Antiviral Activity of Liposomes Containing Natural Compounds Against CHIKV
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
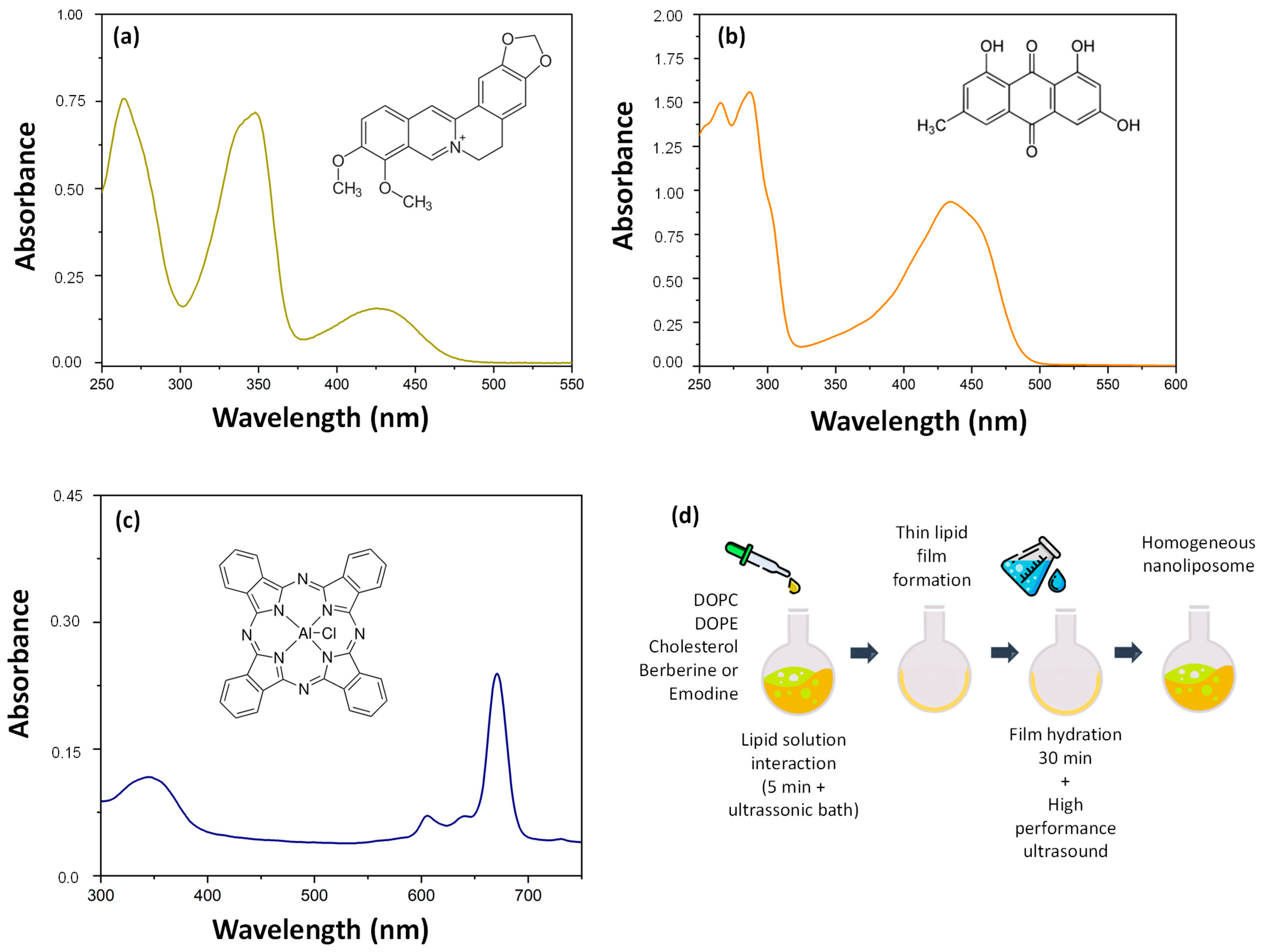
2.1. Synthesis of Liposomes
2.2. Liposome Characterization
2.3. Drug Content (DC) and Encapsulation Efficiency (EE)
2.4. Accelerated Stability and Shelf-Life Measurements
2.5. Cell Lines
2.6. Liposome Cytotoxicity
2.7. Confocal Microscopy Analysis of the Uptake of the Proposed Liposomes in BHK-21 and Huh7 Cell Lines
2.8. Virus
2.9. Liposome Dose-Dependence Assay
2.10. Investigation of the Effect of Liposomes on the Direct Inactivation of Extracellular Viral Particles (Virucidal Activity)
2.11. Time-of-Addition Assay
2.12. Analysis of Inhibition of Viral RNA Replication
2.13. Analysis of CHIKV Protein Expression by Western Blotting
2.14. dsRNA Intercalation Assay
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
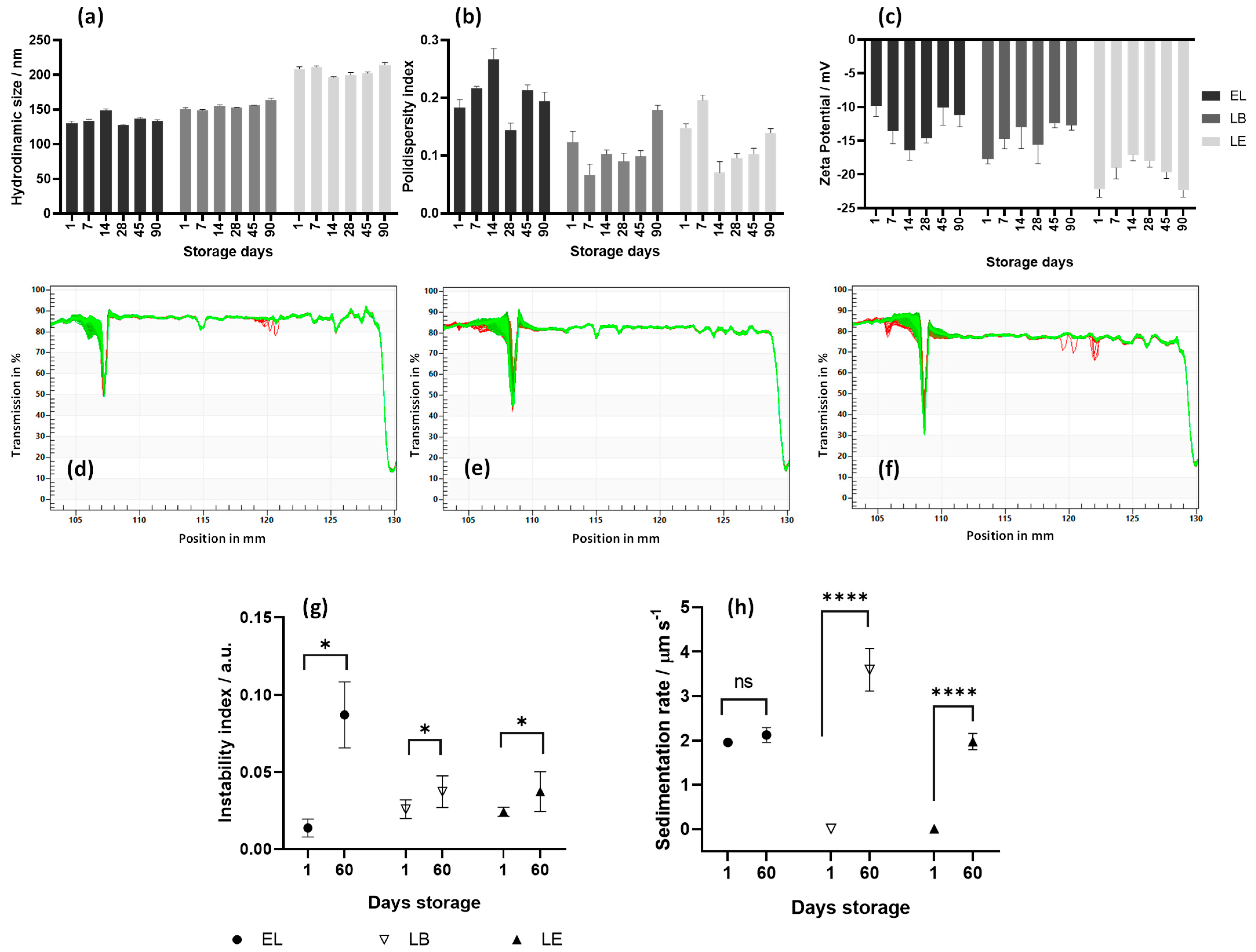
3.1. Analysis of Particle Size, Polydispersity (PDI), and Zeta Potential of LB and LE
3.2. Accelerated Stability and Shelf Life of Liposomes
3.3. Liposome Cytotoxicity
3.4. Liposomes Uptake by BHK-21 and Huh7 Cells
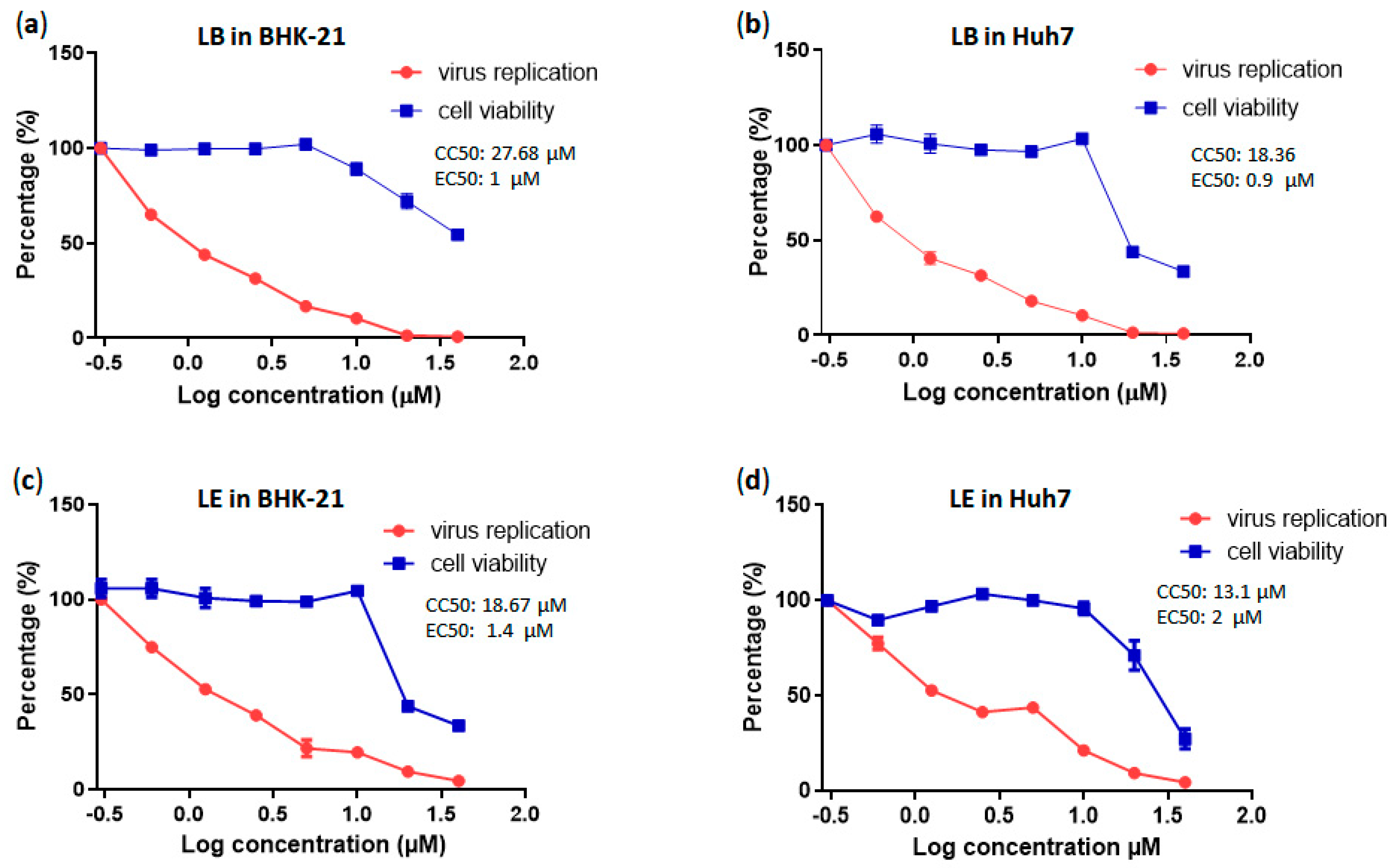
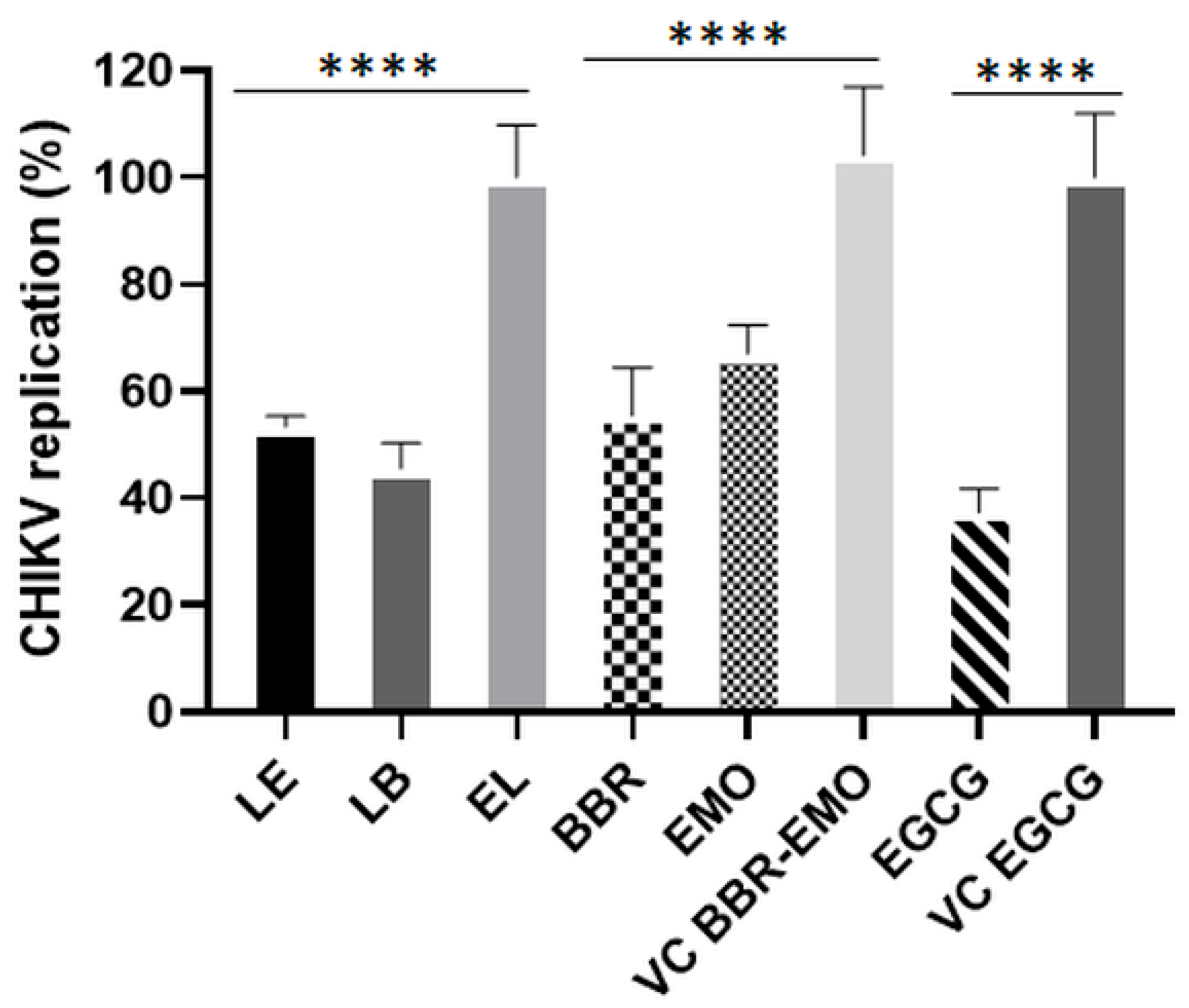
3.5. LE and LB Inhibit CHIKV Replication in a Dose-Dependent Manner
3.6. LB and LE Lack Virucidal Activity
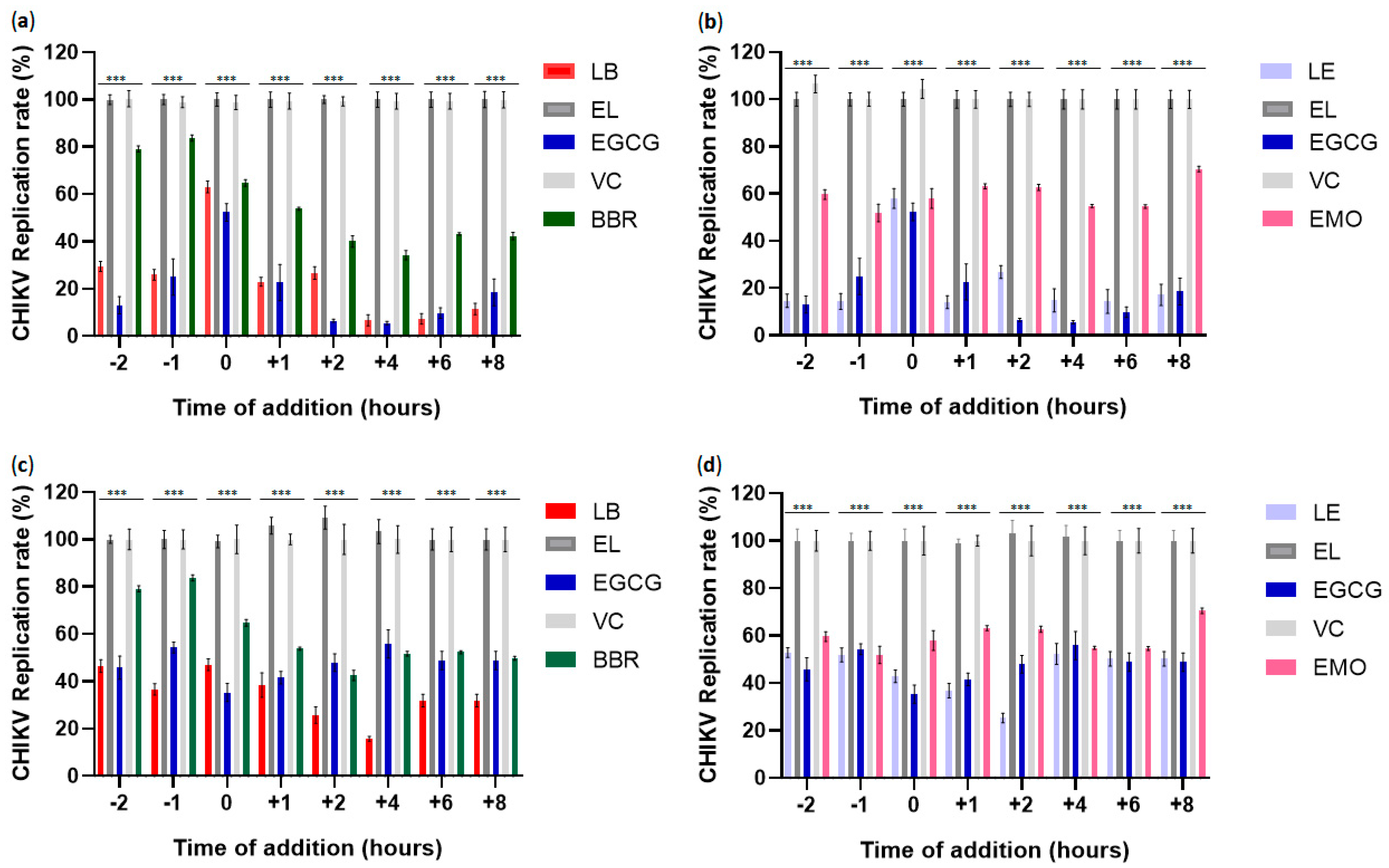
3.7. Time-of-Addition Assays Using Berberin, Emodin, LB, and LE
3.8. Antiviral Effects of LB and LE on CHIKV RNA Replication
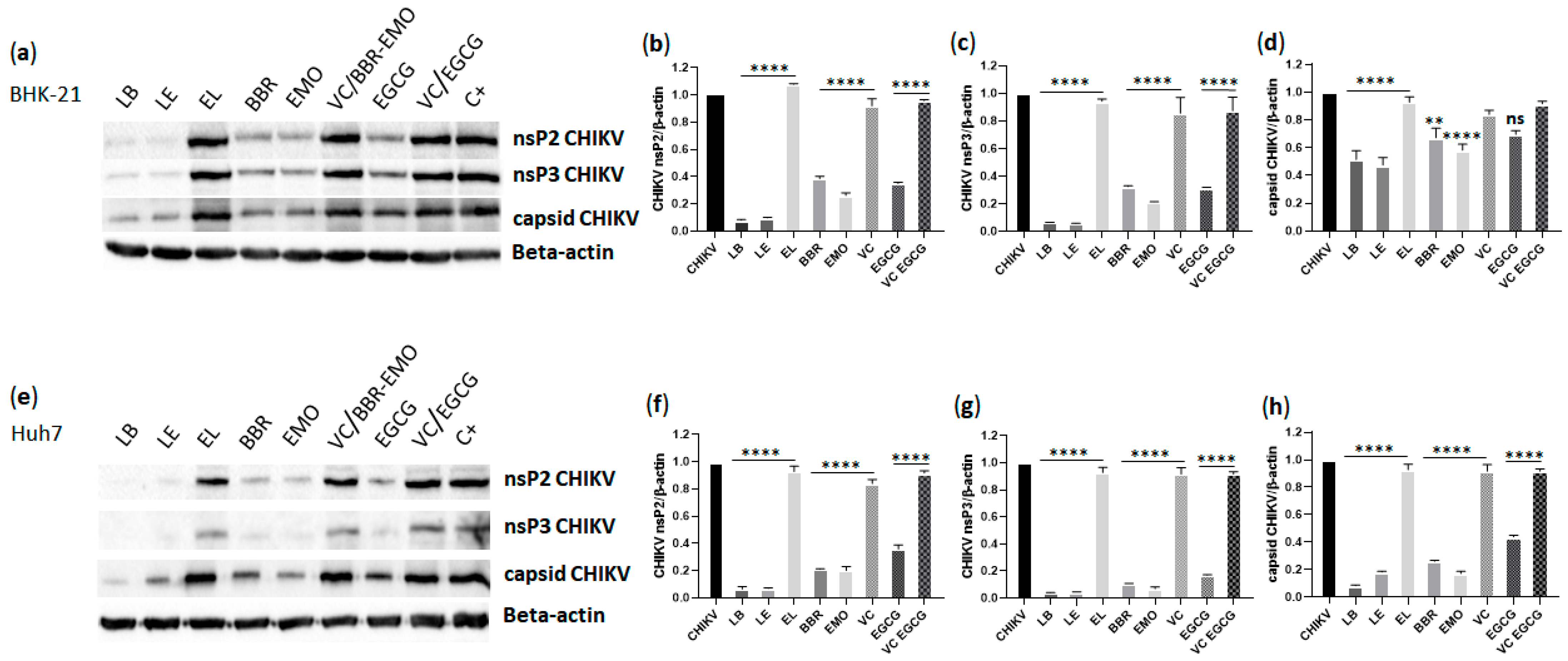
3.9. Analysis of CHIKV nsP2, nsP3 and Capsid Protein Expression
3.10. Liposome Containing Berberine or Emodin Do Not Intercalate with Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavalcanti, T.Y.V.D.; Pereira, M.R.; de Paula, S.O.; Franca, R.F.D. A review on Chikungunya virus epidemiology, pathogenesis and current vaccine development. Viruses 2022, 14, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Kumar, S.; Mamidi, P.; Datey, A.; Sengupta, S.; Mahish, C.; Laha, E.; De, S.; Keshry, S.; Nayak, T.; et al. DNA damage response signaling is crucial for effective Chikungunya virus replication. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0133422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.W. The Newala epidemic. III. The virus: Isolation, pathogenic properties and relationship to the epidemic. J. Hyg. 1956, 54, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahid, B.; Ali, A.; Rafique, S.; Idrees, M. Global expansion of Chikungunya virus: Mapping the 64-year history. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 58, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.; Streblow, D.; Coffey, L. Chikungunya virus vaccines: A review of IXCHIQ and PXVX0317 from pre-clinical evaluation to licensure. Biodrugs 2024, 38, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noret, M.; Herrero, L.; Rulli, N.; Rolph, M.; Smith, P.N.; Li, R.W.; Roques, P.; Gras, G.; Mahalingam, S. Interleukin 6, RANKL, and osteoprotegerin expression by Chikungunya virus-infected human osteoblasts. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Zamora, E.; Mendoza-Cano, O.; Trujillo-Hernández, B.; Alberto Sánchez-Piña, R.; Guzmán-Esquivel, J. Persistent arthralgia and related risks factors in laboratory-confirmed cases of Chikungunya virus infection in Mexico. Rev. Panam. Salud. Publica 2017, 41, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, G.; Allah, S.A.; Ezzat, R. Pharmacological activities and medicinal uses of berberine: A review. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 2024, 14, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Neag, M.A.; Mocan, A.; Echeverría, J.; Pop, R.M.; Bocsan, C.I.; Crişan, G.; Buzoianu, A.D. Berberine: Botanical occurrence, traditional uses, extraction methods, and relevance in cardiovascular, metabolic, hepatic, and renal disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.C.; Jassey, A.; Liu, C.H.; Lin, C.J.; Lin, C.C.; Wong, S.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Yen, M.H.; Lin, L.T. Berberine inhibits hepatitis C virus entry by targeting the viral E2 glycoprotein. Phytomedicine 2019, 53, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratanakomol, T.; Roytrakul, S.; Wikan, N.; Smith, D.R. Berberine inhibits dengue virus through dual mechanisms. Molecules 2021, 26, 5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannone, D.; Piccini, L.; Brunetti, J.; Quintana, V.; Damonte, E.; Castilla, V. Berberine inhibitory action against zika and dengue viruses in cell cultures. Acta Virologica 2023, 67, 11931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Ma, T. Berberine prevents lethal EV71 neurological infection in newborn mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1027566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wu, S.; Qin, H.; Zhen, X.; Song, B.; Weng, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Z. Anti-influenza activity of berberine improves prognosis by reducing viral replication in mice. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2560–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Fu, J.; Yin, X.; Cao, S.; Li, X.; Lin, L.; Huyiligeqi; Ni, J. Emodin: A review of its pharmacology, toxicity and pharmacokinetics. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Luo, J.; Hou, W.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Z. The effect of emodin, an anthraquinone derivative extracted from the roots of Rheum tanguticum, against herpes simplex virus in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Wang, K.; Yu, W.; Sun, B.; Schwarz, W. Emodin inhibits current through SARS-associated coronavirus 3a protein. Antivir. Res. 2011, 90, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Liu, T.; Wang, W.; Liu, T.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z. Promising role of emodin as therapeutics to against viral infections. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 902626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J. Rheum emodin inhibits enterovirus 71 viral replication and affects the host cell cycle environment. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, M.; Braga, A.; Campos, G.; Souza, M.; de Matos, R.; Lopes, T.; Candido, N.; Lima, M.; Machado, F.; de Andrade, S.; et al. Natural products isolated from oriental medicinal herbs inactivate zika virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Ou, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Yang, S. Berberine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles are concentrated in the liver and ameliorate hepatosteatosis in db/db mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 5049–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkol, E.K.; Tatlı, I.I.; Karatoprak, G.; Ağar, O.T.; Yücel, Ç.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Capasso, R. Is emodin with anticancer effects completely innocent? Two sides of the coin. Cancers 2021, 13, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alolga, R.