Modeling of Body Weight Metrics for Effective and Cost-Efficient Conventional Factor VIII Dosing in Hemophilia A Prophylaxis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Population Generation
2.2. Definitions of Weight Metrics
- Lean body weight (LBW) [29]
- Ideal body weight (IBW—Lorentz formula)
- Adjusted body weight (ABW)
2.3. Population Pharmacokinetic Model
2.4. Simulation and Assessment of Treatment Regimens
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Den Uijl, I.E.; Mauser Bunschoten, E.P.; Roosendaal, G.; Schutgens, R.E.; Biesma, D.H.; Grobbee, D.E.; Fischer, K. Clinical severity of haemophilia A: Does the classification of the 1950s still stand? Haemophilia 2011, 17, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manco-Johnson, M.J.; Abshire, T.C.; Shapiro, A.D.; Riske, B.; Hacker, M.R.; Kilcoyne, R.; Ingram, J.D.; Manco-Johnson, M.L.; Funk, S.; Jacobson, L.; et al. Prophylaxis versus episodic treatment to prevent joint disease in boys with severe hemophilia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.; Collins, P.W.; Ozelo, M.C.; Srivastava, A.; Young, G.; Blanchette, V.S. When and how to start prophylaxis in boys with severe hemophilia without inhibitors: Communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berntorp, E.; Spotts, G.; Patrone, L.; Ewenstein, B.M. Advancing personalized care in hemophilia A: Ten years’ experience with an advanced category antihemophilic factor prepared using a plasma/albumin-free method. Biologics 2014, 8, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrini, P. Identifying and overcoming barriers to prophylaxis in the management of haemophilia. Haemophilia 2007, 13 (Suppl. 2), 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenburg, J. Optimal treatment strategies for hemophilia: Achievements and limitations of current prophylactic regimens. Blood 2015, 125, 2038–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkman, S.; Folkesson, A.; Jonsson, S. Pharmacokinetics and dose requirements of factor VIII over the age range 3–74 years: A population analysis based on 50 patients with long-term prophylactic treatment for haemophilia A. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, M.; Berntorp, E.; Bjorkman, S.; Lethagen, S.; Ljung, R. Improved cost-effectiveness by pharmacokinetic dosing of factor VIII in prophylactic treatment of haemophilia A. Haemophilia 1997, 3, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, A.; Keepanasseril, A.; Foster, G.; Navarro-Ruan, T.; McEneny-King, A.; Edginton, A.N.; Thabane, L. WAPPS-Hemo co-investigator network Development of a Web-Accessible Population Pharmacokinetic Service-Hemophilia (WAPPS-Hemo): Study Protocol. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2016, 5, e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEneny-King, A.; Foster, G.; Iorio, A.; Edginton, A.N. Data Analysis Protocol for the Development and Evaluation of Population Pharmacokinetic Models for Incorporation into the Web-Accessible Population Pharmacokinetic Service—Hemophilia (WAPPS-Hemo). JMIR Res. Protoc. 2016, 5, e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingram, G.I. Calculating the dose of factor VIII in the management of haemophilia. Br. J. Haematol. 1981, 48, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, M.C.; Lee, A. Individualized prophylaxis for optimizing hemophilia care: Can we apply this to both developed and developing nations? Thromb. J. 2016, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullman, M.; Zhang, Q.C.; Brown, D.; Grant, A.; Soucie, J.M. Hemophilia Treatment Center Network Investigators Association of overweight and obesity with the use of self and home-based infusion therapy among haemophilic men. Haemophilia 2014, 20, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revel-Vilk, S.; Komvilaisak, P.; Blanchette, V.; Stain, A.M.; Floros, G.; Cochrane, A.; Blanchette, C.; Hang, M.; Roberts, E.A.; Ling, S.C. The changing face of hepatitis in boys with haemophilia associated with increased prevalence of obesity. Haemophilia 2011, 17, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, G. New challenges in hemophilia: Long-term outcomes and complications. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2012, 2012, 362–368. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, A.D.; Korth-Bradley, J.; Poon, M.C. Use of pharmacokinetics in the coagulation factor treatment of patients with haemophilia. Haemophilia 2005, 11, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrard, S.; Speybroeck, N.; Hermans, C. Impact of being underweight or overweight on factor VIII dosing in hemophilia A patients. Haematologica 2013, 98, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeay, S.C.; Morrish, G.A.