Recent Advances in Nose-to-Brain Gene Delivery for Central Nervous System Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
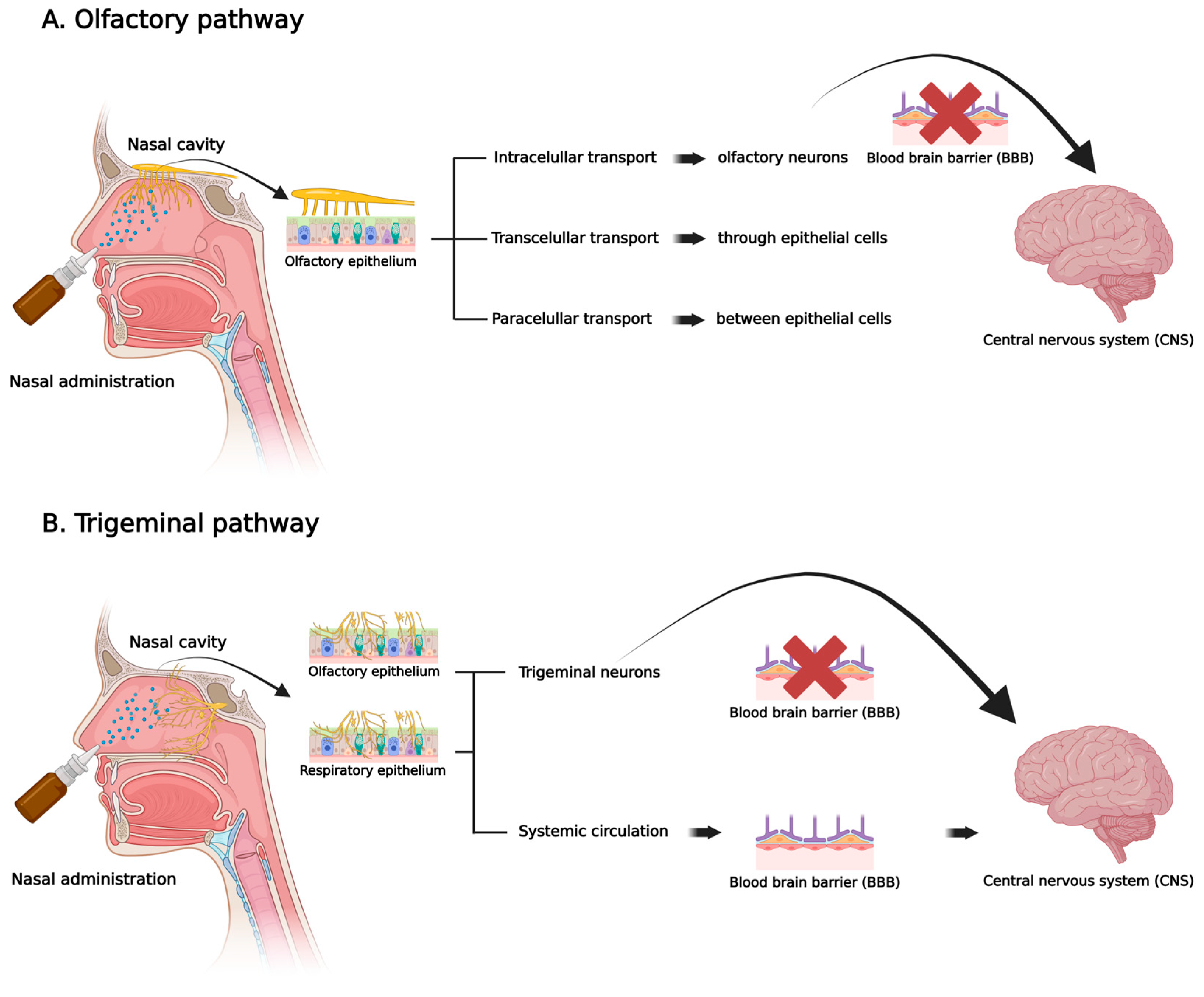
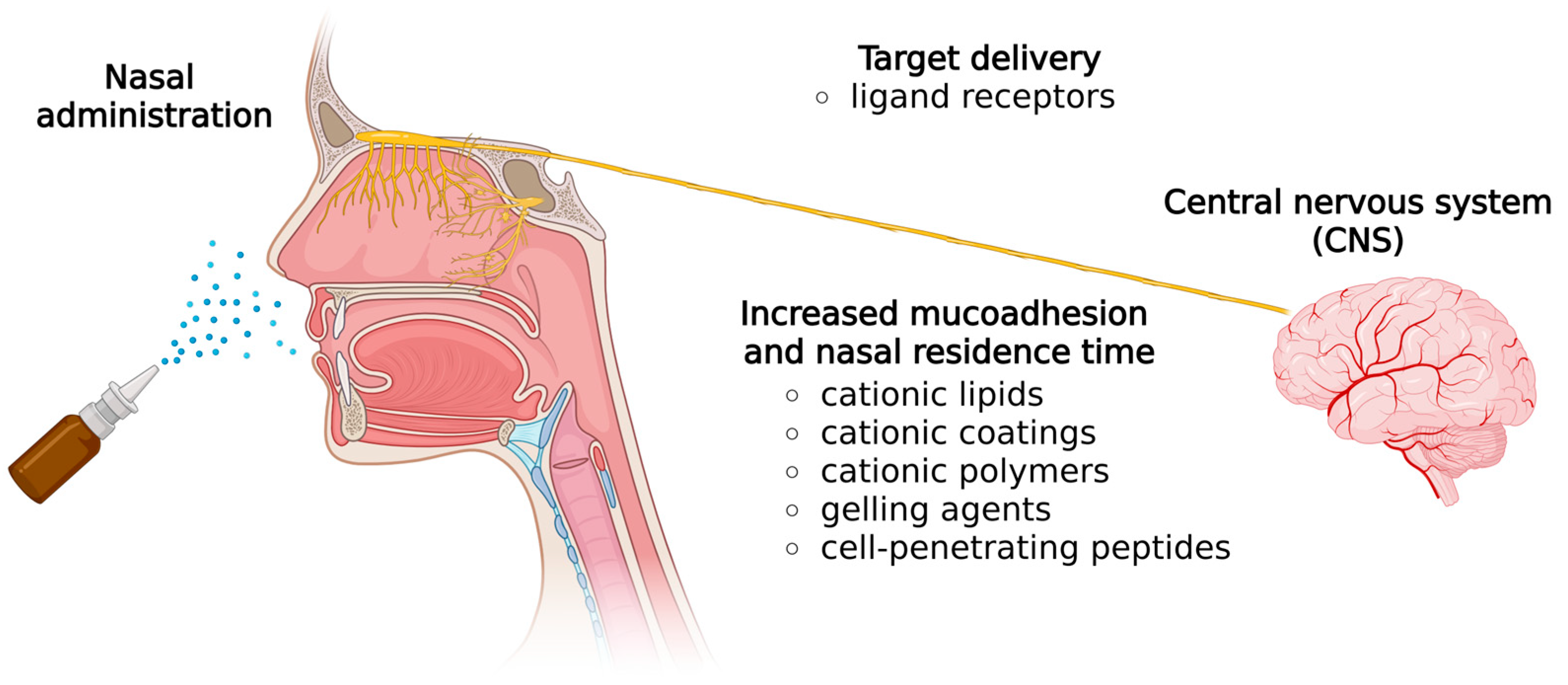
2. Nasal Route
3. Nose-to-Brain Nucleic Acids Delivery
4. Nose-to-Brain Gene Delivery Vectors
4.1. Viral Transduction and Non-Viral Transfection
4.2. Viral Vectors
4.3. Non-Viral Vectors
Nanostructures and Biomaterials
5. Preclinical Advancements in Gene Delivery for CNS Disorders
5.1. Brain Injuries
5.2. Neurodegenerative Disorders
5.3. Brain Tumors
5.4. Neuropsychiatric Disorders
5.5. Congenital Metabolic Disorders
6. Clinical Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, A.R.; Liu, M.; Khan, M.W.; Zhai, G. Progress in Brain Targeting Drug Delivery System by Nasal Route. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 364–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Lalan, M.; Barve, K. Intranasal Delivery: An Attractive Route for the Administration of Nucleic Acid Based Therapeutics for CNS Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 974666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochhead, J.J.; Thorne, R.G. Intranasal Delivery of Biologics to the Central Nervous System. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassin-Delyle, S.; Buenestado, A.; Naline, E.; Faisy, C.; Blouquit-Laye, S.; Couderc, L.J.; Le Guen, M.; Fischler, M.; Devillier, P. Intranasal Drug Delivery: An Efficient and Non-Invasive Route for Systemic Administration-Focus on Opioids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 134, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, V.-A.; Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Maeng, H.-J. Recent Advances in Intranasal Liposomes for Drug, Gene, and Vaccine Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, A.; Stolnik, S.; Illum, L. Nanoparticles for Direct Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 379, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berillo, D.; Zharkinbekov, Z.; Kim, Y.; Raziyeva, K.; Temirkhanova, K.; Saparov, A. Stimuli-Responsive Polymers for Transdermal, Transmucosal and Ocular Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaba, N.; Garcia-Fuentes, M.; Alonso, M.J. Nanoparticles for Nasal Vaccination. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 140–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwoke, M.I.; Agu, R.U.; Verbeke, N.; Kinget, R. Nasal Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery: Background, Applications, Trends and Future Perspectives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1640–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffleur, F.; Bauer, B. Progress in Nasal Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 120994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopapa, C.; Siamidi, A.; Pavlou, P.; Vlachou, M. Excipients Used for Modified Nasal Drug Delivery: A Mini-Review of the Recent Advances. Materials 2022, 15, 6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paun, J.S.; Bagada, A.; Raval, M.K. Nasal Drug Delivery–As an Effective Tool for Brain Targeting-A Review. Int. J. Pharm. Appl. Sci. 2010, 1, 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Mujawar, N.; Ghatage, S.; Navale, S.; Sankpal, B.; Patil, S.; Patil, S. Nasal Drug Delivery: Problem Solution and Its Application. J. Curr. Pharma Res. 2014, 4, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Wadhwa, K.; Kumar, S.; Singh, G.; Pahwa, R. Revolutionizing Parkinson’s Treatment: Harnessing the Potential of Intranasal Nanoemulsions for Targeted Therapy. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 2589–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrajo, M.L.; Alonso, M.J. Using Nanotechnology to Deliver Biomolecules from Nose to Brain—Peptides, Proteins, Monoclonal Antibodies and RNA. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 862–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patharapankal, E.J.; Ajiboye, A.L.; Mattern, C.; Trivedi, V. Nose-to-Brain (N2B) Delivery: An Alternative Route for the Delivery of Biologics in the Management and Treatment of Central Nervous System Disorders. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdő, F.; Bors, L.A.; Farkas, D.; Bajza, Á.; Gizurarson, S. Evaluation of Intranasal Delivery Route of Drug Administration for Brain Targeting. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 143, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, Y.; Kapoor, D.N.; Sharma, A.K.; Bhatia, A. Drug Delivery Systems and Strategies to Overcome the Barriers of Brain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 28, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.R.; Yang, X.; Fu, M.; Zhai, G. Recent Progress of Drug Nanoformulations Targeting to Brain. J. Control. Release 2018, 291, 37–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskaya, L.; Abou-Kaoud, M.; Stepensky, D. Quantitative Analysis of Drug Delivery to the Brain via Nasal Route. J. Control. Release 2014, 189, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, Y.B. Drug Delivery to the Brain via the Nasal Route of Administration: Exploration of Key Targets and Major Consideration Factors. J. Pharm. Investig. 2023, 53, 119–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, A.; Nozohouri, S.; Bleier, B.S.; Amiji, M.M. CNS Delivery of Nucleic Acid Therapeutics: Beyond the Blood–Brain Barrier and Towards Specific Cellular Targeting. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 77–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, J.A.; Witzigmann, D.; Thomson, S.B.; Chen, S.; Leavitt, B.R.; Cullis, P.R.; van der Meel, R. The Current Landscape of Nucleic Acid Therapeutics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, G.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Yuan, W.; Shu, Y. Viral and Non-Viral Vectors in Gene Therapy: Current State and Clinical Perspectives. EBioMedicine 2025, 118, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Chukwu, C.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chen, H. Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Delivery to the Brain: Technology Advancements and Clinical Applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2024, 211, 115363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, S.R.; Hudry, E.; Maguire, C.A.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Grandi, P. Viral Vectors for Therapy of Neurologic Diseases. Neuropharmacology 2017, 120, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirange, R.H.; Chaudhari, R.B. Utilizing Mucoadhesive Polymers for Nasal Drug Delivery System. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 8, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, H.F.; Bruxel, F.; Fraga, M.; Schuh, R.S.; Zorzi, G.K.; Matte, U.; Fattal, E. Cationic Nanoemulsions as Nucleic Acids Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 534, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, K.; Zhao, J.; Ullah, I.; Guo, J.; Ren, X.K.; Feng, Y. Ligand Targeting and Peptide Functionalized Polymers as Non-Viral Carriers for Gene Therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 64–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, R.; Baldo, G.; Teixeira, H. Nanotechnology Applied to Treatment of Mucopolysaccharidoses. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabal, Y.M.; Kamel, A.O.; Sammour, O.A.; Elshafeey, A.H. Effect of Surface Charge on the Brain Delivery of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers in Situ Gels via the Nasal Route. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 442–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Gandham, S.K.; Panicucci, R.; Amiji, M.M. Intranasal Brain Delivery of Cationic Nanoemulsion-Encapsulated TNFalpha SiRNA in Prevention of Experimental Neuroinflammation. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 987–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.E.; Zahid, M. Cell Penetrating Peptides, Novel Vectors for Gene Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashida, M.; Kawakami, S.; Yamashita, F. Lipid Carrier Systems for Targeted Drug and Gene Delivery. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matta, J.; Maalouf, R. Delivery of SiRNA Therapeutics: PLGA Nanoparticles Approach. Front. Biosci. (Sch. Ed) 2019, 11, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditto, A.J.; Shah, P.N.; Yun, Y.H. Non-Viral Gene Delivery Using Nanoparticles. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonferoni, M.C.; Rossi, S.; Sandri, G.; Ferrari, F.; Gavini, E.; Rassu, G.; Giunchedi, P. Nanoemulsions for “Nose-to-Brain” Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.T.; Wang, S.H.; Ciotti, S.; Makidon, P.E.; Smith, D.M.; Fan, Y.; Schuler, C.F.; Baker, J.R. Formulation and Characterization of Nanoemulsion Intranasal Adjuvants: Effects of Surfactant Composition on Mucoadhesion and Immunogenicity. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Yu, S.-Y. Cationic Nanoemulsions as Non-Viral Vectors for Plasmid DNA Delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, R.S.; Gonzalez, E.A.; Tavares, A.M.V.; Seolin, B.G.; Elias, L.S.; Vera, L.N.P.; Kubaski, F.; Poletto, E.; Giugliani, R.; Teixeira, H.F.; et al. Neonatal Nonviral Gene Editing with the CRISPR/Cas9 System Improves Some Cardiovascular, Respiratory, and Bone Disease Features of the Mucopolysaccharidosis I Phenotype in Mice. Gene Ther. 2020, 27, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuh, R.S.; Poletto, É.; Fachel, F.N.S.; Matte, U.; Baldo, G.; Teixeira, H.F. Physicochemical Properties of Cationic Nanoemulsions and Liposomes Obtained by Microfluidization Complexed with a Single Plasmid or along with an Oligonucleotide: Implications for CRISPR/Cas Technology. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, R.S.; de Carvalho, T.G.; Giugliani, R.; Matte, U.; Baldo, G.; Teixeira, H.F. Gene Editing of MPS I Human Fibroblasts by Co-Delivery of a CRISPR/Cas9 Plasmid and a Donor Oligonucleotide Using Nanoemulsions as Nonviral Carriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 122, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romøren, K.; Thu, B.J.; Bols, N.C.; Evensen, Ø. Transfection Efficiency and Cytotoxicity of Cationic Liposomes in Salmonid Cell Lines of Hepatocyte and Macrophage Origin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2004, 1663, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuh, R.S.; Bidone, J.; Poletto, E.; Pinheiro, C.V.; Pasqualim, G.; de Carvalho, T.G.; Farinon, M.; da Silva Diel, D.; Xavier, R.M.; Baldo, G.; et al. Nasal Administration of Cationic Nanoemulsions as Nucleic Acids Delivery Systems Aiming at Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Gene Therapy. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, L.N.P.; Schuh, R.S.; Fachel, F.N.S.; Poletto, E.; Piovesan, E.; Kubaski, F.; Couto, E.; Brum, B.; Rodrigues, G.; Souza, H.; et al. Brain and Visceral Gene Editing of Mucopolysaccharidosis I Mice by Nasal Delivery of the CRISPR/Cas9 System. J. Gene Med. 2022, 24, e3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azambuja, J.H.; Schuh, R.S.; Michels, L.R.; Gelsleichter, N.E.; Beckenkamp, L.R.; Iser, I.C.; Lenz, G.S.; de Oliveira, F.H.; Venturin, G.; Greggio, S.; et al. Nasal Administration of Cationic Nanoemulsions as CD73-SiRNA Delivery System for Glioblastoma Treatment: A New Therapeutical Approach. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, H.K.; Fan, Y.; Kim, J.; Amiji, M.M. Intranasal Delivery and Transfection of MRNA Therapeutics in the Brain Using Cationic Liposomes. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Mumper, R.J. Intranasal Administration of Plasmid DNA-Coated Nanoparticles Results in Enhanced Immune Responses. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.; Lapierre, J.; Ojha, C.; Kaushik, A.; Batrakova, E.; Kashanchi, F.; Dever, S.; Nair, M.; El-Hage, N. Intranasal Drug Delivery of Small Interfering RNA Targeting Beclin1 Encapsulated with Polyethylenimine (PEI) in Mouse Brain to Achieve HIV Attenuation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, H.T.; Zupančič, O.; Laffleur, F.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Mucoadhesive Properties of Polyacrylates: Structure–Function Relationship. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2021, 107, 102857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, A.; Martien, R.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Thiolated Polycarbophil as an Adjuvant for Permeation Enhancement in Nasal Delivery of Antisense Oligonucleotides. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, A.