Hybrid GOMP–ROMP Algorithm for Sparse Channel Estimation in mmWave MIMO: Enhancing Convergence and Reducing Computational Complexity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Traditional Channel Estimation Schemes
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Channel Estimation
2.3. OMP-Based Channel Estimation
2.4. OMP Variant-Based Channel Estimation
2.5. Contributions
- Hybrid algorithm innovation: A new hybrid GOMP–ROMP algorithm is introduced that combines the group selection efficiency of GOMP and the stability and regularization of ROMP. The hybridization facilitates faster convergence with much less computational complexity and preserves NMSE performance equivalent to ROMP.
- Comprehensive performance benchmarking: A thorough quantitative comparison between OMP, GOMP, SOMP, ROMP, and the new hybrid approach with regards to NMSE and computational complexity is performed. Genie-aided and SBL estimators are also added to establish upper-bound performance references.
- Trade-off between complexity and accuracy: This research examines computational complexity scaling behavior with rising antenna dimensions and assesses normalized performance efficiency measures that balance both NMSE and computational cost.
- Practical relevance: The suggested algorithm shows four times reduced computational complexity and 0.04 NMSE gain over OMP for 32 × 32 MIMO configurations, making it appropriate for real-time mmWave massive MIMO deployments in 5G/6G systems.
3. System Model
3.1. mmWave Channel Model
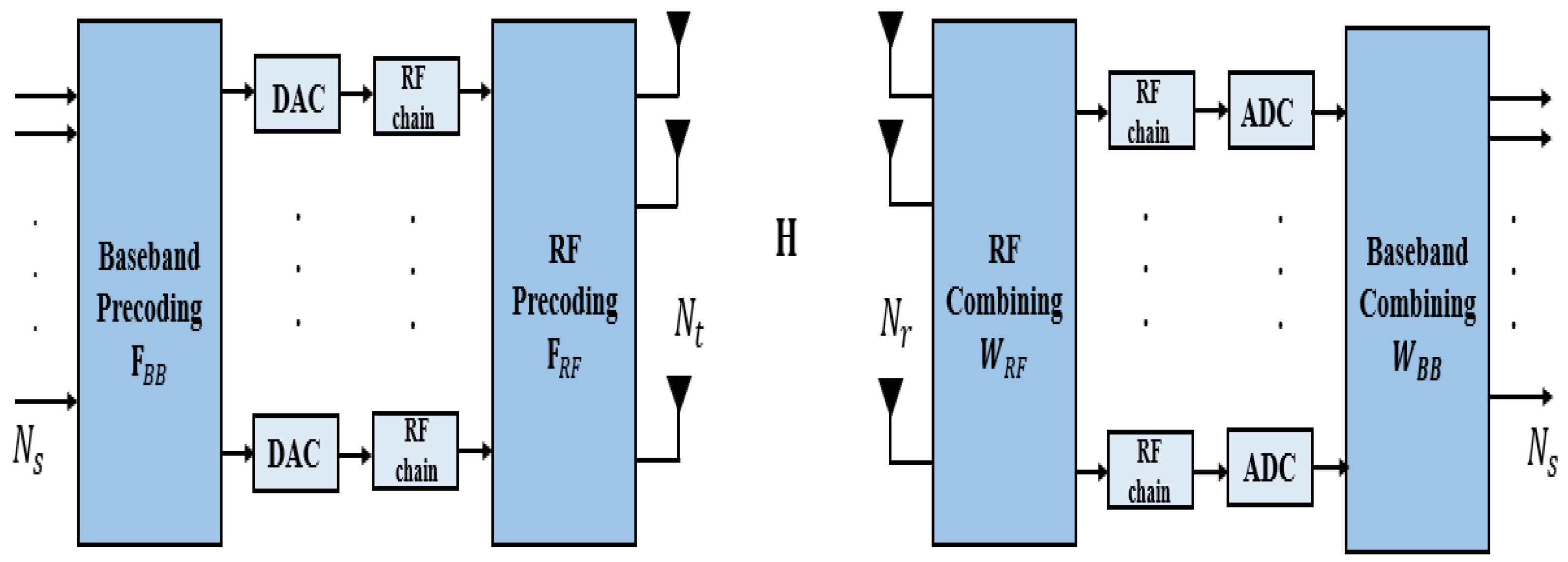
3.2. Hybrid Architecture
4. mmWave Channel Estimation
4.1. Genie-Aided Channel Estimation
4.2. OMP
| Algorithm 1 mmWave channel estimation based on OMP |
| Input: , , Output: |
| Step 1. Initialize the variables , , , = { } |
| Step 2. While 2.1 Compute correlations: 2.2 Select index of the largest correlation: = arg max (||) 2.3 Update support set: = ∪{ 2.4 Solve LS = y 2.5 Update residual: 2.6 |
| Step 3. Construct sparse solution: |
4.3. GOMP
| Algorithm 2 mmWave channel estimation based on GOMP |
| Input: , , Output: |
| Step 1. Initialize the variables , , , = { } |
| Step 2. While 2.1 Compute correlations: 2.2 Find the top K indices of | |: 2.3 Update support set: = ∪ { 2.4 Solve LS: = y 2.5 Update residual: 2.6 |
| Step 3. Construct sparse solution: |
4.4. ROMP
| Algorithm 3 mmWave channel estimation based on ROMP |
| Input: , , Output: |
| Step 1. Initialize the variables , , , = { } |
| Step 2. While 2.1 Compute correlations: 2.2 Sort | | in descending order 2.3 Form groups: - Group columns with similar magnitudes - Create several candidate groups 2.4 Select the group with the highest sum of squared correlations, J. 2.5 Update support set: = ∪ { 2.6 Solve LS: = y 2.7 Update residual: 2.8 |
| Step 3. Construct sparse solution: |
4.5. SOMP
| Algorithm 4 mmWave channel estimation based on SOMP |
| Input: , , Output: |
| Step 1. Initialize the variables , , = { } |
| Step 2. While 2.1 Compute correlations: 2.2 Select index of the largest correlation: = 2.3 Update support set: = ∪ 2.4 Solve LS: = 2.5 Update residual: 2.6 |
| Step 3. Construct sparse solution: |
4.6. Hybrid GOMP–ROMP
| Algorithm 5 mmWave channel estimation based on hybrid GOMP–ROMP |
| Input: , , Output: |
| Step 1. Initialize the variables , , , = { } |
| Step 2. While 2.1 Compute correlations: 2.2 Find the top K indices of | |: (GOMP selection) 2.3 Apply ROMP regularization within the selected group - Extract the correlation magnitude - Sort | | in descending order - Group columns with similar magnitudes - Create several candidate groups - Select the group with the highest sum of squared correlations, J. 2.4 Update support set: = ∪ { 2.5 Solve LS: = y 2.6 Update residual: 2.7 |
