Impact of Oral Fast Release Amantadine on Movement Performance in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study design
2.2. Subjects
| N | sex | Age | height | weight | duration | MMSE | UPDRS | I | II | III | IV | HYS | DA | LD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 62 | 178 | 85 | 7 | 25 | 45 | 2 | 14 | 28 | 1 | 3 | - | 0 |
| 2 | 2 | 63 | 168 | 73 | 2 | 29 | 35 | 3 | 8 | 24 | 0 | 1.5 | 40 mg DHEC | 200 |
| 3 | 2 | 55 | 168 | 68.5 | 2 | 29 | 49 | 2 | 12 | 34 | 1 | 3 | 2.5 mg pergolide | 300 |
| 6 | 2 | 65 | 162 | 71 | 10 | 30 | 21 | 0 | 5 | 15 | 1 | 1 | - | 500 |
| 5 | 1 | 66 | 1.69 | 80 | 2 | 30 | 34 | 1 | 8 | 24 | 1 | 1.5 | - | 0 |
| 7 | 1 | 46 | 178 | 76 | 7 | 30 | 23 | 0 | 9 | 13 | 1 | 1.5 | 3.75 mg pergolide | 0 |
| 8 | 1 | 63 | 175 | 80 | 2 | 30 | 27 | 1 | 9 | 17 | 0 | 1.5 | 30 bromocriptine | 400 |
| 4 | 1 | 79 | 172 | 87 | 5 | 25 | 65 | 3 | 24 | 37 | 1 | 2 | 0.36 pramipexole | 400 |
| 5 | 2 | 66 | 159 | 53 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 1 | 13 | 30 | 1 | 1.5 | 3 mg pergolide | 350 |
| 6 | 2 | 71 | 163 | 71 | 4 | 30 | 53 | 2 | 22 | 28 | 1 | 2 | 9 mg ropinirole | 500 |
| 7 | 1 | 63 | 179 | 113 | 4 | 25 | 28 | 1 | 5 | 22 | 0 | 1.5 | 5 mg ropinirole | 500 |
| 3 | 1 | 66 | 168 | 70 | 0.5 | 30 | 35 | 2 | 8 | 25 | 0 | 1.5 | - | 0 |
2.3. Instrumental tasks
2.4. Assessment of complex movements: peg insertion
2.5. Assessment of simple movement: tapping
2.6. Blood samples
2.7. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Motor symptoms
| Baseline | 30 minutes | 60 minutes | 90 minutes | 120 minutes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIS | 128.98 ± 16.64; 109.02 - 167.35 | 125.76 ± 17.85; 104.25 - 160.65 | 122.34 ± 17.62; 100.33 - 156.38 | 126.12 ± 16.84; 105.85 - 161.06 | 122.64 ± 15.63; 98.99 - 147.39 |
| p | ns | 0.01 | ns | 0.01 | |
| tapping | 312.58 ± 41.84; 243 - 375 | 310.75 ± 45.57; 216 - 378 | 309.67 ± 53.33; 186 - 388 | 314.08 ± 50.36; 208 - 390 | 329.75 ± 38.13; 251 - 391 |
| p | ns | Ns | ns | ns | |
| UPDRS III | 26.42 ± 7.95; 18 - 44 | 20.75 ± 8.29; 7- 33 | 20.25 ± 8.35; 7 - 33 | 20 ± 7.9; 7 - 32 | 19.92 ± 8.60; 6 - 33 |
| p | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |
| akinesia | 11.58 ± 2.15; 9 - 16 | 8.58 ± 3.18; 1 - 12 | 8.50 ± 3.03; 1 - 11 | 8.5 ± 3.06; 1 - 11 | 8.58 ± 2.81;1 - 11 |