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Nasal Delivery of Antisense Oligonucleotides: In Vitro Evaluation of a Thiomer/Glutathione Microparticulate Delivery System. J. Drug Target. 2010, 18, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Wang, T. Chitosan Nanoparticle as Protein Delivery Carrier—Systematic Examination of Fabrication Conditions for Efficient Loading and Release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 59, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sava, V.; Fihurka, O.; Khvorova, A.; Sanchez-Ramos, J. Enriched Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded with SiRNA Are Effective in Lowering Huntington’s Disease Gene Expression Following Intranasal Administration. Nanomedicine 2020, 24, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.-F.; Lin, M.C.-M. Nucleic Acid Delivery with Chitosan and Its Derivatives. J. Control Release 2009, 134, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Sun, W.; Kissel, T. Chitosan-Based Formulations for Delivery of DNA and SiRNA. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, V.R.; Singla, A.K.; Wadhawan, S.; Kaushik, R.; Kumria, R.; Bansal, K.; Dhawan, S. Chitosan Microspheres as a Potential Carrier for Drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 274, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, U.; Chauhan, S.; Nagaich, U.; Jain, N. Current Advances in Chitosan Nanoparticles Based Drug Delivery and Targeting. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A.P.; Mundiña-Weilenmann, C.; Romero, E.L.; Morilla, M.J. Increased Brain Radioactivity by Intranasal P-Labeled SiRNA Dendriplexes within in Situ-Forming Mucoadhesive Gels. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Villa, C. Poloxamer Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Otormin, F.; Duro Castaño, A.; Conejos-Sanchez, I.; Vicent, M. Envisioning the Future of Polymer Therapeutics for Brain Disorders. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol 2018, 11, e1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Oh, Y.-K.; Yoon, H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, C.-K. In Situ Gelling and Mucoadhesive Polymer Vehicles for Controlled Intranasal Delivery of Plasmid DNA. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 59, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, X.; Tang, L.; Tian, Y.; Men, K.; Yang, L. Enhanced Nose-to-Brain Delivery of SiRNA Using Hyaluronan-Enveloped Nanomicelles for Glioma Therapy. J. Control. Release 2022, 342, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, T.; Akiyama, F.; Kakizaki, S.; Takashima, Y.; Seta, Y. Delivery of SiRNA to the Brain Using a Combination of Nose-to-Brain Delivery and Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Modified Nano-Micelles. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9220–9226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muolokwu, C.E.; Chaulagain, B.; Gothwal, A.; Mahanta, A.K.; Tagoe, B.; Lamsal, B.; Singh, J. Functionalized Nanoparticles to Deliver Nucleic Acids to the Brain for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1405423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Sun, B.; Gao, X.; Dong, X.; Fu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Han, B. Intranasal Delivery of Targeted Nanoparticles Loaded with MiR-132 to Brain for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Paredes, A.; Sitia, L.; Ruyra, A.; Morris, C.J.; Wheeler, G.N.; McArthur, M.; Gasco, P. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Anti-Microbial Oligonucleotides. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 134, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.-E.; Kim, C.