CIAA-RepDroid: A Fine-Grained and Probabilistic Reputation Scheme for Android Apps Based on Sentiment Analysis of Reviews
Abstract
1. Introduction
- CIAA-RepDroid, a fine-grained security-related reputation based on sentiment analysis of security-related reviews and probabilistic classification model of polarities;
- a decomposition of reputation into confidentiality, integrity, authentication and availability reputations;
- experiments against existing rating system approaches demonstrating effectiveness of CIAA-RepDroid to related security flaws in Android apps.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Security of Android Apps
2.2. Classification of Reviews Based on Polarities
2.3. Extraction and Summarization of Key Topics
2.4. Consideration of Reviews in the Updates
2.5. Mining Security Issues
2.6. Reputation and Rating Schemes
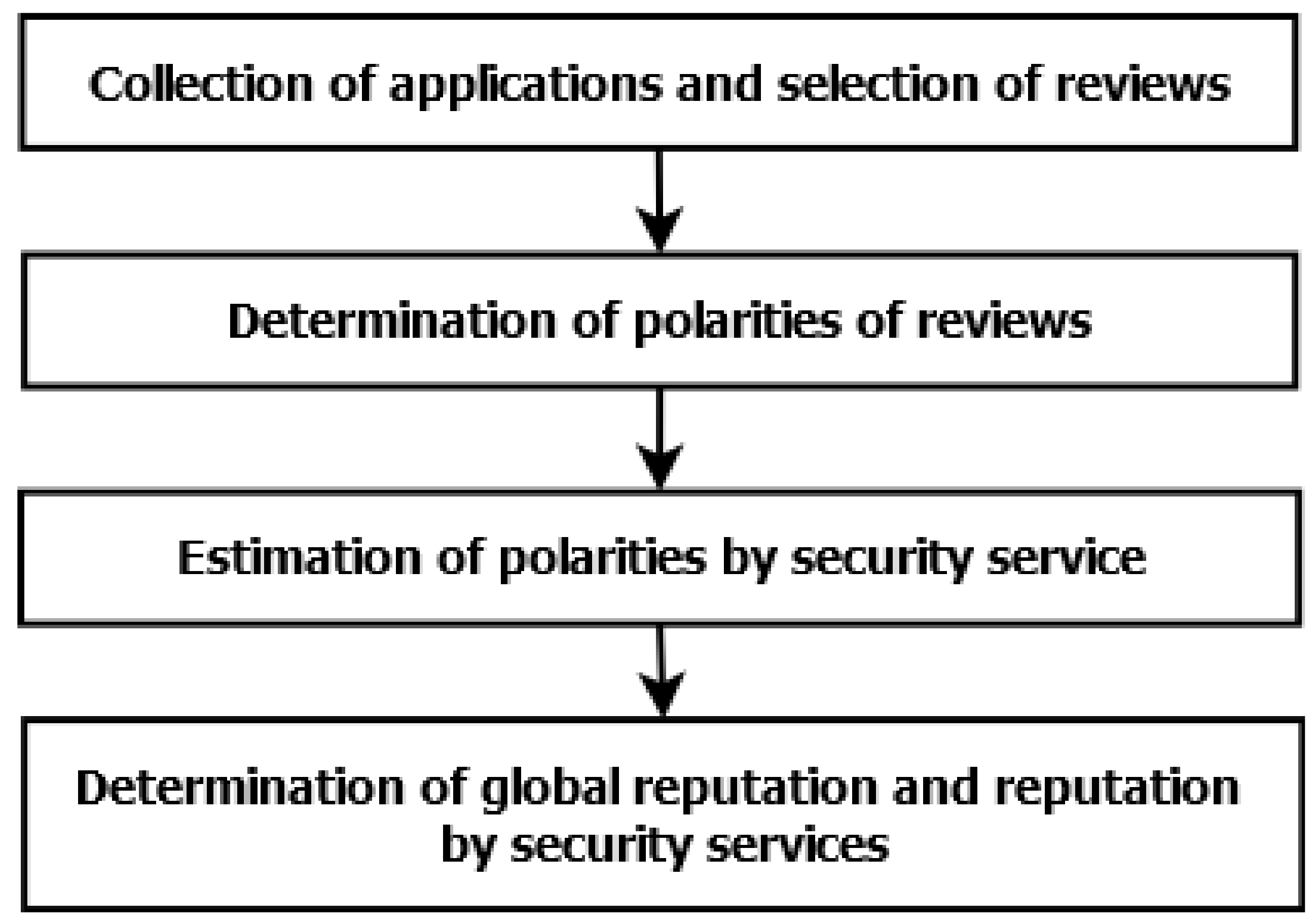
3. Reputation Model
3.1. Collecting Applications and Selecting Reviews
3.2. Determination of Review Polarity
3.3. Polarity Classification by Security Service
- C1 has a negative polarity in terms of confidentiality and availability;
- C2 has a negative polarity in terms of integrity and availability;
- C3 has a negative polarity in terms of integrity and availability;
- C4 has a negative polarity in terms of availability;
- C5 has a positive polarity in terms of authentication and availability; etc.
