Abstract
The human body generates infrared radiation through the thermal movement of molecules. Based on this phenomenon, infrared images of the human body are often used for monitoring and tracking. Among them, key point location on infrared images of the human body is an important technology in medical infrared image processing. However, the fuzzy edges, poor detail resolution, and uneven brightness distribution of the infrared image of the human body cause great difficulties in positioning. Therefore, how to improve the positioning accuracy of key points in human infrared images has become the main research direction. In this study, a multi-scale convolution fusion deep residual network (Mscf-ResNet) model is proposed for human body infrared image positioning. This model is based on the traditional ResNet, changing the single-scale convolution to multi-scale and fusing the information of different receptive fields, so that the extracted features are more abundant and the degradation problem, caused by the excessively deep network, is avoided. The experiments show that our proposed method has higher key point positioning accuracy than other methods. At the same time, because the network structure of this paper is too deep, there are too many parameters and a large volume of calculations. Therefore, a more lightweight network model is the direction of future research.
1. Introduction
Infrared imaging technology has the advantages of night vision, good concealment, strong transmission ability, and immunity from electromagnetic wave interference [1]. In addition to military applications, infrared imaging technology is also widely used in many civilian fields, such as industrial monitoring [2], medical treatment [3], remote sensing [4], and night vision [5]. In China, infrared images are gradually being combined with traditional Chinese medicine, playing a huge role in medical diagnosis [6,7]. As shown in Figure 1, for normal legs, the temperature distribution of the legs is basically symmetrical, while for diseased legs, the temperature distribution of the legs is asymmetrical [3]. Key point detection in human body infrared images is an important research direction in relation to human body pose estimation, and it is widely used in various fields of computer vision. Changes in human body posture caused by body bending or deformation make it difficult to locate key points. However, in recent years, with the development of convolutional neural networks (CNNs), the positioning of key points of the human body has become more and more accurate. Human body key point positioning consists of locating the key parts of the human body in pictures or videos, such as the shoulders, elbows, wrists, and other areas. Two-dimensional key point positioning is used to estimate the two-dimensional coordinate information of key points from the image [8], and three-dimensional key point positioning is used to estimate three-dimensional coordinate information [9]. In this paper, 2D human body key point positioning is studied.
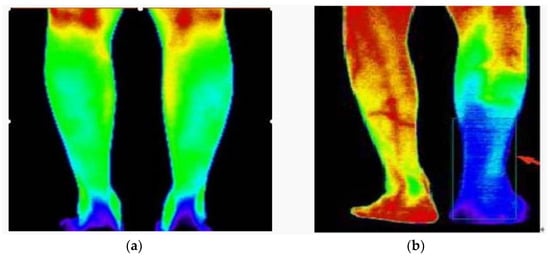
Figure 1.
Infrared images of breasts. (a) Infrared image of normal leg; (b) Infrared image of diseased leg.
The traditional, classical methods include tree models [10,11], random forest models [12,13], random field models [14], dependency graph models [15], and so on. These methods mainly use graphical structures to represent human body parts and predict the location of key points based on hand-made features. Although these methods are relatively simple and easy to implement, the positioning accuracy of these methods is not high owing to the changeability of human posture.
The use of deep neural networks for key point positioning greatly improves the accuracy of the positioning and has gradually become the mainstream method for key point positioning. According to different situations, it can be divided into single-person key point positioning and multi-person key point positioning. Single-person key point positioning can only handle one person in the center of the picture. Toshev et al. [16] introduced the use of a CNN into key point positioning for the first time. This method uses cascaded neural networks to regress coordinate points. However, owing to the changeability of attitudes, this method has great limitations. Tompson et al. [17] proposed to use a CNN and a graph model to predict a heat map of the key points, and then find the local maximum in the heat map to obtain the location of the key points. However, this method does not take into consideration the structural information between each key point, and the performance is not good when the characters are partially occluded, so its robustness is poor. In order to overcome the above shortcomings, later neural networks were designed to be more complex. Pfister et al. [18] proposed that, by increasing the receptive field of the neural network, the positional relationship in the image can be better obtained. Wei et al. [19] proposed convolutional pose machines (CPMs) based on a multi-stage detection strategy, which first obtains some rough results, and then continuously refines the results in subsequent stages. In order to avoid the disappearance of the gradient caused by the network being too deep, CPM uses intermediate supervision to calculate the loss in the prediction results of each stage. Newell et al. [20] proposed a U-shaped neural network with multiple hourglass modules stacked. In order to prevent over-fitting caused by the network being too deep, the network model uses a residual module. This method learns the location characteristics of key points through a variety of resolution heat maps and obtains the spatial position relationship of key points by means of multi-scale information. Yang et al. [21] proposed a pyramid residual module, which is a multi-branch structure module; for the same input, it can obtain output features of different resolutions. In addition, Carreira et al. [22] proposed to use iterative error feedback to locate key points and gradually refine the prediction results. Lifshitz et al. [23] proposed to use deep consensus voting to locate key points, and they also obtained good results.
