Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Apoptotic Extracellular Vesicles Improve 5-FU-Induced Delayed Wound Healing by Mitochondrial Transfer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Cell Culture and UMSC Characterization
2.2.1. Isolation and Flow Cytometric Analysis of UMSCs
2.2.2. Multipotency Validation
2.3. Isolation and Characterization of UMSC-apoVs
2.3.1. Isolation
2.3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.3.3. Nanoflow Cytometry (nFCM) and Immunofluorescent Staining
2.4. Isolation and Multipotency Validation of SMSCs
2.5. UMSC-apoV Labeling and Internalization
2.6. MitoTracker Staining of UMSC-apoVs
2.7. Co-Culture for UMSC-apoVs and SMSCs with Mitochondrial Staining
2.8. Skin Wound Healing
2.9. Histological Staining
2.10. Cell Viability Assay
2.11. Ki67 Proliferation Assay
2.12. Scratch Migration Assay
2.13. ROS Detection In Vitro and In Vivo
2.14. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
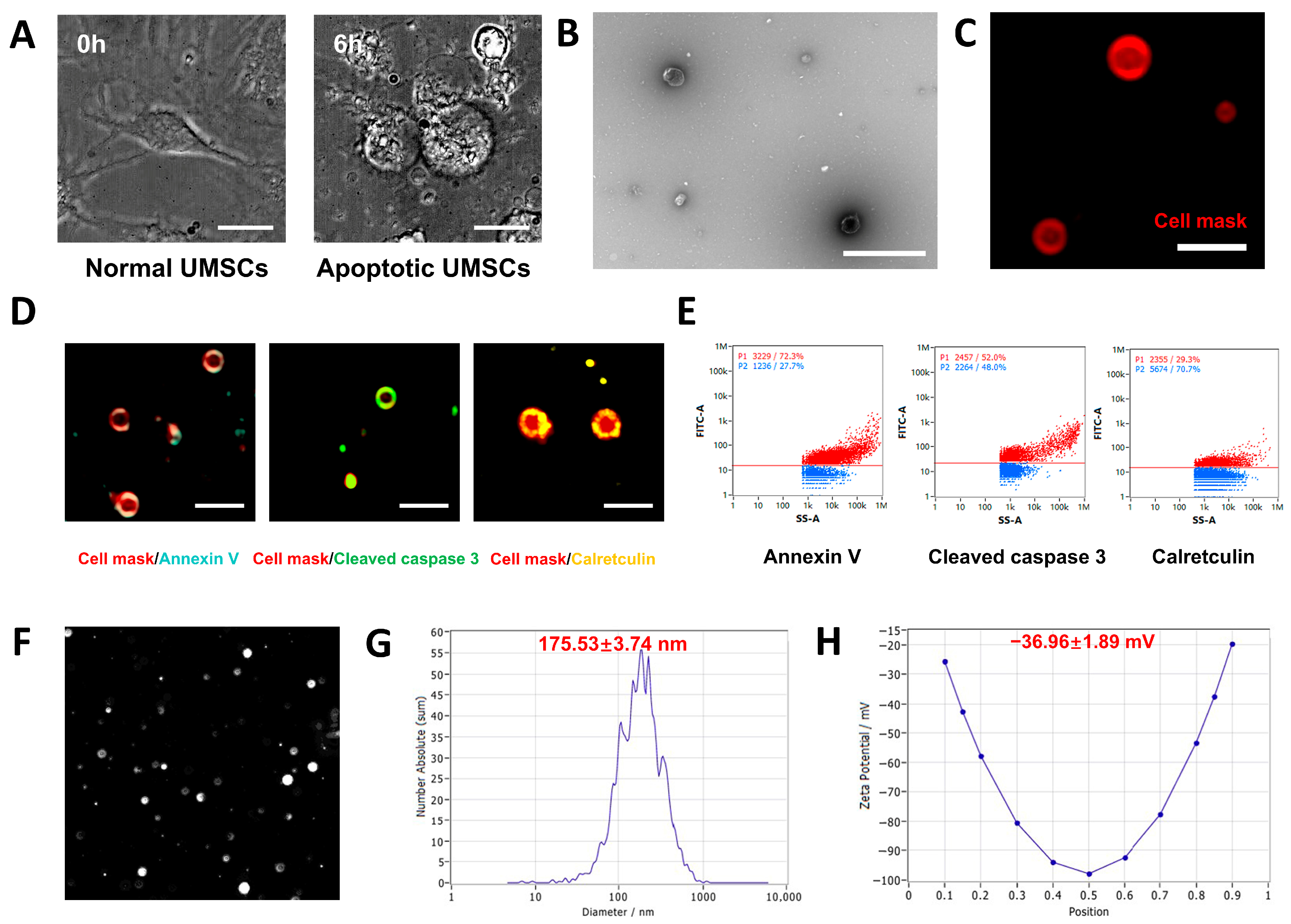
3.1. Isolation and Identification of UMSCs
3.2. Characterization of UMSC-apoVs
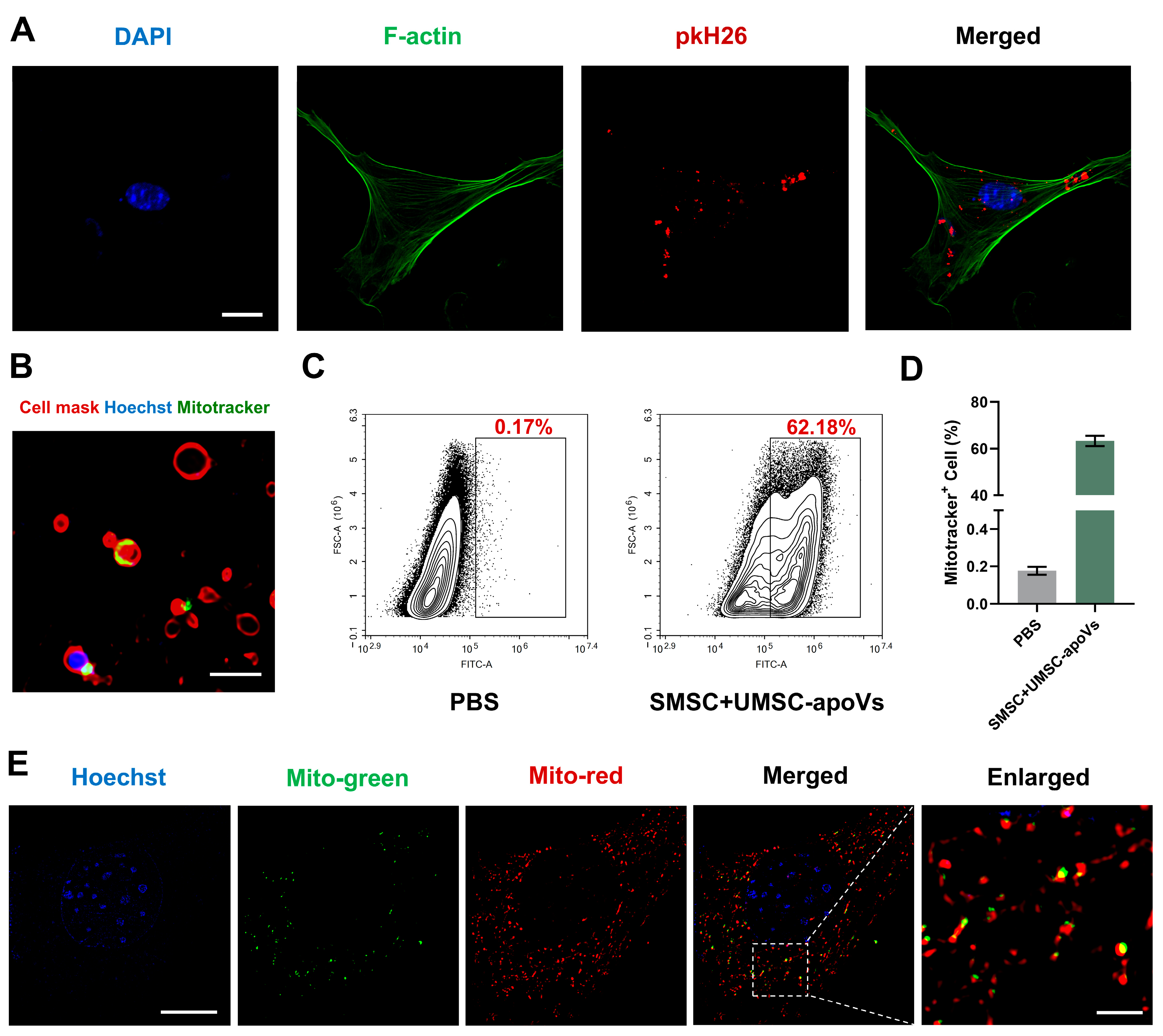
3.3. UMSC-apoVs Deliver Mitochondria to SMSCs
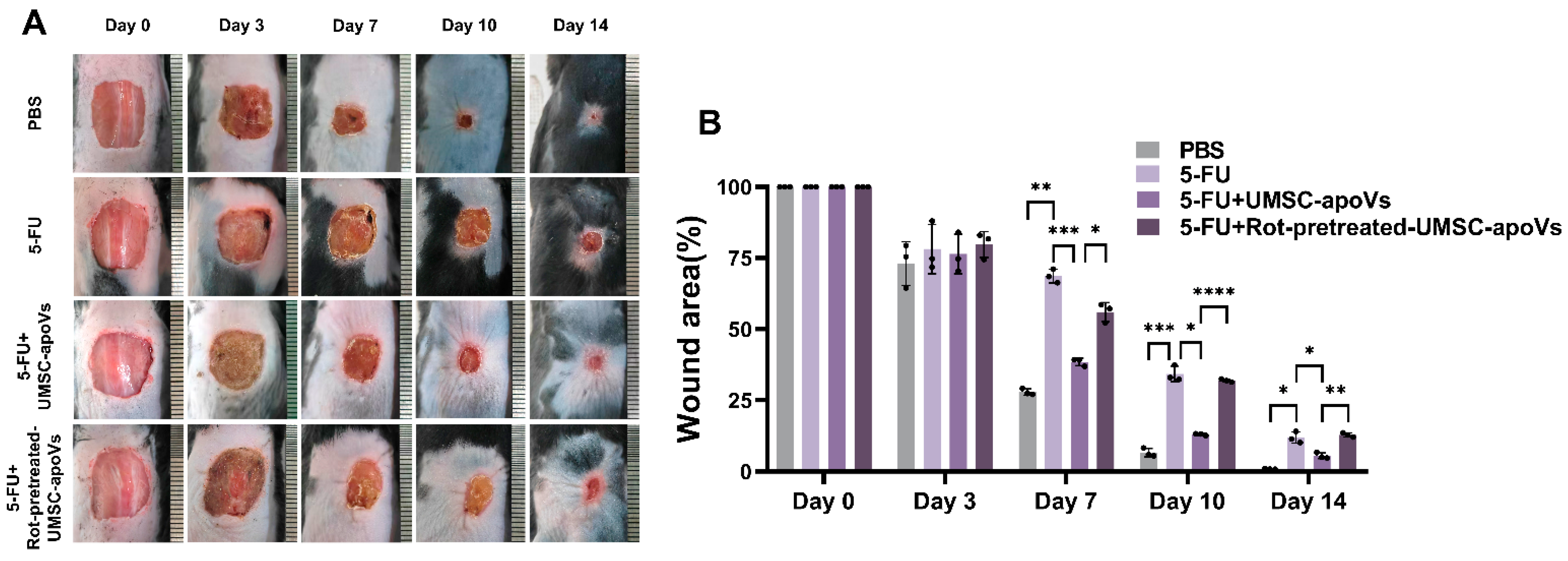
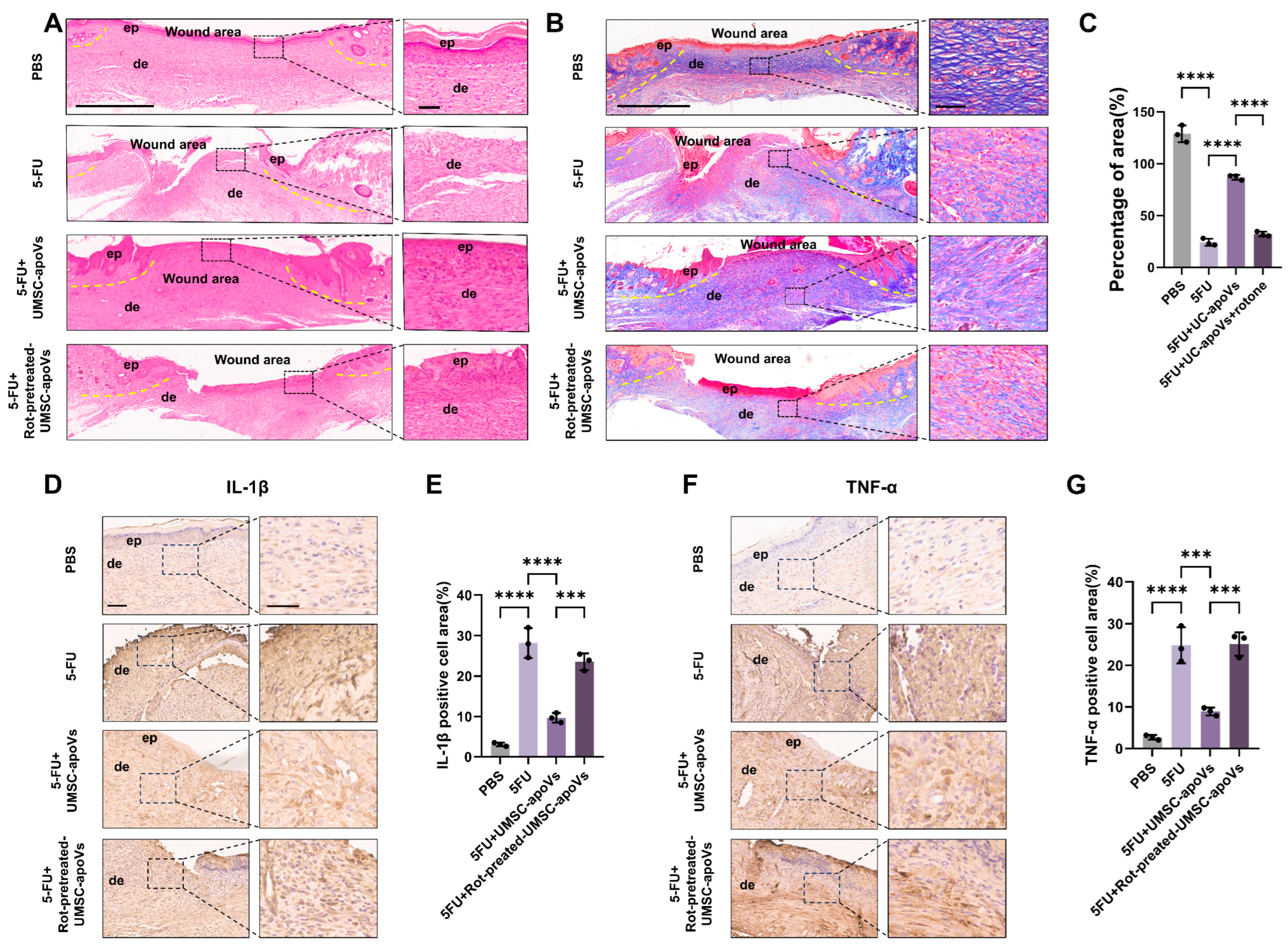
3.4. UMSC-apoVs Improved 5-FU-Induced Delayed Wound Healing by Mitochondrial Transfer
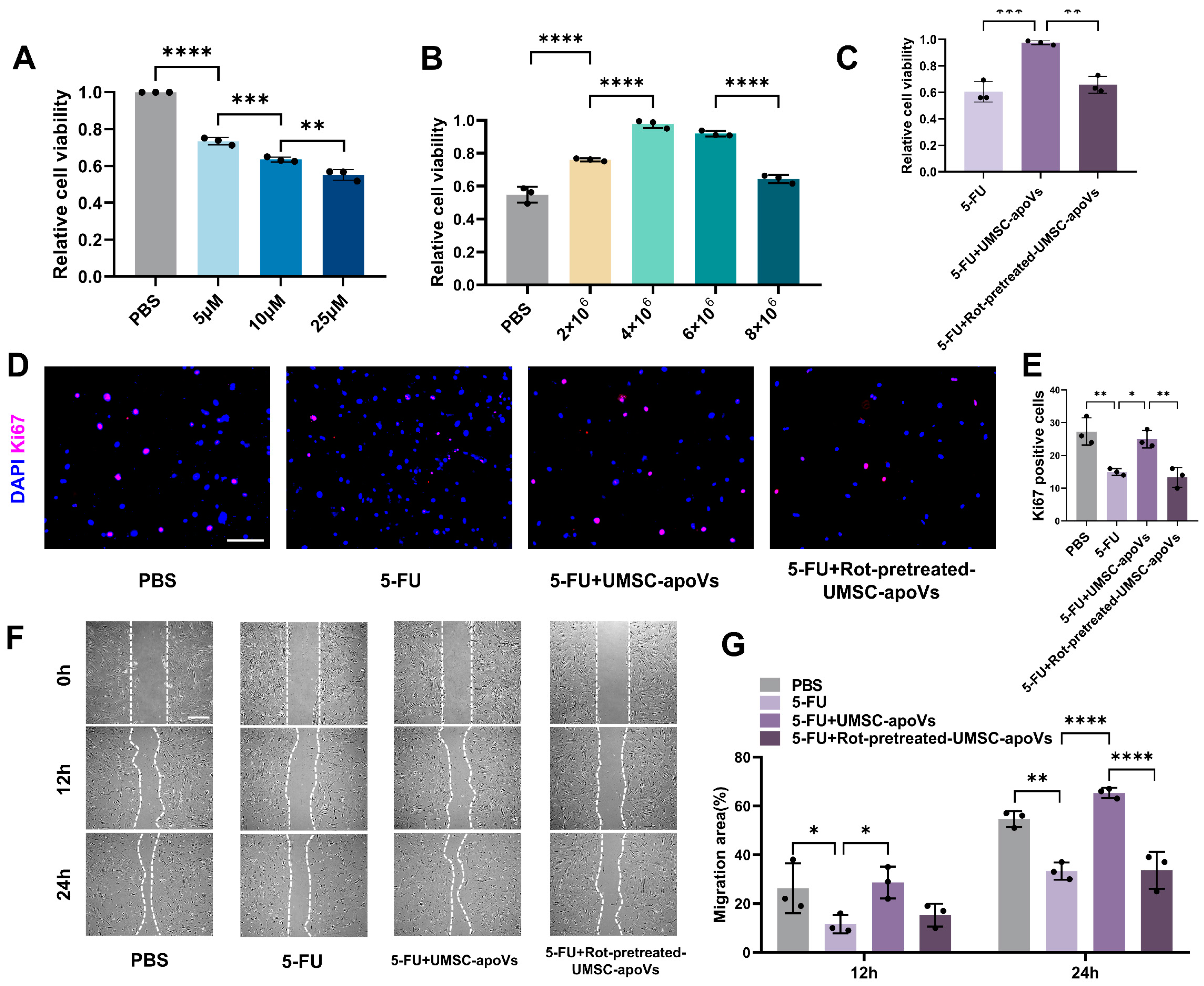
3.5. UMSC-apoVs Enhance Viability, Proliferation, and Migration of SMSCs by Mitchondrial Transfer
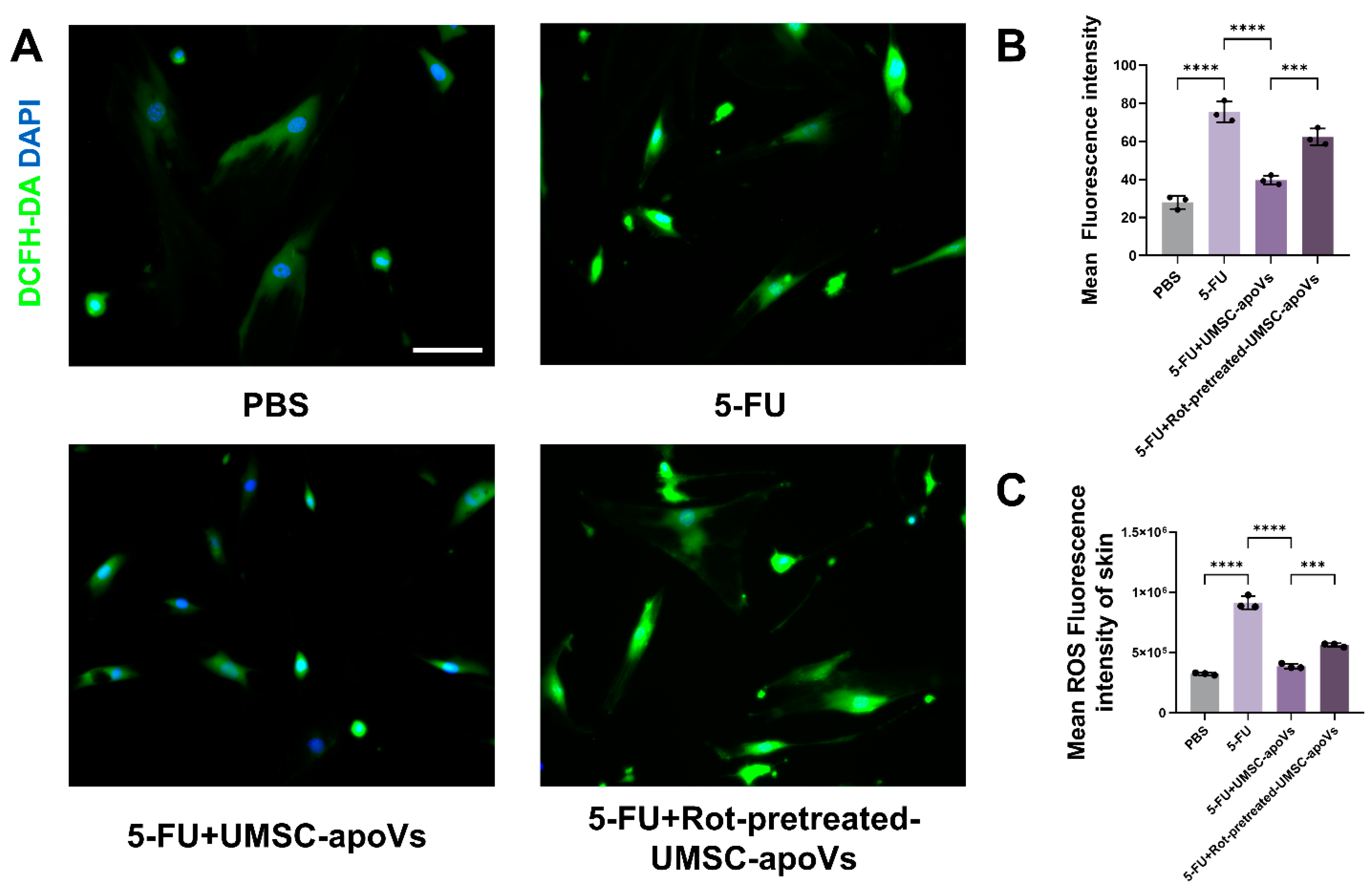