3.4. Determination of Reputation by Security Service and Global Reputation
- = ∑ = (total number of positive polarity);
- = ∑ = (total number of negative polarity)
- (resp.) is the positive (resp. negative) polarity value for the service confidentiality;
- (resp.) is the positive (resp. negative) polarity value for the service integrity;
- (resp.) is the positive (resp. negative) polarity value for the service authentication;
- (resp.) is the positive (resp. negative) polarity value for the service availability.
- Confidentiality: .
- Integrity: .
- Authentication: .
- Availability: .
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Reputation Based on Security
4.3. Reputation Based on Functionality
4.4. Reputation-Based Security vs. Reputation-Based Functionality
4.5. Comparison of CIAA-RepDroid to SERS and Google Play Rating
5. Study of Change from CIAA-RepDroid Keywords to SRR-Miner Keywords
- The increase and the decrease of the number of reviews;
- the reduction of badness and goodness of app reputations;
- the stagnation of reputations despite the variation of the number of reviews.
5.1. CIAA-RepDroid Advantages
- CIAA-RepDroid reveals that reviews can be effective to indicate security flaws to overcome across updated versions;
- CIAA-RepDroid is able to prioritize security services in terms of reinforcement in the next version;
- CIAA-RepDroid is able to provide fine-grained security reputations. The model finds through opinions various CIIA security pitfalls to overcome before one installs inside the smartphone. It can be exploited to recommend developers and vendors.
- The reputation based on functionality is in major cases much higher than the reputation based on security except some applications;
- CIAA-RepDroid is more expressive and precise in terms of security than existing rating schemes;
- CIAA-RepDroid keeps a certain robustness despite the change of security-related keywords.
5.2. Limitations and Recommendations
- This model does not distinguish fake reviews from real ones. We assumed all reviews as true reviews.
- The consideration of the date of publication of reviews is not taken into account. Over time, applications can have improvements thanks to updates and customers change their feelings to positive.
- We have only considered one application source: Google Play Store. People can make reviews on the same application through different application stores.
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
- CIAA-RepDroid will be extended to consider fake reviews;
- CIAA-RepDroid will include the fact reviews update with time and versions;
- CIAA-RepDroid will consider the fact that for an application, reviews are made in different stores.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Security Aspect | Keywords | Justifications |
|---|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Sniffing, spoofing | Sniffing refer to capturing and listening data that are transmitted across the whole system/network. The attacker violates confidentiality to achieve such actions. Spoofing helps the attacker to disguise as original entity to infiltrate a system. By doing that, one obtains privilege to access confidential information. |
| Intrusion, usurpation, | An attacker needs to violate confidentiality by stealing identify to intrude the system. Then, he accesses unauthorized data. | |
| Steal, hacked, abuse | These terms refer to personal data used without the permission of the owner, and sometimes these data are used to harm the owner or other people. | |
| Malicious, virus, compromise, trojan | These terms refer to software that infects a computer system without the knowledge of its user by exploiting human or technical vulnerabilities They compromise confidentiality. | |
| Fake, alert, relentless | Some terms often used to deceive the user or influence opinion on a particular subject. The finality is to lure to bring out unknowingly confidential data. | |
| Authentication | Scam, theft, breach, sniffing, spoofing, | We recall sniffing and spoofing since they rely on authentication to proceed. Additionally, attackers escalate authentication via scamming, identity theft and exploitation of vulnerabilities. |
| Anomaly, authorized, erroneous, vulnerable, protect, certified | These terms refer to authentication in the sense that a user cannot access his account, but he nevertheless provides the correct information. The user can also spot suspicious activity in their account. During authentication process, a system must certify identities and prevent erroneous authorizations. Based on vulnerabilities, a malware profit to pose anomaly activities. | |
| Integrity | Repudiation, nonsense, anomaly, abnormal | Once the state of the system changed and those data are altered, some related elements become nonsense. This alteration shows abnormal and anomaly behaviors throughout the system. Alterations are helpful to detect attacker traces. The latter generally uses repudiation measures to evade detections. |
| Fraud, spam, lie, scammer, scam | These terms relate to social engineering attacks consisting of luring user to provide critical data. The reason why we put them into the integrity category is that their objective is the infiltration to the target. This infiltration makes the state changed. | |
| Availability | Wrong, Error, Bug, Bugger, nonsense, Available, Crash, impractical | These terms refer to the inaccessibility or unavailability of a service or feature when using an application. Most of the time, users encounter access errors, applications that crash during their user, which sometimes leads to data loss. |
| Review 1 | Original | il n y a aucun moyen de denoncer des comptes fake !! je passe mon temps a bloquer des personnes qui volent et utilisent les photos d autres comptes et qui drague de manière très agressive !! review faire pour nous proteger de cela !! Pour ne pas changer votre mise à jour BUG!!! cela devient très fatigant car ça se produit à chaque fois depuis presque 1an. |
| Translated | There is no way to report fake accounts!! I spend my time blocking people who steal and use photos from other accounts and who flirt very aggressively!! how to protect us from that !! To not change your BUG update!!! it becomes very tiring because it has been happening every time for almost 1 year. | |