| Step 3. Construct sparse solution: |
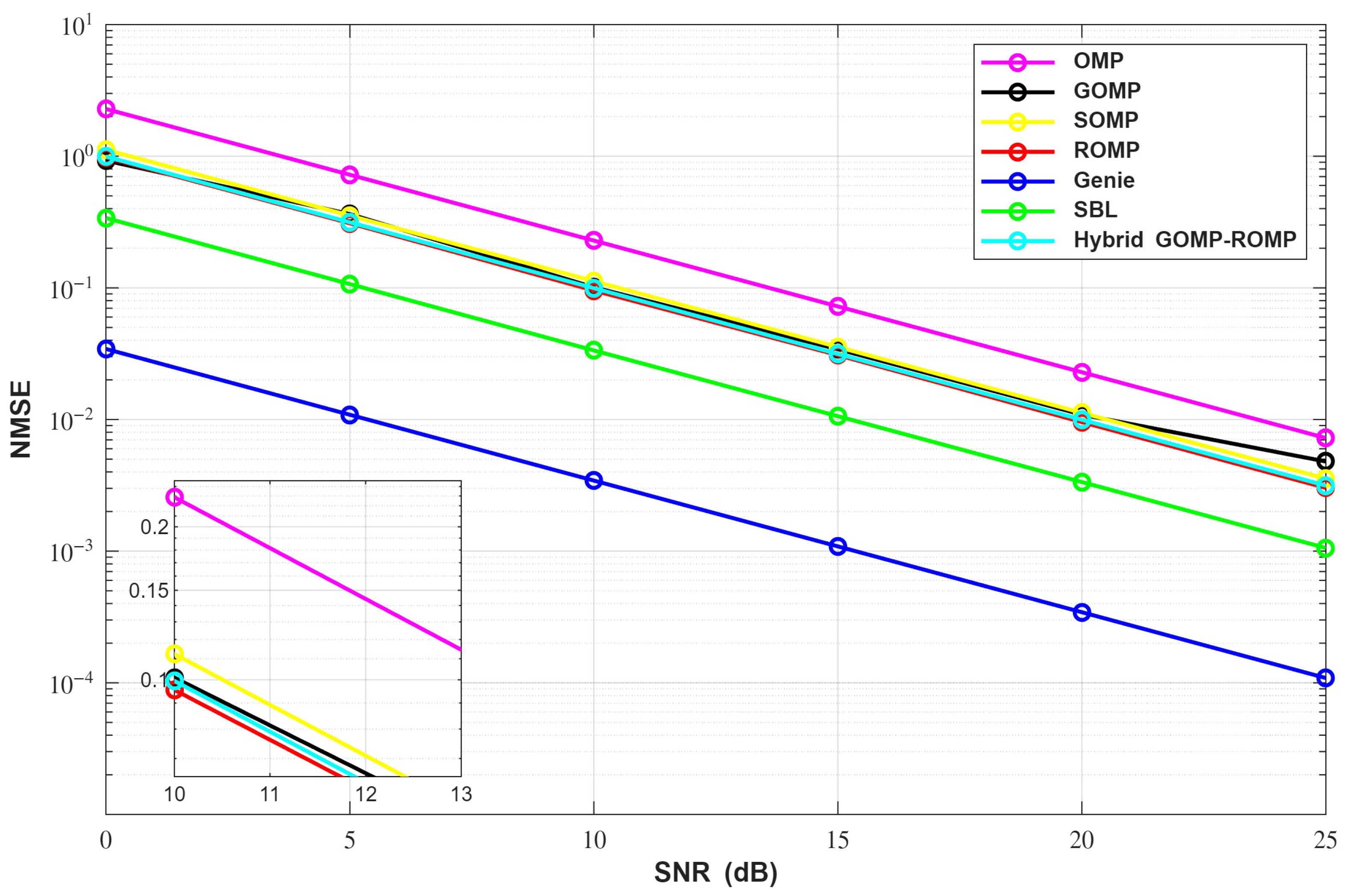
5. Results and Discussion
Computational Complexity
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5G | Fifth-Generation |
| 6G | Sixth-Generation |
| AoA | Angle of Arrival |
| AoD | Angle of Departure |
| CS | Compressive Sensing |
| GOMP | Generalized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit |
| LS | Least Squares |
| MIMO | Multiple-Input Multiple-Output |
| NMSE | Normalized Mean Square Error |
| OMP | Orthogonal Matching Pursuit |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| ROMP | Regularized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| SOMP | Simultaneous Orthogonal Matching Pursuit |
| ULA | Uniform Linear Array |
References
- Drubin, C. Ericsson Mobility Report: Early Movers Pursue Performance-Based Business Models. Microw. J. 2025, 68, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, H.; Huang, C.; Yu, J.; Shen, X. A survey of mmwave radar-based sensing in autonomous vehicles, smart homes and industry. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2024, 27, 463–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, M.; Xu, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Song, K. Millimeter-Wave Antennas for 5G Wireless Communications: Technologies, Challenges, and Future Trends. Sensors 2025, 25, 5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimi, I. Key Methods for Efficient and High-Speed FWA Solutions. In5G Fixed Wireless Access: Revolutionizing Connectivity In The Digital Age; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 95–118. [Google Scholar]
- Sambhwani, S.; Chae, H.; Chiu, S.; Fan, B.; Sarkas, I.; Sun, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, X. Extending mmWave deployment in the next-generation network: Coverage and reliability enhancements. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2025, 32, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Roy, A.; Kumar, R. Millimeter wave antennas: A state-of-the-art survey of recent developments, principles, and applications. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2024, 104, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, S.; Singh, S. Others Estimation of channel for millimeter-wave hybrid massive MIMO systems using Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (OMP). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2327, 012040. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; He, D.; Yin, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Quek, T. Hybrid Beamforming for mmWave Integrated Sensing and Communication with Multi-static Cooperative Localization. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.; Xu, W.; Yu, X.; Yin, H. An improved orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm for cs-based channel estimation. Sensors. 2023, 23, 9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Lin, H.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; You, X. High-performance channel estimation for mmWave wideband systems with hybrid structures. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 2503–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, D.; Murthy, C. mmWave channel estimation via compressive covariance estimation: Role of sparsity and intra-vector correlation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 2356–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, P.; Qiao, B.; Wei, Z.; Li, B.; Zhao, C. Highly accurate millimeter wave channel estimation in massive MIMO system. IET Commun. 