Dynamic Cost-Aware Routing of Web Requests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Load Balancing by Spatial Pricing
2.2. Routing Work Loads to Renewable Energy Powered DCs
3. Problem Definition
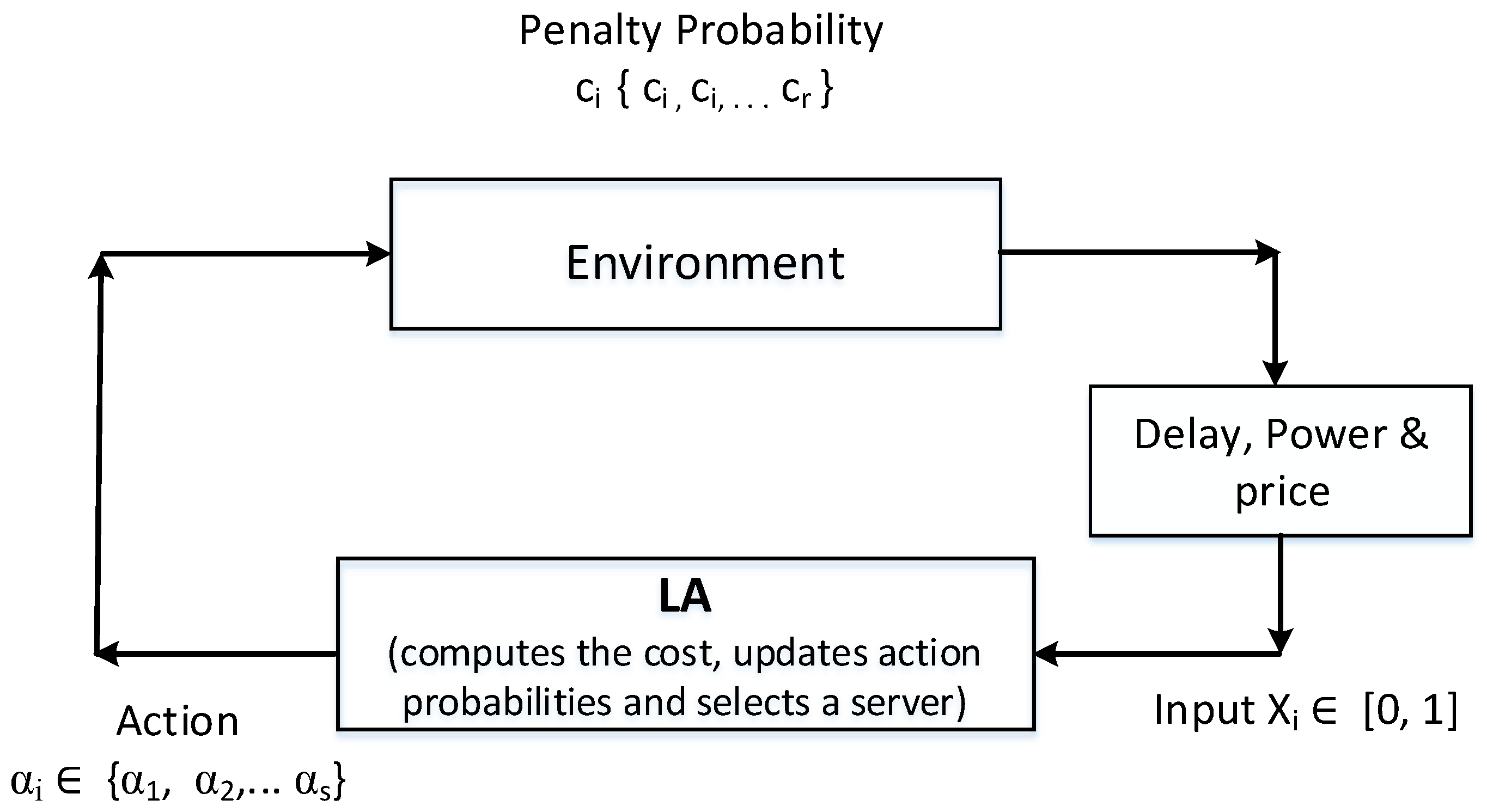
4. Routing with Learning Automata
- Reward Penalty (RP): The learning parameter b = a and the selection probability of the server is rewarded or penalized equally when the selected server resulted in favorable or unfavorable performance.
- Reward Inaction (RI): When , there will be no penalty for unfavorable response from the selected server (No action) and the server will be rewarded for favorable response.
- Reward Penalty- (RP-): ba, the selected action is penalized very little for unfavorable response.