| Review 2 | Original | Depuis quelques temps, les bugs s’enchaînent sur cette appli et ça devient agaçant.. Cette fois-ci, impossible de recharger une page, impossible de voir les messages privées et impossible de se reconnecter sans avoir un message indiquant “une erreur s’est produite“. Faites quelque chose! |
| Translated | For some time, bugs are linked on this app and it becomes annoying. This time, impossible to reload a page, impossible to see private messages and impossible to reconnect without having a message indicating “an error is produced “. Do something! | |
| Review 3 | Original | Je ne peux même plus liker, reviewer ou m’abonner et lorsque je signale le problème, Instagram ne réponds pas. J’ai bien signaler le problème au moins 4 fois mais rien ne se passe. Le service est très mal organisé. Merci de me remettre les options qui m’ont été prises. |
| Translated | I can’t even like, review or subscribe anymore and when I report the problem, Instagram doesn’t respond. I did report the problem at least 4 times but nothing happens. The service is very poorly organized. Thank you for giving me the options that have been taken. | |
| Review 4 | Original | Malheureusement, il y a de plus en plus de beugs avec cette application. Que ça soi au niveau des stories ou du partage de photos dans notre fils d’actualité, ça fait déjà la troisième fois (en même pas 1 mois !) que je rencontre des soucis avec Instagram.. |
| Translated | Unfortunately, there are more and more bugs with this application. Whether it’s at the level of stories or sharing photos in our news feed, it’s already been the third time (not even 1 month!) That I have encountered problems with Instagram. | |
| Review 5 | Original | Je suis dans l’incapacité de me connecter sur mon compte car le site ne reconnaît pas mon adresse mail. J’ai vérifier son orthographe mais toujours rien. Je me connecte alors en utilisant mon nom d’utilisateur, je suis redirigé vers une page disant qu’une connexion suspecte à été détectée, d’aller sur la page d’aide afin de pouvoir me connecter. Là aucune information ne correspond à mon cas. Je ne peux pas non plus créer un nouveau compte parce que là mon adresse mail est reconnue… |
| Translated | I am unable to log into my account because the site does not recognize my email address. I checked his spelling but still nothing. I then connect using my username, I am redirected to a page saying that a suspicious connection has been detected, to go to the help page so that I can connect. There no information corresponds to my case. I also cannot create a new account because my email address is recognized there … | |
| Review 6 | Original | j’aime cette application d’Instagram. Je conseil énergiquement de surfer sur ce réseau social…il faut toujours soutenir toutes initiatives qui conduisent à la communication, à tout moment je peux avoir accès à mes ancienne photo, c’est vraiment bien. |
| Translated | I like this Instagram app. I strongly advise to surf on this social network … you must always support all initiatives that lead to communication, at any time I can have access to my old photo, it’s really good. | |
| Review 7 | Original | Ça fait bien 3 ou 4 fois que mon compte est repris ou piraté par un tiers, je ne sais plus me connecter et quand je recherche mon profil il est attribué à quelqu’un d’autre. Impossible de joindre quelqu’un chez Instagram qui pourrait m’aider. M’expliquer pourquoi ça arrive et pourquoi autant de fois? Soit je deviens parano soit il y a une explication… Soit j’arrête Instagram pour de bon. |
| Translated | It’s been 3 or 4 times that my account is taken over or hacked by a third party, I no longer know how to log in and when I search for my profile it is assigned to someone else. Can’t reach someone on Instagram who could help me. Explain to me why it happens and why so many times? Either I become paranoid or there is an explanation … Either I stop Instagram for good. | |
| Review 8 | Original | Très déçu de Instagram récemment. Je ne parviens pas à me connecter à mon compte car l’utilisateur n’existe pas. Mais je ne peux pas créer d’autres compte car mon adresse email est déjà utilisée !! veuillez régler ce problème MAJEUR quu m’empêche d’utiliser votre application. |
| Translated | Very disappointed with Instagram recently. I cannot connect to my account because the user does not exist. But I cannot create other accounts because my email address is already used !! Please resolve this MAJOR problem that prevents me from using your application. | |
| Review 9 | Original | Depuis la dernière mise à jour, les conversations privées sont impraticables. Les messages prennent beaucoup plus de place, les images et les gifs prennent absolument toute la page, les déformant, et rendant la conversation illisible et surtout, il est devenu impossible de cliquer dessus pour mieux les voir. Si vous pouviez régler rapidement ce problème car ce n’est pas la première fois qu’il y a des bugs après de MAJ et ça arrive de plus en plus souvent, ça en dit long sur l’intérêt que vous portez à votre appli… |
| Translated | Since the last update, private conversations have been impractical. The messages take up much more space, the images and gifs take up the whole page, distorting them, and making the conversation unreadable and above all, it has become impossible to click on them to better see them. If you could quickly resolve this problem because it is not the first time that there are bugs after update and it happens more and more often, it says a lot about the interest you have in your app… | |
| Review 10 | Original | Ça fait déjà plusieurs années que je suis sur instagram et je n’ai jamais été insatisfait de ce réseau social. Si je devais vous en recommander un, ce serait celui-ci. Cette application permet de poster de publications d’une manière simple et fluide, de plus nous disposons de filtres assez sympas. Vraiment cool! |
| Translated | I have been on Instagram for several years now and I have never been dissatisfied with this social network. If I had to recommend one, it would be this. This application allows you to post publications in a simple and fluid way, plus we have pretty cool filters. Really cool! |
References
- Rasool, G.; Ali, A. Recovering Android Bad Smells from Android Applications. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, S. Global Market Share Smartphone Operating Systems of Unit Shipments 2014–2023; Technology Telecommunications: Lanzhou, China, 2020; Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/272307/market-share-forecast-for-smartphone-operating-systems/ (accessed on 12 July 2020).
