Exploring miRNA Research in Colorectal Cancer: Insights from a Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
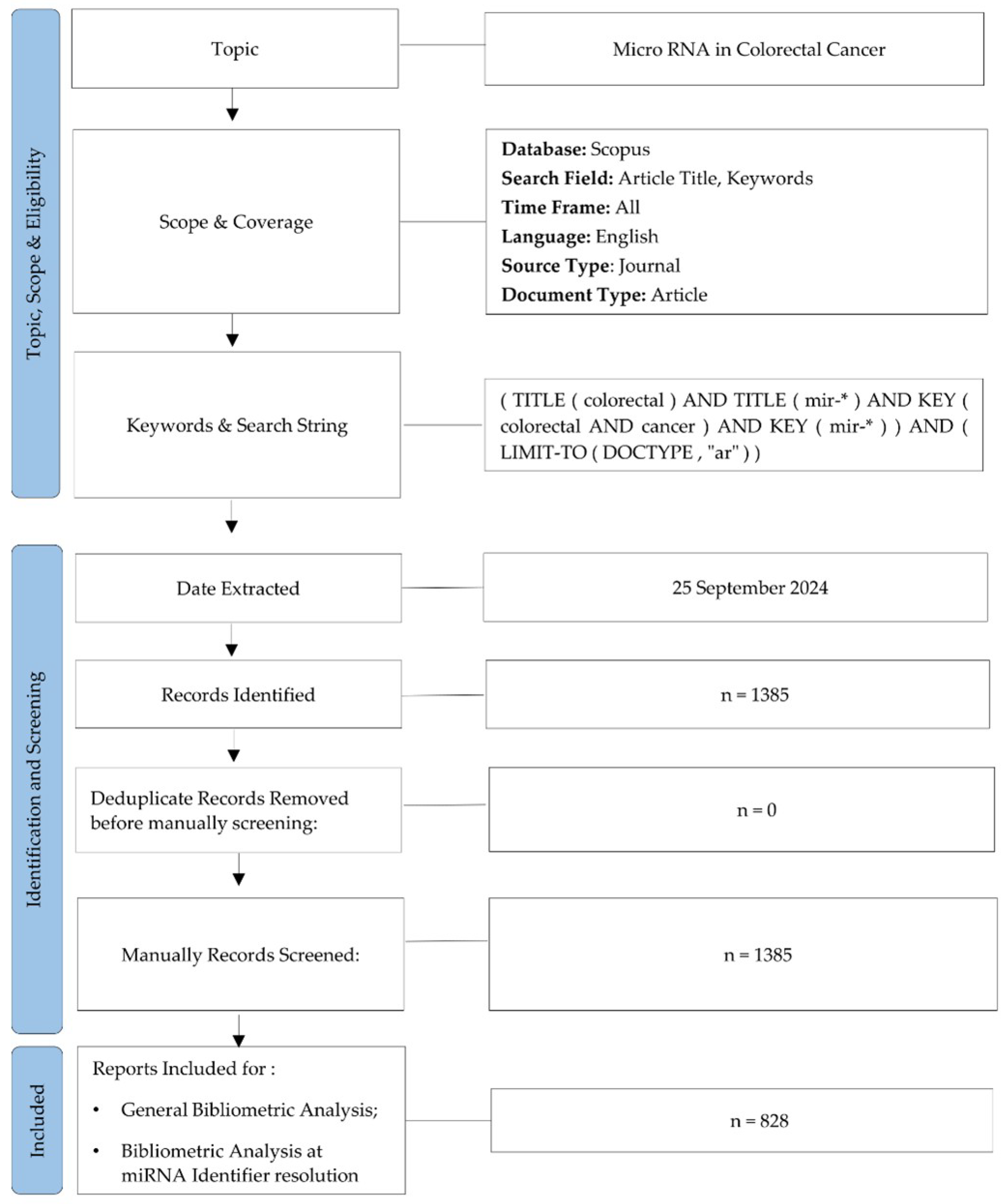
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Identification and Screening
2.2. Bibliometric Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Publication and Citation Trends
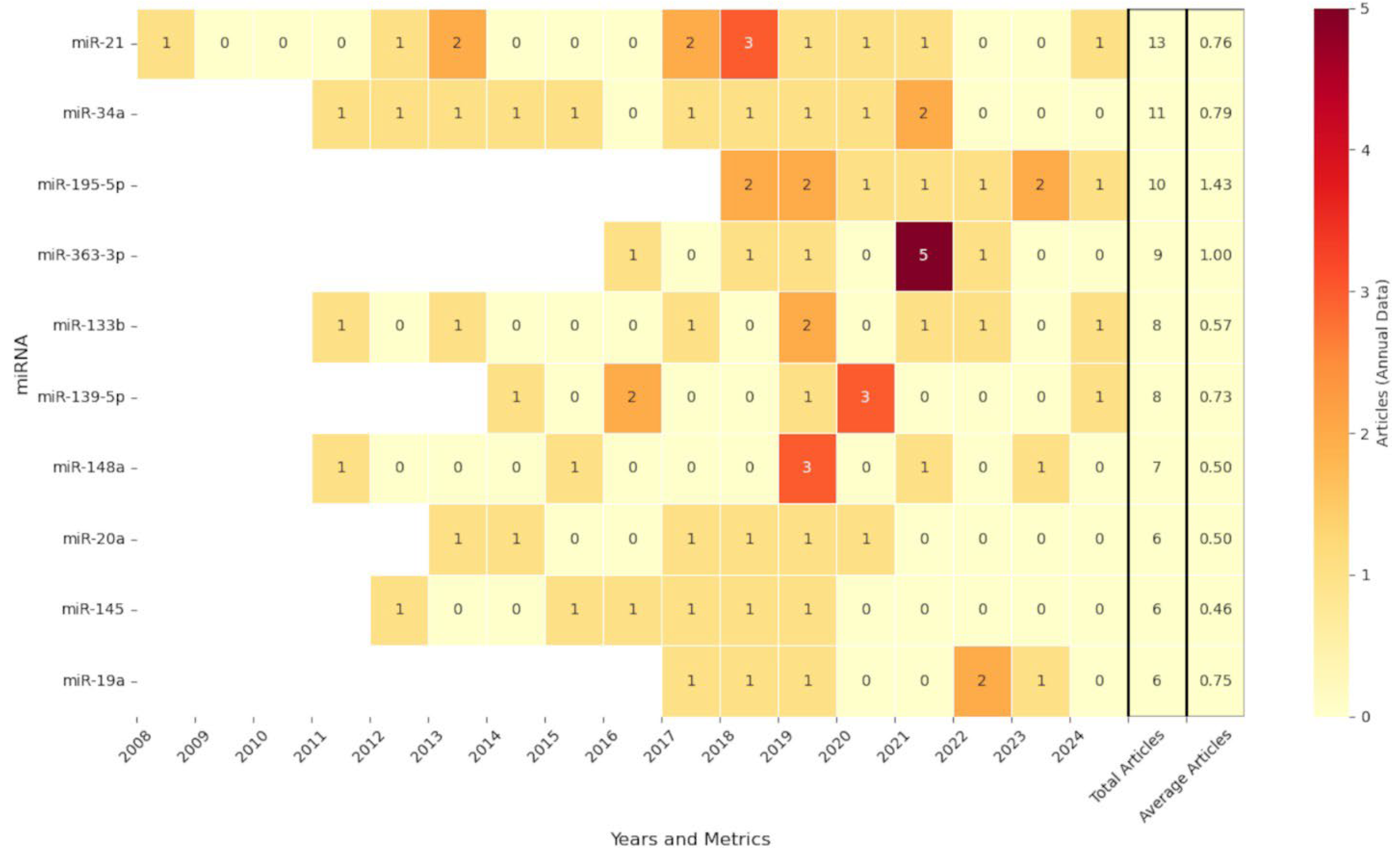
3.2. Distribution of Annual Publications Based on miRNA Identifier Level
3.3. Most Cited Documents
3.4. Geographical Distribution and Collaboration
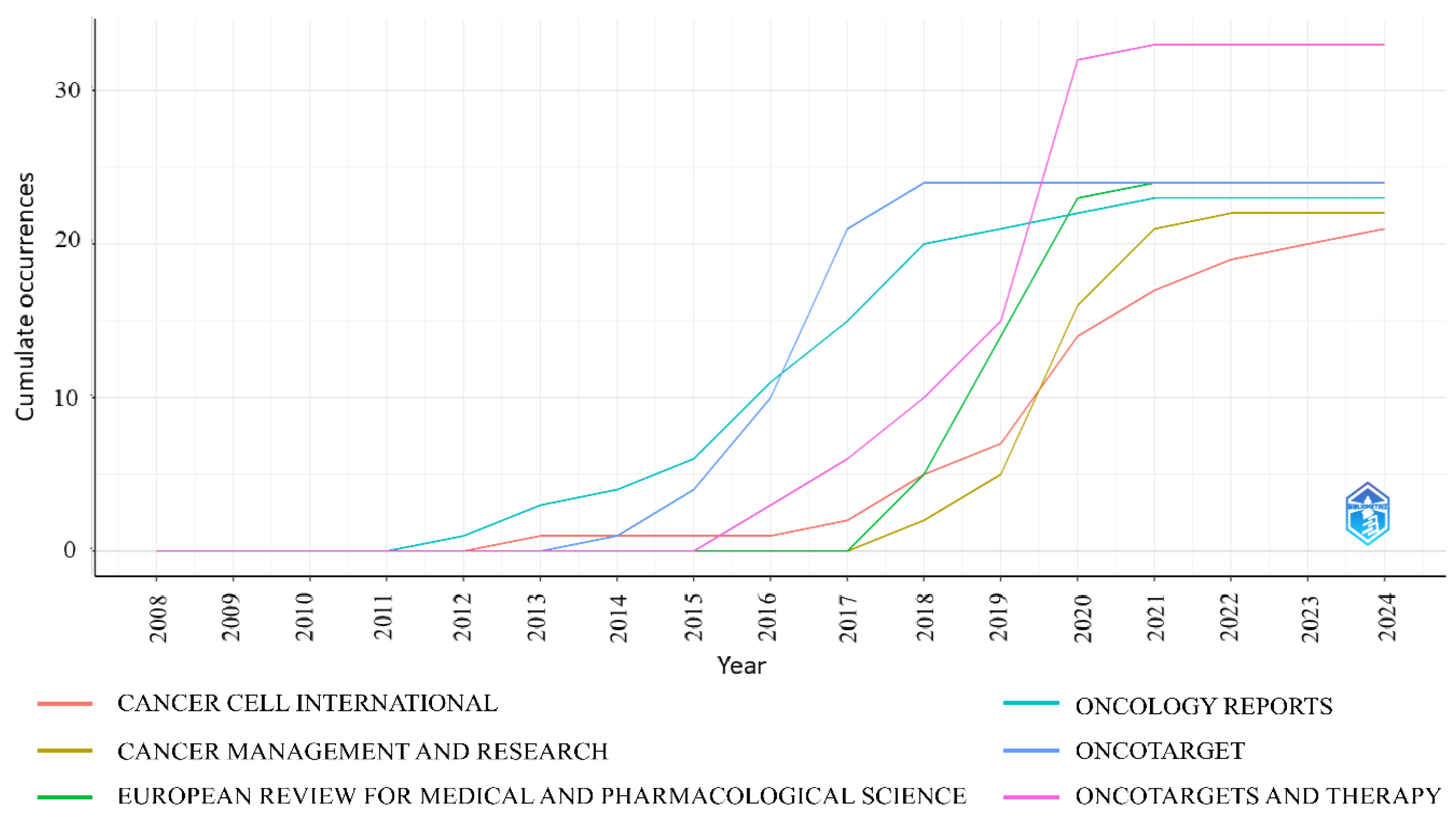
3.5. Most Productive Journals
3.6. Most Productive Institutions
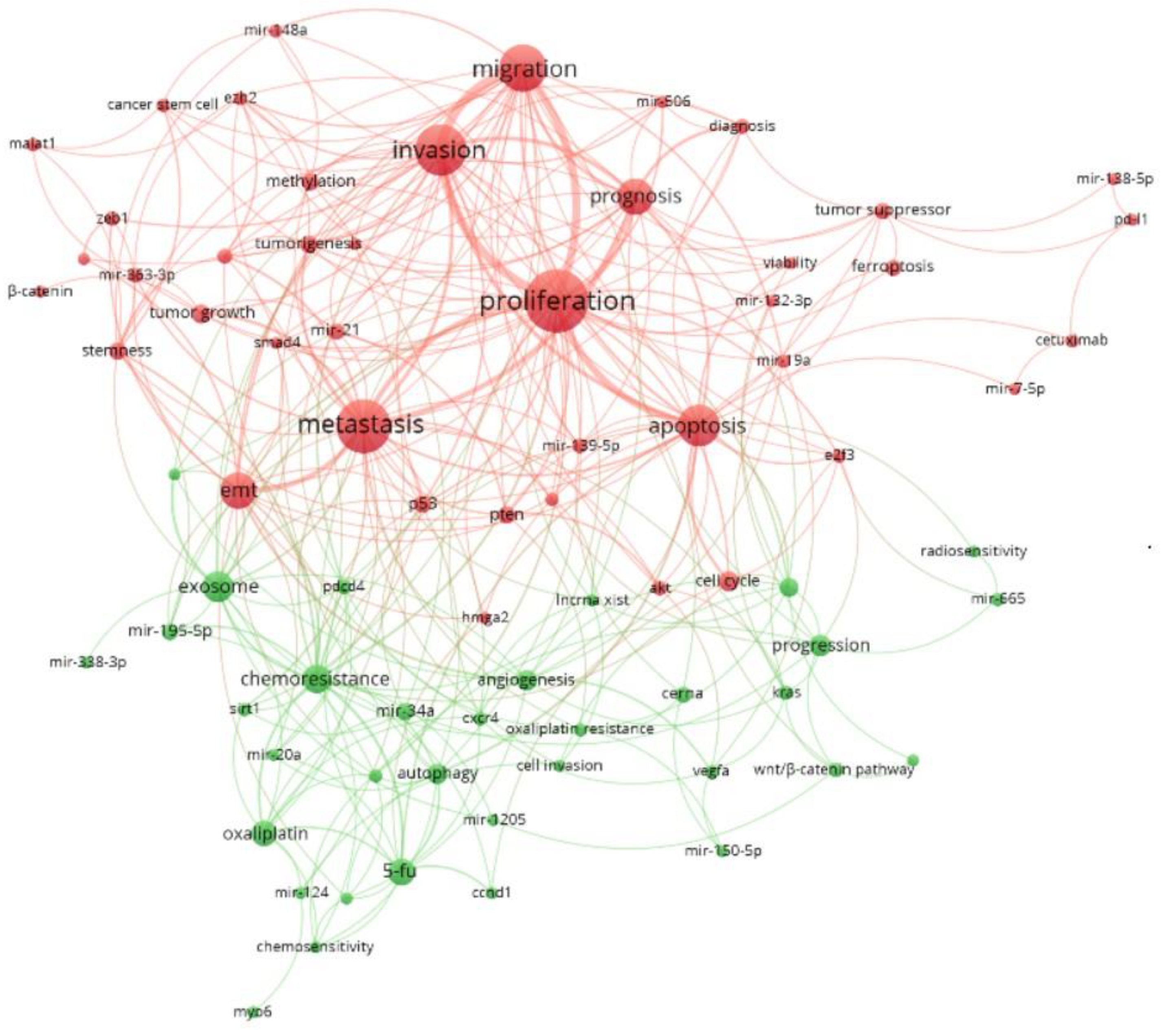
3.7. Word Cloud Frequencies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Sierra, M.S.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 2017, 66, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Vecchia, M.; Sala, G.; Sculco, M.; Aspesi, A.; Dianzani, I. Genetics, diet, microbiota, and metabolome: Partners in crime for colon carcinogenesis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ždralević, M.; Radović, A.; Raonić, J.; Popovic, N.; Klisic, A.; Vučković, L. Advances in microRNAs as Emerging Biomarkers for Colorectal Cancer Early Detection and Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA: Trends in clinical trials of cancer diagnosis and therapy strategies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xuan, G.; Chen, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhao, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, E. MicroRNAs are key molecules involved in the gene regulation network of colorectal cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 828128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Kitai, H.; Suzuki, H.I. Network regulation of microRNA biogenesis and target interaction. Cells 2023, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakawa, H.-o.; Tomari, Y. Life of RISC: Formation, action, and degradation of RNA-induced silencing complex. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, A.A. Trials and tribulations of MicroRNA therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.W.; Dinger, M.E. Endogenous microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, S.; Izaurralde, E. Towards a molecular understanding of microRNA-mediated gene silencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, T.; Doss, G.P.C. Non-coding RNAs in human health and disease: Potential function as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2023, 23, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Peffers, M.J.; Ormseth, M.J.; Jurisica, I.; Kapoor, M. The non-coding RNA interactome in joint health and disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooij, L.A.; Mastebroek, D.J.; Ten Voorde, N.; van der Wall, E.; van Diest, P.J.; Moelans, C.B. The microRNA lifecycle in health and cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellakwa, D.E.