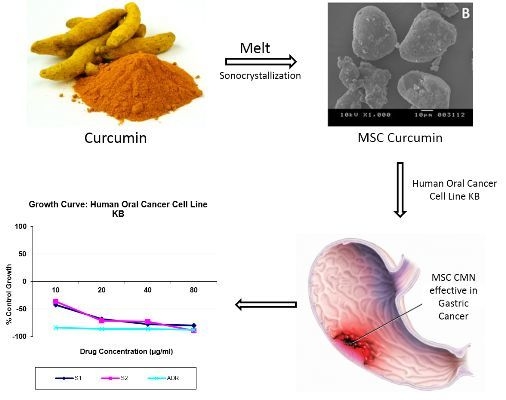
Product Development Studies on Sonocrystallized Curcumin for the Treatment of Gastric Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodologies
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methodologies
2.2.1. Preparation of Melt Sonocrystallized Form
2.2.2. Evaluation
Particle Size and Its Distribution
Flow Properties
Equilibrium Solubility
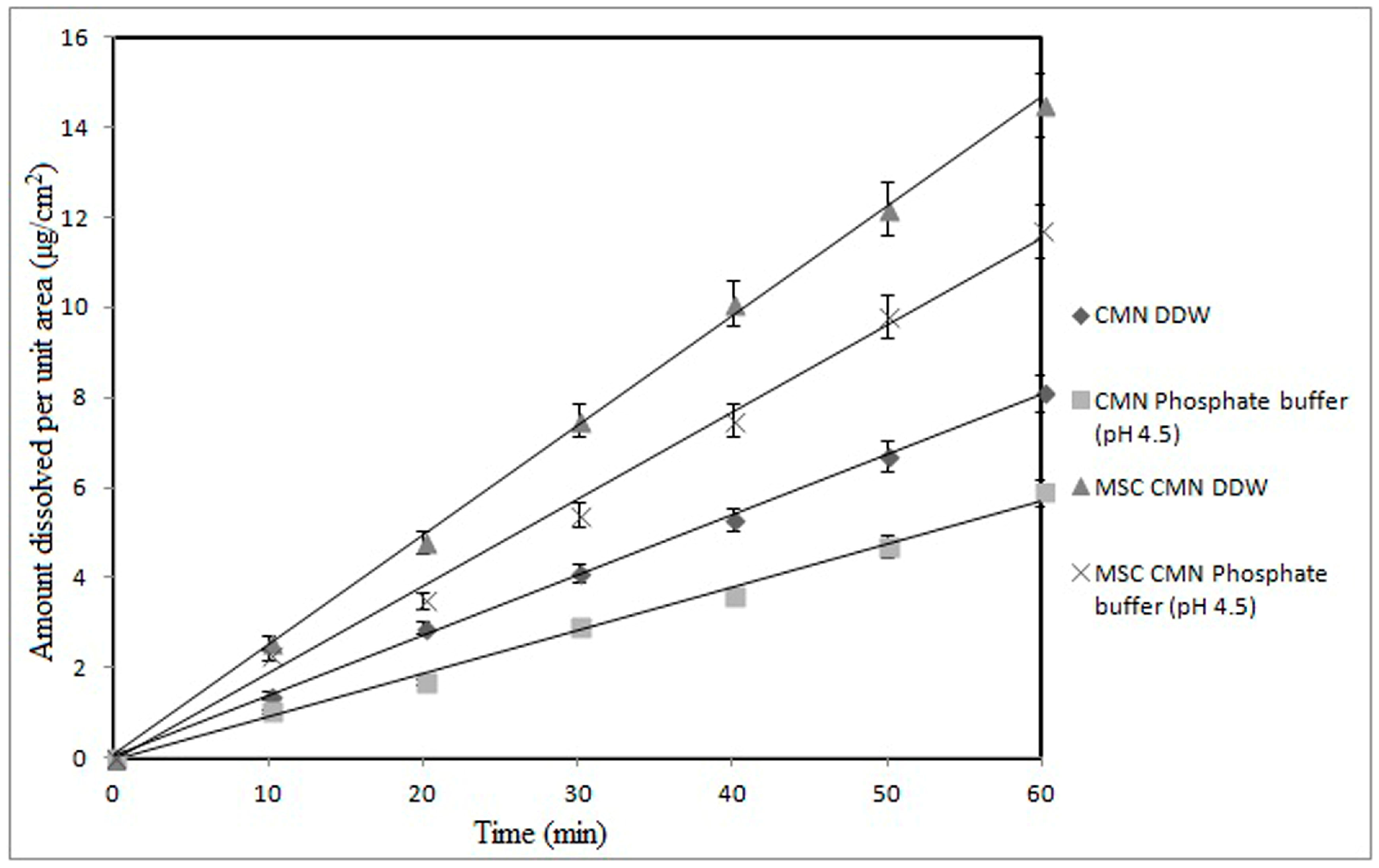
Intrinsic Dissolution Rate
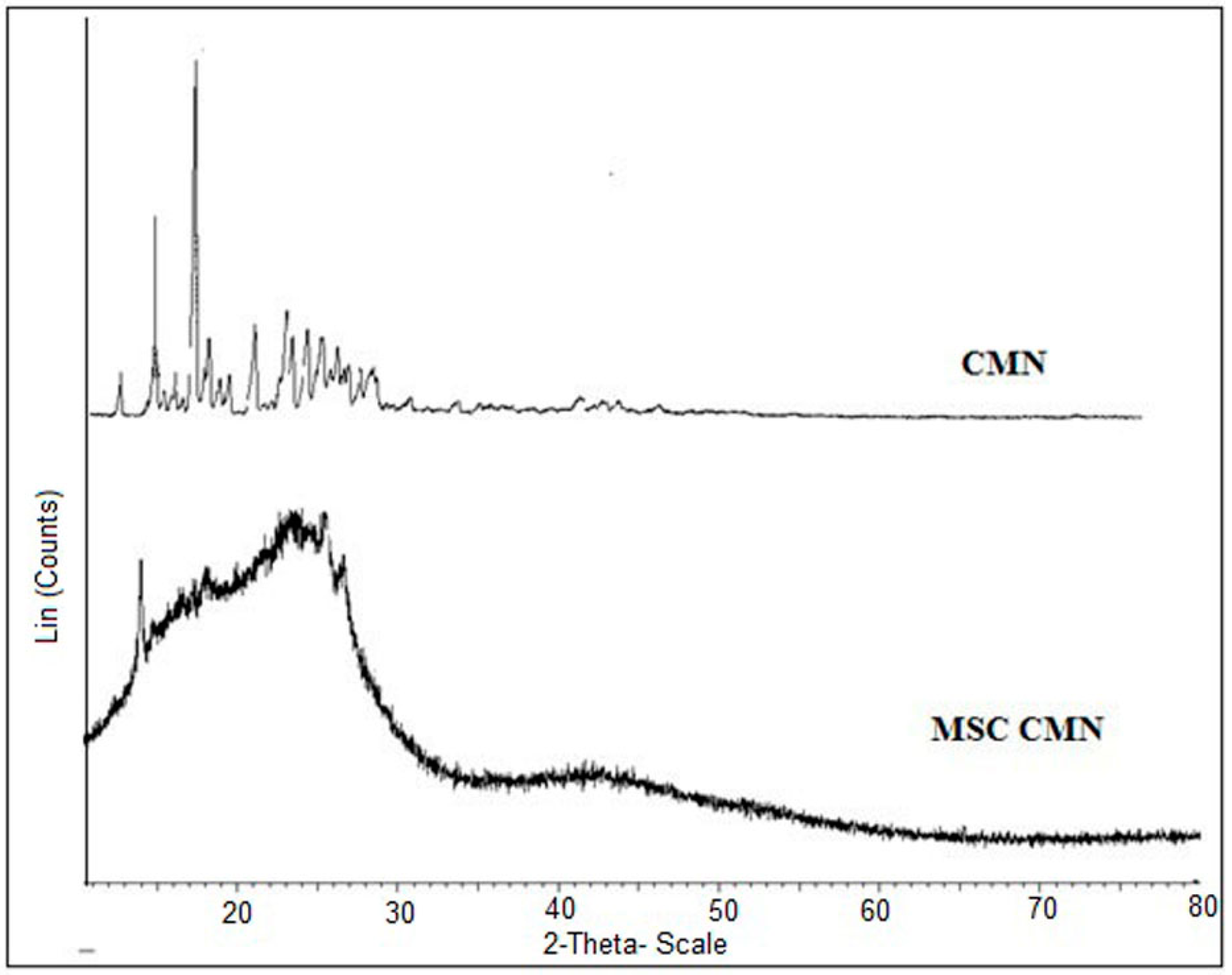
X-ray Diffraction
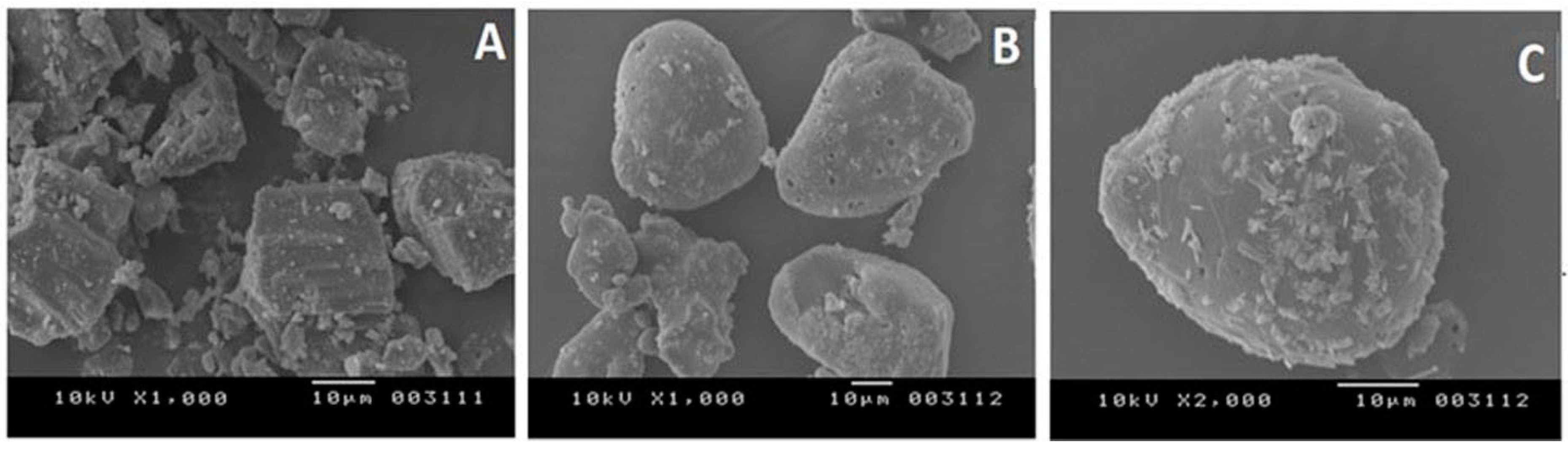
Scanning Electron Microscopy
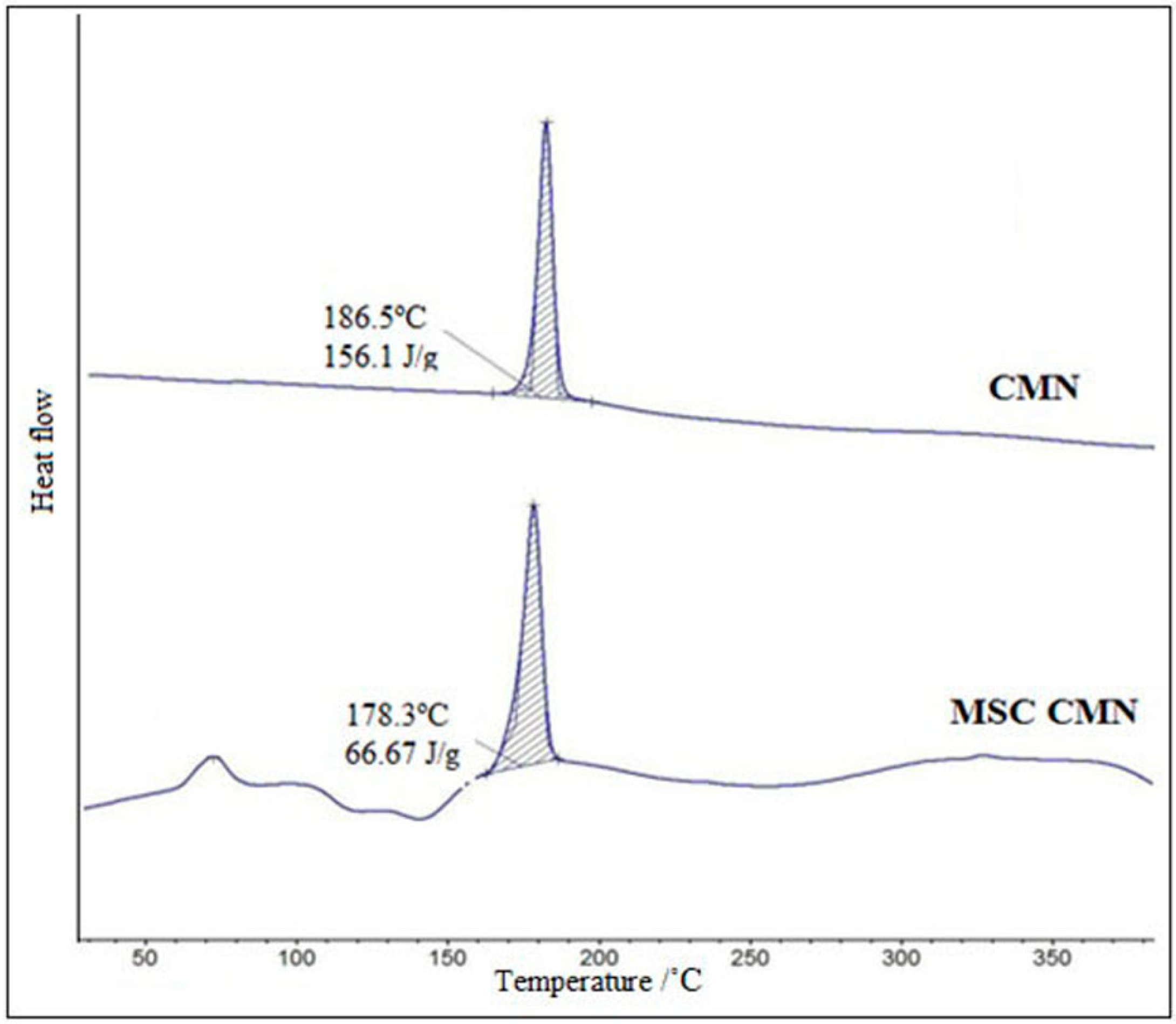
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
Fourier Transform Infra-Red Spectroscopy (FTIR)
In Vitro Cytotoxicity
2.2.3. Preparation of Floating Tablets of MSC CMN
| Code | Drug(mg) | HPMC K 15M (mg) | Sodium Alginate (mg) | Sodium Bicarbonate (mg) | Citric Acid (mg) | MCC PH101 (mg) | Magnesium Stearate (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 50 | 200 | – | 70 | – | 71 | 9 |
| F2 | 50 | – | 200 | 70 | – | 71 | 9 |
| F3 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 70 | – | 71 | 9 |
| F4 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 70 | 5 | 66 | 9 |
| CT | 50 | 100 | 100 | 70 | 5 | 66 | 9 |
2.2.4. Pharmacotechnical Characterization of Floating Tablets
Thickness, Hardness, Friability and Weight Variation
In Vitro Buoyancy
In Vitro Drug Release