| p | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |
| rigidity | 4.67 ± 3.58; 0 - 12 | 3.42 ± 3.42; 0 - 12 | 3.33 ± 3.23; 0 - 11 | 3 ± 3.3; 0 - 12 | 3.17 ± 3.33; 0 -12 |
| 0.012 | 0.007 | 0.0005 | 0.0018 | ||
| tremor | 4.75 ± 3.08; 1 - 11 | 3.75 ± 2.45; 1 - 8 | 3.42 ± 2.61, 0 - 8 | 3.58 ± 2.54; 0 - 8 | 3.42 ± 2.64; 0 - 8 |
| p | 0.009 | 0.0004 | 0.002 | 0.0004 |
3.2. Instrumental motor tests
3.3. Pharmacokinetics of amantadine
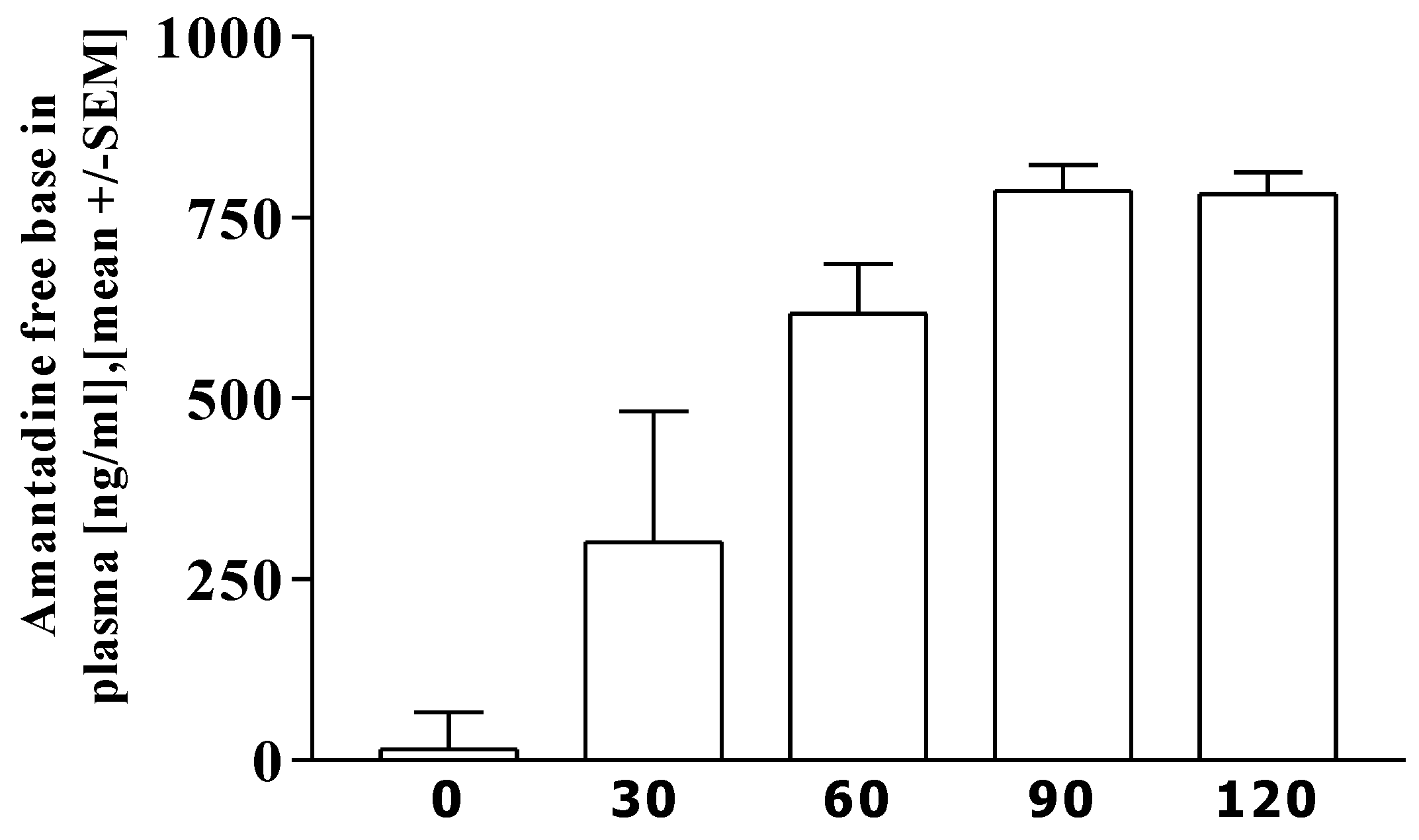
3.4. Correlation analysis
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
References
- Metman, L.V.; Del Dotto, P.; LePoole, K.; Konitsiotis, S.; Fang, J.; Chase, T.N. Amantadine for levodopa-induced dyskinesias: a 1-year follow-up study. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Iacono, D.; Luciano, A.L.; Armellino, K.; Di Iorio, A.; Onofrj, M. Duration of amantadine benefit on dyskinesia of severe Parkinson's disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 2004, 75, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, T.; Kuhn, W.; Schulte, T.; Przuntek, H. Intravenous amantadine sulphate application improves the performance of complex but not simple motor tasks in patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 339, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.K.; Lee, C.S.; Samii, A.; Schulzer, M.; Stoessl, A.J.; Mak, E.K.; Wudel, J.; Dobko, T.; Tsui, J.K. Alternating two finger tapping with contralateral activation is an objective measure of clinical severity in Parkinson's disease and correlates with PET. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2001, 7, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuente-Fernandez, R.; Stoessl, A.J. The biochemical bases of the placebo effect. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2004, 10, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.G.; Laska, E.; Hicking, C.; Damier, P.; Müller, T.; Nutt, J.; Warren, O.C.; Rascol, O.; Russ, H. Placebo influences on dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease. Movement Disord. 2008, 23, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlack, S.; Konietzka, S.; Woitalla, D.; Przuntek, H.; Muller, T. Simple movement sequences better correlate to levodopa plasma levels than complex ones. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 2004, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, L.M.; Abbott, D.F.; Egan, G.F.; Tochon-Danguy, H.J.; Donnan, G.A. The functional neuroanatomy and long-term reproducibility of brain activation associated with a simple finger tapping task in older healthy volunteers: a serial PET study. Neuroimage 2000, 11, 124–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, N.C.; Cohen, G.; Harris, G.; Cizadlo, T.; Parkkinen, J.; Rezai, K.; Swayze, V.W. Image processing for the study of brain structure and function: problems and programs. J. Neuropsychiatr. Clin. Neurosci. 1992, 4, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Pinter, M.M.; Birk, M.; Helscher, R.J.; Binder, H. Short-term effect of amantadine sulphate on motor performance and reaction time in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease. J. Neural Transm. 1999, 106, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Muhlack, S.; Müsch, P.; Konietzka, S.; Woitalla, D.; Przuntek, H.; Müller, T. Impact of Oral Fast Release Amantadine on Movement Performance in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmaceutics 2010, 2, 313-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2030313
Muhlack S, Müsch P, Konietzka S, Woitalla D, Przuntek H, Müller T. Impact of Oral Fast Release Amantadine on Movement Performance in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmaceutics. 2010; 2(3):313-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2030313
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuhlack, Siegfried, Patricia Müsch, Sandra Konietzka, Dirk Woitalla, Horst Przuntek, and Thomas Müller. 2010. "Impact of Oral Fast Release Amantadine on Movement Performance in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease" Pharmaceutics 2, no. 3: 313-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2030313
APA StyleMuhlack, S., Müsch, P., Konietzka, S., Woitalla, D., Przuntek, H., & Müller, T. (2010). Impact of Oral Fast Release Amantadine on Movement Performance in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmaceutics, 2(3), 313-320. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics2030313