-S.; Mushtaq, N.; Khan, S.; Jabbar, A.; Abdelmalek, M.A.; Wadan, A.-H.S.; Ellakwa, T.E.; Raza, A. Molecular functions of microRNAs in colorectal cancer: Recent roles in proliferation, angiogenesis, apoptosis, and chemoresistance. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 5617–5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Mao, J.; Zhan, Z.; Duan, S. miRNA interplay: Mechanisms and therapeutic interventions in cancer. MedComm–Oncol. 2024, 3, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Lin, C.; Jia, X.; Zhu, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. Noncoding RNAs regulate alternative splicing in Cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.T.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Yang, B.B. Targeting circular RNAs as a therapeutic approach: Current strategies and challenges. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Melo, S.A. Non-coding RNAs in exosomes: New players in cancer biology. Curr. Genom. 2015, 16, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makler, A.; Asghar, W. Exosomal biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and patient monitoring. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.S.; Brenner, A.J.; Sachdev, J.; Borad, M.; Kang, Y.-K.; Stoudemire, J.; Smith, S.; Bader, A.G.; Kim, S.; Hong, D.S. Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.-K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Brenner, A.J.; Park, K.; Lee, J.-L.; Kim, T.-Y. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, G.; Guido, D.; Tagliabue, A. A bibliometric study of scientific literature on the dietary therapies for epilepsy in Scopus. Nutr. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perna, S.; Peroni, G.; Miccono, A.; Riva, A.; Morazzoni, P.; Allegrini, P.; Preda, S.; Baldiraghi, V.; Guido, D.; Rondanelli, M. Multidimensional effects of soy isoflavone by food or supplements in menopause women: A systematic review and bibliometric analysis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1934578X1601101127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallardi, D.; Maqoud, F.; Guido, D.; Aloisio, M.; Linsalata, M.; Russo, F. Mapping Research Trends on Intestinal Permeability in Irritable Bowel Syndrome with a Focus on Nutrition: A Bibliometric Analysis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. scientometrics 2009, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranckutė, R. Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The titans of bibliographic information in today’s academic world. Publications 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, J.; Schotten, M.; Plume, A.; Côté, G.; Karimi, R. Scopus as a curated, high-quality bibliometric data source for academic research in quantitative science studies. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2020, 1, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South, A. rworldmap: A new R package for mapping global data. R J. 2011, 3, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- bibliometrix.org. FAQ. Available online: https://www.bibliometrix.org/home/index.php/faq (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L.; Dekker, R.; Van Den Berg, J. A comparison of two techniques for bibliometric mapping: Multidimensional scaling and VOS. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2405–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rossum, G.; Drake, F.L. Python 3 Reference Manual: (Python Documentation Manual Part 2); CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Asangani, I.A.; Rasheed, S.A.; Nikolova, D.; Leupold, J.; Colburn, N.; Post, S.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Mi, Y.; Guan, B.; Zheng, B.; Wei, P.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, X. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-934 induces macrophage M2 polarization to promote liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Li, J.-W.; Zhang, B.-M.; Lv, J.-C.; Li, Y.-M.; Gu, X.-Y.; Yu, Z.-W.; Jia, Y.-H.; Bai, X.-F.; Li, L. The lncRNA CRNDE promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance via miR-181a-5p-mediated regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, M.; Munding, J.; Grüner, M.; Liffers, S.-T.; Verdoodt, B.; Hauk, J.; Steinstraesser, L.; Tannapfel, A.; Hermeking, H. Frequent concomitant inactivation of miR-34a and miR-34b/c by CpG methylation in colorectal, pancreatic, mammary, ovarian, urothelial, and renal cell carcinomas and soft tissue sarcomas. Virchows Arch. 2011, 458, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, W.M.; Parkin, R.; Mitchell, P.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Washington, M.; Paraskeva, C.; Willson, J.; Kaz, A. Epigenetic silencing of the intronic microRNA hsa-miR-342 and its host gene EVL in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3880–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toiyama, Y.; Hur, K.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Serum miR-200c is a novel prognostic and metastasis-predictive biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. 