Characterisation and In Vitro Drug Release Profiles of Oleanolic Acid- and Asiatic Acid-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) for Oral Administration
Abstract
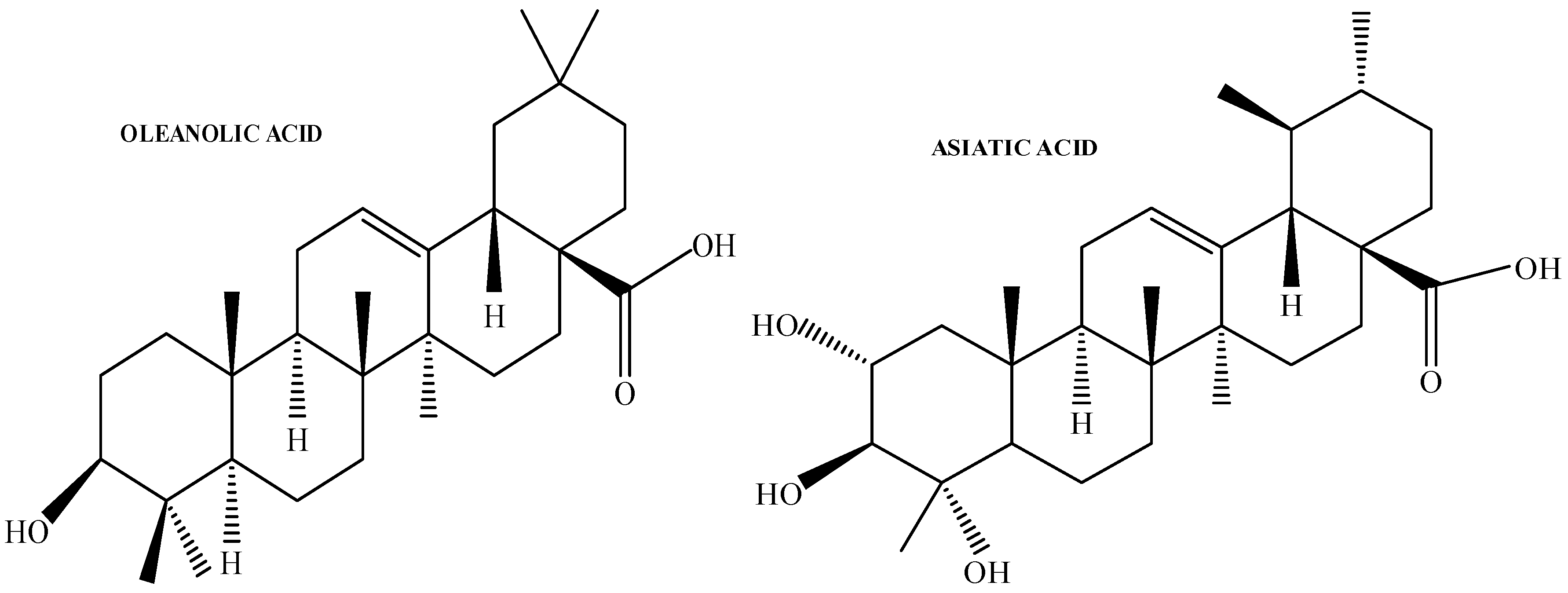
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Isolation and Characterisation of OA from Cloves
2.3. Preparation and Characterisation of OA- and AA-Loaded SLNs
2.3.1. Particle Size, Polydispersity Index, and Zeta Potential Determination
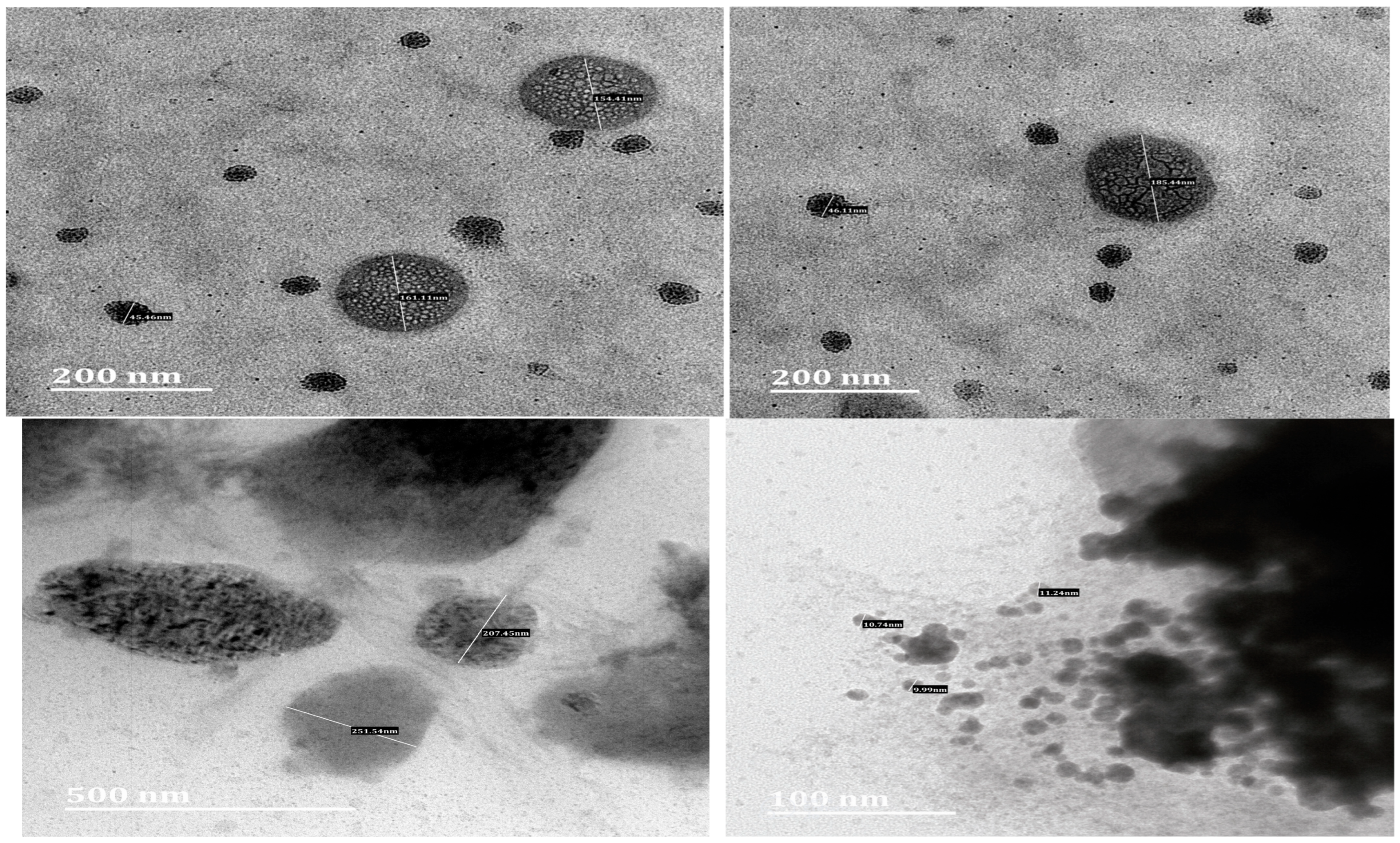
2.3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.3.3. HPLC Analysis Method
2.4. Entrapment Efficiency (EE%) of OA- and AA-Loaded SLNs
2.5. Stability Study of OA- and AA-Loaded SLNs
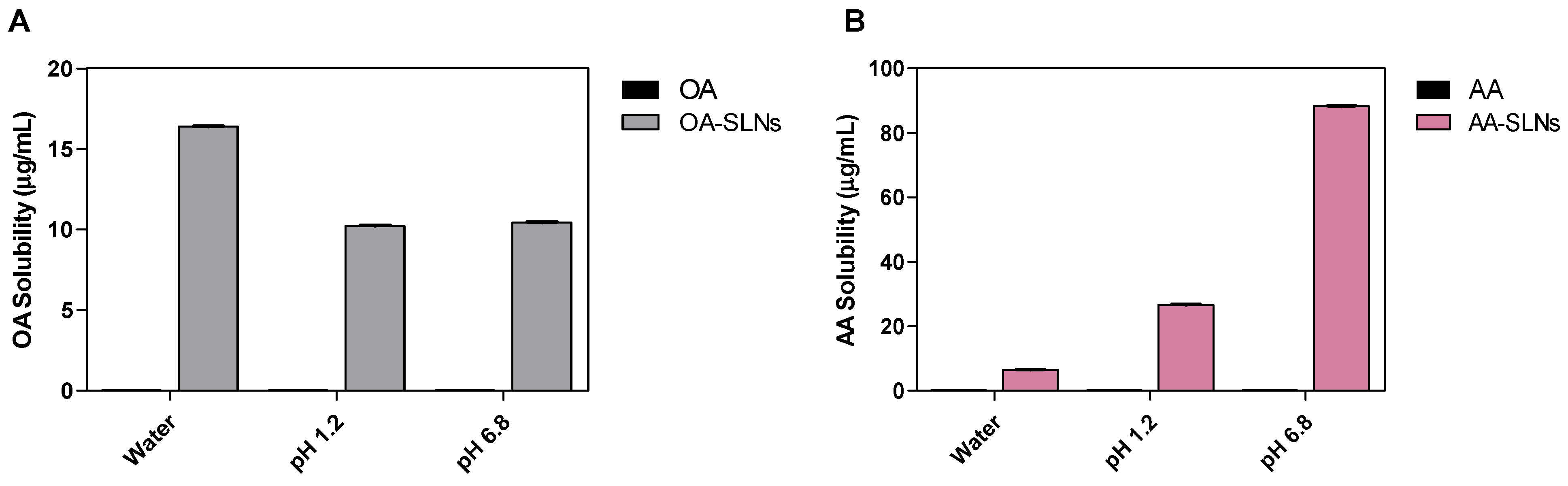
2.6. Solubility Study of OA- and AA-Loaded SLNs
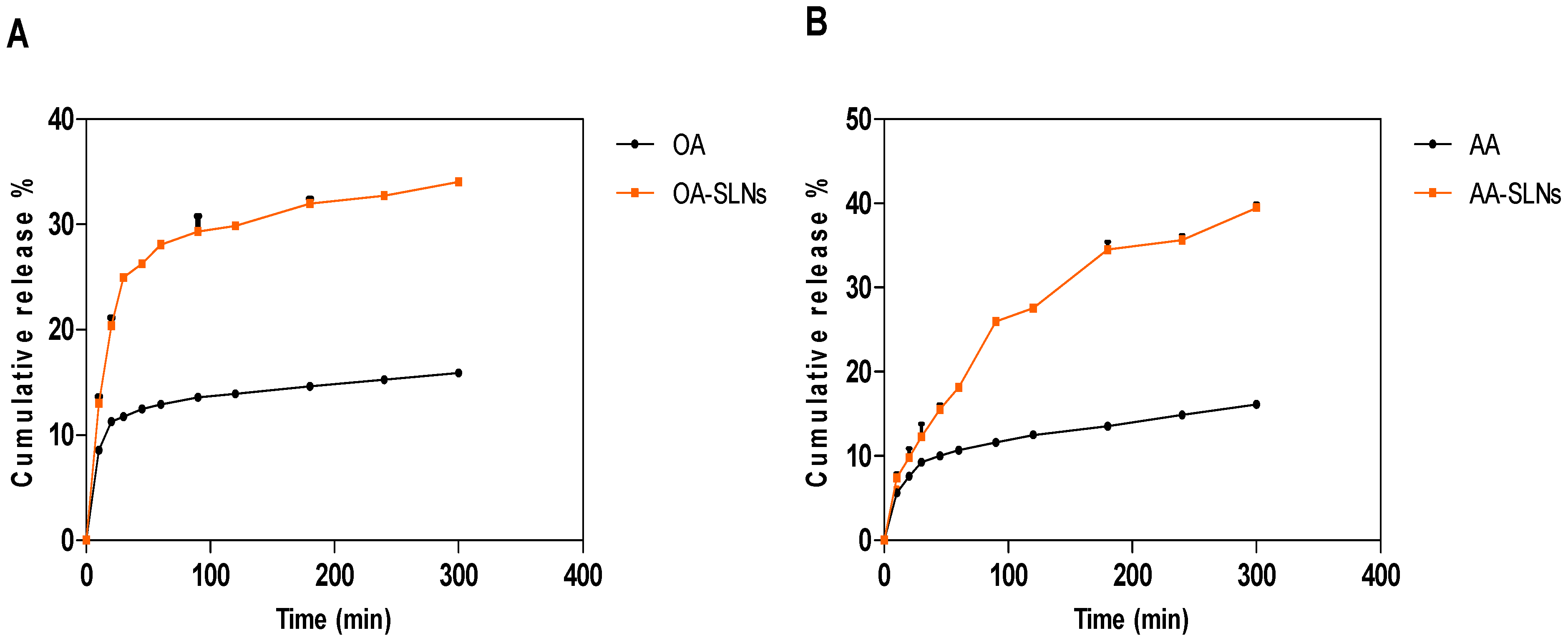
2.7. In Vitro Drug Release Profiles of OA- and AA-Loaded SLNs
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
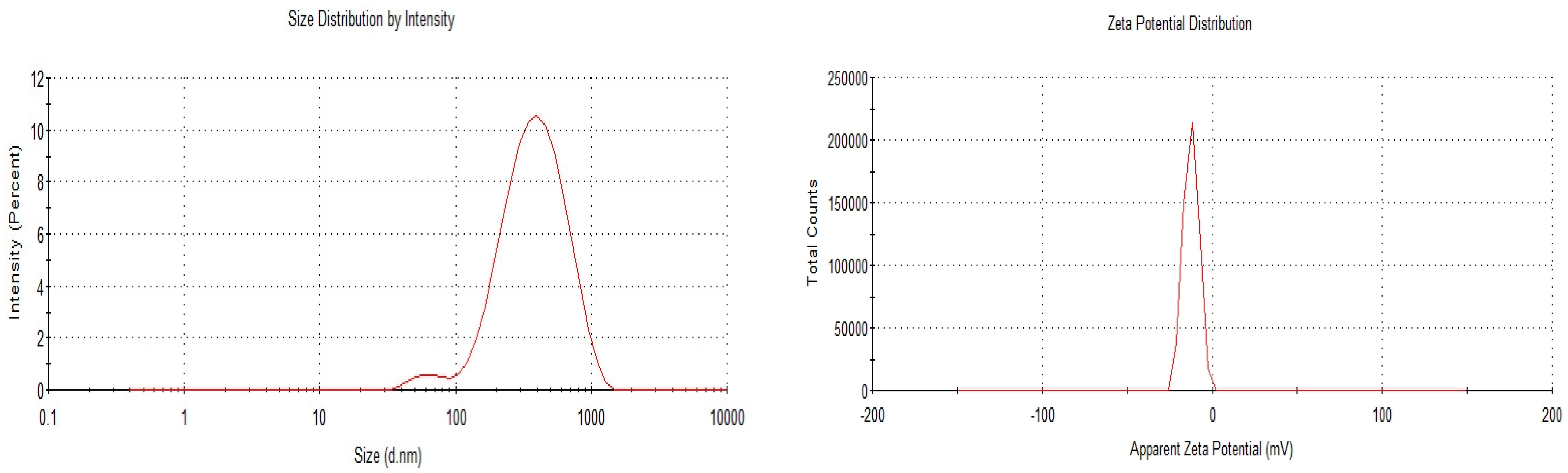
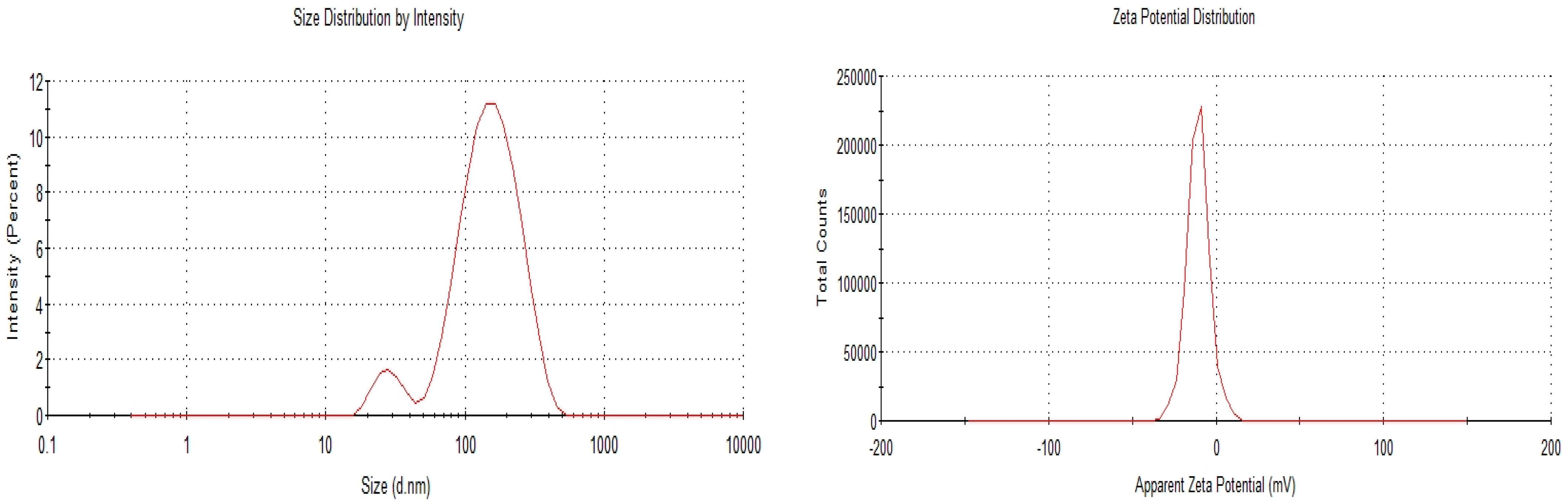
3.1. Characterisation of OA- and AA-Loaded SLN
Stability of OA- and AA-Loaded SLNs
3.2. Solubility Study OA- and AA-Loaded SLNs
3.3. In Vitro Drug Release Properties of OA- and AA-Loaded SLNs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Justino, A.B.; Santana, E.C.; Franco, R.R.; Queiroz, J.S.; Silva, H.C.G.; de Lima Júnior, J.P.; Saraiva, A.L.; Martins, M.M.; de Morais, S.A.L.; de Oliveira, A. Antioxidant compounds of Kielmeyera coriacea Mart. with α-amylase, lipase and advanced glycation end-product inhibitory activities. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 206, 114387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iskender, H.; Dokumacioglu, E.; Terim Kapakin, K.A.; Yenice, G.; Mohtare, B.; Bolat, I.; Hayirli, A. Effects of oleanolic acid on inflammation and metabolism in diabetic rats. Biotech. Histochem. 2022, 97, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, M.O.; Kadasah, S.F.; Aljubiri, S.M.; Alrefaei, A.F.; El-Maghrabey, M.H.; El Hamd, M.A.; Tateishi, H.; Otsuka, M.; Fujita, M. Harnessing oleanolic acid and its derivatives as modulators of metabolic nuclear receptors. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, J.M.; Ramos-Romero, S.; Perona, J.S. Oleanolic acid: Extraction, characterization and biological activity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Al Harrasi, A.; Hussain, H.; Hamaed, A.; Supuran, C.T. The management of diabetes mellitus-imperative role of natural products against dipeptidyl peptidase-4, α-glucosidase and sodium-dependent glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2). Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 86, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.-H.; Liu, Y.-W.; Wei, F.; Tan, H.-Z.; Han, Z.-D. Asiatic acid ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin (BLM) via suppressing pro-fibrotic and inflammatory signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.; Bai, P.; Yang, B.; Feng, X.; Qiu, F. Asiatic acid alleviates metabolism disorders in ob/ob mice: Mechanistic insights. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 6934–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, Y.; Wada, K.; Nakatani, M.; Yamada, S.; Onoue, S. Formulation design for poorly water-soluble drugs based on biopharmaceutics classification system: Basic approaches and practical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug solubility: Importance and enhancement techniques. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.Q.; Ling, L.S.; Chellian, J.; Madheswaran, T.; Panneerselvam, J.; Kunnath, A.P.; Gupta, G.; Satija, S.; Mehta, M.; Hansbro, P.M. Applications of nanocarriers as drug delivery vehicles for active phytoconstituents. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 4580–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, K. Therapeutic potential of oleanolic acid in liver diseases. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 4537–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, H.H.; Ji, H.Y.; Yoo, S.D.; Choi, W.R.; Lee, S.M.; Han, C.K.; Lee, H.S. Dose-linear pharmacokinetics of oleanolic acid after intravenous and oral administration in rats. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2007, 28, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, L.; Wu, B.; Chen, F. Improving solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs by protein-based strategy: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 634, 122704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, N.; Jennotte, O.; Grignard, B.; Lechanteur, A.; Evrard, B. Impregnation of mesoporous silica with poor aqueous soluble molecule using pressurized carbon dioxide: Is the solubility in the supercritical and subcritical phase a critical parameter? Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 150, 105332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, N.; Awasthi, R.; Sharma, B.; Kharkwal, H.; Kulkarni, G.T. Lipid nanoparticles as carriers for bioactive delivery. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 580118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, C.; Patrício, A.B.; Prata, J.M.; Nadhman, A.; Chintamaneni, P.K.; Fonte, P. Solid lipid nanoparticles vs. nanostructured lipid carriers: A comparative review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippov, S.K.; Khusnutdinov, R.; Murmiliuk, A.; Inam, W.; Zakharova, L.Y.; Zhang, H.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Dynamic light scattering and transmission electron microscopy in drug delivery: A roadmap for correct characterization of nanoparticles and interpretation of results. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 5354–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, W.; Mäder, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles: Production, characterization and applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, J.R.; Khude, P.A.; Dua, K. Development and evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticles of mometasone furoate for topical delivery. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2014, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshmand, S.; Jaafari, M.R.; Movaffagh, J.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B.; Iranshahi, M.; Moghaddam, A.S.; Najaran, Z.T.; Golmohammadzadeh, S. Preparation, characterization, and optimization of auraptene-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles as a natural anti-inflammatory agent: In vivo and in vitro evaluations. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 164, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Chaudhury, A. Recent advances in lipid nanoparticle formulations with solid matrix for oral drug delivery. Aaps Pharmscitech 2011, 12, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, J.B.; Vijayasankar, G.R.; Venkateswarlu, B.S.; Rajappa, M.C. Mechanistic outcomes of lipid core on solid lipid nanoparticles characterisation. Indian Drugs 2024, 61, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, M.; Abu el-naga, M.N.; Sokary, R.; Fahim, R.A.; El-Sawy, N.M. Radiation-induced synthesis of tween 80 stabilized silver nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2020, 55, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bide, Y.; Fashapoyeh, M.A.; Shokrollahzadeh, S. Structural investigation and application of Tween 80-choline chloride self-assemblies as osmotic agent for water desalination. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, M.; Morrison, R.A.; Chong, S. Commonly used surfactant, Tween 80, improves absorption of P-glycoprotein substrate, digoxin, in rats. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2003, 26, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aburahma, M.H.; Badr-Eldin, S.M. Compritol 888 ATO: A multifunctional lipid excipient in drug delivery systems and nanopharmaceuticals. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlin, P.; Kristl, J.; Pecar, S.; Strancar, J.; Sentjurc, M. The effect of lipophilicity of spin-labeled compounds on their distribution in solid lipid nanoparticle dispersions studied by electron paramagnetic resonance. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Aditya, N.; Ko, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs): Delivery vehicles for food bioactives. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30902–30911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Chen, Y.; Sarkar, M.; Xie, H. Surfactant Mediated Accelerated and Discriminatory In Vitro Drug Release Method for PLGA Nanoparticles of Poorly Water-Soluble Drug. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Bansal, K.K.; Verma, A.; Yadav, N.; Thakur, S.; Sudhakar, K.; Rosenholm, J.M. Solid lipid nanoparticles: Emerging colloidal nano drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhong, Z.; Tan, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Recent advances in nanoparticle formulation of oleanolic acid. Chin. Med. 2011, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islamie, R.; Myint, S.L.L.; Rojanaratha, T.; Ritthidej, G.; Wanakhachornkrai, O.; Wattanathamsan, O.; Rodsiri, R. Neuroprotective effect of nose-to-brain delivery of Asiatic acid in solid lipid nanoparticles and its mechanisms against memory dysfunction induced by Amyloid Beta1-42 in mice. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musabayane, C.; Tufts, M.; Mapanga, R. Synergistic antihyperglycemic effects between plant-derived oleanolic acid and insulin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Ren. Fail. 2010, 32, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapanga, R.F.; Tufts, M.; Shode, F.; Musabayane, C. Renal effects of plant-derived oleanolic acid in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Ren. Fail. 2009, 31, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.N.; Le, H.H.; Le, T.G.; Duong, T.H.A.; Ngo, V.Q.T.; Dang, C.T.; Nguyen, V.M.; Tran, T.H.; Nguyen, C.N. Formulation and characterization of hydroxyethyl cellulose-based gel containing metronidazole-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for buccal mucosal drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 194, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, E. Magnetic loaded compritol ATO based lipid carriers as a targeted anti-cancer drug delivery system. Nanomed. Res. J. 2025, 9, 264–273. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.-X.; Hua, H.-Y.; Liu, L. Development and validation of an HPLC method for determination of oleanolic acid content and partition of oleanolic acid in submicron emulsions. Die Pharm. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 64, 491–494. [Google Scholar]
- Hebbar, S.; Dubey, A.; Ravi, G.; Kumar, H.; Saha, S. RP-HPLC method development and validation of Asiatic acid isolated from the plant Centella asiatica. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 11, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, U.H.; Devnarain, N.; Omolo, C.A.; Mocktar, C.; Govender, T. Biomimetic pH/lipase dual responsive vitamin-based solid lipid nanoparticles for on-demand delivery of vancomycin. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 120960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branham, M.L.; Moyo, T.; Govender, T. Preparation and solid-state characterization of ball milled saquinavir mesylate for solubility enhancement. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefani, C.; Lodovichi, J.; Albonetti, L.; Salvatici, M.C.; Quintela, J.C.; Bilia, A.R.; Bergonzi, M.C. Solubility and Permeability Enhancement of Oleanolic Acid by Solid Dispersion in Poloxamers and γ-CD. Molecules 2022, 27, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayyad, N.; Maji, R.; Omolo, C.A.; Ibrahim, U.H.; Pathan, T.K.; Devnarain, N.; Karpoormath, R.; Dhawan, S.; Obakachi, V.A.; Merugu, S.R. Development of niosomes for encapsulating captopril-quercetin prodrug to combat hypertension. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 609, 121191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Ng, W.K.; Kanaujia, P.; Kim, S.; Tan, R.B. Formulation design, preparation and physicochemical characterizations of solid lipid nanoparticles containing a hydrophobic drug: Effects of process variables. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arana, L.; Gallego, L.; Alkorta, I. Incorporation of antibiotics into solid lipid nanoparticles: A promising approach to reduce antibiotic resistance emergence. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honary, S.; Zahir, F. Effect of zeta potential on the properties of nano-drug delivery systems-a review (Part 1). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 255–264. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, M.K.; Pedersen, J.N.; Marie, R. Size and surface charge characterization of nanoparticles with a salt gradient. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaycioglu, G.D.; Aydogan, N. Preparation and investigation of solid lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 510, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Maaben, S.; Weyhers, H.; Mehnert, W. Phagocytic uptake and cytotoxicity of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) sterically stabilized with poloxamine 908 and poloxamer 407. J. Drug Target. 1996, 4, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.T.M.; Hassan, M.; Shamma, R.N.; Makky, A.; Hassan, D.H. Controlling the evolution of selective vancomycin resistance through successful ophthalmic eye-drop preparation of vancomycin-loaded nanoliposomes using the active-loading method. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, Z.; Imran, M.; Hussain, M.; Saeed, F.; Imran, A.; Umar, M.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; El-Ghorab, A.H.; Ahmed, A.; Alsagaby, S.A. Asiatic acid: A review on its polypharmacological properties and therapeutic potential against various Maladies. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 1244–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triaa, N.; Znati, M.; Ben Jannet, H.; Bouajila, J. Biological activities of novel oleanolic acid derivatives from bioconversion and semi-synthesis. Molecules 2024, 29, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Ahmad, S.; Madni, A.; Rao, I.; Ghazwani, M.; Hani, U.; Umair, M.; Ahmad, I.; Rai, N.; Ahmed, M. Compritol-based alprazolam solid lipid nanoparticles for sustained release of alprazolam: Preparation by hot melt encapsulation. Molecules 2022, 27, 8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, M.; Ibrahim, U.H.; Aljoundi, A.; Omolo, C.A.; Devnarain, N.; Gafar, M.A.; Mocktar, C.; Govender, T. Enzyme-responsive biomimetic solid lipid nanoparticles for antibiotic delivery against hyaluronidase-secreting bacteria. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 640, 122967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathali, A.; Ekambaram, P.; Priyanka, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles: A review. Sci. Rev. Chem. Commun. 2012, 2, 80–102. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.B.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Patri, A.K.; McNeil, S.E. Characterization of nanoparticles for therapeutics. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michen, B.; Geers, C.; Vanhecke, D.; Endes, C.