Correction: Castro et al. Biocompatibility Assessment of Polycaprolactone/Polylactic Acid/Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Composites Under In Vivo Conditions for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2196
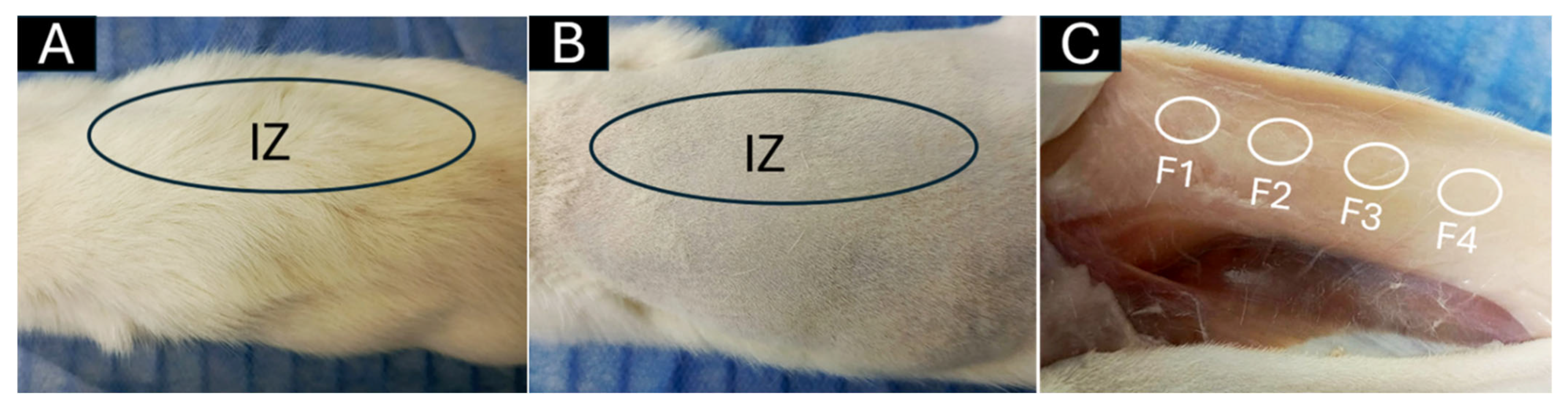
Error in Figure
References
- Castro, J.I.; Araujo-Rodríguez, D.G.; Valencia-Llano, C.H.; López Tenorio, D.; Saavedra, M.; Zapata, P.A.; Grande-Tovar, C.D. Biocompatibility Assessment of Polycaprolactone/Polylactic Acid/Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Composites Under In Vivo Conditions for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande-Tovar, C.D.; Castro, J.I.; Valencia Llano, C.H.; López Tenorio, D.; Saavedra, M.; Zapata, P.A.; Chaur, M.N. Polycaprolactone (PCL)-Polylactic Acid (PLA)-Glycerol (Gly) Composites Incorporated with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) and Tea Tree Essential Oil (TTEO) for Tissue Engineering Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castro, J.I.; Araujo-Rodríguez, D.G.; Valencia-Llano, C.H.; López Tenorio, D.; Saavedra, M.; Zapata, P.A.; Grande-Tovar, C.D. Correction: Castro et al. Biocompatibility Assessment of Polycaprolactone/Polylactic Acid/Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Composites Under In Vivo Conditions for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2196. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091113
Castro JI, Araujo-Rodríguez DG, Valencia-Llano CH, López Tenorio D, Saavedra M, Zapata PA, Grande-Tovar CD. Correction: Castro et al. Biocompatibility Assessment of Polycaprolactone/Polylactic Acid/Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Composites Under In Vivo Conditions for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2196. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(9):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091113
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastro, Jorge Iván, Daniela G. Araujo-Rodríguez, Carlos Humberto Valencia-Llano, Diego López Tenorio, Marcela Saavedra, Paula A. Zapata, and Carlos David Grande-Tovar. 2025. "Correction: Castro et al. Biocompatibility Assessment of Polycaprolactone/Polylactic Acid/Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Composites Under In Vivo Conditions for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2196" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 9: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091113
APA StyleCastro, J. I., Araujo-Rodríguez, D. G., Valencia-Llano, C. H., López Tenorio, D., Saavedra, M., Zapata, P. A., & Grande-Tovar, C. D. (2025). Correction: Castro et al. Biocompatibility Assessment of Polycaprolactone/Polylactic Acid/Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Composites Under In Vivo Conditions for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2196. Pharmaceutics, 17(9), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17091113