2014, 259, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.l.; Xu, L.l.; Wang, F. Hsa_circ_0020397 regulates colorectal cancer cell viability, apoptosis and invasion by promoting the expression of the miR-138 targets TERT and PD-L1. Cell Biol. Int. 2017, 41, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yu, H.; Yi, S.; Peng, X.; Su, P.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, R.; Tang, A.; Li, X.; Liu, F. The tumor suppressor miR-138-5p targets PD-L1 in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 45370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimanski, C.C.; Frerichs, K.; Rahman, F.; Berger, M.; Lang, H.; Galle, P.R.; Moehler, M.; Gockel, I. High miR-196a levels promote the oncogenic phenotype of colorectal cancer cells. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2009, 15, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaayvaz, M.; Zhai, H.; Ju, J. miR-129 promotes apoptosis and enhances chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, L.; Zhi, X.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, P.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Qin, J. Hsa_circRNA_103809 regulated the cell proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer via miR-532–3p/FOXO4 axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, W.; Zhuoqi, X.; Baocheng, W.; Dongsheng, Z.; Chuan, Z.; Yueming, S. Hsa_circ_0071589 promotes carcinogenesis via the miR-600/EZH2 axis in colorectal cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.; Liang, Q.; Xu, K.; Cui, D.; Jiang, L.; Yin, P.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, J. MiR-139 inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xi, Z.; Chen, H.; Shi, H.; Xin, T.; Shen, R.; Wang, T. MiR-4319 suppresses colorectal cancer progression by targeting ABTB1. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Li, C.; Zhao, T.; Li, D.; Yang, L.; Zhang, B. LncRNA H19/miR-29b-3p/PGRN axis promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells by acting on Wnt signaling. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 423–435. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, J. The novel long noncoding RNA TUSC7 inhibits proliferation by sponging MiR-211 in colorectal cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Uzair-Ur-Rehman Guo, Y.; Liang, H.; Cheng, R.; Yang, F.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, M.; Yu, M.; Zhou, X.; et al. miR-181b functions as an oncomiR in colorectal cancer by targeting PDCD4. Protein Cell 2016, 7, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wan, G.; Spizzo, R.; Ivan, C.; Mathur, R.; Hu, X.; Ye, X.; Lu, J.; Fan, F.; Xia, L.; et al. miR-203 induces oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer cells by negatively regulating ATM kinase. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Pan, B.; Zeng, K.