There are two ways to locate the key points of multiple people: top-down and bottom-up methods. The bottom-up method consists of directly predicting all the key points of everyone in the image, and then assigning and connecting the key points according to certain rules. DeepCut [24] uses a CNN to extract body part candidates. Each candidate area corresponds to a joint point. Each joint point is used as a node in the graph, and all nodes form a connection graph. The correlation between the nodes is used as the weight between the nodes in the graph, the joint points belonging to the same person are classified into one category, and each person is regarded as a separate category. This method can solve the problem of multi-person pose estimation, but, because of the use of an adaptive fast R-CNN [25] and integer linear programming, the computational complexity is very large. Deepercut [26] improves on Deepcut. This method uses a residual network to extract body part information and obtains results of higher accuracy. At the same time, it uses image-conditioned pairwise terms to compress candidate region nodes to a certain number of nodes. Aiming at the problem of key point matching and connection, semantic part segmentation [27] uses a segmentation method to provide information for key point connections. This method divides the human body into six parts to provide the key points and the specific part of the human body’s subordinate relationship. The partial affinity fields [28] not only carry the affiliation information between key points and body parts, but also the direction information of each pixel.
The top-down method involves first accurately locating each pedestrian, and then locating each person’s key points. In order to accurately detect the person in the image, most methods use the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) detection method. For example, the method proposed by Papandreou et al. [29] used the SOTA detection method. This method predicts the offset of the heat map and the heat map relative to the true value at the same time, and then the offset is applied to the heat map to obtain the final key point prediction result. The SSD network proposed by Liu et al. [30] first detects the person in the image, and then also uses the SOTA single-person state estimation model to obtain the key point’s position. The mask R-CNN method proposed by He et al. [31] first predicts the bounding box of the human body, and then crops the feature map based on the bounding box, which is used for key point detection. Chen et al. [32] proposed a new network structure called a cascaded pyramid network (CPN), which includes a global network and a refined network. The global network roughly detects all the key points, and the refined network specifically detects some key points that are difficult to identify.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents a brief review of the residual neural network model; Section 3 describes the proposed Mscf-ResNet module; Section 4 outlines the key point positioning experiments and analyzes the positioning results; and Section 5 summarizes the proposed method.
2. Related Work
2.1. Conventional CNN Models
A convolutional neural network [33,34] is a multi-layer neural network, which mainly includes a convolutional layer, a pooling layer, and a fully connected layer. Each layer is composed of multiple two-dimensional planes, and each two-dimensional plane is composed of multiple independent neuron compositions. The purpose of the convolution operation is to extract different features of the input. The parameters of each convolution unit can be optimized through the back-propagation algorithm [35]. The parameter-sharing mechanism greatly reduces the number of training parameters as well as the risk of overfitting [36]. After the continuous convolutional layer is the pooling layer; the function of the pooling layer is downsampling, mainly including max-pooling [37] and mean-pooling [38]. Max-pooling consists of taking the maximum value of the feature in a certain area of the image. The feature data obtained using this method better retain the texture characteristics of the image. Mean-pooling involves taking the average value of all non-zero pixels in a certain area of the image. This method better preserves the extraction of image background information. The fully connected layer [39] integrates the features extracted from the front, and each of its nodes is connected to all the nodes of the previous layer.
2.2. Residual Learning
There is no limit to the number of CNN layers. Generally, deeper neural network models can extract richer features. However, when the depth of the network is too deep, it is easy for the gradient to disappear in the back propagation process. This makes it difficult for the network to obtain optimal weight parameters, and even leads to network degradation. In response to this problem, He et al. [40] proposed a deep residual network (Resnet), which not only deepens the network, but also improves the accuracy. As shown in Figure 2, the basic unit of the deep residual network is the residual unit.