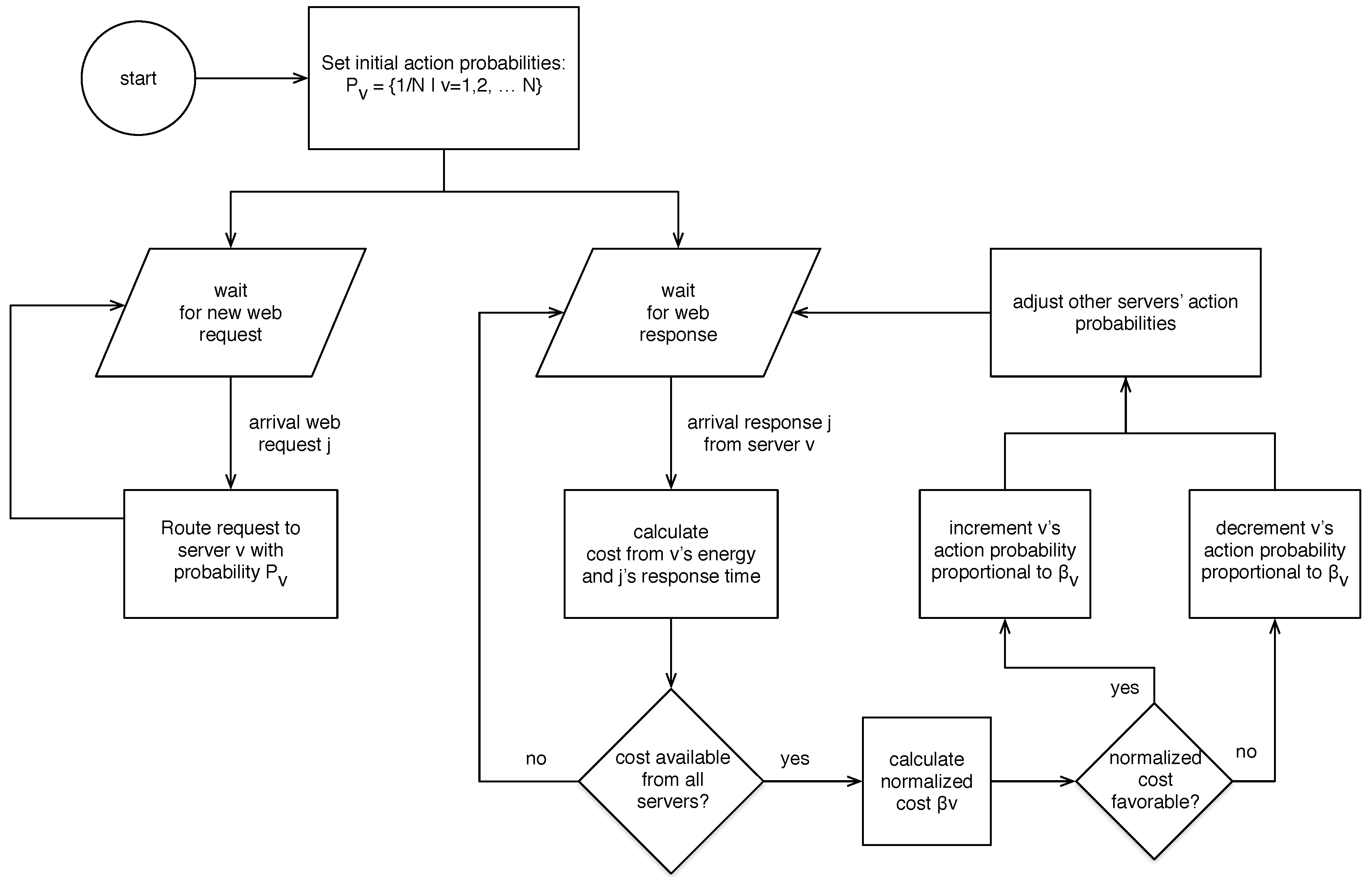
5. Cost-Aware S-Model Reward Penalty Epsilon (CA-S) Learning Automaton
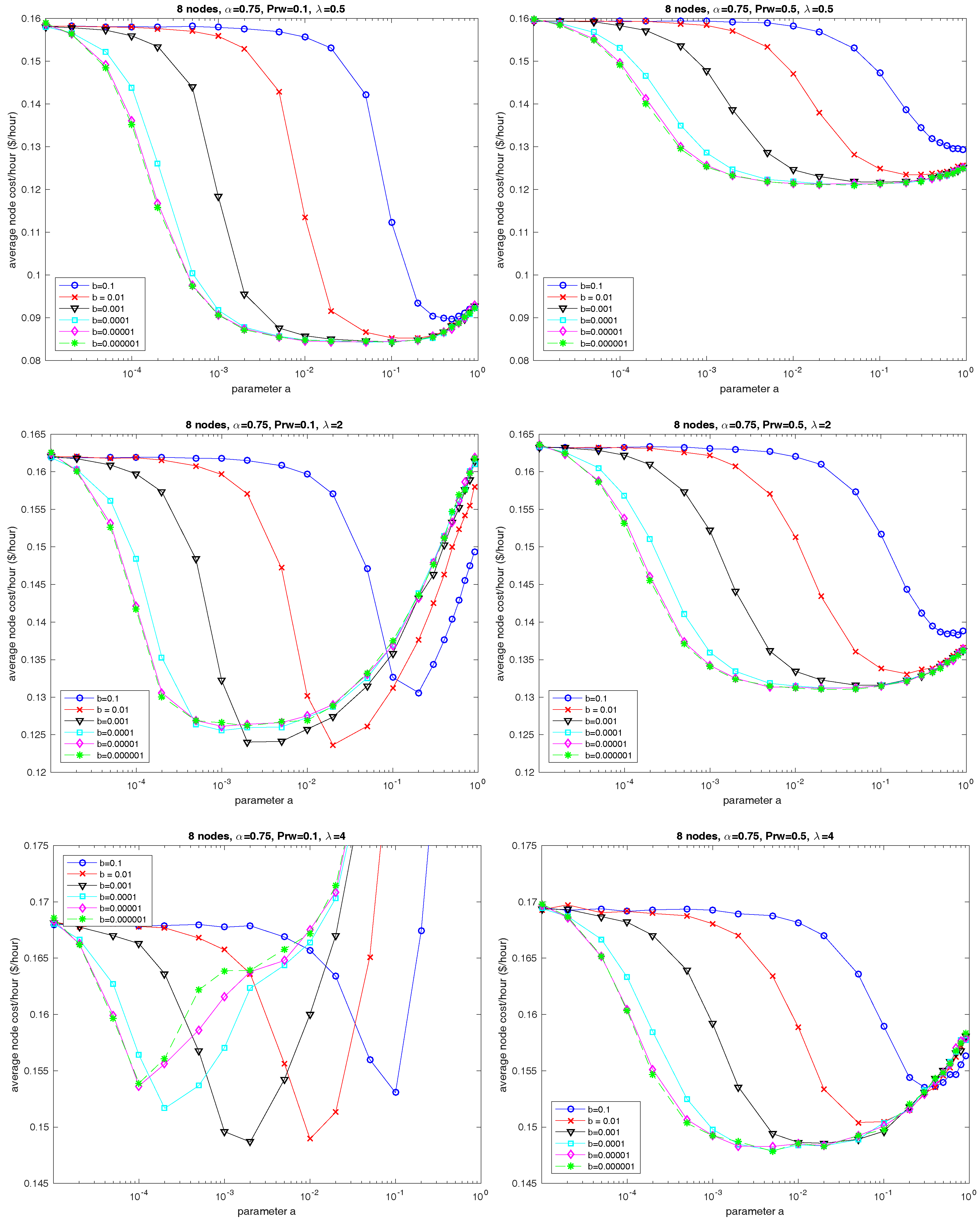
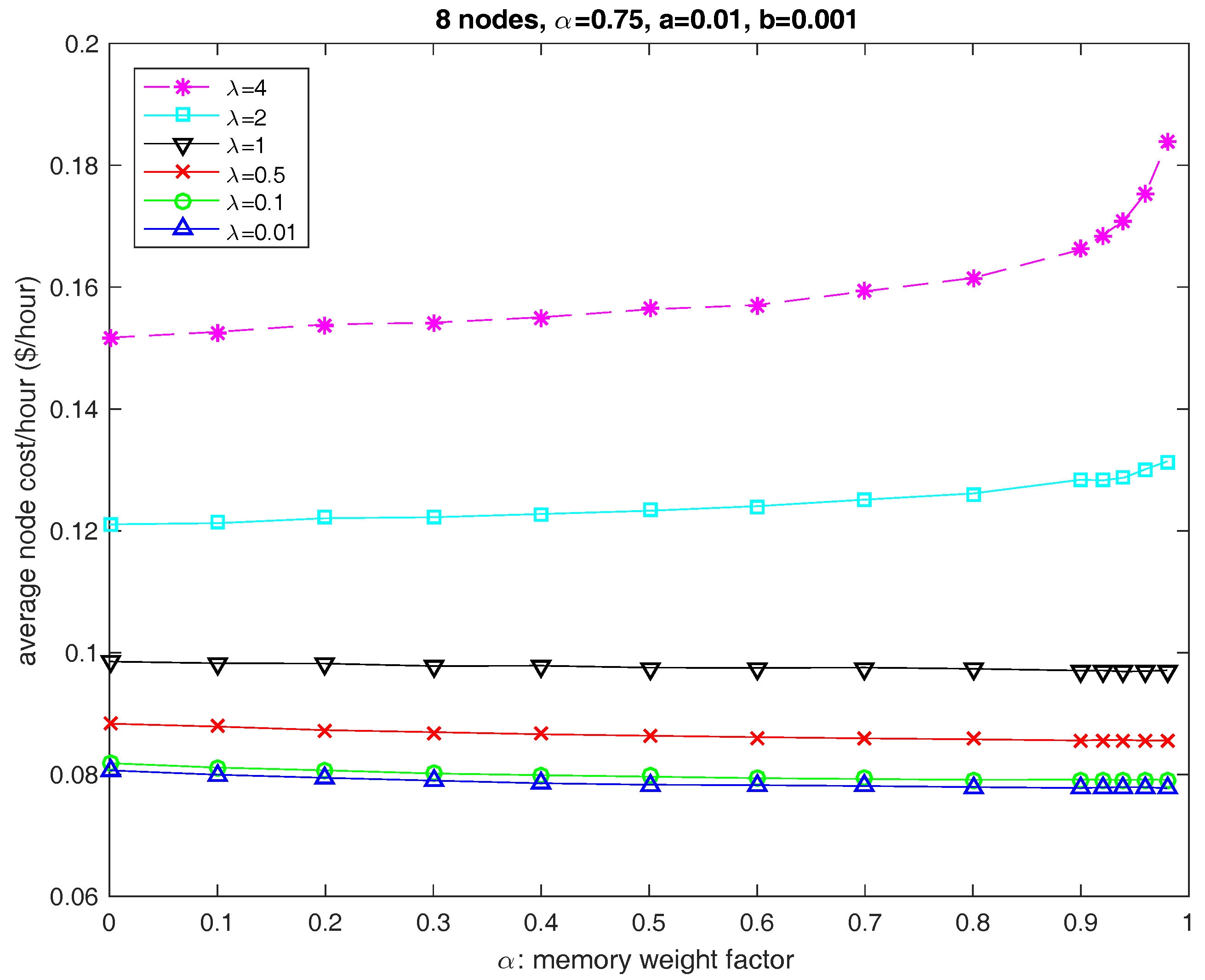
6. Evaluation of Parameter Selection Using Simulation
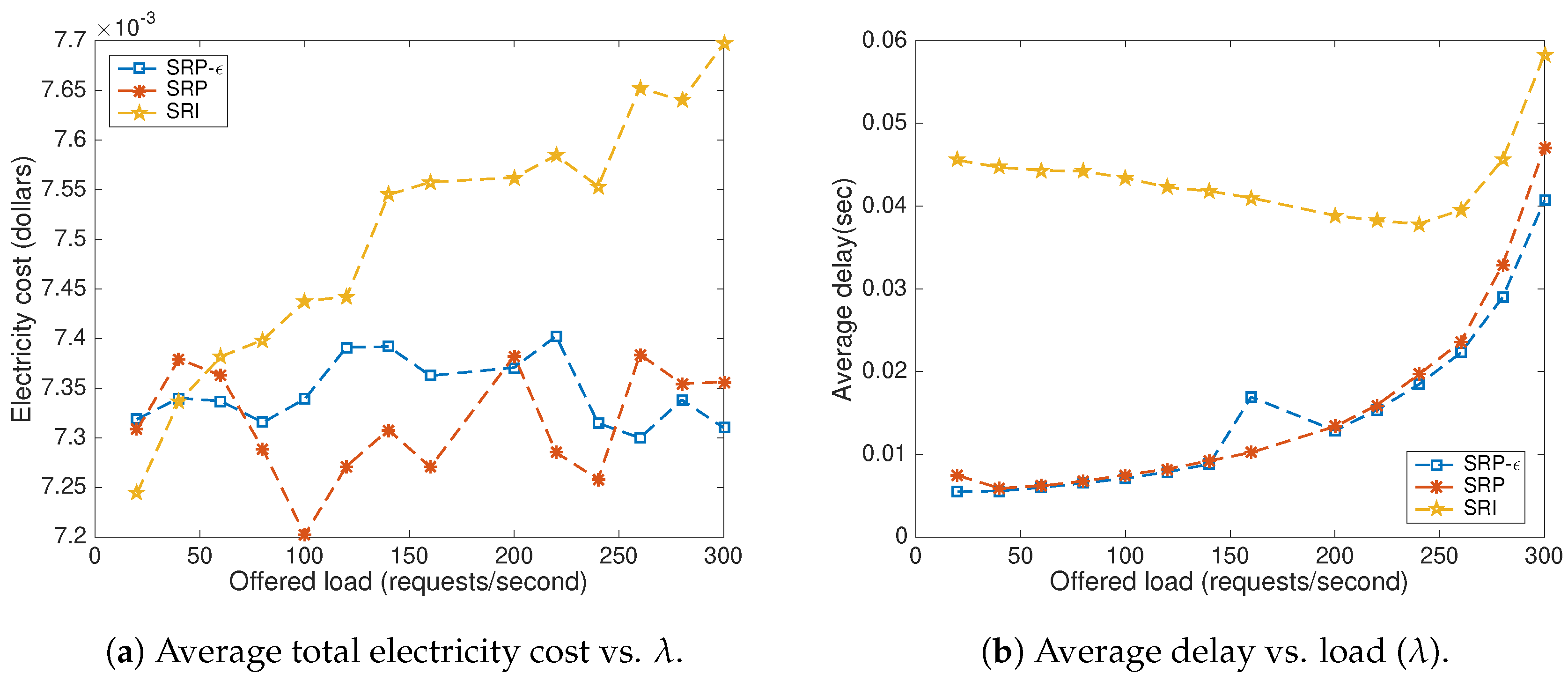