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; He, B.; Pan, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. miR-150-5p suppresses tumor progression by targeting VEGFA in colorectal cancer. Aging 2018, 10, 3421–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, D.; Dong, M.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J. miR-1 inhibits the progression of colon cancer by regulating the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, K.; Han, B.; Bai, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L. MicroRNA-21 (Mir-21) promotes cell growth and invasion by repressing tumor suppressor PTEN in colorectal cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Tang, L. MicroRNA-34 family: A potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-C.; Wentzel, E.A.; Kent, O.A.; Ramachandran, K.; Mullendore, M.; Lee, K.H.; Feldmann, G.; Yamakuchi, M.; Ferlito, M.; Lowenstein, C.J. Transactivation of miR-34a by p53 broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Xu, N.; Mi, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, C.; Qu, J. MicroRNA-195 chemosensitizes colon cancer cells to the chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin by targeting the first binding site of BCL2L2 mRNA. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Basnet, S.; Li, S.; Xu, B.; Ge, H. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-195-5p regulates cell growth and inhibits cell cycle by targeting cyclin dependent kinase 8 in colon cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 2088. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. MicroRNA-195: A review of its role in cancers. Oncotargets Ther. 2018, 11, 7109–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinno, E.; Scalavino, V.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. miR-195-5p as Regulator of γ-Catenin and Desmosome Junctions in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinno, E.; Scalavino, V.; Labarile, N.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. miR-195-5p Inhibits Colon Cancer Progression via KRT23 Regulation. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinno, E.; Scalavino, V.; Labarile, N.; De Marinis, L.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. Identification of a Novel miR-195-5p/PNN Axis in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinno, E.; Scalavino, V.; Labarile, N.; Bianco, G.; Savino, M.T.; Armentano, R.; Giannelli, G.; Serino, G. Downregulation of γ-Catenin by miR-195-5p Inhibits Colon Cancer Progression, Regulating Desmosome Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ji, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M.; Su, Y.n.; Zhang, X. lncRNA RMST suppresses the progression of colorectal cancer by competitively binding to miR-27a-3p/RXRα axis and inactivating Wnt signaling pathway: RMST suppresses the progression of colorectal cancer. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2023, 55, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Tao, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, S.; Che, G.; Yu, Y.; He, L. miR-133b suppresses colorectal cancer cell stemness and chemoresistance by targeting methyltransferase DOT1L. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 385, 111597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lin, M.; Wang, X. Overexpression of miR-19a inhibits colorectal cancer angiogenesis by suppressing KRAS expression. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Yang, F.; Cheng, R.; Chen, X.; Cui, S.; Gu, Y.; Sun, W.; You, C.; Liu, Z. miR-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, C.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: From cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 2022, 38, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Ye, W.; Shao, C. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes colorectal cancer development by sponging miR-363-3p to regulate EZH2 expression. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 331–343. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Peng, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C.; Jin, K.; Ji, D.; Peng, W.; Tang, J.; Feng, Y. Long non-coding RNA CCDC144NL-AS1 promotes cell proliferation by regulating the miR-363-3p/GALNT7 axis in colorectal cancer. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Min, J.; Cao, X.; Liu, L.; Ge, Z.; Hu, J.; Li, X. MiR-363-3p inhibits the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and suppresses metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting Sox4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 474, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, K.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, P.; He, L. MiR-1 suppresses tumor cell proliferation in colorectal cancer by inhibition of Smad3-mediated tumor glycolysis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, L. Tumor suppressor miR-1 restrains epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of colorectal carcinoma via the MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, S.; Xu, X.; Wu, S.; Chen, R.; Jiang, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. The potential value of miR-1 and miR-374b as biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 2840. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; You, C.; Lu, P.; Feng, H.