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Lai, M.; Li, P.; Qi, L. Significant pharmacokinetic differences of berberine are attributable to variations in gut microbiota between Africans and Chinese. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhadi, E.; Rezaee, M.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. Nano strategies for berberine delivery, a natural alkaloid of Berberis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Hussain, A.; Attar, F.; Bloukh, S.; Edis, Z.; Sharifi, M.; Balali, E.; Nemati, F.; Derakhshankhah, H.; Zeinabad, H.; et al. A review of the berberine natural polysaccharide nanostructures as potential anticancer and antibacterial agents. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Li, Y.; Ye, L.; Hu, M.; Liu, Z. Coupling of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and multidrug resistance-associated proteins is responsible for the intestinal disposition and poor bioavailability of emodin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 265, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ding, Z.; Ma, K.; Sun, C.; Zheng, X.; You, Y.; Zhang, S.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, J. Cysteine-based protein covalent binding and hepatotoxicity induced by emodin. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahibzada, M.U.K.; Zahoor, M.; Sadiq, A.; Ur Rehman, F.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; Shahid, M.; Naz, S.; Ullah, R. Bioavailability and hepatoprotection enhancement of berberine and its nanoparticles prepared by liquid antisolvent method. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xia, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xie, Z. Berberine Hydrochloride-loaded Liposomes Gel: Preparation, Characterization and Antioxidant Activity. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2023, 57, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.T.; Isomäki, A.; Paaver, U.; Laidmäe, I.; Tõnisoo, A.; Yen, T.T.H.; Kogermann, K.; Raal, A.; Heinämäki, J.; Pham, T.M. Nanoformulation and evaluation of oral berberine-loaded liposomes. Molecules 2021, 26, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.; Giorgini, G.; Minnelli, C.; Mobbili, G.; Guardiani, C.; Giacomello, A.; Galeazzi, R. Membrane composition allows the optimization of berberine encapsulation in liposomes. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 5818–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Ji, C.; Luo, X.; Lan, Y.; Han, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, Q.; Lu, F.; Wu, X.; et al. Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of emodin via colonic irrigation attenuates renal injury in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 606227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zou, T.; Lan, M.; Li, L.; Liu, F.; Cai, T.; Cai, Y. Polymeric lipid hybrid nanoparticles as a delivery system enhance the antitumor effect of emodin in vitro and in vivo. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 2986–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Ji, X.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Y.; Tan, R.; Jiang, H.; Wu, X. Aloe-emodin: Progress in pharmacological activity, safety, and pharmaceutical formulation applications. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2024, 24, 1784–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harijan, M.; Singh, M. Zwitterionic polymers in drug delivery: A review. J. Mol. Recognit. 