6.1. Parameters a and b
6.2. Parameter
6.3. Parameter
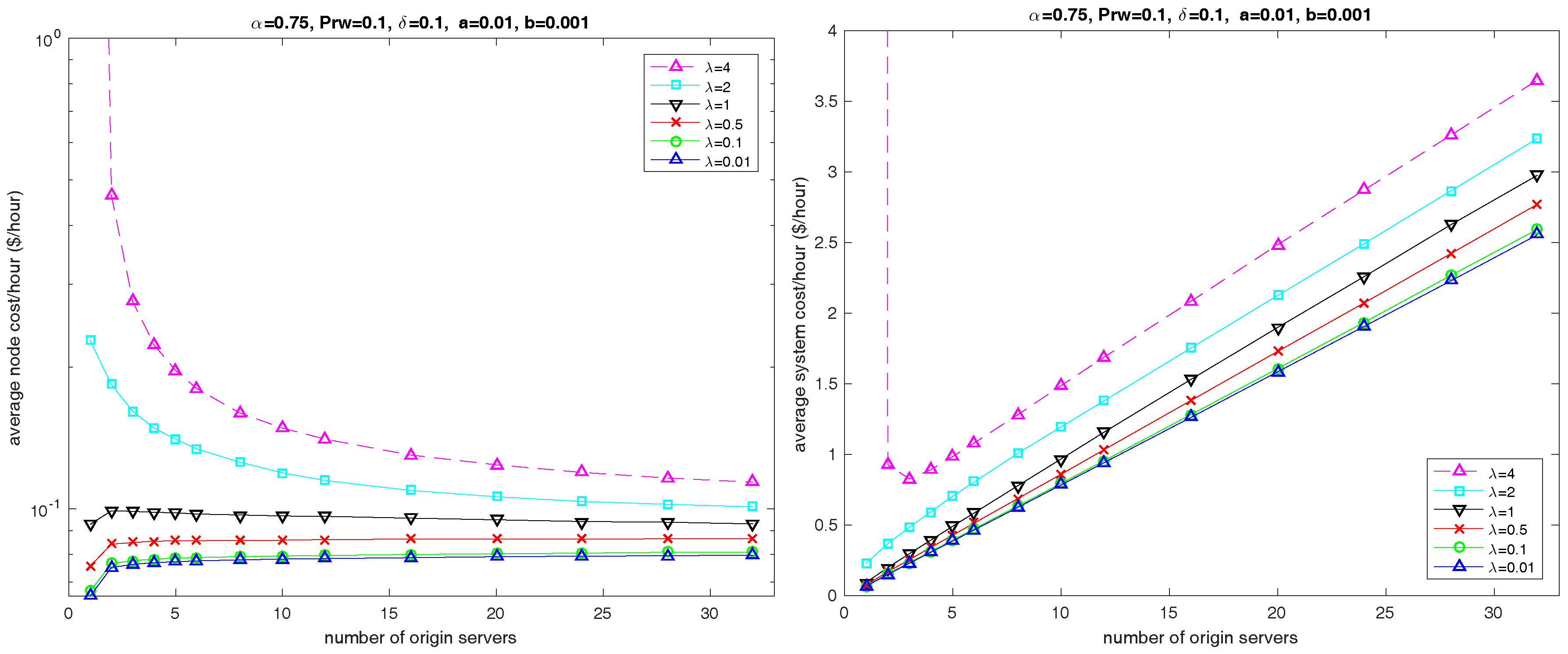
6.4. Number of Servers
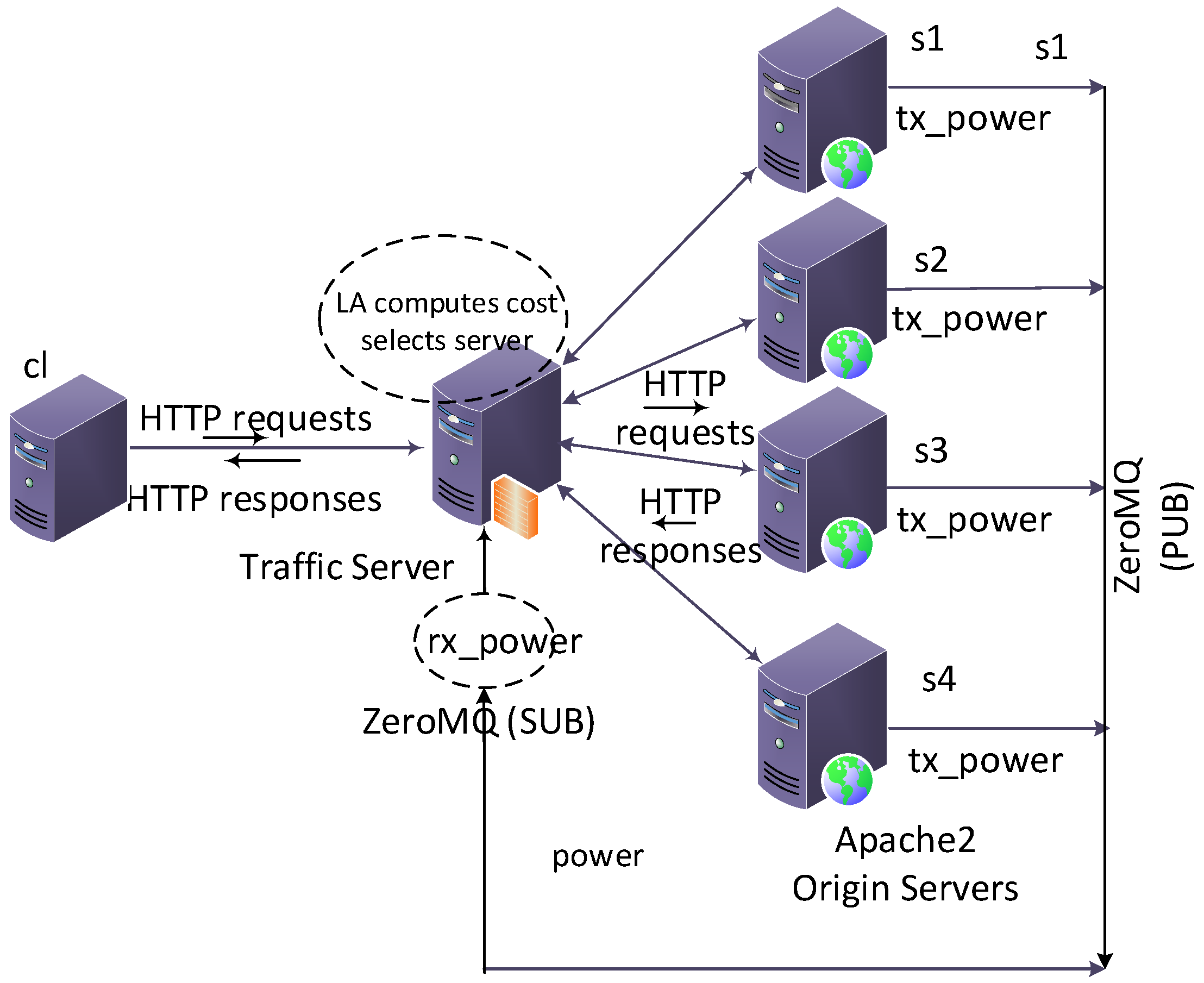
7. Testbed Evaluation
8. Results
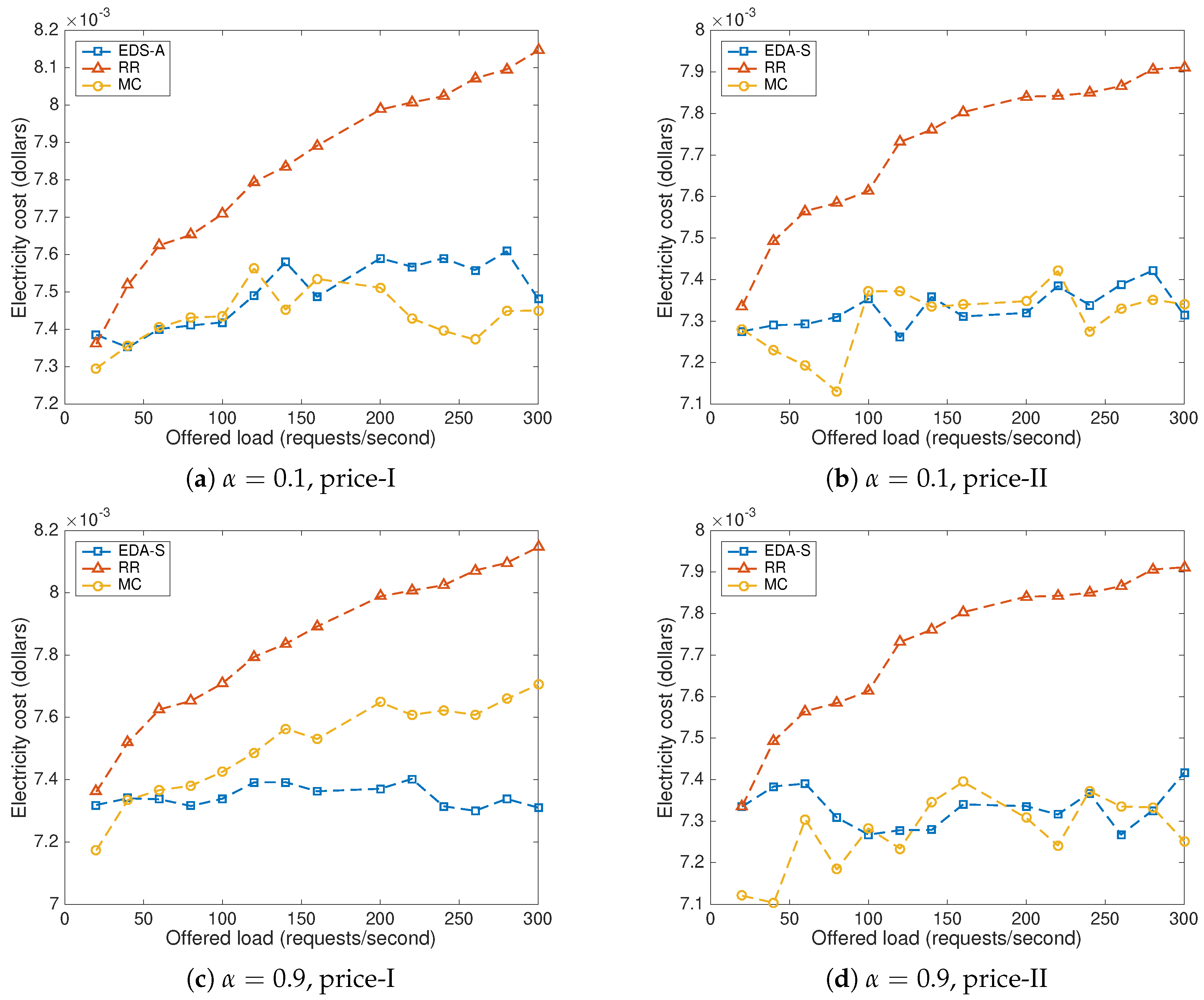
8.1. Baseline Methods
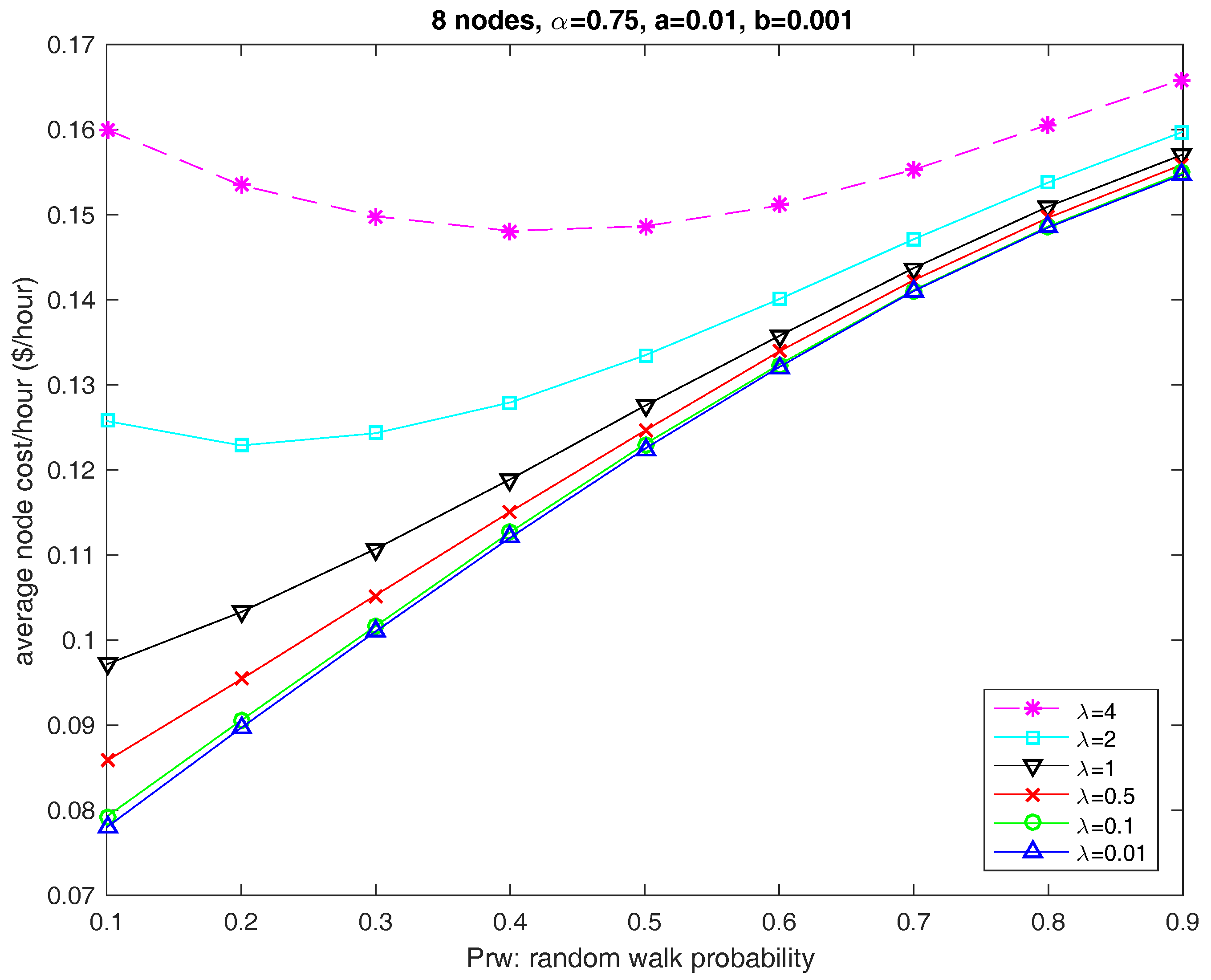