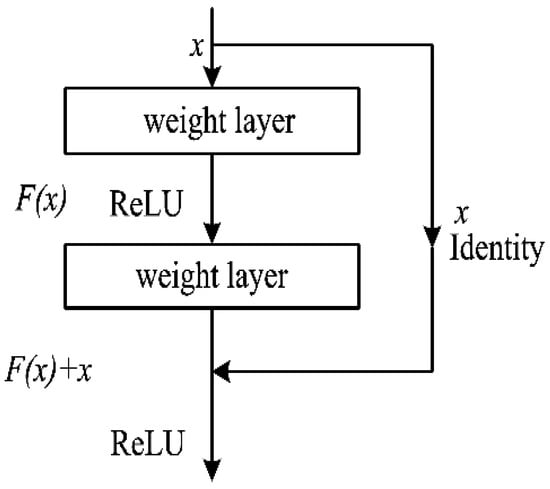
Figure 2.
Residual unit structure.
In the process of forward propagation, the input of the -th residual unit is , and the output is as follows:
where is the residual mapping, is the weight parameter, and is the nonlinear activation function ReLU. The deeper the network, the more training parameters are used. In order to reduce the volume of calculations, a bottleneck module is proposed [40]. As shown in Figure 3, the bottleneck module contains three convolutional layers, two convolutions and one convolution. The first convolution is used to reduce the dimensionality and the second is used to increase the dimensionality, which not only deepens the network, but also reduces the number of parameters and calculations. The shortcut connection in the bottleneck module has the function of identity mapping [11], as shown in Equations (2) and (3):
where is the -th residual block; is the -th convolutional layer of the -th residual block; is the input feature map; is the output feature map; is the identity mapping operation for ; is the activation function ReLU; is the weight; and is the convolution operation.
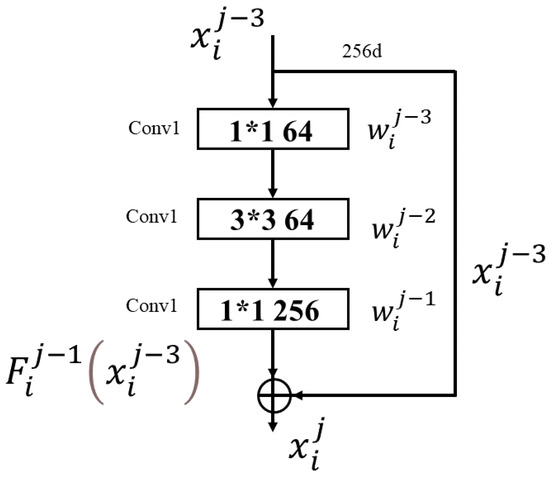
Figure 3.
Bottleneck module.
3. The Key Point Location Model for Human Infrared Images
In order to improve the accuracy of the positioning of key points in the infrared image of the human body, this paper proposes a Mscf-ResNet model based on residual learning. This section first uses the bottleneck module to design the feature extraction module, then proposes the Mscf module, and finally designs the Mscf-ResNet model by combining each module.
3.1. Feature Extraction Module
As shown in Figure 4, the feature extraction module consists of a 5 × 5 convolutional layer, a pooling layer, and eight bottleneck modules. The modules are connected in series, and the output of the previous bottleneck is used as the input of the next bottleneck. A bottleneck uses Conv1 to reduce the dimensionality, thereby reducing the training parameters, and then restores the number of feature map channels through Conv3.
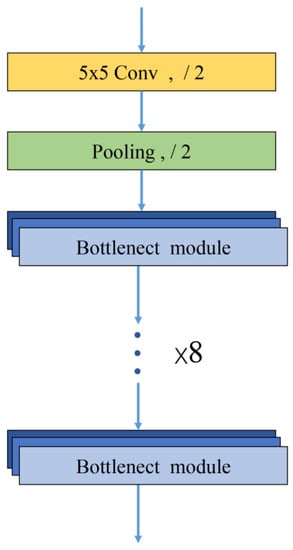
Figure 4.
Feature extraction module structure.
