Assessment of Antioxidant Activity and Dose-Dependent Effect on Genotoxicity/Antigenotoxicity of Pulmonaria officinalis Ethanolic Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Reagents, and Media
2.2. Plant Material and Extraction Procedure
2.3. Cell Culture and Cultivation Conditions
2.4. Chemical Analysis of P. officinalis Extract
2.5. Phytochemical Composition
2.5.1. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.5.2. Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
2.5.3. Total Phenolic Acid Content (TPA)
2.6. Antioxidant Activity
2.6.1. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Assay
2.6.2. Ferrous Ion Chelating Capacity (FIC)
2.6.3. Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC)
2.6.4. Potassium Ferricyanide Reducing Power Assay (PFRAP)
2.7. Antigenotoxicity Testing
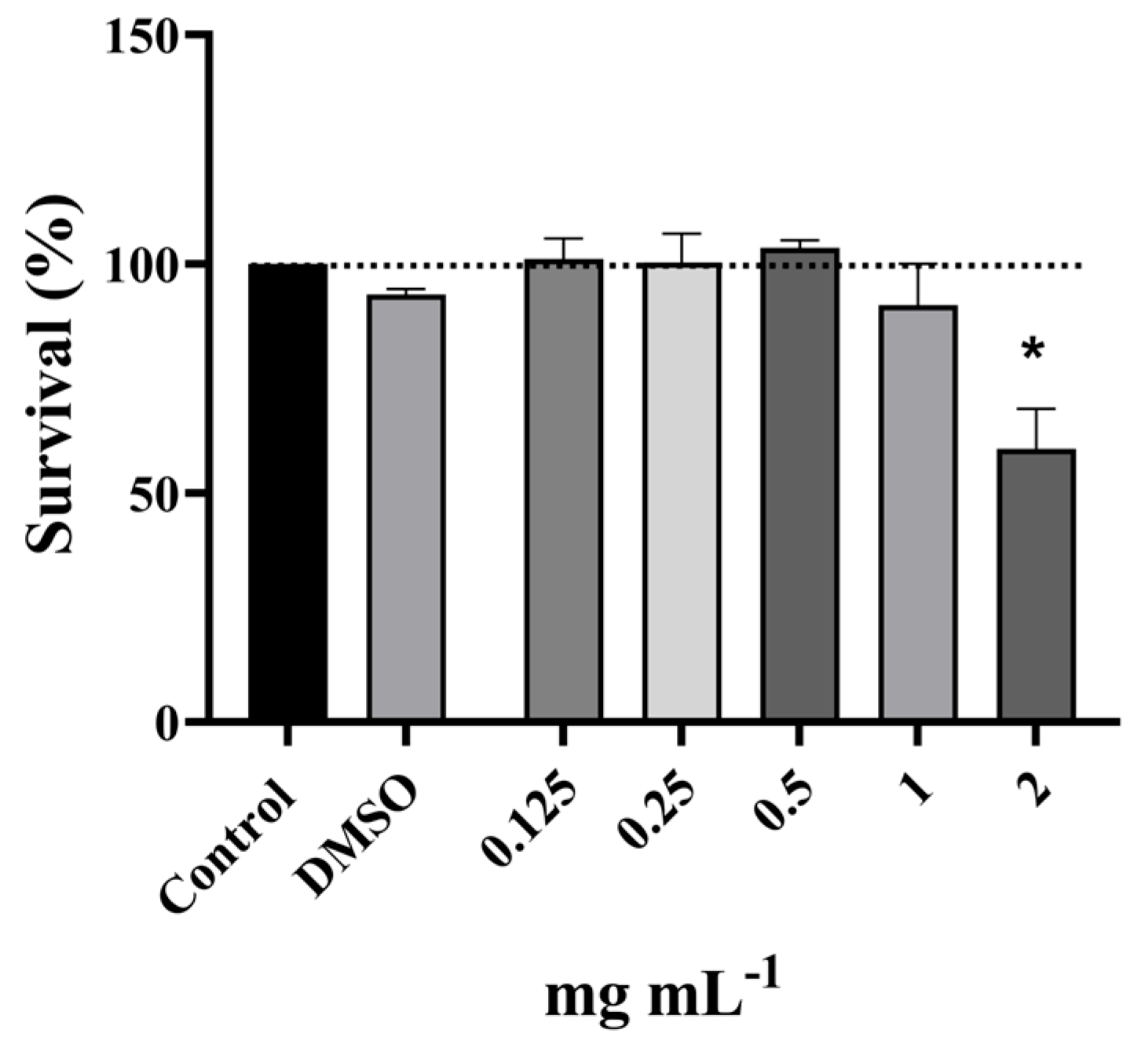
2.7.1. Determination of the Non-Cytotoxic Concentrations of P. officinalis Extract
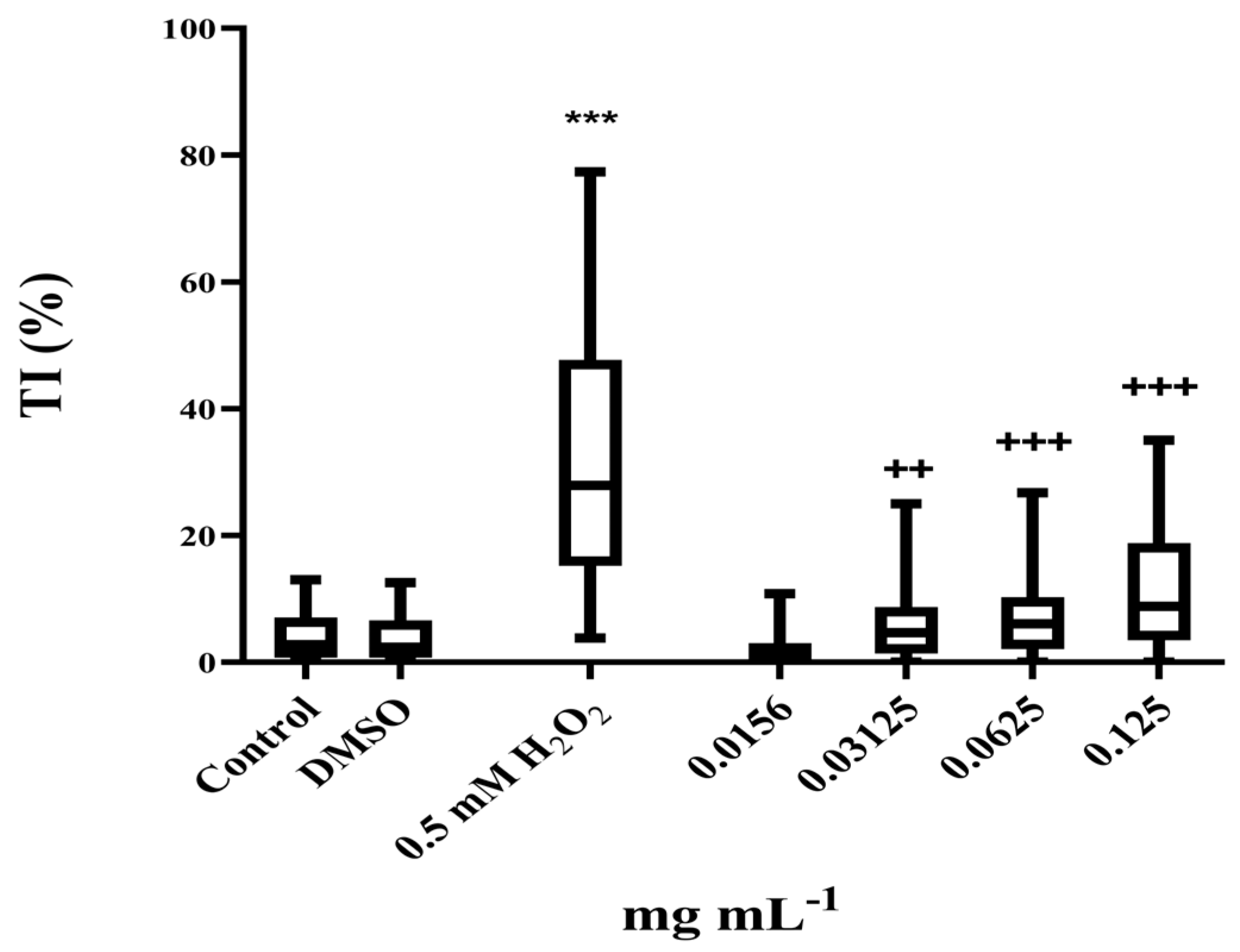
2.7.2. Determination of the Non-Genotoxic Concentrations of P. officinalis Extract
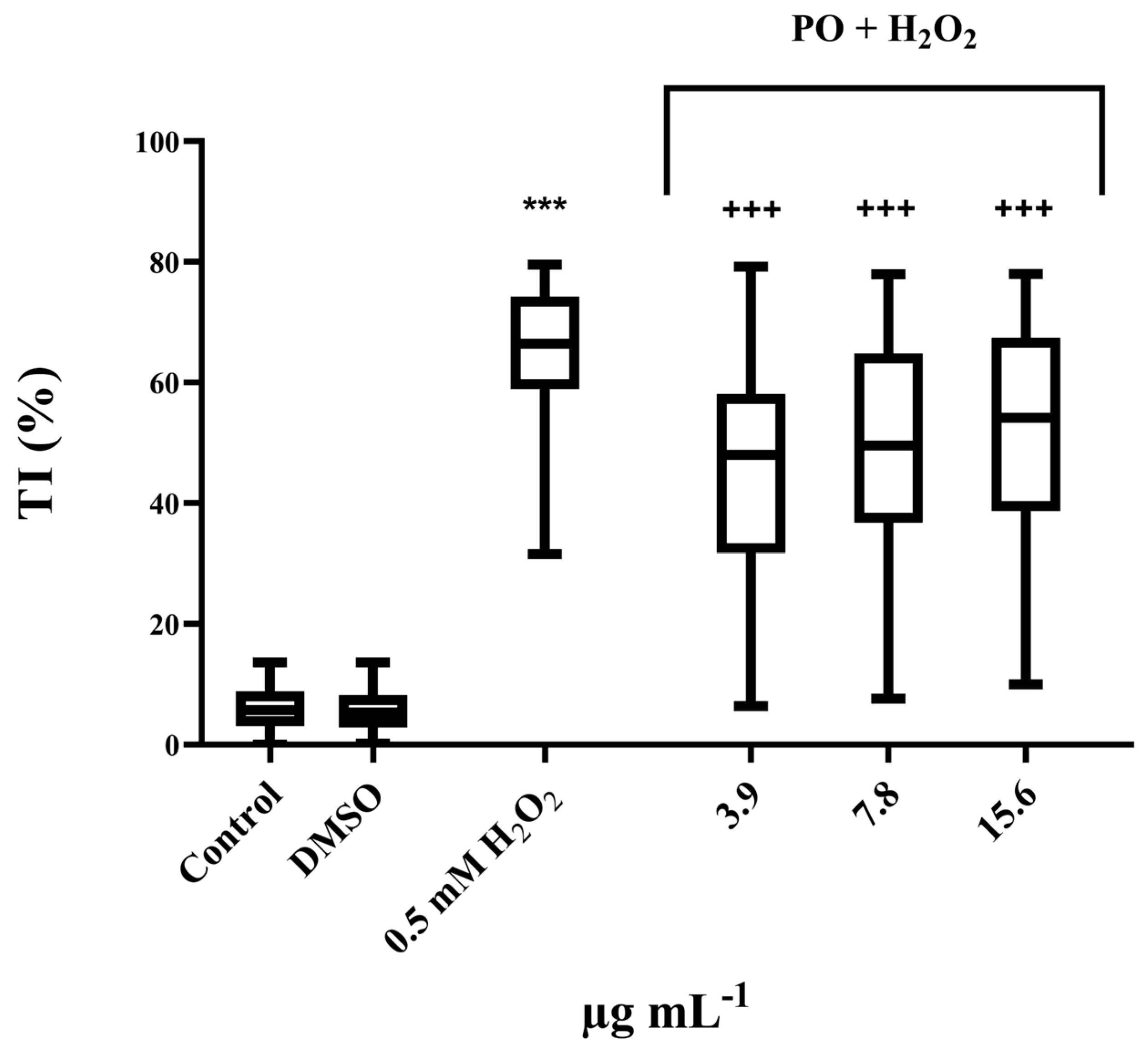
2.7.3. Antigenotoxicity Testing
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Analysis of P. officinalis Extract
3.2. Yield of the Main Phytochemical Groups
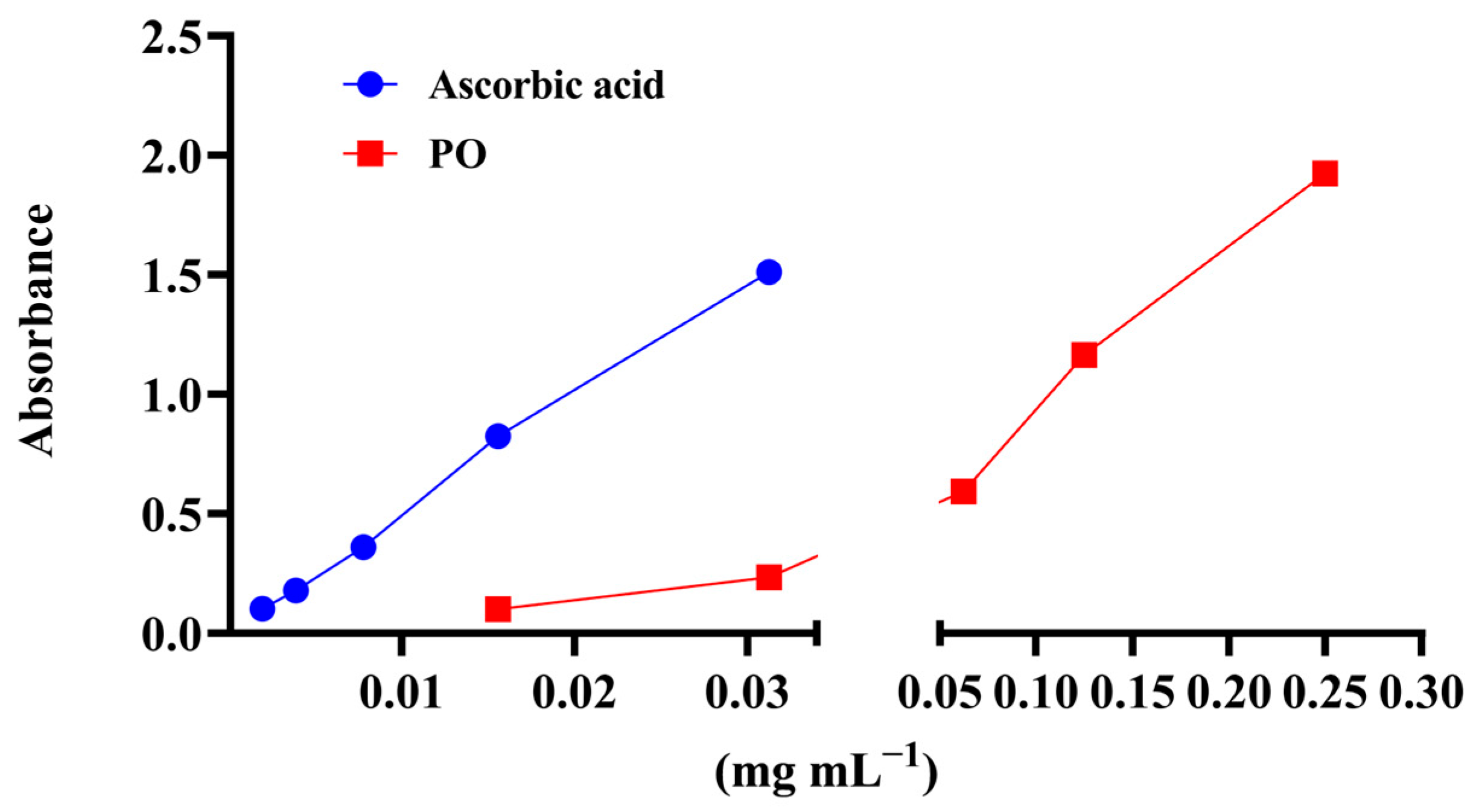
3.3. Antioxidant Activity of P. officinalis Extract
3.4. Antigenotoxic Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giustarini, D.; Dalle-Donne, I.; Tsikas, D.; Rossi, R. Oxidative Stress and Human Diseases: Origin, Link, Measurement, Mechanisms, and Biomarkers. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2009, 46, 241–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senguttuvan, J.; Paulsamy, S.; Karthika, K. Phytochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Leaf and Root Parts of the Medicinal Herb, Hypochaeris radicata. For In Vitro Antioxidant Activities. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, S359–S367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martemucci, G.; Costagliola, C.; Mariano, M.; D’andrea, L.; Napolitano, P.; D’alessandro, A.G. Free Radical Properties, Source and Targets, Antioxidant Consumption and Health. Oxygen 2022, 2, 48–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, S.; Reed, T.T.; Venditti, P.; Victor, V.M. Role of ROS and RNS Sources in Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1245049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Hunt, C.P.; Wadhwa, M.; Sanders, L.H. DNA Damage by Oxidative Stress: Measurement Strategies for Two Genomes. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozelle, A.L.; Cheun, Y.; Vilas, C.K.; Koag, M.-C.; Lee, S. DNA Interstrand Cross-Links Induced by the Major Oxidative Adenine Lesion 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoadenine. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, F.; Arcaro, A.; Pizzimenti, S.; Daga, M.; Cetrangolo, G.P.; Dianzani, C.; Lepore, A.; Graf, M.; Ames, P.R.J.; Barrera, G. DNA Damage by Lipid Peroxidation Products: Implications in Cancer, Inflammation and Autoimmunity. AIMS Genet. 2017, 4, 103–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Izakovic, M.; Mazur, M.; Rhodes, C.J.; Telser, J. Role of Oxygen Radicals in DNA Damage and Cancer Incidence. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 266, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; DELLA-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative Stress, Aging, and Diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelic, M.D.; Mandic, A.D.; Maricic, S.M.; Srdjenovic, B.U. Oxidative Stress and its Role in Cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2021, 17, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koklesova, L.; Liskova, A.; Samec, M.; Qaradakhi, T.; Zulli, A.; Smejkal, K.; Kajo, K.; Jakubikova, J.; Behzadi, P.; Pec, M.; et al. Genoprotective Activities of Plant Natural Substances in Cancer and Chemopreventive Strategies in the Context of 3p Medicine. EPMA J. 2020, 11, 261–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, D.M.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Lungu, I.I.; Radu, C.I.; Vladâcenco, O.; Roza, E.; Costăchescu, B.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, R.I. An Overview of Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, V.P. Oxidative Stress in Health and Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, C.; Vitillo, P.; Di Pietro, P.; Visco, V.; Strianese, A.; Virtuoso, N.; Ciccarelli, M.; Galasso, G.; Carrizzo, A.; Vecchione, C. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Aging and Cardiovascular Diseases. Life 2021, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, D.; Chen, M.-M.; Wu, H.; Deng, S.; Hu, X. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Skeletal Muscle Myogenesis and Muscle Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surh, Y.-J. Cancer Chemoprevention with Dietary Phytochemicals. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tsao, R. Dietary Polyphenols, Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 8, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, İ. Antioxidants and antioxidant methods: An updated overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 651–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belščak-Cvitanović, A.; Durgo, K.; Huđek, A.; Bačun-Družina, V.; Komes, D. Overview of Polyphenols and their Properties. In Polyphenols: Properties, Recovery, and Applications; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliar, T.; Maliarová, M.; Blažková, M.; Kunštek, M.; Uváčková, Ľ.; Viskupičová, J.; Purdešová, A.; Beňovič, P. Simultaneously Determined Antioxidant and Pro-Oxidant Activity of Randomly Selected Plant Secondary Metabolites and Plant Extracts. Molecules 2023, 28, 6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeus, S.; Brys, R.; Honnay, O.; Jacquemyn, H. Biological Flora of the British Isles: Pulmonaria officinalis. J. Ecol. 2013, 101, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Jaiswal, V.; Cho, Y.-I.; Lee, H.-J. Biological Activities and Phytochemicals of Lungworts (Genus Pulmonaria) Focusing on Pulmonaria officinalis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neagu, E.; Radu, G.L.; Albu, C.; Paun, G. Antioxidant Activity, Acetylcholinesterase and Tyrosinase Inhibitory Potential of Pulmonaria Officinalis and Centarium Umbellatum Extracts. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżanowska-Kowalczyk, J.; Kowalczyk, M.; Ponczek, M.B.; Pecio, Ł.; Nowak, P.; Kolodziejczyk-Czepas, J. Pulmonaria obscura and Pulmonaria officinalis Extracts as Mitigators of Peroxynitrite-Induced Oxidative Stress and Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors–In Vitro and In Silico Studies. Molecules 2021, 26, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, S.; Nastasijević, B.; Mitić-Ćulafić, D.; Đukanović, S.; Tenji, D.; Knežević-Vukčević, J.; Nikolić, B. New Insight into the Antigenotoxic Activity of Gentiana Lutea Extracts—Protective Effect Against Food Borne Mutagens. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2020, 858–860, 503251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žarković, L.D.; Mileski, K.S.; Matejić, J.S.; Gašić, U.M.; Rajčević, N.F.; Marin, P.D.; Džamić, A.M. Phytochemical Characterisation, In Vitro Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activity of Rosa Arvensis Huds. Extracts. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkowski, A.; Tasarz, P.; Szypua, E. Antioxidant Activity of Herb Extracts from Five Medicinal Plants from lamiaceae, subfamily lamioideae. J. Med. Plants Res. 2008, 2, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Vuletić, S.; Bekić, M.; Tomić, S.; Nikolić, B.; Cvetković, S.; Ganić, T.; Mitić-Ćulafić, D. Could Alder Buckthorn (Frangula alnus mill) be a Source of Chemotherapeutics Effective Against Hepato- and Colorectal Carcinoma? An In Vitro Study. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2023, 892, 503706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, S.; Vuletić, S.; Vunduk, J.; Klaus, A.; Mitić-Ćulafić, D.; Nikolić, B. The Role of Gentiana lutea Extracts in Reducing UV-Induced DNA Damage. Mutagenesis 2022, 38, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.B.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Musa, A.M.; Musa, A.O.; Kiplimo, J.J.; Oyewale, A.O. Free radical Scavenging and Total Antioxidant Capacity of Root Extracts of Anchomanes Difformis Engl. (Araceae). Acta. Pol. Pharm. 2013, 70, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.; Xu, T.; Lu, B.; Liu, R. Guidelines for Antioxidant Assays for Food Components. Food Front. 2020, 1, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, S.; Ignjatijević, A.; Kukić-Marković, J.; Vuletić, S.; Ušjak, L.; Milutinović, V.; Mitić-Ćulafić, D.; Petrović, S.; Nikolić, B. Further Insights into Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Potential of Achillea Millefolium Herb Methanol and Dichloromethane Extracts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 225, 120553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, P.P.; Thomas, J.; Mathew, S.; Skaria, B.P. Medicinal Plants. Trop. Hortic. 1998, 2, 449–632. [Google Scholar]
- Krzyżanowska-Kowalczyk, J.; Pecio, Ł.; Mołdoch, J.; Ludwiczuk, A.; Kowalczyk, M. Novel Phenolic Constituents of Pulmonaria officinalis L. LC-MS/MS Comparison of Spring and Autumn Metabolite Profiles. Molecules 2018, 23, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, D.; Gerova, D.; Chervenkov, T.; Yankova, T. Polyphenols and Antioxidant Capacity of Bulgarian Medicinal Plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-H.; Liou, Y.-L.; Li, S.-M.; Liao, H.-R.; Chen, J.-J. Antioxidant, Anti-α-Glucosidase, Anti-Tyrosinase, and Anti-Acetylcholinesterase Components from Stem of Rhamnus formosana with Molecular Docking Study. Antioxidants 2024, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesiada, A.; Tomczak, A. Biotic and Abiotic Factors Affecting the Content of the Chosen Antioxidant Compounds in Vegetables. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2012, 76, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-P.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.-J.; Li, H.-B. Natural Antioxidants in Foods and Medicinal Plants: Extraction, Assessment and Resources. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, I.D.; Rawat, S.; Rawal, R.S. Antioxidants in medicinal plants. In Biotechnology for Medicinal Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 295–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowska, P. Effect of Flavonoids Content on Antioxidant Activity of Commercial Cosmetic Plant Extracts. Herba Pol. 2013, 59, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asomadu, R.O.; Ezeorba, T.P.C.; Ezike, T.C.; Uzoechina, J.O. Exploring the Antioxidant Potential of Endophytic Fungi: A Review on Methods for Extraction and Quantification of Total Antioxidant Capacity (Tac). 3 Biotech 2024, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejin, B.; Savic, A.; Sokovic, M.; Glamoclija, J.; Ciric, A.; Nikolic, M.; Radotic, K.; Mojovic, M. Further In Vitro Evaluation of Antiradical and Antimicrobial Activities of Phytol. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villaño, D.; Fernández-Pachón, M.S.; Moyá, M.L.; Troncoso, A.M.; García-Parrilla, M.C. Radical Scavenging Ability of Polyphenolic Compounds Towards DPPH Free Radical. Talanta 2007, 71, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozarski, M.; Klaus, A.; Niksic, M.; Jakovljevic, D.; Helsper, J.P.; Van Griensven, L.J. Antioxidative and Immunomodulating Activities of Polysaccharide Extracts of the Medicinal Mushrooms Agaricus Bisporus, Agaricus Brasiliensis, Ganoderma Lucidum and Phellinus Linteus. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perron, N.R.; Brumaghim, J.L. A Review of the Antioxidant Mechanisms of Polyphenol Compounds Related to Iron Binding. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 53, 75–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.C.D.M.P.; Salvadori, M.S.; Mota, V.G.; Costa, L.M.; De Almeida, A.A.C.; De Oliveira, G.A.L.; Costa, J.P.; de Sousa, D.P.; De Freitas, R.M.; De Almeida, R.N. Antinociceptive and Antioxidant Activities of Phytol in vivo and in vitro Models. Neurosci. J. 2013, 2013, 949452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Živković, L.; Bajić, V.; Bruić, M.; Borozan, S.; Popić, K.; Topalović, D.; Santibanez, J.; Spremo-Potparević, B. Antigenotoxic and Antioxidant Potential of Medicinal Mushrooms (Immune Assist) Against DNA Damage Induced by Free Radicals-An In Vitro Study. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2019, 845, 403078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainslie, A.; Huiting, W.; Barazzuol, L.; Bergink, S. Genome Instability and Loss of Protein Homeostasis: Converging Paths to Neurodegeneration? Open Biol. 2021, 11, 200296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demma, J.; Engidawork, E.; Hellman, B. Potential Genotoxicity of Plant Extracts Used in Ethiopian Traditional Medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, G.; O’BRien, P.J. Potential Toxicity of Flavonoids and other Dietary Phenolics: Significance for their Chemopreventive and Anticancer Properties. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alencar, M.V.O.B.; Islam, M.T.; dos Reis, A.C.; Santos, J.V.d.O.; Nunes, A.M.V.; da Silva, F.C.C.; Machado, K.d.C.; Sousa, J.M.d.C.e.; Reiner, Ž.; Martorell, M.; et al. Oxidative Stress Mediated Cytogenotoxicological Effects of Phytol in Wistar Albino Rats. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2022, 23, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardoloi, A.; Soren, A.D. Genotoxicity Induced by Medicinal Plants. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2022, 46, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaseth, T.; Kuzminov, A. Prompt Repair of Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced DNA Lesions Prevents Catastrophic Chromosomal Fragmentation. DNA Repair 2016, 41, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.J.; Dubin, N.; Kurland, D.; Ma, B.-L.; Roush, G.C. The Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide on DNA Repair Activities. Mutat. Res. Repair 1995, 336, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Mattson, M.P. How Does Hormesis Impact Biology, Toxicology, and Medicine? npj Aging Mech. Dis. 2017, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Borstel, R.; Higgins, J.A. Janus Carcinogens and Mutagens. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1998, 402, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.K.; Khandelwal, N.; Hintzsche, H.; Stopper, H. Antigenotoxic Effects of Resveratrol: Assessment of in vitro and in vivo Response. Mutagenesis 2015, 31, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ikumawoyi, V.; Agbaje, E.; Awodele, O. Antigenotoxic and Antioxidant Activity of Methanol Stem Bark Extract of Napoleona Vogelii Hook & Planch (Lecythidaceae) In Cyclophosphamide-Induced Genotoxicity. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, V.K.; Mehara, A.K.; Mahto, V.K.; Singh, A.K. Antigenotoxic and antitumor properties of polyphenols. In Bioactive Polyphenols for Health and Pathology Treatment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 251–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuenter, E.; Creylman, J.; Verheyen, G.; Pieters, L.; Van Miert, S. Development of a Classification Model for the Antigenotoxic Activity of Flavonoids. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 98, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, G.R.M.; Grotto, D.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Serpeloni, J.M.; Rocha, B.A.; Bastos, J.K.; Barbosa, F. Evaluation of Antigenotoxic Effects of Plant Flavonoids Quercetin and Rutin on HepG2 Cells. Phytotherapy Res. 2011, 25, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carocho, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. A Review on Antioxidants, Prooxidants and Related Controversy: Natural and Synthetic Compounds, Screening and Analysis Methodologies and Future Perspectives. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.-N.; Trang, N.M.; Kang, H.; Kim, K.H.; Jeong, G.-S. Phytol Suppresses Osteoclast Differentiation and Oxidative Stress through Nrf2/HO-1 Regulation in RANKL-Induced RAW264.7 Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | Rt (min) | Relative Amount (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Phytol | 47.30 | 9.96 |
| 2. | 5,6,6-Trimethyl-5-(3-oxobut-1-enyl)-1-oxaspiro [2.5]octan-4-one | 39.60 | 3.68 |
| 3. | Tetracyclo [6.2.2.2(4,9).0(4,10)]tetradecan-2-one, 10,12-dihydroxy-1,3,7,8-tetramethyl- | 45.10 | 2.38 |
| 4. | 1,2,3,6-Tetrahydrobenzylalcohol, acetate | 12.70 | 2.20 |
| 5. | Phorbol | 51.40 | 1.78 |
| 6. | Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, (dodecahydro-6a-hydroxy-9a-methyl-3-methylene-2,9-dioxoazuleno [4,5-b]furan-6-yl)methyl ester, [3aS-(3aα,6ß,6aα,9aß,9bα)]- | 42.70 | 1.74 |
| 7. | 2-Hexadecanol | 35.00 | 1.63 |
| 8. | 8-Octadecenal | 49.40 | 1.62 |
| 9. | Hexadecanoic acid, ethyl ester | 43.10 | 1.46 |
| 10. | 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxypropyl ester, (Z,Z,Z)- | 46.20 | 1.34 |
| 11. | 12-Methyl-E,E-2,13-octadecadien-1-ol | 38.20 | 1.23 |
| 12. | 4-Methoxyphenoxyformamide, N-methyl-N-[4-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-2-butynyl]- | 54.50 | 1.15 |
| 13. | 1-Decanol, 2-methyl- | 20.60 | 1.13 |