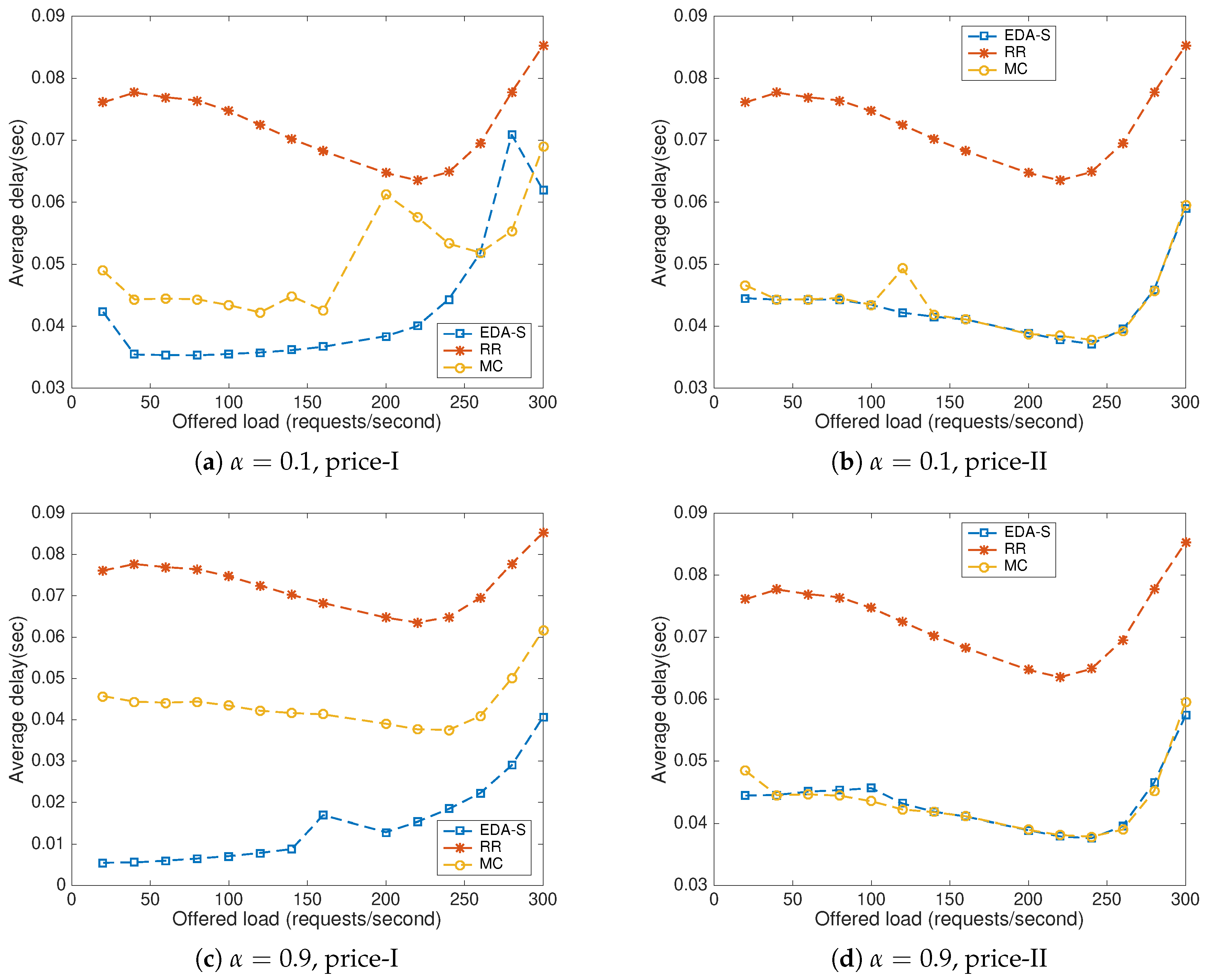
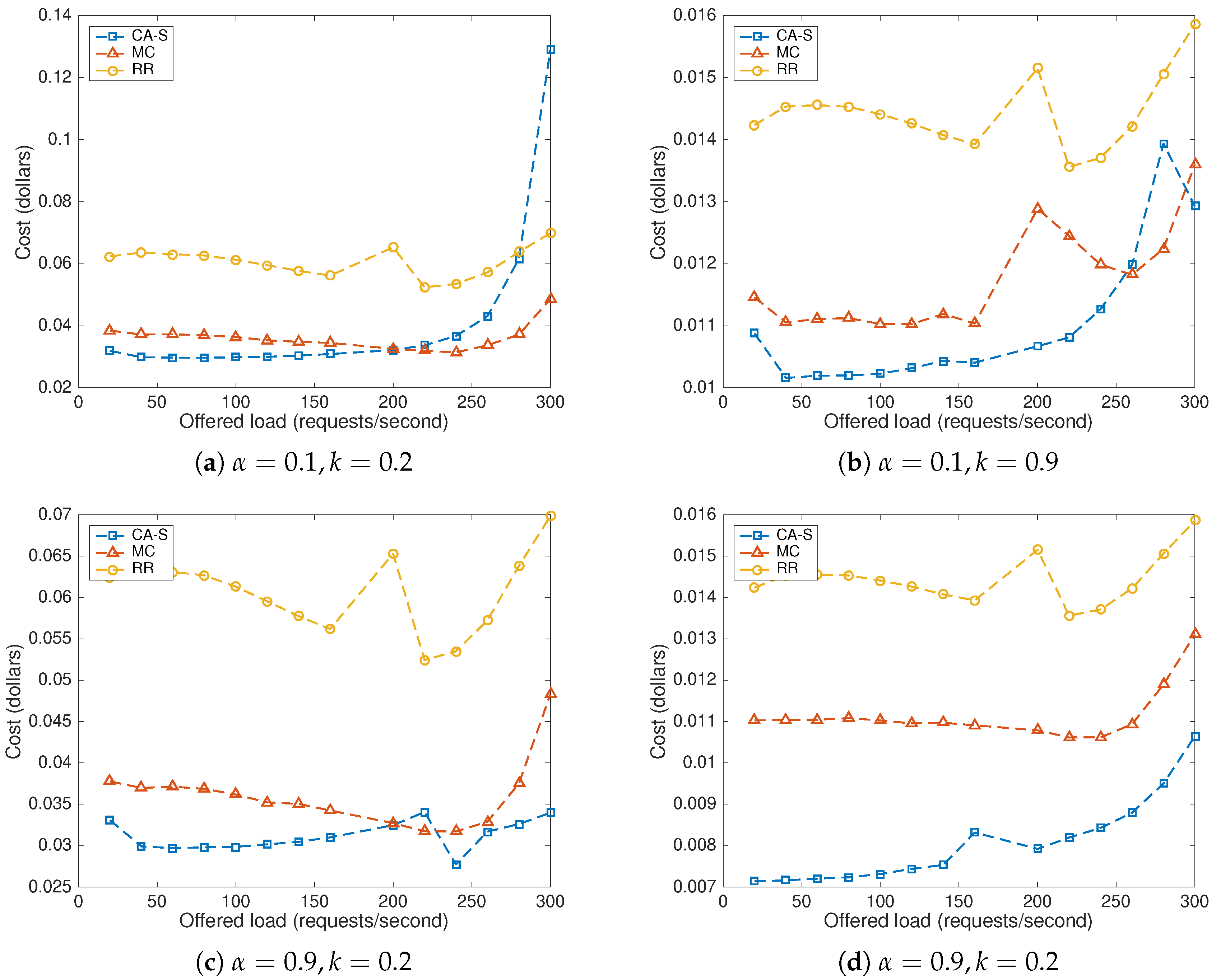
8.2. Impact of the Offered Load and the Price Scenario
8.3. Parameter b
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fleisch, E. What is the Internet of things? An economic perspective. Econ. Manag. Financ. Mark. 2010, 5, 125–157. [Google Scholar]
- Cisco. The Zettabyte Era: Trends and Analysis. 2017. Available online: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/visual-networking-index-vni/vni-hyperconnectivity-wp.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2018).
- Whitney, J.; Delforge, P. Data Center Efficiency Assessment; Issue paper on NRDC (The Natural Resource Defense Council); NRDC: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Energy. United States Electricity Industry Primer. 2015. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2015/12/f28/united-states-electricity-industry-primer.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2017).
- Energy Primer. 2015. Available online: https://www.ferc.gov/market-oversight/guide/energy-primer.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2017).