3.2. Mscf Module
In the infrared image, the temperature on the contour of the object gradually decreases from the inside to the outside, so multiple temperature contours are generated [41]. Because of differences in postures and body shapes, there are obvious differences in the image area occupied by the human body. These factors will lead to deviations in the positioning of key points of the human body and reduce the generalization ability of the network. In order to solve these problems, in this paper, we propose a multi-scale convolutional fusion residual network (Mscf-ResNet). As shown in Figure 5, compared with the traditional residual neural network using only one convolution kernel in the same layer, Mscf-ResNet uses three convolutions of , , and in the same convolution layer. The function of the three different scales of convolution kernels is to allow the convolution layer to extract different features from different receptive fields. The larger convolution kernel focuses on the extraction of global features, and the smaller convolution kernel can extract more local features. This can enrich the extracted features and improve the generalization ability of the network. In order to accelerate the network convergence, a batch normalization (BN) [42] layer is added after each convolutional layer. In addition, the activation function in this article does not involve ReLU, because ReLU often causes the permanent inactivation of neurons during the training process. These inactive neurons will occupy computing resources and affect the ability to perform image feature extraction. In order to make up for the shortcomings of ReLU, this paper uses the Mish activation function [43]. The gradient of Mish is smoother, and the positive value can be any value, thus avoiding the saturation caused by the capping of the function value.
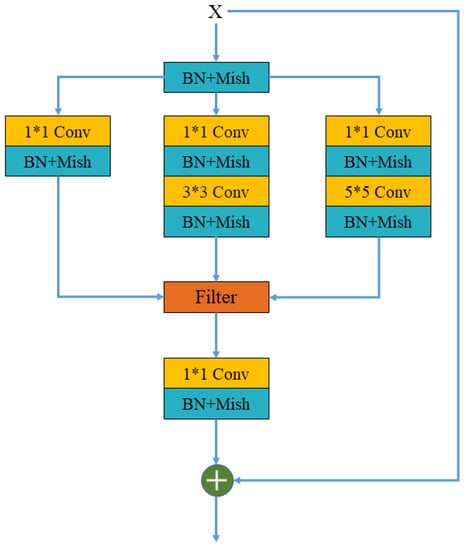
Figure 5.
Mscf module structure.
3.3. Mscf-ResNet Module
In order to accurately locate the key points of the infrared image of the human body, in this paper, the Mscf-ResNet model is constructed based on the feature extraction module and the Mscf module. As shown in Figure 6, in order to reduce the amount of parameters, the input image is first down-sampled using a 3 × 3 convolutional layer to reduce the size of the image by half, then it passes through the feature extraction module, then a total of 32 Mscf modules are used for richer feature extraction. In order to suppress over-fitting and improve the generalization ability of the network, the network model adds a dropout layer to remove some neurons with a certain probability. Finally, the key point coordinates are output through the fully connected layer.
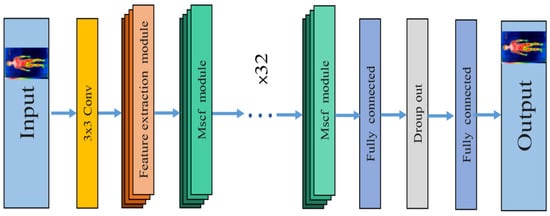
Figure 6.
Multi-scale convolution fusion deep residual network structure.
4. Experiment and Analysis
4.1. Data and Operating Environment
This experiment uses a short-wave infrared camera with a spectral response of 0.9~1.7 um, which is calibrated using a calibration method based on active vision. The three postures (stand with hands raised, stand akimbo, and stand with hands down) of the front and back of the human body are photographed, respectively. Thereby, a data set containing 1000 pictures is obtained. The data set is preprocessed before using it. First, the data enhancement technology is used to preprocess the infrared thermal image of the human body, and then it is made into a data set with a resolution of 1280 × 720. The key points that need to be located are marked on the infrared image of the human body. As shown in Figure 7, L1–L6 and R1–R6 indicate key point L1 to key point L6 and key point R1 to key point R6. The experiments were performed on a workstation with an Intel i7-11700K CPU, NVIDIA GeForce RTX2060, and 32 GB of memory. The deep learning framework used was Tensorflow, and the computing platform was CUDA 8.0. In this paper, the data set was divided into a training set and a test set according to the ratio of 8:2, and the learning rate was set to 0.003.