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation
3.1.1. Particle Size and Its Distribution
| Parameter | CMN | MSC CMN | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean particle size (µm) | 30.10 | 13.44 | |
| Standard deviation (µm) | 22.57 | 9.646 | |
| Specific surface area (cm2/mL) | 6937 | 10730 | |
| Skewness | 0.922 | 1.320 | |
| Kurtosis | 0.290 | 2.154 | |
| IQCS | 0.203 | 0.166 | |
| Span | 63.43 | 26.04 | |
| Variance (µm2) | 509.4 | 93.04 | |
| Dynamic angle of repose (°) | 38.21 ± 1.53 | 21.67 ± 1.72 | |
| Density (g/cc) | Bulk density | 0.29 ± 1.48 | 0.49 ± 2.10 |
| Tapped density | 0.43 ± 1.26 | 0.53 ± 1.81 | |
| Carr’s Index (%) | 31.29 ± 1.62 | 18.49 ± 1.79 | |
| Hausner’s ratio | 1.46 ± 1.13 | 1.23 ± 1.70 | |
| Solubility (µg/mL) | Distilled water | 8.92 ± 1.41 | 21.14 ± 1.36 |
| Phosphate buffer, pH 4.5 | 6.301 ± 1.15 | 15.139 ± 1.23 | |
| Intrinsic dissolution rate (mg/cm2/min) | Distilled water | 0.135 ± 1.39 | 0.242 ± 1.42 |
| Phosphate buffer, pH 4.5 | 0.098 ± 1.50 | 0.195 ± 1.26 | |

3.1.2. Flow Properties
3.1.3. Equilibrium Solubility
3.1.4. Intrinsic Dissolution Rate
3.1.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.1.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy

3.1.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.1.8. Fourier Transformed Infra-Red Spectroscopy (FTIR)

3.1.9. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
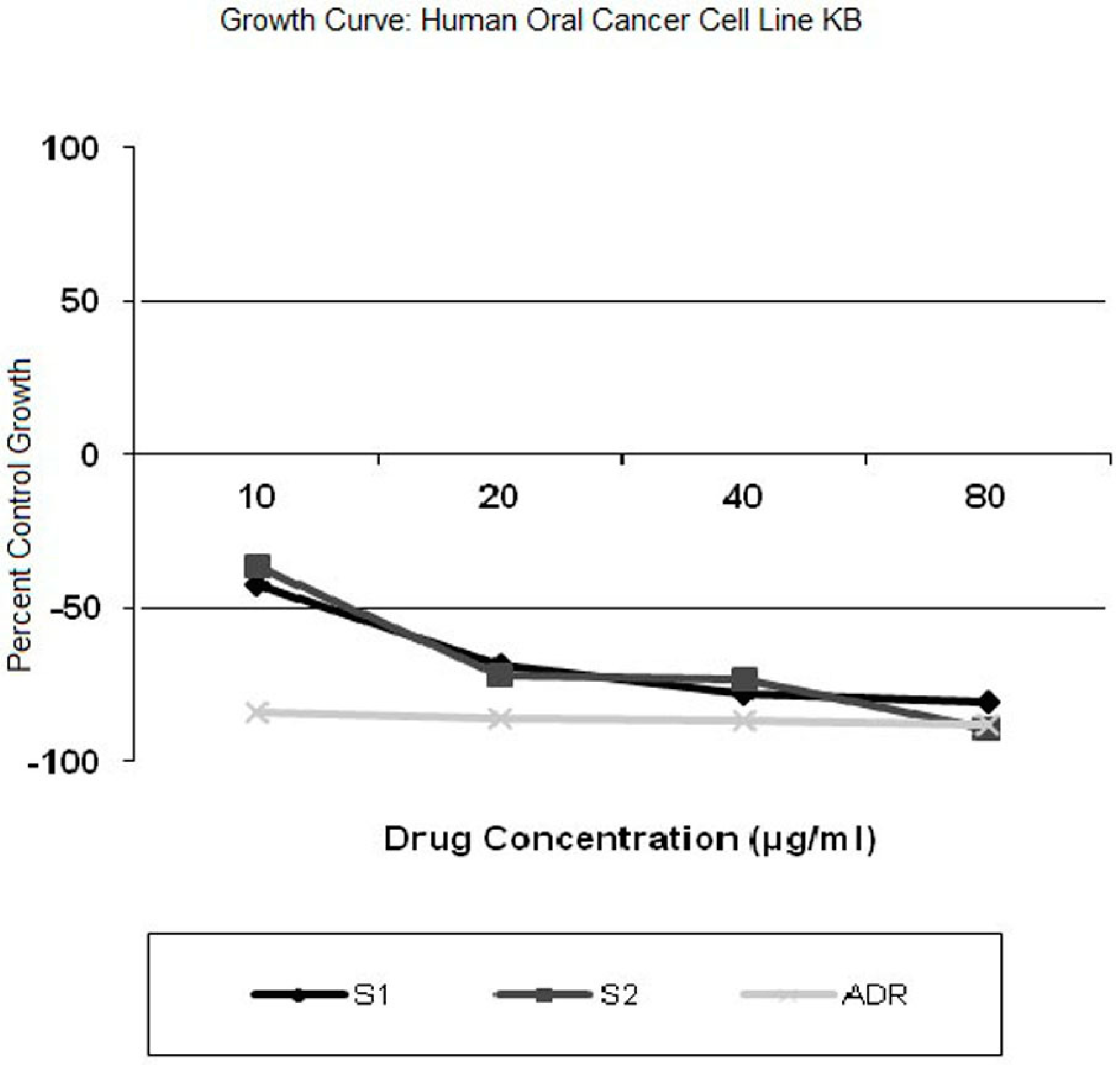
3.2. Product Development
