Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model of Apixaban for Biopharmaceutics Risk Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Available Literature Data on Apixaban
2.2. Dissolution Model of Apixaban
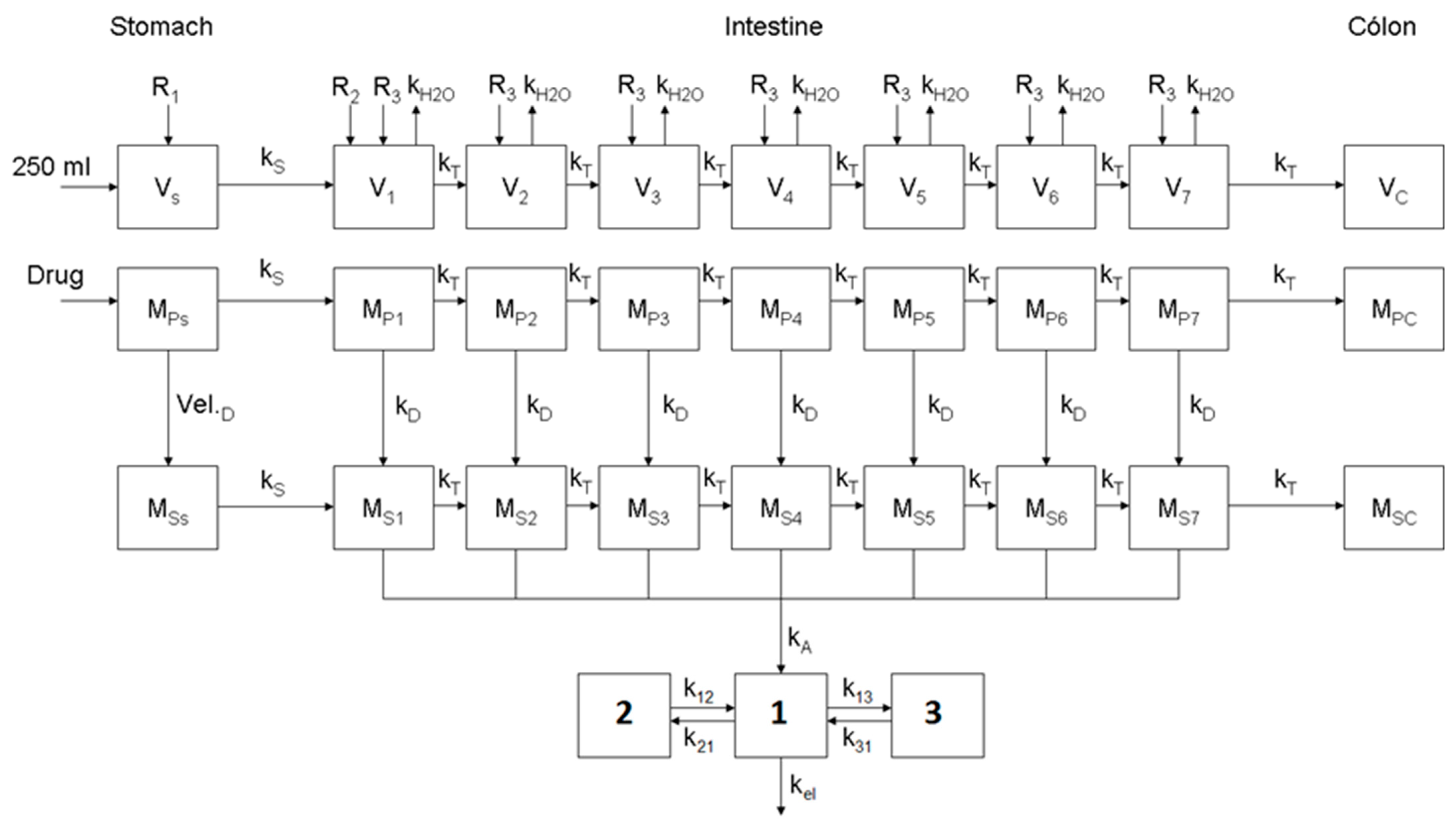
2.3. Disposition Model of Apixaban
2.4. Optimization of the Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model for Oral Formulations of Apixaban
2.5. Simulations Based on the Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model of Apixaban
3. Results
3.1. Dissolution Model of Apixaban
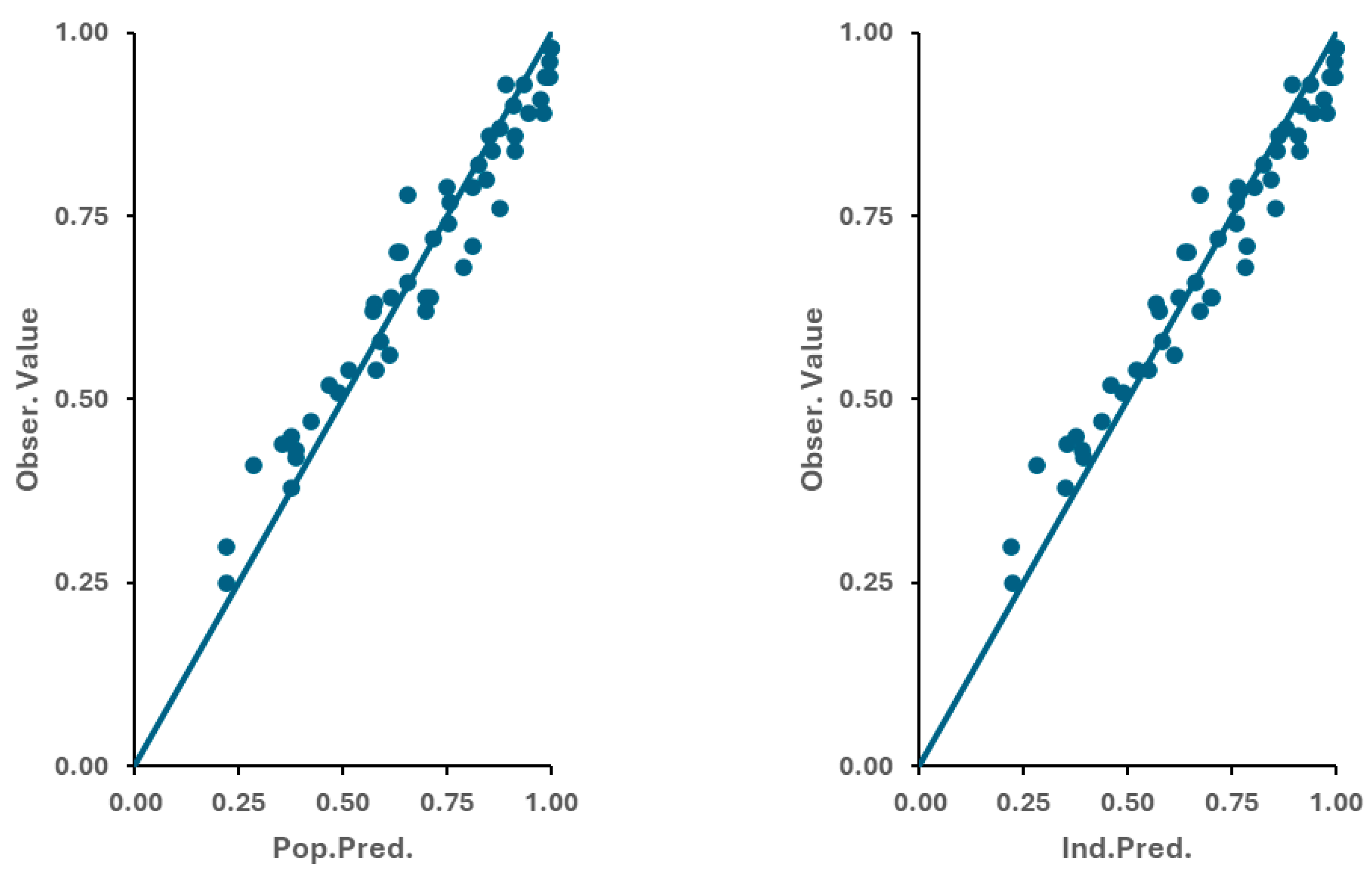
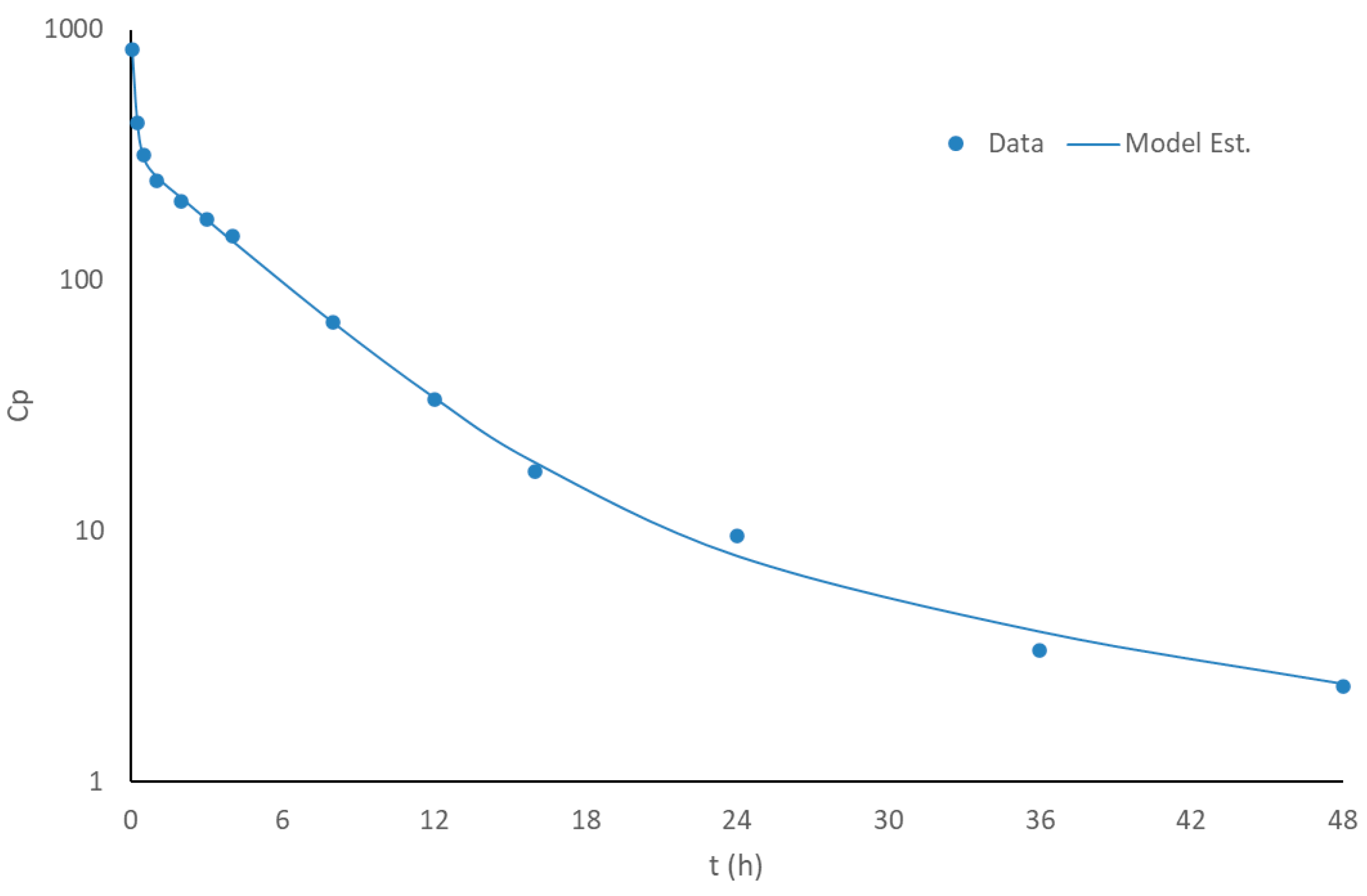
3.2. Disposition Model of Apixaban