- My Android Apps. Google, USA. 2020. Available online: https://play.google.com/apps (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- The AppInChina App Store Index. AppInChina, China. 2020. Available online: https://www.appinchina.co/market/app-stores/ (accessed on 27 July 2020).
- Anzhi Market. Anzhi, China. 2020. Available online: http://www.anzhi.com/ (accessed on 28 July 2020).
- Number of Available Applications in the Google Play Store from December 2009 to December 2019; Statista: Hamburg, Germany, 2020; Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/266210/number-of-available-applications-in-the-google-play-store/ (accessed on 27 July 2020).
- Pan, Y.; Ge, X.; Fang, C.; Fan, Y. A Systematic Literature Review of Android Malware Detection Using Static Analysis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 116363–116379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazab, M.; Alazab, M.; Shalaginov, A.; Mesleh, A.; Awajan, A. Intelligent mobile malware detection using permission requests and API calls. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 107, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, R.; Ghahramani, M.; Javidan, R.; Shojafar, M.; Pooranian, Z.; Conti, M. Similarity-based Android malware detection using Hamming distance of static binary features. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 105, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakounté, F.; Hayata, F. Supervised Learning Based Detection of Malware on Android. In Mobile Security and Privacy: Advances, Challenges and Future Research Directions; Syngress Publishing: Rockland, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 101–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakounté, F.; Djakene Wandala, A.; Tiguiane, Y. Detection of Android Malware based on Sequence Alignment of Permissions. Int. J. Comput. (IJC) 2019, 35, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Martinelli, F.; Medvet, E.; Mercaldo, F.; Santone, A. Visualizing the outcome of dynamic analysis of Android malware with VizMal. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2020, 50, 102423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajrani, J.; Laxmi, V.; Tripathi, M.; Gaur, M.S.; Zemmari, A.; Mosbah, M.; Conti, M. Effectiveness of state-of-the-art dynamic analysis techniques in identifying diverse Android malware and future enhancements. In Advances in Computers; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 119, pp. 73–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, Z.; Muhadi, F.W.; Saudi, M.M.; Hamid, I.R.A.; Foozy, C.F.M. Android Ransomware Detection Based on Dynamic Obtained Features. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 978 AISC, pp. 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, R.; Wang, K.; Gu, X.; Xu, Z. A novel hybrid method to analyze security vulnerabilities in android applications. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2020, 25, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuraman, C.; Suresh, S.; Shivshankar, S.; Chapaneri, R. Static and dynamic malware analysis using machine learning. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 1045, pp. 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, G.; Liu, X.; Mao, W.; Si, C.; Pedrycz, W.; Wang, W. Identifying vulnerabilities of SSL/TLS certificate verification in Android apps with static and dynamic analysis. J. Syst. Softw. 2020, 167, 110609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzaylaee, M.K.; Yerima, S.Y.; Sezer, S. DL-Droid: Deep learning based android malware detection using real devices. Comput. Secur. 2020, 89, 101663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, D.W.; Moore, T. Cyber Warranties: Market Fix or Marketing Trick? Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrikx, F.; Bubendorfer, K.; Chard, R. Reputation systems: A survey and taxonomy. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2015, 75, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R. Numeric rating of Apps on Google Play Store by sentiment analysis on user reviews. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information and Communication Technology, ICEEICT 2014, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 10–12 April 2014; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojica Ruiz, I.J.; Nagappan, M.; Adams, B.; Berger, T.; Dienst, S.; Hassan, A.E. Examining the Rating System Used in Mobile-App Stores. IEEE Softw. 2016, 33, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc-Nayebi, N.; Abran, A. A systematic literature review: Opinion mining studies from mobile app store user reviews. J. Syst. Softw. 2017, 125, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, N.; Kelly, L. A survey of utilizing user-reviews posted on Google play store. In Proceedings of the the 29th Annual International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering, CASCON’19, Toronto, ON, Canada, 4–6 November 2019; ACM: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2019; pp. 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureña, R.; Kou, G.; Dong, Y.; Chiclana, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E. A review on trust propagation and opinion dynamics in social networks and group decision making frameworks. Inf. Sci. 2019, 478, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, A.; Marcinek, P.; Alzahrani, A.; Alshahrani, H.; Fu, H. Puredroid: Permission Usage and Risk Estimation for Android Applications; ACM International Conference Proceeding Series; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, L.; Yan, Q.; Li, Z.; Srisa-An, W.; Ye, H. Significant Permission Identification for Machine-Learning-Based Android Malware Detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 3216–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, S.; He, Q.; Feng, Z.; Xue, X. An Android application risk evaluation framework based on minimum permission set identification. J. Syst. Softw. 2020, 163, 110533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.A.; Arshad, S.; Robertson, W.; Wilson, C. Tracing Information Flows Between Ad Exchanges Using Retargeted Ads. In Proceedings of the the 25th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, SEC’16, Austin, TX, USA, 10–12 August 2016; ACM: Austin, TX, USA, 2016; pp. 481–496. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Wei, T.; Lui, J.C. TaintART: A practical multi-level information-flow tracking system for Android RunTime. In Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, New York, NY, USA, 24–28 October 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, M.Y.; Lin, Y.D. Deep learning for sentiment analysis on google play consumer review. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration, IRI 2017, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–6 August 2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Azhari, A.; Belhaouri, S.B.; Qureshi, A.A. Machine Learning Algorithm’s Measurement and Analytical Visualization of User’s Reviews for Google Play Store. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyebode, O.; Alqahtani, F.; Orji, R. Using Machine Learning and Thematic Analysis Methods to Evaluate Mental Health Apps Based on User Reviews. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 111141–111158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, E.; Maalej, W. How do users like this feature? A fine grained sentiment analysis of App reviews. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 22nd International Requirements Engineering Conference, RE 2014-Proceedings, Karlskrona, Sweden, 25–29 August 2014; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Stefanidis, K. A Sentiment-Statistical Approach for Identifying Problematic Mobile App Updates Based on User Reviews. Information 2020, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, H.; Shihab, E.; Nagappan, M.; Hassan, A.E. What do mobile app users complain about? IEEE Softw. 2015, 32, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Kim, S. What parts of your apps are loved by users? In Proceedings of the 2015 30th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, ASE 2015, Lincoln, NE, USA, 9–13 November 2015; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Derr, E.; Backes, M.; Bugiel, S. Short text, large effect: Measuring the impact of user reviews on android app security & privacy. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomba, F.; Salza, P.; Ciurumelea, A.; Panichella, S.; Gall, H.; Ferrucci, F.; De Lucia, A. Recommending and Localizing Change Requests for Mobile Apps Based on User Reviews. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACM 39th International Conference on Software Engineering, ICSE 2017, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 20–28 May 2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Lin, J.; Liy, L.; Faloutsos, C.; Hong, J.; Sadeh, N. Why people hate your App-Making sense of user feedback in a mobile app store. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Chicago, IL, USA, 11–14 August 2013; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume Part F128815, pp. 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroel, L.; Bavota, G.; Russo, B.; Oliveto, R.; Di Penta, M. Release planning of mobile apps based on user reviews. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Software Engineering, IEEE Computer Society, Austin, TX, USA, 14–22 May 2016; pp. 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zeng, J.; Lyu, M.R.; King, I. Online App Review Analysis for Identifying Emerging Issues; Association for Computing Machinery (ACM): New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Wang, B.; He, P.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lyu, M.R. PAID: Prioritizing App Issues for Developers by Tracking User Reviews over Versions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 26th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering, ISSRE 2015, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2–5 November 2015; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, H.; Luo, X.; Liu, K. Localizing function errors in mobile apps with user reviews. In Proceedings of the 48th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks, DSN, Luxembourg, 25–28 June 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamian, M.; Serna, J.; Rannenberg, K. Revealing the unrevealed: Mining smartphone users privacy perception on app markets. Comput. Secur. 2019, 83, 332–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Guo, H.; Huang, Z. Identifying security issues for mobile applications based on user review summarization. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2020, 122, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfay, W.B.; Booth, T.; Andersson, K. Reputation based security model for android applications. In Proceedings of the 11th IEEE Int. Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications, TrustCom-2012-11th IEEE Int. Conference on Ubiquitous Computing and Communications, IUCC-2012, Liverpool, UK, 25–27 June 2012; pp. 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.S.; Raje, R.R. SERS: A security-related and evidence-based ranking scheme for mobile apps. In Proceedings of the 1st IEEE International Conference on Trust, Privacy and Security in Intelligent Systems and Applications, TPS-ISA 2019, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 12–14 December 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Shukla, S.K. The State of Android Security; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakounté, F.; Ndjeumou Ngassi, R.C.; Kamla, V.C.; Udagepola, K.P. LimonDroid: A system coupling three signature-based schemes for profiling Android malware. Iran J. Comput. Sci. 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Azhari, A.; Aldabbas, H.; Alruily, M.; Belhaouri, S.B.; Qureshi, A.A. Classification of Google Play Store Application Reviews Using Machine Learning. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D. Google Play Store Application Scraper. MIT, USA. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/danieliu/play-scraper (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- App Review & Ratings Analysis for Mobile Teams. AppBot, Australia. 2020. Available online: https://appbot.co/ (accessed on 27 July 2020).
