifier | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | MSE Loss | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | MSE Loss |
| Stochastic gradient descent | 0.024 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.65 | 0.58 | 0.36 | 0.012 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.70 | 0.74 | 0.25 |
| Gradient boosting classifier | 0.048 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.55 | 0.58 | 0.32 | 0.048 | 0.72 | 0.60 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.32 |
| Optimized distributed gradient boosting classifier | 0.008 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.26 | 0.012 | 0.72 | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.34 |
| Long short-term memory classifier | 0.001 | 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.012 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 0.15 |
| Convolutional neural network classifier | 0.024 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.016 | 0.77 | 0.83 | 0.77 | 0.40 | 0.09 |
| Scenario One | Scenario Two | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classifier | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | MSE Loss | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | MSE Loss |
| LSTM | 0.001 | 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.20 | - | 0.012 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 0.60 | 0.40 | - |
| Classifier 1 | 0.024 | 0.66 | 0.55 | 0.62 | 0.55 | 0.43 | 0.024 | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.37 |
| Classifier 2 | 0.048 | 0.69 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 0.048 | 0.72 | 0.75 | 0.64 | 0.63 | 0.34 |
| Classifier 3 | 0.020 | 0.67 | 0.59 | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.028 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.40 |
| Classifier 4 | 0.001 | 0.62 | 0.64 | 0.55 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.001 | 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.60 | 0.05 | 0.16 |
| Classifier 5 | 0.008 | 0.68 | 0.70 | 0.63 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.008 | 0.67 | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.20 | 0.14 |
| Scenario One | Scenarios Two | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classifier GB | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss |
| Model 1 | 0.004 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.24 | 0.012 | 0.62 | 0.66 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.19 |
| Model 2 | 0.012 | 0.68 | 0.75 | 0.68 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 0.024 | 0.61 | 0.60 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 0.10 |
| Model 3 | 0.008 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.53 | 0.55 | 0.19 | 0.024 | 0.62 | 0.65 | 0.60 | 0.41 | 0.14 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.028 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 0.012 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.54 | 0.39 | 0.18 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.012 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 0.56 | 0.55 | 0.19 | 0.016 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.13 |
| BER | SNR | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach | Extended Configuration Approach | Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach (dB) | Extended Configuration Approach (dB) | |||||||
| Classifier GB | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station |
| Model 1 | 0.004 | 0.012 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.012 | −11.40 | −10.30 | −11.30 | −10.10 |
| Model 2 | 0.012 | 0.024 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.012 | 0.024 | −09.20 | −09.30 | −10.20 | −10.30 |
| Model 3 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.024 | −11.30 | −13.40 | −12.40 | −13.50 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.028 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.028 | 0.012 | −10.20 | −10.30 | −10.40 | −09.60 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.012 | 0.016 | −10.20 | −10.40 | −09.80 | −10.40 |
| Scenario One | Scenario Two | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classifier LSTM | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss |
| Model 1 | 0.012 | 0.62 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.55 | 0.24 | 0.024 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.48 | 0.16 |
| Model 2 | 0.004 | 0.61 | 0.69 | 0.66 | 0.48 | 0.21 | 0.024 | 0.62 | 0.68 | 0.53 | 0.38 | 0.24 |
| Model 3 | 0.008 | 0.63 | 0.74 | 0.58 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 0.016 | 0.64 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.47 | 0.15 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.012 | 0.62 | 0.60 | 0.61 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.016 | 0.65 | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.49 | 0.23 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.028 | 0.68 | 0.62 | 0.68 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 0.012 | 0.65 | 0.67 | 0.61 | 0.39 | 0.13 |
| BER | SNR | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach | Extended Configuration Approach | Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach (dB) | Extended Configuration Approach (dB) | |||||||