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Balog, S.; Petri-Fink, A. Avoiding drying-artifacts in transmission electron microscopy: Characterizing the size and colloidal state of nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Sara, U.V.S. Solid lipid nanoparticles for nose to brain delivery of haloperidol: In vitro drug release and pharmacokinetics evaluation. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Khatak, S.; Sara, U.S. Solid lipid nanoparticles-a review. Int. J. Appl. Pharm 2013, 5, 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- van den Anker, J.; Reed, M.D.; Allegaert, K.; Kearns, G.L. Developmental changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 58, S10–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.-L.; Yao, J.; Wu, C.; Deng, J.-H.; Mo, Y.-H.; Lu, T.-B.; Chen, J.-M. Solubility and permeability improvement of allopurinol by cocrystallization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 5160–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Baidya, A.T.; Mathew, A.T.; Yadav, A.K.; Kumar, R. Structural modification aimed for improving solubility of lead compounds in early phase drug discovery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2022, 56, 116614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.U.; Minhas, M.U.; Badshah, S.F.; Suhail, M.; Ahmad, A.; Ijaz, S. Overview of nanoparticulate strategies for solubility enhancement of poorly soluble drugs. Life Sci. 2022, 291, 120301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leilei, L.; Wenke, Q.; Yuyuan, L.; Sihang, L.; Xue, S.; Weiqiang, C.; Lianbao, Y.; Ying, W.; Yan, L.; Ming, L. Oleanolic acid-loaded nanoparticles attenuate activation of hepatic stellate cells via suppressing TGF-β1 and oxidative stress in PM2. 5-exposed hepatocytes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 437, 115891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojanaratha, T.; Tienthai, P.; Woradulayapinij, W.; Yimsoo, T.; Boonkanokwong, V.; Ritthidej, G.C. Preparation, physicochemical characterization, ex vivo, and in vivo evaluations of asiatic acid-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles formulated with natural waxes for nose-to-brain delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 203, 106935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Chakraborty, P.; Basak, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, N.; Chatterjee, S.; Dewanjee, S.; Sil, P.C. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of in vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo antitumor activity of asiatic acid-loaded poly lactic-co-glycolic acid nanoparticles: A strategy of treating breast cancer. Life Sci. 2022, 307, 120876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mang Sung Thluai, L.; Titapiwatanakun, V.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Boonpisuttinant, K.; Chutoprapat, R. Development of effervescent cleansing tablets containing asiatic-acid-loaded solid lipid microparticles. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwowska, K.; Gniadek, M.; Urbaniak, W.; Petelska, A.D. Physicochemical and electrical properties of DPPC bilayer membranes in the presence of oleanolic or asiatic acid. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, J.g.; Zhou, W.; Liang, X.; Zhou, G.; Han, C.C.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y. Mechanism of a long-term controlled drug release system based on simple blended electrospun fibers. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Shu, L.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Li, N. Preparation and evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticles of baicalin for ocular drug delivery system in vitro and in vivo. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaad, A.A.; Hussien, A.A.; Gareeb, M.M. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) as a novel drug delivery system: A theoretical review. Syst. Rev. Pharm 2020, 11, 259–273. [Google Scholar]
- zur Mühlen, A.; Schwarz, C.; Mehnert, W. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery–drug release and release mechanism. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 45, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soma, D.; Attari, Z.; Reddy, M.S.; Damodaram, A.; Koteshwara, K.B.G. Solid lipid nanoparticles of irbesartan: Preparation, characterisation, optimisation and pharmacokinetic studies. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 53, e15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordillo-Galeano, A.; Mora-Huertas, C.E. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: A review emphasizing on particle structure and drug release. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 133, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Ihsan, A.; Madni, A.; Bajwa, S.Z.; Shi, D.; Webster, T.J.; Khan, W.S. Solid lipid nanoparticles for thermoresponsive targeting: Evidence from spectrophotometry, electrochemical, and cytotoxicity studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 8325–8336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ud Din, F.; Zeb, A.; Shah, K.U. Development, in-vitro and in-vivo evaluation of ezetimibe-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles and their comparison with marketed product. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
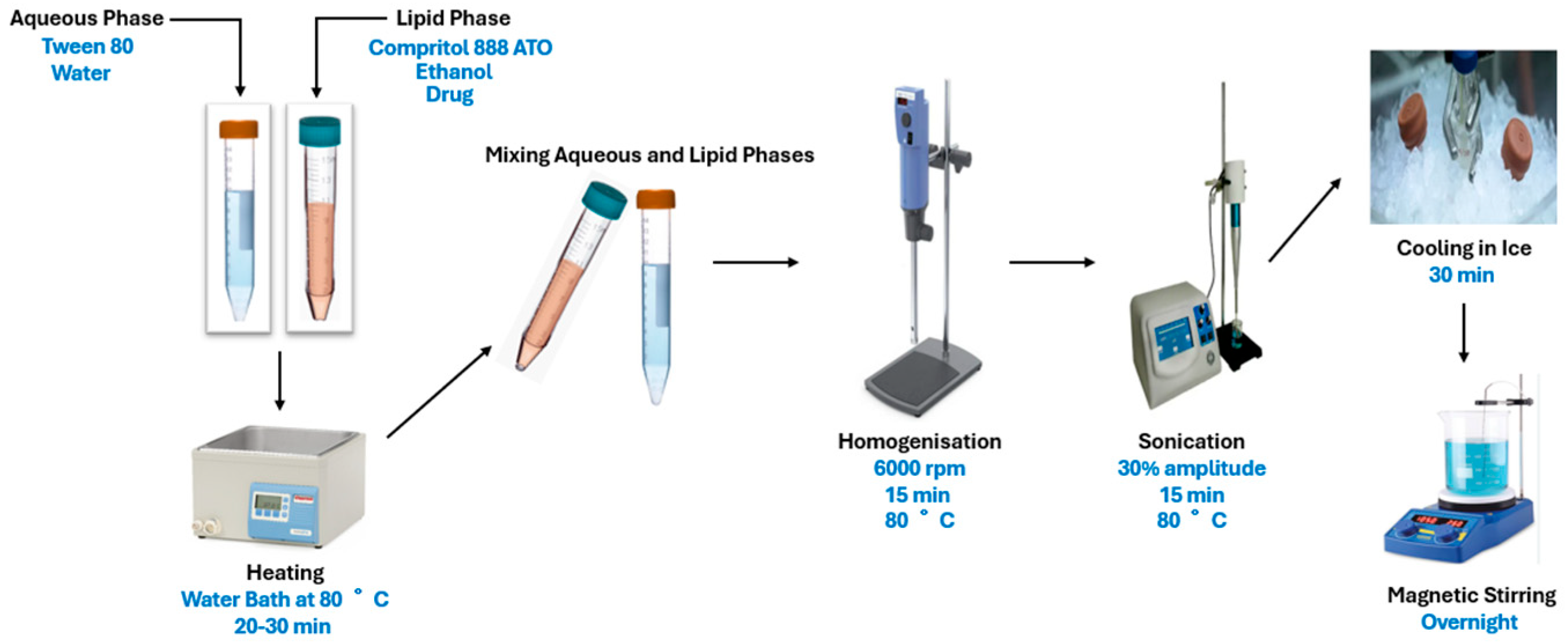
| Drug:Lipid Ratio | Drug | Lipid | Polysorbate 80 | Ethanol | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 10 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 3 mL | 10 mL |
| 1:2 | 10 mg | 20 mg | 40 mg | 3 mL | 10 mL |
| 1:4 | 10 mg | 40 mg | 80 mg | 3 mL | 10 mL |
| OA:Lipid Ratio | PS (nm) | PDI | ZP (mV) | EE% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 312.9 ± 3.617 | 0.157 ± 0.014 | −17.0 ± 0.513 | 86.54 ± 1.818 |
| 1:2 | 346.6 ± 1.617 | 0.217 ± 0.115 | −13.2 ± 0.115 | 87.80 ± 1.024 |
| 1:4 | 412.2 ± 7.002 | 0.378 ± 0.074 | −9.2 ± 0.357 | 88.93 ± 0.516 |
| AA:Lipid ratio | PS (nm) | PDI | ZP (mV) | EE% |
| 1:1 | 162.0 ± 0.681 | 0.272 ± 0.006 | −12.5 ± 0.208 | 78.96 ± 0.503 |