- Vidas, T.; Votipka, D.; Christin, N. All your droid are belong to us: A survey of current android attacks. In Proceedings of the 5th USENIX Conference on Offensive technologies (WOOT’11), San Francisco, CA, USA, 8 August 2011; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Tourette, A. Advanced SEO Tool. Alyze, France. 2020. Available online: https://en.alyze.info/ (accessed on 27 July 2020).
- Keyword Tool. Keywordtool, Hong Kong. 2020. Available online: https://keywordtool.io/ (accessed on 27 July 2020).
- Haryanto, B.; Ruldeviyani, Y.; Rohman, F.; Julius Dimas, T.N.; Magdalena, R.; Muhamad Yasil, F. Facebook analysis of community sentiment on 2019 Indonesian presidential candidates from Facebook opinion data. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 161, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, O.; Steurer, J.; Hofman, A. The Bayes’ Theorem Framework for Diagnostic Research. In Clinical Research Transformed; Springer Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Language Toolkit. 2020. Available online: https://www.nltk.org/ (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Raybaut, P. SpiderLib. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/jromang/spyderlib (accessed on 27 July 2020).

| Reviews | Positive Polarity (%) | Negative Polarity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.22 | 0.78 |
| C2 | 0.16 | 0.84 |
| C3 | 0.27 | 0.73 |
| C4 | 0.31 | 0.69 |
| C5 | 0.32 | 0.68 |
| C6 | 0.51 | 0.49 |
| C7 | 0.36 | 0.64 |
| C8 | 0.33 | 0.67 |
| C9 | 0.22 | 0.78 |
| C10 | 0.64 | 0.36 |
| Sentiment | Confidentiality Related Words | Integrity Words | Authentication Related Words | Availability Related Words | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | Negative | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| C2 | Negative | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| C3 | Negative | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| C4 | Negative | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| C5 | Negative | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| C6 | Positive | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| C7 | Negative | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| C8 | Negative | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| C9 | Negative | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| C10 | Positive | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Reviews | Polarity Index (+/−) | () | () | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con. | Int. | Aut. | Ava. | Con. | Int. | Aut. | Ava. | ||
| C1 | − | 0.15 | 0 | 0 | 0.07 | 0.52 | 0 | 0 | 0.26 |
| C2 | − | 0 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.11 | 0 | 0.28 | 0 | 0.56 |
| C3 | − | 0 | 0.13 | 0 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.36 | 0 | 0.37 |
| C4 | − | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.69 |
| C5 | − | 0 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0 | 0 | 0.33 | 0.35 |
| C6 | + | 0 | 0.25 | 0 | 0.26 | 0 | 0.24 | 0 | 0.25 |
| C7 | − | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0 | 0.22 |
| C8 | − | 0 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0 | 0 | 0.22 | 0.45 |
| C9 | − | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0 | 0.39 |
| C10 | + | 0 | 0.21 | 0 | 0.43 | 0 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.24 |
| Total: | |||||||||
| Application | Category | Security Related Reviews | Functionality Related Reviews | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social media | 100 | 2,288,402 | 4.5 | |
| Social media | 150 | 1,479,779 | 4.2 | |
| CIC | Finance | 90 | 1715 | 4.7 |
| Messenger | Communication | 150 | 101,065 | 4.2 |
| SGC Connect | Finance | 6 | 10 | 4.2 |
| Whatapp | Communication | 150 | 2,824,936 | 4.3 |
| QR scanner | Tools | 80 | 11,026 | 4.7 |
| Ecobank | Finance | 150 | 643 | 3.5 |
| Clean Master | Security tools | 98 | 139,070 | 4.5 |
| Security Master | Security tools | 103 | 78,840 | 2.8 |
| Age Scanner Finger | Entertainment | 105 | 118 | 2.3 |
| Express Union | Finance | 13 | 13 | 3.6 |
| BICEC Mobile | Finance | 2 | 5 | 3.8 |
| Application | Number Security Related Reviews | Application Polarity | E () Security | E (p) by Security Service | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Con. | Int. | Aut. | Ava. | ||||
| 100 | − | 0.40 | 0.36 | 0.45 | 0.32 | 0.47 | |