2023, 17, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, J. A Model-Driven Channel Estimation Method for Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO Systems. Sensors 2023, 23, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbir, A.; Mishra, K.; Shankar, M.; Ottersten, B. A family of deep learning architectures for channel estimation and hybrid beamforming in multi-carrier mm-wave massive MIMO. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2021, 8, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhong, C.; Li, G.; Soriaga, J.; Behboodi, A. Deep learning-based channel estimation for wideband hybrid mmWave massive MIMO. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 3679–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Qi, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J. Sparse channel estimation and hybrid precoding using deep learning for millimeter wave massive MIMO. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 68, 2838–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Gil, G.; Lee, Y. Channel estimation via orthogonal matching pursuit for hybrid MIMO systems in millimeter wave communications. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2016, 64, 2370–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yang, L.; Tang, M.; Tan, W.; Zhao, J. Channel estimation for mmwave massive MIMO systems with mixed-ADC architecture. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2023, 4, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Ma, T.; Yu, Y.; Lei, X.; Zhou, J. An iterative channel estimation algorithm based on OMP for OCDM systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2024, 28, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, F.; Chung, H.; Wu, P. Efficient Channel Estimation for Millimeter-Wave RIS-Assisted SIMO-OFDM Systems With Reduced Complexity and Pilot Overhead. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 14809–14821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, N.; Gupta, N. Channel estimation for sparse mm-wave mimo system. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2023, 129, 2123–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadji, B.; Aissa-El-Bey, A.; Fergani, L.; Djeddou, M. Joint hybrid precoding and combining design based multi-stage compressed sensing approach for mmWave MIMO channel estimation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 112398–112413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigka, M.; Mavrokefalidis, C.; Berberidis, K. Efficient Distributed Multi-Task Schemes for mmWave MIMO Channel Estimation. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 105232–105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Mumtaz, S.; Li, X.; Da Costa, D. An Effective Simultaneous Channel Estimation and Sensing Algorithm for MmWave MIMO-OFDM Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 17054–17069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, J. Low complexity hybrid-field channel estimation based on simultaneous weighted OMP algorithm in Extreme Large-scale MIMO systems. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 46551–46561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, Y.; Abbas, H. Millimeter wave massive MIMO channel estimation using subspace pursuit greedy algorithm. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 870, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possenti, L.; Barbiroli, M.; Vitucci, E.; Fuschini, F.; Fosci, M.; Degli-Esposti, V. A study on mm-wave propagation in and around buildings. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2023, 4, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Chatterjee, I.; Srivastava, S.; Agrahari, A.; Jagannatham, A.; Hanzo, L. Hybrid transceiver design and optimal power allocation for the cognitive mmWave multiuser MIMO downlink relying on limited feedback. IEEE Open J. Veh. Technol. 2023, 4, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, A.; Orimolade, J.; Adejumobi, I.; Amusa, K.; Olajuwon, B. Channel estimation via compressed sampling matching pursuit for hybrid MIMO architectures in millimeter wave communication. Int. J. Electron. Lett. 2025, 13, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kwon, S.; Shim, B. Generalized orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 6202–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needell, D.; Vershynin, R. Uniform uncertainty principle and signal recovery via regularized orthogonal matching pursuit. Found. Comput. Math. 2009, 9, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Determe, J.; Louveaux, J.; Jacques, L.; Horlin, F. On the noise robustness of simultaneous orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 65, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ref. | mmWave | Hybrid MIMO | OMP Based | OMP Variant | Sensing Matrix Design | Channel Sparsity | Performance Metric | Computa-tional Complexity Analysis | Massive MIMO Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | × | × | NMSE | × | 8 × 16 |
| [11] | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | × | ✓ | NMSE | ✓ | 128 × 16 |
| [12] | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | × | ✓ | NMSE | ✓ | 64 × 64 |
| [13] | ✓ | × | × | × | × | ✓ | NMSE | ✓ | 32 × 32 |
| [14] | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | × | ✓ | NMSE,SE | ✓ | 16 × 128 |
| [15] | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | × | × | NMSE | ✓ | 32 × 32 |
| [16] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | ✓ | NMSE,SE | × | 1 × 64 |
| [17] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ | NMSE,SE | ✓ | 16 × 16, 32 × 32 |
| [18] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | ✓ | NMSE | × | 16 × 32 |
| [19] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | ✓ | BER | × | × |
| [20] | ✓ | × | ✓ | × | × | ✓ | NMSE | ✓ | × |
| [21] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | ✓ | NMSE | ✓ | 32 × 32 |
| [22] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ (GOMP) | ✓ | ✓ | NMSE,SE | ✓ | 32 × 32 |
| [23] | ✓ | × | × | ✓ (SOMP) | × | ✓ | NMSE | ✓ | × |
| [24] | × | ✓ | × | ✓ (SOMP) | × | ✓ | RMSE | ✓ | 9 × 64 |
| [25] | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ (SWOMP) | × | ✓ | NMSE | ✓ | 1 × 512 |
| [26] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ (ROMP) | × | ✓ | NMSE | × | 16 × 32 |
| This Work | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ (GOMP, ROMP, SOMP, Hybrid GOMP–ROMP) | ✓ | ✓ | NMSE | ✓ | 16 × 16, 32 × 32 |
| Notation | Description |
|---|---|
| H | mmWave channel |
| Estimated channel | |
| L | Total number of multipath components |
| d | Distance between antennas |
| Complex gain of lth multipath component | |
| Wavelength | |
| Array response vector at transmitter | |
| Array response vector at receiver | |
| Number of transmitting antennas | |
| Number of receiving antennas | |
| AoD of lth multipath component | |
| AoA of lth multipath component | |