-K. Charge-Mediated Topical Delivery of Plasmid DNA with Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles to the Skin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassu, G.; Soddu, E.; Posadino, A.M.; Pintus, G.; Sarmento, B.; Giunchedi, P.; Gavini, E. Nose-to-Brain Delivery of BACE1 SiRNA Loaded in Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Alzheimer’s Therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 152, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, S. Biological Nanoparticles and Their Influence on Organisms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 28, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hasan, A.; Nejadi Babadaei, M.M.; Behzadi, E.; Nouri, M.; Sharifi, M.; Falahati, M. Exosomes: Multiple-Targeted Multifunctional Biological Nanoparticles in the Diagnosis, Drug Delivery, and Imaging of Cancer Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Wang, N.; Peng, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Enhanced Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Combined Small Interfering RNAs Using Lesion-Recognizing Nanoparticles for the Synergistic Therapy of Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 53177–53188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Immunological and Hematological Toxicities Challenging Clinical Translation of Nucleic Acid-Based Therapeutics. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2015, 15, 1023–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Patel, B.; Wairkar, S. Intranasal Delivery of Biotechnology-Based Therapeutics. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 103371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, B.T.; Aly, A.E.; Padegimas, L.; Sesenoglu-Laird, O.; Cooper, M.J.; Waszczak, B.L. Intranasal Administration of Plasmid DNA Nanoparticles Yields Successful Transfection and Expression of a Reporter Protein in Rat Brain. Gene Ther. 2014, 21, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.E.-E.; Harmon, B.; Padegimas, L.; Sesenoglu-Laird, O.; Cooper, M.J.; Yurek, D.M.; Waszczak, B.L. Intranasal Delivery of HGDNF Plasmid DNA Nanoparticles Results in Long-Term and Widespread Transfection of Perivascular Cells in Rat Brain. Nanomedicine 2019, 16, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Ramos, J.; Song, S.; Kong, X.; Foroutan, P.; Martinez, G.; Dominguez-Viqueria, W.; Mohapatra, S.; Mohapatra, S.; Haraszti, R.A.; Khvorova, A.; et al. Chitosan-Mangafodipir Nanoparticles Designed for Intranasal Delivery of SiRNA and DNA to Brain. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 43, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova, A.I.; Kubajewska, I.; Vaideanu, A.; Schätzlein, A.G.; Uchegbu, I.F. Gene Targeting to the Cerebral Cortex Following Intranasal Administration of Polyplexes. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gaamouch, F.; Audrain, M.; Lin, W.J.; Beckmann, N.; Jiang, C.; Hariharan, S.; Heeger, P.S.; Schadt, E.E.; Gandy, S.; Ehrlich, M.E.; et al. VGF-Derived Peptide TLQP-21 Modulates Microglial Function through C3aR1 Signaling Pathways and Reduces Neuropathology in 5xFAD Mice. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamptey, R.N.L.; Gothwal, A.; Trivedi, R.; Arora, S.; Singh, J. Synthesis and Characterization of Fatty Acid Grafted Chitosan Polymeric Micelles for Improved Gene Delivery of VGF to the Brain through Intranasal Route. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmakumar, S.; Jones, G.; Pawar, G.; Khorkova, O.; Hsiao, J.; Kim, J.; Amiji, M.M.; Bleier, B.S. Minimally Invasive Nasal Depot (MIND) Technique for Direct BDNF AntagoNAT Delivery to the Brain. J. Control. Release 2021, 331, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakova, M.; Stuke, K.; Schuemberg, K.; Mueller, K.; Schoenknecht, P.; Schroeter, M.L. BDNF as a Biomarker for Successful Treatment of Mood Disorders: A Systematic & Quantitative Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 174, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, T.; Yoshimura, R.; Ikuta, T.; Iwata, N. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Major Depressive Disorder: Evidence from Meta-Analyses. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Wang, C.; Bedi, R.