| 150 | − | 0.31 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.11 | 0.33 | |
| CIC | 90 | − | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 0.18 | 0.26 |
| Messenger | 150 | + | 0.51 | 0.57 | 0.43 | 0.37 | 0.66 |
| SGC Connect | 6 | − | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.17 |
| Whatapp | 150 | + | 0.58 | 0.38 | 0.58 | 0.68 | 0.67 |
| QR scanner | 80 | + | 0.51 | 0.46 | 0.57 | 0.34 | 0.68 |
| Ecobank | 150 | − | 0.30 | 0.52 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.22 |
| Clean Master | 98 | − | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.43 |
| Security Master | 103 | − | 0.42 | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.67 | 0.43 |
| Age Scanner Finger | 105 | − | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.1 | 0.56 |
| Express Union | 13 | − | 0.41 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.64 | 0.23 |
| BICEC Mobile | 2 | − | 0.41 | 0.34 | 0.47 | 0.45 | 0.38 |
| Applications | Number of Reviews | Positive Sentiments (%) | Negative Sentiments (%) | E (p, ) Functionality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2,288,402 | 75% | 25% | 0.75 | |
| 1,479,779 | 63% | 37% | 0.63 | |
| CIC | 1715 | 76% | 24% | 0.76 |
| Messenger | 1,010,765 | 65% | 35% | 0.65 |
| SGC Connect | 10 | 50% | 50% | 0.50 |
| Whatapp | 2,824,936 | 70% | 30% | 0.70 |
| QR scanner | 11,026 | 82% | 18% | 0.82 |
| Ecobank | 643 | 43% | 57% | 0.43 |
| Clean Master | 139,070 | 83% | 17% | 0.83 |
| Sécurity Master | 78.840 | 86% | 14% | 0.86 |
| Age Scanner Finger | 118 | 5% | 95% | 0.05 |
| Express Union | 13 | 15% | 85% | 0.15 |
| BICEC Mobile | 5 | 60% | 40% | 0.60 |
| App Characteristics | Our Model | SERS | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| App Id | #Total Reviews | #Security Reviews | Global Reputation (R1) | Con. R11 | Int. R12 | Aut. R13 | Ava. R14 | Rating Based Reviews (R2) | Rating Based Static Analysis (R3) | Global Rating (R4) | Traditional Rating (R5) |
| 1 | 2573 | 21 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 2.6 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 4.09 | 4.22 | 3.66 | 4.1 |
| 2 | 2586 | 5 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 4.44 | 3.98 | 3.95 | 4.6 |
| 3 | 2590 | 52 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 4.21 | 4.08 | 3.82 | 4.5 |
| 4 | 2567 | 41 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 4.23 | 4.46 | 3.86 | 4.5 |
| 5 | 2598 | 28 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 4.37 | 4.92 | 4.46 | 4.5 |
| 6 | 2586 | 62 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 2.81 | 4.51 | 3.43 | 4.3 |
| 7 | 2566 | 24 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 4.22 | 4.37 | 3.95 | 4.1 |
| 8 | 2546 | 22 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 4.32 | 2.81 | 4.52 | 4.4 |
| 9 | 2578 | 37 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 3.79 | 4.22 | 2.51 | 4 |
| 10 | 2580 | 40 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 3.61 | 4.32 | 4.25 | 4.1 |
| 11 | 2572 | 54 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 4.27 | 3.79 | 4.19 | 4.6 |
| 12 | 2598 | 43 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 3.91 | 3.61 | 3.44 | 4.6 |
| 13 | 2500 | 42 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 3.51 | 4.27 | 3.29 | 4.2 |
| 14 | 2598 | 43 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 2.79 | 3.91 | 3.89 | 4.2 |
| 15 | 2552 | 65 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 3.32 | 3.51 | 2.55 | 4.1 |
| Average | 2573 | 39 | 1.70 | 1.63 | 1.78 | 1.72 | 1.68 | 3.85 | 4.06 | 3.71 | 4 |
| Our Scheme | SERS | Gaps | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| App Id | # Total Reviews | # Security Reviews | Global Reputation (R1) | Rating Based Reviews (R2) | Rating Based Static Analysis (R3) | Global Rating (R4) | Traditional Rating (R5) | Gap R1-R2 | Gap R1-R3 | Gap R1-R4 | Gap R1-R5 |
| 1 | 2573 | 21 | 1.9 | 4.09 | 4.22 | 3.66 | 4.1 | 2.19 | 2.32 | 1.76 | 2.2 |
| 2 | 2586 | 5 | 2.2 | 4.44 | 3.98 | 3.95 | 4.6 | 2.24 | 1.78 | 1.75 | 2.4 |
| 3 | 2590 | 52 | 1.7 | 4.21 | 4.08 | 3.82 | 4.5 | 2.51 | 2.38 | 2.12 | 2.8 |
| 4 | 2567 | 41 | 1.6 | 4.23 | 4.46 | 3.86 | 4.5 | 2.63 | 2.86 | 2.26 | 2.9 |
| 5 | 2598 | 28 | 1.6 | 4.37 | 4.92 | 4.46 | 4.5 | 2.77 | 3.32 | 2.86 | 2.9 |
| 6 | 2586 | 62 | 1.6 | 2.81 | 4.51 | 3.43 | 4.3 | 1.21 | 2.91 | 1.83 | 2.7 |
| 7 | 2566 | 24 | 1.8 | 4.22 | 4.37 | 3.95 | 4.1 | 2.42 | 2.57 | 2.15 | 2.3 |