3.2.1. Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of MSC CMN
3.2.2. Pharmacotechnical Characterization of Floating Tablets
Thickness, Hardness, Friability and Weight Variation
| Code | Thickness (mm) | Weight (mg) | Diameter (mm) | Hardness (kg/cm2) | Friability (%) | Floating Lag Time (min) | Floating Duration (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 3.01 ± 1.24 | 398 ± 1.16 | 8.050 ± 1.20 | 3.37 ± 1.23 | 0.56 ± 1.64 | 120 ± 1.38 | 7.50 ± 1.12 |
| F2 | 2.98 ± 1.19 | 397 ± 1.58 | 8.052 ± 1.17 | 3.33 ± 1.53 | 0.53 ± 1.39 | 60 ± 1.53 | 9.45 ± 1.15 |
| F3 | 3.00 ± 1.27 | 398 ± 1.16 | 8.054 ± 1.61 | 3.58 ± 1.78 | 0.59 ± 1.15 | 3.0 ± 1.09 | 11.30 ± 1.21 |
| F4 | 3.02 ± 1.13 | 399 ± 1.85 | 8.051 ± 1.14 | 3.50 ± 1.52 | 0.57 ± 1.36 | Within 3 s | 18.26 ± 1.35 |
In Vitro Buoyancy
In Vitro Drug Release
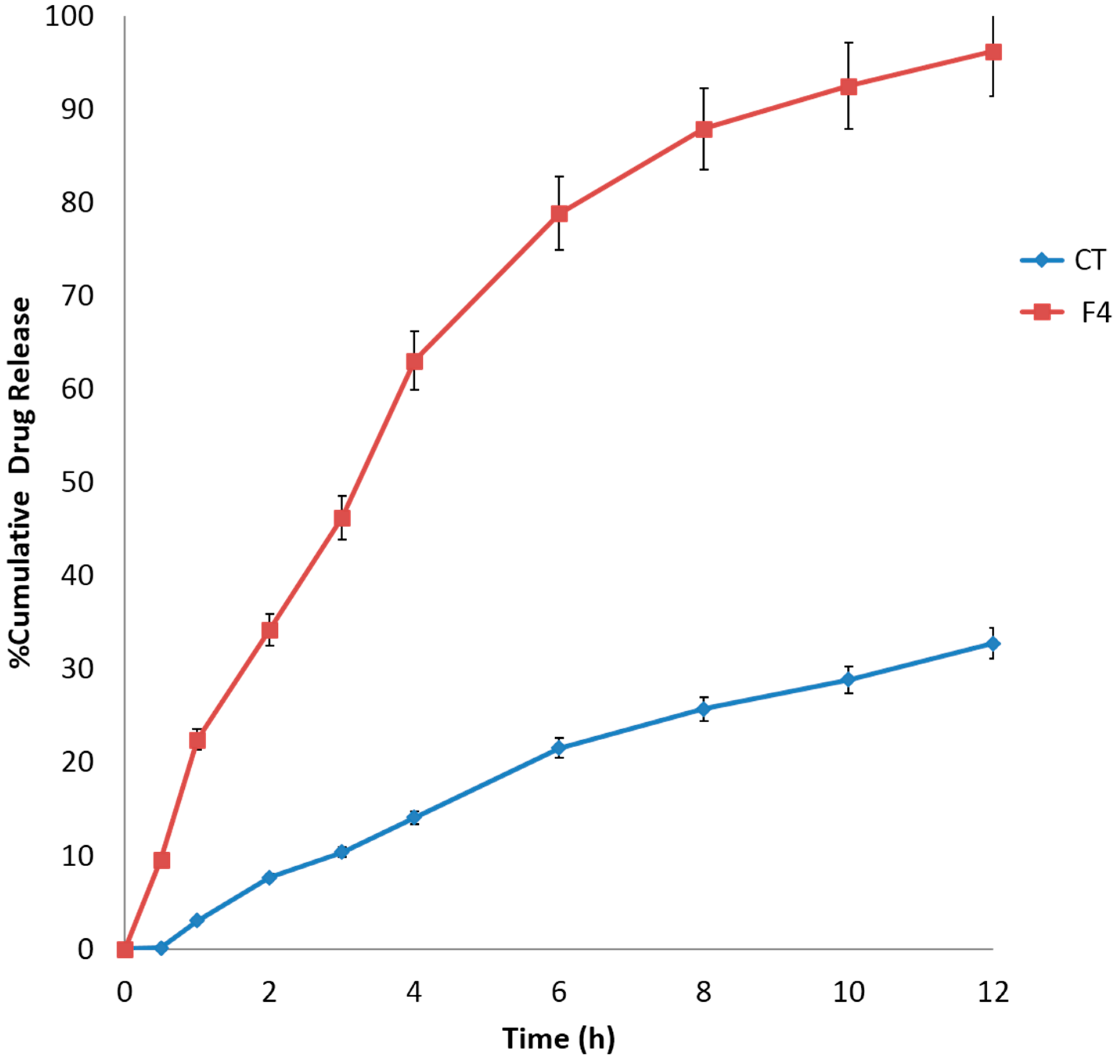
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgment
Authors Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, J.; Wang, H.S.; Gao, Y.Y.; Sang, L.M.; Zhang, L. Synergistic anti-tumor effect of KLF4 and curcumin in human gastric carcinoma cell line. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 7747–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Huang, Q. Improving the oral bioavailability of curcumin using novel organo gel based nano emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5373–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurien, B.T.; Singh, A.; Matsumoto, H.; Scofield, R.H. Improving the solubility and pharmacological efficacy of curcumin by heat treatment. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2007, 5, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goindi, S.G.; Gupta, N.; Aggarwal, N. Bioavailability enhancement and targeting of stomach tumours using gastro retentive floating drug delivery system of curcumin-a technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoba, G.; Joy, D.; Joseph, T.; Majeed, M.; Rajendran, R.; Srinivas, P.S. Influence of piperine on the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in animals and human volunteers. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sav, A.; Desai, H.; Meer, T.; Purnima, A. Solubility and dissolution rate enhancement of curcumin using kollidon VA64 by solid dispersion technique. Int. J. PharmTech Res. 2012, 4, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Rai, A.K. Development and evaluation of floating microspheres of curcumin. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.M.; Chien, C.F.; Lin, L.C.; Tsai, T.H. Curcumin and its nano-formulation: The kinetics of tissue distribution & blood-brain-barrier penetration. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, P.Y.; Parve, B.S.; Rawat, S.; Rathod, S.S.; Varandal, A.B. Different approaches towards the solubility enhancement of drug: A review. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 625–646. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuji, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Kawashima, Y. Particle design of poorly water soluble drug substances using supercritical fluid technologies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, N. Floating drug delivery system. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2011, 7, 6–20. [Google Scholar]
- Setya, S.; Talegonkar, S.; Razdan, B.K. Nanoemulsions: Formulation methods and stability aspects. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 2214–2228. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Garg, G.; Sharma, P.K. Nanospheres: A novel approach for targeted drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2010, 5, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, N.C.; Keskar, N.J.; Argade, P.D. Nanoparticles: Advances in drug delivery systems. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 922–929. [Google Scholar]
- Sanphui, P.; Goud, N.R.; Khandavilli, U.B.R.; Nangia, A. Fast dissolving curcumin cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 4135–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambhrunkar, S.; Karmakar, S.; Popat, A.; Yu, M.; Yu, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles enhance the cytotoxicity of curcumin. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambhrunkar, S.; Qu, Z.; Popat, A.; Yang, J.; Noonan, O.; Acauan, L.; Nor, Y.A.; Yu, C.; Karmakar, S. Effect of Surface Functionality of Silica Nanoparticles on Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3642–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Niu, Y.; Popat, A.; Jambhrunkar, S.; Karmakar, S.; Yu, C. Rod-like mesoporous silica nanoparticles with rough surfaces for enhanced cellular delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Karmakar, S.; Yu, M.; Popat, A. Synthesis of silica vesicles with small sizes and reduced aggregation for photodynamic therapy. Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, A.; Karmakar, S.; Jambhrunkar, S.; Xu, C.; Yu, C. Curcumin-cyclodextrin encapsulated chitosan nanoconjugates with enhanced solubility and cell cytotoxicity. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 1, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, V.; Deshmukh, T.; Deshmukh, M.; Jadhav, P. Design and development of melt sonocrystallization technique for carbamazepine. Ind. J. Pharm. Edu. Res. 2013, 47, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Bao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, M. Rapid sonocrystallization in the salting-out process. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 247, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Srour, M.; Tang, P.; Chiou, H.; Chan, H.; Romagnoli, L. Sonocrystallization of sodium chloride particles for inhalation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucar, D.K.; Elliott, J.A.; Eddleston, M.D.; Cockcroft, J.K.; Jones, W. Sonocrystallization Yields Monoclinic Paracetamol with Significantly Improved Compaction Behavior. Angew. Chem. 2014, 127, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinko, P.J. Martin’s Physical Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 5th ed.; Wolters Kluwer (India) Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2008; pp. 533–559. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, N.Y.; Chan, H.K. Effect of powder polydispersity on aerosol generation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 5, 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Aulton, M.E. The Design and Manufacturing of Medicines, 3rd ed.; Harcourt Publishers Limited: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 16–31, 355–357. [Google Scholar]
- Issa, M.G.; Ferraz, H.G. Intrinsic dissolution as a tool for evaluating drug solubility in accordance with the biopharmaceutics classification system. Dissolution Technol. 2011, 18, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, P.; Pathak, K. Assessing the viability of microsponges as gastro retentive drug delivery system of curcumin: Optimization and pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 460, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indian Pharmacopeia. Indian Pharmacopoeial Commission, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; Indian Pharmacopeia: Ghaziabad, India, 2007; pp. 183–184.