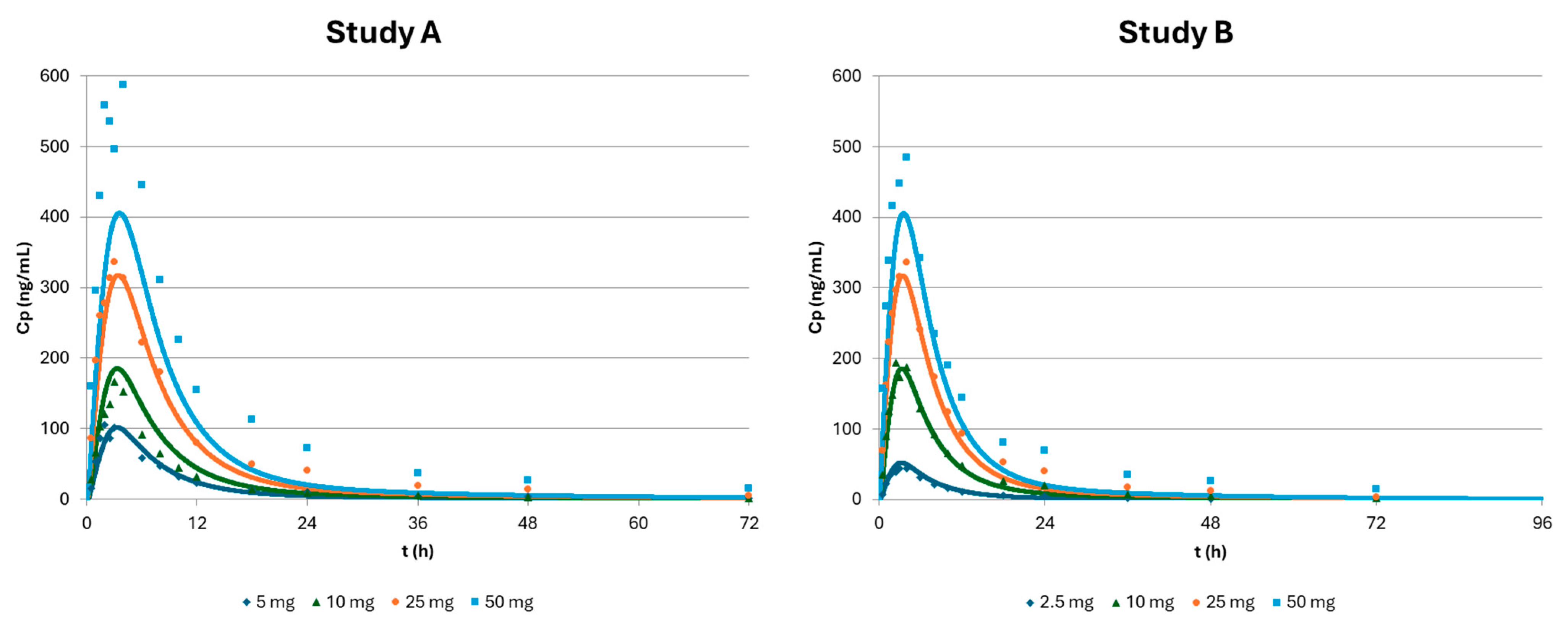
3.3. Optimization of the Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model of Apixaban
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| API | Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BA | Bioavailability |
| BCS | Biopharmaceutics Classification System |
| BE | Bioequivalence |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| Cmax | Maximum Plasma Concentration |
| CQAs | Critical quality attributes |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal tract |
| GOF | Goodness-of-fit |
| ICH | International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use |
| IV | Intravenous |
| MIDD | Model-informed drug development |
| Obs | Observed |
| PBBM | Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling |
| PBPK | Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic |
| %PE | Prediction error |
| Peff | Effective permeability |
| Pred | Predicted |
| PK | Pharmacokinetics |
| QbD | Quality by Design |
| Tmax | Time to Reach Maximum Plasma Concentration |
References
- Mitra, A.; Suarez-Sharp, S.; Pepin, X.J.; Flanagan, T.; Zhao, Y.; Kotzagiorgis, E.; Parrott, N.; Sharan, S.; Tistaert, C.; Heimbach, T.; et al. Applications of Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM) to Support Drug Product Quality: A Workshop Summary Report. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 594–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Guideline on the Reporting of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modelling and Simulation; European Medicines Agency, Ed.; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2018.
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. The Use of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Analyses—Biopharmaceutics Applications for Oral Drug Product Development, Manufacturing Changes, and Controls; Food and Drug Administration, Ed.; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research: Beltsville, MD, USA, 2020.