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Mohapatra, S. Magnetic Micelles for DNA Delivery to Rat Brains after Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Nanomedicine 2014, 10, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidahl, A.C.; Klukinov, M.; Tzabazis, A.Z.; Sorensen, J.C.; Yeomans, D.C. Nasal Application of HSV Encoding Human Preproenkephalin Blocks Craniofacial Pain in a Rat Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Le, W. Differential Roles of M1 and M2 Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mishra, K.P.; Ganju, L.; Singh, S.B. Intranasally Delivered Small Interfering RNA-Mediated Suppression of Scavenger Receptor Mac-1 Attenuates Microglial Phenotype Switching and Working Memory Impairment Following Hypoxia. Neuropharmacology 2018, 137, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozuka, T.; Omori, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Tarusawa, E.; Yamamoto, H.; Chaya, T.; Furuhashi, M.; Morita, M.; Sato, T.; Hirose, S.; et al. MiR-124 Dosage Regulates Prefrontal Cortex Function by Dopaminergic Modulation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzei Taj, S.; Kho, W.; Riou, A.; Wiedermann, D.; Hoehn, M. MiRNA-124 Induces Neuroprotection and Functional Improvement after Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Biomaterials 2016, 91, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Sun, B.; Yang, L.; Ma, C.; Li, S. RVG29-Modified MicroRNA-Loaded Nanoparticles Improve Ischemic Brain Injury by Nasal Delivery. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Perets, N.; Betzer, O.; Ben-Shaul, S.; Sheinin, A.; Michaelevski, I.; Popovtzer, R.; Offen, D.; Levenberg, S. Intranasal Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Loaded with Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog SiRNA Repairs Complete Spinal Cord Injury. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10015–10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, K.J.; Webber, C.A.; Martinez, J.A.; Singh, B.; Zochodne, D.W. PTEN Inhibition to Facilitate Intrinsic Regenerative Outgrowth of Adult Peripheral Axons. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9306–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Tahara, K.; Maxwell, J.A.; Lalonde, R.; Fukuiwa, T.; Fujihashi, K.; Van Kampen, K.R.; Kong, F.; Tang, D.C.; Fukuchi, K. Nasal Inoculation of an Adenovirus Vector Encoding 11 Tandem Repeats of Aβ1--6 Upregulates IL--10 Expression and Reduces Amyloid Load in a Mo/Hu APPswe PS1dE9 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Gene Med. 2007, 9, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazan, N.G.; Palacios-Pelaez, R.; Lukiw, W.J. Hypoxia Signaling to Genes: Significance in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2002, 26, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peers, C.; Dallas, M.L.; Boycott, H.E.; Scragg, J.L.; Pearson, H.A.; Boyle, J.P. Hypoxia and Neurodegeneration. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1177, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Xie, J.-W.; Cai, J.-H.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; An, L. CD36 Upregulation Mediated by Intranasal LV-NRF2 Treatment Mitigates Hypoxia-Induced Progression of Alzheimer’s-Like Pathogenesis. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2014, 21, 2208–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnati, H.K.; Panigrahi, M.K.; Gutti, R.K.; Greig, N.H.; Tamargo, I.A. MiRNAs: Key Players in Neurodegenerative Disorders and Epilepsy. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 48, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M.; Conti, G.O. Environment and Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Update on MiRNA Role. MicroRNA 2017, 6, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy Bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Pathoanatomy of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. 2000, 247, II3–II10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Arís, D.; Recasens, A.; Galofré, M.; Carballo-Carbajal, I.; Zacchi, N.; Ruiz-Bronchal, E.; Pavia-Collado, R.; Chica, R.; Ferrés-Coy, A.; Santos, M.; et al. Selective α-Synuclein Knockdown in Monoamine Neurons by Intranasal Oligonucleotide Delivery: Potential Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 550–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, A.E.