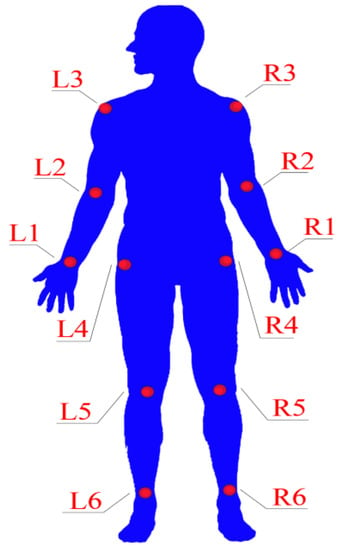
Figure 7.
The distribution of key points on the human body.
4.2. Experimental Evaluation
Owing to the different body shapes in infrared thermal images, this paper uses the Euclidean distance from key point L4 to key point R4 as the specific value for the evaluation of key point positioning. If the Euclidean distance between the true value of the key point and the predicted value is less than the product of the threshold value and the specified value, the result is correct. Otherwise, the result is wrong. The Euclidean distance is shown in (4), and the average accuracy rate is shown in (5):
In the above formula, represents the Euclidean distance between the true value and the predicted value of the n-th key point in the m-th graph; and are the true and predicted values of the abscissa; and are the true and predicted values of the ordinate; is the total number of images; is the average accuracy of the n-th key point; threshold t = 0.4; and is the Euclidean distance between key point L4 and key point R4.
4.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed network model, the proposed network model is compared with other neural network models, including cascaded pyramid network (CPN) [32], convolutional pose machines (CPMs) [19], open pose [28], MobileNetV2 [44], and ResNet-101 [40]. This paper uses the accuracy rate and recall rate to evaluate the effectiveness of the network, for which the formulae are as follows:
where the four parameters are as follows: (i) true positive (TP): the prediction is correct, and the positive samples are classified as the number of positive samples; (ii) false positive (FP): the prediction is wrong, and the negative samples are classified as the number of positive samples; (iii) true negative (TN): the prediction is correct, and the negative samples are classified as negative samples; and (iv) false negative (FN): the prediction is wrong, and the positive samples are classified as negative samples.
The human infrared image data set is used to train and test each neural network. The accuracy of each key point and the average accuracy of all points are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that both ResNet-101 and the proposed network model have an accuracy rate of more than 90%, but it obviously shows that the proposed network model performs better, with an average accuracy rate of 93.6%. As shown in Figure 8, each neural network is used to locate the key points of the infrared image of the human body in different poses. When the size and posture of the human body change, the proposed network model can locate the key points more accurately. Therefore, the proposed network model has better key point location performance than other neural network models.

Table 1.
Neural network performance comparison: the accuracy of positioning of different key points.
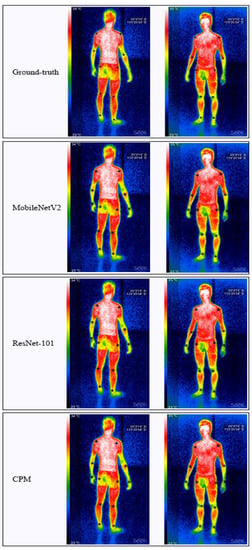
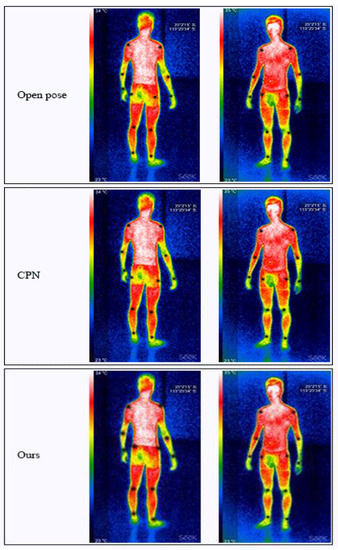
Figure 8.
Comparison of the location results of the infrared image set. The images in the first row are ground truth images, those in the second row are the location results using the MobileNetV2 method, those in the third row are the location results using the ResNet-101 method, those in the fourth row are the location results using the CPM method, those in the fifth row are the location results using the open pose method, those in the sixth row are the location results using the CPN method, and those in the last row are the location results using our proposed method.