- Rosa, M.; Zia, H.; Rhodes, T. Dosing and testing in vitro of a bio-adhesive and floating drug delivery system for oral application. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 105, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohel, M.C.; Mehta, P.R.; Dave, R.K.; Bariya, N.H. A more relevant dissolution method for evaluation of floating drug delivery system. Dissolution Technol. 2004, 11, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Thomas, S.G.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Sundaram, C.; Harikumar, K.B.; Sung, B.; Tharakan, S.T.; Misra, K.; Priyadarsini, I.K.; Rajasekharan, K.N.; et al. Biological activities of curcumin and its analogues (congeners) made by man and mother nature. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 1590–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.D.; Uttekar, P.S. Melt sonocrystallization: A novel particle engineering technology for solubility enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2009, 1, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Derle, D.V.; Pawar, A.Y.; Patel, J.S.; Rathi, M.N.; Kothawade, P.I. Solubility enhancement of aceclofenac by solvent deposition method. Int. J. PharmTech Res. 2010, 2, 843–846. [Google Scholar]
- Jagtap, V.A.; Vidyasagar, G.; Dvivedi, S.C. Solubility enhancement of rosiglitazone by using melt sonocrystallization techniques. J. Ultrasound. 2014, 17, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, R.; Biradar, S.V.; Mishra, B.; Paradkar, A.R. Study of polymorphs of progesterone by novel melt sonocrystallization technique: A technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamoli, K.; Jain, D.; Pathak, K. Effect of milling on correlation between Interquartile coefficient of skewness and coefficient of kurtosis in pharmaceutical powders—II. Ind. J. Pharm. Edu. Res. 2008, 40, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Dhumal, R.S.; Biradar, S.V.; Yamamura, S.; Paradkar, A.; York, P. Preparation of amorphous cefuroxime axetil nanoparticles by sonoprecipitation for enhancement of bioavailability. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhi, B.K.; Chougule, M.B.; Misra, A. Aerosol performance of large respirable particles of amikacin sulfate produced by spray and freeze drying techniques. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, M.; Jahagirdar, H.; Paradkar, A. Melt sonocrystallization of ibuprofen: Effect on crystal properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 25, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Philip, A.K.; Pathak, K. Modified polysaccharides as fast disintegrating excipients for oro dispersible tablets of roxithromycin. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008, 9, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansel, L.V.; Popovich, N.G.; Ansel, H.C. Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems, 8th ed.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kamel, A.H. Improvement of physiochemical and biopharmaceutical properties of flurbiprofen using melt sonocrystallization technique. Drug Dev. Res. 2008, 69, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, P.G.; Sharma, V.; Pathak, K. Melt sonocrystallizedpiroxicam for oral delivery: Particle characterization, solid state analysis and pharmacokinetics. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Ahuja, A.; Ali, J.; Baboota, S. Curcumin loaded nano globules for solubility enhancement: Preparation, characterization and ex vivo release study. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 8293–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanphui, P.; Goud, N.R.; Khandavilli, U.B.R.; Bhanoth, S.; Nangia, A. New polymorphs of curcumin. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5013–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewnopparat, N.; Kaewnopparat, S.; Jangwang, A.; Maneenaun, D.; Chuchome, T.; Panichayupakaranant, P. Increased solubility, dissolution and physicochemical studies of curcumin-polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 solid dispersions. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2009, 31, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaraju, P.L.; Meka, A.K.; Jambhrunkar, S.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Popat, A.; Yu, C. Floating tablets from mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 8298–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kohli, S. Floating drug delivery of antidiabetic drugs: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2012, 3, 456–471. [Google Scholar]
- Negi, J.S.; Trivedi, A.; Khanduri, P.; Negi, V.; Kasliwal, N. Effect of bioadhesion on initial in vitro buoyancy of effervescent floating matrix tablets of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2011, 2, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakthivel, M.; Kannan, K.; Manavalan, R.; Senthamasai, R. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of noisome containing oxcarbazepine. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 563–567. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.A.; Akhtar, N.; Sharma, V.; Pathak, K. Product Development Studies on Sonocrystallized Curcumin for the Treatment of Gastric Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 43-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7020043
Khan MA, Akhtar N, Sharma V, Pathak K. Product Development Studies on Sonocrystallized Curcumin for the Treatment of Gastric Cancer. Pharmaceutics. 2015; 7(2):43-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7020043
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Mohammad Ashif, Nida Akhtar, Vijay Sharma, and Kamla Pathak. 2015. "Product Development Studies on Sonocrystallized Curcumin for the Treatment of Gastric Cancer" Pharmaceutics 7, no. 2: 43-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7020043
APA StyleKhan, M. A., Akhtar, N., Sharma, V., & Pathak, K. (2015). Product Development Studies on Sonocrystallized Curcumin for the Treatment of Gastric Cancer. Pharmaceutics, 7(2), 43-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics7020043