-E.; Harmon, B.T.; Padegimas, L.; Sesenoglu-Laird, O.; Cooper, M.J.; Waszczak, B.L. Intranasal Delivery of PGDNF DNA Nanoparticles Provides Neuroprotection in the Rat 6-Hydroxydopamine Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, C.M.; Gash, D.M. GDNF Protects Nigral Dopamine Neurons against 6-Hydroxydopamine in vivo. Brain Res. 1995, 672, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirik, D.; Georgievska, B.; Björklund, A. Localized Striatal Delivery of GDNF as a Treatment for Parkinson Disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sava, V.; Fihurka, O.; Khvorova, A.; Sanchez-Ramos, J. Kinetics of HTT Lowering in Brain of YAC 128 Mice Following Single and Repetitive Intranasal Dosing of SiRNA Packaged in Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatani, A.S.; Petkova, A.; Schatzlein, A.G.; Uchegbu, I.F. Dose-Dependent Delivery of Genes to the Cerebral Cortex via the Nasal Route. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 644, 123343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Teng, Y.; Samykutty, A.; Mu, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cao, P.; Rong, Y.; Yan, J.; Miller, D.; et al. Grapefruit-Derived Nanovectors Delivering Therapeutic MiR17 Through an Intranasal Route Inhibit Brain Tumor Progression. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, U.K.; Bose, R.J.C.; Malhotra, M.; Babikir, H.A.; Afjei, R.; Robinson, E.; Zeng, Y.; Chang, E.; Habte, F.; Sinclair, R.; et al. Intranasal Delivery of Targeted Polyfunctional Gold–Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded with Therapeutic MicroRNAs for Combined Theranostic Multimodality Imaging and Presensitization of Glioblastoma to Temozolomide. Biomaterials 2019, 218, 119342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Wang, D.; Yao, S.; Lu, L.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Zhou, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Core-Shell Lipoplexes Inducing Active Macropinocytosis Promote Intranasal Delivery of c-Myc SiRNA for Treatment of Glioblastoma. Acta Biomater. 2022, 138, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otte, C.; Gold, S.M.; Penninx, B.W.; Pariante, C.M.; Etkin, A.; Fava, M.; Mohr, D.C.; Schatzberg, A.F. Major Depressive Disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménard, C.; Hodes, G.E.; Russo, S.J. Pathogenesis of Depression: Insights from Human and Rodent Studies. Neuroscience 2016, 321, 138–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, W.; Jia, M.; Wang, C.; Dong, Y.; Dang, Y.; Gao, C. Intranasal Delivery of Recombinant AAV Containing BDNF Fused with HA2TAT: A Potential Promising Therapy Strategy for Major Depressive Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Dong, Y.; Liu, F.; Gao, C.; Ji, C.; Dang, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, Y. A Study of Antidepressant Effect and Mechanism on Intranasal Delivery of BDNF-HA2TAT/AAV to Rats with Post-Stroke Depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Deng, L.; Ma, C.; Zhang, H.; Dang, Y. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Delivered Intranasally Relieves Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms Caused by a Single Prolonged Stress in Rats. Neuropsychobiology 2023, 82, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubaski, F.; de Oliveira Poswar, F.; Michelin-Tirelli, K.; da Silveira Matte, U.; Horovitz, D.D.; Barth, A.L.; Baldo, G.; Vairo, F.; Giugliani, R. Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belur, L.R.; Temme, A.; Podetz-Pedersen, K.M.; Riedl, M.; Vulchanova, L.; Robinson, N.; Hanson, L.R.; Kozarsky, K.F.; Orchard, P.J.; Frey, W.H.; et al. Intranasal Adeno-Associated Virus Mediated Gene Delivery and Expression of Human Iduronidase in the Central Nervous System: A Noninvasive and Effective Approach for Prevention of Neurologic Disease in Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, S.; Ikehata, H.; Tanabe, M.; Umeda, T.; Tomiyama, T.; Tanaka, A.; Furubayashi, T.; Sakane, T.; Kiwa, T.; Washino, M.; et al. Investigating the Efficacy of Nasal Administration for Delivering Magnetic Nanoparticles into the Brain for Magnetic Particle Imaging. J. Control. Release 2024, 367, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xia, X.; Li, H.; Qin, M.; Gao, H. Nanotechnology for Enhanced Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery in Treating Neurological Diseases. J. Control. Release 2024, 366, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Nucleic Acid | Gene | Delivery Strategy | Key Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA plasmid | IDUA (alpha-L-iduronidase) | Nanoemulsions (DOPE, DOTAP, MCT, and DSPE-PEG) | The complexes enhanced enzyme activity in vitro and in vivo in a mouse model of MPS I. | [44,45] |