| 14. | Undecane, 2-methyl- | 21.20 | 1.09 |
| 15. | 5,6,6-Trimethyl-5-(3-oxobut-1-enyl)-1-oxaspiro [2.5]octan-4-one | 44.40 | 1.09 |
| 16. | 1-Heptatriacotanol | 48.20 | 1.07 |
| 17. | Diethyl phthalate | 34.00 | 1.02 |
| 18. | Glycine, N-[(3α,5ß,7α,12α)-24-oxo-3,7,12-tris[(trimethylsilyl)oxy]cholan-24-yl]-, methyl ester | 59.50 | 1.01 |
| 19. | 3-(1-Cyclopentenyl)furan | 23.90 | 1.00 |
| Assay/Extract | Total Phenolics (mg·GAE·gdw−1) | Total Flavonoid (mg·QHE·gdw−1) | Total Phenolic Acid (mg CAE gdw−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PO | 286.23 ± 7.18 | 158.31 ± 0.27 | 365.01 ± 2.307 |
| EC50 (mg·mL−1) | mg·AAE·gdw−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Assay/Extract | DPPH | Ferrous ion Chelating Capacity | Total Antioxidant Capacity |
| PO | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 1.24 ± 0.03 | 273.97 ± 0.83 |
| VitC (µg mL−1) | 1.94 ± 0.004 | nt | nt |
| EDTA (mg mL−1) | nt | 0.06 ± 0.01 | nt |
| PO | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| µg mL−1 | 3.9 | 7.8 | 15.6 |
| Inhibition of genotoxicity | 28% | 23% | 20% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ignjatijević, A.; Anđić, T.; Lješević, M.; Nikolić, B.; Ganić, T.; Spasović, S.; Vuletić, S. Assessment of Antioxidant Activity and Dose-Dependent Effect on Genotoxicity/Antigenotoxicity of Pulmonaria officinalis Ethanolic Extract. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091134
Ignjatijević A, Anđić T, Lješević M, Nikolić B, Ganić T, Spasović S, Vuletić S. Assessment of Antioxidant Activity and Dose-Dependent Effect on Genotoxicity/Antigenotoxicity of Pulmonaria officinalis Ethanolic Extract. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(9):1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091134
Chicago/Turabian StyleIgnjatijević, Ana, Tamara Anđić, Marija Lješević, Biljana Nikolić, Tea Ganić, Stefana Spasović, and Stefana Vuletić. 2025. "Assessment of Antioxidant Activity and Dose-Dependent Effect on Genotoxicity/Antigenotoxicity of Pulmonaria officinalis Ethanolic Extract" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 9: 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091134
APA StyleIgnjatijević, A., Anđić, T., Lješević, M., Nikolić, B., Ganić, T., Spasović, S., & Vuletić, S. (2025). Assessment of Antioxidant Activity and Dose-Dependent Effect on Genotoxicity/Antigenotoxicity of Pulmonaria officinalis Ethanolic Extract. Pharmaceutics, 17(9), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091134