3.6. UMSC-apoVs Reduce 5-FU-Induced Oxidative Stress via Mitochondrial Transfer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eming, S.A.; Martin, P.; Tomic-Canic, M. Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 265sr266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Ji, G.; Shi, X.; Sun, Z.; Liu, C.; Yu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Hu, H. The male reproductive toxicity after 5-Fluorouracil exposure: DNA damage, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction in vitro and in vivo. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2024, 278, 116465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cui, H.; Qu, M.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C. Impact of preoperative chemotherapy on cutaneous wound healing in lung cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Int. Wound J. 2024, 21, e14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słonimska, P.; Sachadyn, P.; Zieliński, J.; Skrzypski, M.; Pikuła, M. Chemotherapy-Mediated Complications of Wound Healing: An Understudied Side Effect. Adv. Wound Care 2024, 13, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapa, S.F.; Magliocca, G.; Pepe, G.; Amodio, G.; Autore, G.; Campiglia, P.; Marzocco, S. Protective Effect of Pomegranate on Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response Induced by 5-Fluorouracil in Human Keratinocytes. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferriol, A.; del Carmen Morán, M. Enhanced performance of gelatin 5-fluorouracil-containing nanoparticles against squamous cell carcinoma in simulated chronic wounds conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 124, 112073. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Tamaki, N.; Kudo, Y.; Tsunematsu, T.; Miki, K.; Ishimaru, N.; Ito, H.-O. Protective effects of resveratrol against 5-fluorouracil-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in human keratinocytes. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2021, 69, 238. [Google Scholar]