2022, 35, e2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Qi, Y.; Peng, C.; Wang, N.; Fan, H.; Li, Y. Zwitterionic polymers: Addressing the barriers for drug delivery. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira-Moura, M.; Primo, F.; Espreafico, E.; Tedesco, A. Development, characterization, and photocytotoxicity assessment on human melanoma of chloroaluminum phthalocyanine nanocapsules. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Ossa, D.; Ligresti, A.; Gil-Alegre, M.; Aberturas, M.; Molpeceres, J.; Di Marzo, V.; Suárez, A. Poly-ε-caprolactone microspheres as a drug delivery system for cannabinoid administration: Development, characterization and in vitro evaluation of their antitumoral efficacy. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Diniz, L.; Sousa, R.; Honorato, T.; Simao, D.; Araújo, C.; Gonçalves, T.; Rolim, L.; Goto, P.; Tedesco, A.; et al. Preparation and characterization of nanoemulsion containing a natural naphthoquinone. Quim. Nova 2018, 41, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detloff, T.; Sobisch, T.; Lerche, D. Particle size distribution by space or time dependent extinction profiles obtained by analytical centrifugation (concentrated systems). Powder Technol. 2007, 174, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohjala, L.; Utt, A.; Varjak, M.; Lulla, A.; Merits, A.; Ahola, T.; Tammela, P. Inhibitors of alphavirus entry and replication identified with a stable Chikungunya replicon cell line and virus-based Assays. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkovic, R.; Bernard, E.; Fontanel, S.; Eldin, P.; Chazal, N.; Hersi, D.H.; Merits, A.; Peloponese, J.M.; Briant, L. The host DHX9 DExH-box helicase is recruited to Chikungunya virus replication complexes for optimal genomic RNA translation. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01764-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.; Noske, G.D.; Bitencourt, N.V.; Sanches, P.R.S.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Gawriljuk, V.O.; de Souza, E.P.; Nogueira, V.H.R.; de Godoy, M.O.; Nakamura, A.M.; et al. Non-toxic dimeric peptides derived from the bothropstoxin-I are potent SARS-CoV-2 and papain-like protease inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26, 4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, M.; Wasowska-Lukawska, M.; Oszczapowicz, I.; Boguszewska-Chachulska, A. Amidinoanthracyclines—A new group of potential anti-hepatitis C virus compounds. Biol. Chem. 2009, 390, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential—What they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, G.; Story, S.; Arya, D. A careful look at lipid nanoparticle characterization: Analysis of benchmark formulations for encapsulation of RNA cargo size gradient. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briuglia, M.; Rotella, C.; McFarlane, A.; Lamprou, D. Influence of cholesterol on liposome stability and on in vitro drug release. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2015, 5, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L. Preparation of curcumin-loaded liposomes and evaluation of their skin permeation and pharmacodynamics. Molecules 2012, 17, 5972–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Ye, A.; Peng, S.; Wei, F.; Liu, C.; Han, J. Environmental stress stability of microencapsules based on liposomes decorated with chitosan and sodium alginate. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Rosfa, S.; Wlodarski, A.; Kuharev, J.; Rekik, A.; Knauer, S.; Bantz, C.; Nawroth, T.; Bier, C.; et al. Nanoparticle size is a critical physicochemical determinant of the human blood plasma corona: A comprehensive quantitative proteomic analysis. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7155–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, O.; Stalet, M.; Leclerc, L.; Forest, V. Influence of the physicochemical features of TiO2 nanoparticles on the formation of a protein corona and impact on cytotoxicity. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 43950–43959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarsenker, M.; Londhe, V. Preparation and evaluation of a liposomal formulation of sodium cromoglicate. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 251, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingyuad, P.; Sinthuvanich, C.; Leepasert, T.; Thongyoo, P.; Boonrungsiman, S. Preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation of calothrixin B liposomes. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonechi, C.; Donati, A.; Tamasi, G.; Leone, G.; Consumi, M.; Rossi, C.; Lamponi, S.; Magnani, A. Protective effect of quercetin and rutin encapsulated liposomes on induced oxidative stress. Biophys. Chem. 2018, 233, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caddeo, C.; Manconi, M.; Fadda, A.; Lai, F.; Lampis, S.; Diez-Sales, O.; Sinico, C. Nanocarriers for antioxidant resveratrol: Formulation approach, vesicle self-assembly and stability evaluation. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerche, D.; Sobisch, T. Direct and accelerated characterization of formulation stability. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2011, 32, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayme, C.; Rezende, N.; Fernandes, D.; Paula, L.; de Castro, B.; Takahashi, L.; Tedesco, A. Target selectivity of cholesterol-phosphatidylcholine liposome loaded with phthalocyanine for breast cancer diagnosis and treatment by photodynamic therapy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 39, 102992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, K.; Rappolt, M.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, F. The stabilization and release performances of curcumin-loaded liposomes coated by high and low molecular weight chitosan. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumanhal-Masarweh, H.; da Silva, D.; Poley, M.; Zinger, A.; Goldman, E.; Krinsky, N.; Kleiner, R.; Shenbach, G.; Schroeder, J.; Shklover, J.; et al. Tailoring the lipid composition of nanoparticles modulates their cellular uptake and affects the viability of triple negative breast cancer cells. J. Control. Release 2019, 307, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montizaan, D.; Yang, K.; Reker-Smit, C.; Salvati, A. Comparison of the uptake mechanisms of zwitterionic and negatively charged liposomes by HeLa cells. Nanomed.-Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2020, 30, 102300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, M.; Thompson, D. Chloroaluminum phthalocyanine tetrasulfonate delivered via acid-labile diplasmenylcholine-folate liposomes: Intracellular localization and synergistic phototoxicity. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 93, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, F.; Hussain, S.; Rodrigues-Lima, F.; Baeza-Squiban, A.; Boland, S. Nanoparticles: Molecular targets and cell signalling. Arch. Toxicol. 