The training process of different networks, shown in Figure 9, demonstrates the accuracy of different epochs. The accuracy of CPM was the lowest; the accuracy of open pose was improved, but open pose could not extract the information of multi-scale context features of the image, so the positioning performance was not outstanding. Compared with MobileNetV2, ResNet-101 had a deeper network structure, so it had a higher accuracy. CPN used ResNet as the backbone to extract richer features, and the accuracy was only lower than that of the proposed network model; the proposed neural network model used a multi-scale approach. The convolution kernel removed the feature extraction step, so it can extract richer features. Compared with other neural networks, the proposed neural network model obtained the highest accuracy rate and demonstrated very good key point positioning performance. Figure 10 shows the loss values of different neural networks during training. It can be seen from the figure that the proposed neural network model can reduce the loss value to a lower value under a smaller epoch and perform parameter training smoothly.
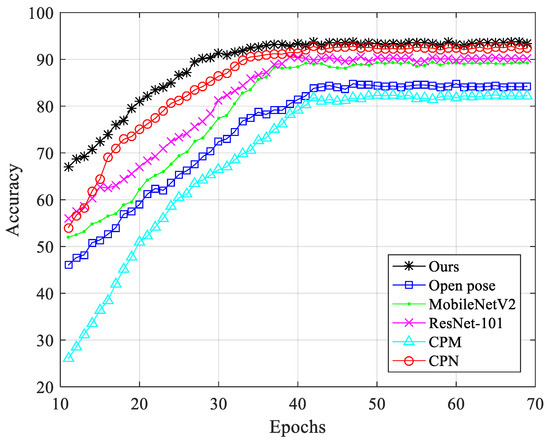
Figure 9.
Comparison of the accuracy of each network model.
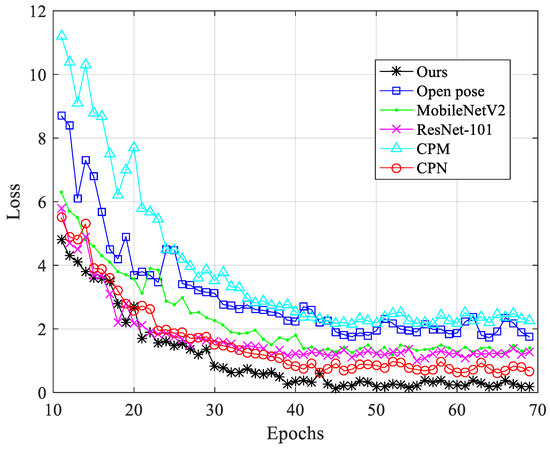
Figure 10.
Comparison of the loss of each network model.
5. Conclusions
The main objective of this paper is to solve the inaccurate positioning of the key points of the infrared image of the human body, and propose a key point positioning method based on the Mscf-ResNet model. The network model first uses the feature extraction module to obtain the feature map after residual learning, then uses multiple Mscf modules to extract richer features, and finally outputs the key point coordinates. The reason this paper can more accurately locate the key points is because the Mscf module uses different scale convolution kernels for feature extraction, and different receptive fields complement and enrich the detailed features. The experiments show that our proposed network model demonstrates higher key point positioning accuracy and stronger robustness than other networks on the human infrared image data set.
Author Contributions
Supervision, S.N.M.R.; conceptualization, S.G. and S.N.M.R.; methodology, S.G. and S.N.M.R.; writing, S.G. and S.N.M.R.; software, S.G.; data acquisition and preparation, S.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
No funding was received for this paper.