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, R. MicroRNA-181a promotes angiogenesis in colorectal cancer by targeting SRCIN1 to promote the SRC/VEGF signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.-L.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-W.; Chen, P.-J.; Li, C.-C.; Su, W.-C.; Chang, T.-K.; Yeh, Y.-S.; Yin, T.-C. MicroRNA-148a induces apoptosis and prevents angiogenesis with bevacizumab in colon cancer through direct inhibition of ROCK1/c-Met via HIF-1α under hypoxia. Aging 2022, 14, 6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, F.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Qi, X. Knockdown of Mir-135b sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin-induced apoptosis through increase of FOXO1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cheng, X.-H. MiR-29b reverses oxaliplatin-resistance in colorectal cancer by targeting SIRT1. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 12304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Chang, L.; Ding, J.; Wu, D.; Wang, L. Investigating the role of MicroRNA-519d-3p in enhancing chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to 5-Fluorouracil through PFKFB3 targeting. Clinics 2025, 80, 100606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Li, J.; Tang, K.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B.; Hou, N.; Huang, C. miR-338-3p confers 5-fluorouracil resistance in p53 mutant colon cancer cells by targeting the mammalian target of rapamycin. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Zhan, L.; Lou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y. GDPD5, a target of miR-195-5p, is associated with metastasis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. A tale of two databases: The use of Web of Science and Scopus in academic papers. Scientometrics 2020, 123, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, O.; Kocaman, R.; Kanbach, D.K. How to design bibliometric research: An overview and a framework proposal. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2024, 18, 3333–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciamani, G.E.; Chu, T.N.; Sanford, D.I.; Abreu, A.; Duddalwar, V.; Oberai, A.; Kuo, C.-C.J.; Liu, X.; Denniston, A.K.; Vasey, B. PRISMA AI reporting guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analyses on AI in healthcare. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Year | NP | Percentage (%) | TC | TC/NP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 2 | 0.2 | 108 | 53.89 |
| 2009 | 1 | 0.1 | 11 | 10.94 |
| 2010 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | N.D. |
| 2011 | 5 | 0.6 | 52 | 10.4 |
| 2012 | 7 | 0.8 | 42 | 5.93 |
| 2013 | 10 | 1.2 | 72 | 7.18 |
| 2014 | 21 | 2.5 | 124 | 5.92 |
| 2015 | 31 | 3.7 | 157 | 5.06 |