| Classifier LSTM | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station |
| Model 1 | 0.012 | 0.024 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.012 | 0.024 | −09.10 | −10.40 | −10.20 | −12.20 |
| Model 2 | 0.004 | 0.024 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.024 | −11.40 | −12.40 | −12.30 | −12.50 |
| Model 3 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.016 | −11.30 | −11.40 | −11.20 | −11.30 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.012 | 0.016 | −10.10 | −10.90 | −10.30 | −10.80 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.028 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.028 | 0.012 | −10.30 | −10.10 | −11.10 | −10.30 |
| Scenario One | Scenarios Two | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classifier CNN | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss |
| Model 1 | 0.012 | 0.61 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.37 | 0.15 | 0.004 | 0.67 | 0.72 | 0.54 | 0.45 | 0.14 |
| Model 2 | 0.016 | 0.64 | 0.75 | 0.53 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 0.024 | 0.63 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.47 | 0.21 |
| Model 3 | 0.004 | 0.66 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 0.028 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.53 | 0.21 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.016 | 0.60 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 0.52 | 0.22 | 0.016 | 0.61 | 0.69 | 0.61 | 0.42 | 0.19 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.028 | 0.61 | 0.66 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.12 | 0.008 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.53 | 0.43 | 0.24 |
| BER | SNR | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach | Extended Configuration Approach | Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach (dB) | Extended Configuration Approach (dB) | |||||||
| Classifier CNN | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station |
| Model 1 | 0.012 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.012 | 0.004 | −10.20 | −11.90 | −10.40 | −12.40 |
| Model 2 | 0.016 | 0.024 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 0.024 | −11.20 | −12.40 | −11.20 | −13.80 |
| Model 3 | 0.004 | 0.028 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.028 | −13.20 | −11.40 | −13.70 | −11.80 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.016 | −10.30 | −10.30 | −11.20 | −11.50 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.028 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.028 | 0.008 | −12.40 | −11.40 | −13.40 | −12.50 |
| Scenario One | Scenarios Two | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classifier ODGB | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss |
| Model 1 | 0.004 | 0.68 | 0.65 | 0.56 | 0.55 | 0.23 | 0.012 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.55 | 0.46 | 0.25 |
| Model 2 | 0.008 | 0.64 | 0.63 | 0.62 | 0.35 | 0.22 | 0.016 | 0.66 | 0.62 | 0.70 | 0.54 | 0.22 |
| Model 3 | 0.012 | 0.66 | 0.62 | 0.67 | 0.53 | 0.21 | 0.008 | 0.64 | 0.62 | 0.54 | 0.31 | 0.18 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.016 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.34 | 0.24 | 0.012 | 0.61 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.32 | 0.25 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.016 | 0.66 | 0.73 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 0.19 | 0.028 | 0.63 | 0.67 | 0.61 | 0.33 | 0.22 |
| BER | SNR | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach | Extended Configuration Approach | Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach (dB) | Extended Configuration Approach (dB) | |||||||
| Classifier ODGB | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station |
| Model 1 | 0.004 | 0.012 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.012 | −13.90 | −12.80 | −13.50 | −11.80 |
| Model 2 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.016 | −12.60 | −12.30 | −11.90 | −11.90 |
| Model 3 | 0.012 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.012 | 0.008 | −13.30 | −13.40 | −13.70 | −12.90 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.016 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 0.012 | −11.30 | −14.20 | −11.40 | −14.10 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.016 | 0.028 | - | - | - | - | 0.016 | 0.028 | - | - | - | - |
| Scenario One | Scenarios Two | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classifier SGD | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss |
| Model 1 | 0.008 | 0.62 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.012 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.62 | 0.22 | 0.23 |
| Model 2 | 0.012 | 0.61 | 0.60 | 0.66 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.024 | 0.61 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.21 | 0.20 |