| Dictionary of array response vectors at transmitter | |
| Dictionary of array response vectors at receiver | |
| mmWave beam space channel matrix | |
| Baseband precoding matrix | |
| RF precoding matrix | |
| RF combining matrix | |
| Baseband combining matrix | |
| Pilot matrix | |
| Noise matrix | |
| Received signal matrix | |
| Number of pilot symbols at transmitter side | |
| Number of pilot symbols at receiver side | |
| P | Power of pilot signal |
| Sensing matrix for OMP | |
| Sensing matrix for genie-aided estimation | |
| Vectorization of | |
| Vectorization of | |
| Vectorization of | |
| Threshold | |
| Correlation vector | |
| Residue vector | |
| n | Iteration counter |
| Support set | |
| j | Index of the maximum value of correlation vector in OMP |
| k | Index of the maximum value of correlation vector in GOMP |
| … | Candidate groups in ROMP |
| Hermitian operator | |
| Transpose operator | |
| ⊗ | Kronecker product |
| Frobenius norm | |
| Expectation operator | |
| vec(.) | Vectorization operator |
| Simulation Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of transmit antennas | 16, 32 |
| Number of receive antennas | 16, 32 |
| Number of RF chains | 4, 8 |
| Sparsity level | 5 |
| Number of pilot beams | 12, 24 |
| Threshold | 1 |
| Number of columns selected in GOMP | 4 |
| Algorithms | NMSE of 16 × 16 MIMO | NMSE of 32 × 32 MIMO |
|---|---|---|
| OMP | 0.072291 | 0.077927 |
| GOMP | 0.034216 | 0.035162 |
| ROMP | 0.03083 | 0.032603 |
| SOMP | 0.035533 | 0.036967 |
| Hybrid GOMP–ROMP | 0.031468 | 0.034540 |
| Algorithm | Computational Complexity | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Genie | 16,777,216 | 1,073,741,824 | |
| SBL | 16,777,216 | 1,073,741,824 | |
| OMP | 184,445 | 2,949,120 | |
| GOMP | 52,489 | 745,280 | |
| ROMP | 184,445 | 2,949,120 | |
| SOMP | 184,445 | 2,949,120 | |
| Hybrid GOMP–ROMP | 46,205 | 737,405 |
| Algorithm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMSE | Complexity | Normalized EI | NMSE | Complexity | Normalized EI | |
| OMP | 0.072291 | 184,445 | 0.1090 | 0.077927 | 2,949,120 | 0.1090 |
| GOMP | 0.034216 | 52,489 | 0.8095 | 0.035162 | 745,280 | 0.8096 |
| ROMP | 0.030834 | 184,445 | 0.2556 | 0.032603 | 2,949,120 | 0.2557 |
| SOMP | 0.035533 | 184,445 | 0.2218 | 0.036967 | 2,949,120 | 0.2218 |
| Hybrid GOMP–ROMP | 0.031468 | 46,205 | 1.0000 | 0.034539 | 737,405 | 1.0000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babu Sujatha, A.; Kumaravelu, V.B. Hybrid GOMP–ROMP Algorithm for Sparse Channel Estimation in mmWave MIMO: Enhancing Convergence and Reducing Computational Complexity. Future Internet 2025, 17, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17110498
Babu Sujatha A, Kumaravelu VB. Hybrid GOMP–ROMP Algorithm for Sparse Channel Estimation in mmWave MIMO: Enhancing Convergence and Reducing Computational Complexity. Future Internet. 2025; 17(11):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17110498
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabu Sujatha, Anjana, and Vinoth Babu Kumaravelu. 2025. "Hybrid GOMP–ROMP Algorithm for Sparse Channel Estimation in mmWave MIMO: Enhancing Convergence and Reducing Computational Complexity" Future Internet 17, no. 11: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17110498
APA StyleBabu Sujatha, A., & Kumaravelu, V. B. (2025). Hybrid GOMP–ROMP Algorithm for Sparse Channel Estimation in mmWave MIMO: Enhancing Convergence and Reducing Computational Complexity. Future Internet, 17(11), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi17110498