| 2016 | 44 | 5.3 | 184 | 4.19 |
| 2017 | 62 | 7.5 | 401 | 6.47 |
| 2018 | 96 | 11.6 | 552 | 5.75 |
| 2019 | 87 | 10.5 | 545 | 6.27 |
| 2020 | 125 | 15.1 | 664 | 5.31 |
| 2021 | 115 | 13.9 | 409 | 3.56 |
| 2022 | 89 | 10.7 | 224 | 2.52 |
| 2023 | 71 | 8.6 | 117 | 1.65 |
| 2024 ^ | 62 | 7.5 | 20 | 0.32 |
| SCR | First Author and Year | Journal IF | TC | TC/Y | miRNA ID | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Asangani IA, 2008 [36] | Oncogene (7.22, Q1) | 1669 | 92.72 | miR-21 | Therapeutic target |
| 2 | Zhao S, 2020 [37] | J Hematol Oncol (17.39, Q1) | 465 | 77.5 | miR-934 | Prognostic biomarker |
| 3 | Han P, 2017 [38] | Mol Cancer (7.78, Q1) | 445 | 49.44 | miR-181a-5p | Prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target |
| 4 | Vogt M, 2011 [39] | Virchows Arch (2.49, Q1) | 299 | 19.93 | miR-34a, b, c | Diagnostic biomarker |
| 5 | Grady WM, 2008 [40] | Oncogene (7.22, Q1) | 271 | 15.06 | miR-342 | Therapeutic target |
| 6 | Toiyama Y, 2014 [41] | Ann Surg (8.33, Q1) | 261 | 21.75 | miR-200c | Prognostic biomarker |
| 7 | Zhang X, 2017 [42] | Cell Biol Int (1.94 2017, Q1) | 206 | 22.89 | miR-138-5p | Therapeutic target |
| 8 | Zhao L, 2016 [43] | Oncotarget (5.17, Q2) | 192 | 19.2 | miR-138-5p | Therapeutic target |
| 9 | Schimanski CC, 2009 [44] | World J Gastroenterol (2.09, Q1) | 186 | 10.94 | miR-196a | Prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target |
| 10 | Karaayvaz M, 2013 [45] | Cell Death Dis (5.18, Q2) | 180 | 13.85 | miR-129 | Therapeutic target |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piccinno, E.; Aloisio, M.; Scalavino, V.; Russo, F.; Giannelli, G.; Guido, D.; Serino, G. Exploring miRNA Research in Colorectal Cancer: Insights from a Bibliometric Analysis. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081084
Piccinno E, Aloisio M, Scalavino V, Russo F, Giannelli G, Guido D, Serino G. Exploring miRNA Research in Colorectal Cancer: Insights from a Bibliometric Analysis. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(8):1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081084
Chicago/Turabian StylePiccinno, Emanuele, Michelangelo Aloisio, Viviana Scalavino, Francesco Russo, Gianluigi Giannelli, Davide Guido, and Grazia Serino. 2025. "Exploring miRNA Research in Colorectal Cancer: Insights from a Bibliometric Analysis" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 8: 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081084
APA StylePiccinno, E., Aloisio, M., Scalavino, V., Russo, F., Giannelli, G., Guido, D., & Serino, G. (2025). Exploring miRNA Research in Colorectal Cancer: Insights from a Bibliometric Analysis. Pharmaceutics, 17(8), 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17081084