| 8 | 2546 | 22 | 1.6 | 4.32 | 2.81 | 4.52 | 4.4 | 2.72 | 1.21 | 2.92 | 2.8 |
| 9 | 2578 | 37 | 1.6 | 3.79 | 4.22 | 2.51 | 4 | 2.19 | 2.62 | 0.91 | 2.4 |
| 10 | 2580 | 40 | 1.7 | 3.61 | 4.32 | 4.25 | 4.1 | 1.91 | 2.62 | 2.55 | 2.4 |
| 11 | 2572 | 54 | 1.6 | 4.27 | 3.79 | 4.19 | 4.6 | 2.67 | 2.19 | 2.59 | 3 |
| 12 | 2598 | 43 | 1.7 | 3.91 | 3.61 | 3.44 | 4.6 | 2.21 | 1.91 | 1.74 | 2.9 |
| 13 | 2500 | 42 | 1.6 | 3.51 | 4.27 | 3.29 | 4.2 | 1.91 | 2.67 | 1.69 | 2.6 |
| 14 | 2598 | 43 | 1.7 | 2.79 | 3.91 | 3.89 | 4.2 | 1.09 | 2.21 | 2.19 | 2.5 |
| 15 | 2552 | 65 | 1.7 | 3.32 | 3.51 | 2.55 | 4.1 | 1.62 | 1.81 | 0.85 | 2.4 |
| Average | 2573 | 39 | 1.70 | 3.85 | 4.06 | 3.71 | 4 | 2.15 | 2.35 | 2.01 | 2.61 |
| Reviews | |
|---|---|
| app 2 | it’s always in my apps using my data, even after I uninstalled it and I am sick of it. been hacked |
| Very very disappointing app don’t install this video app % fake | |
| it’s a after thought a copy cat FaceTime…. where is your imagination???? and what’s up with all the animation and Kitty shows this is supposed to be Facebook not fake book not babysitter book the mon where is the news we used to have the party that used to have the fun Facebook used to be now it’s just bogus people are raising their beers and their fingers to the whole it would have been better had it been passed off as a lesbian game show 0h. …………). yyyb be by | |
| always crashes and video never clear st | |
| Receiving calls causes crashing of the app. |
| # Security Review | Global Reputation | Conf. Reputation | Int. Reputation | Auth. Reputation | Avail. Reputation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| App ID | # Total Reviews | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 2573 | 21 | 26 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 1 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.7 |
| 2 | 2586 | 5 | 9 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 3 | 2.1 | 2 | 2.8 |
| 3 | 2590 | 52 | 41 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 2 |
| 4 | 2567 | 41 | 32 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| 5 | 2598 | 28 | 43 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.3 |
| 6 | 2586 | 62 | 78 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| 7 | 2566 | 24 | 35 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.7 |
| 8 | 2546 | 22 | 30 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| 9 | 2578 | 37 | 29 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.7 |
| 10 | 2580 | 40 | 31 | 1.7 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 2.6 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 1.6 | 2.9 |
| 11 | 2572 | 54 | 68 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.1 |
| 12 | 2598 | 43 | 57 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.9 |
| 13 | 2500 | 42 | 34 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.7 |
| 14 | 2598 | 43 | 39 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.5 |
| 15 | 2552 | 65 | 81 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.6 |
| Average | 2572.7 | 38.6 | 42.2 | 1.70 | 1.75 | 1.63 | 1.69 | 1.78 | 1.89 | 1.72 | 1.72 | 1.68 | 1.87 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tchakounté, F.; Yera Pagor, A.E.; Kamgang, J.C.; Atemkeng, M. CIAA-RepDroid: A Fine-Grained and Probabilistic Reputation Scheme for Android Apps Based on Sentiment Analysis of Reviews. Future Internet 2020, 12, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12090145
Tchakounté F, Yera Pagor AE, Kamgang JC, Atemkeng M. CIAA-RepDroid: A Fine-Grained and Probabilistic Reputation Scheme for Android Apps Based on Sentiment Analysis of Reviews. Future Internet. 2020; 12(9):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12090145
Chicago/Turabian StyleTchakounté, Franklin, Athanase Esdras Yera Pagor, Jean Claude Kamgang, and Marcellin Atemkeng. 2020. "CIAA-RepDroid: A Fine-Grained and Probabilistic Reputation Scheme for Android Apps Based on Sentiment Analysis of Reviews" Future Internet 12, no. 9: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12090145
APA StyleTchakounté, F., Yera Pagor, A. E., Kamgang, J. C., & Atemkeng, M. (2020). CIAA-RepDroid: A Fine-Grained and Probabilistic Reputation Scheme for Android Apps Based on Sentiment Analysis of Reviews. Future Internet, 12(9), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi12090145