- CloudLab. Available online: https://www.cloudlab.us/index.php (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Qureshi, A.; Weber, R.; Balakrishnan, H.; Guttag, J.; Maggs, B. Cutting the electric bill for internet-scale systems. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, Barcelona, Spain, 16–21 August 2009; Volume 39, pp. 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Sankaranarayanan, A.N.; Sharangi, S.; Fedorova, A. Global cost diversity aware dispatch algorithm for heterogeneous data centers. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM/SPEC International Conference on Performance Engineering, Karlsruhe, Germany, 14–16 March 2011; Volume 36, pp. 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, J.; Shorten, R.; O’Mahony, D. Stratus: Load balancing the cloud for carbon emissions control. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2013, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojevic, R.; Shorten, R. Distributed dynamic speed scaling. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM, San Diego, CA, USA, 14–19 March 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, L.; Liu, X.; Xie, L.; Liu, W. Minimizing electricity cost: Optimization of distributed internet data centers in a multi-electricity-market environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM, San Diego, CA, USA, 14–19 March 2010; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, L.; Liu, X.; Ilic, M.D.; Liu, J. Distributed coordination of internet data centers under multiregional electricity markets. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 269–282. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Rao, L.; Liu, X.; D-pro, Y.Q. dynamic data center operations with demand-responsive electricity prices in smart grid. Smart Grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yang, S.; Yang, X.; Yu, W.; Lin, J. Energy-efficient Geo-Distributed Big Data Analytics. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1708.03184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, P. Joint bidding and geographical load balancing for datacenters: Is uncertainty a blessing or a curse? In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2017—IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Atlanta, GA, USA, 1–4 May 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, M.; Wierman, A.; Low, S.H.; Andrew, L.L. Geographical load balancing with renewables. ACM SIGMETRICS Perform. Eval. Rev. 2011, 39, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiriani, N.; Kesidis, G.; Wang, D. Optimal Peak Shaving Using Batteries at Datacenters: Characterizing the Risks and Benefits. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 25th International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis, and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems (MASCOTS), Banff, AB, Canada, 20–22 September 2017; pp. 164–174. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Liu, Z.; Wierman, A.; Andrew, L.L. Online algorithms for geographical load balancing. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Green Computing Conference (IGCC), San Jose, CA, USA, 4–8 June 2012; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Toosi, A.N.; Buyya, R. A fuzzy logic-based controller for cost and energy efficient load balancing in geo-distributed data centers. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/ACM 8th International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing (UCC), Limassol, Cyprus, 7–10 December 2015; pp. 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Toosi, A.N.; Qu, C.; de Assunção, M.D.; Buyya, R. Renewable-aware geographical load balancing of web applications for sustainable data centers. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 83, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, M.; Wierman, A.; Low, S.; Andrew, L.L. Greening geographical load balancing. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. (TON) 2015, 23, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Qi, Y.; Wei, W.; Song, H. A two-time-scale load balancing framework for minimizing electricity bills of internet data centers. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2016, 20, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, K.; Li, P.; Xia, R.; Guo, S.; Guo, M. Renewable Energy-Aware Big Data Analytics in Geo-distributed Data Centers with Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Zhong, W.D.; Bose, S.K. Energy Aware Pricing in a Three-Tiered Cloud Service Market. Electronics 2016, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, K.S.; Thathachar, M.A. Learning Automata: An Introduction; Courier Corporation: Mineola, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Narendra, K.S.; Thathachar, M.A. Learning automata—A survey. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1974, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Introduction to Reinforcement Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; Volume 135. [Google Scholar]
- Oommen, B.J.; Thathachar, M. Multiaction learning automata possessing ergodicity of the mean. Inf. Sci. 1985, 35, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oommen, B.J.; Hansen, E. The asymptotic optimality of discretized linear reward-inaction learning automata. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1984, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnoommen, B. Absorbing and ergodic discretized two-action learning automata. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1986, 16, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendra, K.S.; Thathachar, M.A. On the behavior of a learning automaton in a changing environment with application to telephone traffic routing. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1980, 10, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economides, A.; Silvester, J. Optimal routing in a network with unreliable links. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Networking Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 11–13 April 1988; pp. 288–297. [Google Scholar]
- Nedzelnitsky, O.V.; Narendra, K.S. Nonstationary models of learning automata routing in data communication networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1987, 17, 1004–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakos, A.V.; Moschonas, C.A.; Paximadis, C.T. Variable window flow control and ergodic discretized learning algorithms for adaptive routing in data networks. Comput. Netw. ISDN Syst. 1991, 22, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakos, A.V. Nonlinear ergodic ε-optimal discretized reward-penalty learning automata and their application to adaptive routing algorithms. Neurocomputing 1991, 3, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, Z.; Movaghar, A.; Hoseinzadeh, M. A learning automata and clustering-based routing protocol for named data networking. Telecommun. Syst. 2017, 65, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Chilamkurti, N.; Rodrigues, J.J. Learning automata-based opportunistic data aggregation and forwarding scheme for alert generation in vehicular ad hoc networks. Comput. Commun. 2014, 39, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardo, G.; Riska, A.; Smirni, E. EQUILOAD: A load balancing policy for clustered web servers. Perform. Eval. 2001, 46, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nuaimi, K.; Mohamed, N.; Al Nuaimi, M.; Al-Jaroodi, J. A survey of load balancing in cloud computing: Challenges and algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2012 Second Symposium on Network Cloud Computing and Applications, London, UK, 3–4 December 2012; pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, S.; Shah, M.A. Load balancing algorithms in cloud computing: A survey of modern techniques. In Proceedings of the 2015 National Software Engineering Conference (NSEC), Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 17 December 2015; pp. 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Mesbahi, M.; Rahmani, A.M. Load balancing in cloud computing: a state of the art survey. Int. J. Mod. Educ. Comput. Sci. 2016, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Thayananthan, V.; Katib, I. Analysis of round-robin load-balancing algorithm with adaptive and predictive approaches. In Proceedings of the 2016 UKACC 11th International Conference on Control (CONTROL), Belfast, UK, 31 August–2 September 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- EIA. Electric Power Monthly. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/electricity/monthly/epm_table_grapher.php?t=epmt_5_6_a (accessed on 24 May 2018).

| Scenario | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | ||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Velusamy, G.; Lent, R. Dynamic Cost-Aware Routing of Web Requests. Future Internet 2018, 10, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi10070057
Velusamy G, Lent R. Dynamic Cost-Aware Routing of Web Requests. Future Internet. 2018; 10(7):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi10070057
Chicago/Turabian StyleVelusamy, Gandhimathi, and Ricardo Lent. 2018. "Dynamic Cost-Aware Routing of Web Requests" Future Internet 10, no. 7: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi10070057
APA StyleVelusamy, G., & Lent, R. (2018). Dynamic Cost-Aware Routing of Web Requests. Future Internet, 10(7), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi10070057