| Model 3 | 0.008 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.20 | 0.28 | 0.016 | 0.65 | 0.68 | 0.64 | 0.30 | 0.25 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.024 | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.028 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.32 | 0.25 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.028 | 0.70 | 0.65 | 0.69 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.032 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.62 | 0.21 | 0.25 |
| BER | SNR | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach | Extended Configuration Approach | Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach (dB) | Extended Configuration Approach (dB) | |||||||
| Classifier SGD | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station |
| Model 1 | 0.008 | 0.012 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.012 | −11.30 | −09.30 | −10.30 | −10.30 |
| Model 2 | 0.012 | 0.024 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.012 | 0.024 | −10.30 | −12.40 | −10.10 | −12.50 |
| Model 3 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.016 | −11.30 | −11.40 | −11.20 | −11.30 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.024 | 0.028 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.024 | 0.028 | −13.20 | −10.30 | −12.70 | −10.40 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.028 | 0.032 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.028 | 0.032 | −10.30 | −11.20 | −11.10 | −10.70 |
| Scenario One | Scenarios Two | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classifier HGB | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss | Learning Rate | Test Accuracy | Test Precision | Test Recall | Test F1 Score | Log Loss |
| Model 1 | 0.004 | 0.62 | 0.70 | 0.67 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.024 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.62 | 0.33 | 0.28 |
| Model 2 | 0.016 | 0.62 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.048 | 0.61 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.29 | 0.26 |
| Model 3 | 0.032 | 0.61 | 0.66 | 0.62 | 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.048 | 0.67 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.024 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.024 | 0.70 | 0.61 | 0.65 | 0.30 | 0.24 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.032 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.65 | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.036 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.69 | 0.22 | 0.12 |
| BER | SNR | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach | Extended Configuration Approach | Learning Rate | Conventional Configuration Approach (dB) | Extended Configuration Approach (dB) | |||||||
| Classifier HGB | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station | Dataset Is Collected from All the 10 Base Stations | Dataset Is Collected from Only One Base Station |
| Model 1 | 0.004 | 0.024 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.024 | −11.40 | −10.30 | −11.30 | −09.90 |
| Model 2 | 0.016 | 0.048 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.048 | −10.40 | −11.20 | −10.40 | −11.20 |
| Model 3 | 0.032 | 0.048 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.032 | 0.048 | −10.50 | −11.10 | −11.20 | −11.20 |
| Model 1 and 2 | 0.024 | 0.024 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.024 | 0.024 | −12.40 | −13.50 | −13.50 | −14.40 |
| Model 2 and 3 | 0.032 | 0.036 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.032 | 0.036 | −10.30 | −10.40 | −10.40 | −10.30 |
| Model Type | Best Accuracy | Best F1 Score | Lowest BER | Highest SNR | Best Ensemble |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.68 (M2 + M3) | 0.6 | 0.002 | −13.5 dB | M2 + M3 |
| CNN | 0.67 (M1) | 0.56 (M2 + M3) | 0.003 | −13.7 dB | M2 + M3 |
| GB | 0.66 (M2) | 0.36 (M2) | 0.002 | −13.5 dB | M1 + M2 |
| ODGB | 0.68 (M1) | 0.7 | 0.002 | −11.8 dB | Mixed |
| SGD | 0.69 (M1 + M2) | 0.34 | 0.002 | −13.2 dB | M1 + M2 |
| HGB | 0.70 (M2 + M3) | 0.70 (M3) | 0.002 | −10.3 dB | M2 + M3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muralitharan, R.; Jayasinghe, U.; Ragel, R.G.; Lee, G.M. Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Atmospheric Duct Interference Detection and Mitigation in TD-LTE Networks. Future Internet 2025, 17, 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17060237
Muralitharan R, Jayasinghe U, Ragel RG, Lee GM. Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Atmospheric Duct Interference Detection and Mitigation in TD-LTE Networks. Future Internet. 2025; 17(6):237. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17060237
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuralitharan, Rasendram, Upul Jayasinghe, Roshan G. Ragel, and Gyu Myoung Lee. 2025. "Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Atmospheric Duct Interference Detection and Mitigation in TD-LTE Networks" Future Internet 17, no. 6: 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17060237
APA StyleMuralitharan, R., Jayasinghe, U., Ragel, R. G., & Lee, G. M. (2025). Machine Learning and Deep Learning-Based Atmospheric Duct Interference Detection and Mitigation in TD-LTE Networks. Future Internet, 17(6), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17060237