- ICH (Ed.) M13A—Bioequivalence For Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms; ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- ICH (Ed.) M15—General Principles For Model-Informed Drug Development; ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Li, M. Current State and Challenges of Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling (PBBM) in Oral Drug Product Development. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, T.; Kollipara, S.; Boddu, R.; Bhattiprolu, A.K. Biopharmaceutics Risk Assessment-Connecting Critical Bioavailability Attributes with In Vitro, In Vivo Properties and Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Modeling to Enable Generic Regulatory Submissions. AAPS J. 2023, 25, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byon, W.; Garonzik, S.; Boyd, R.A.; Frost, C.E. Apixaban: A Clinical Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Review. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimbach, T.; Tshinanu, F.M.; Raines, K.; Borges, L.; Kijima, S.; Malamatari, M.; Moody, R.; Veerasingham, S.; Seo, P.; Turner, D.; et al. PBBM Considerations for Base Models, Model Validation, and Application Steps: Workshop Summary Report. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 5353–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollipara, S.; Bhattiprolu, A.K.; Boddu, R.; Ahmed, T.; Chachad, S. Best Practices for Integration of Dissolution Data into Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Models (PBBM): A Biopharmaceutics Modeling Scientist Perspective. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, D.J.P.; Orwat, M.J.; Koch, S.; Rossi, K.A.; Alexander, R.S.; Smallwood, A.; Wong, P.C.; Rendina, A.R.; Luettgen, J.M.; Knabb, R.M.; et al. Discovery of 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo [3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide (apixaban, BMS-562247), a highly potent, selective, efficacious, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of blood coagulation factor Xa. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5339–5356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Frost, C.; Jia, J.; Vema-Varapu, C. Apixaban Formulations. U.S. Patent No. EP3246021A1, 24 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vakkalagadda, B.; Frost, C.; Byon, W.; Boyd, R.A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Z.; Dias, C.; Shenker, A.; LaCreta, F. Effect of Rifampin on the Pharmacokinetics of Apixaban, an Oral Direct Inhibitor of Factor Xa. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2016, 16, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, C.; Wang, J.; Nepal, S.; Schuster, A.; Barrett, Y.C.; Mosqueda-Garcia, R.; Reeves, R.A.; LaCreta, F. Apixaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor: Single dose safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and food effect in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, C.; Shenker, A.; Jhee, S.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Bragat, A.; Pursley, J.; LaCreta, F. Evaluation of the single-dose pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of apixaban in healthy Japanese and Caucasian subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 10, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Argenio, D.Z.; Schumitzky, A.; Wang, X. ADAPT 5 User’s Guide: Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Systems Analysis Software; B.S. Resource: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.X.; Amidon, G.L. A compartmental absorption and transit model for estimating oral drug absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 186, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paixao, P.; Gouveia, L.F.; Morais, J.A. Prediction of the human oral bioavailability by using in vitro and in silico drug related parameters in a physiologically based absorption model. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 429, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanha, M.C.; Diniz, A.; Silva, N.M.E.N.; Kimura, E.; Paixão, P. Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Model on the Oral Drug Absorption in Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Bariatric Patients: Amoxicillin Tablet and Suspension. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 5025–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, N.; Frost, C.E.; Yu, Z.; He, K.; Zhang, H.; Humphreys, W.G.; Pinto, D.; Chen, S.; Bonacorsi, S.; Wong, P.C.; et al. Apixaban metabolism and pharmacokinetics after oral administration to humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofsäss, M.A.; Dressman, J. Suitability of the z-Factor for Dissolution Simulation of Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Potential Pitfalls and Refinements. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepin, X.J.H.; Huckle, J.E.; Alluri, R.V.; Basu, S.; Dodd, S.; Parrott, N.; Riedmaier, A.E. Understanding Mechanisms of Food Effect and Developing Reliable PBPK Models Using a Middle-out Approach. AAPS J. 2021, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Guideline on the Pharmacokinetic and Clinical Evaluation of Modified Release Dosage Forms; European Medicines Agency, Ed.; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2014.