| 1:2 | 115.5 ± 0.458 | 0.255 ± 0.007 | −11.9 ± 0.321 | 76.22 ± 0.436 |
| 1:4 | 189.9 ± 1.818 | 0.259 ± 0.019 | −10.2 ± 0.346 | 79.59 ± 0.214 |
| Day(s) | PS (nm) at 4 °C | PDI at 4 °C | ZP (mV) at 4 °C | PS (nm) at RT | PDI at RT | ZP (mV) at RT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 312.9 ± 3.617 | 0.157 ± 0.014 | −17.0 ± 0.513 | 312.9 ± 3.617 | 0.157 ± 0.014 | −17.0 ± 0.513 |
| 7 | 333.3 ± 7.328 | 0.166 ± 0.243 | −11.8 ± 0.337 | 308.6 ± 1.997 | 0.189 ± 0.100 | −12.9 ± 0.302 |
| 14 | 321.5 ± 2.444 | 0.154 ± 0.026 | −9.8 ± 0.100 | 314.5 ± 1.856 | 0.191 ± 0.026 | −11.1 ± 0.321 |
| 30 | 319.7 ± 1.514 | 0.146 ± 0.003 | −14.4 ± 0.462 | 311.2 ± 0.551 | 0.196 ± 0.011 | −14.9 ± 0.656 |
| 60 | 320.0 ± 0.800 | 0.142 ± 0.018 | −13.8 ± 0.361 | 312.5 ± 4.232 | 0.226 ± 0.014 | −15.4 ± 0.200 |
| Day(s) | PS (nm) at 4 °C | PDI at 4 °C | ZP (mV) at 4 °C | PS (nm) at RT | PDI at RT | ZP (mV) at RT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 115.5 ± 0.458 | 0.255 ± 0.007 | −11.9 ± 0.321 | 115.5 ± 0.458 | 0.255 ± 0.007 | −11.9 ± 0.321 |
| 7 | 116.0 ± 2.313 | 0.266 ± 0.009 | −8.7 ± 0.782 | 113.3 ± 0.656 | 0.265 ± 0.005 | −9.3 ± 0.387 |
| 14 | 117.3 ± 1.929 | 0.257 ± 0.010 | −7.8 ± 0.391 | 123.1 ± 4.203 | 0.277 ± 0.016 | −7.6 ± 0.134 |
| 30 | 116.2 ± 2.325 | 0.259 ± 0.004 | −11.8 ± 0.666 | 114.7 ± 0.404 | 0.249 ± 0.006 | −10.3 ± 0.366 |
| 60 | 119.0 ± 0.265 | 0.263 ± 0.016 | −10.4 ± 0.115 | 118.1 ± 3.166 | 0.257 ± 0.050 | −8.7 ± 1.220 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oboh, M.; Elhassan, E.; Koorbanally, N.A.; Govender, L.; Siwela, M.; Govender, T.; Mkhwanazi, B.N. Characterisation and In Vitro Drug Release Profiles of Oleanolic Acid- and Asiatic Acid-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) for Oral Administration. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060723
Oboh M, Elhassan E, Koorbanally NA, Govender L, Siwela M, Govender T, Mkhwanazi BN. Characterisation and In Vitro Drug Release Profiles of Oleanolic Acid- and Asiatic Acid-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) for Oral Administration. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(6):723. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060723
Chicago/Turabian StyleOboh, Michael, Eman Elhassan, Neil Anthony Koorbanally, Laurencia Govender, Muthulisi Siwela, Thirumala Govender, and Blessing Nkazimulo Mkhwanazi. 2025. "Characterisation and In Vitro Drug Release Profiles of Oleanolic Acid- and Asiatic Acid-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) for Oral Administration" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 6: 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060723
APA StyleOboh, M., Elhassan, E., Koorbanally, N. A., Govender, L., Siwela, M., Govender, T., & Mkhwanazi, B. N. (2025). Characterisation and In Vitro Drug Release Profiles of Oleanolic Acid- and Asiatic Acid-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) for Oral Administration. Pharmaceutics, 17(6), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17060723