2011, 85, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Shen, J.; Wang, M.; Wu, X. Study on the interaction of berberine with nucleic acids in the presence of silver nanoparticles, and the fluorometric determination of nucleic acids. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 29612–29618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Miao, X.; Wang, X.; Pan, H.; Li, P.; Ren, H.; Jia, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, H.; Yuan, L.; et al. Antiproliferation of berberine is mediated by epigenetic modification of constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) metabolic pathway in hepatoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Ju, R.; Shi, J.; Sun, M.; Zhao, W.; Mu, L.; et al. Modulation of drug-resistant membrane and apoptosis proteins of breast cancer stem cells by targeting berberine liposomes. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4452–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafim, T.; Oliveira, P.; Sardao, V.; Perkins, E.; Parke, D.; Holy, J. Different concentrations of berberine result in distinct cellular localization patterns and cell cycle effects in a melanoma cell line. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2008, 61, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vath, P.; Wamer, W.; Falvey, D. Photochemistry and phototoxicity of aloe emodin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 75, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Phasupan, P.; Nguyen, L. Antimicrobial photodynamic efficacy of selected natural photosensitizers against food pathogens: Impacts and interrelationship of process parameters. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 32, 102024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänicke, P.; Lennicke, C.; Meister, A.; Seliger, B.; Wessjohann, L.; Kaluderovic, G. Fluorescent spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with emodin: Synthesis, cellular uptake and anticancer activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 119, 111619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Cui, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Emodin-based nanoarchitectonics with giant two-photon absorption for enhanced photodynamic therapy. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202308019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrayanto, G.; Putra, G.S.; Suhud, F. Validation of in-vitro bioassay methods: Application in herbal drug research. In Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology; Al-Majed, A.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 46, pp. 273–307. [Google Scholar]
- Varghese, F.; Kaukinen, P.; Gläsker, S.; Bespalov, M.; Hanski, L.; Wennerberg, K.; Kümmerer, B.; Ahola, T. Discovery of berberine, abamectin and ivermectin as antivirals against Chikungunya and other alphaviruses. Antivir. Res. 2016, 126, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, F.; Bouma, E.; Hu, G.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Smit, J.; Diamond, M.; Zhang, R. Colocalization of Chikungunya virus with its receptor MXRA8 during cell attachment, internalization, and membrane fusion. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e01557-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seteyen, A.; Guiraud, P.; Gasque, P.; Girard-Valenciennes, E.; Sélambarom, J. In vitro analyses of the multifocal effects of natural alkaloids berberine, matrine, and tabersonine against the o’nyong-nyong arthritogenic alphavirus infection and inflammation. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Gong, L.; Sun, Y.; Song, Z.; Chang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H. Emodin and rhapontigenin inhibit the replication of African swine fever virus by interfering with virus entry. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 284, 109794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomeeusen, K.; Daniel, M.; LaBeaud, D.; Gasque, P.; Peeling, R.; Stephenson, K.; Ng, L.; Ariën, K. Chikungunya fever. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A. Berberine alters epigenetic modifications, disrupts microtubule network, and modulates HPV-18 E6–E7 oncoproteins by targeting p53 in cervical cancer cell HeLa: A mechanistic study including molecular docking. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 744, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoornweg, T.; Bouma, E.; van de Pol, D.; Rodenhuis-Zybert, I.; Smit, J. Chikungunya virus requires an intact microtubule network for efficient viral genome delivery. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, E.; Damas, B.; Mendonça, D.; Abrahao, J.; Bonjardim, C. In-depth characterization of the Chikungunya virus replication cycle. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e01732-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.J.; Brown, R.S.; Kielian, M. Berberine chloride is an alphavirus inhibitor that targets nucleocapsid assembly. mBio 2020, 11, e01382-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, S.; Jia, X.; Song, P.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, E. Inhibitory effect of emodin and Astragalus polysaccharide on the replication of HBV. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 5669–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, R.; Aziz, E.; Mahmood, T.; Tan, B.; Chow, V. Inhibitory activities of extracts of Rumex dentatus, Commelina benghalensis, Ajuga bracteosa, Ziziphus mauritiana as well as their compounds of gallic acid and emodin against dengue virus. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2018, 11, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, M.; Delang, L.; Ng, L.; Priego, E. Chikungunya virus drug discovery: Still a long way to go? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannemann, H. Viral replicons as valuable tools for drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, F.; Thaa, B.; Amrun, S.; Simarmata, D.; Rausalu, K.; Nyman, T.; Merits, A.; McInerney, G.; Ng, L.; Ahola, T. The antiviral alkaloid berberine reduces Chikungunya virus-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9743–9757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisig, R.; Teppke, A.; Behrens, D.; Fichtner, I. Liposomal 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen:: Effect on cellular uptake and resulting cytotoxicity in drug resistant breast cancer cells in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2004, 87, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shao, A.; Zhang, N.; Fang, J.; Ruan, J.; Ruan, B. Cationic Polymethacrylate-modified liposomes significantly enhanced doxorubicin delivery and antitumor activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausalu, K.; Utt, A.; Quirin, T.; Varghese, F.; Zusinaite, E.; Das, P.; Ahola, T.; Merits, A. Chikungunya virus infectivity, RNA replication and non-structural polyprotein processing depend on the nsP2 protease’s active site cysteine residue. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, W.; Strauss, J. Processing the nonstructural polyproteins of sindbis virus—Nonstructural proteinase is in the c-terminal half of nsp2 and functions both in cis and in trans. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 4653–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, Y.; Utt, A.; Tan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, M.; Griffin, P.; Merits, A.; Luo, D. Structural insights into RNA recognition by the Chikungunya virus nsP2 helicase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9558–9567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, Y.; Wang, S.; Tan, Y.; Shih, O.; Utt, A.; Goh, W.; Lian, B.; Chen, M.; Jeng, U.; Merits, A.; et al. Interdomain flexibility of Chikungunya virus nsP2 helicase-protease differentially influences viral RNA replication and infectivity. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01470-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kril, V.; Hons, M.; Amadori, C.; Zimberger, C.; Couture, L.; Bouery, Y.; Burlaud-Gaillard, J.; Karpov, A.; Ptchelkine, D.; Thienel, A.; et al. Alphavirus nsP3 organizes into tubular scaffolds essential for infection and the cytoplasmic granule architecture. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, R.; Uversky, V.; Giri, R. Deciphering the dark proteome of Chikungunya virus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Nehul, S.; Singh, A.; Tomar, S. Identification and evaluation of antiviral potential of thymoquinone, a natural compound targeting Chikungunya virus capsid protein. Virology 2021, 561, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiser, L.; Sokoloski, K.; Hardy, R. Interactions between capsid and viral RNA regulate Chikungunya virus translation in a host-specific manner. Virology 2021, 560, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Liposome | Average Size (nm) | Average Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| EL | 135 ± 7 | −14 ± 2 |
| LE | 206 ± 7 | −19 ± 2 |
| LB | 155 ± 5 | −15 ± 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calmon, M.F.; Gusmão, L.A.; Ruiz, T.F.R.; Campos, G.R.F.; Ayusso, G.M.; Carvalho, T.; Bortolato, I.d.V.F.; Conceição, P.J.P.; Taboga, S.R.; Jardim, A.C.G.; et al. Antiviral Activity of Liposomes Containing Natural Compounds Against CHIKV. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091229
Calmon MF, Gusmão LA, Ruiz TFR, Campos GRF, Ayusso GM, Carvalho T, Bortolato IdVF, Conceição PJP, Taboga SR, Jardim ACG, et al. Antiviral Activity of Liposomes Containing Natural Compounds Against CHIKV. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(9):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091229
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalmon, Marília Freitas, Luiza Araújo Gusmão, Thalles Fernando Rocha Ruiz, Guilherme Rodrigues Fernandes Campos, Gabriela Miranda Ayusso, Tamara Carvalho, Isabella do Vale Francisco Bortolato, Pâmela Joyce Previdelli Conceição, Sebastião Roberto Taboga, Ana Carolina Gomes Jardim, and et al. 2025. "Antiviral Activity of Liposomes Containing Natural Compounds Against CHIKV" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 9: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091229
APA StyleCalmon, M. F., Gusmão, L. A., Ruiz, T. F. R., Campos, G. R. F., Ayusso, G. M., Carvalho, T., Bortolato, I. d. V. F., Conceição, P. J. P., Taboga, S. R., Jardim, A. C. G., Merits, A., Rahal, P., & Tedesco, A. C. (2025). Antiviral Activity of Liposomes Containing Natural Compounds Against CHIKV. Pharmaceutics, 17(9), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091229