- Davit, B.M.; Nwakama, P.E.; Buehler, G.J.; Conner, D.P.; Haidar, S.H.; Patel, D.T.; Yang, Y.; Yu, L.X.; Woodcock, J. Comparing generic and innovator drugs: A review of 12 years of bioequivalence data from the United States Food and Drug Administration. Ann. Pharmacother. 2009, 43, 1583–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsume, Y.; Amidon, G.L. The biowaiver extension for BCS class III drugs: The effect of dissolution rate on the bioequivalence of BCS class III immediate-release drugs predicted by computer simulation. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH (Ed.) M9—Biopharmaceutics Classification System-Based Biowaivers; ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Simulations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solution [14,15] | Tablets [14,15] | BE Study [12] | Reference | |
| Dose (mg) | 0.5, 1, 2.5 | 2.5, 5, 10, 25, 50 | 5 | - |
| Absorption | ||||
| Peff (cm/h) | 1.57 × 10−1 | in vitro [11,18] | ||
| Solubility (µg/mL) | 40 | in vitro [11] | ||
| Dissolution | ||||
| Z | - | 31 | 22.3 | in vitro fitting [12] |
| Particle size (µm) | - | 83 | 50/89 | in vitro [12] |
| Disposition | ||||
| K10 (h−1) | 0.5409 | in vivo fitting [13] | ||
| k12 (h−1) | 0.086 | in vivo fitting [13] | ||
| k21 (h−1) | 0.0441 | in vivo fitting [13] | ||
| k13 (h−1) | 4.319 | in vivo fitting [13] | ||
| k31 (h−1) | 2.24 | in vivo fitting [13] | ||
| V1 (L) | 4.756 | in vivo fitting [13] | ||
| 0.5 mg | 1 mg | 2.5 mg | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs | Pred | %PE | Obs | Pred | %PE | Obs | Pred | %PE | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 8.42 | 11.09 | −32 | 23.46 | 22.19 | 5 | 50.15 | 55.46 | −11 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.00 | 3.00 | −200 | 1.50 | 3.00 | −100 | 1.50 | 3.00 | −100 |
| AUC (ng·h/mL) | 54.10 | 78.06 | −44 | 176.32 | 197.88 | −12 | 454.96 | 494.69 | −9 |
| Study A | 5 mg | 10 mg | 25 mg | 50 mg | ||||||||
| Obs | Pred | %PE | Obs | Pred | %PE | Obs | Pred | %PE | Obs | Pred | %PE | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 105.68 | 101.20 | 4 | 166.54 | 183.75 | −10 | 336.84 | 312.63 | 7 | 587.95 | 401.38 | 32 |
| Tmax (h) | 2.00 | 3.00 | −50 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 0 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 0 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 0 |
| AUC (ng·h/mL) | 982.48 | 906.13 | 8 | 1347.37 | 1667.98 | −24 | 3658.83 | 2961.29 | 19 | 6759.43 | 3906.82 | 42 |
| Study B | 2.5 mg | 10 mg | 25 mg | 50 mg | ||||||||