Informed Consent Statement
The informed consent of all authors was obtained.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the study are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest with any institution or individual regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- Li, X.-D.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.Q.; Song, B.A.; Dai, S.X.; Tie-Feng, X.U.; Nie, Q.H. Infrared imaging system and applications. Laser Infrared 2014, 44, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Resendiz-Ochoa, E.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Benitez-Rangel, J.P.; Romero-Troncoso, R.D.J.; Morales-Hernandez, L.A. Induction motor failure analysis: An automatic methodology based on infrared imaging. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 76993–77003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, M.; Kwanten, W.J.; Carr, J.A.; Chen, I.X.; Posada, J.M.; Srivastava, A.; Bawendi, M.G. Non-invasive monitoring of chronic liver disease via near-infrared and shortwave-infrared imaging of endogenous lipofuscin. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaeian, E.; Sadeghi, M.; Gohardoust, M.R.; Arthur, E.; Effati, M.; Jones, S.B.; Tuller, M. The feasibility of shortwave infrared imaging and inverse numerical modeling for rapid estimation of soil hydraulic properties. Vadose Zone J. 2021, 20, e20089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixson, J.G.; Teaney, B.P.; Graybeal, J.J.; Nehmetallah, G. Analysis and modeling of observer performance while using an infrared imaging system. Opt. Eng. 2020, 59, 033106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinyuan, Q.; Zhangqing, C. Application of thermal infrared technology in traditional Chinese medicine diagnosis. World Sci. Technol. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Med. 2011, 13, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Selvarani, A.; Suresh, G. Infrared thermal imaging for diabetes detection and measurement. J. Med. Syst. 2019, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; He, W.; Qu, S.; Gu, S.; Knoll, A. KAM-Net: Keypoint-Aware and Keypoint-Matching Network for Vehicle Detection from 2D Point Cloud. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sun, W.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Fan, H.; Sun, J. Pvn3d: A deep point-wise 3d keypoints voting network for 6dof pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11632–11641. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Mori, G. Multiple tree models for occlusion and spatial constraints in human pose estimation. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 710–724. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Li, Y. Beyond physical connections: Tree models in human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 596–603. [Google Scholar]
- Dantone, M.; Gall, J.; Leistner, C.; Van Gool, L. Human pose estimation using body parts dependent joint regressors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 3041–3048. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Kohli, P.; Shotton, J. Conditional regression forests for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 3394–3401. [Google Scholar]
- Kiefel, M.; Gehler, P.V. Human pose estimation with fields of parts. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 331–346. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, K.; Chellappa, R. Computationally efficient regression on a dependency graph for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 3390–3397. [Google Scholar]
- Toshev, A.; Szegedy, C.D. Human Pose Estimation via Deep Neural Networks’; CVPR: Columbus, OH, USA, 2014; pp. 1653–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Tompson, J.J.; Jain, A.; LeCun, Y.; Bregler, C. Joint training of a convolutional network and a graphical model for human pose estimation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Pfister, T.; Charles, J.; Zisserman, A. Flowing convnets for human pose estimation in videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1913–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.-E.; Ramakrishna, V.; Kanade, T.; Sheikh, Y. Convolutional pose machines. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4724–4732. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Li, S.; Ouyang, W.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Learning feature pyramids for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1281–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Carreira, J.; Agrawal, P.; Fragkiadaki, K.; Malik, J. Human pose estimation with iterative error feedback. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4733–4742. [Google Scholar]
- Lifshitz, I.; Fetaya, E.; Ullman, S. Human pose estimation using deep consensus voting. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 246–260. [Google Scholar]
- Pishchulin, L.; Insafutdinov, E.; Tang, S.; Andres, B.; Andriluka, M.; Gehler, P.V.; Schiele, B. Deepcut: Joint subset partition and labeling for multi person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4929–4937. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Insafutdinov, E.; Pishchulin, L.; Andres, B.; Andriluka, M.; Schiele, B. Deepercut: A deeper, stronger, and faster multi-person pose estimation model. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 34–50. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, F.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.; Yuille, A.L. Joint multi-person pose estimation and semantic part segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6769–6778. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.-E.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7291–7299. [Google Scholar]
- Papandreou, G.; Zhu, T.; Kanazawa, N.; Toshev, A.; Tompson, J.; Bregler, C.; Murphy, K. Towards accurate multi-person pose estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4903–4911. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Sun, J. Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7103–7112. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oquab, M.; Bottou, L.; Laptev, I.; Sivic, J. Learning and transferring mid-level image representations using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1717–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, R. The backpropagation algorithm. In Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; pp. 149–182. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, D.M. The problem of overfitting. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, N.; Perronnin, F. Generalized max pooling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2473–2480. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Irie, G.; Hiramatsu, K.; Kashino, K. Weighted generalized mean pooling for deep image retrieval. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 495–499. [Google Scholar]
- Sainath, T.N.; Vinyals, O.; Senior, A.; Sak, H. Convolutional, long short-term memory, fully connected deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 4580–4584. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Wang, Y. A Novel Multi-User Face Detection under Infrared Illumination by Real Adaboost. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Software Engineering, Wuhan, China, 11–13 December 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In International Conference on Machine Learning; PMLR: Lille, France, 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Mish, M.D. A self regularized non-monotonic neural activation function. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.08681. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).