| Non-specific pDNA | Cationic nanoparticles (CTAB and Brij 78) | Serum antigen-specific IgG levels increased by 18 to 28 times compared to naked pDNA when pDNA nanoparticles were administered to Balb/C mice. | [48] | |
| mRNA | GFP-mRNA | Liposomes (DPPC, DOTAP, and cholesterol) | In vivo biodistribution revealed 15% higher GFP-mRNA expression in the brain compared to the naked mRNA group. | [47] |
| miRNA | miR-132 | mPEG-PLA nanoparticles | The distribution of WGA-NPs-miR132 in the APP/PS1 mouse model and MCAO rats was notably improved in the brain, demonstrating therapeutic effects, reduced nasal ciliary clearance, and better targeting to neurons. | [66] |
| ODN | PTO | Microparticles coated with PCP-Cys | Microparticles reduced clearance from the nasal cavity, increased contact time with the nasal mucosa, and offered high stability, thereby improving ASO permeation and controlling release. | [51,52] |
| siRNA | CD73 | Nanoemulsions (DOTAP, MCT, and lecithin E-80) | CD73 was silenced in vitro and in vivo, resulting in a 60% decrease in tumor size. | [46] |
| Beclin1 | Cationic PEI-siBeclin1 nanoplexes | siRNA was detected in the glial cells of the prefrontal cortex and the cytoplasm of neurons at 4 and 24 h post-administration, with a notable 65% reduction in protein levels and no signs of toxicity. | [49] | |
| 32-P labeled siRNA | Thermosensitive mucoadhesive gels containing siRNA dendriplexes | Decreased degradation by RNases and enhanced endocytic uptake. | [59] | |
| HTT | Nanoparticles with chitosan | Four nanocarrier formulations were found to reduce HTT mRNA expression by at least 50%. | [54] | |
| VEGF or PLK1 | Multifunctional core–shell nanomicelles coated with hyaluronic acid (HA) and encapsulating the cell-penetrating peptide DP7-C | Successfully delivering the formulation to GL261 tumor-bearing mice resulted in tumor growth inhibition, longer survival times, and smaller tumor volumes. | [63] | |
| Raf-1 | Nanomicelles with PEG-PCL conjugated with the cell-penetrating peptide Tat | Nasal administration of these nanomicelles to rats resulted in a ten-fold increase in siRNA levels in the brain. | [64] | |
| BACE1 | Solid lipid nanoparticles with chitosan and RVG-9R, a cell-penetrating peptide | In vitro tests using the Caco-2 cell line demonstrated that formulations exhibited increased permeability, while those coated with chitosan showed decreased passage through the cell layer. | [69] | |
| BACE1 and Caspase-3 | Exosomes combined with BAP | The exosomes significantly increased brain accumulation of Cy5-labeled siRNA, and treated mice outperformed saline controls in spatial learning and memory tests. | [72] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fachel, F.N.S.; Salatino-Oliveira, A.; Carniel, W.d.S.; Zimmermann, R.; Matte, U.; Teixeira, H.F.; Baldo, G.; Schuh, R.S. Recent Advances in Nose-to-Brain Gene Delivery for Central Nervous System Disorders. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091177
Fachel FNS, Salatino-Oliveira A, Carniel WdS, Zimmermann R, Matte U, Teixeira HF, Baldo G, Schuh RS. Recent Advances in Nose-to-Brain Gene Delivery for Central Nervous System Disorders. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(9):1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091177
Chicago/Turabian StyleFachel, Flávia Nathiely Silveira, Angélica Salatino-Oliveira, Willian da Silva Carniel, Rafaela Zimmermann, Ursula Matte, Helder Ferreira Teixeira, Guilherme Baldo, and Roselena Silvestri Schuh. 2025. "Recent Advances in Nose-to-Brain Gene Delivery for Central Nervous System Disorders" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 9: 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091177
APA StyleFachel, F. N. S., Salatino-Oliveira, A., Carniel, W. d. S., Zimmermann, R., Matte, U., Teixeira, H. F., Baldo, G., & Schuh, R. S. (2025). Recent Advances in Nose-to-Brain Gene Delivery for Central Nervous System Disorders. Pharmaceutics, 17(9), 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091177