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.; Green, B. The relationship between drug clearance and body size: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature published from 2000 to 2007. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheymol, G. Effects of obesity on pharmacokinetics implications for drug therapy. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2000, 39, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, M.J.; Abernethy, D.R.; Greenblatt, D.J. Effect of obesity on the pharmacokinetics of drugs in humans. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkman, S.; Oh, M.; Spotts, G.; Schroth, P.; Fritsch, S.; Ewenstein, B.M.; Casey, K.; Fischer, K.; Blanchette, V.S.; Collins, P.W. Population pharmacokinetics of recombinant factor VIII: The relationships of pharmacokinetics to age and body weight. Blood 2012, 119, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, R.; Lemaire, M.; Steimer, J.L.; Bruelisauer, A.; Niederberger, W.; Rowland, M. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic study on a cyclosporin derivative, SDZ IMM 125. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1994, 22, 327–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuinenburg, A.; Biere-Rafi, S.; Peters, M.; Verhamme, P.; Peerlinck, K.; Kruip, M.J.; Laros-Van Gorkom, B.A.; Roest, M.; Meijers, J.C.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; et al. Obesity in haemophilia patients: Effect on bleeding frequency, clotting factor concentrate usage, and haemostatic and fibrinolytic parameters. Haemophilia 2013, 19, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, B.N.; Bork, S.J.; Kim, S.; Moffett, B.S.; Yee, D.L. Evaluation of weight-based dosing of unfractionated heparin in obese children. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risebrough, N.; Oh, P.; Blanchette, V.; Curtin, J.; Hitzler, J.; Feldman, B.M. Cost-utility analysis of Canadian tailored prophylaxis, primary prophylaxis and on-demand therapy in young children with severe haemophilia A. Haemophilia 2008, 14, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.A.; Zhou, Z.Y. Costs of Care in Hemophilia and Possible Implications of Health Care Reform. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2011, 1, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, S.; Ostrenga, A.; Latzman, R.D.; Payne, C.; Hunt, Q.; Morris, A.; Iyer, R. Pharmacoeconomic impact of obesity in severe haemophilia children on clotting factor prophylaxis in a single institution. Haemophilia 2011, 17, 717–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryar, C.D.; Gu, Q.; Ogden, C.L.; Flegal, K.M. Anthropometric Reference Data for Children and Adults: United States, 2011–2014. Vital Health Stat. 3 2016, 39, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Janmahasatian, S.; Duffull, S.B.; Ash, S.; Ward, L.C.; Byrne, N.M.; Green, B. Quantification of lean bodyweight. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, B.; Duffull, S.B. What is the best size descriptor to use for pharmacokinetic studies in the obese? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 58, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garmann, D.; McLeay, S.; Shah, A.; Vis, P.; Maas Enriquez, M.; Ploeger, B.A. Population pharmacokinetic characterization of BAY 81–8973, a full-length recombinant factor VIII: Lessons learned—Importance of including samples with factor VIII levels below the quantitation limit. Haemophilia 2017, 23, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.W.; Blanchette, V.S.; Fischer, K.; Bjorkman, S.; Oh, M.; Fritsch, S.; Schroth, P.; Spotts, G.; Astermark, J.; Ewenstein, B. Break-through bleeding in relation to predicted factor VIII levels in patients receiving prophylactic treatment for severe hemophilia A. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.; Faradji, A.; Morfini, M.; Enriquez, M.M.; Schwartz, L. Efficacy and safety of secondary prophylactic vs. on-demand sucrose-formulated recombinant factor VIII treatment in adults with severe hemophilia A: Results from a 13-month crossover study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.W.; Fischer, K.; Morfini, M.; Blanchette, V.S.; Bjorkman, S.; International Prophylaxis Study Group Pharmacokinetics Expert Working Group. Implications of coagulation factor VIII and IX pharmacokinetics in the prophylactic treatment of haemophilia. Haemophilia 2011, 17, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, M.; Williams, M.; Chalmers, E.; Liesner, R.; Collins, P.; Vidler, V.; Hanley, J. Paediatric Working Party of the United Kingdom Haemophilia Doctors’ Organisation A United Kingdom Haemophilia Centre Doctors’ Organization guideline approved by the British Committee for Standards in Haematology: Guideline on the use of prophylactic factor VIII concentrate in children and adults with severe haemophilia A. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.D. Long-lasting recombinant factor VIII proteins for hemophilia A. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2013, 2013, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrowcliffe, T.W. Monitoring haemophilia severity and treatment: New or old laboratory tests? Haemophilia 2004, 10 (Suppl. 4), 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.W.; Bjorkman, S.; Fischer, K.; Blanchette, V.; Oh, M.; Schroth, P.; Fritsch, S.; Casey, K.; Spotts, G.; Ewenstein, B.M. Factor VIII requirement to maintain a target plasma level in the prophylactic treatment of severe hemophilia A: Influences of variance in pharmacokinetics and treatment regimens. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljung, R. Aspects of prophylactic treatment of hemophilia. Thromb. J. 2016, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.C.; Yang, M.; Minuk, L.; Sholzberg, M.; St-Louis, J.; Iorio, A.; Card, R.; Poon, M.C. Prophylaxis in older Canadian adults with hemophilia A: Lessons and more questions. BMC Hematol. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenburg, J.; Brackmann, H.H. Prophylaxis in adult patients with severe haemophilia A. Thromb. Res. 2014, 134 (Suppl. 1), S33–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, A.; Jaworski, K. Pharmacokinetic analysis of anti-hemophilic factor in the obese patient. Haemophilia 2014, 20, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komwilaisak, P.; Blanchette, V. Pharmacokinetic studies of coagulation factors: Relevance of plasma and extracellular volume and body weight. Haemophilia 2006, 12 (Suppl. 4), 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
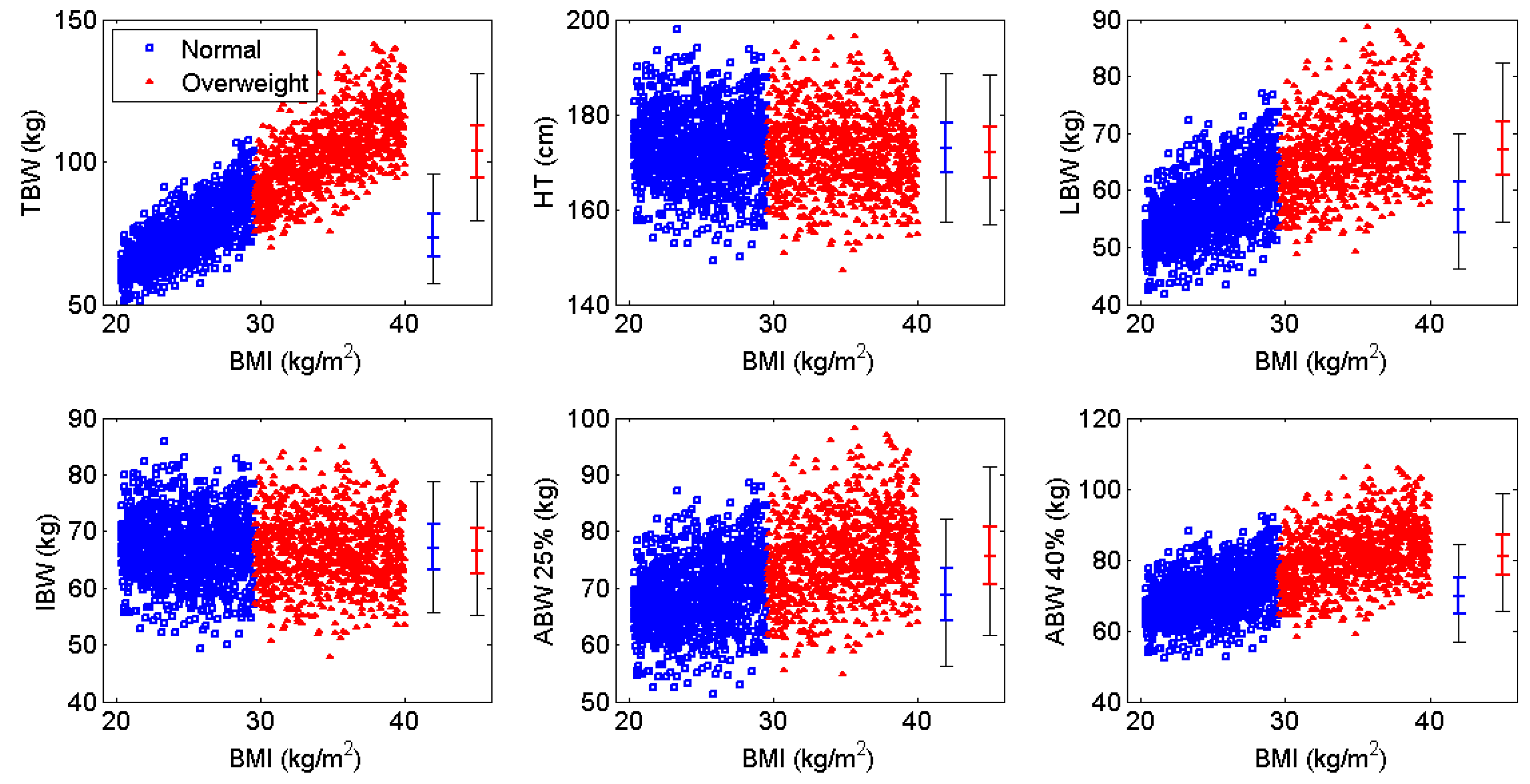
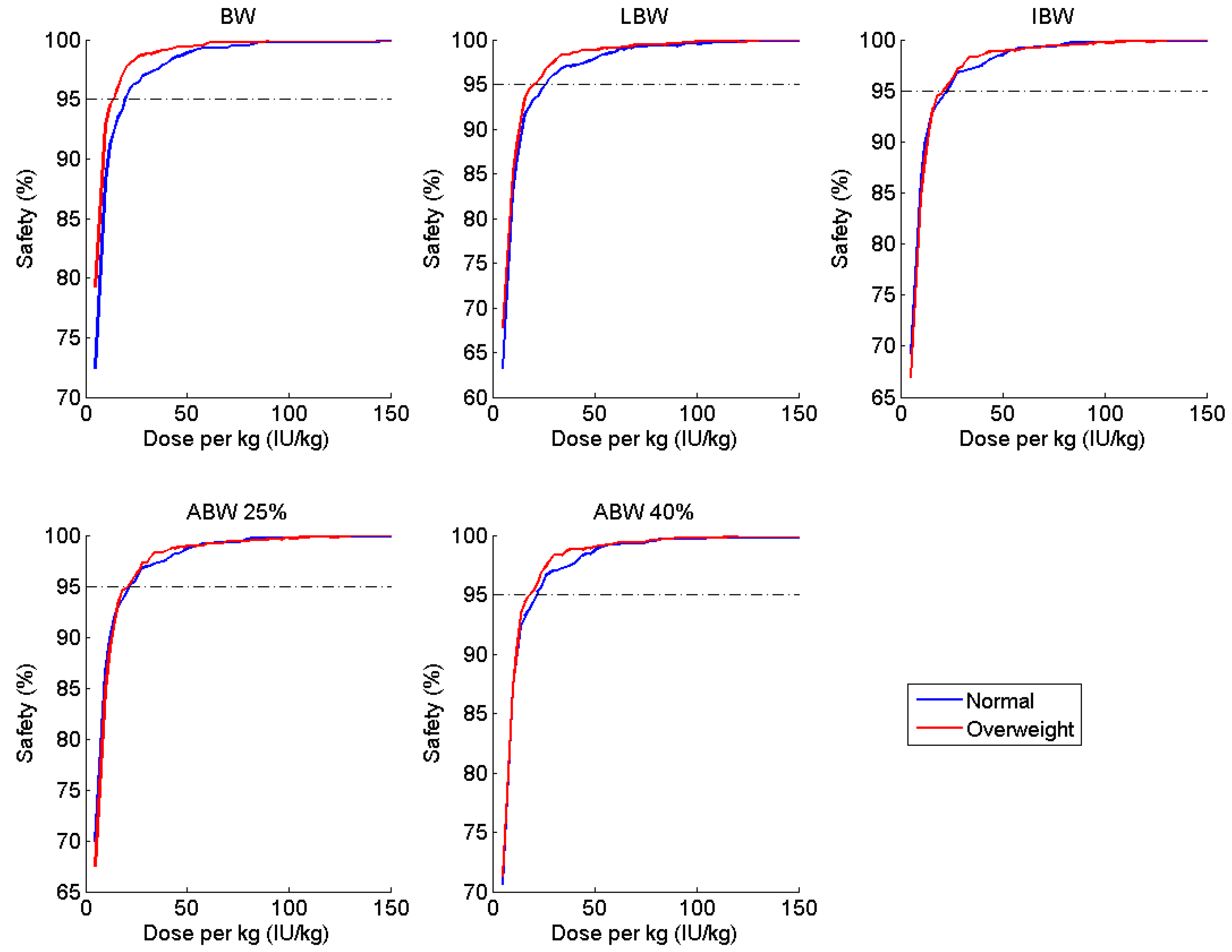

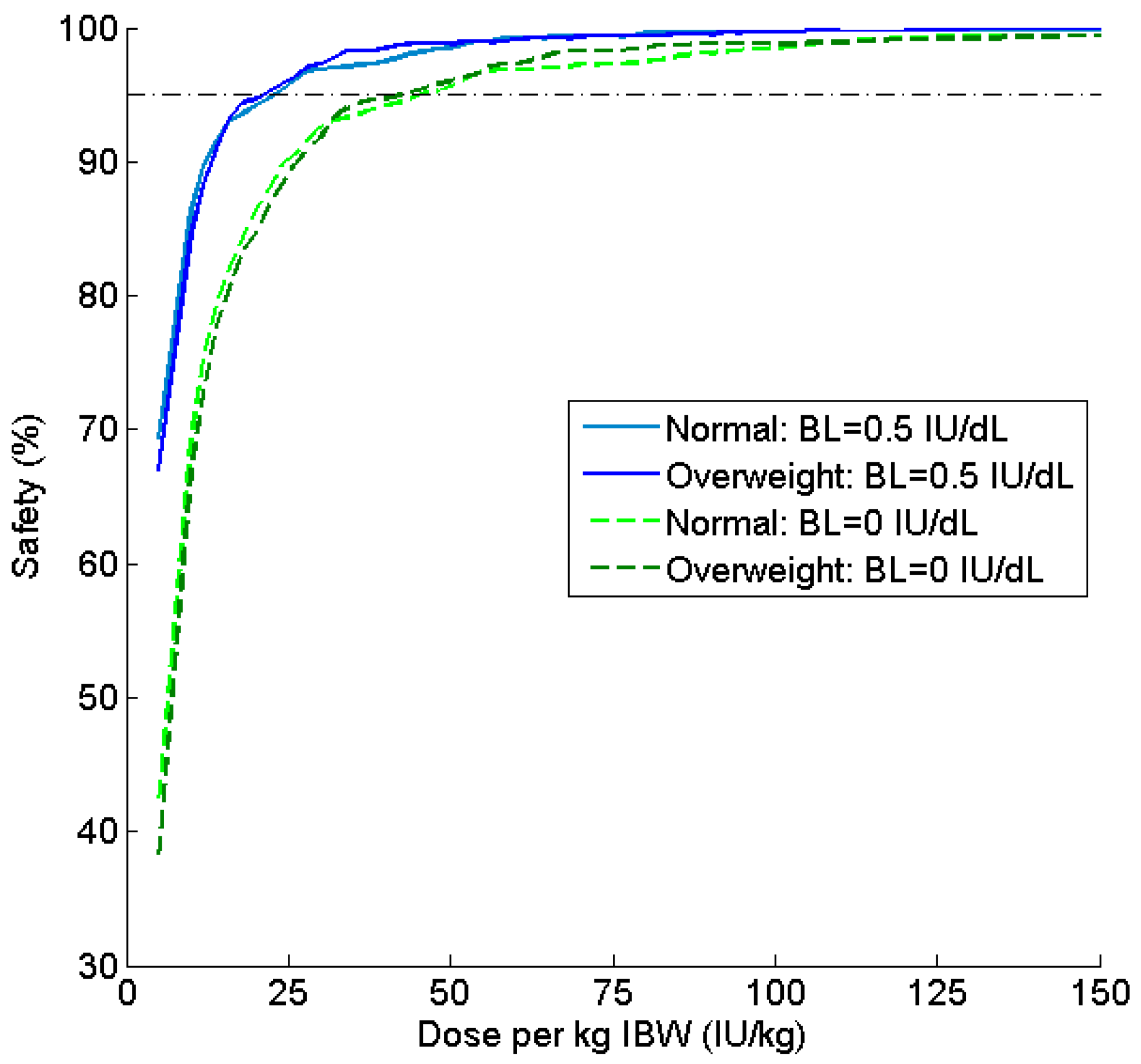
| Parameter | Estimate | Covariate Effect | BSV (%CV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CL (dL∙h−1) | 1.88 | 37.0 | |
| Q (dL∙h−1) | 1.90 | ||
| V1 (dL) | 30.0 | 11.2 | |
| V2 (dL) | 6.37 | ||
| Proportional RUV (%CV) | 26.7 | ||
| Additive RUV (IU dL−1) | 1.10 |
| Measure | Regimen | |
|---|---|---|
| 20 IU kg−1 TBW, Q48 h | 14 IU kg−1 TBW, Q48 h | |
| Cmin (IU dL−1) | 5.4 (1.2–17.3) | 3.9 (1.0–12.3) |
| Consumption (IU per person per week) | 7260 (5730–8780) | 5080 (4010–6140) |