- Bettle, G., 3rd; Bell, D.P.; Bakewell, S.J. A Novel Comprehensive Therapeutic Approach to the Challenges of Chronic Wounds: A Brief Review and Clinical Experience Report. Adv. Ther. 2024, 41, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissemond, J.; Chadwick, P.; Weir, D.; Alves, P.; Isoherranen, K.; Lázaro Martínez, J.L.; Swanson, T.; Gledhill, A.; Malone, M.M.M.O.I.S.T. Concept for the Local Therapy of Chronic Wounds: An International Update. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds, 2024; 15347346241245159, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolimi, P.; Narala, S.; Nyavanandi, D.; Youssef, A.A.A.; Dudhipala, N. Innovative Treatment Strategies to Accelerate Wound Healing: Trajectory and Recent Advancements. Cells 2022, 11, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, N.; Mashal, M. Mesenchymal stem cells: The past present and future. Cell Biol. Transl. Med. Stem Cell Ther. Potential Chall. 2020, 11, 107–129. [Google Scholar]
- Margiana, R.; Markov, A.; Zekiy, A.O.; Hamza, M.U.; Al-Dabbagh, K.A.; Al-Zubaidi, S.H.; Hameed, N.M.; Ahmad, I.; Sivaraman, R.; Kzar, H.H. Clinical application of mesenchymal stem cell in regenerative medicine: A narrative review. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, X.; Hao, J.; Xu, G.; Zhang, W. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration. Cell Transpl. 2020, 29, 0963689720908500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Wu, C. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A regulator and carrier for targeting bone-related diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, G.; Santoso, M.R.; Tada, Y.; Li, A.M.; Vaskova, E.; Jung, J.-H.; O’Brien, C.; Egan, E.; Ye, J.; Yang, P.C. Mitochondria-rich extracellular vesicles from autologous stem cell–derived cardiomyocytes restore energetics of ischemic myocardium. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1073–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Sagar, S.; Ravindran, R.; Najor, R.H.; Quiles, J.M.; Chi, L.; Diao, R.Y.; Woodall, B.P.; Leon, L.J.; Zumaya, E. Mitochondria are secreted in extracellular vesicles when lysosomal function is impaired. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, K.M.; Venna, V.R.; Rao, K.S.; Stolz, D.B.; Brady, B.; Quaicoe, V.A.; Maniskas, M.E.; Hildebrand, E.E.; Green, D.; Chen, M. Mitochondria-containing extracellular vesicles from mouse vs. human brain endothelial cells for ischemic stroke therapy. J. Control. Release 2024, 373, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, L.; Lei, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, B.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Hu, K.; et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived apoptotic extracellular vesicles ameliorate cutaneous wound healing in type 2 diabetic mice via macrophage pyroptosis inhibition. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 14, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; He, Y.; Meng, B.; Zhang, X.; Ding, J.; Kou, X.; Teng, W.; Shi, S. Apoptotic vesicles inherit SOX2 from pluripotent stem cells to accelerate wound healing by energizing mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2022, 149, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin-Smith, G.K.; Tixeira, R.; Paone, S.; Mathivanan, S.; Collins, C.; Liem, M.; Goodall, K.J.; Ravichandran, K.S.; Hulett, M.D.; Poon, I.K.H. A novel mechanism of generating extracellular vesicles during apoptosis via a beads-on-a-string membrane structure. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, E.N.; Cruz, T.M.; Bowlin, G.L. Mitochondria as a therapeutic: A potential new frontier in driving the shift from tissue repair to regeneration. Regen. Biomater. 2023, 10, rbad070. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Lei, Q.; Luo, X.; Yin, J.; Chen, S.; Hao, C.; Shiyu, L.; Ma, D. Advances in biological functions and applications of apoptotic vesicles. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gregory, C.D.; Rimmer, M.P. Extracellular vesicles arising from apoptosis: Forms, functions, and applications. J. Pathol. 2023, 260, 592–608. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, J.; Kou, X.; Huang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, K.; Li, C.; Hao, M.; Qu, Y. Proteomic analysis of MSC-derived apoptotic vesicles identifies Fas inheritance to ameliorate haemophilia a via activating platelet functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12240. [Google Scholar]
- Manickam, D.S. Delivery of mitochondria via extracellular vesicles—A new horizon in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2022, 343, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wu, M.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Huan, Y.; Ye, Q.; Yang, X.; Guo, H.; Liu, A.; Huang, X. Apoptotic vesicles activate autophagy in recipient cells to induce angiogenesis and dental pulp regeneration. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3193–3208. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Mu, Q.; Ku, W.; Zheng, Y.; Yi, P.; Lin, L.; Li, P.; Wang, B.; Wu, J.; Yu, D.; et al. Functional extracellular vesicles from SHEDs combined with gelatin methacryloyl promote the odontogenic differentiation of DPSCs for pulp regeneration. J. Nanobiotechnology 2024, 22, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, D.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Kin Kwok, R.T.; Tang, B.; Sui, B.; Zhang, X.; et al. Apoptotic extracellular vesicles are metabolized regulators nurturing the skin and hair. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 19, 626–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Kou, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Yu, T.; Yang, R.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Circulating apoptotic bodies maintain mesenchymal stem cell homeostasis and ameliorate osteopenia via transferring multiple cellular factors. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 918–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Tang, J.; He, Y.; Huang, Z.; Mao, X.; Shi, S.; Kou, X. Apoptotic Extracellular Vesicles Ameliorate Multiple Myeloma by Restoring Fas-Mediated Apoptosis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14360–14372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.; Sanmillan, M.L.; Cai, T.; Zhou, Y.; Giraudo, C.; Le, A.; Shi, S. The Fas/Fap-1/Cav-1 complex regulates IL-1RA secretion in mesenchymal stem cells to accelerate wound healing. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaai8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, M.; Sobue, T.; Thompson, A.; Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A. Chemotherapy Induces Oral Mucositis in Mice Without Additional Noxious Stimuli. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.J.; Zhou, W.; Nie, Z.W.; Shin, K.T.; Cui, X.S. Melatonin enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and protects against rotenone-induced mitochondrial deficiency in early porcine embryos. J. Pineal Res. 2020, 68, e12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; An, N.; Zhang, J.; Meng, W.; Wang, W.; Wu, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yin, W. Platelet-Derived Mitochondria Attenuate 5-FU-Induced Injury to Bone-Associated Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2023, 2023, 7482546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.; Torres, M.; Bachar-Wikström, E.; Wikström, J.D. Multifaceted roles of mitochondria in wound healing and chronic wound pathogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1252318. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco-Fernandez, B.; Castaño, O.; Mateos-Timoneda, M.; Engel, E.; Pérez-Amodio, S. Nanotechnology Approaches in Chronic Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.L.; Eng, S.P.; Hafez, P.; Abdul Karim, N.; Law, J.X.; Ng, M.H. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Mitochondrial Transfer as a Cell Rescue Strategy in Regenerative Medicine: A Review of Evidence in Preclinical Models. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2022, 11, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Hu, X. Platelet-derived respiratory-competent mitochondria transfer to mesenchymal stem cells to promote wound healing via metabolic reprogramming. Platelets 2022, 33, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, T.; Ma, M.; Fan, L.; Ren, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, B.; Xia, J.; Hao, Z. Extracellular vesicles meet mitochondria: Potential roles in regenerative medicine. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 206, 107307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, H.; Lin, L.; Pan, Y.; Wang, B.; Ma, L.; Zhao, W. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Apoptotic Extracellular Vesicles Improve 5-FU-Induced Delayed Wound Healing by Mitochondrial Transfer. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040453
Lai H, Lin L, Pan Y, Wang B, Ma L, Zhao W. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Apoptotic Extracellular Vesicles Improve 5-FU-Induced Delayed Wound Healing by Mitochondrial Transfer. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(4):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040453
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Hongbin, Ling Lin, Yanrui Pan, Boqun Wang, Lan Ma, and Wei Zhao. 2025. "Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Apoptotic Extracellular Vesicles Improve 5-FU-Induced Delayed Wound Healing by Mitochondrial Transfer" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 4: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040453
APA StyleLai, H., Lin, L., Pan, Y., Wang, B., Ma, L., & Zhao, W. (2025). Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Apoptotic Extracellular Vesicles Improve 5-FU-Induced Delayed Wound Healing by Mitochondrial Transfer. Pharmaceutics, 17(4), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17040453