| Obs | Pred | %PE | Obs | Pred | %PE | Obs | Pred | %PE | Obs | Pred | %PE | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 44.21 | 51.74 | −17 | 194.09 | 183.75 | 5 | 335.98 | 312.63 | 7 | 484.65 | 401.38 | 17 |
| Tmax (h) | 4.00 | 3.00 | 25 | 2.50 | 3.00 | −20 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 25 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 0 |
| AUC (ng·h/mL) | 451.03 | 461.70 | −2 | 1917.80 | 1667.98 | 13 | 3653.04 | 2961.29 | 19 | 5681.64 | 3906.82 | 31 |
| 5 mg/50 µm | 5 mg/89 µm | BE | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs | Pred | %PE | Obs | Pred | %PE | Obs | Pred | %PE | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 101.80 | 104.23 | −2 | 87.80 | 94.93 | −8 | 0.86 | 0.91 | −6 |
| AUC (ng∙h/mL) | 1088.00 | 938.55 | 14 | 1030.00 | 856.75 | 17 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 4 |
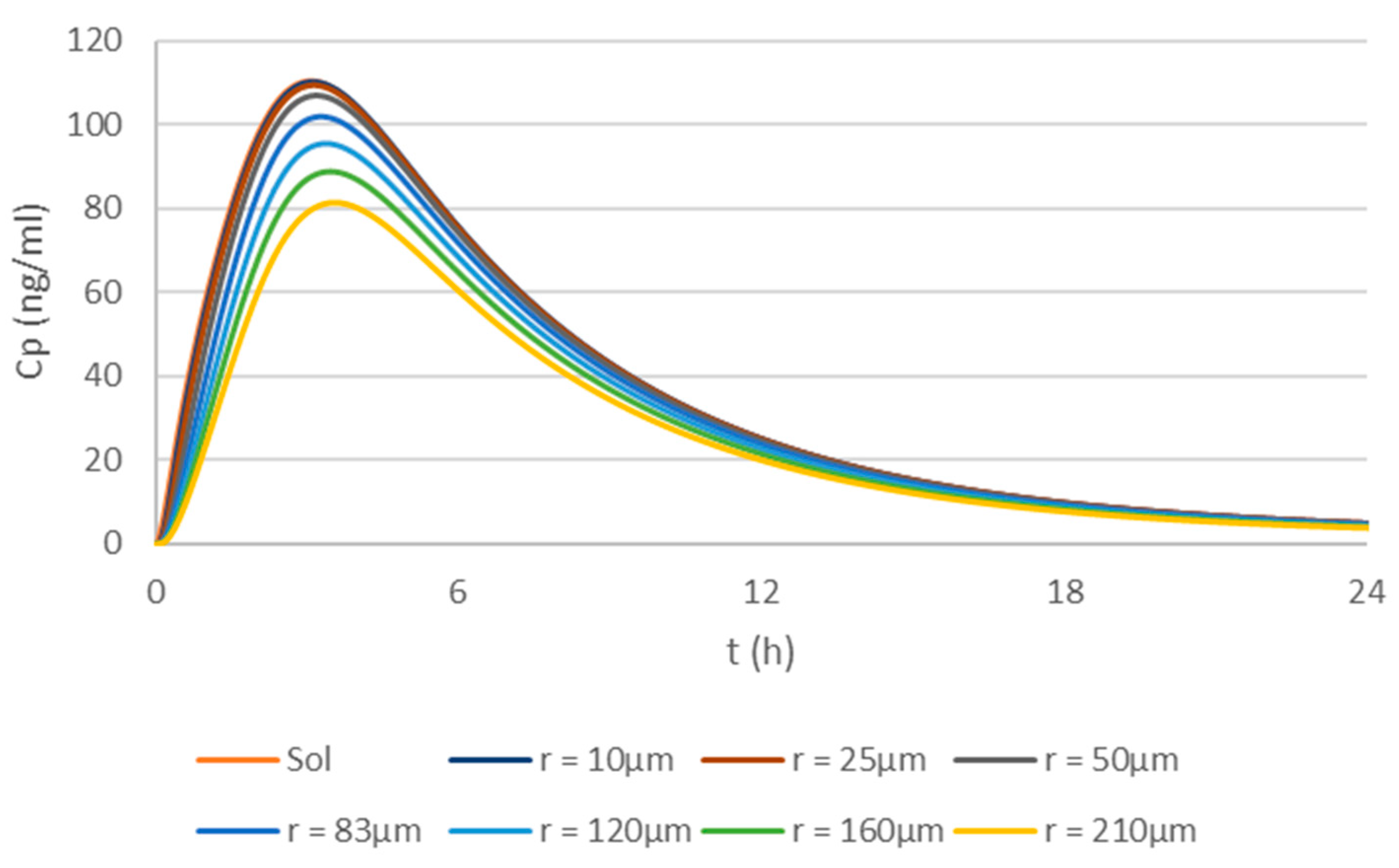
| T/R1 Ratio | Solution | 10 µm | 25 µm | 50 µm | 83 µm | 120 µm | 160 µm | 210 µm |
| Cmax | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.74 |
| Tmax | 1.00 | 1.01 | 1.02 | 1.04 | 1.06 | 1.10 | 1.12 | 1.15 |
| AUC | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.74 |
| T/R2 Ratio | Solution | 10 µm | 25 µm | 50 µm | 83 µm | 120 µm | 160 µm | 210 µm |
| Cmax | 1.08 | 1.08 | 1.07 | 1.05 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.80 |
| Tmax | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 1.03 | 1.05 | 1.08 |
| AUC | 1.09 | 1.09 | 1.08 | 1.05 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paixão, P.; Petric, Z.; Morais, J.A.G. Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model of Apixaban for Biopharmaceutics Risk Assessment. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030382
Paixão P, Petric Z, Morais JAG. Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model of Apixaban for Biopharmaceutics Risk Assessment. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(3):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030382
Chicago/Turabian StylePaixão, Paulo, Zvonimir Petric, and José A. G. Morais. 2025. "Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model of Apixaban for Biopharmaceutics Risk Assessment" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 3: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030382
APA StylePaixão, P., Petric, Z., & Morais, J. A. G. (2025). Physiologically Based Biopharmaceutics Model of Apixaban for Biopharmaceutics Risk Assessment. Pharmaceutics, 17(3), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030382