| Metric | Normal | Overweight and Obese | All BMI Categories | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose (IU kg−1) | Mean Consumption (IU per Person per Week) | Dose (IU kg−1) | Consumption (IU per Person per Week) | Dose (IU kg−1) | Mean Consumption (IU per Person per Week) | Difference in Consumption from TBW | |
| TBW | 20.0 | 5202 | 14.0 | 5074 | 18.0 | 5603 | - |
| LBW | 25.6 | 5114 | 21.3 | 5028 | 23.8 | 5186 | −417 |
| IBW | 22.2 | 5222 | 20.7 | 4828 | 22.1 | 5176 | −427 |
| ABW25 | 21.7 | 5239 | 20.0 | 5311 | 20.4 | 5171 | −432 |
| ABW40 | 21.1 | 5173 | 18.0 | 5129 | 20.0 | 5301 | −302 |
| Metric | Normal | Overweight and Obese | All BMI Categories | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose (IU kg−1) | Consumption (IU per Person per Week) | Dose (IU kg−1) | Consumption (IU per Person per Week) | Dose (IU kg−1) | Consumption (IU per Person per Week) | Difference in Consumption from TBW | |
| TBW | 74 | 8174 | 54 | 9320 | 62 | 8716 | - |
| LBW | 94 | 8082 | 82 | 8740 | 88 | 8442 | −274 |
| IBW | 78 | 8213 | 84 | 8543 | 80 | 8312 | −404 |
| ABW25 | 78 | 8195 | 72 | 8558 | 76 | 8459 | −258 |
| ABW40 | 76 | 8126 | 68 | 8792 | 72 | 8481 | −235 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McEneny-King, A.; Chelle, P.; Henrard, S.; Hermans, C.; Iorio, A.; Edginton, A.N. Modeling of Body Weight Metrics for Effective and Cost-Efficient Conventional Factor VIII Dosing in Hemophilia A Prophylaxis. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics9040047
McEneny-King A, Chelle P, Henrard S, Hermans C, Iorio A, Edginton AN. Modeling of Body Weight Metrics for Effective and Cost-Efficient Conventional Factor VIII Dosing in Hemophilia A Prophylaxis. Pharmaceutics. 2017; 9(4):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics9040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcEneny-King, Alanna, Pierre Chelle, Severine Henrard, Cedric Hermans, Alfonso Iorio, and Andrea N. Edginton. 2017. "Modeling of Body Weight Metrics for Effective and Cost-Efficient Conventional Factor VIII Dosing in Hemophilia A Prophylaxis" Pharmaceutics 9, no. 4: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics9040047
APA StyleMcEneny-King, A., Chelle, P., Henrard, S., Hermans, C., Iorio, A., & Edginton, A. N. (2017). Modeling of Body Weight Metrics for Effective and Cost-Efficient Conventional Factor VIII Dosing in Hemophilia A Prophylaxis. Pharmaceutics, 9(4), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics9040047





